|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
TRICHINELLOSIS
|
Progression Larvae Cysts Inflammation Muscle fibers Infection Myopathy Necrosis Chronic |

|
Trichinellosis: Active |

|
Trichinella Infection & Myopathy: Progression
- General Stages
- Ingestion: Foodbourne cysts
- Enteral: Organisms infect GI tract
- Parenteral: Systemic spread of larvae
- Muscle
- Small larvae
- Emerge from vessels
- Invade muscle fibers
- Produce delta shaped lesions in fibers
- May be present within, or at edge of, delta lesions
- Larval growth
- Larvae
- Progressive increased size within muscle fibers
- Move: To extracellular space & surrounded by capsule
- Muscle fibers
- Develop difusely abnormal internal architecture
- Some fibers become necrotic
- Larvae
- Histiocytic inflammation
- Replaces muscle fiber cytoplasm in fibers with larvae
- Surround larvae that become extracellular
- Muscle has multifocal cellularity
- Cysts
- Extracellular larvae become surrounded by cysts composed of collagen
- Cysts contain larvae, nurse cells and fluid
- Cysts often have little associated inflammation
- Cysts containing larvae are infectious if ingested and wall is degraded
- Chronic
- Cyst walls can persist without organisms
- Some cysts develop calcification inside
- Small larvae
Trichinellosis: Active Myopathy
- Multifocal
- Fiber size: Varied
- Necrosis
- Replacement of muscle fibers by histiocytic cells
- Regeneration
- Focal invasion: Scattered
Myopathy: Multifocal, Ongoing
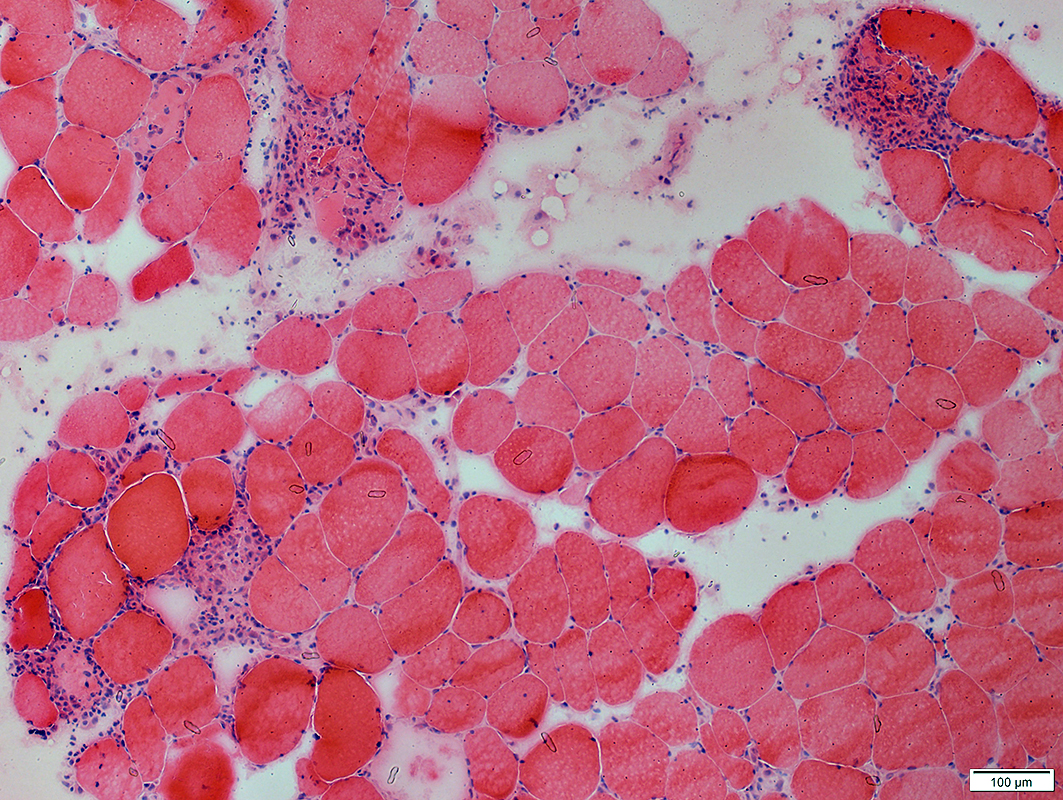 H&E stain |
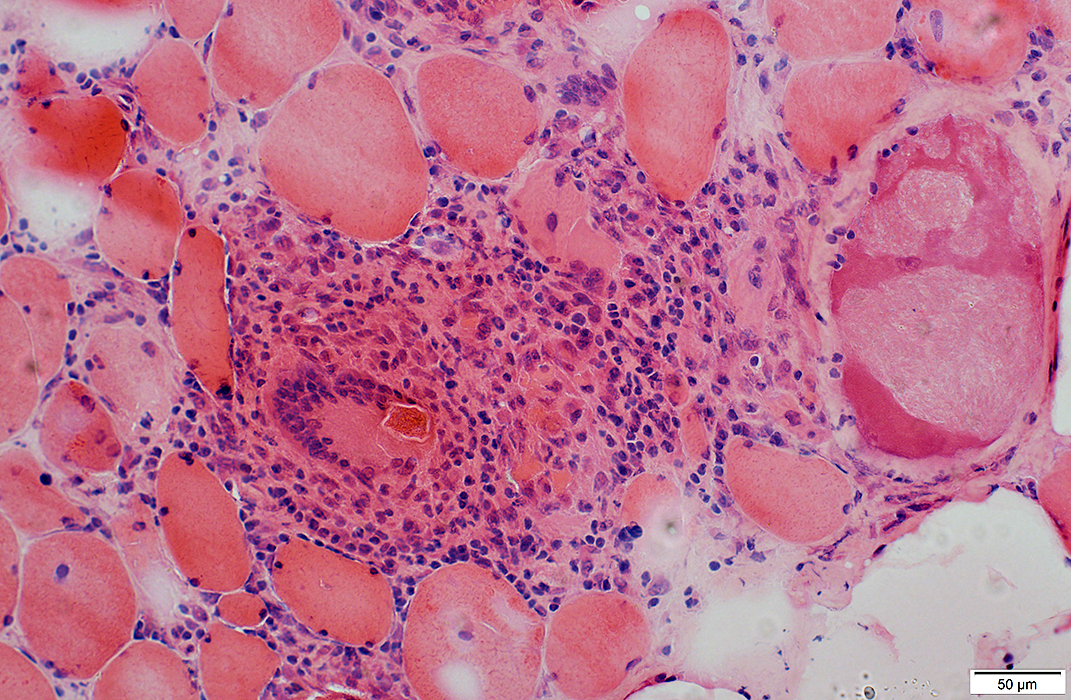 H&E stain |
Muscle fibers: Necrosis & Replacement by large histiocytic cells
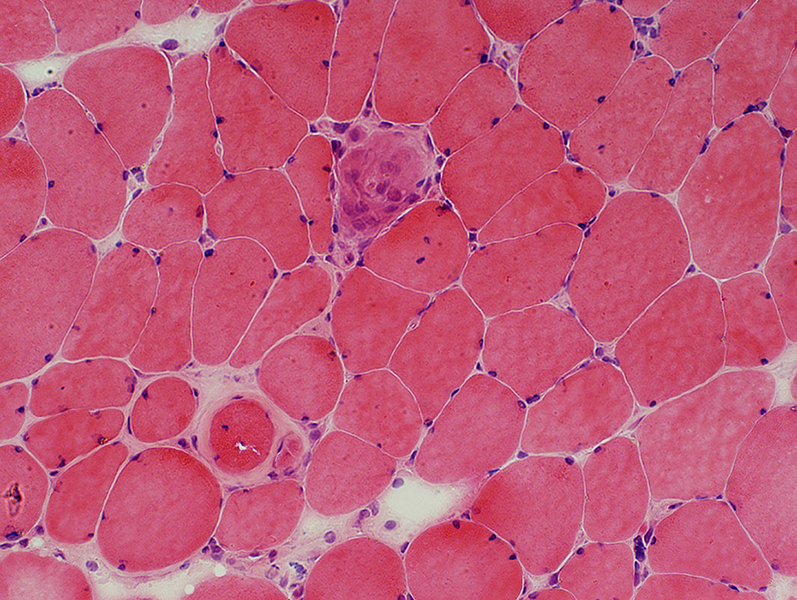 H&E stain |
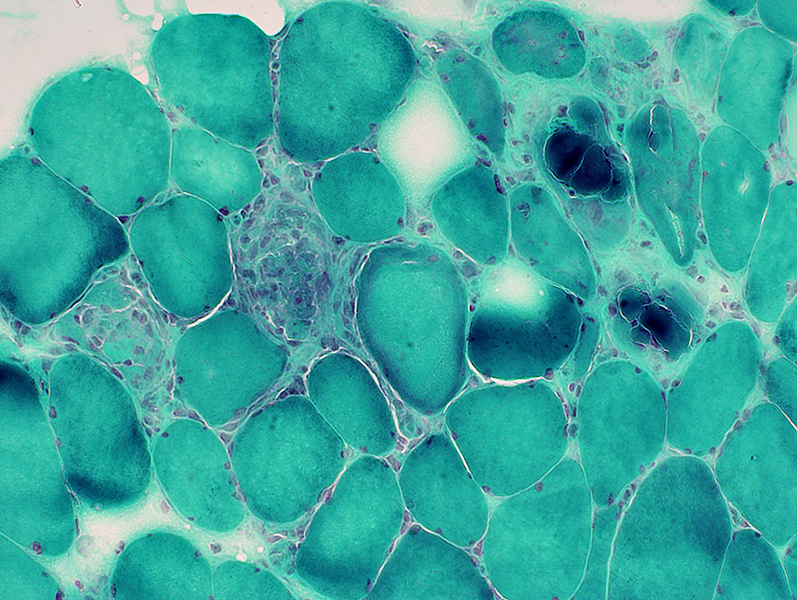 Gomori trichrome stain |
Ongoing myopathy: Necrosis & Replacement by large histiocytic cells
Chronic changes: Internal nuclei in some muscle fibers
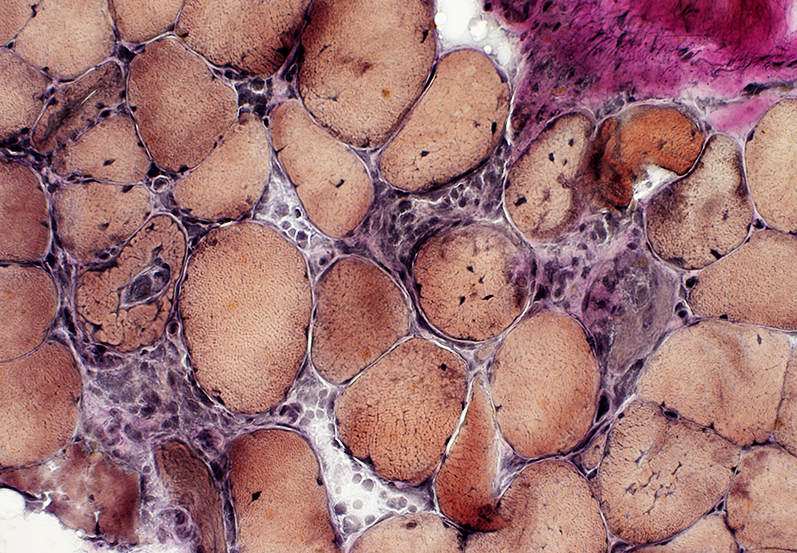 VvG stain |
Muscle Fiber Damage: Stages
Muscle Fiber Necrosis
Pale muscle fiber cytoplasm (Arrow)
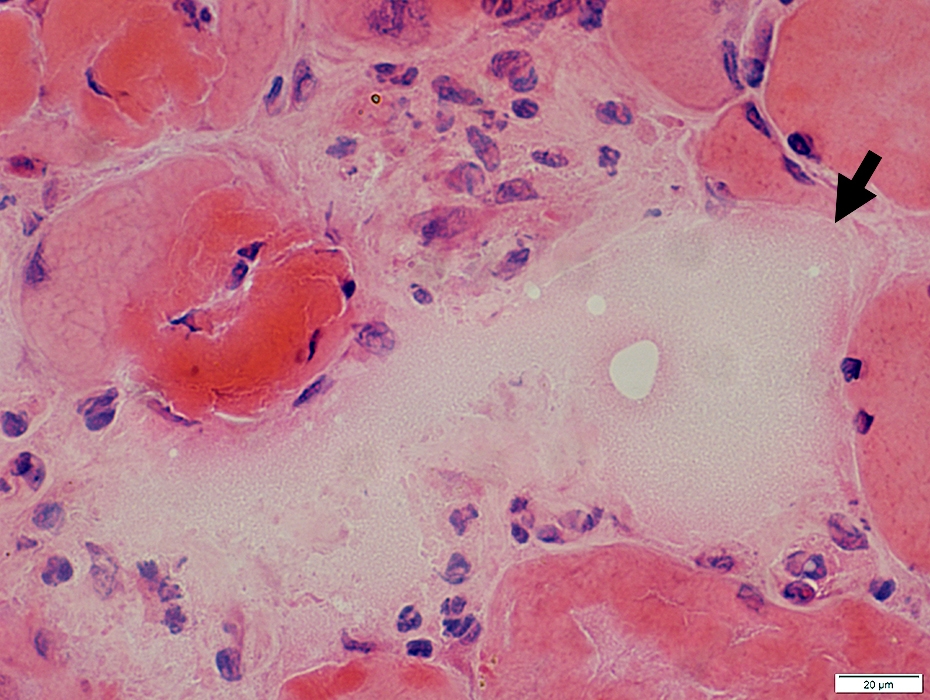 H&E stain |
Muscle Fiber Necrosis: Cell invasion
Cells in muscle fiber cytoplasm
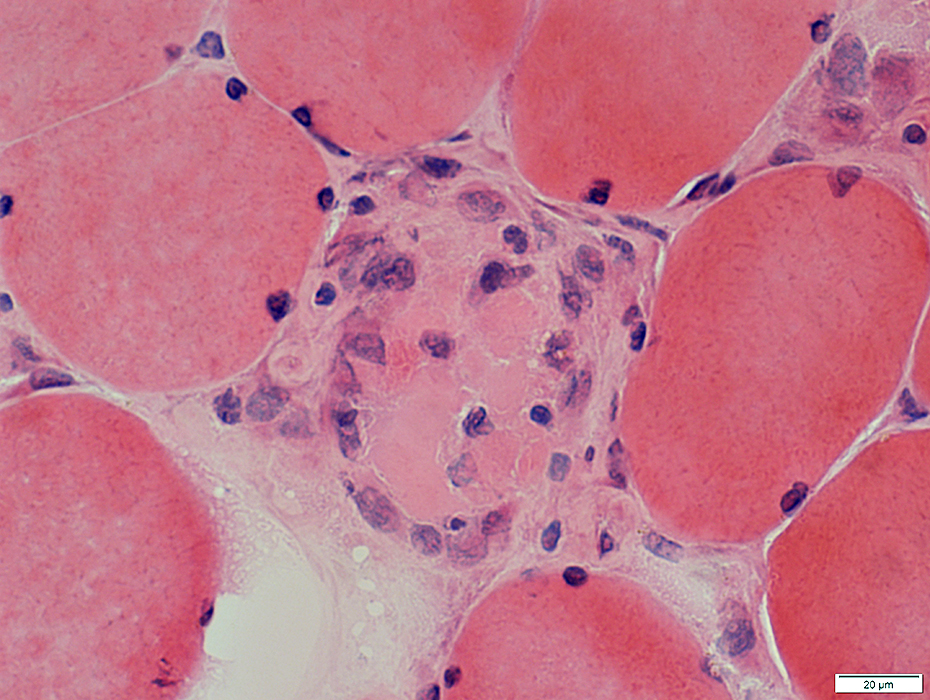 H&E stain |
Muscle Fiber Necrosis: Cell replacement
Cells (Large, Histiocytic) replace muscle fiber
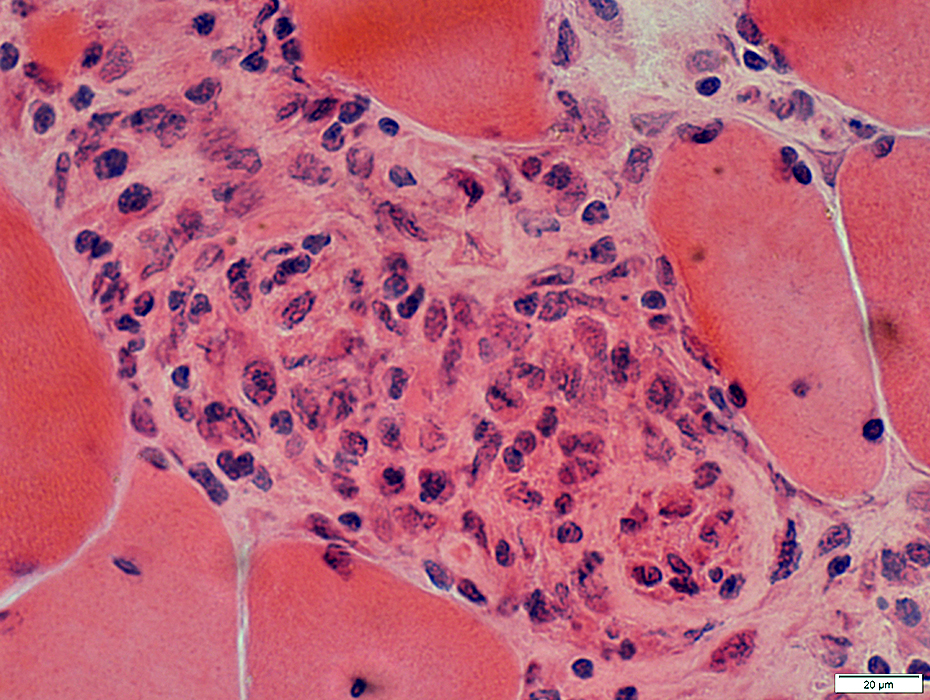 H&E stain |
Trichinellosis: Muscle Fiber Invasion
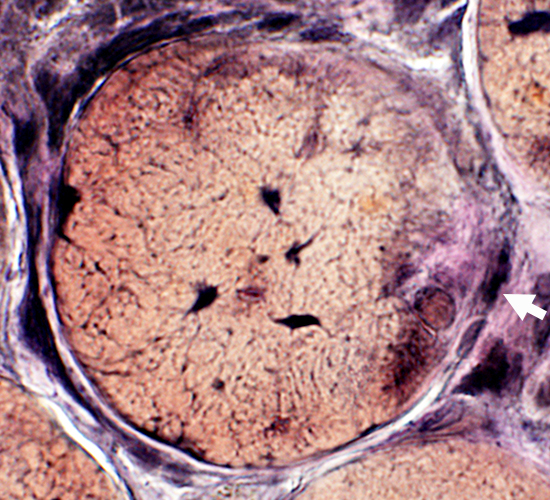 VvG stain |
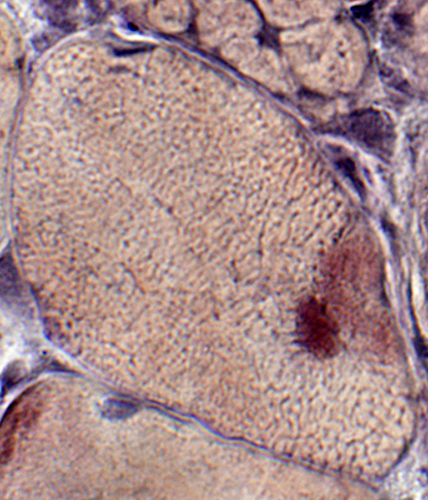 VvG stain |
Focal, Subsarcolemmal (Early) changes in muscle fibers after larval invasion
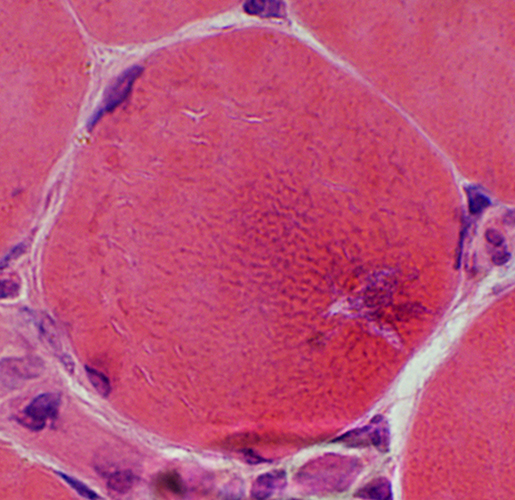 H&E stain |
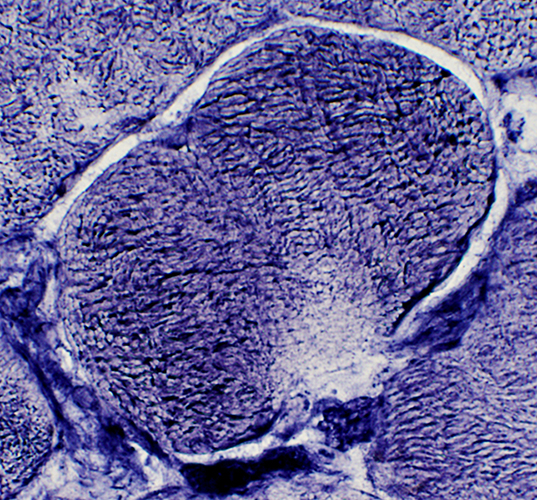 NADH stain |
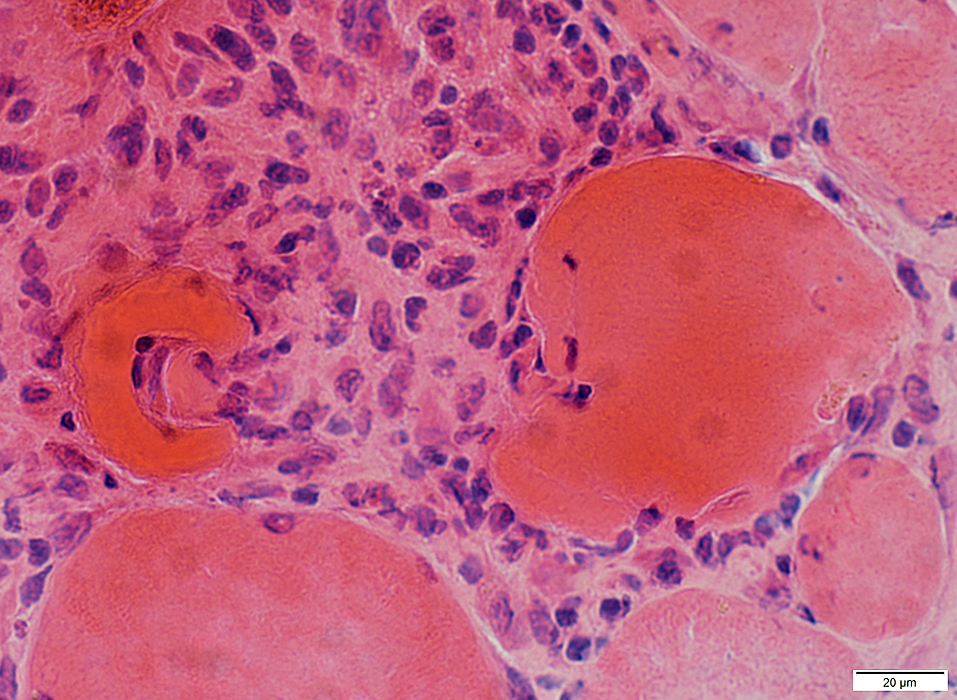 H&E stain |
Inclusions in Muscle fibers
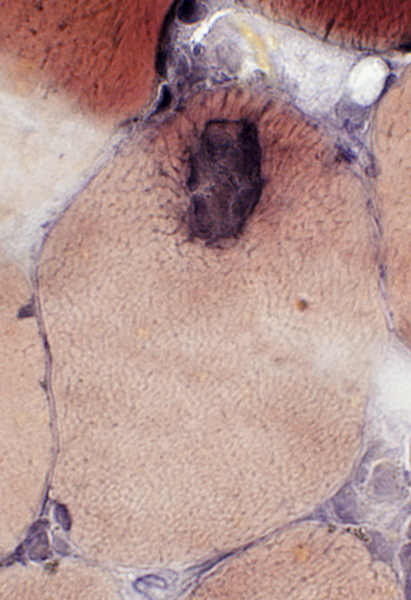 VvG stain |
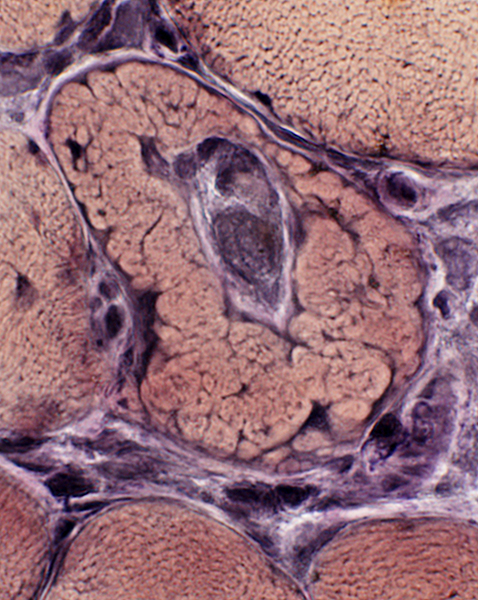 VvG stain |
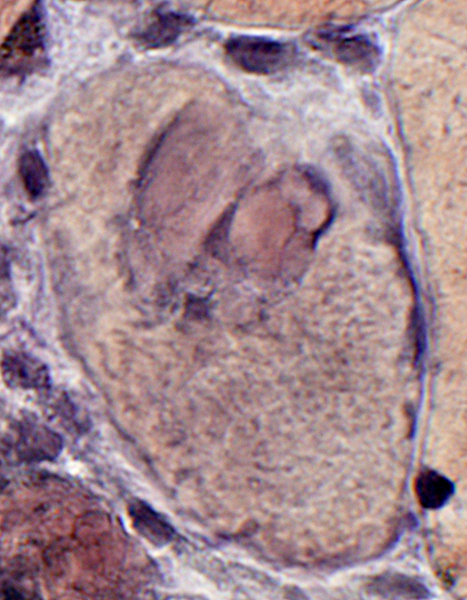 VvG stain |
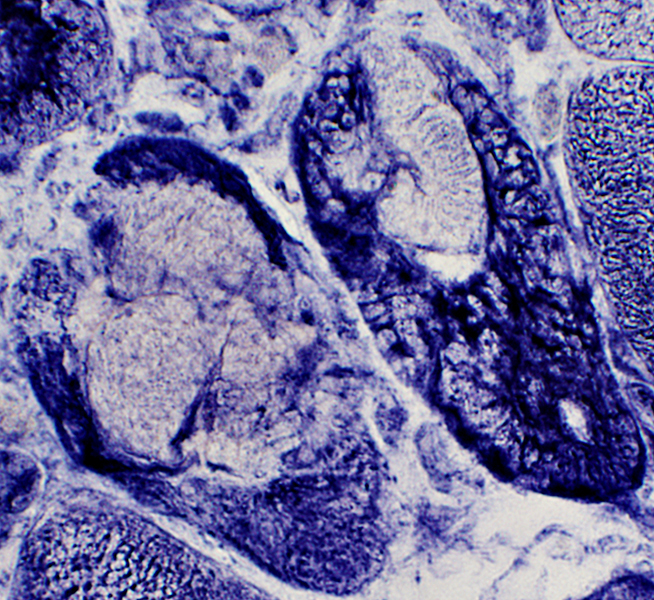 NADH stain |
Muscle fibers: Other pathology
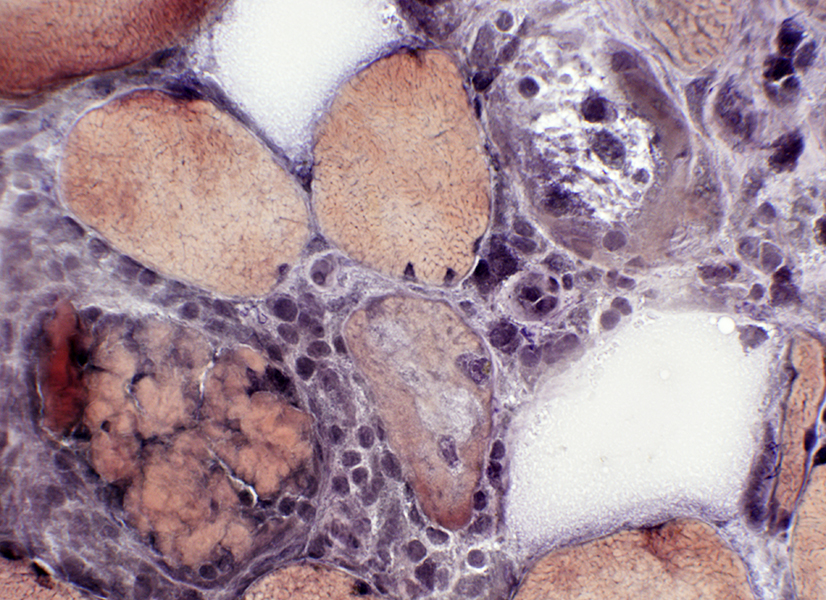 VvG stain |
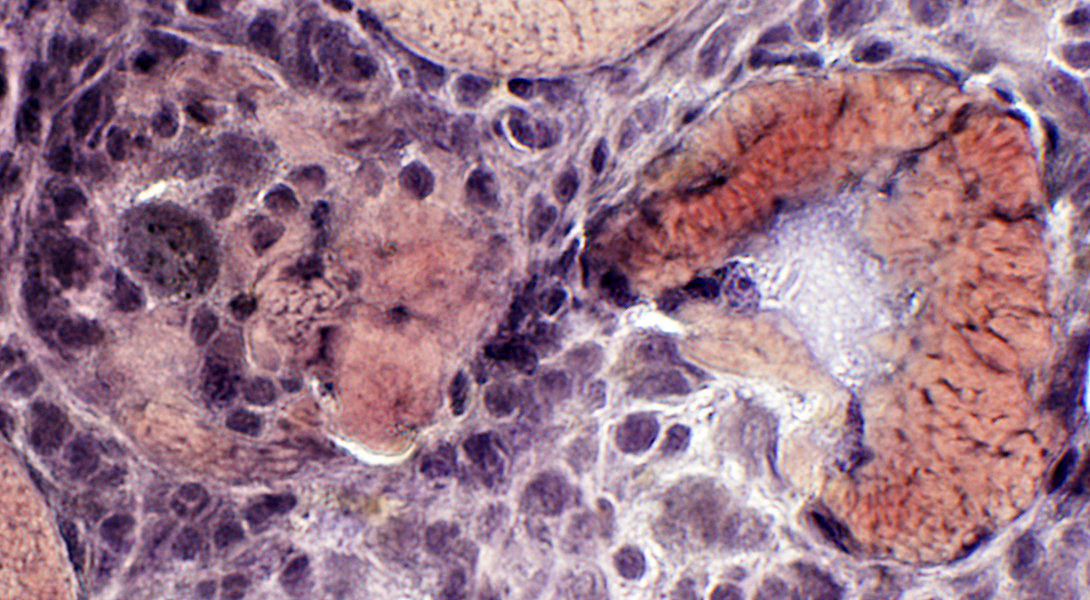 VvG stain |
Necrosis
Vacuolation
Invasion by larvae
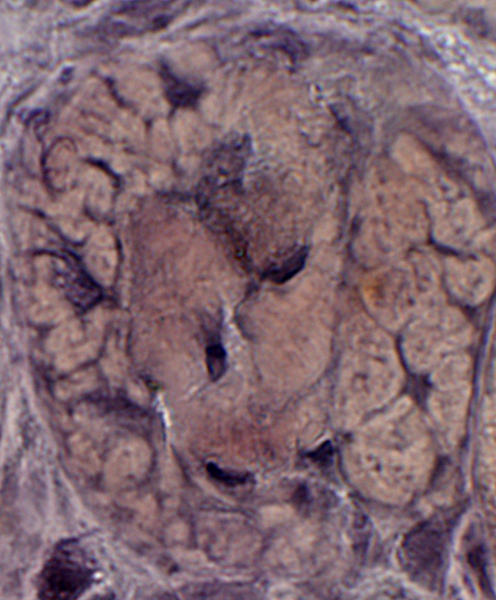 VvG stain |
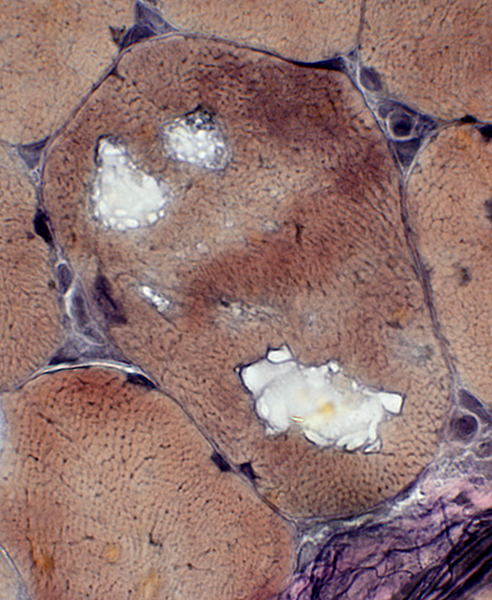 VvG stain |
Trichinellosis: Larvae
Extracellular, in endomysium, indenting muscle fibers
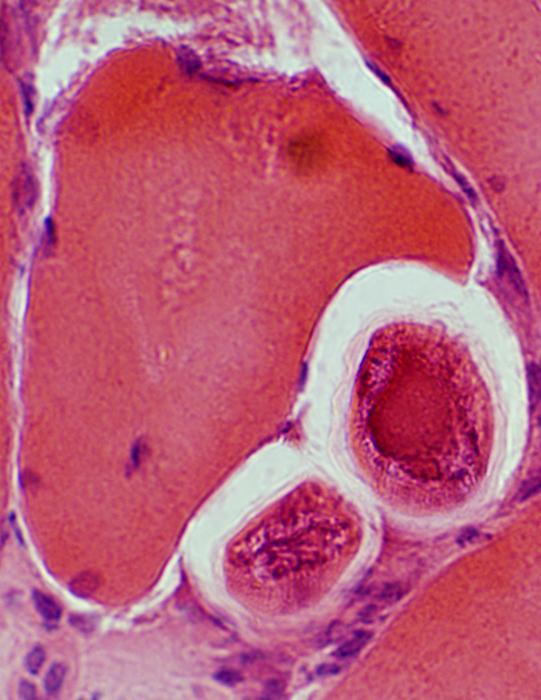 H&E stain |
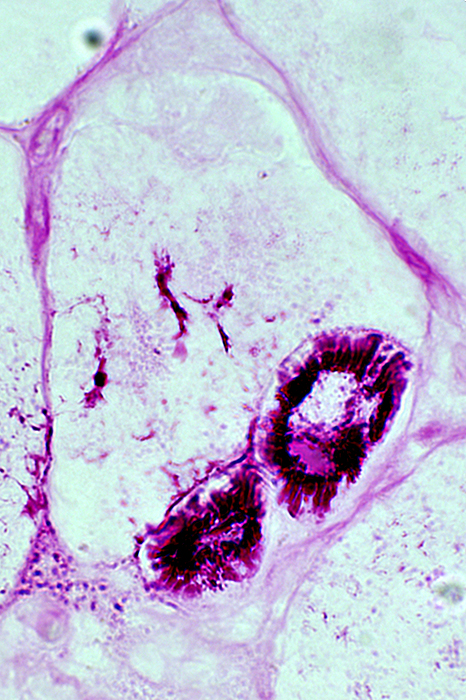 PAS stain |
Trichinellosis: Unencysted extracellular larvae
 H&E stain |
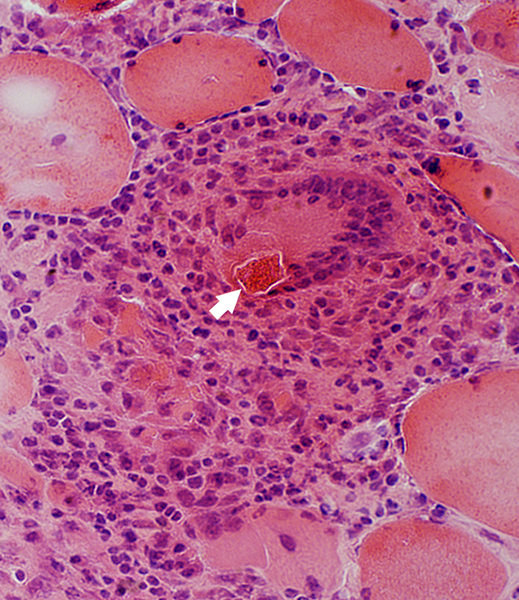 H&E stain |
|
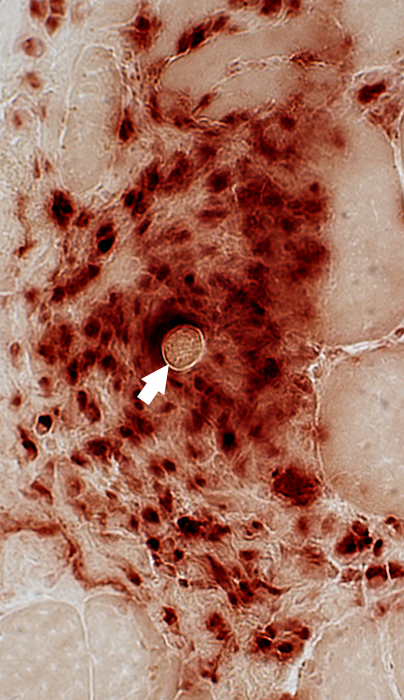 Acid phosphatase stain |
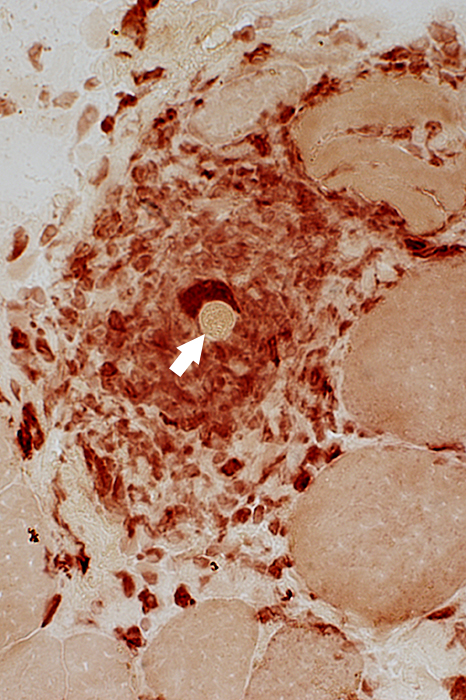 Esterase stain |
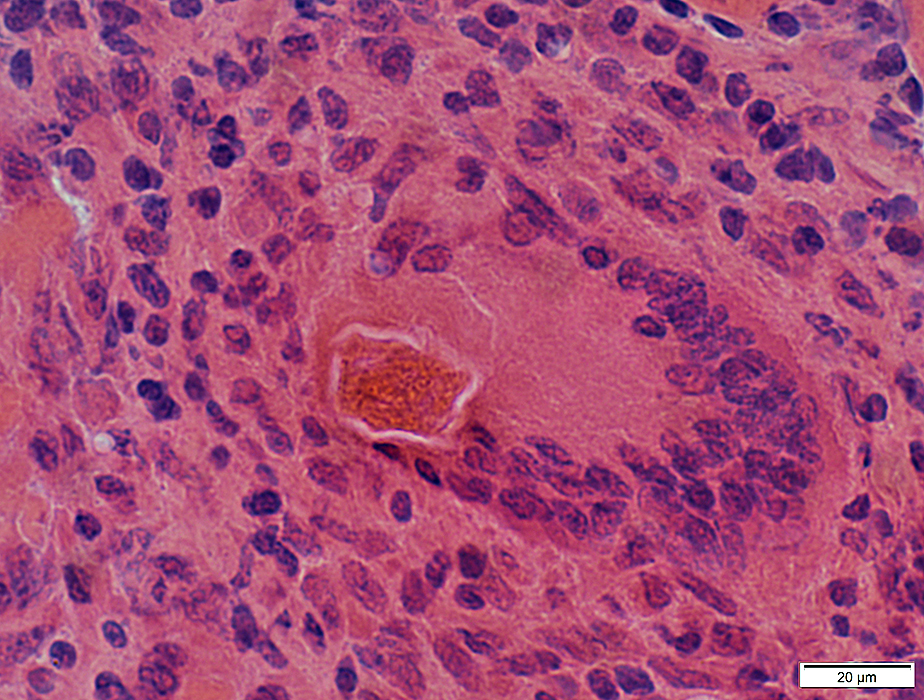
Multinucleated Giant Cell containing a Larva
 H&E stain |
Larva, extracellular: Surrounded by cells
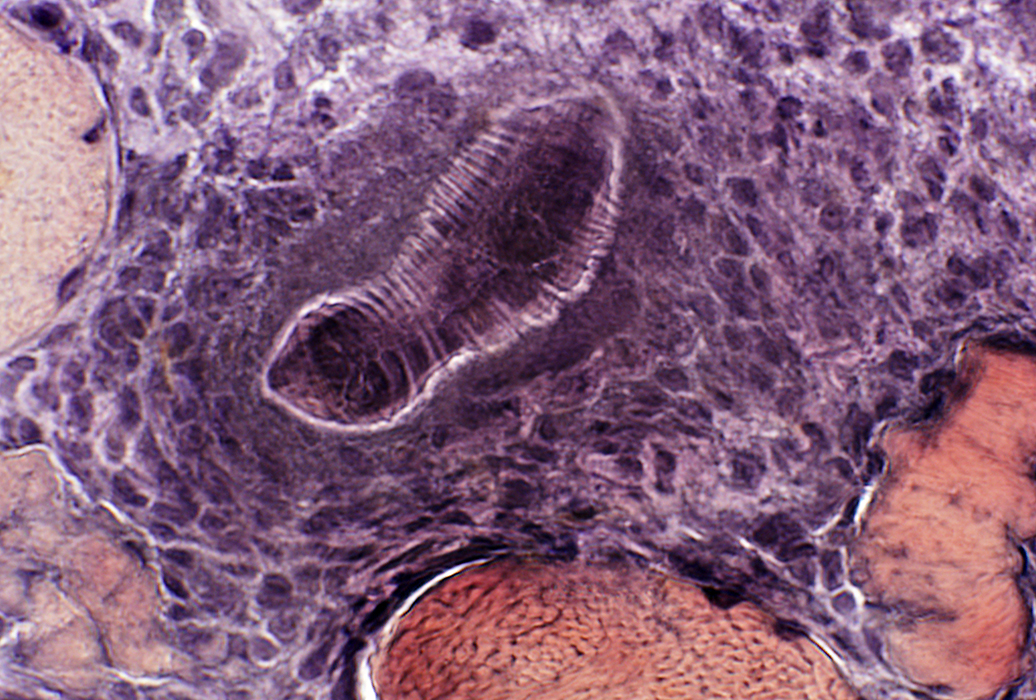 VvG stain |
Trichinellosis: CystsContain larvae & Nurse cells | |
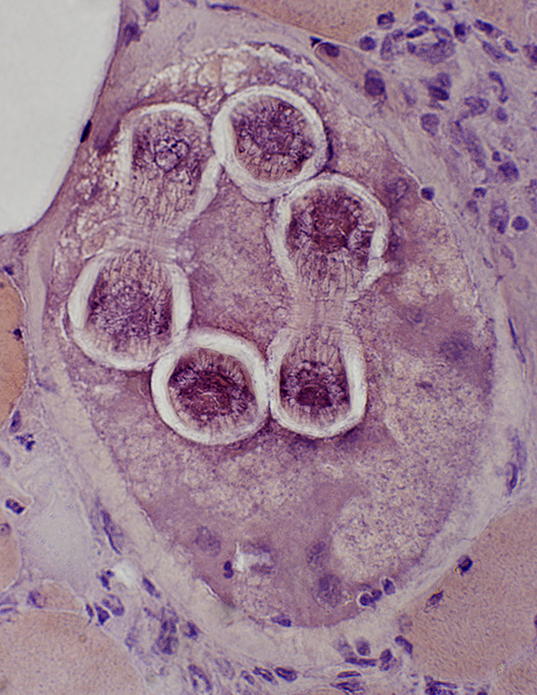 Congo red stain |
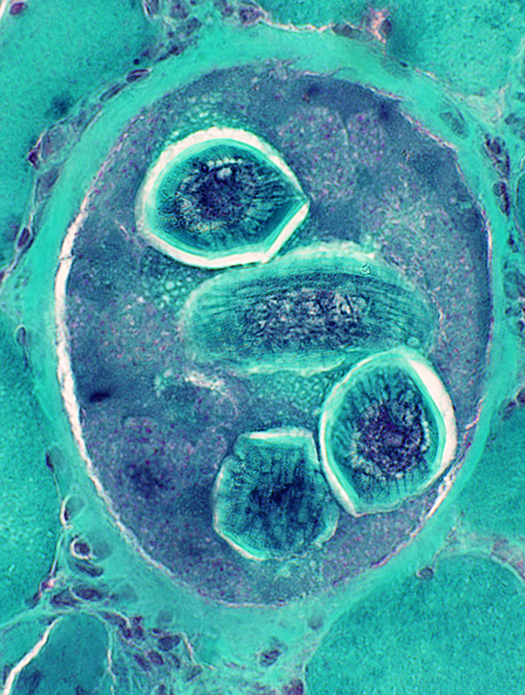 Gomori trichrome stain |
|
|
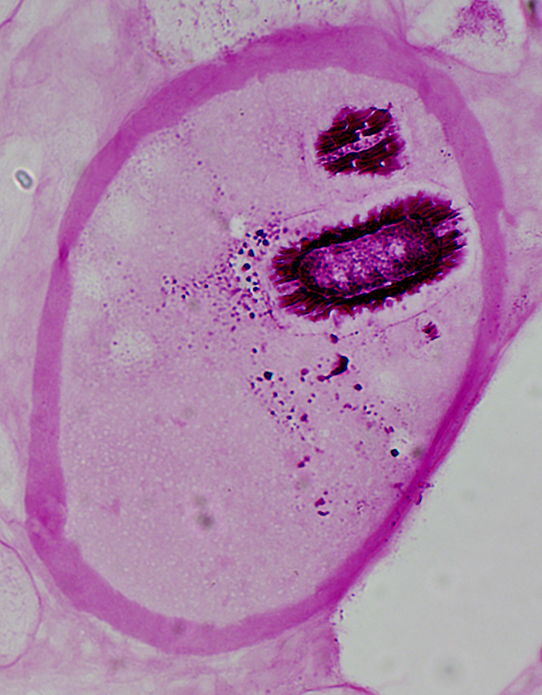 PAS stain |
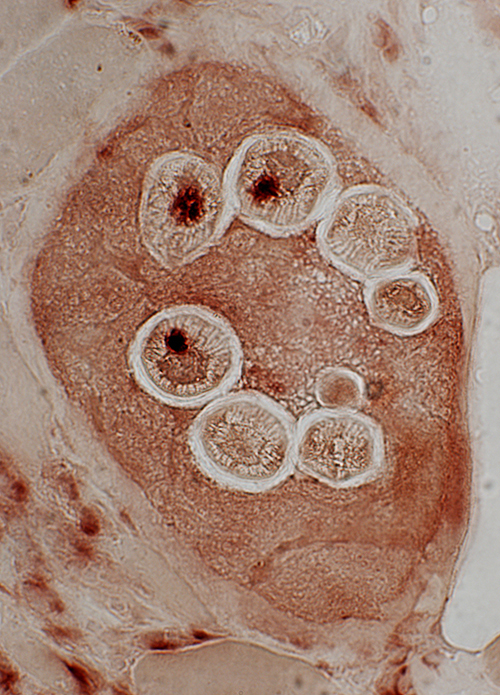 Acid phosphatase stain |
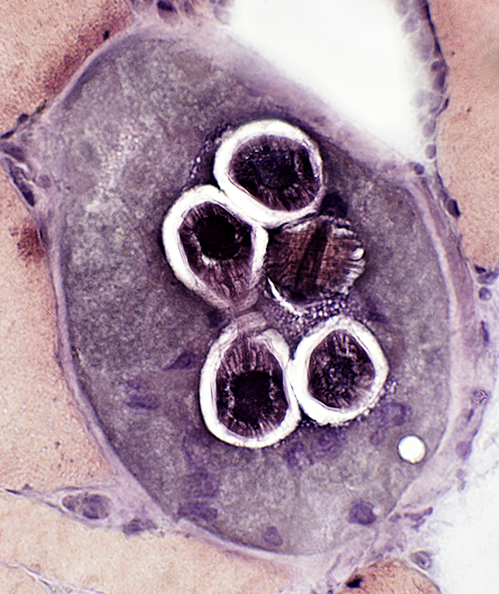 VvG stain |
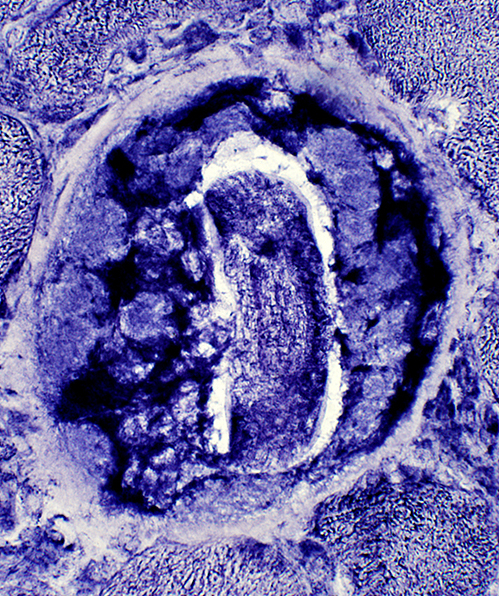 NADH stain |
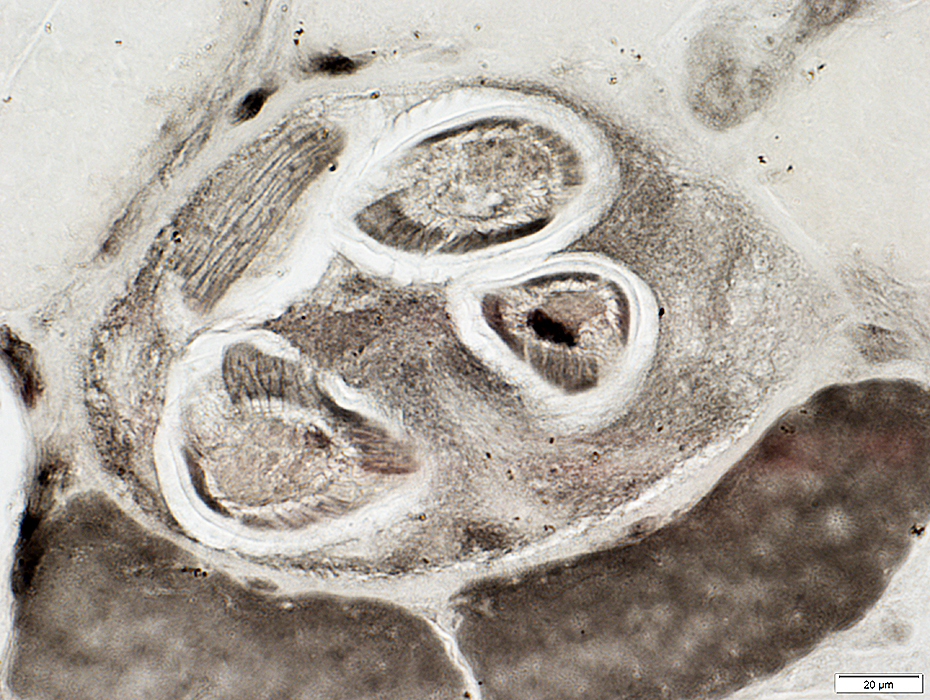 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
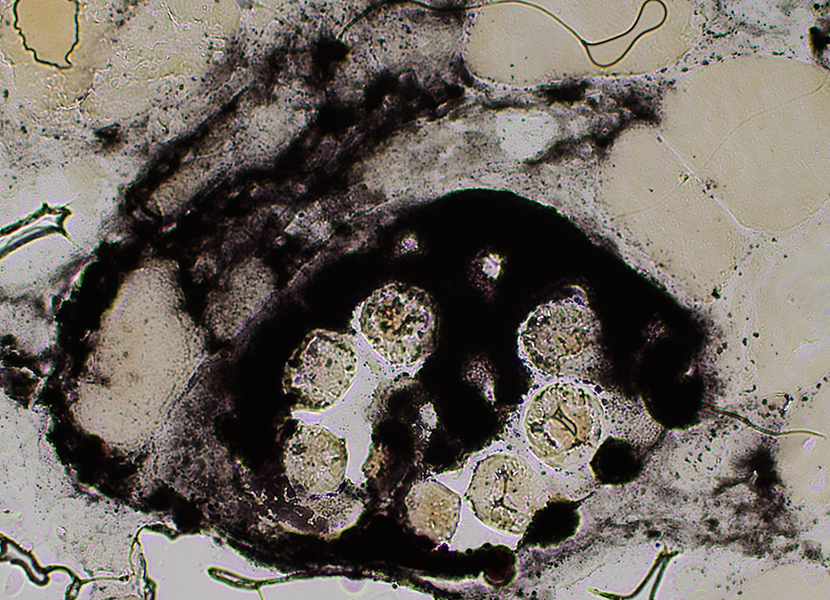 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
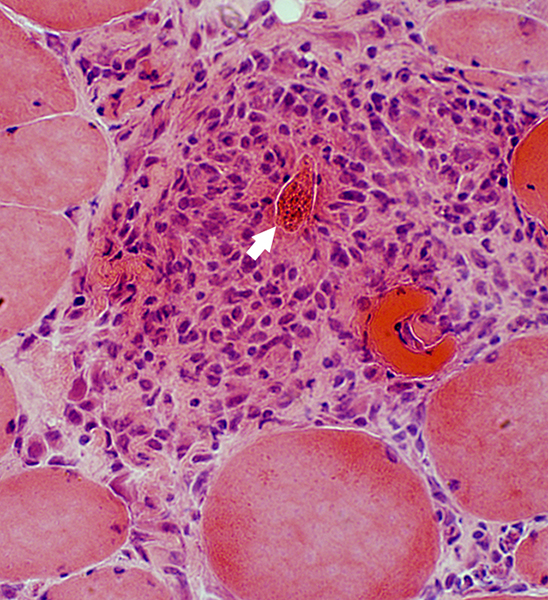
Eosinophils
Present in vessel but not in extravascular regions
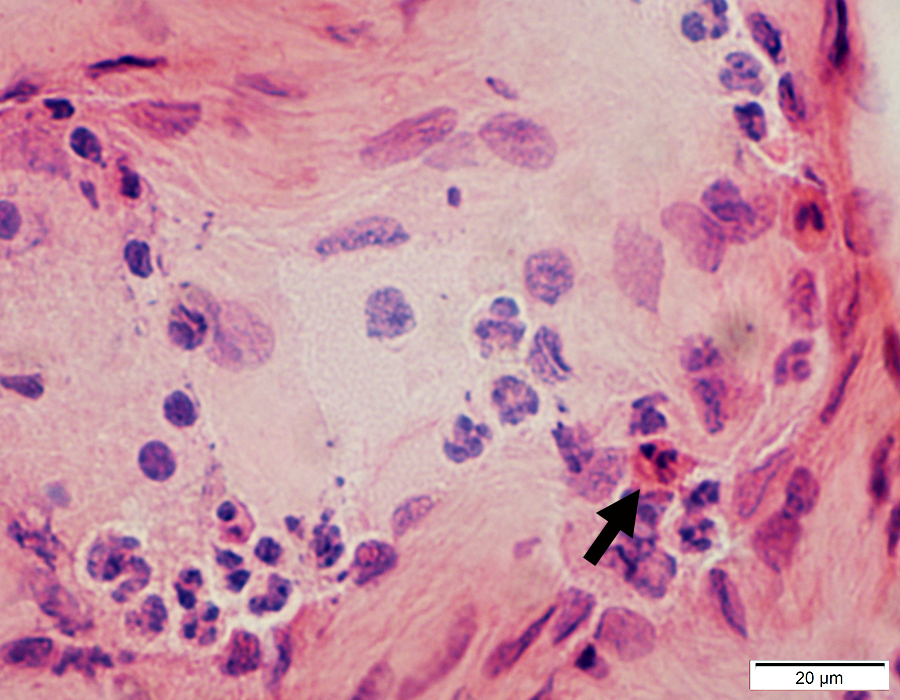 H&E stain |
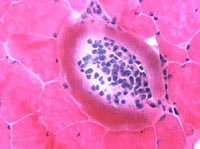
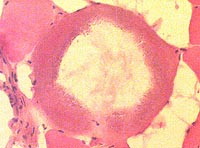
Trichinellosis: Chronic
Cysts without larvae
|
|
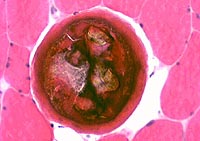 |
|
Cyst Inflammatory cells No larvae 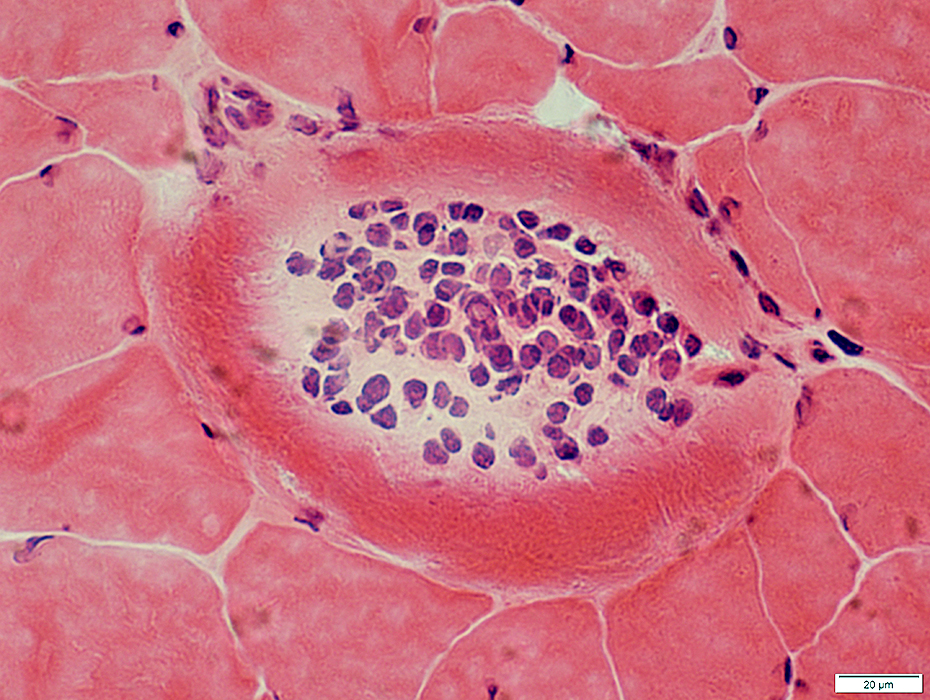 H&E stain |
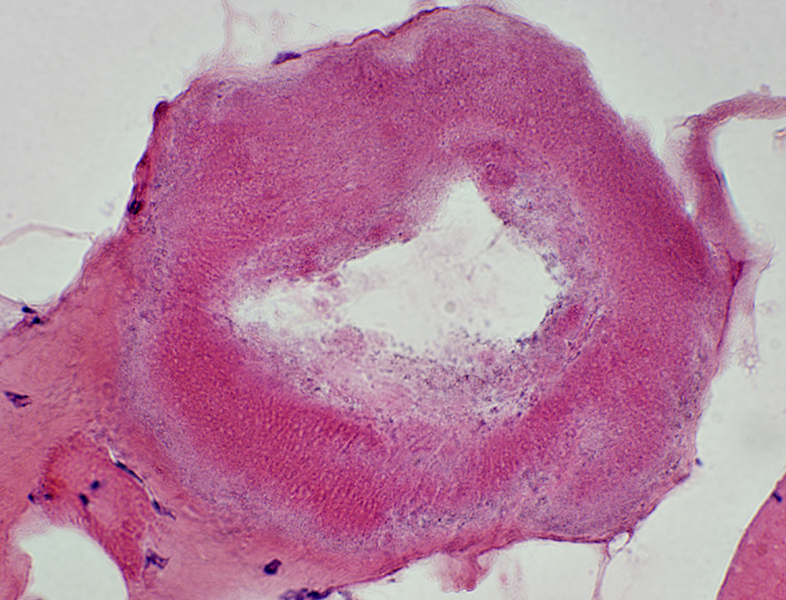 H&E stain |
Surrounding muscle: No inflammation or active myopathic changes
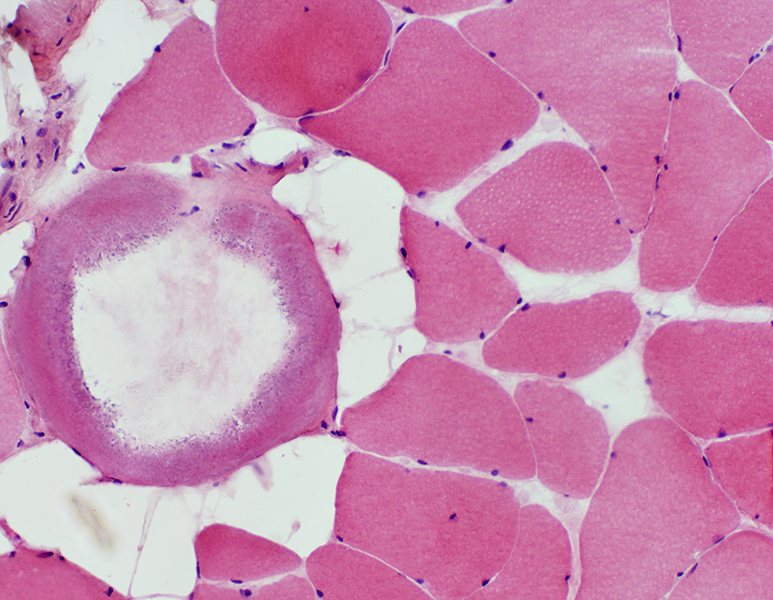 H&E stain |
|
Calcification inside cyst 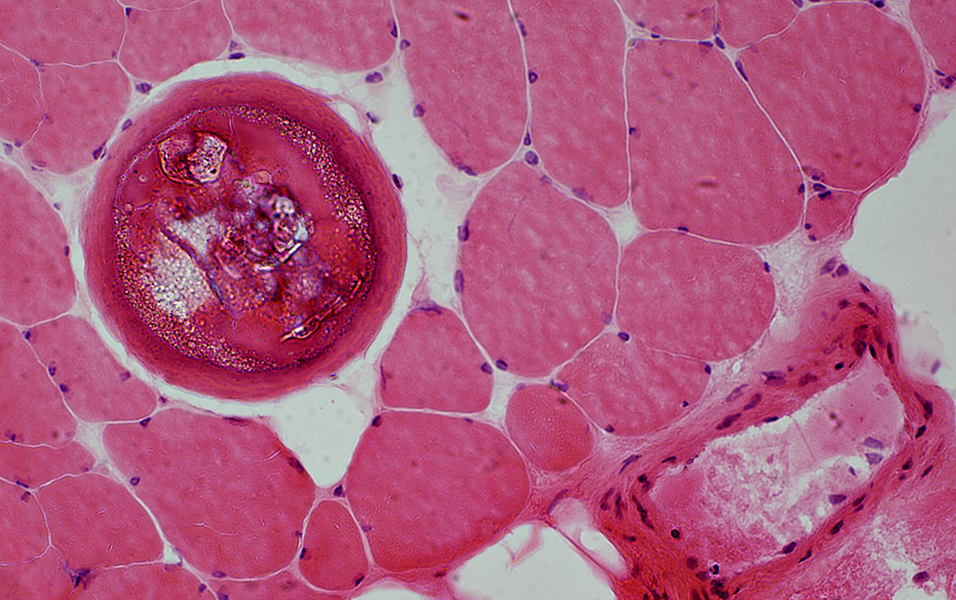 H&E stain |
Trichinella spiralis: Lifecycle
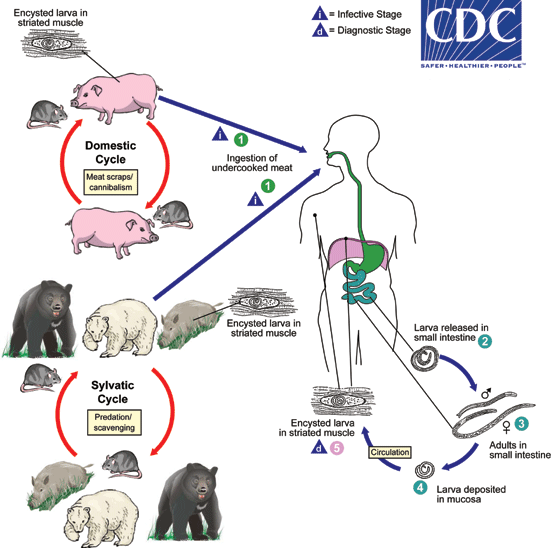
CDC
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Return to Inflammation
Return to Trichinosis
11/25/2020