Brachio-Cervical Inflammatory Myopathy (BCIM)
Alternative names
Specific: B-Cell Inflammatory Myopathy (BCIM)
General: Polymyositis
|
Myopathy Immaturity Necrosis Regeneration Focal invasion Varied size Immune features Lymphocyte foci (ELS) Endomysium Perimysium Foci + Vessels Cell types Complement Endomysial pathology MHC-I Vessels Within lymphocyte foci Clinical |
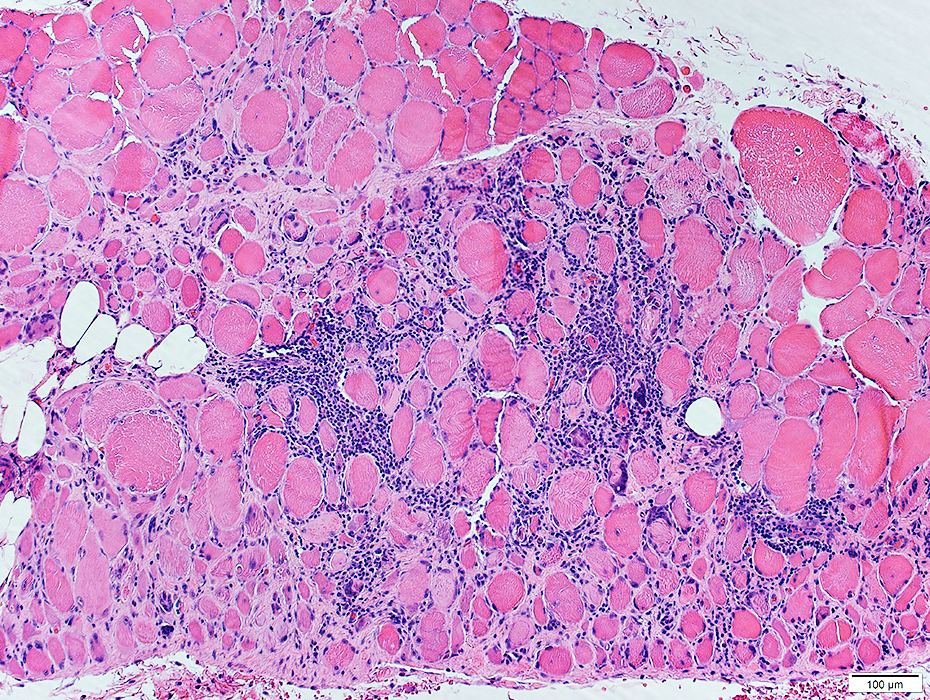 H&E stain |
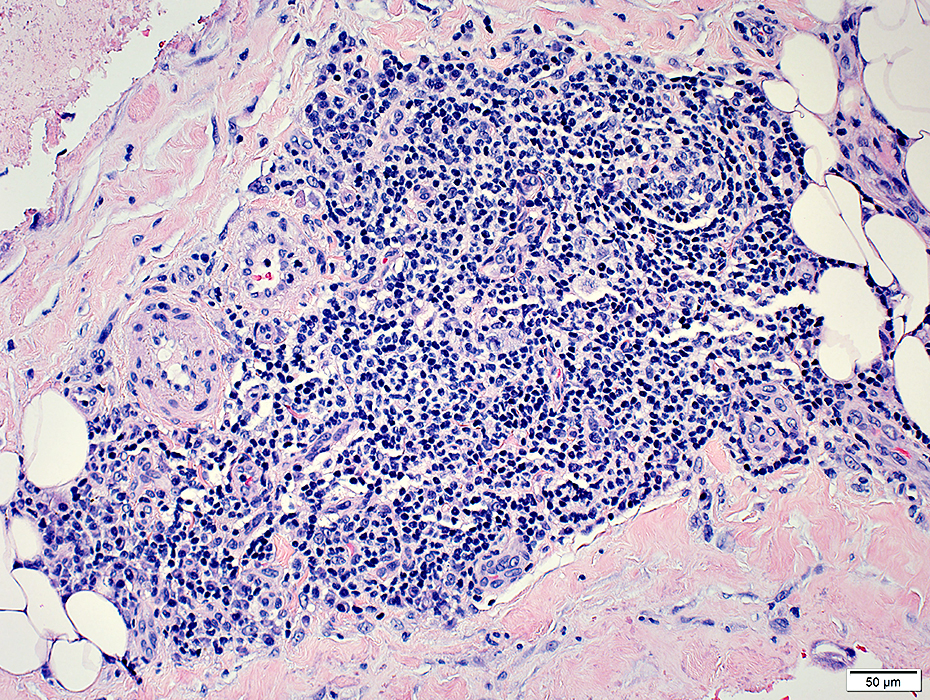
Inflammatory Cell Foci: Ectopic Lymphoid Structures (ELS) 1
Lymphocyte foci contain: B-cells & Atypical vessels (Venules)Nosology
- Extralymphatic Germinal Centers (EGC)
- Tertiary Lymphoid Structures (TLS)
- Vessels
- Type: High endothelial venules
- Size: Intermediate or Small
- Walls
- Size: Thick
- No fibrils: Unlike normal veins
- Endothelial cells
- Size: Large
- Stain for
- Features of normal endothelial cells: UEA I, CD31, MHC 1
- Feature specific for ELS vessels: Esterase
- Locations
- ELS: May be within, at edge of, or outside, regions of inflammation
- Tissue: Perimysium or Endomysium
- Lymphocytes
- B-cells & T-cells
- T/B separation: Occupy somewhat different areas in cell foci
- T/B separation: Occupy somewhat different areas in cell foci
- May be clumped
- B-cells & T-cells
- No Capsule or Afferent lymphatic vessels
- General: Target organs of immune disorders
- Muscle
- Endomysium: Between muscle fibers
- Perimysium: Between fascicles
- BCIM: PMScl-100 antibody
- Multinodular myositis
- DM-VP: NXP-2 & Tif1-γ antibody
- Orbital myositis
- Myasthenia gravis: Thymus Δ; AChR antibody
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Synovial tissue
- Citrullinated protein & Rheumatoid factor antibodies
- Sjögren
- Salivary glands
- Ro/SSA & La/SSB antibodies
- Hashimoto thyroiditis
- Thyroid
- Thyroglobulin/Thyroperoxidase antibodies
- Diabetes, Type I/Pancreas
- Lupus erythematosis/Kidneys: dsDNA antibodies
- Multiple sclerosis/Meninges
- Graft rejection, chronic
- Solid tumors
- Lymphoid toxins & chemokines: CXCL12; CXCL13; CCL19; CCL21
- Inflammatory cytokines: IL-17; IL-21; IL-22; IL-23; TNF
- Enzyme activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID; AICDA)

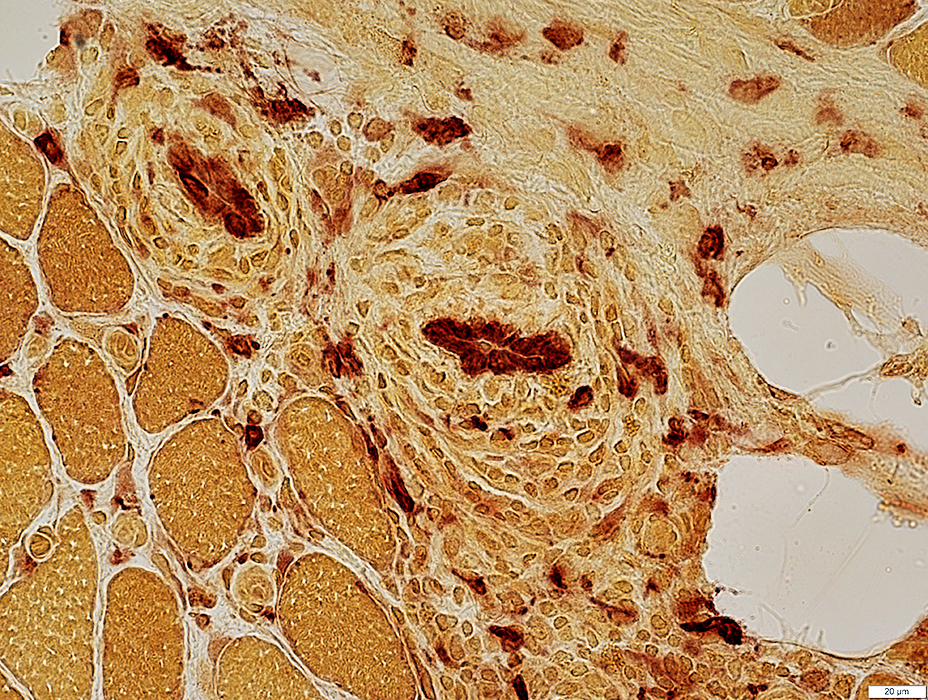
ELS: Location
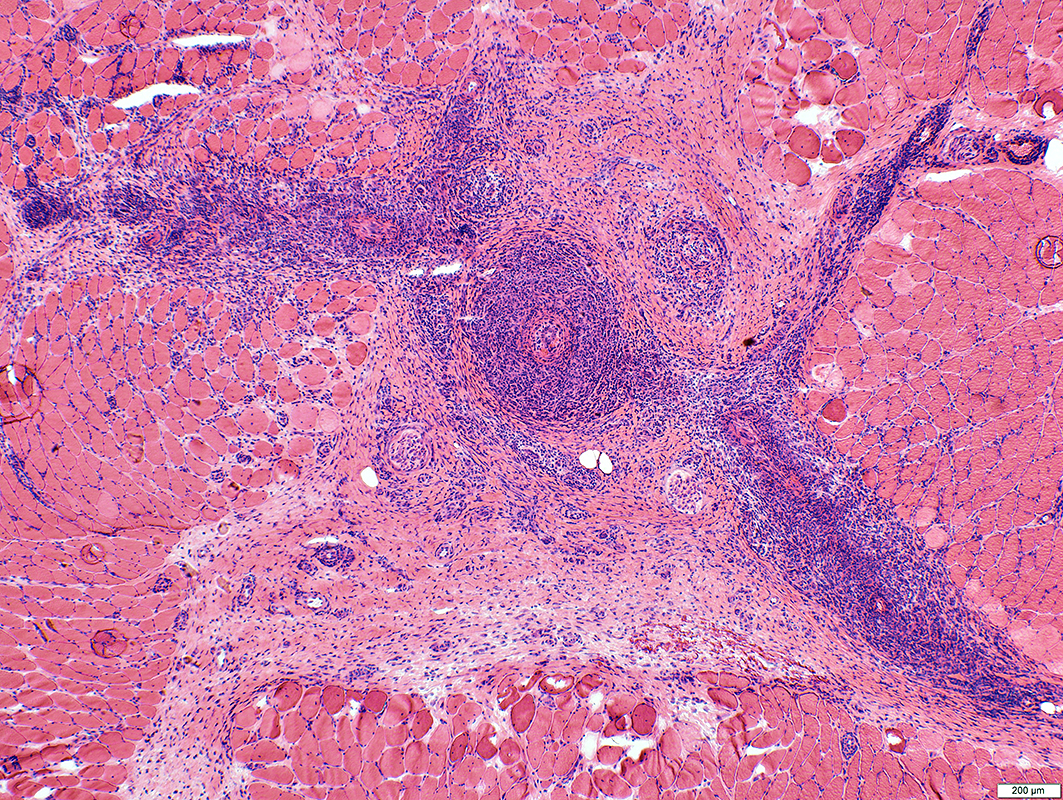 H&E stain |
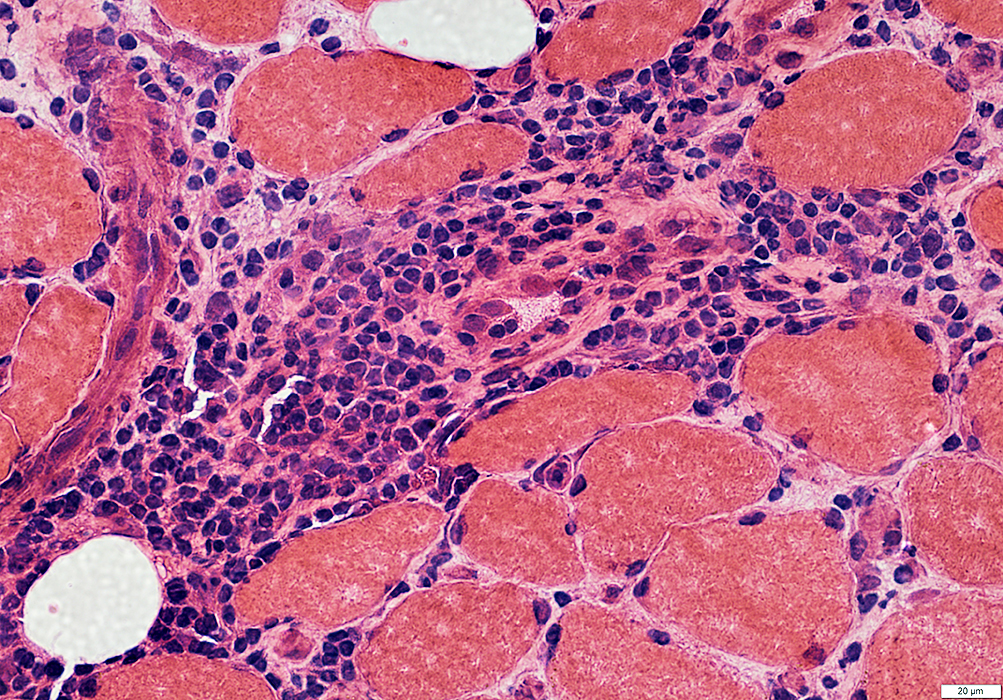
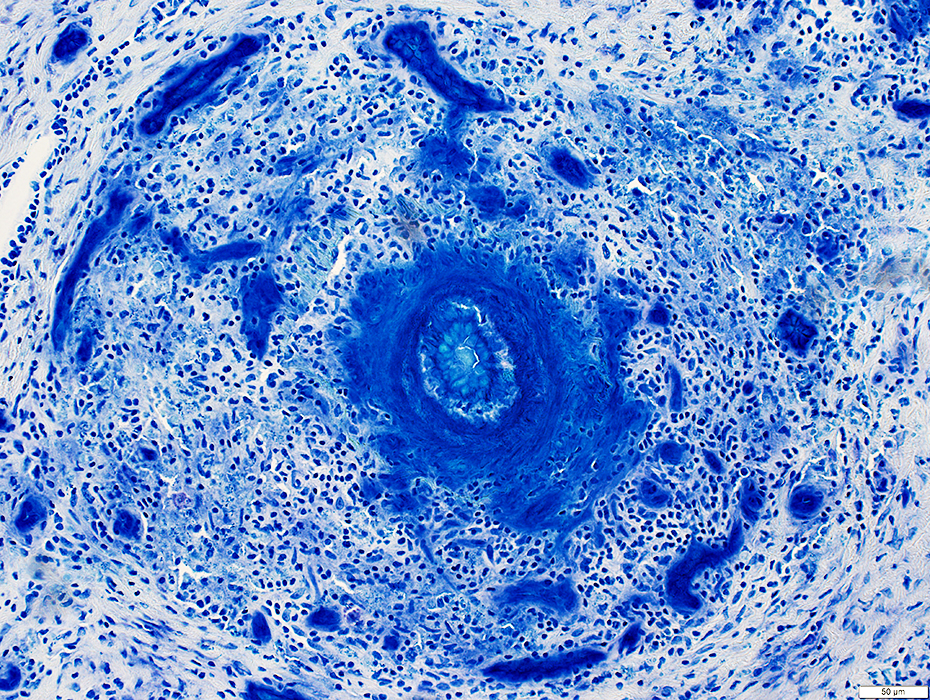
Lymphocyte foci: Multiple
Location: In abnormally widened perimysium
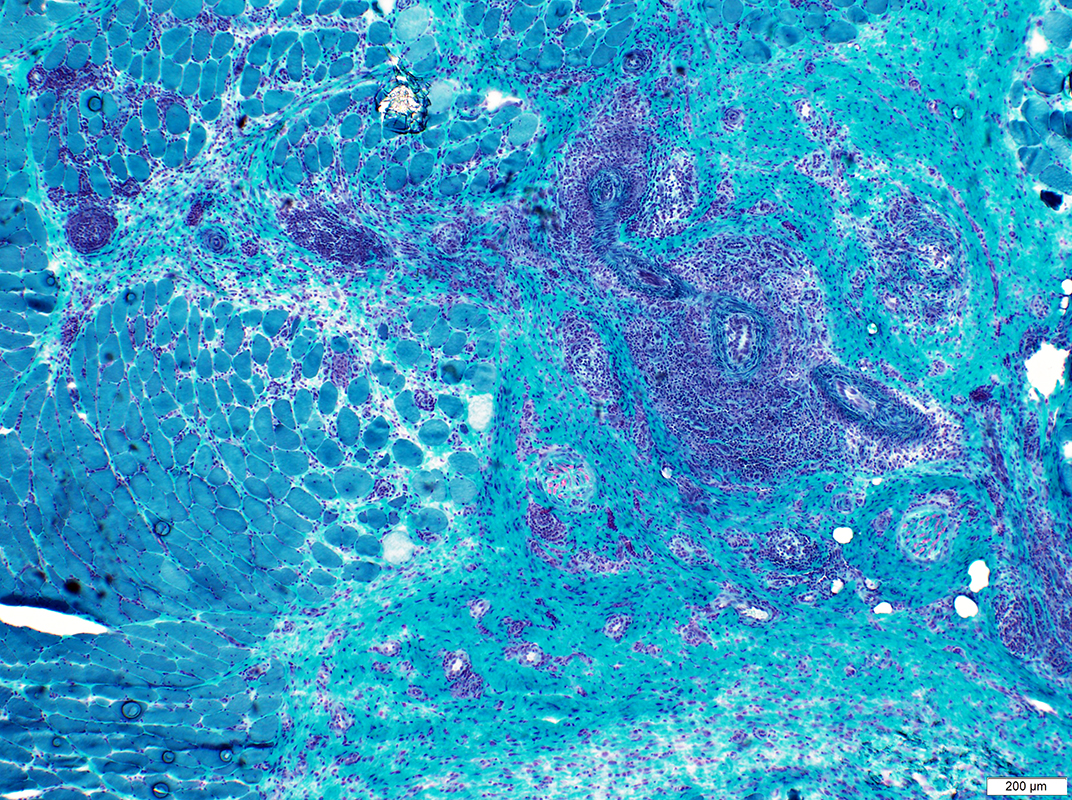 Gomori trichrome stain |
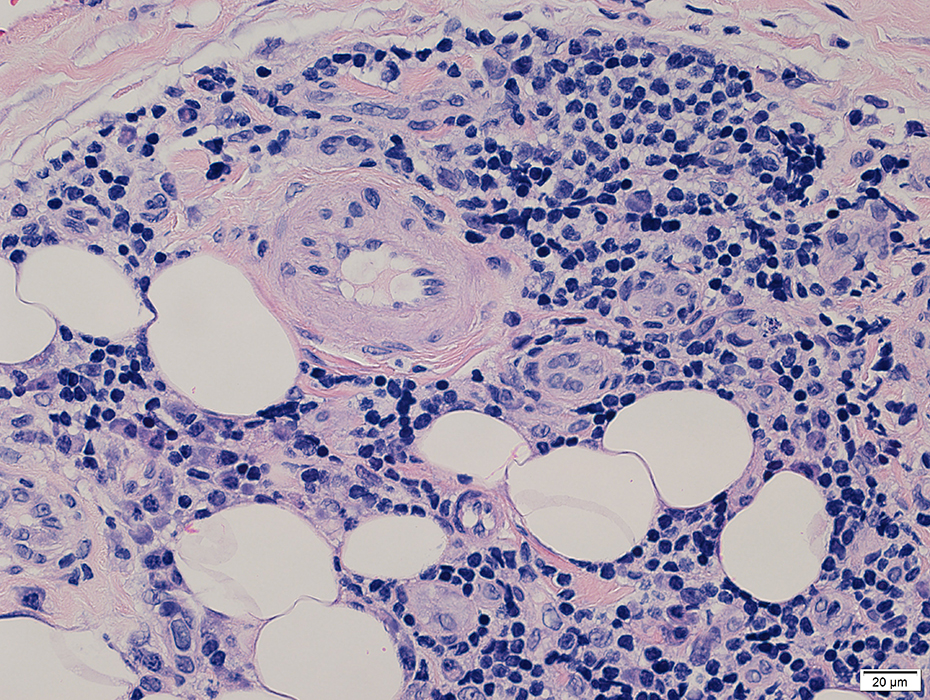
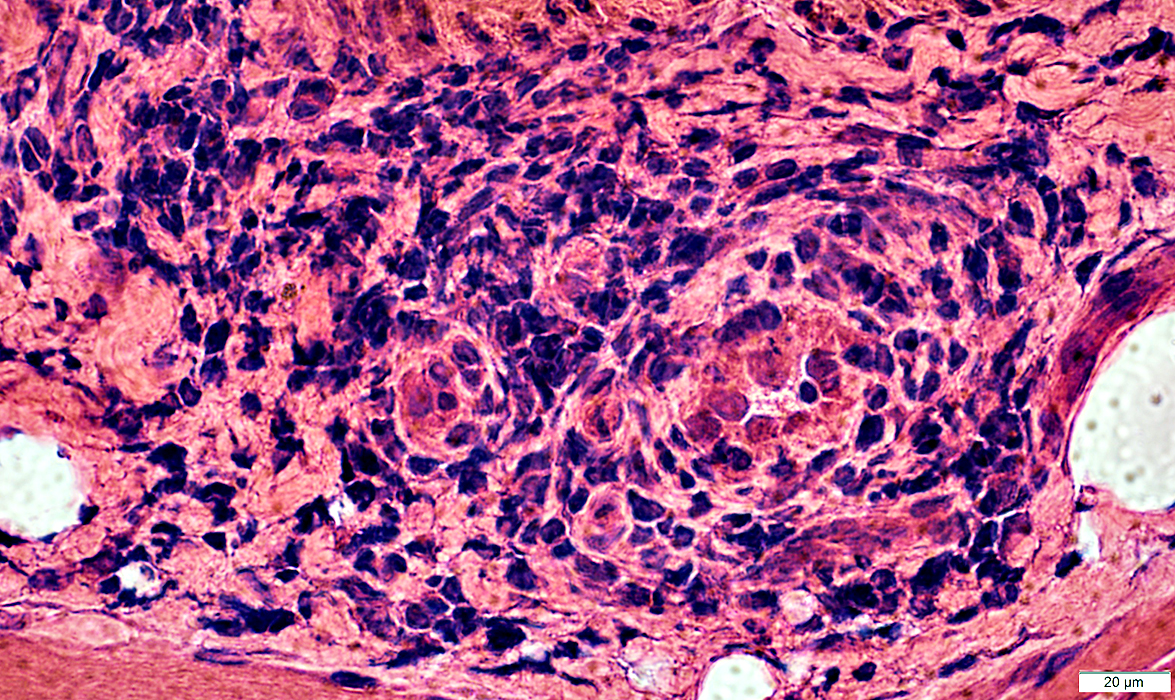
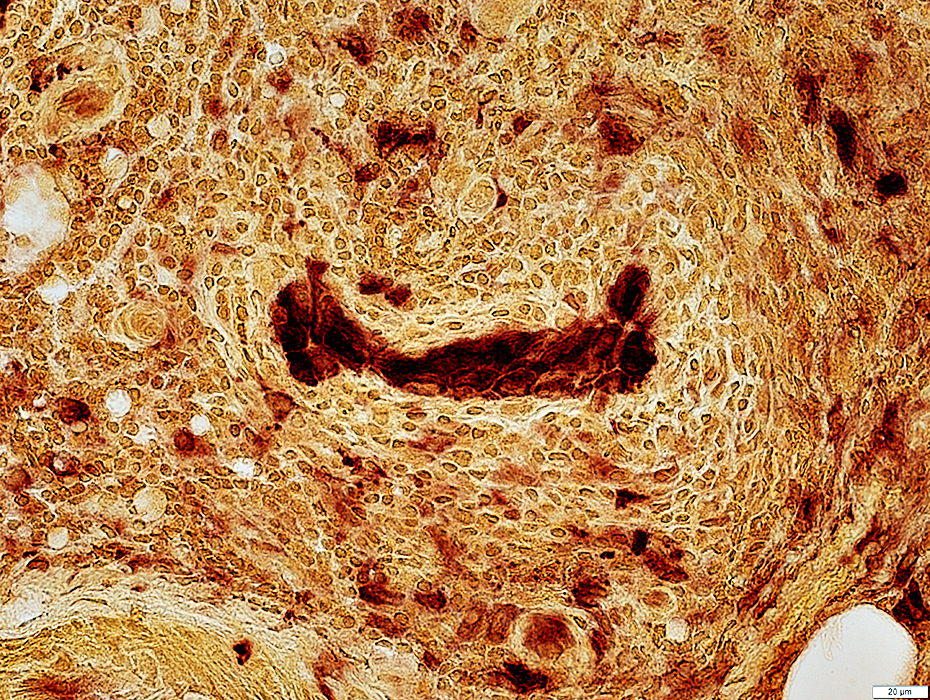
ELS Structure
 H&E stain |
 H&E stain |
 H&E stain |
 H&E stain |
 H&E stain |
 H&E stain |
 H&E stain |
ELS Vessels
|
Large Small |
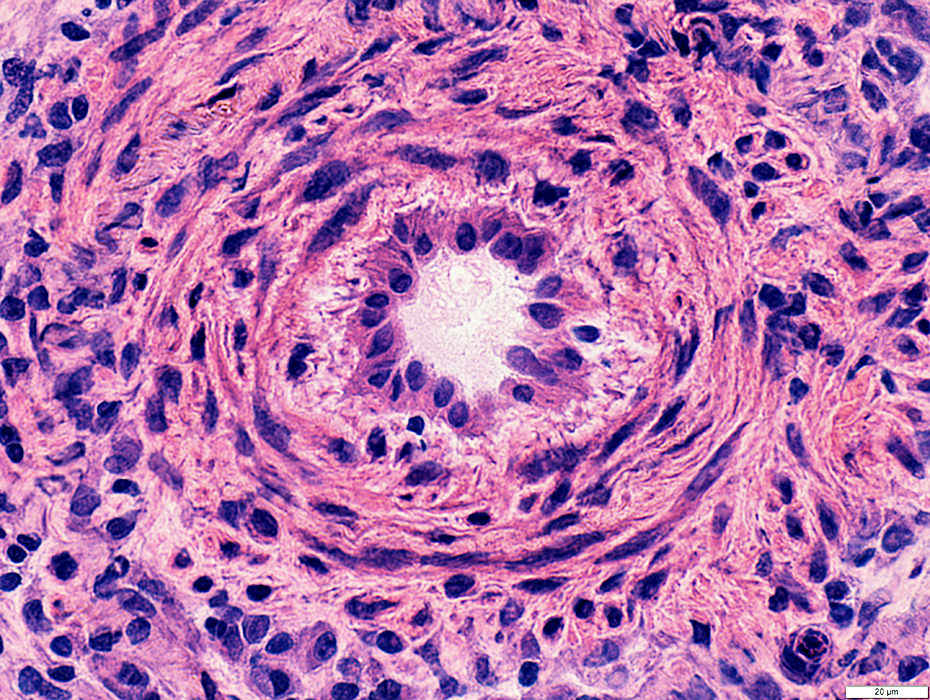 H&E stain |
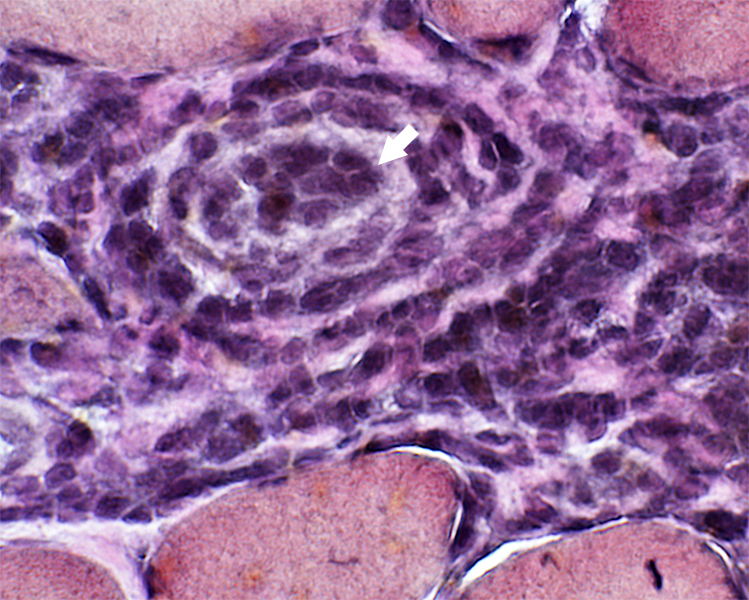
Endothelium: Prominent; Large cells
Wall: Thick
Location: Often in center of ELS
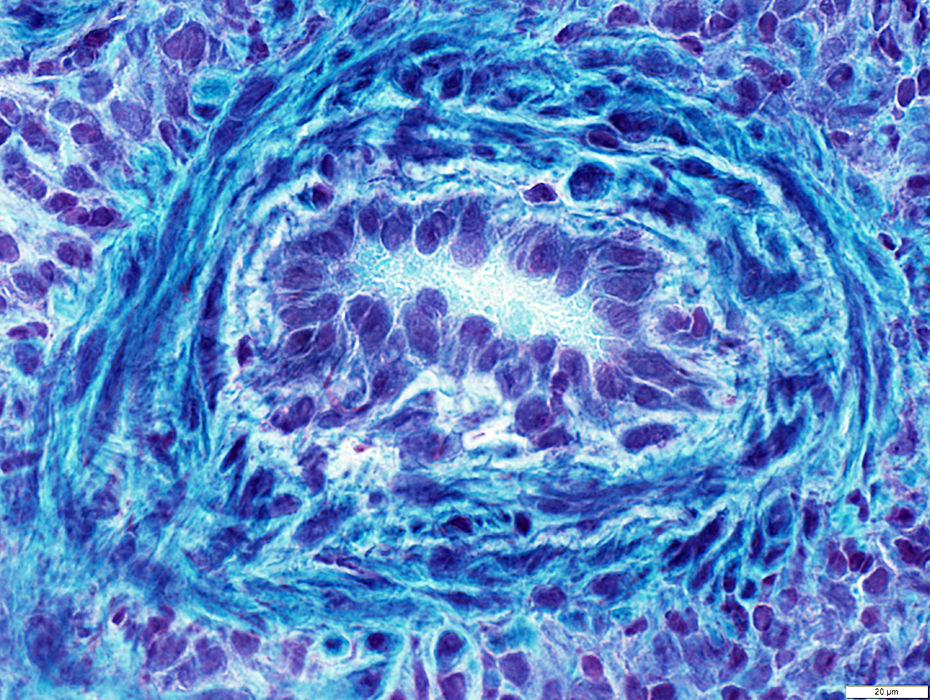 Gomori trichrome stain |
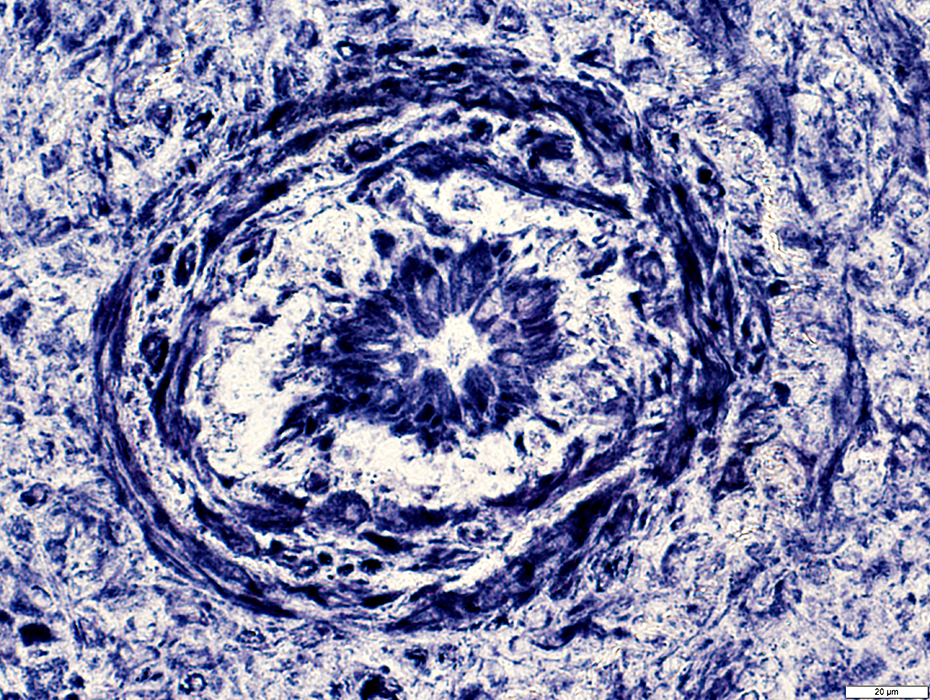 NADH stain |
Endothelium: Cells stain for NADH & Esterase
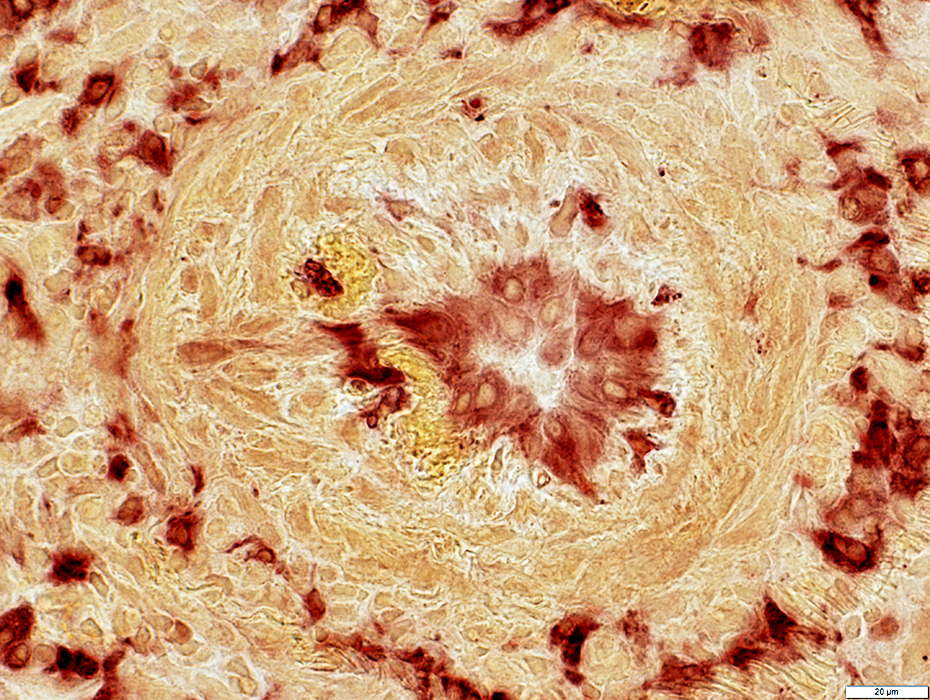 Esterase stain |
ELS Vessel: Large
Smooth muscle: Thin layer outside endothelium
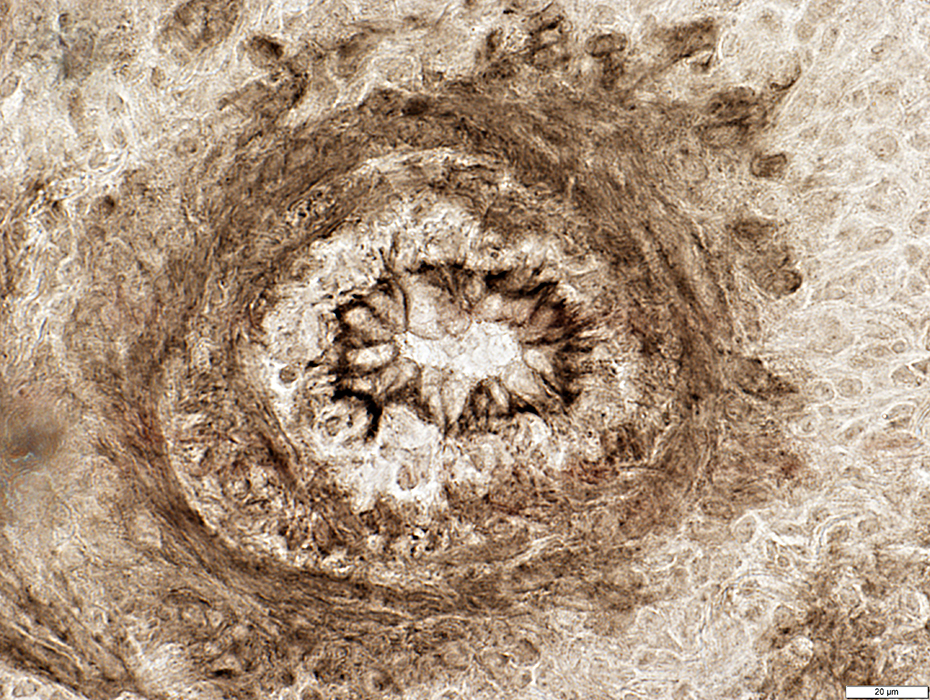 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
ELS Vessel: Large
Few histiocytic cells in wall
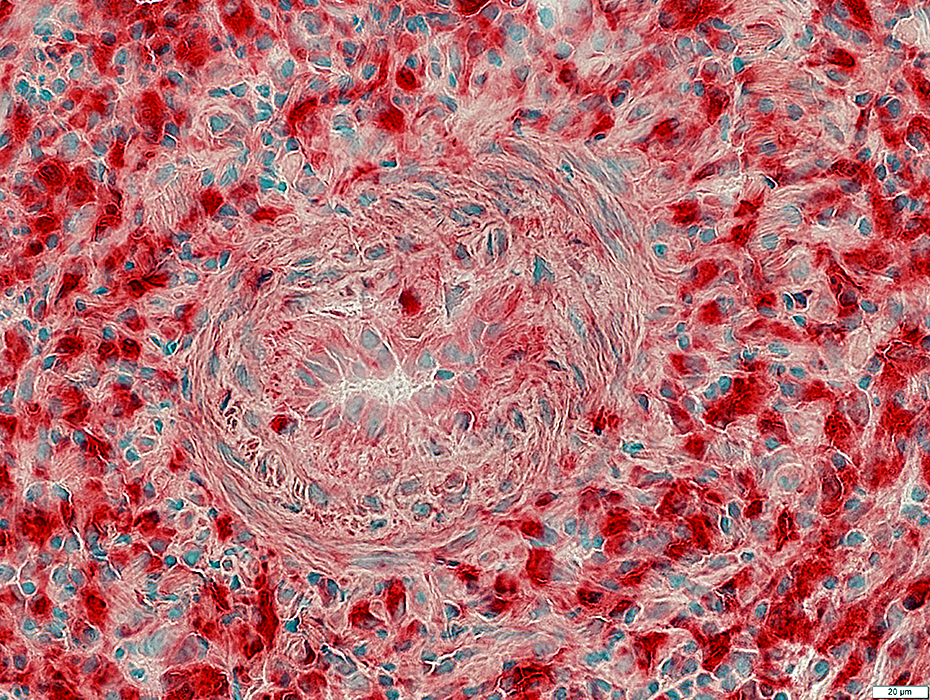 Acid phosphatase stain |
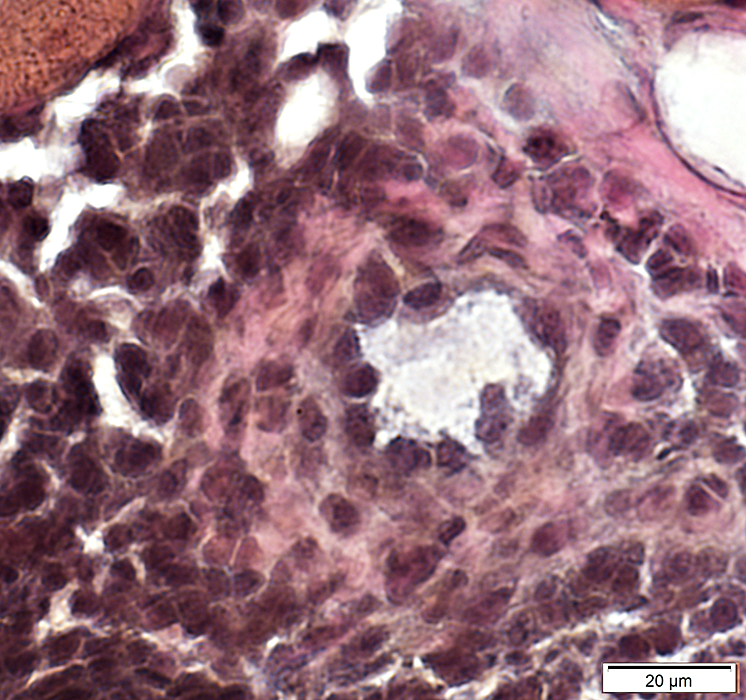
ELS Vessels: Small
Distributed through cell focus
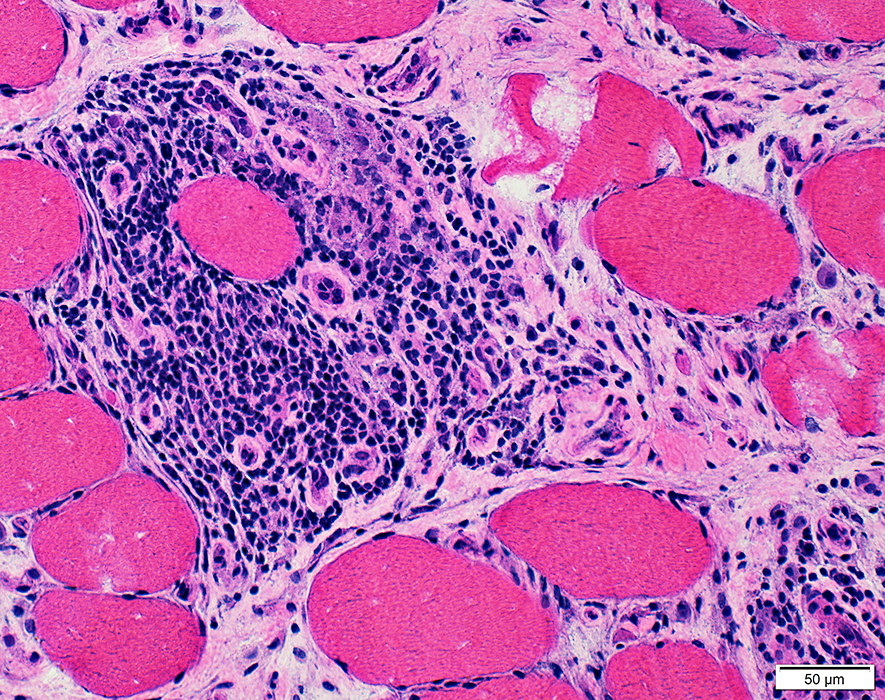 H&E stain |
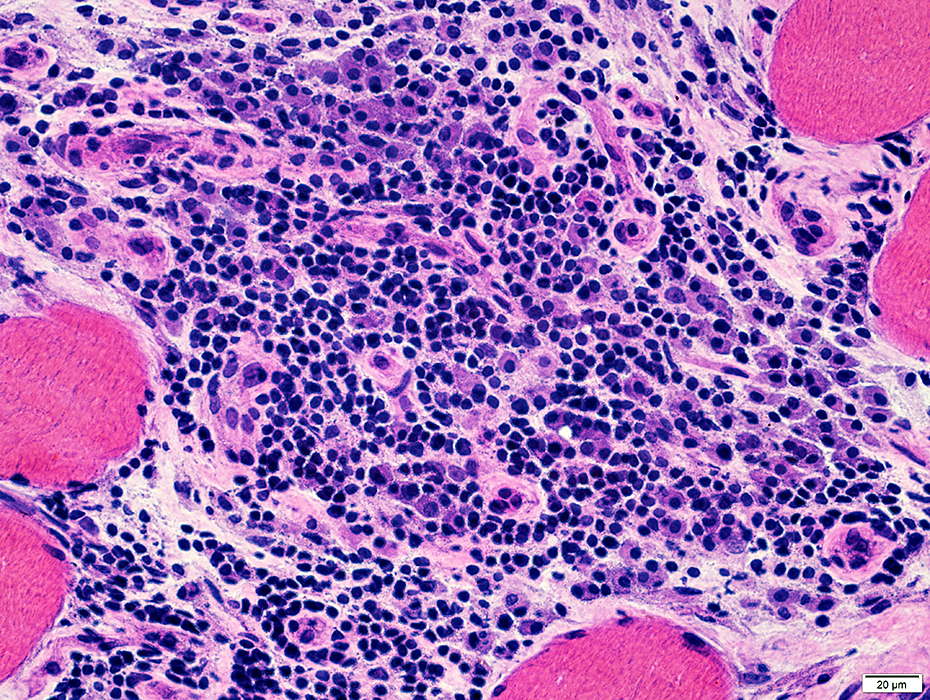 H&E stain |
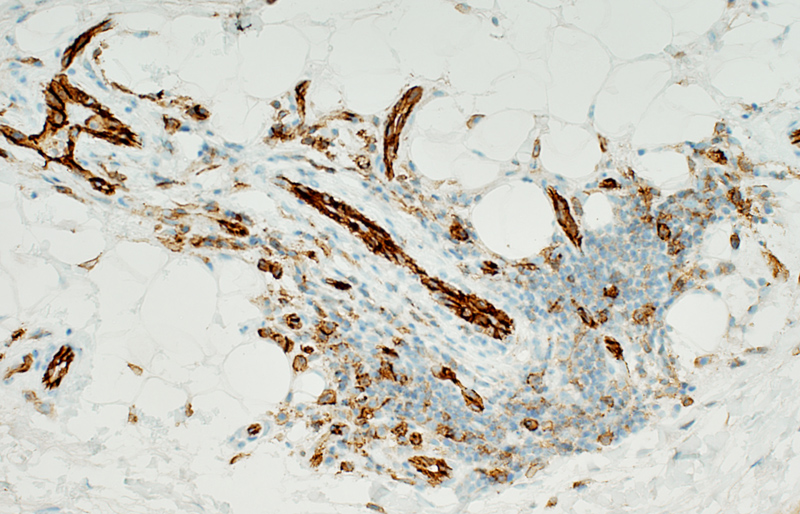 CD31 stain CD31+ endothelial cells are present in Small vessels within inflammatory foci Lumen of intermediate-sized vessel Vessels stain for ATPase (Below) 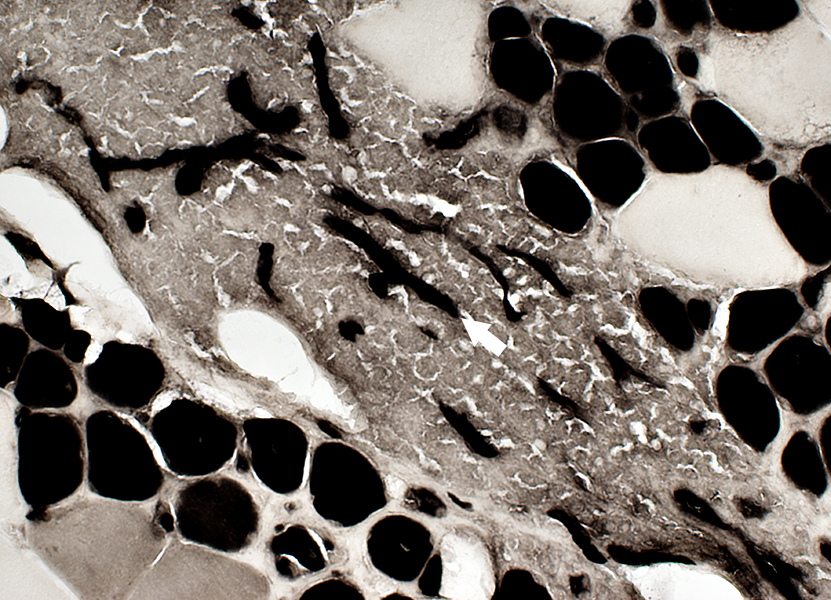 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Vessels in an ELS cell focus
May be large & small
Large vessel in center of cell focus
 ATPase pH 4.3 + TB stain |
|
Vessel in region of inflammation (Arrow) Endothelial cells Large Often Esterase+ Vessel wall: No fibrils 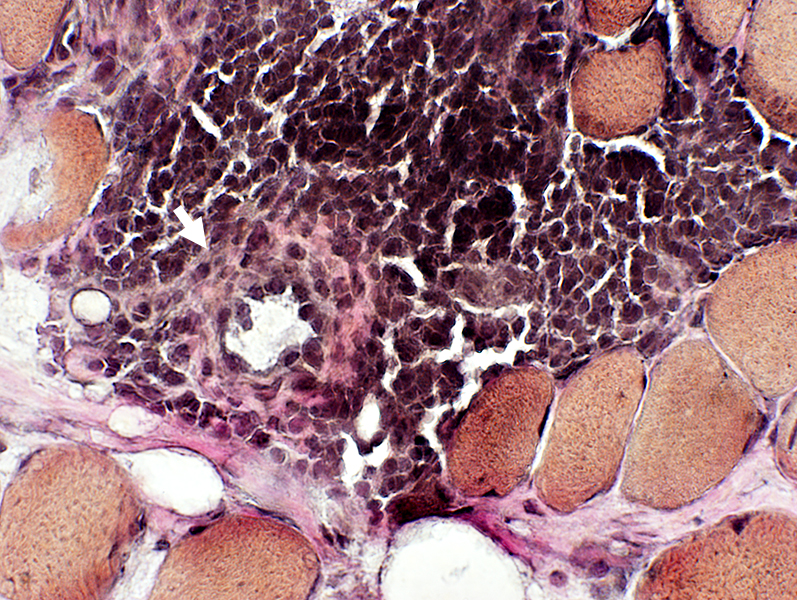 VvG |
Endothelial cells in vessel: Large (Arrow)
 VvG stain |
 VvG stain |
Endothelial cells: Large; Often Esterase+
Vessel wall: No fibrils
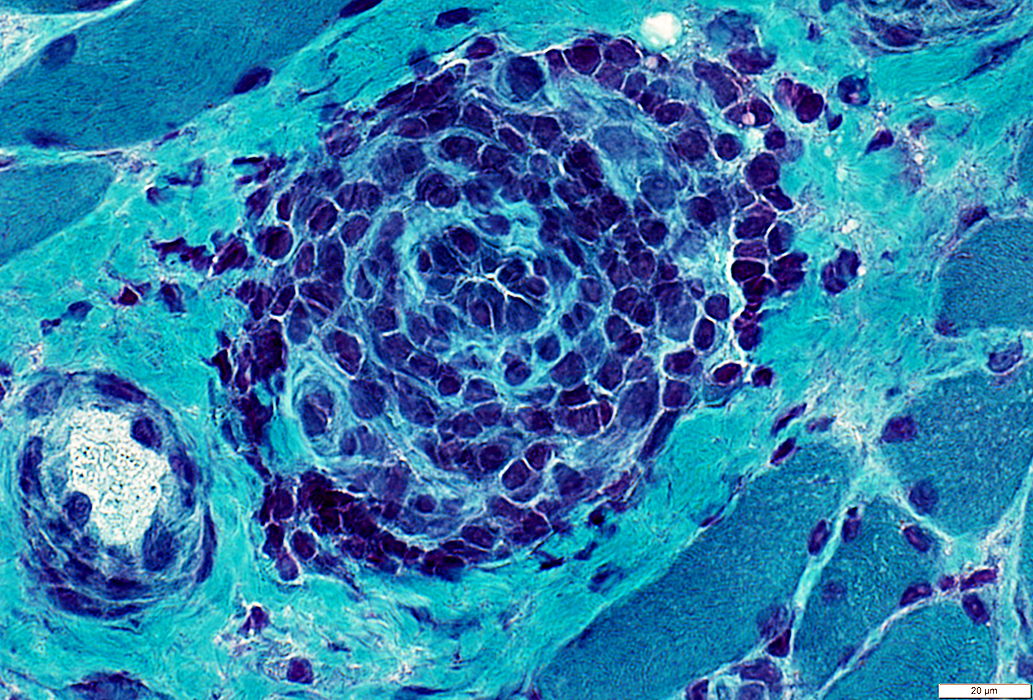 Gomori trichrome stain |
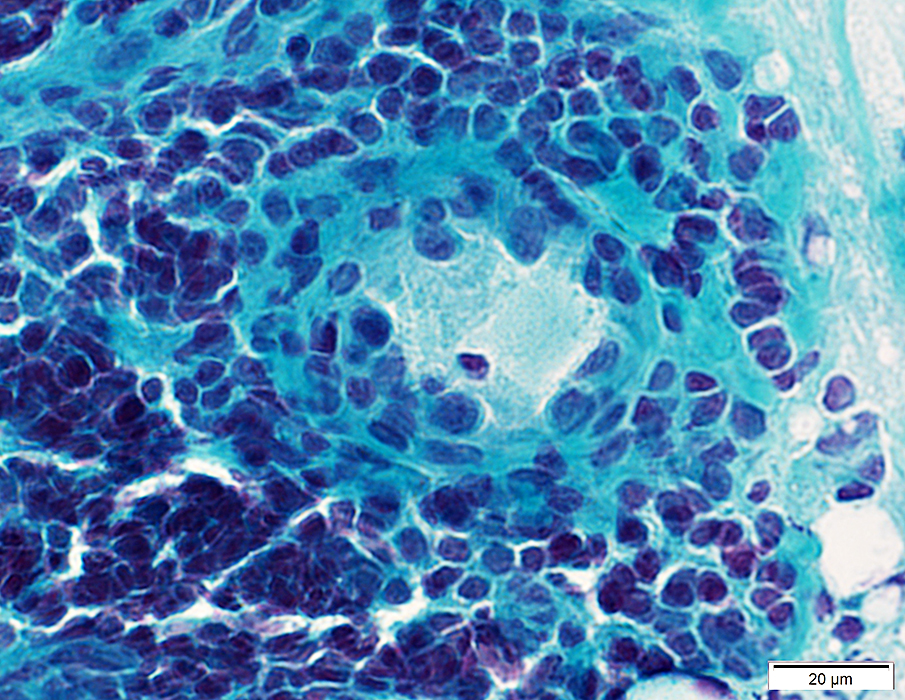 Gomori trichrome stain |
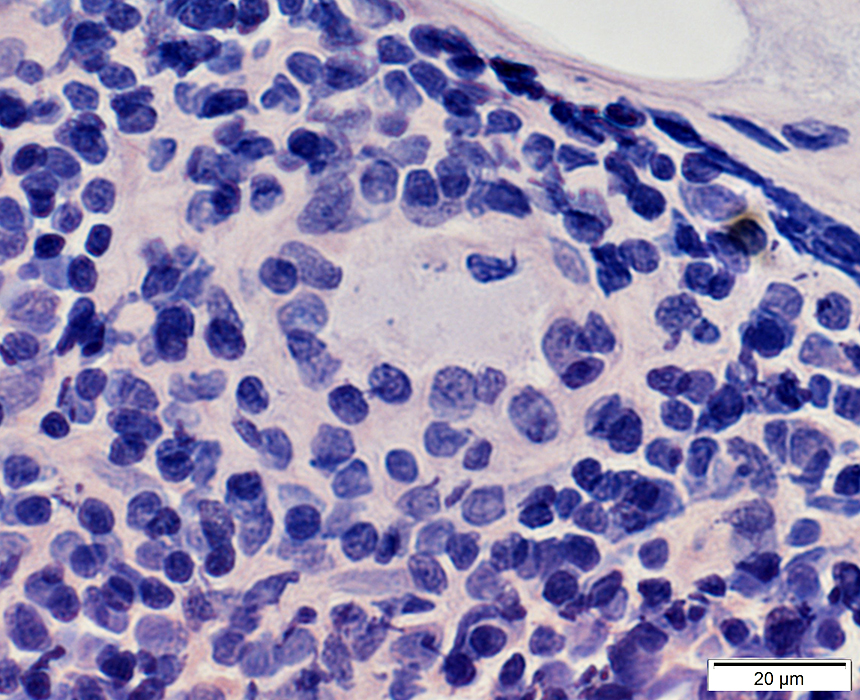 Congo red stain |
Endothelial cells in vessels in EGC (ELS)
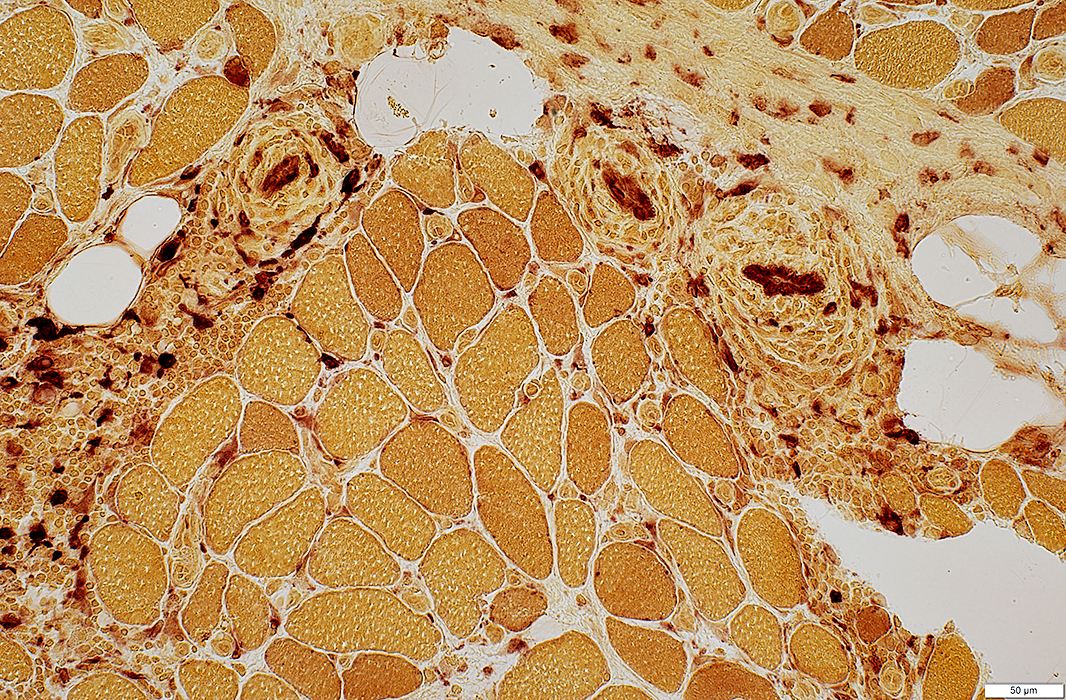 Esterase stain |
 Esterase stain |
 Esterase stain |
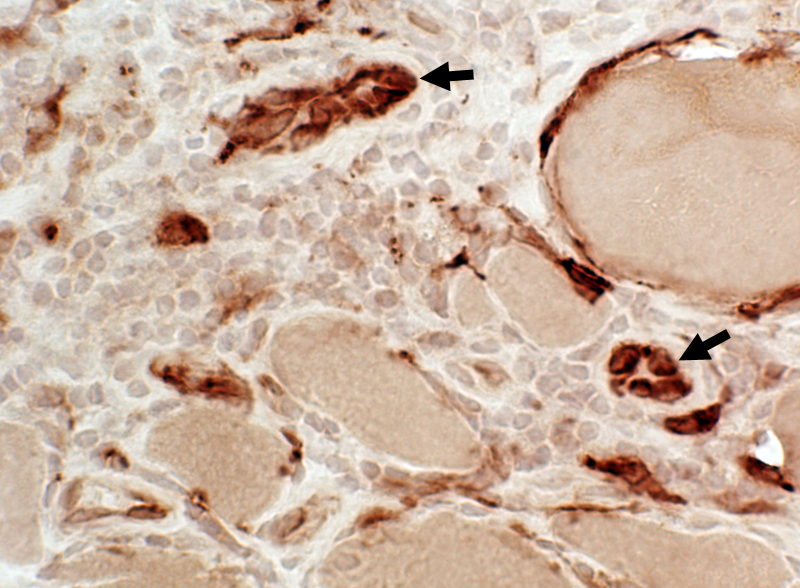 Esterase stain Intermediate-sized vessels in inflammatory foci: Endothelial cells Large Stain abnormally for esterase (Arrows) & Acid phosphatase 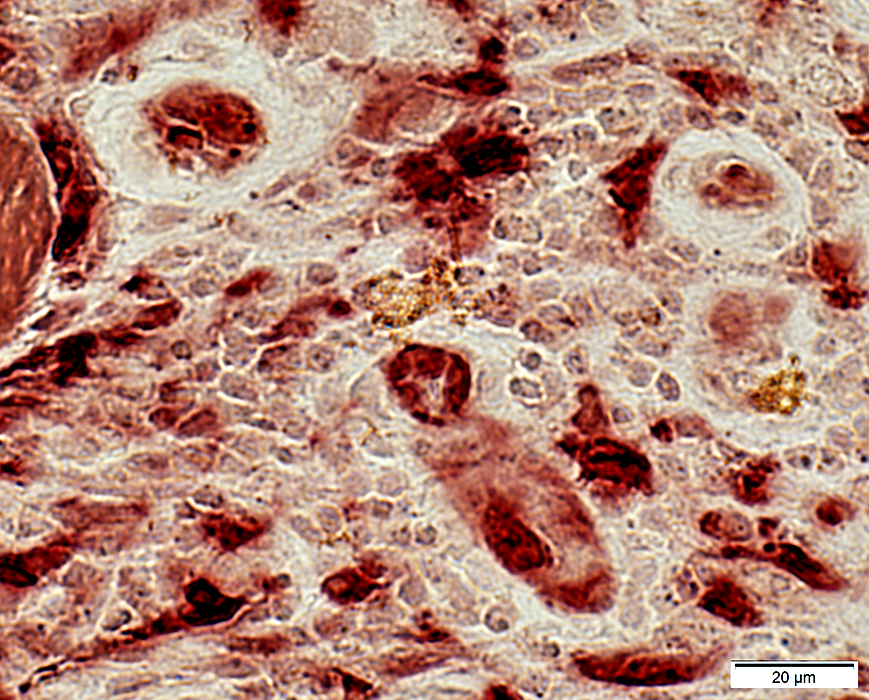 Esterase stain |
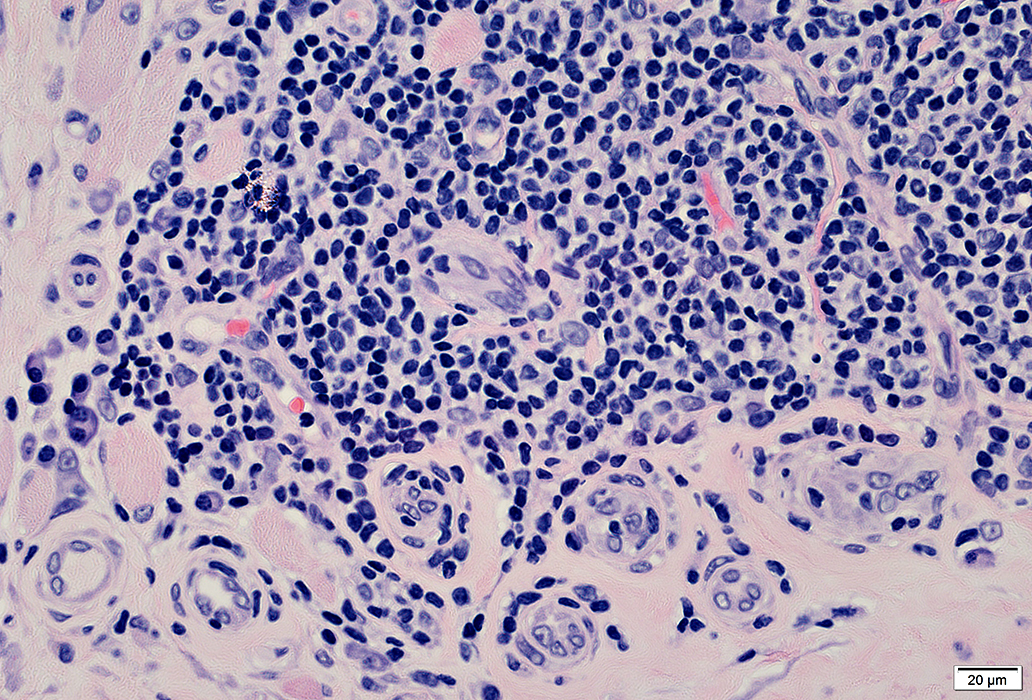 H&E stain |
Vessels
May be Large (Right, Below) or small (Left & Above)
Larger & Contain more endothelial cells than capillaries
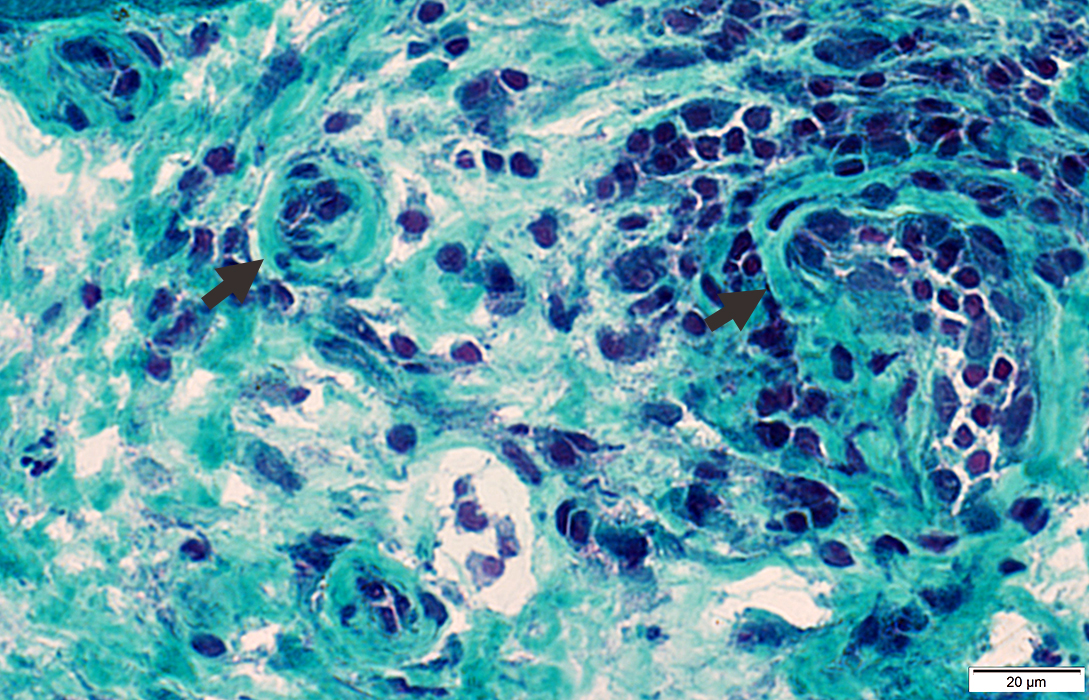 Gomori trichrome stain |
Endomysial vessels
Enlarged in some regions without inflammation
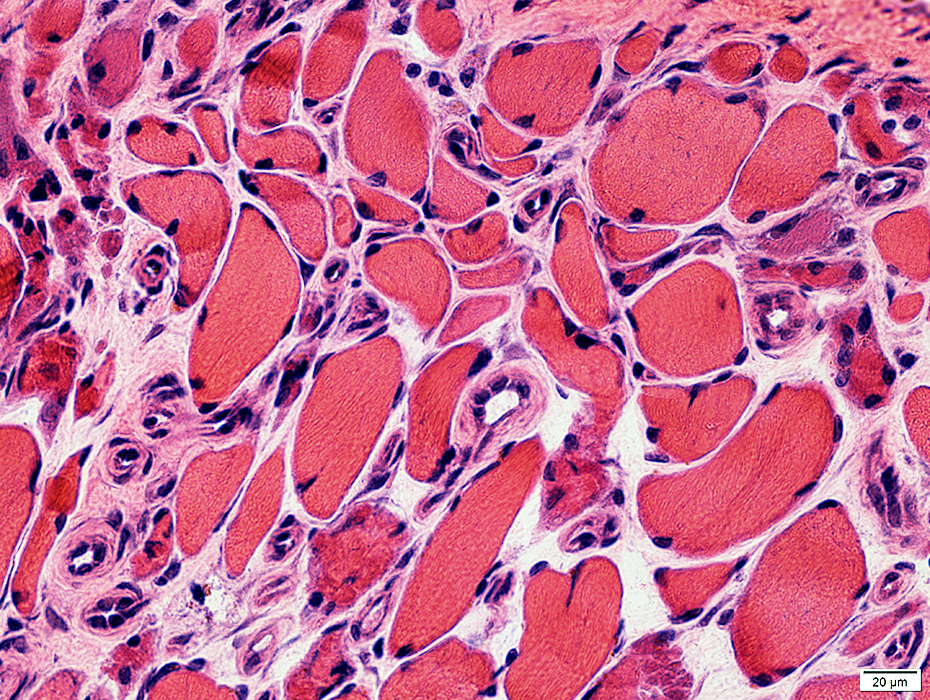 H&E stain |
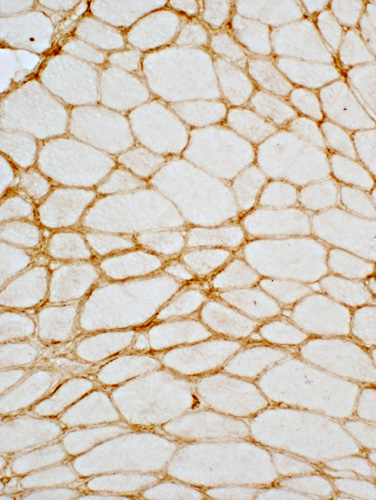
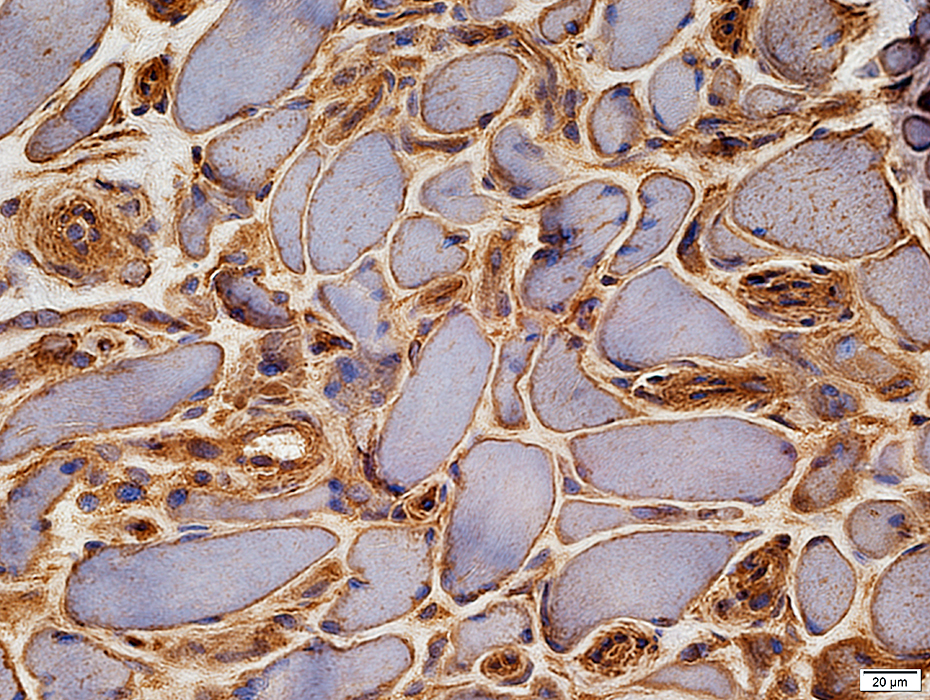 MHC Class I stain |
Endothelium of enlarged endomysial vessels
Muscle fiber surface membranes
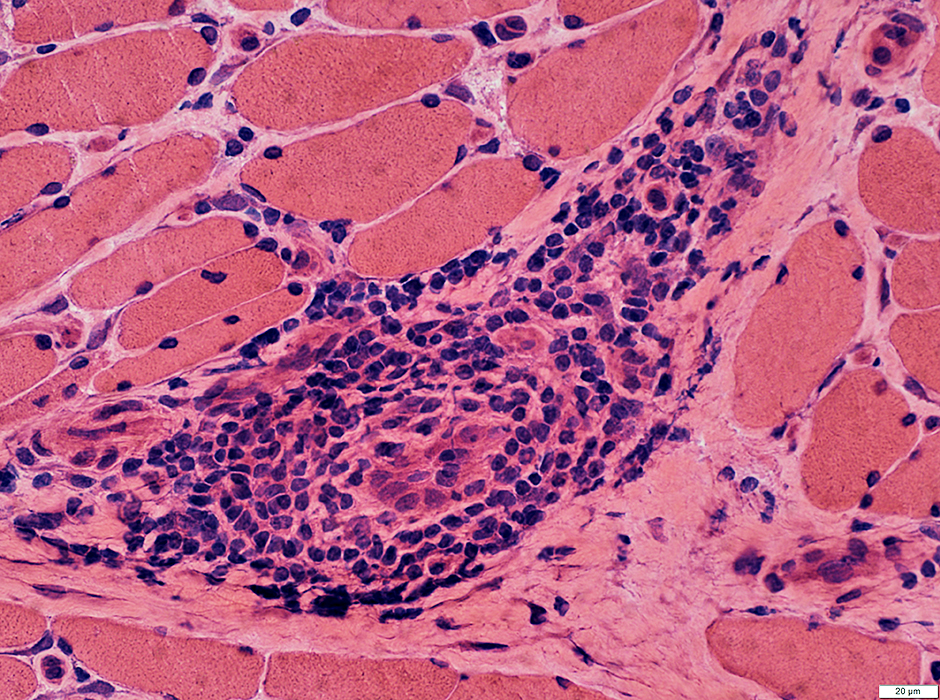
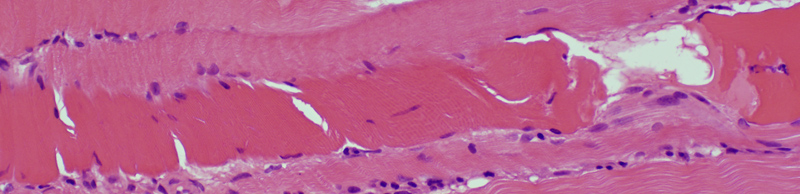
BCIM inflammation: Lymphocyte foci also containing Vessels
Lymphocyte foci: Perimysium
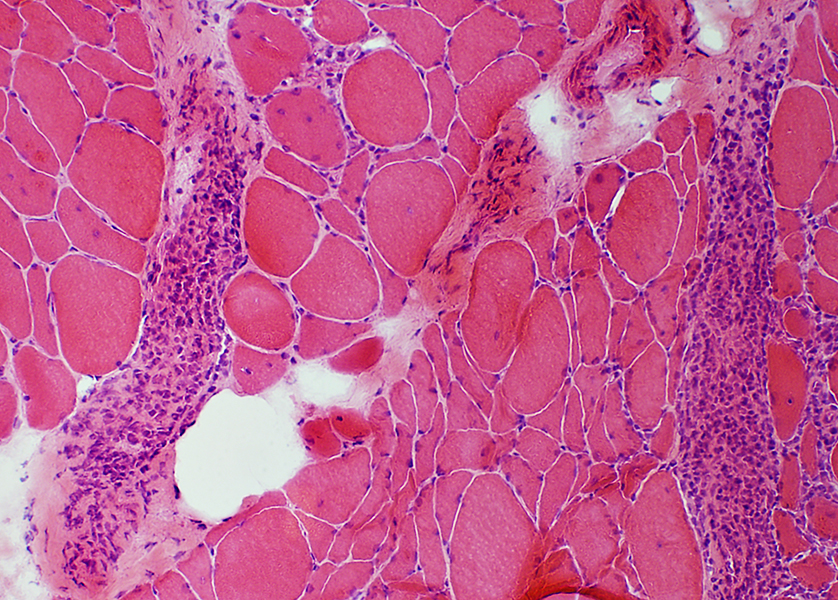
|
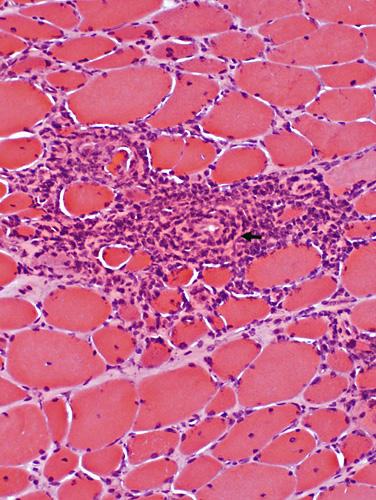 H&E stain |
|
Inflammation: Cell foci Cell type: Lymphocytes Location: Perimysium, Endomysium or both Myopathic changes Fiber size: Varied Endomysial connective tissue: Variably increased |
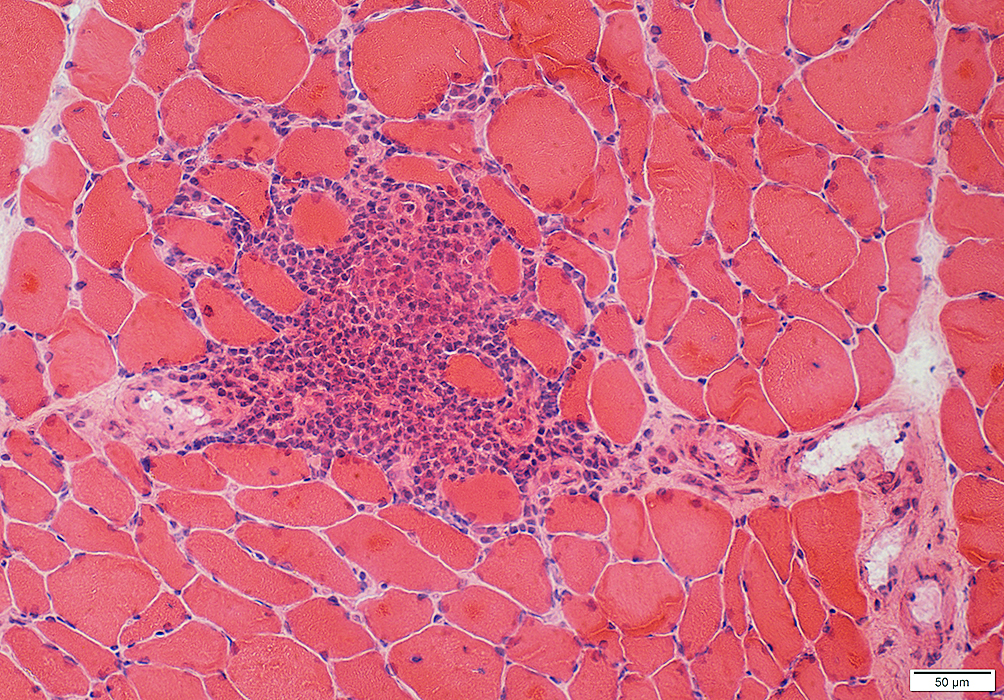 H&E stain |
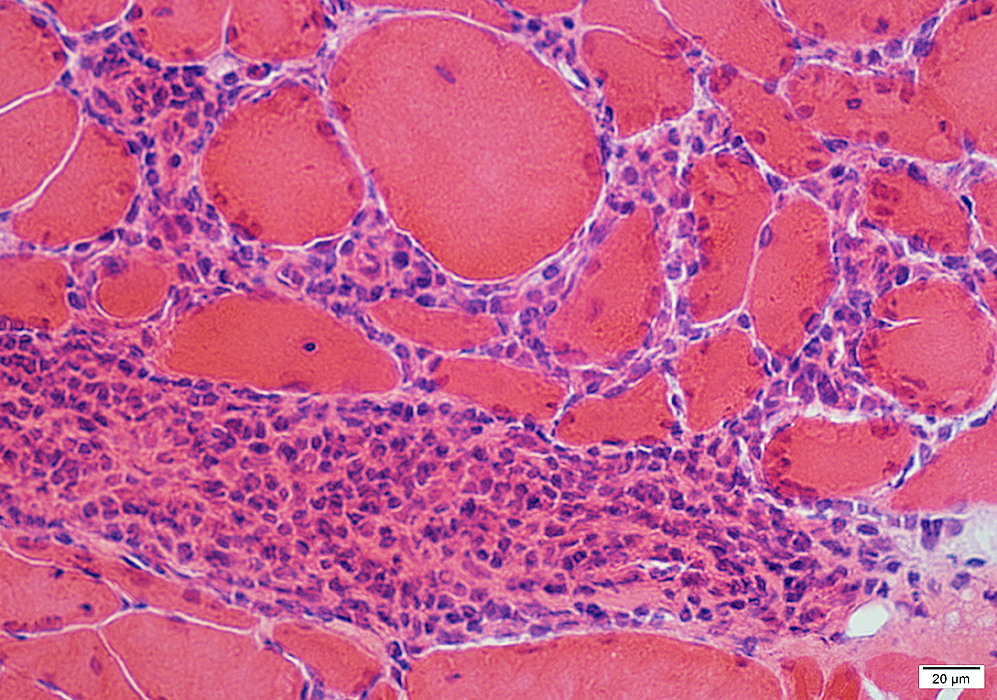 H&E stain |
Lymphocyte foci: Endomysium
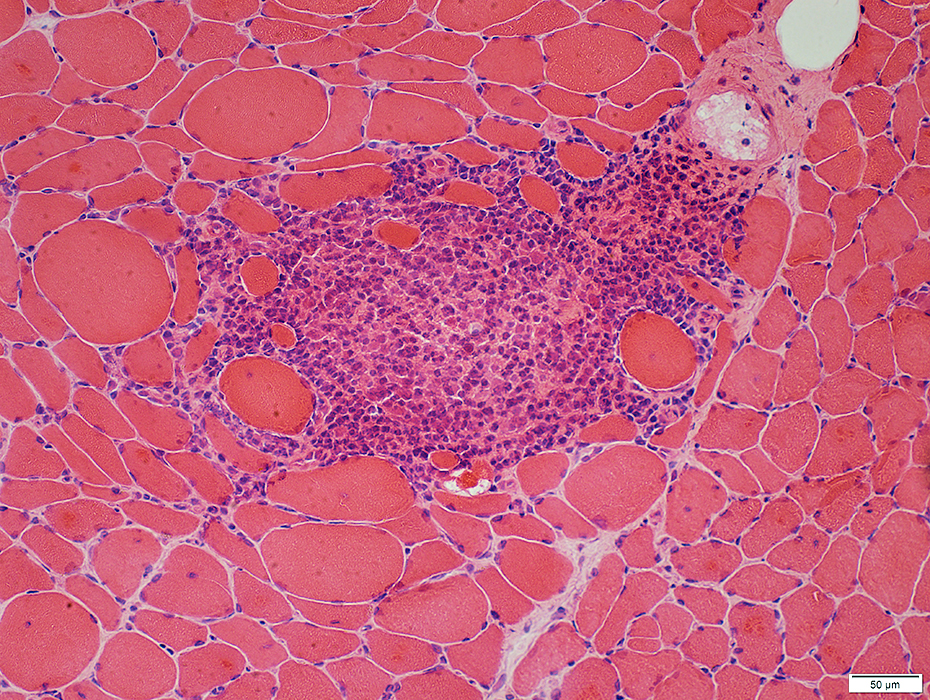 H&E stain |
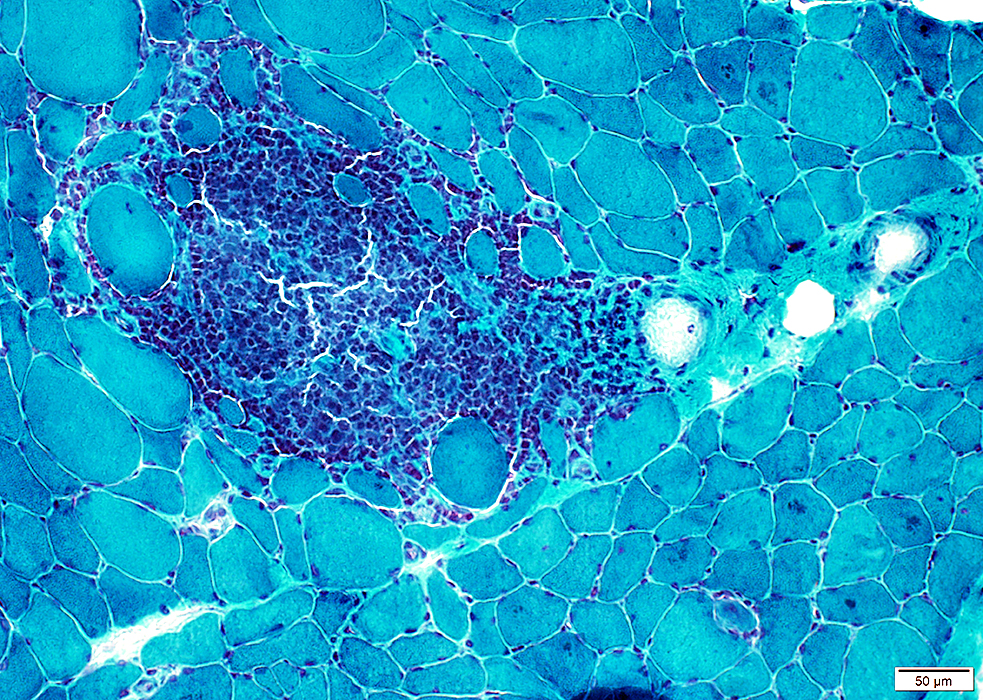 Gomori trichrome stain |
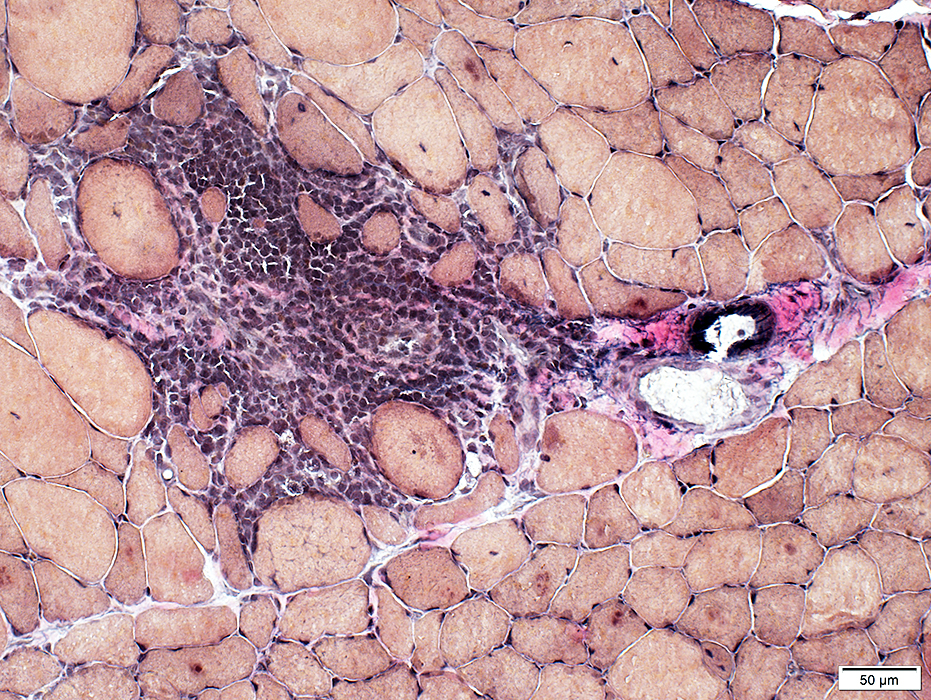 VvG stain |
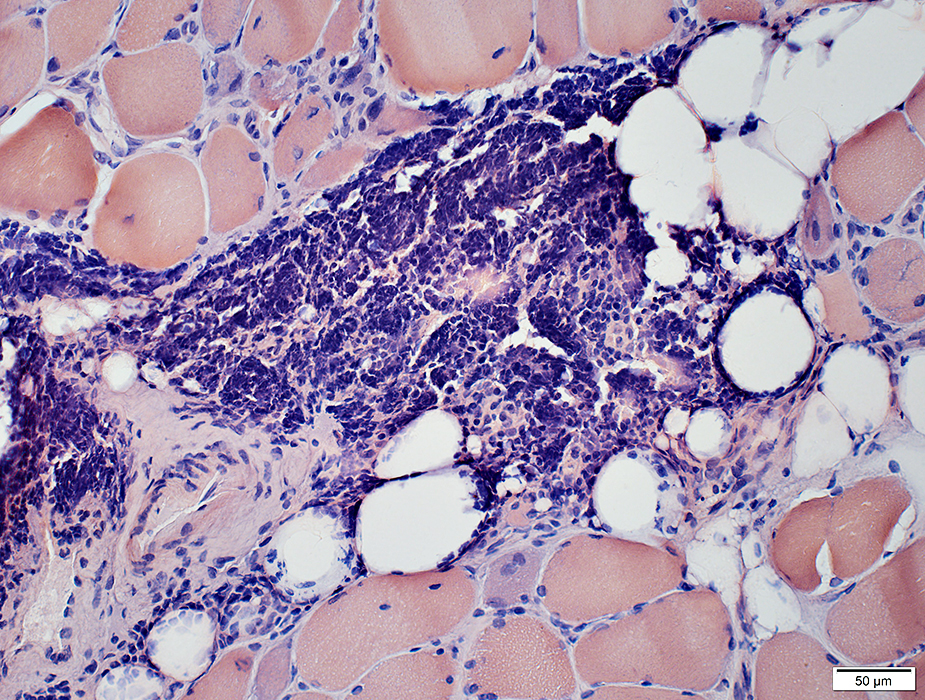 Congo red stain |
|
Inflammatory cell focus Some lymphocytes are clumped Inflammatory cell focus contains intermediate-sized & small vessels 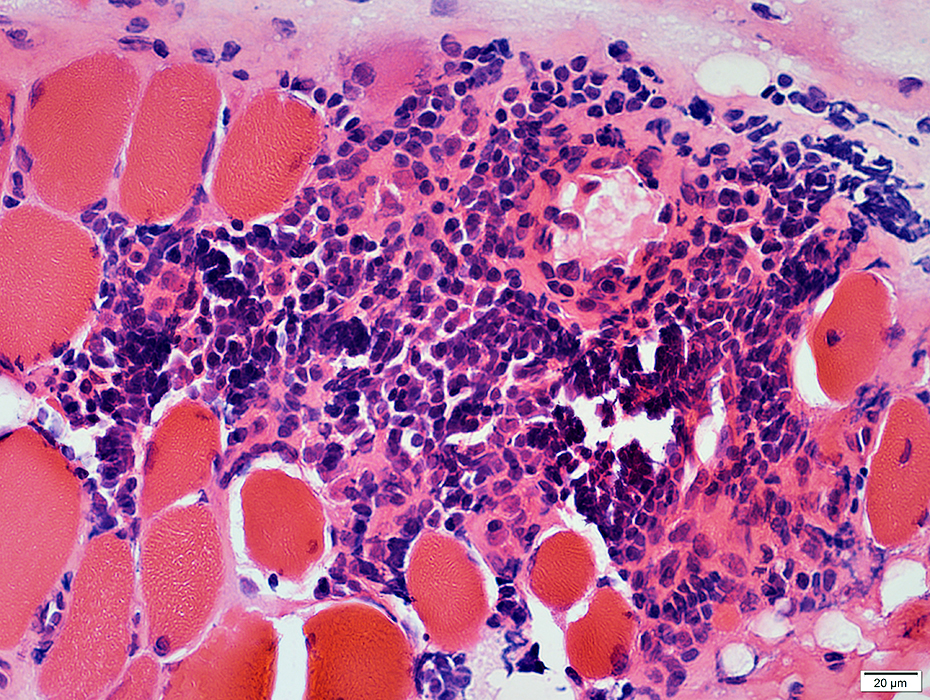 H&E stain |
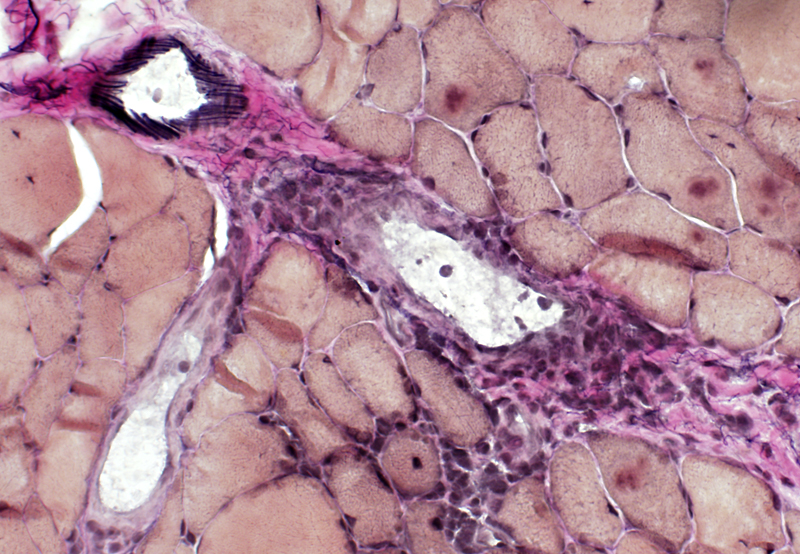 VvG stain |
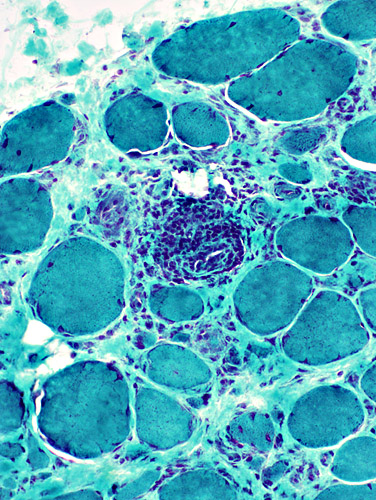 Gomori trichrome stain |
Surrounds & contains intermediate-sized & small vessels
No elastin fibrils in vessel wall.
Location: Perimysium, Endomysium or both
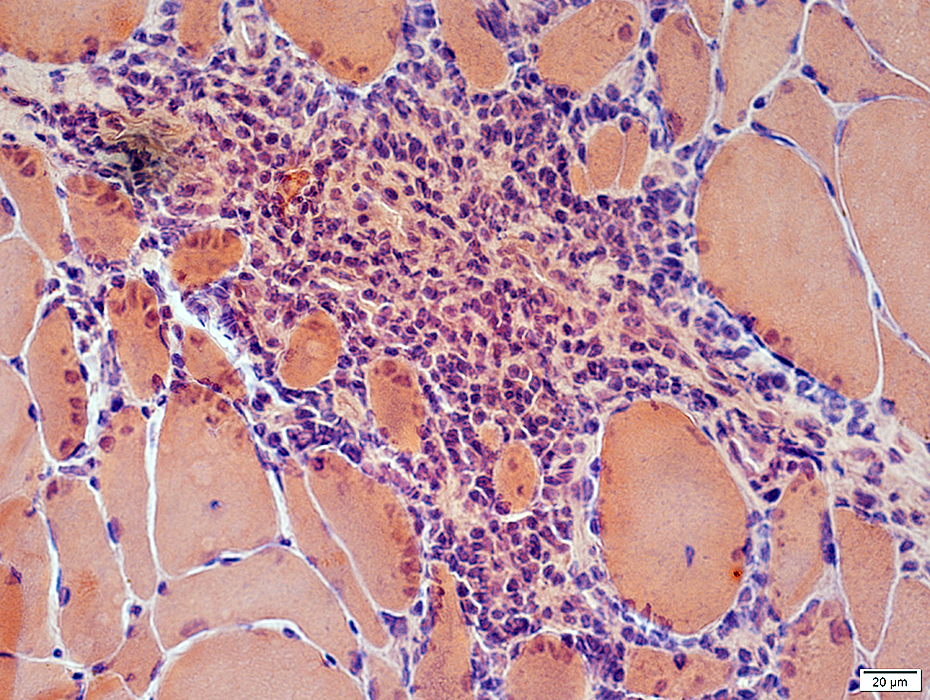 Congo red stain |
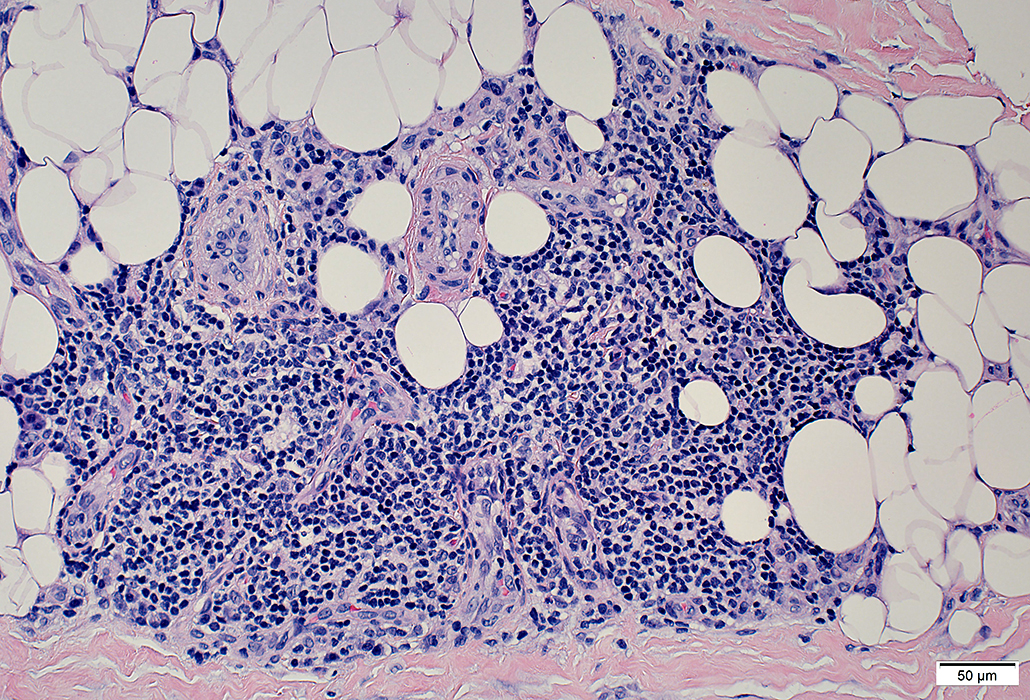
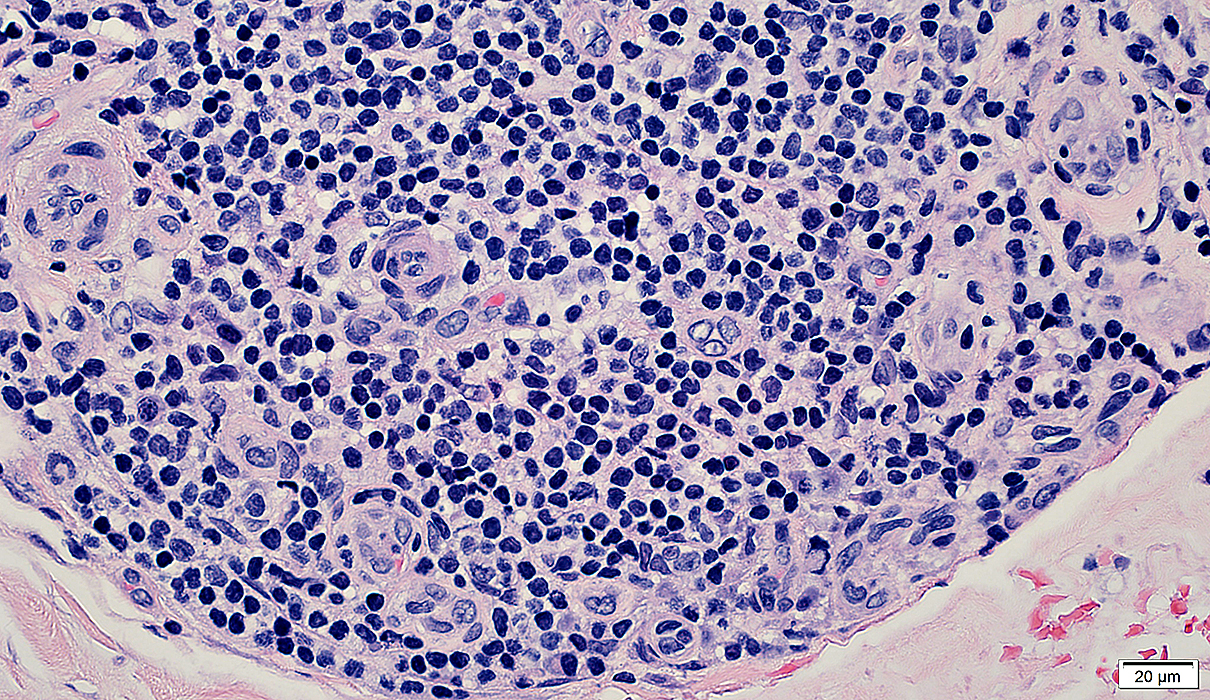
BCIM: Cell types in lymphocyte foci
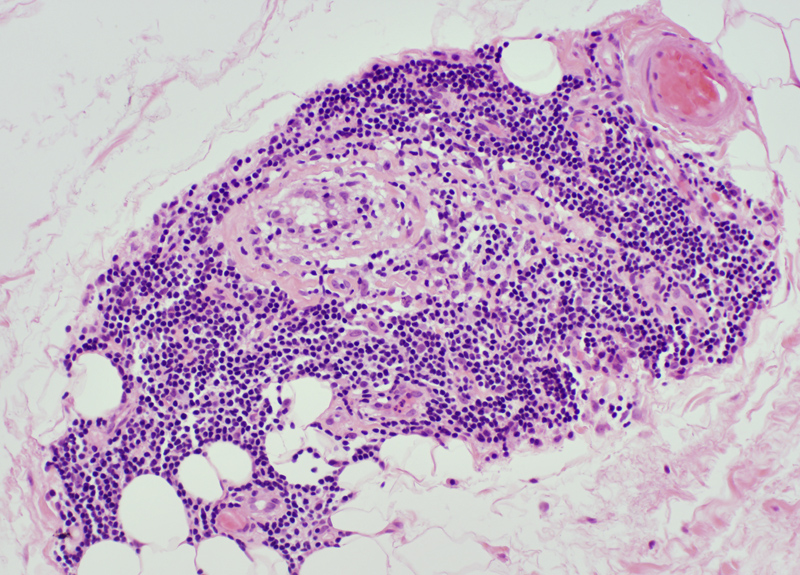 H&E stain Small dark cells with little cytoplasm surround an intermediate sized, and several small, vessels 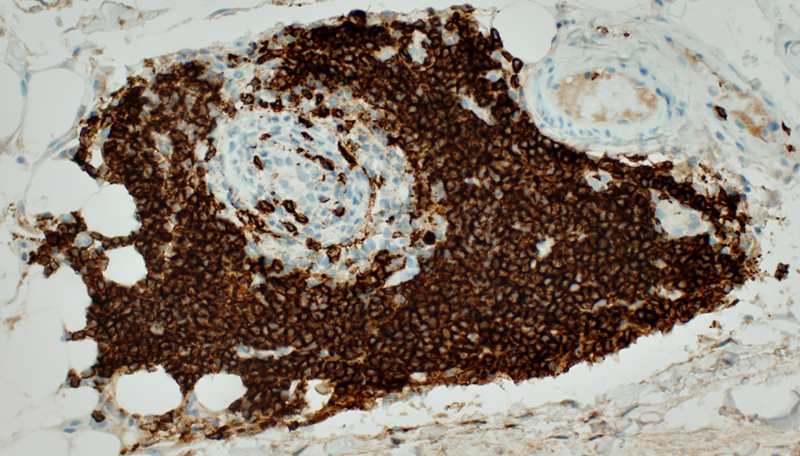 CD20 stain CD20+ B-cells are a prominent component of some perivascular inflammatory foci. |
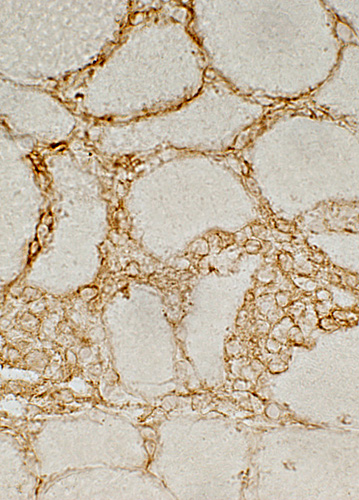 CD4 stain |
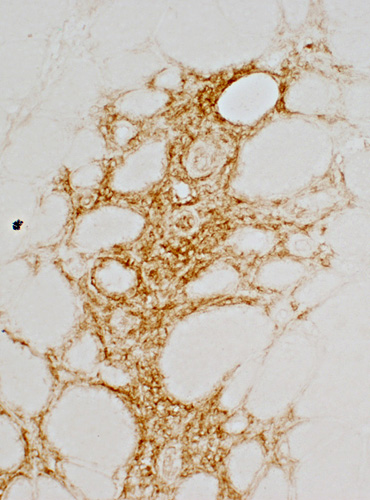 CD20 stain |
|
CD4 T-lymphocytes in endomysial connective tissue |
CD20 B-lymphocytes in perimysium extending into endomysium |
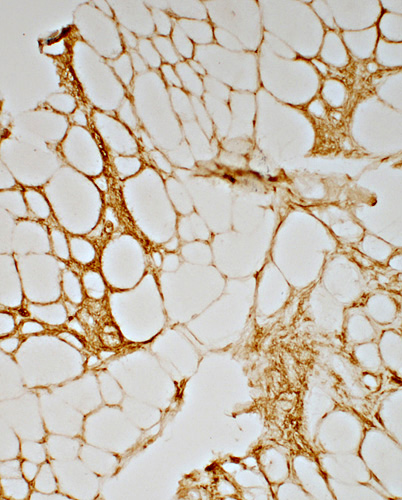 CD4 stain CD4 T-lymphocytes Present in perimysium, extending into endomysium |
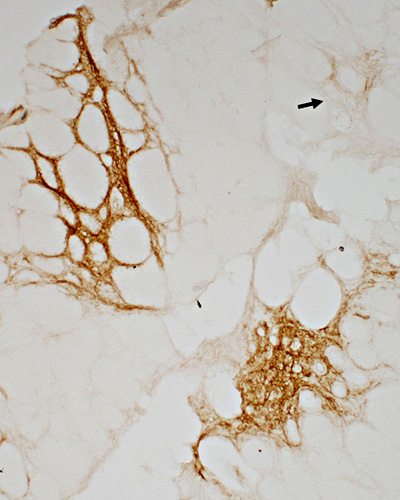 CD20 stain CD20 B-lymphocytes Present in subset of inflammatory foci |
| Serial sections: B-cell foci are present in some but not all (arrow) regions of CD4 cellularity | ||
|
| ||
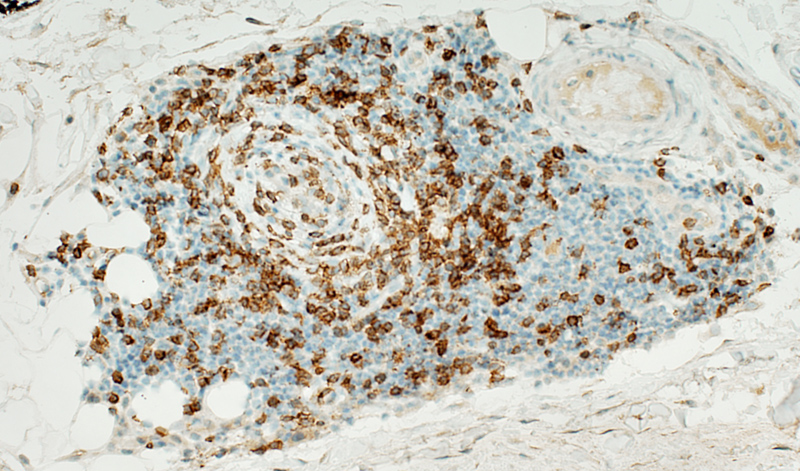 CD3 stain A minority of the perivascular cells stain for CD3 (T-cells) 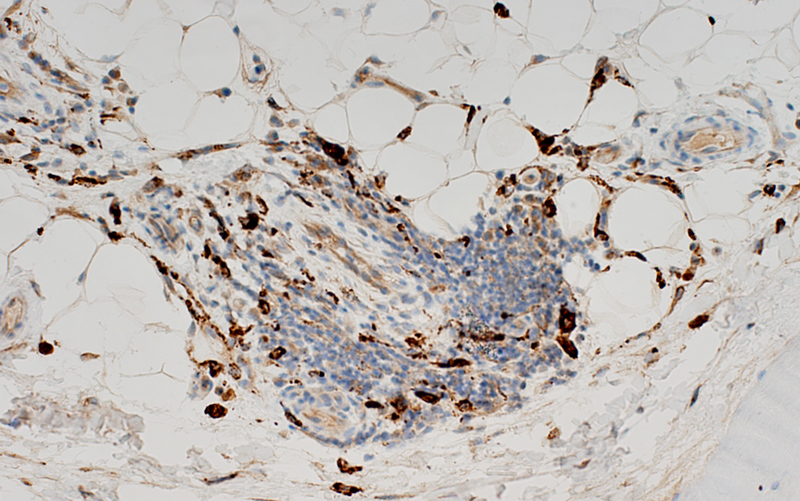 CD68 stain CD68+ macrophages are scattered through the infiltrate and in neighboring connective tissue 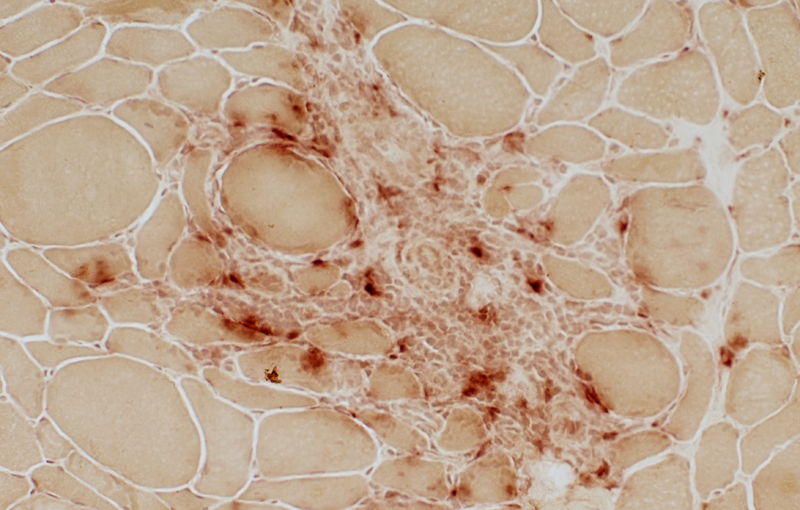 Acid phosphatase stain Acid phosphatase positive histiocytic cells: Scattered through the cell focus Most cells in focus are Acid phosphatase negative |
BCIM: Endomysial pathology
Complement Deposition (C5b-9; MAC) on endomysial connective tissue
 C5b-9 stain |
 C5b-9 stain |
|
BCIM muscle: C5b-9 components of complement are deposited in endomysial connective tissue |
Control muscle: No C5b-9 components of complement are deposited in muscle |
|
C5b-9 deposits Endomysial connective tissue Necrotic muscle fibers: Cytoplasm 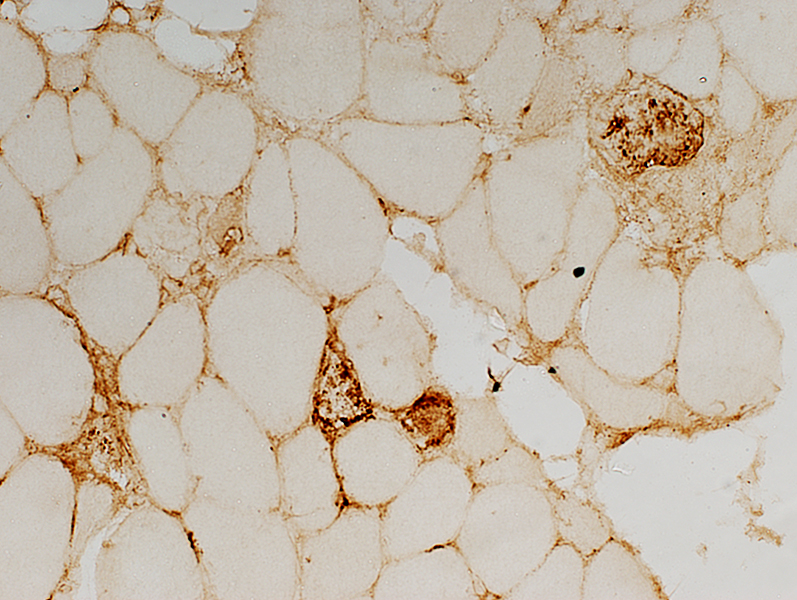 C5b-9 stain |
IgM: Deposited on endomysial connective tissue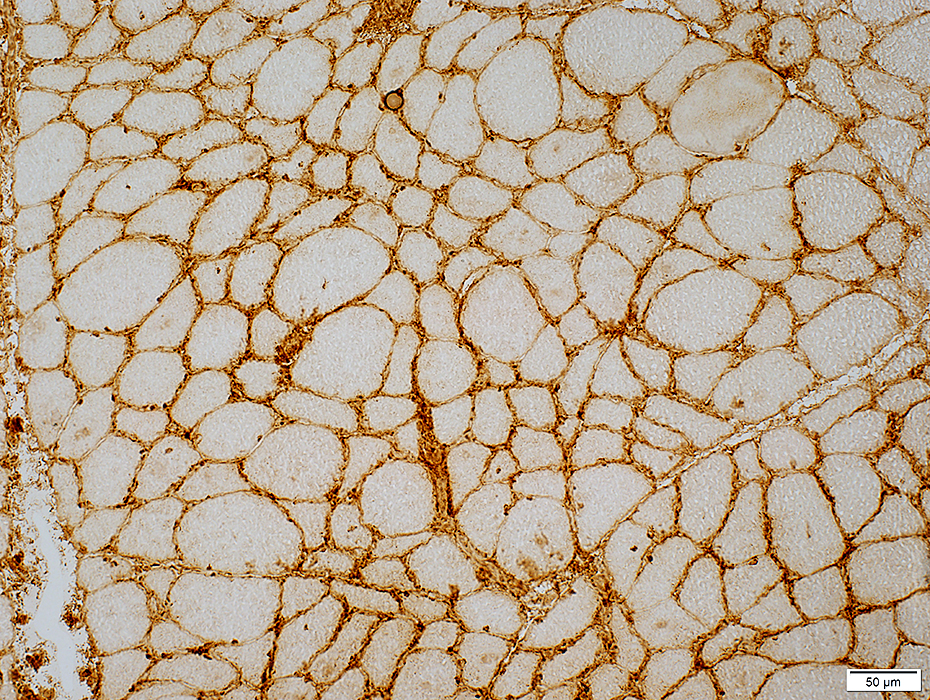 IgM stain |
Brachio-Cervical Inflammatory Myopathy: Myopathic changes
Muscle fiber damge may beNecrosis & Regeneration
Focal invasion by cells
Small, immature fibers
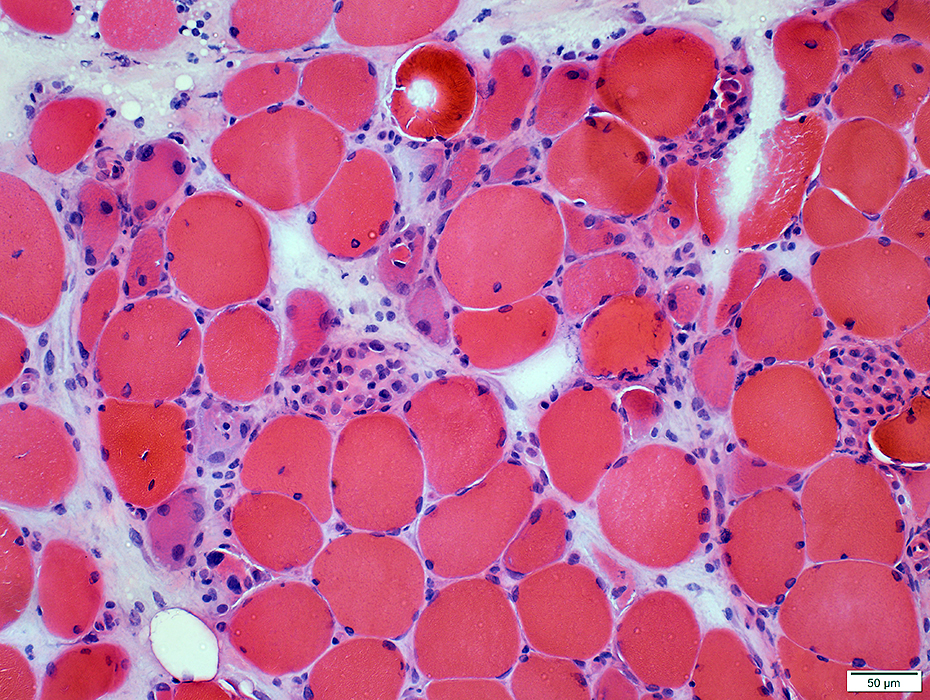 H&E stain |
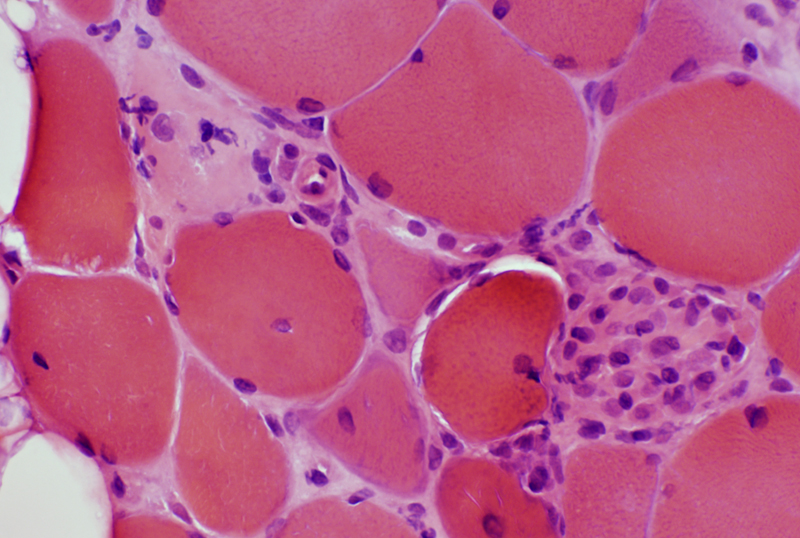 H&E stain |
Necrotic muscle fibers: Scattered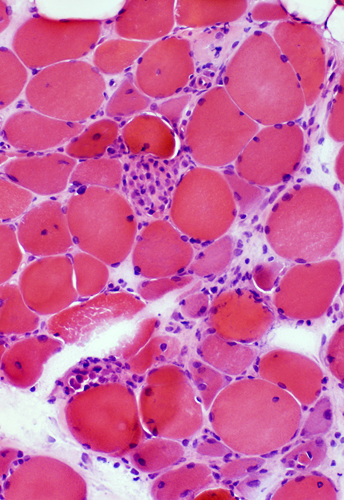 H&E stain |
BCIM: Necrotic muscle fiber
Invaded by large histiocytic cells
Pale cytoplasm
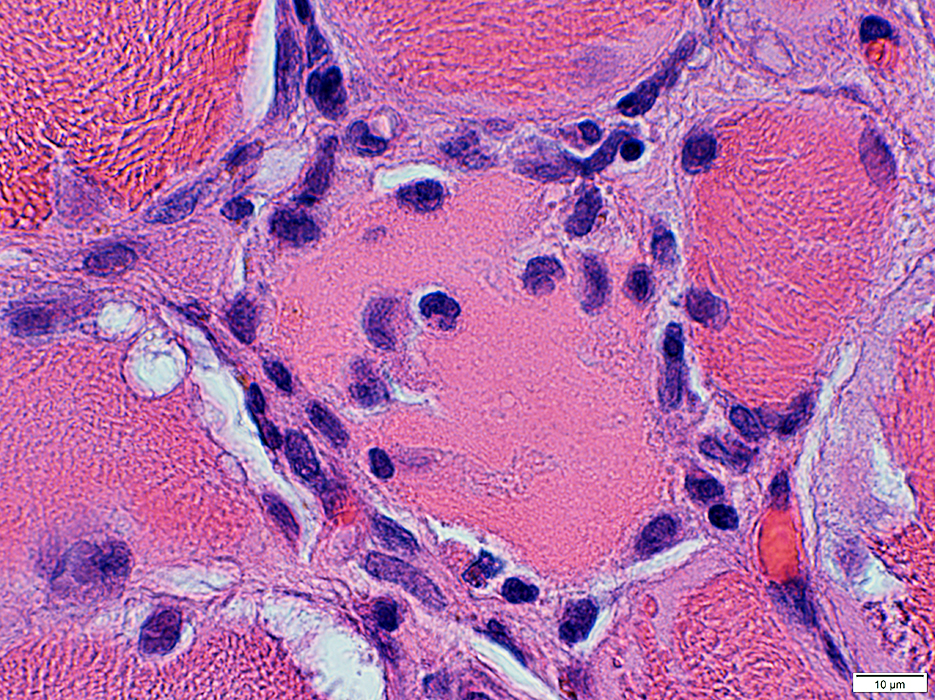 H&E phosphatase stain |
Necrotic muscle fibers in varied stages of phagocytosis by histiocytic cells
 Acid phosphatase stain |
Muscle fiber necrosis: Changes in individual muscle fibers
 H&E stain Early necrosis: Dark muscle fiber with loss of cytoplasmic structure 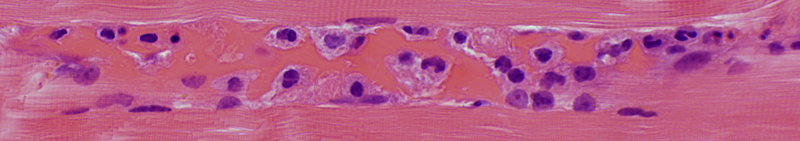 H&E stain Later stage of necrosis: Muscle fiber invaded by cells with large nuclei and abundant foamy cytoplasm 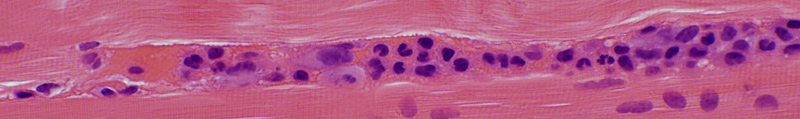 H&E stain Later stage of necrosis: Collapsed muscle fiber largely replaced by cells 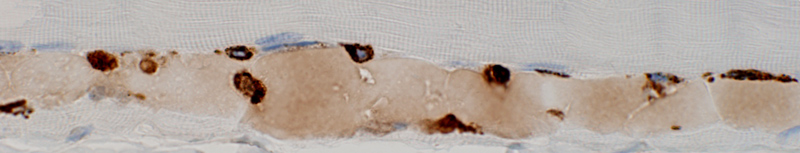 CD68 stain Muscle fiber necrosis: CD68+ histiocytic cells invading fiber 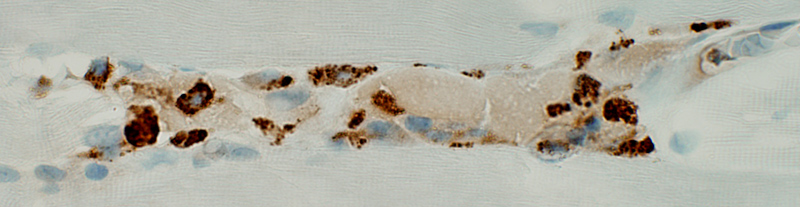 CD68 stain Segmental muscle fiber necrosis: CD68+ histiocytic cells 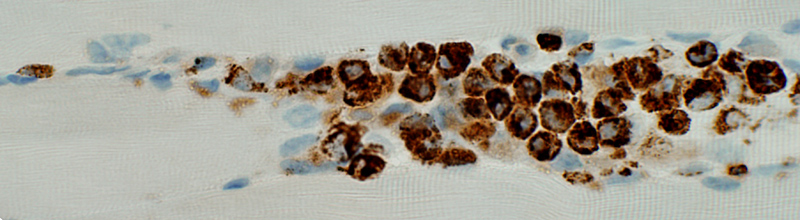 CD68 stain Muscle fiber necrosis: CD68+ histiocytic cells replacing part of a fiber |
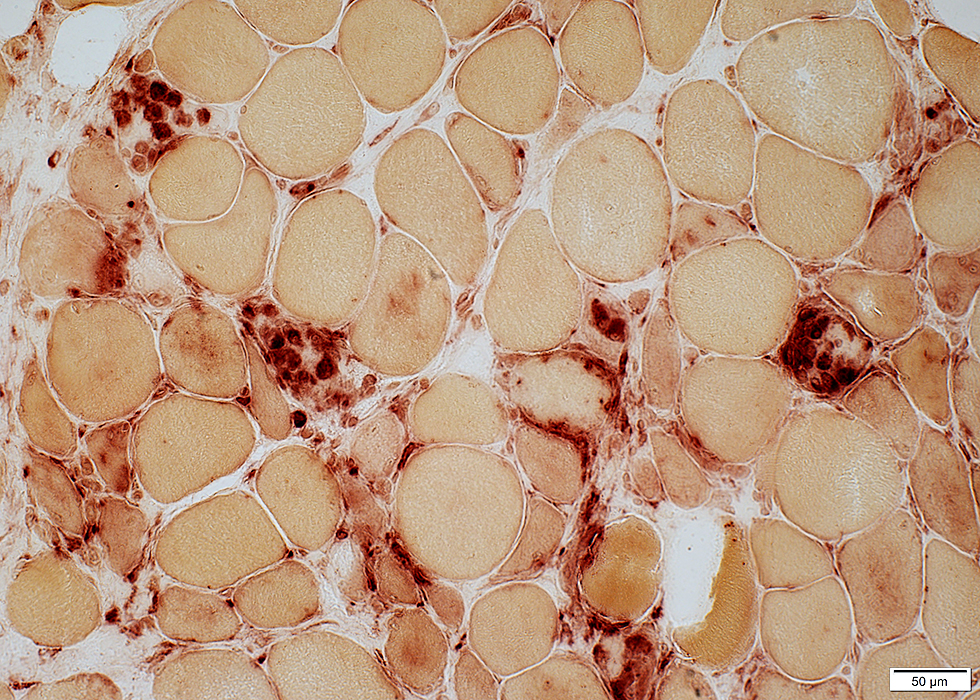
BCIM: Myopathy, Varied muscle fiber size
Chronic-Severe myopathy
Varied fiber size
Bimodal distribution
Small muscle fibers: Rounded or Polygonal
Large muscle fibers: Mild hypertrophy
Internal nuclei: Scattered muscle fibers
Endomysial connective tissue: Mildly increased
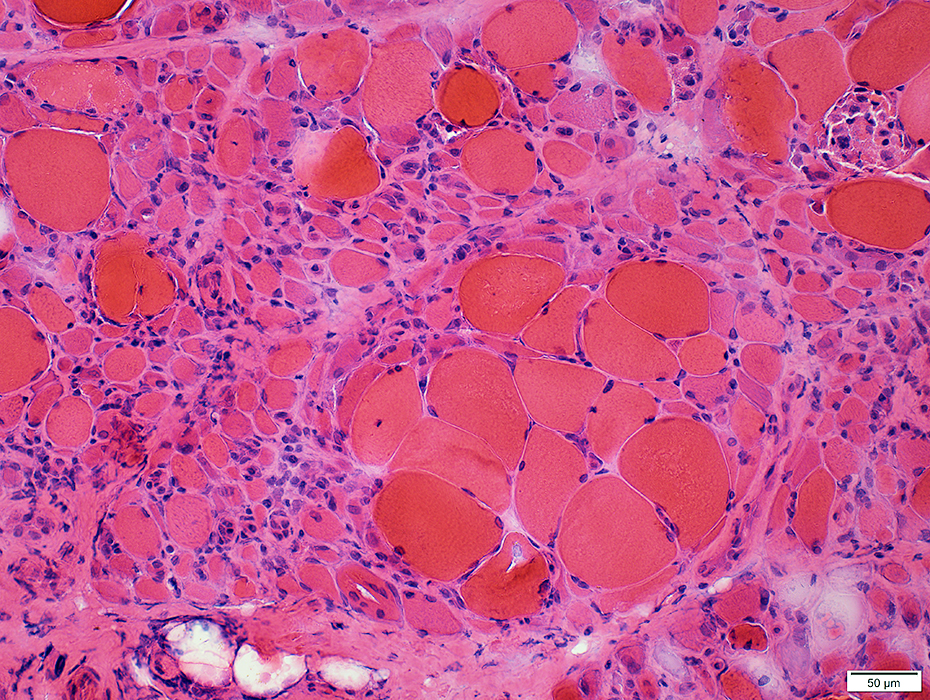 H&E stain |
|
Mild-Moderate myopathy: Varied fiber size Fiber sizes: Bimodal distribution Type 1 & Type 2 fibers are small and large. 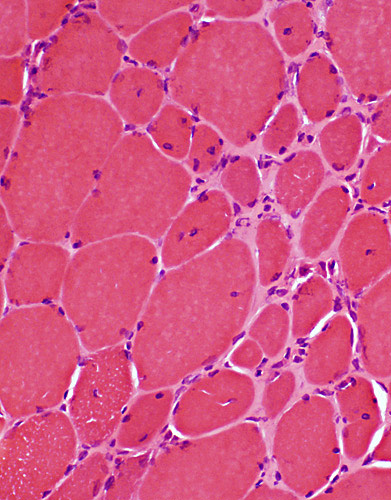 H&E stain |
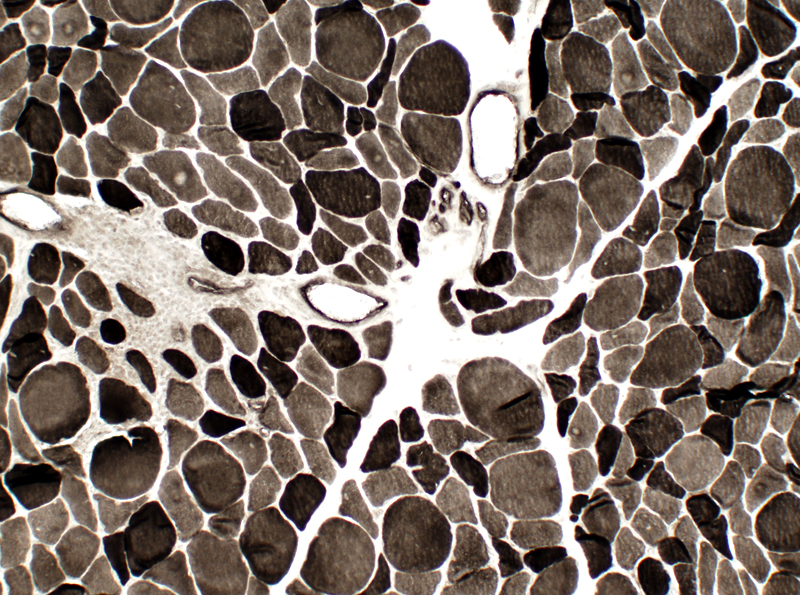 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
BCIM: Muscle fiber Regeneration & Immaturity
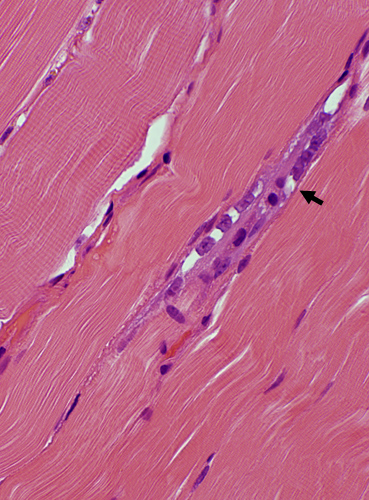 Basophilic regenerating muscle fibers: Bluish cytoplasm & Large nuclei
Basophilic regenerating muscle fibers: Bluish cytoplasm & Large nuclei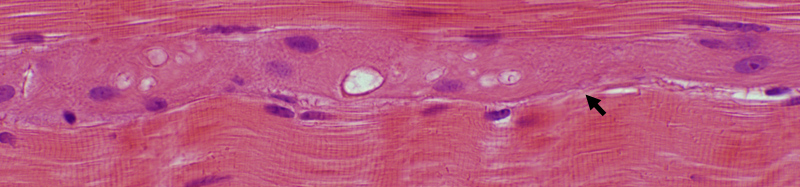 H&E stain |
BCIM: Immature muscle fibers, Many, Small size, Type 2C
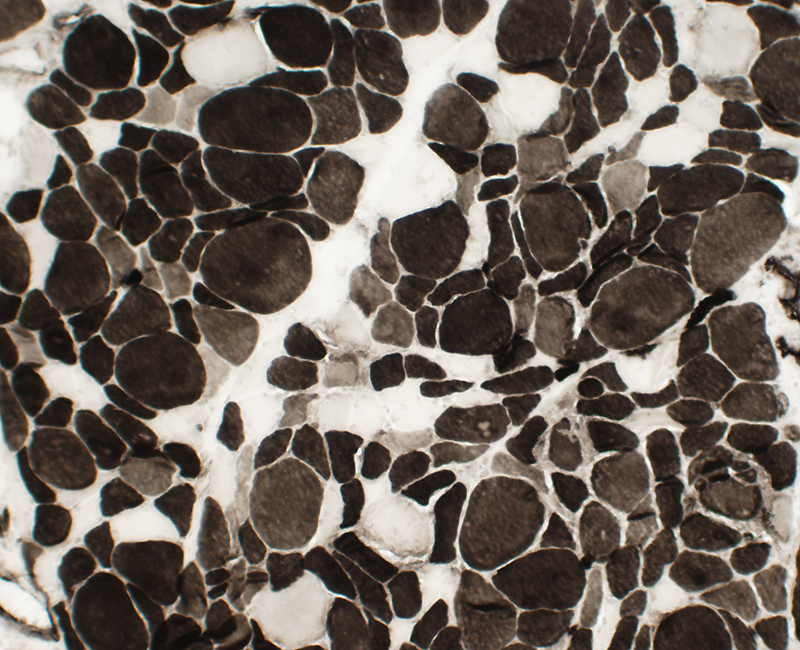 ATPase pH 4.3 stain Many muscle fibers are type 2C with intermediate staining. |
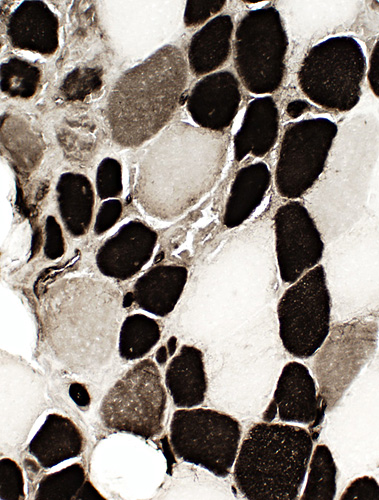 ATPase pH4.3 stain |
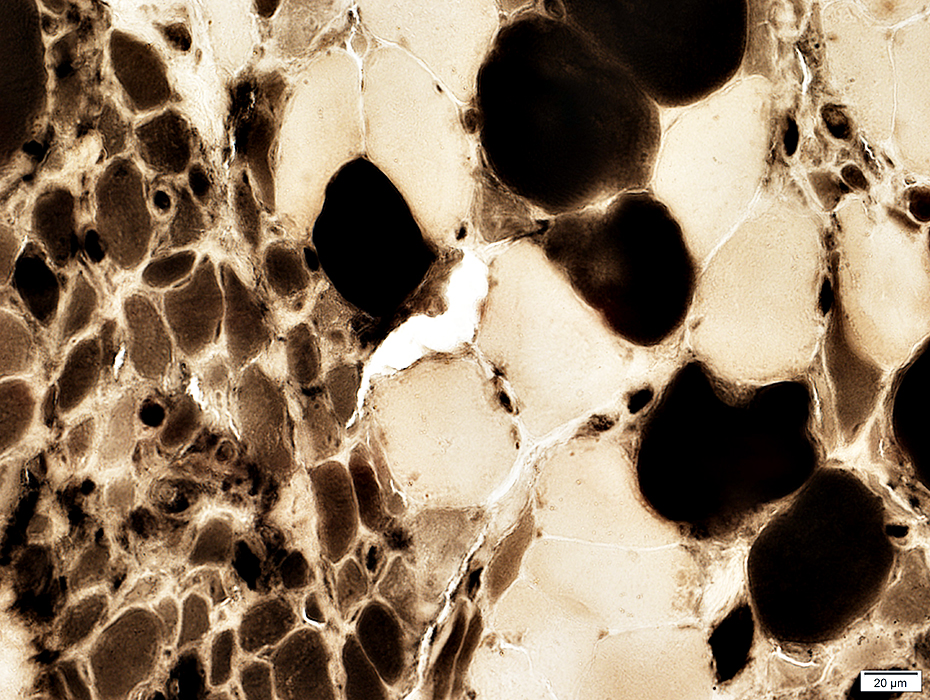 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Immature, small muscle fibers: Cytoplasm stains with alkaline phosphatase
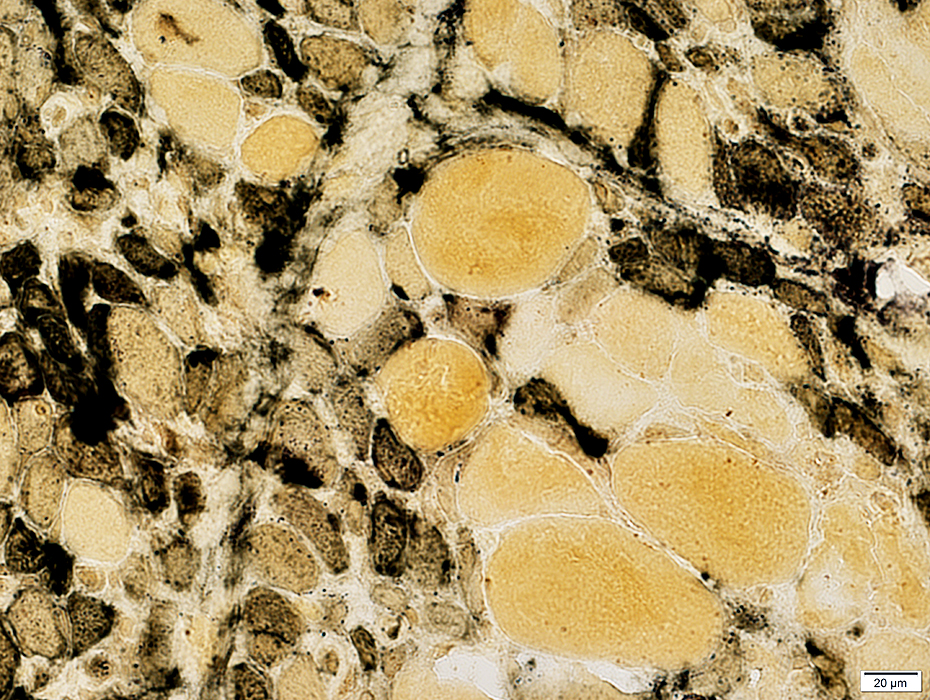 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Immature, small muscle fibers: Cytoplasm stains darkly with NADH
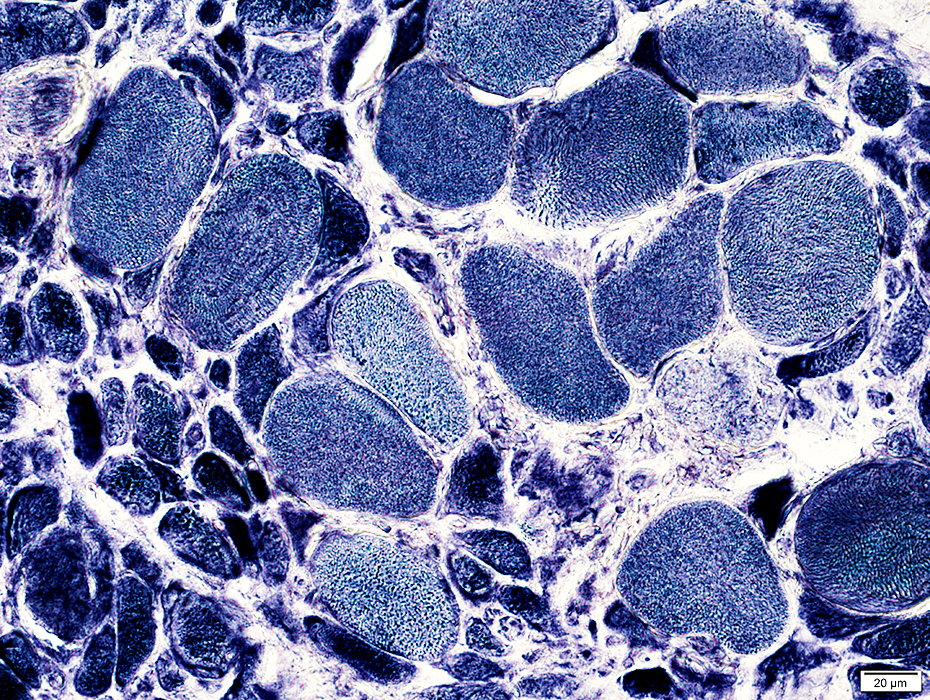 NADH stain |
Immature, small muscle fibers: Cytoplasm stains pale with AMPDA
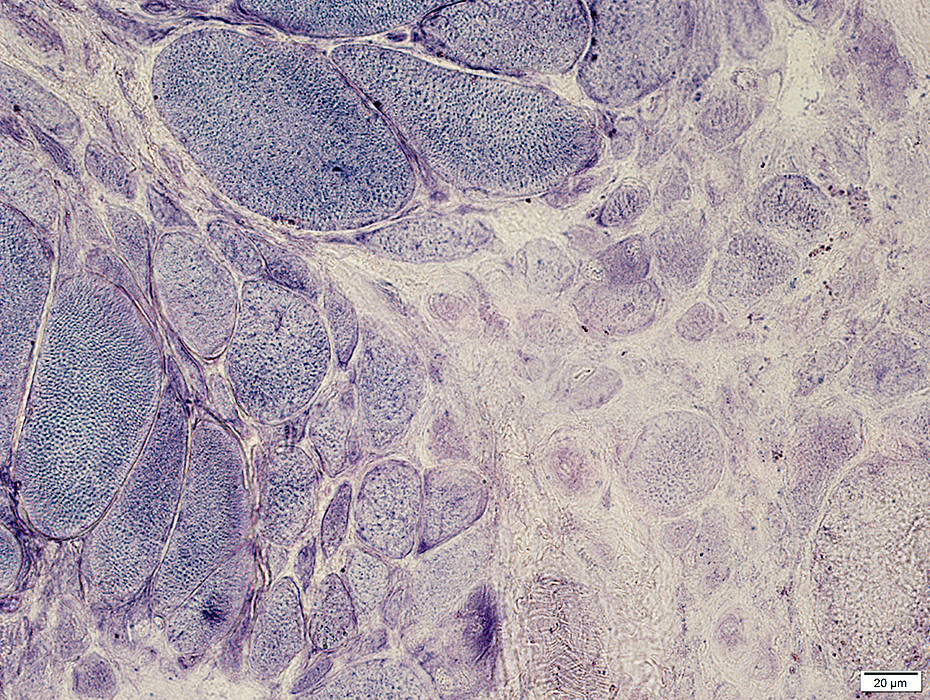 AMPDA stain |
BCIM: Focal invasion of muscle fibers by histiocytic cells & lymphocytes
Present in some patients
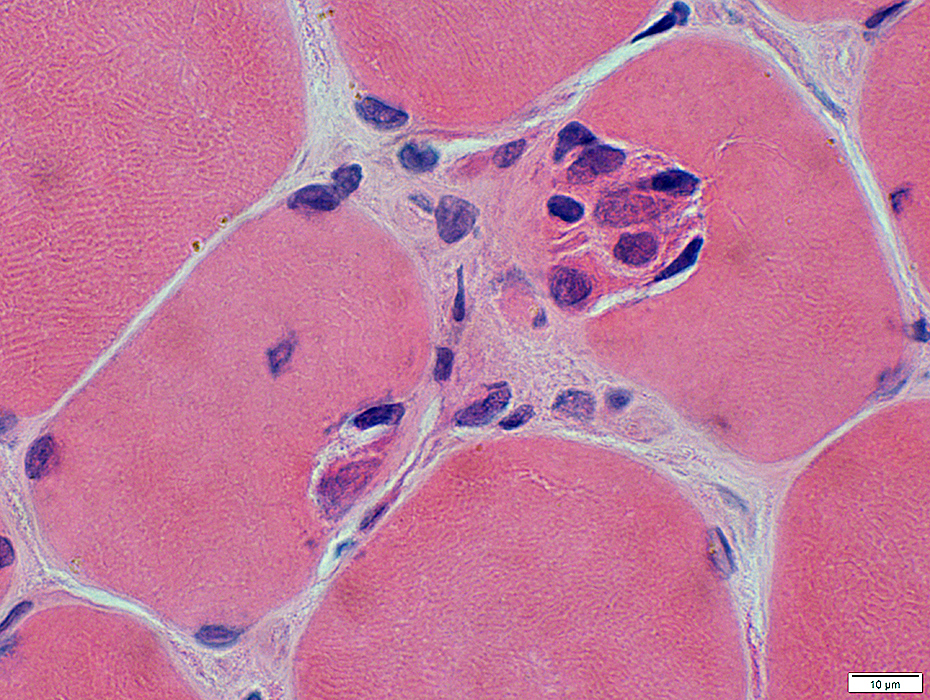 H&E stain |
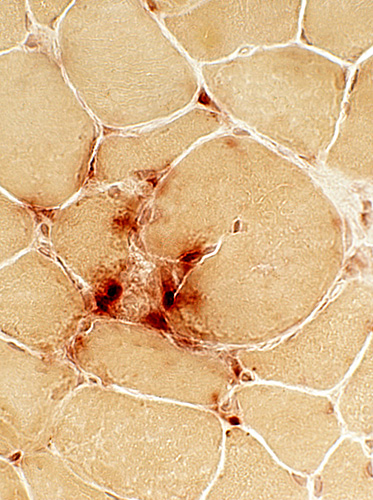 Acid phosphatase stain |
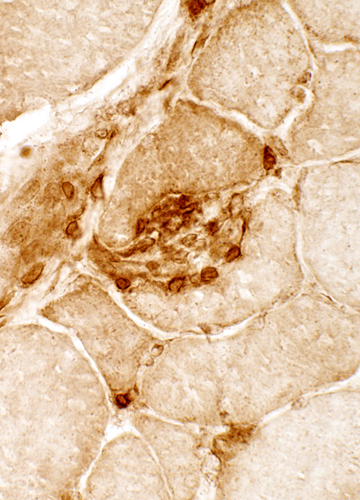 CD4 stain |
|
BCIM: MHC Class I Upregulation on muscle fibers, especially surface Expressed on cells in inflammatory foci 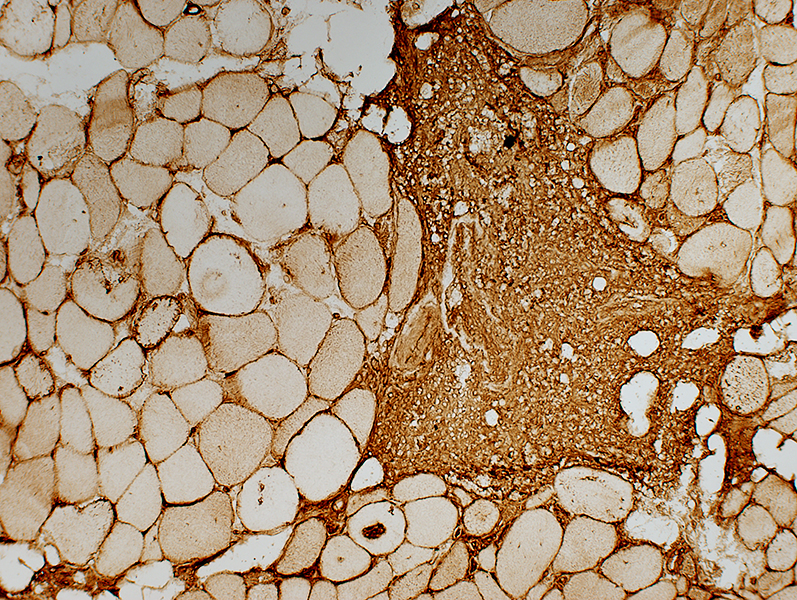 MHC Class I stain |
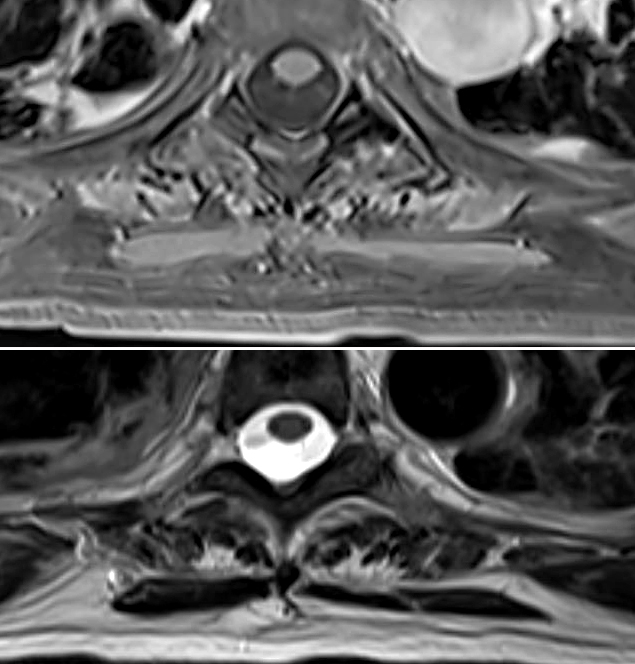
BCIM: MRI
Paraspinous muscle atrophy
<
|
Temporalis muscle
BCIM (Left): Contrast enhancement (Arrow)
Myotonic Dystrophy 1 (Right): Atrophy with no enhancement
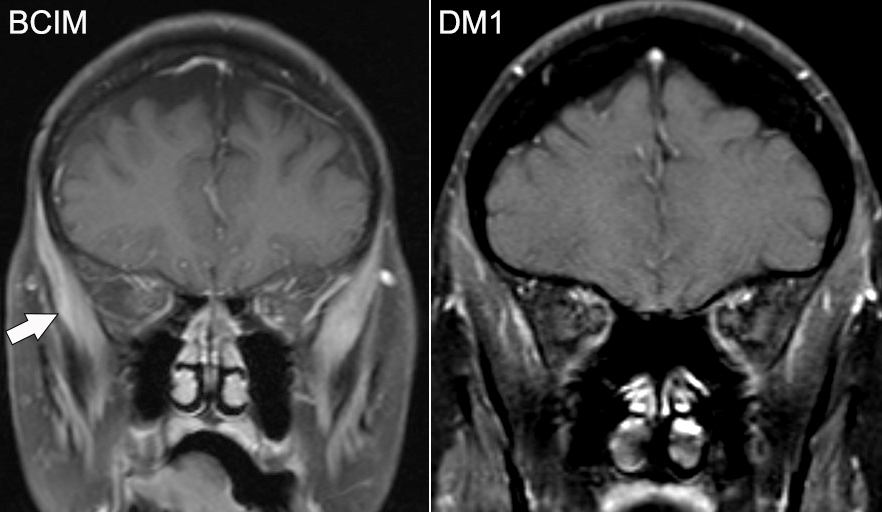 From: Manu Goyal |
References
1. Curr Opin Immunol 2019 Feb 21;57:46-52
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Return to Inflammation
Return to Inflammatory myopathies
Return to BCIM
5/21/2025