INFLAMMATION: Cellular Patterns
|
Lymphocytic B-cell Focal inflammation Focal invasion of muscle fibers IM-VAMP (IBM) Lymphorrhages Myositis Histiocytes Granuloma Muscle fiber necrosis Pathology types Also see: Inflammatory myopathy |
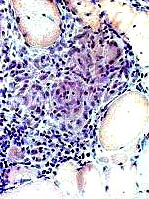
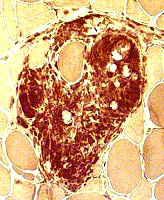
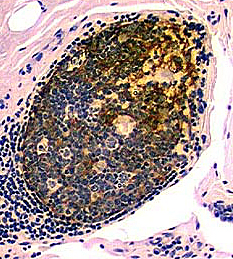
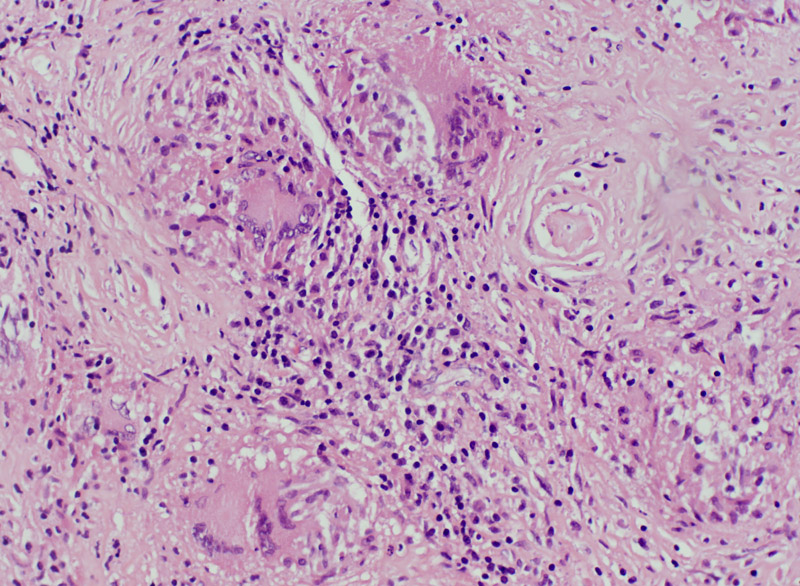
Focal lymphocytic inflammation: Nongranulomatous | |
 H&E |
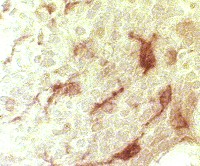 Esterase |
|
|
Granulomas
|
Differential diagnosis Myopathy General Myopathy: Clinical Pathology Giant cells Muscle Nerve Endoneurial Perivascular Other: Tissue changes Perimysium Tuberculosis |
|
Granulomas: Differential Diagnosis
|
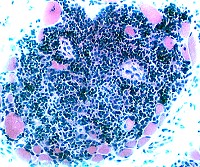
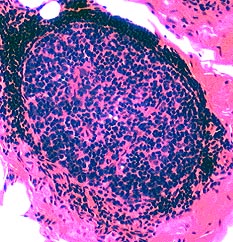 H&E stain |
|
Granulomas: Features Focal cell collections Histiocytic cells Location: Central Nuclei: Large Cytoplasm: Prominent Stain with Acid phosphatase: Perinuclear Esterase: Cytoplasm Antibodies: CD68; CD4 Giant cells: Markers Present Lysozyme α1-antichymotrypsin Chitinase 1 CD86 CD206 Absent: Myoglobin Lymphocytes Location: Peripheral Nuclei: Small; Dark Cytoplasm: Little Component: γδ T-cells Humoral Factors: associated TNF IL8 |
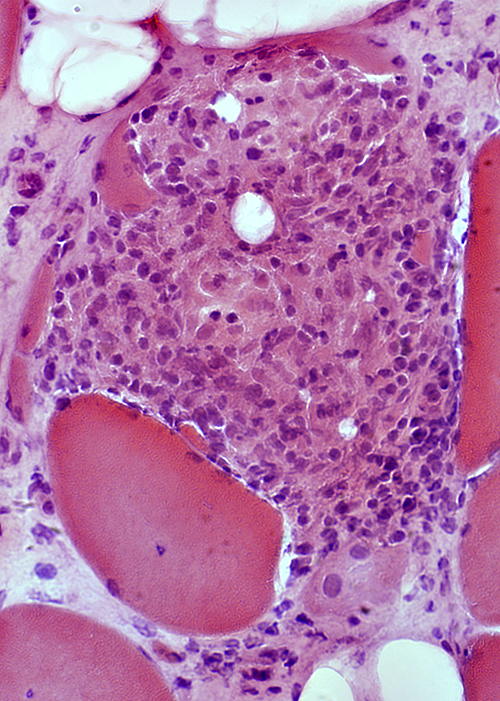
|
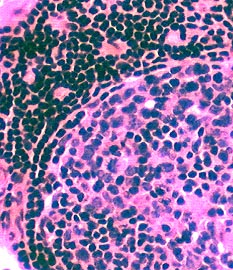 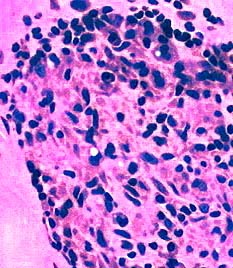 H&E stain  H&E stain |
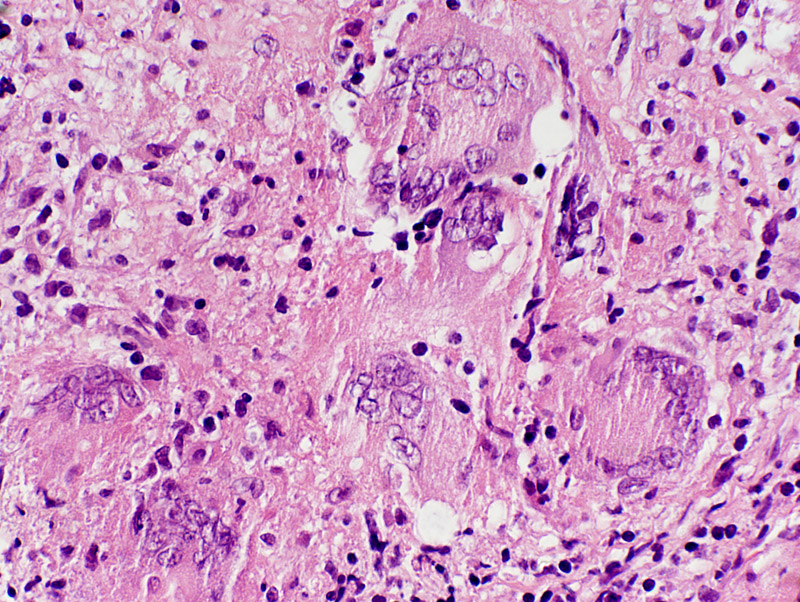
Histiocytic cells in Granuloma
Features: Abundant cytoplasm; Large, pale nuclei
Location: May occupy region of lost muscle fiber
 Congo red stain |
Granulomas: Locations & Staining Patterns
Granuloma location: May cross tissue borders
 Congo red stain |
Location: Extend into both Endomysium & Perimysium
Composed of clusters of Histiocytic cells: Have abundant cytoplasm & large nuclei
Also see: Granuloma in nerve extending into both Endoneurium & Perineurium
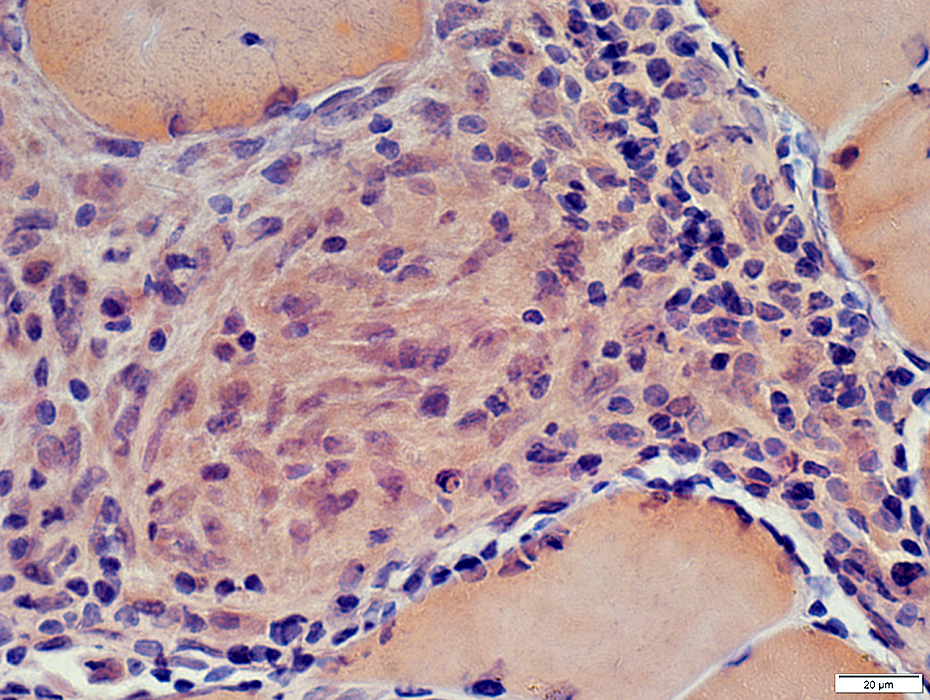
Granuloma location: Perimysial Granuloma
 Congo red stain Granuloma contains Large histiocytic cells: Have abundant cytoplasm & large nuclei Giant cell |
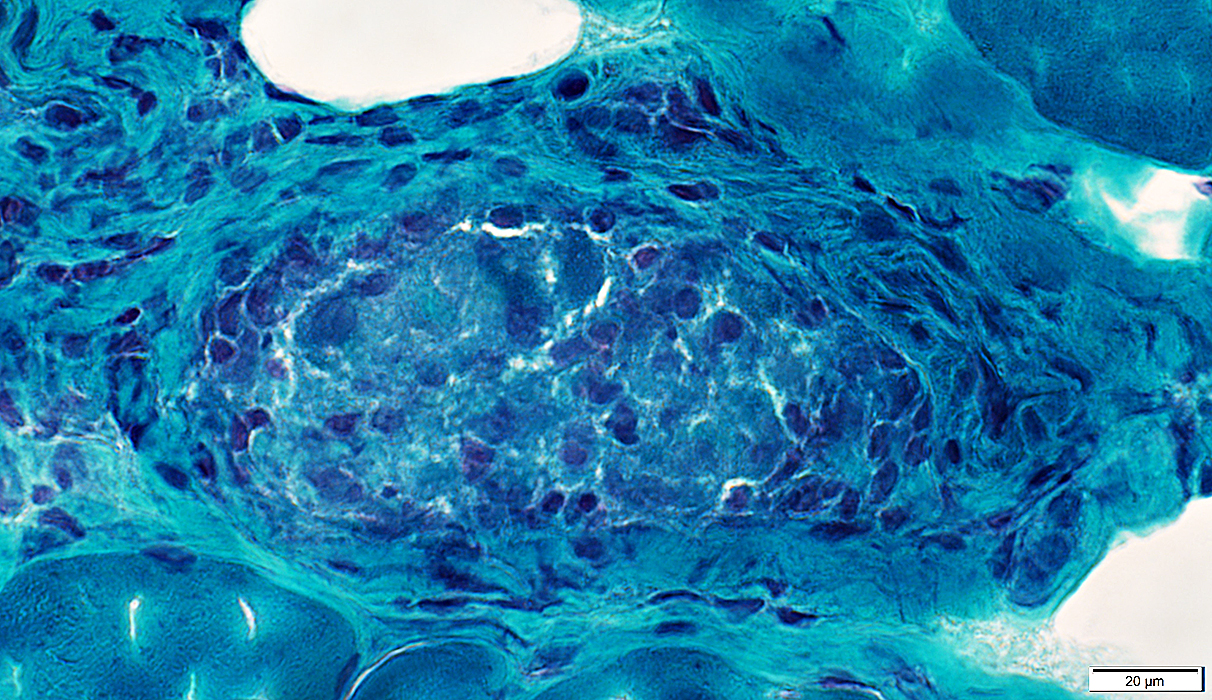 Gomori trichrome stain |
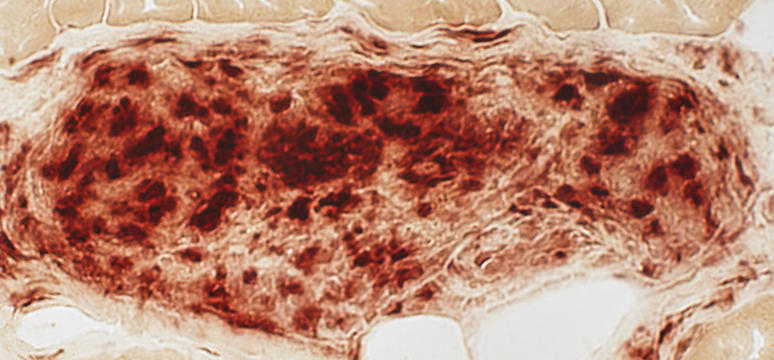 Acid phosphatase stain |
| Acid phosphatase (Above): Stains perinuclear region of granuloma cells This differs from the confluent staining in IMAM cell foci Esterase (Below) shows confluent staining of cells in granulomas |
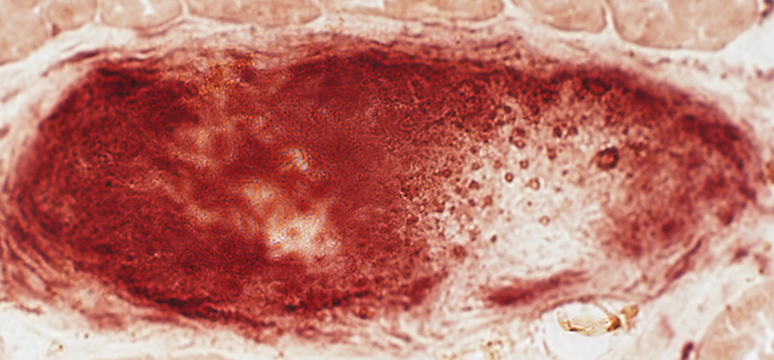 Esterase stain |
Granulomatous Disease: Perimysium
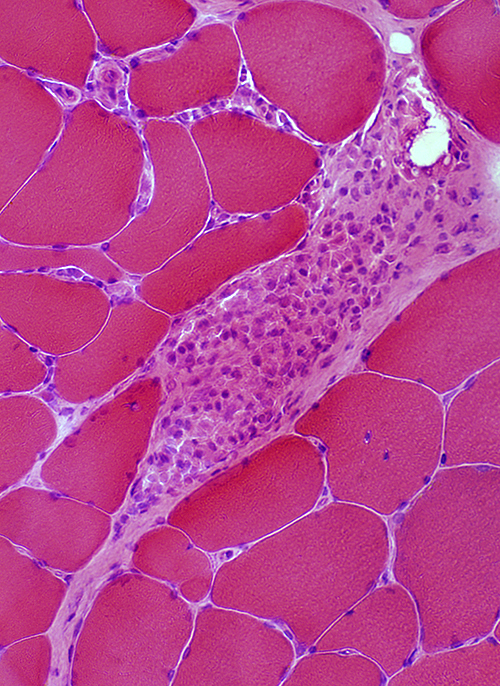
|
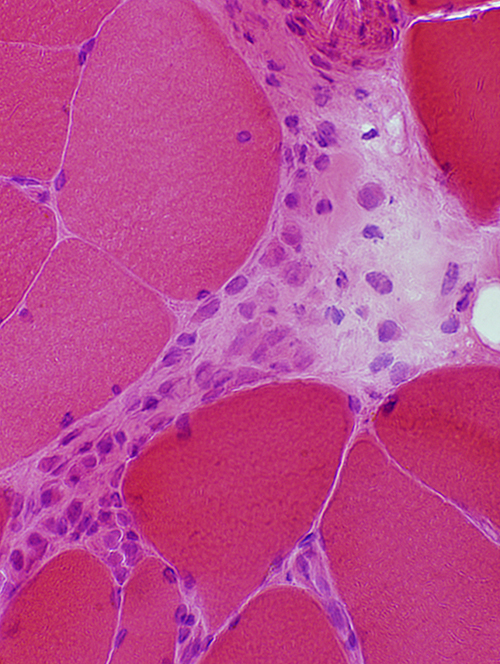 H&E stain |
Granuloma in perimysium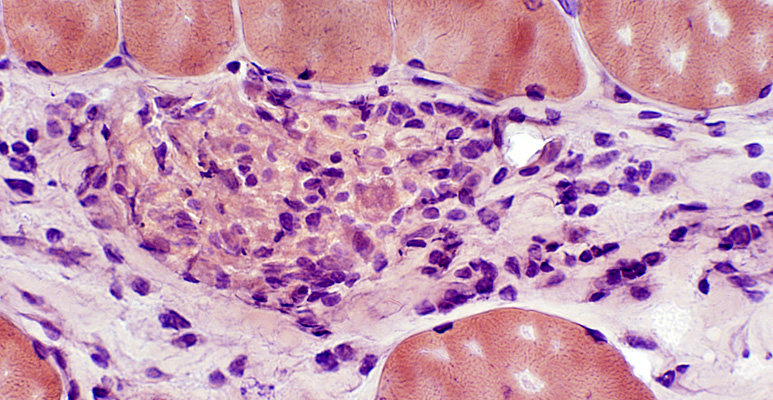 Congo red |
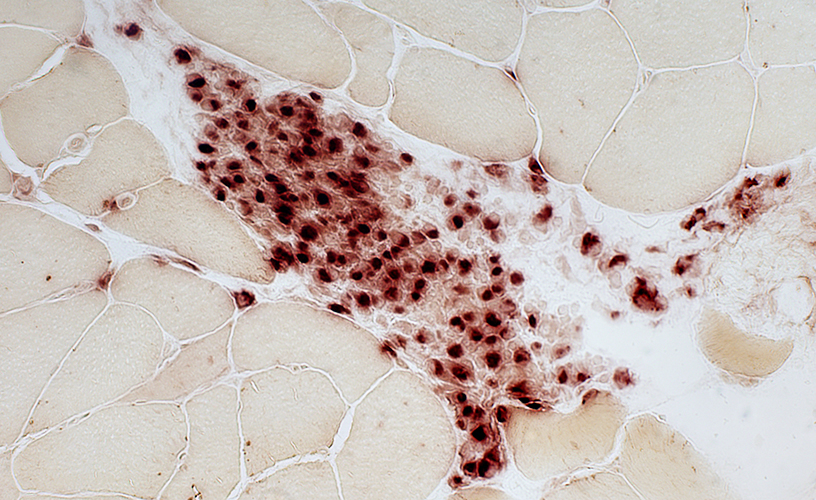 Acid phosphatase stain |
Granulomatous Myopathy, Chronic
GranulomasEndomysial
Muscle fibers
Varied size: Hypertrophy & Atrophy
Internal nuclei
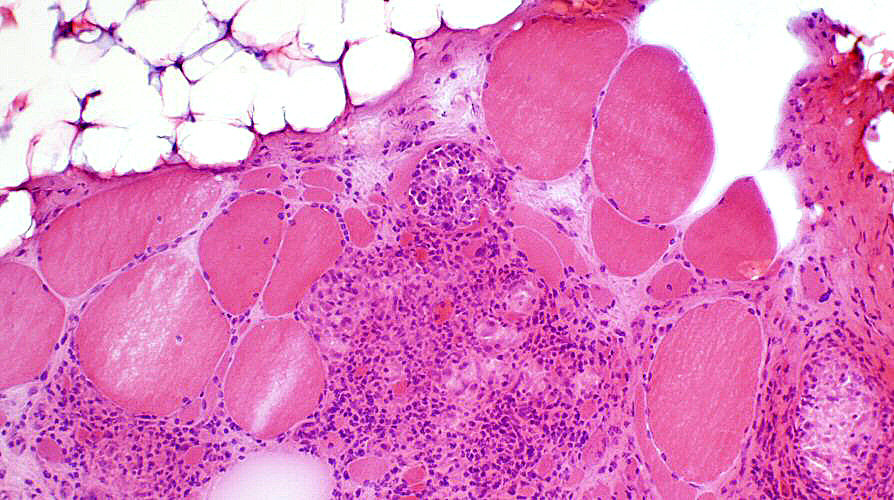 H&E stain |
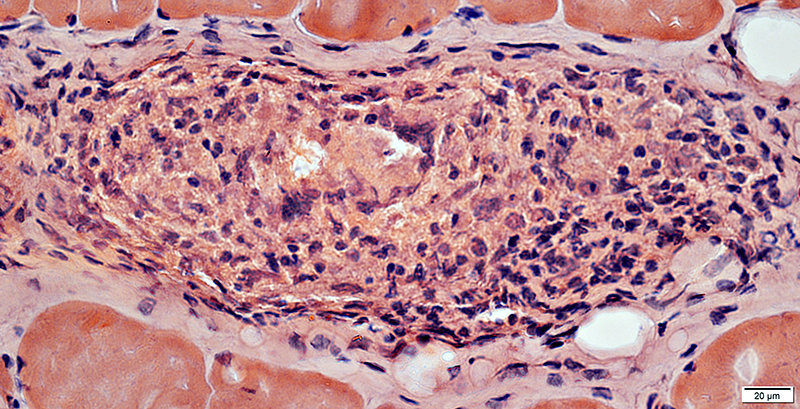
Granuloma location: Endomysial Granuloma
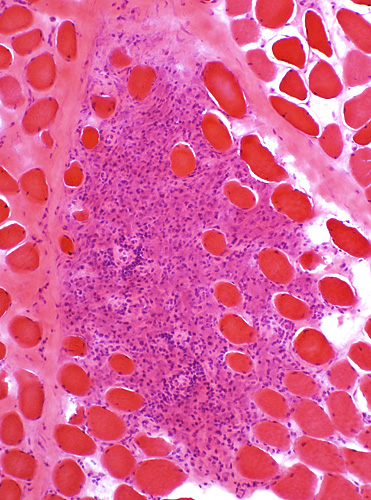 H & E stain Large cells in granuloma |
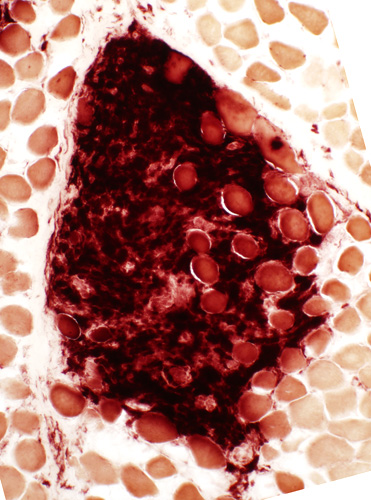 Esterase stain Confluent staining of cells in granuloma |
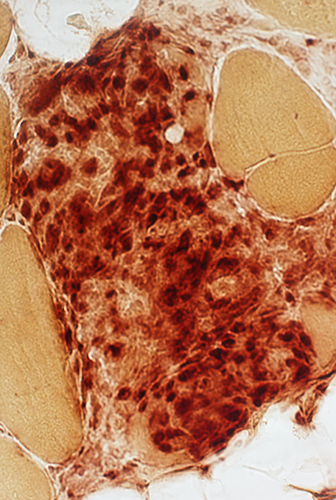 Acid phosphatase stain Perinuclear staining of most cells in granuloma |
Granulomatous myopathy: Muscle fiber pathology
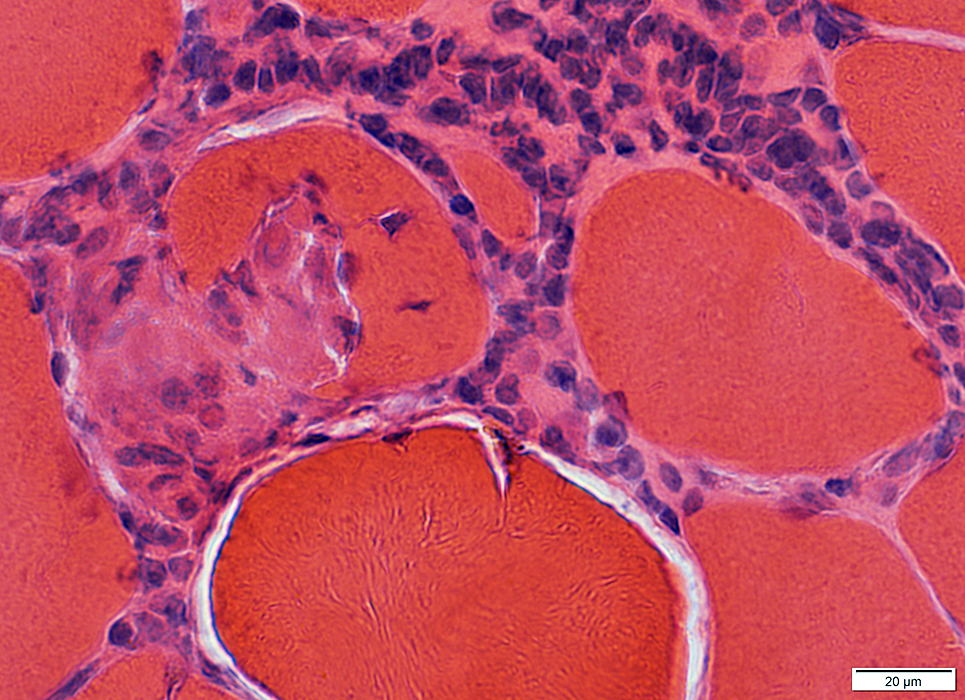 H&E stain |
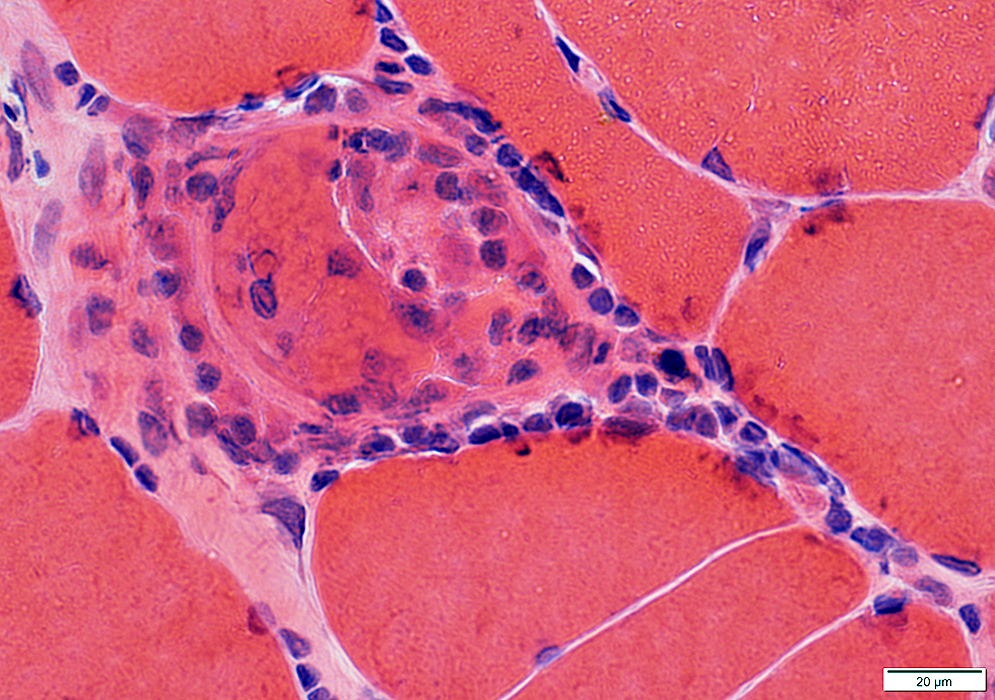 H&E stain |
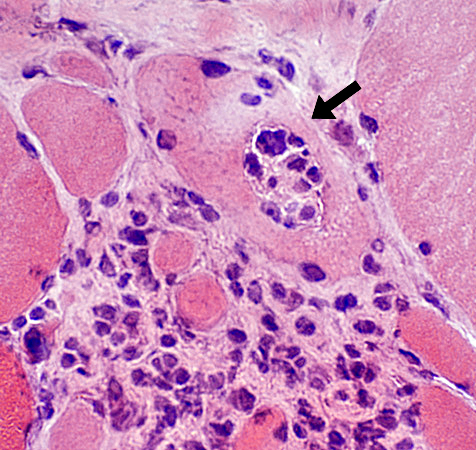
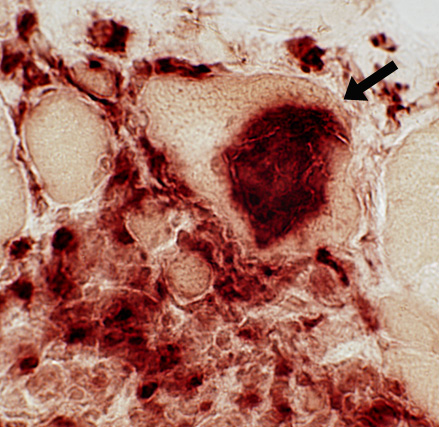 |
Granuloma cells: Large & Stain with acid phosphatase
Muscle fibers: Progressively invaded & replaced by granuloma cells (Arrows)
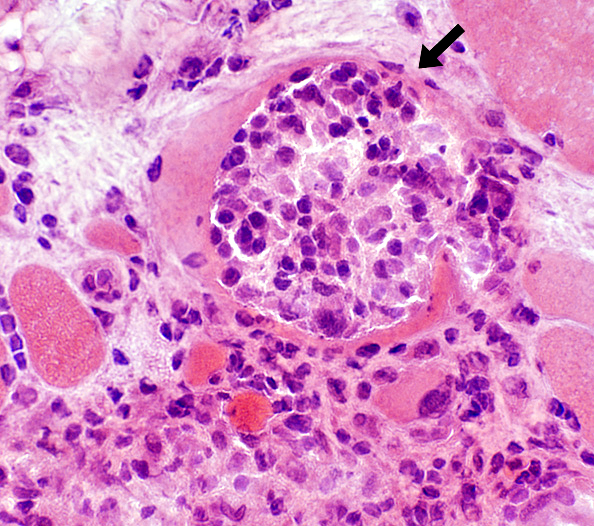 H&E stain |
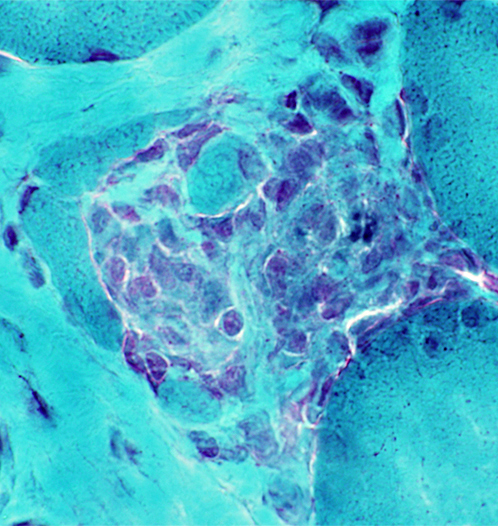 Gomori trichrome stain |
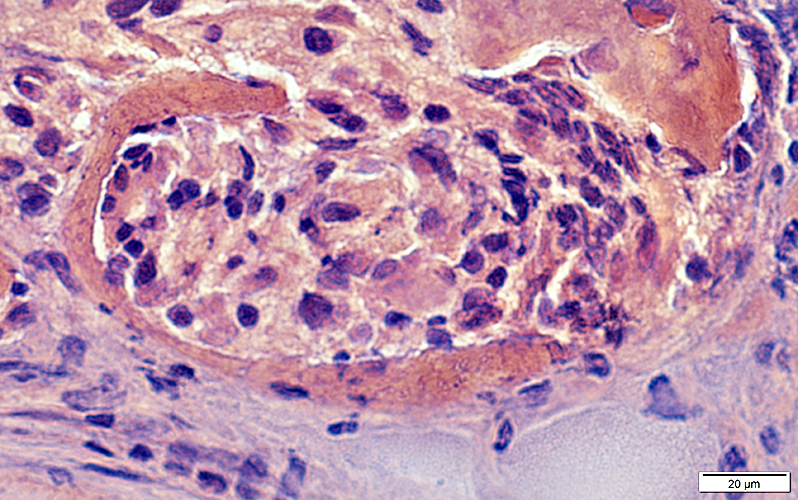 Congo red stain |
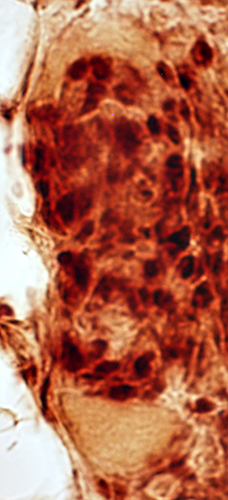 Acid phosphatase stain |
|
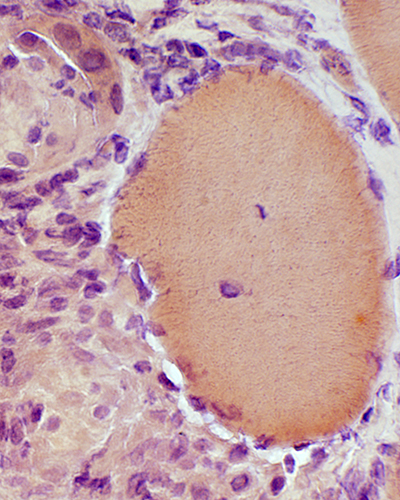
Erosion of non-necrotic muscle fibers around & along their edges by Histiocytic granuloma cells 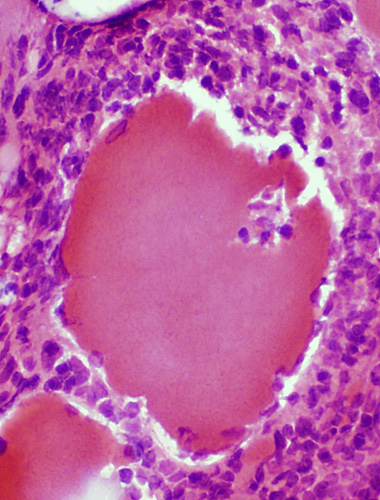

|
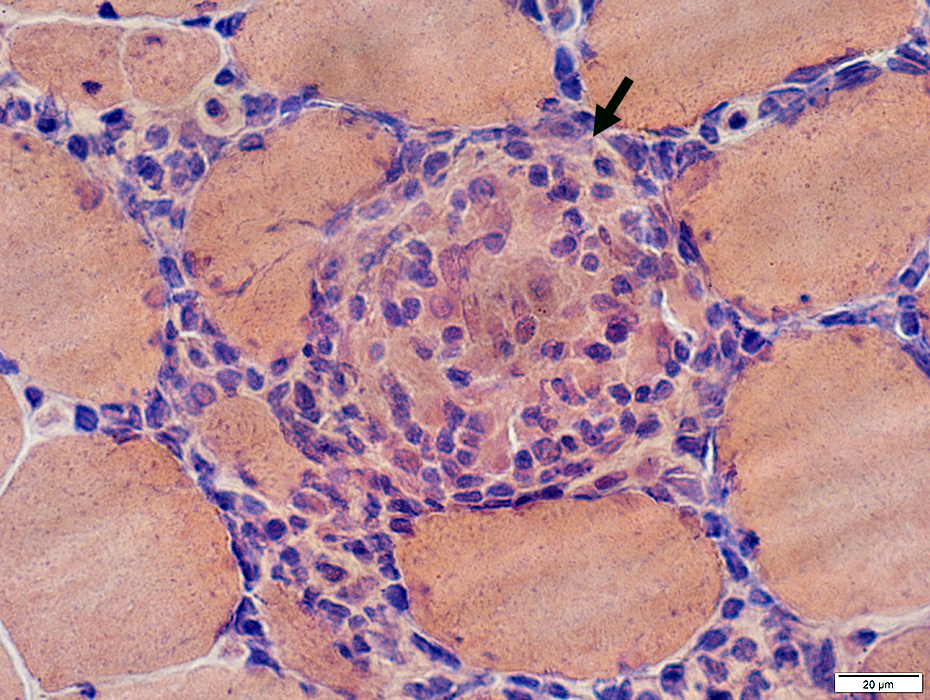 Congo red stain |
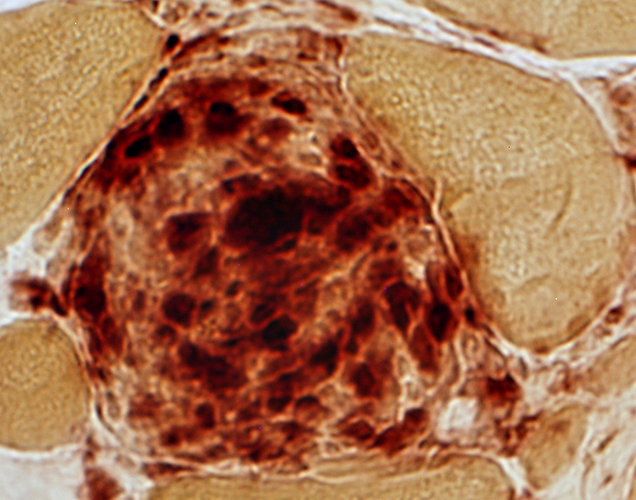 Acid phosphatase stain |
MHC expression by muscle fibers & granuloma cells
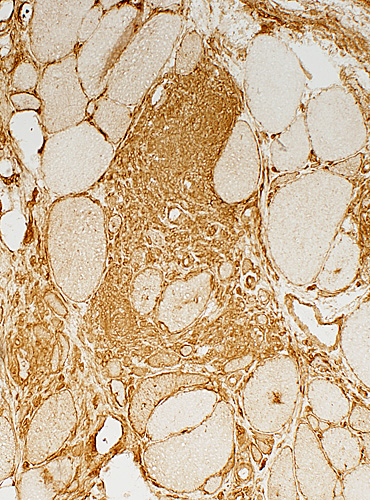
|
Control muscle: MHC expression only in vessels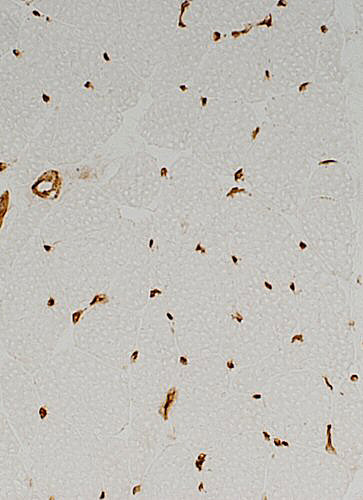 |
Other immune features | |
Alkaline phosphatase staining of perimysium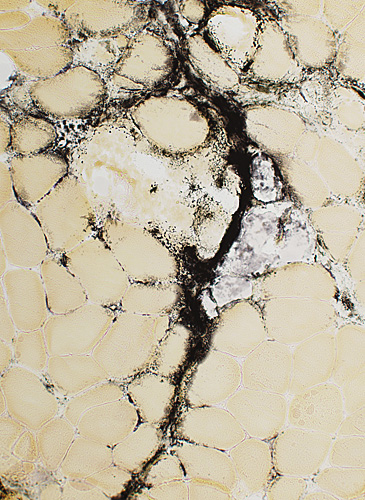
|
CD4 staining of granuloma cells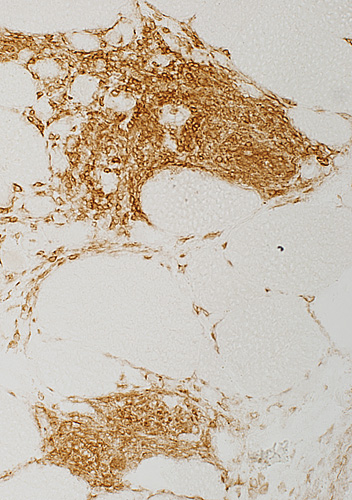 |
Giant cells, Multinucleated
Frozen sections
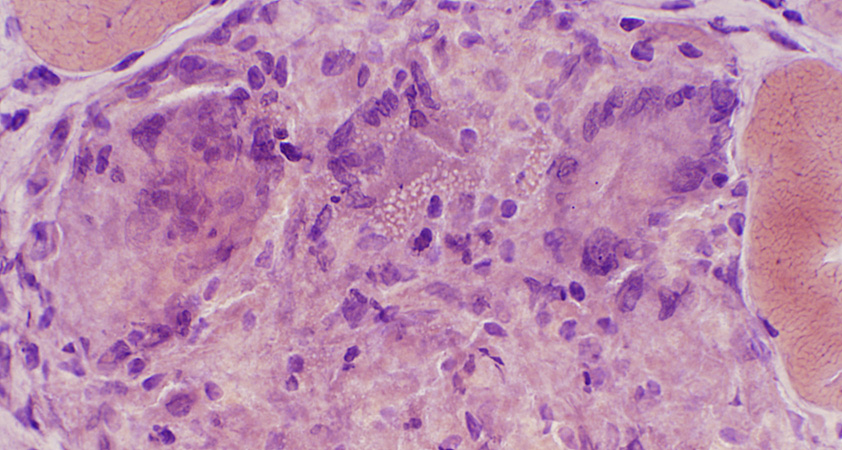 |
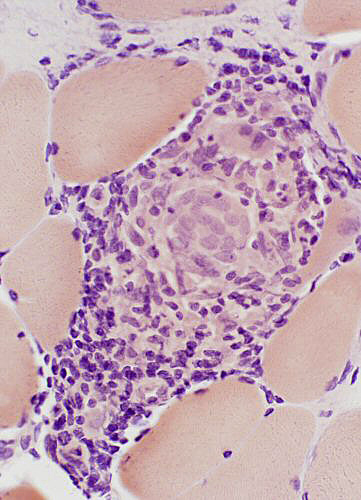
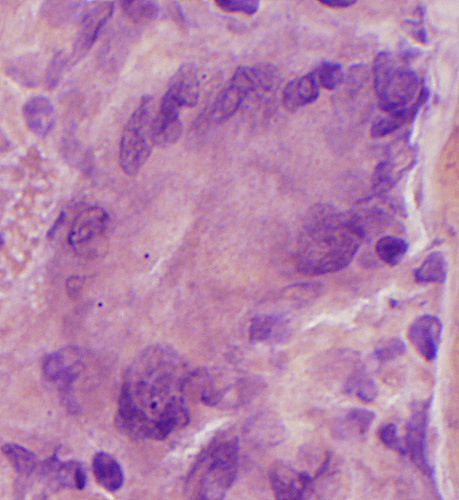 Congo red |
Size: Very large
Nuclei: Several in one cell; Large
Cytoplasm: May stain strongly for lysosomal markers
Molecular marker: Chitinase 1
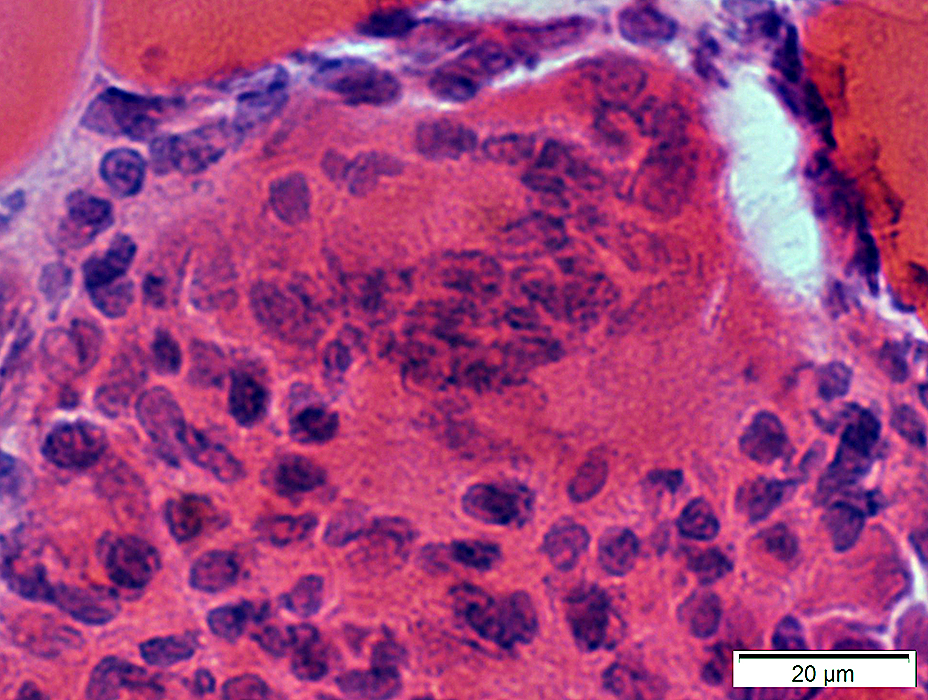 H&E stain |
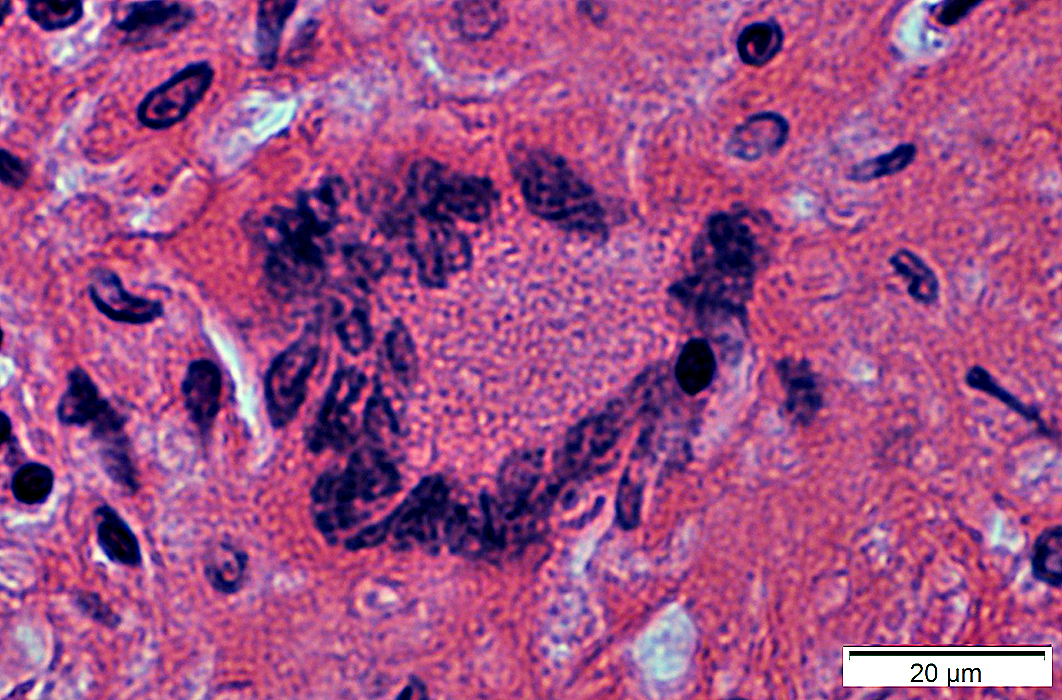 H&E stain |
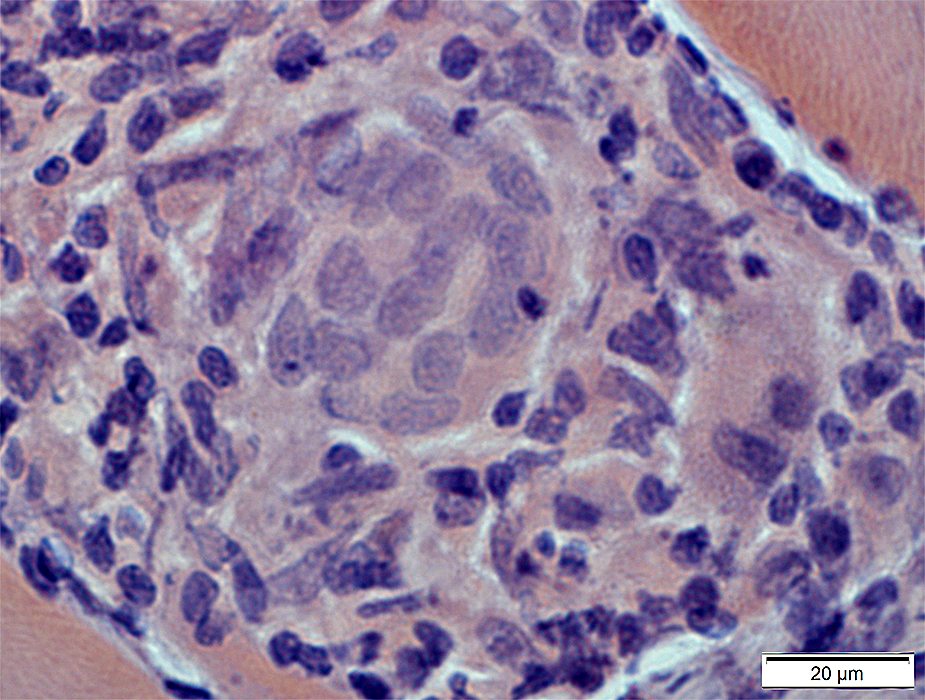 Congo red stain |
Giant cells stain for acid phosphatase (Arrow)
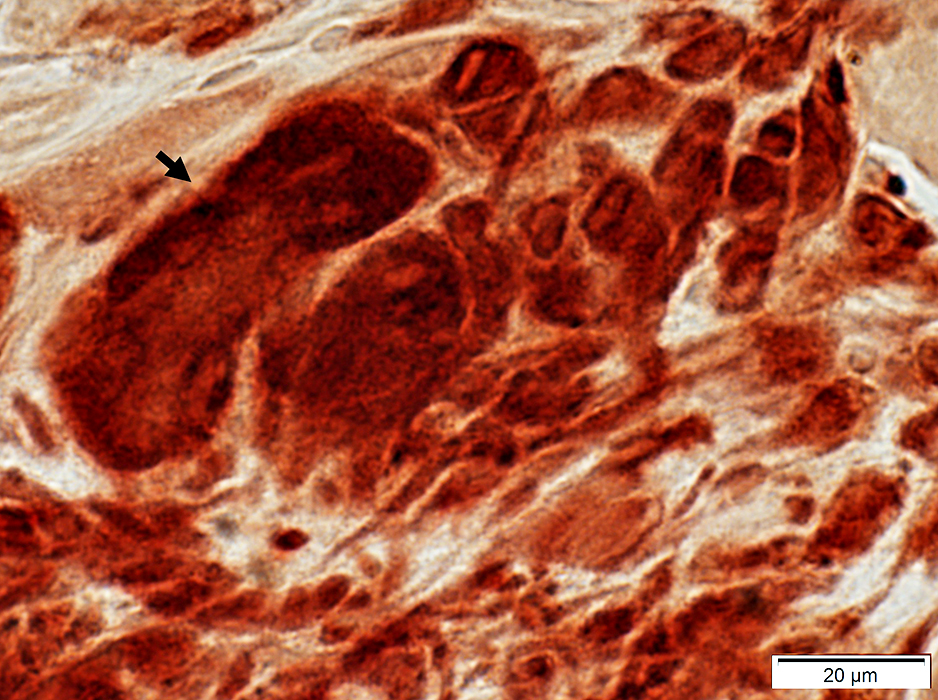 Acid phosphatase stain |
Fixed muscle sections
 H&E stain |
 H&E stain |
 H&E stain |
Granulomatous Myopathy: Connective tissue pathology, Epimysial & Perimysial
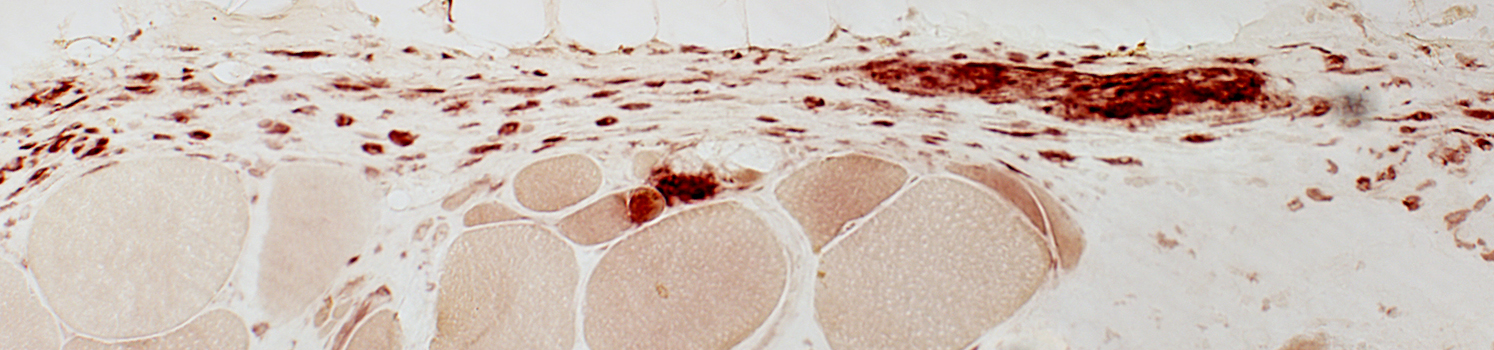 Acid phosphatase stain |
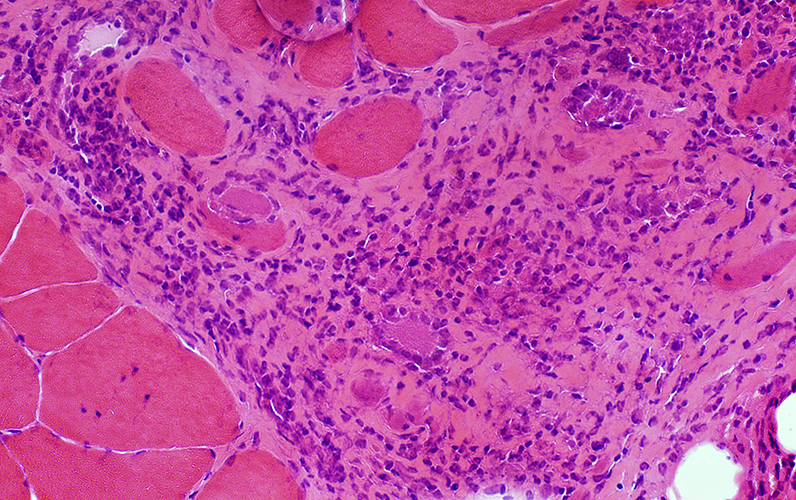 H&E stain |
Scattered cells in Perimysium
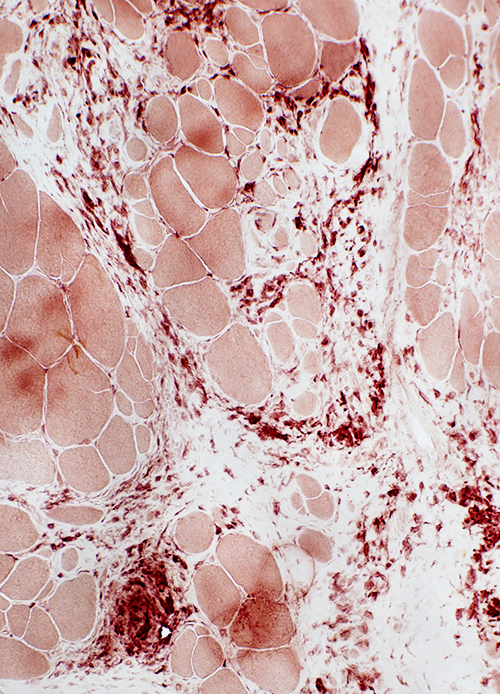 Acid phosphatase stain |
Scattered cells in Perimysium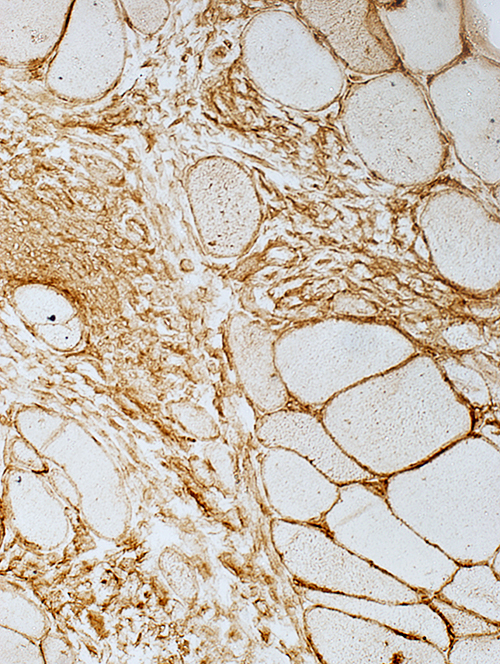 MHC Class I stain |
Granulomatous Disease: Nerve, Perivascular
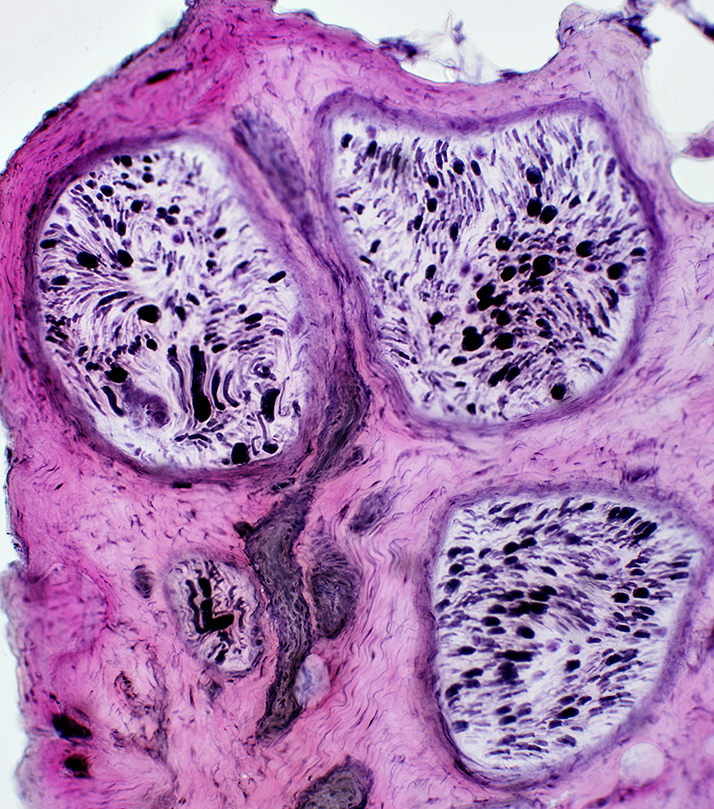 VvG stain Axon loss: Myelinated axons Varied within fascicles |
 Acid phosphatase stain Histiocytic perivascular cells |
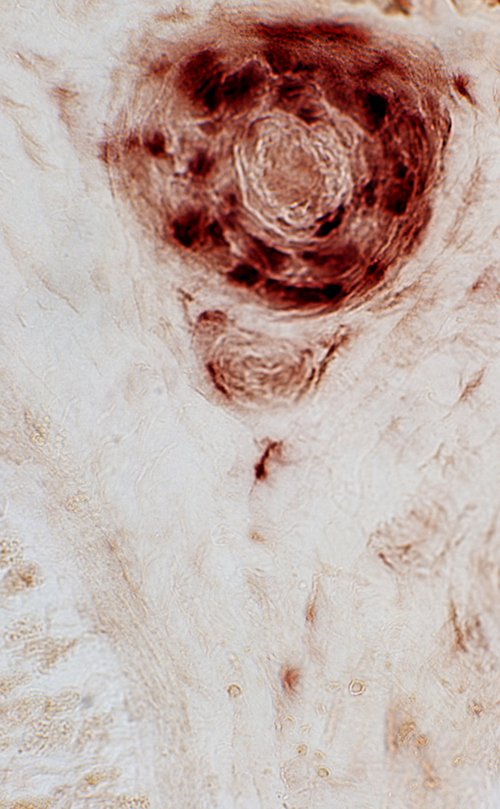
Granulomatous Vasculitis, Nerve
Location: Epineurium, PerivascularSerum antibody: pANCA
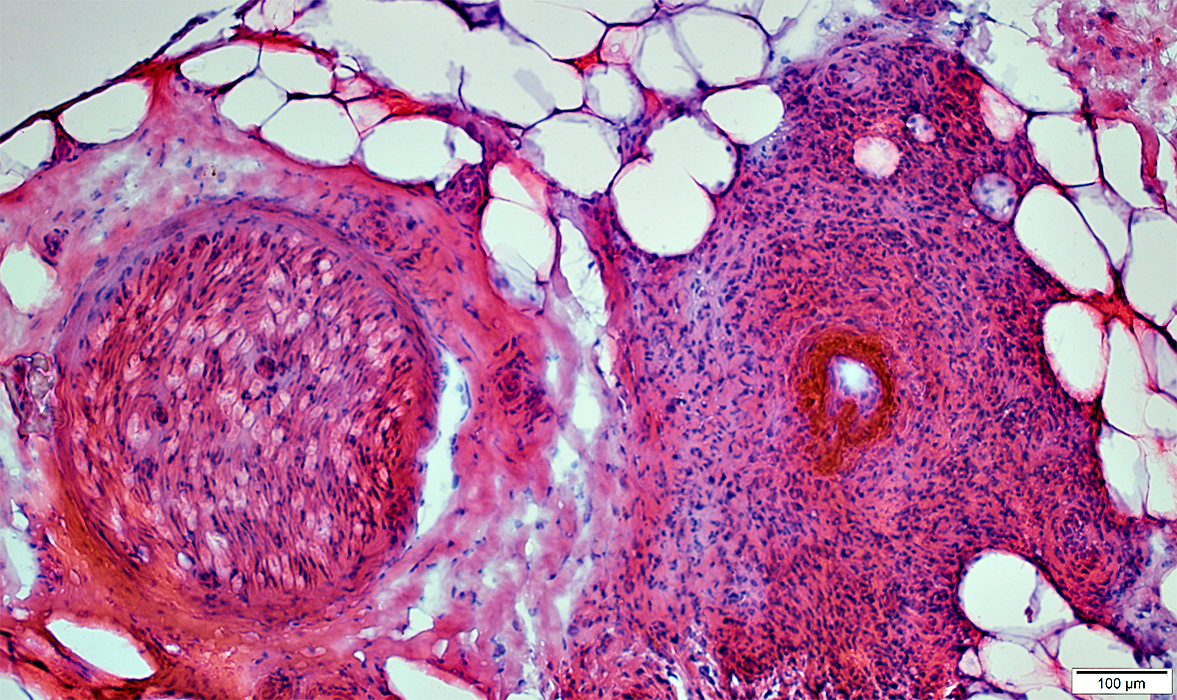 H&E stain |
Damaged vessel wall: Fibrinoid necrosis
 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
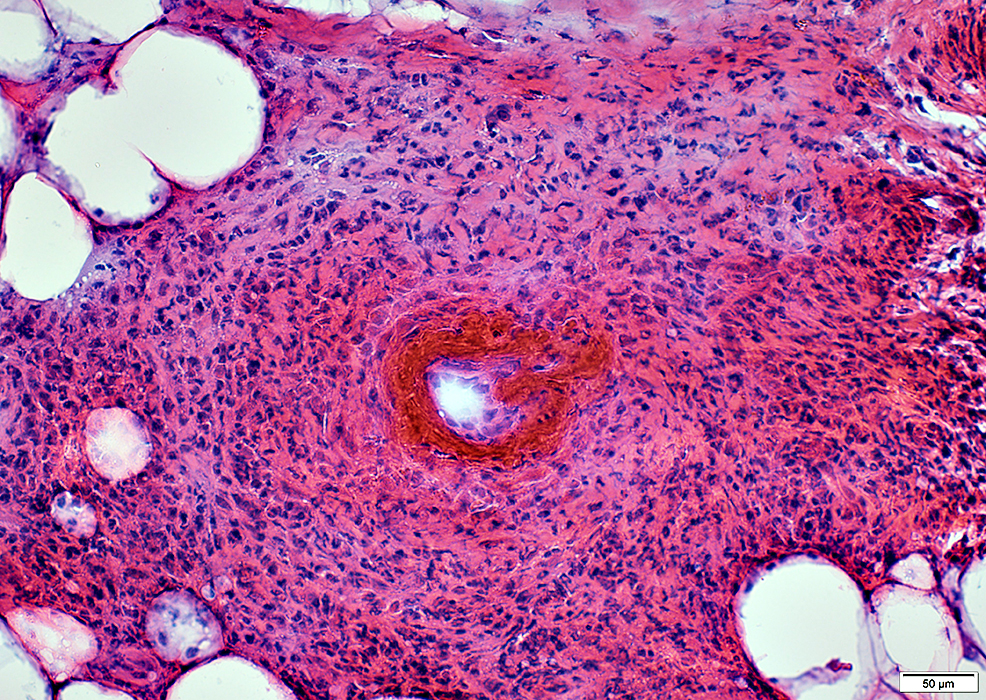 H&E stain |
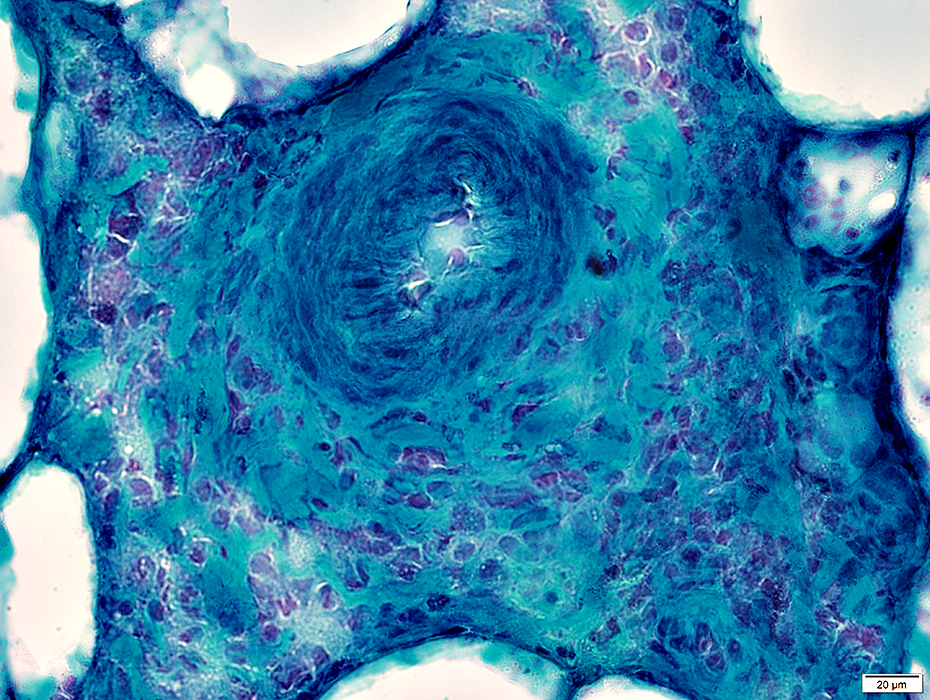 Gomori trichrome stain |
Cells around vessel
Histiocytic: Large, Abundant cytoplasm
Eosinophils: Scattered
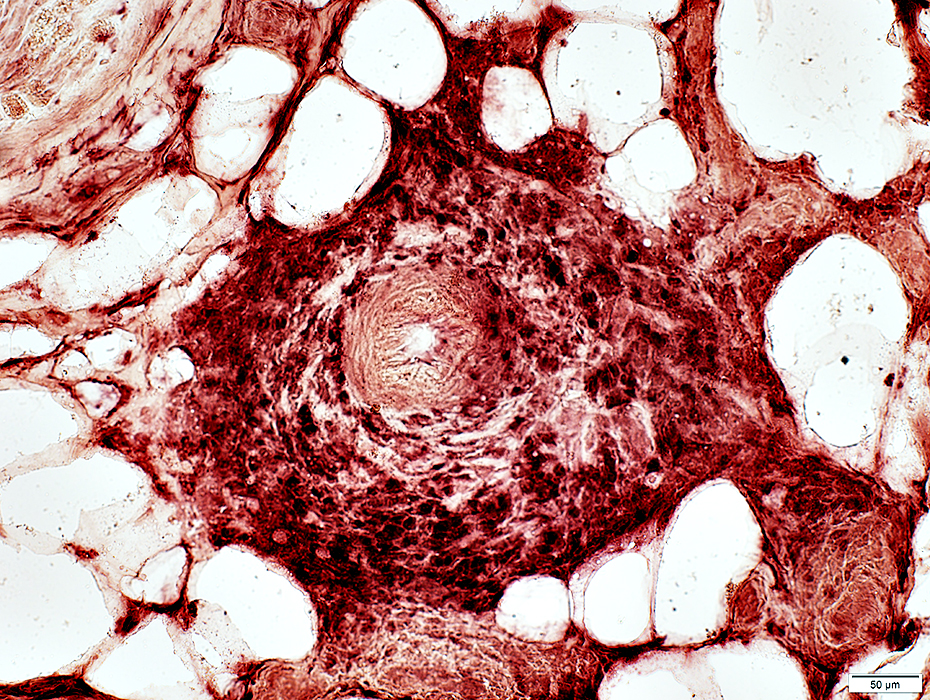
 Congo red stain |
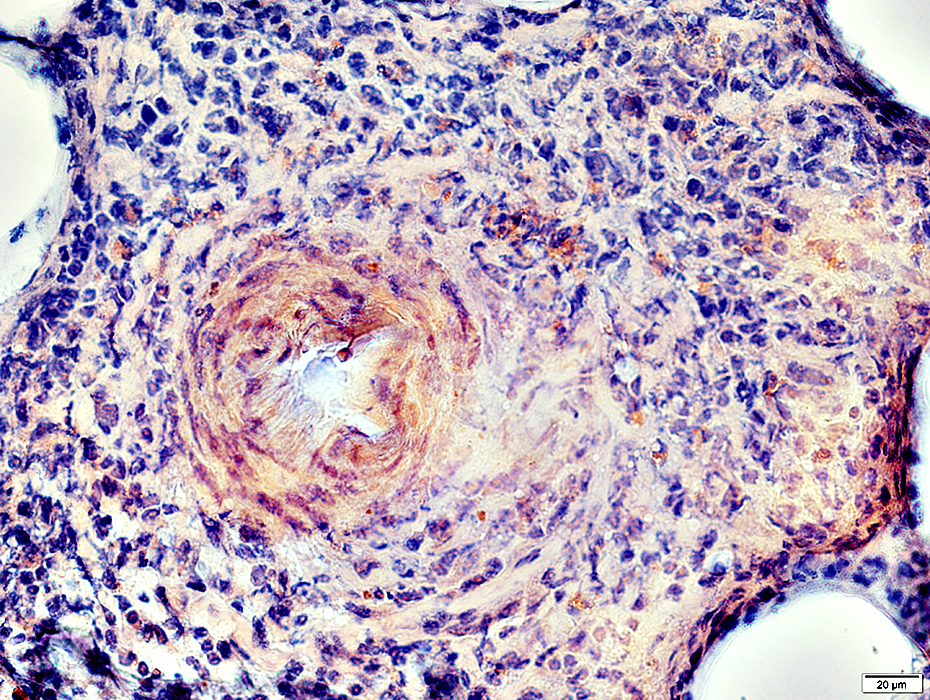
 Acid phosphatase stain |
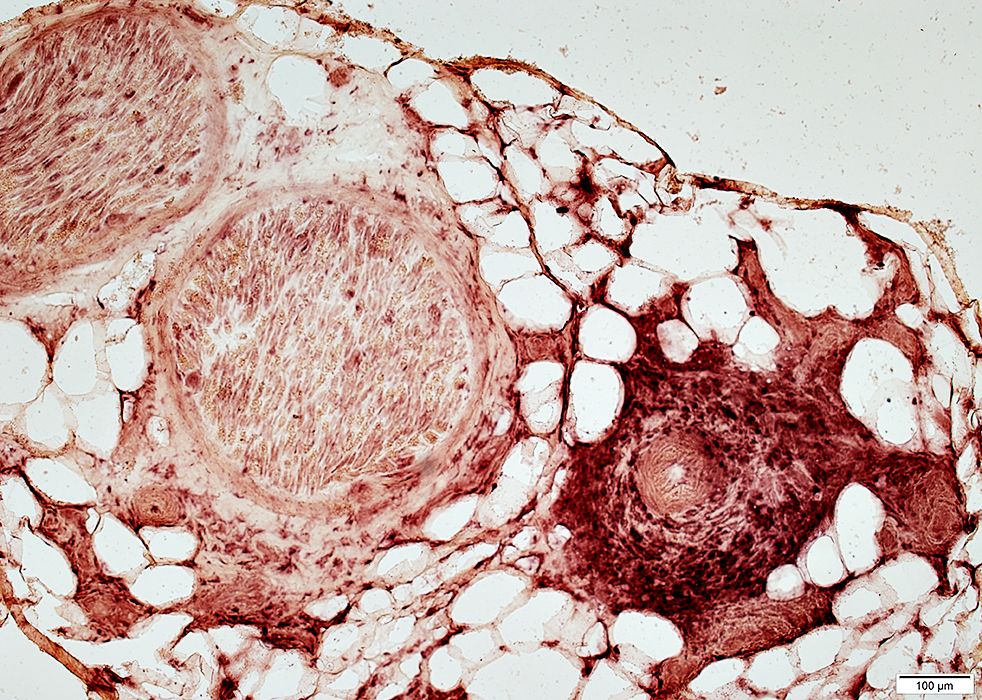 Acid phosphatase stain |
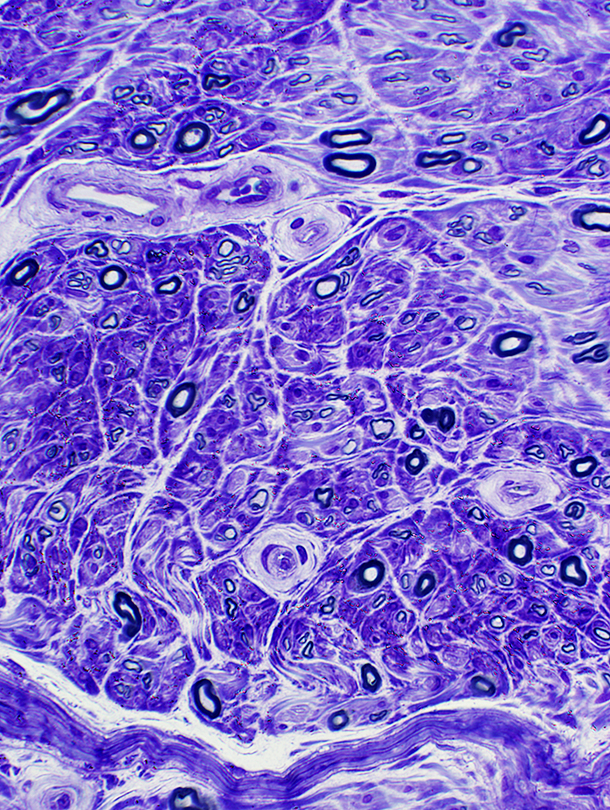 Toluidine blue stain Axon loss Large & Small myelinated Regenerating clusters: Small, Few |
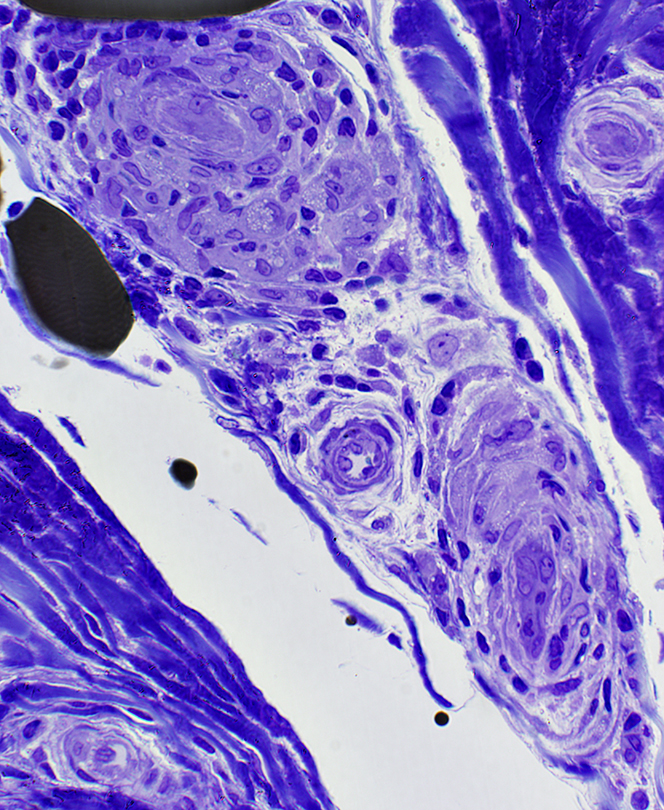 Toluidine blue stain Cells in Vessel Walls Size: Large Nuclei: Large Cytoplasm: Abundant |
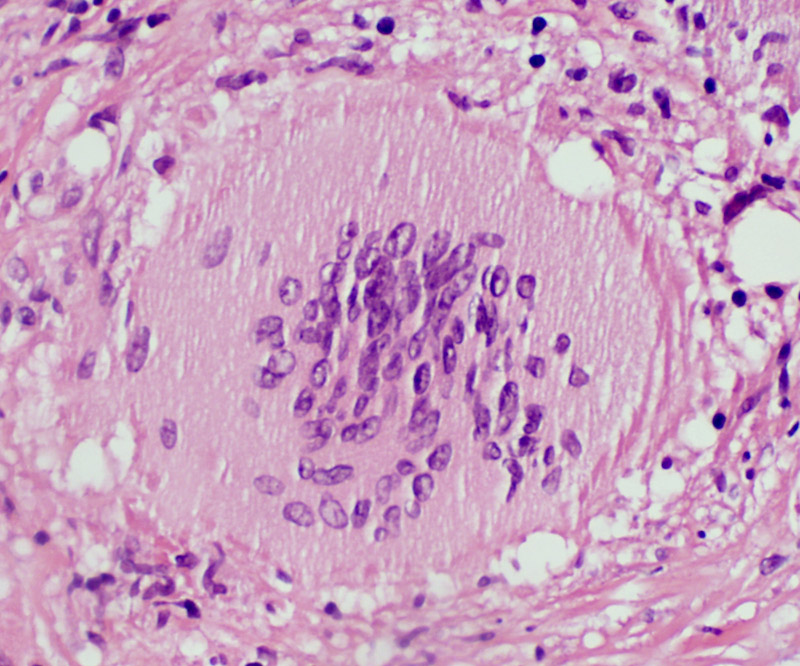
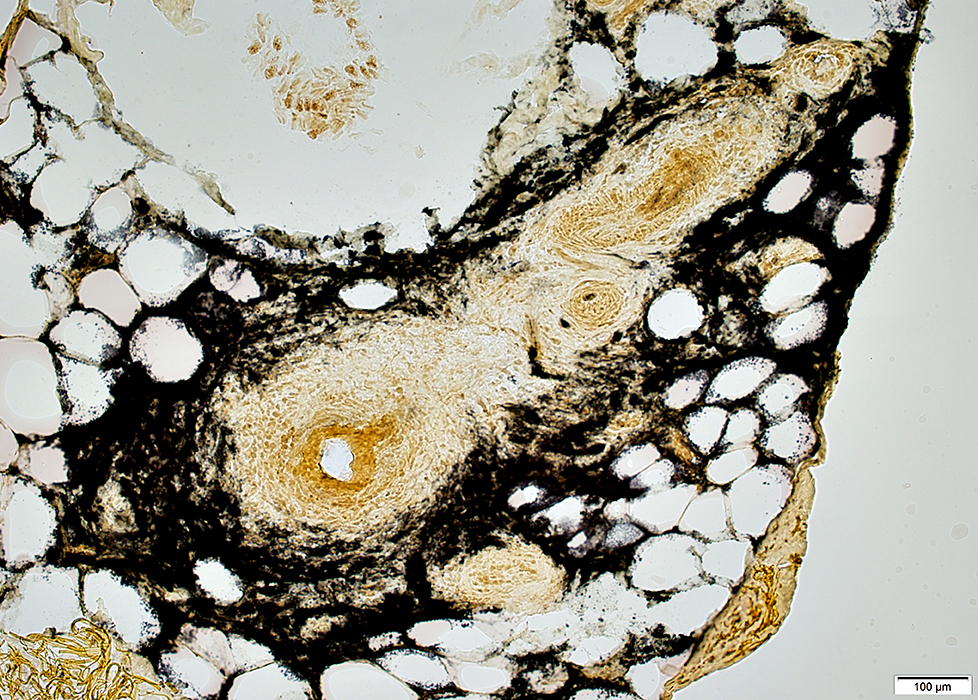
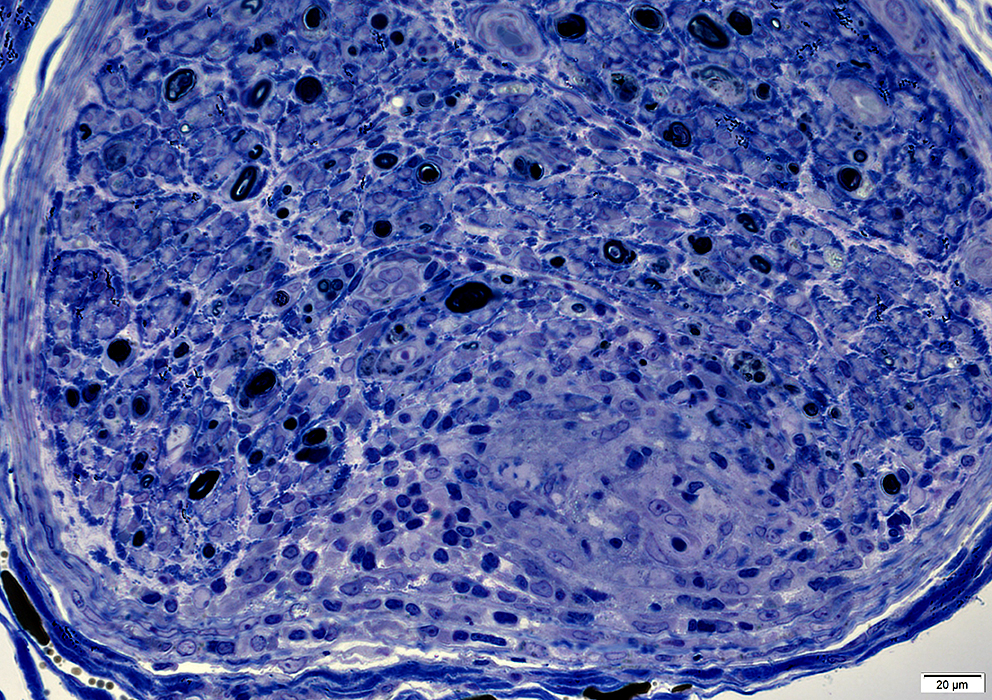
Granulomatous Disease, Nerve
Location: Endoneurium & Perineurium
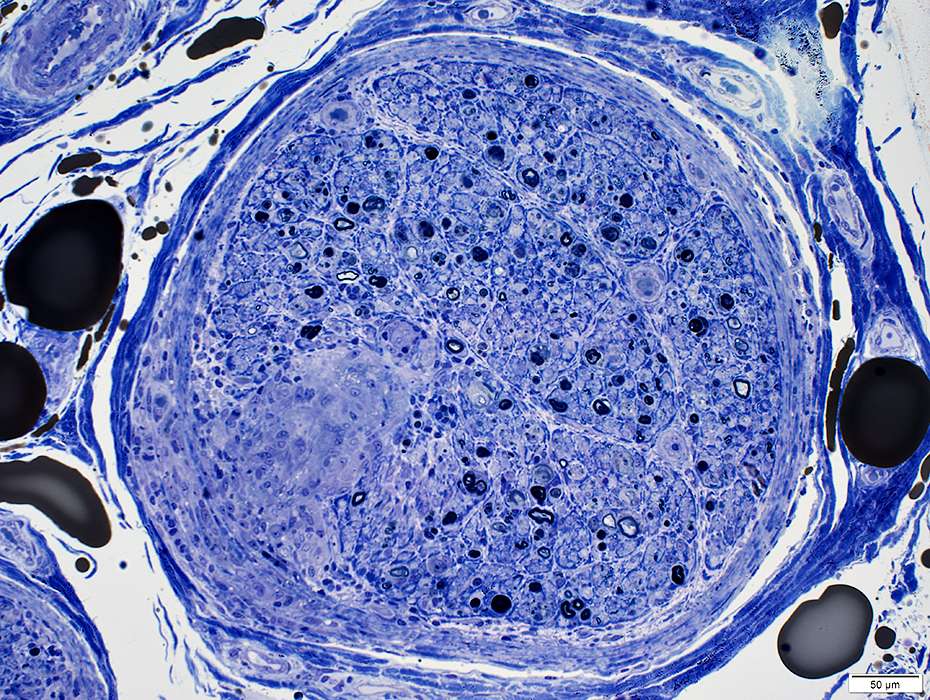
|
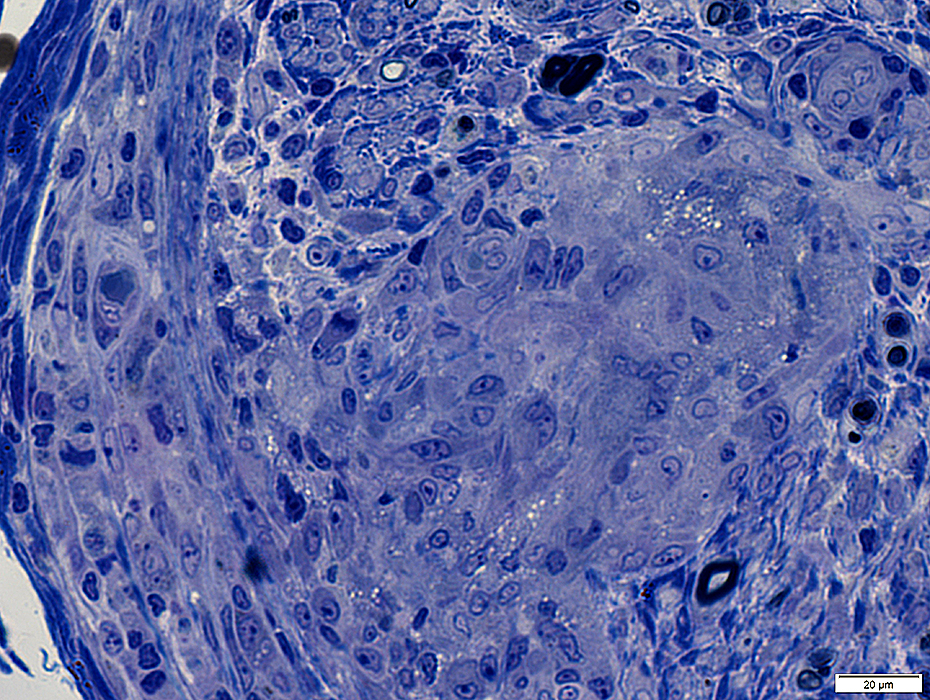
Clusters of large cells extending into perineurium & endoneurium
|
|
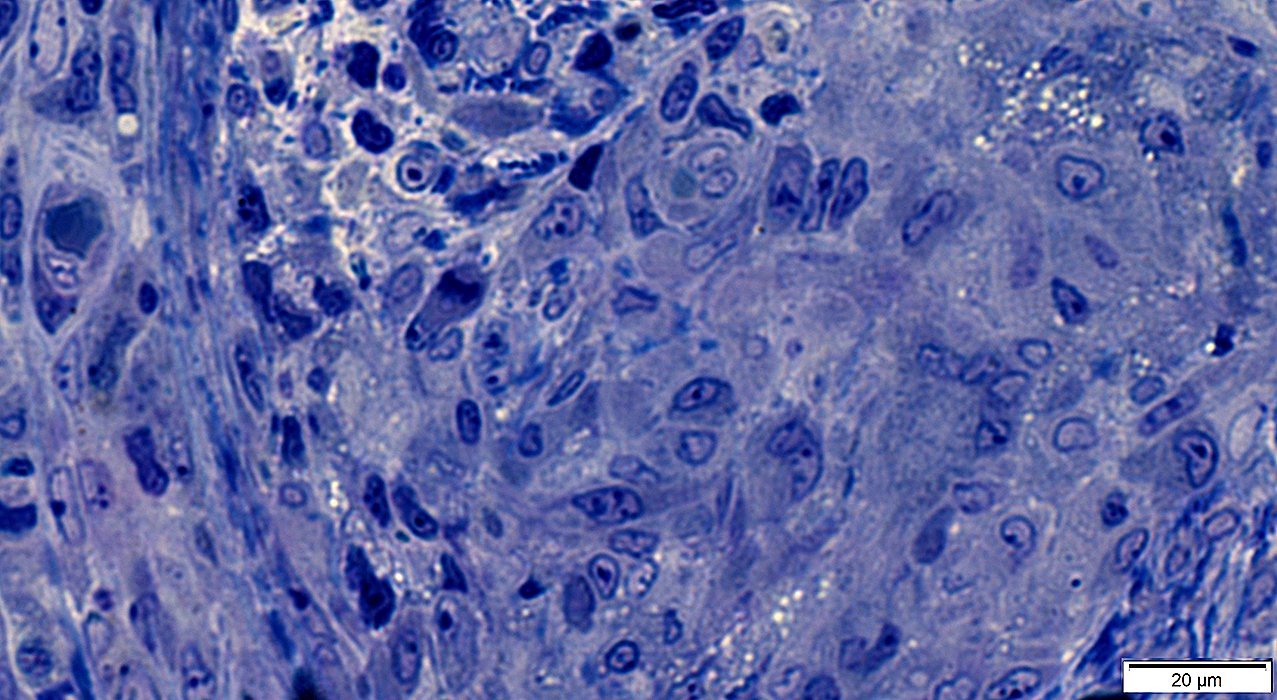
Clusters of large cells
Cells have large nuclei & abundant cytoplasm
Some cells contain lipid droplets
|
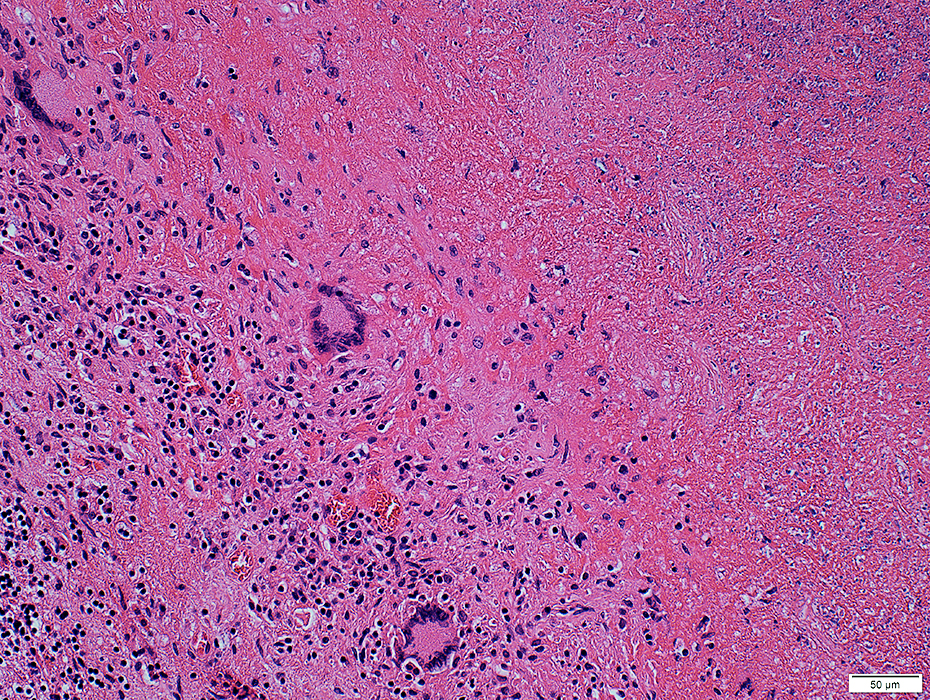
Granulomatous Changes: Tuberculosis (Cerebellum)
Regional changesNecrotic tissue (Top Right)
Granulomatous pathology (Bottom Left)
Multinucleated giant cells
Histiocytic cells: Scattered
 H&E stain |
Granulomatous tissue
Multinucleated giant cells
Scattered histiocytes
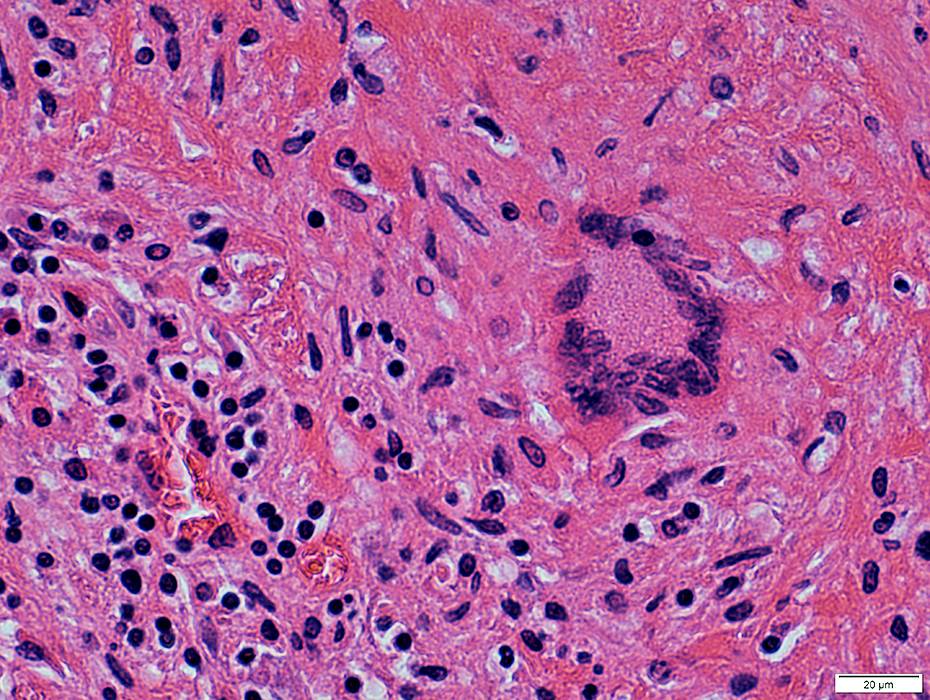 H&E stain |
Tuberculous bacilli
Small, red-stained structures
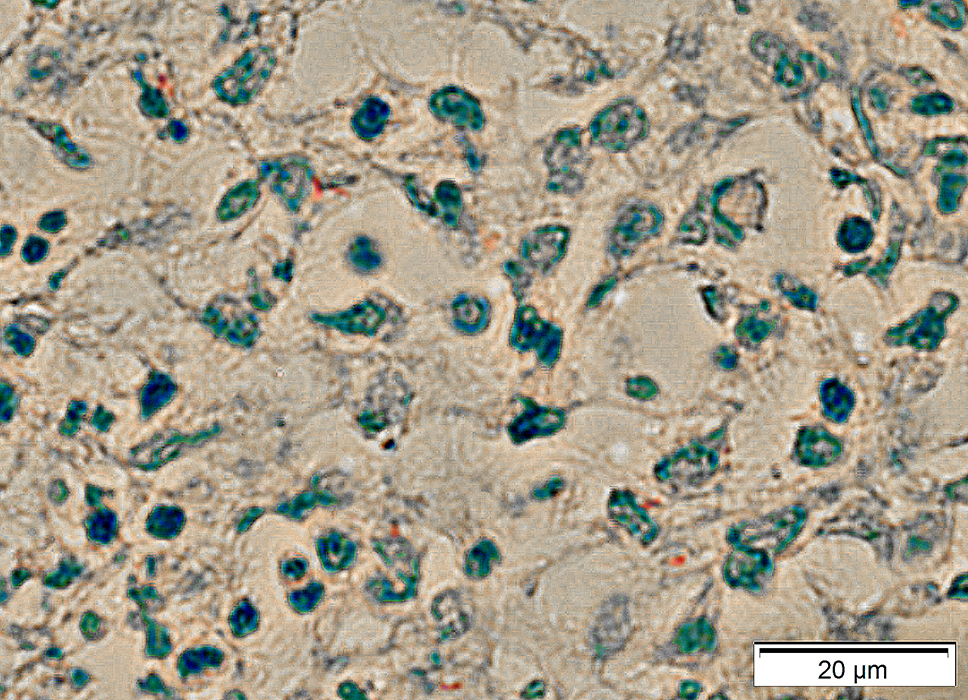 Acid fast stain |
References
1. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2025;51:e70040
Return to Inflammatory myopathies
Return to Neuromuscular Syndromes
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
1/14/2026