AXONS: PATHOLOGIC CHANGES
|
Beaded Giant Axonal Neuropathy Polyglucosan bodies Swellings Differential diagnosis Sprouts with membrane profiles Tubulovesicular Impaired axon growth |
Axon Swellings
|
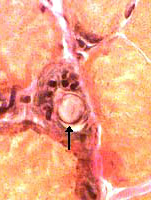
Giant Axonal Neuropathy
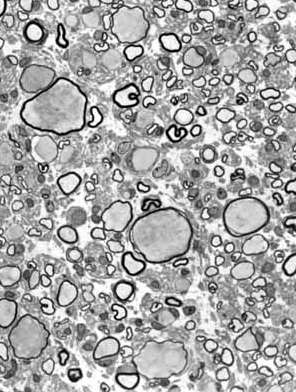
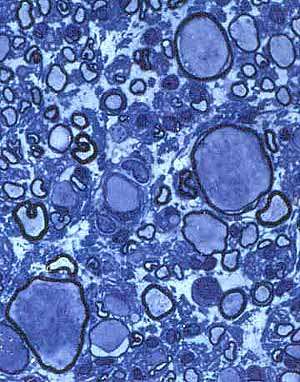 From Pr P Landrieu |
|
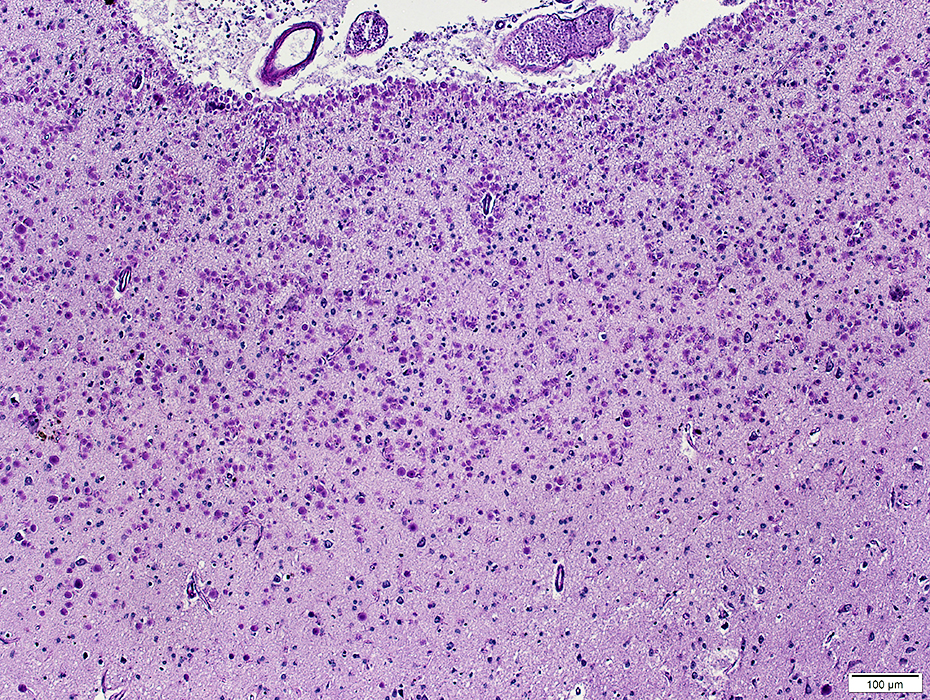
Many enlarged thinly myelinated, or unmyelinated, axons. Reduced number of myelinated axons. |
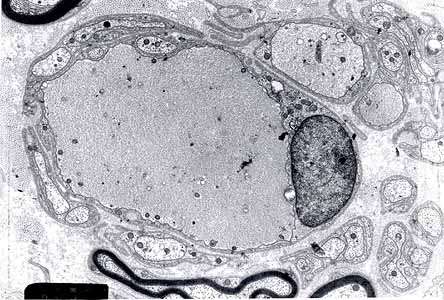
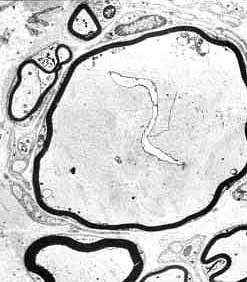 From Pr P Landrieu |
|
Enlarged unmyelinated, or thinly myelinated, axons. |
 From Pr P Landrieu |
|
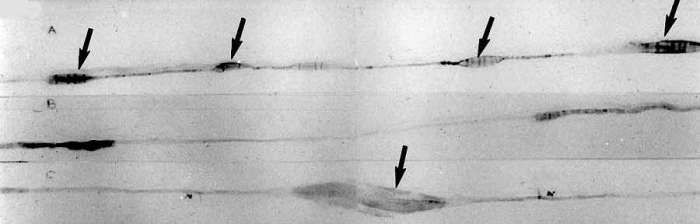
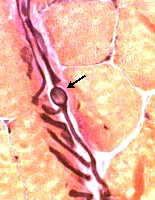
Teased axons with focal swellings (Arrows).
|
 From T Mozaffar |
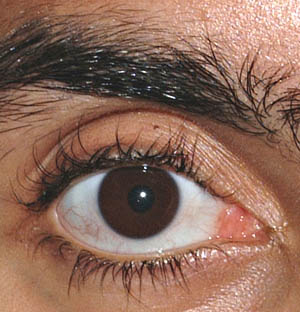
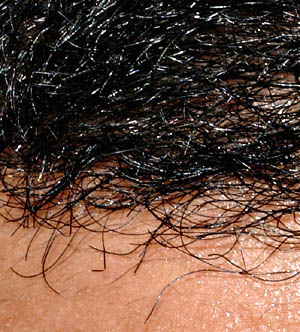
| Long curly eyelashes; Curled scalp hair |
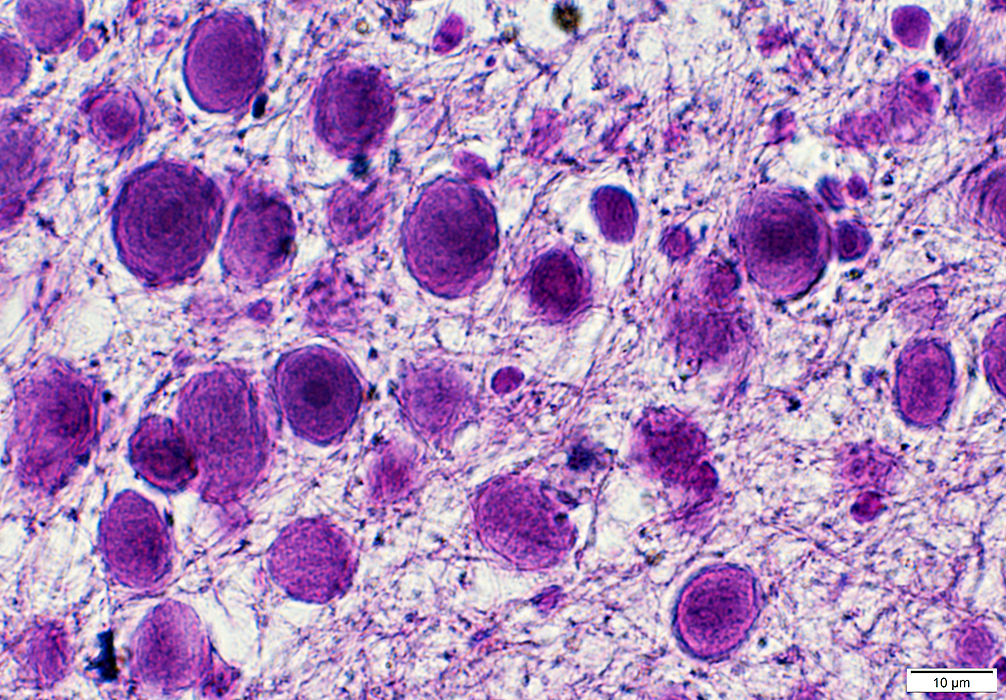
Polyglucosan Bodies
- Staining properties
- H&E: Basophilic
- Toluidine blue: Metachromatic
- PAS: Positive
- Other postive stains: Iodine; Silver; Alcian blue
- Electron microscopy
- Contents: Randomly arranged granules & branched filaments
- No limiting membrane
- Location
- PNS: Within myelinated axons
- CNS
- Location: Astrocyte processes
- Similar structures: Corpora amylacea; Lafora bodies; Bielchowsky bodies
- Associations
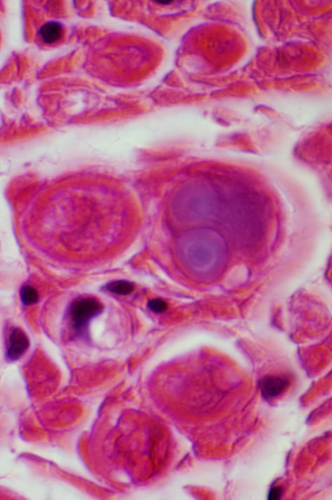
H&E stain |
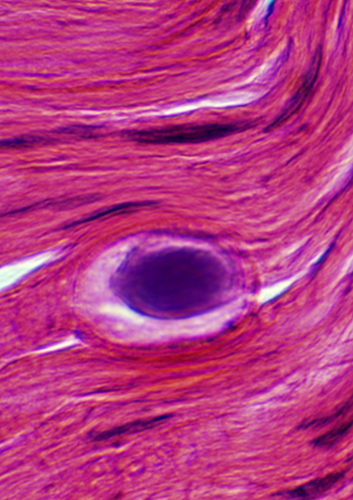 |
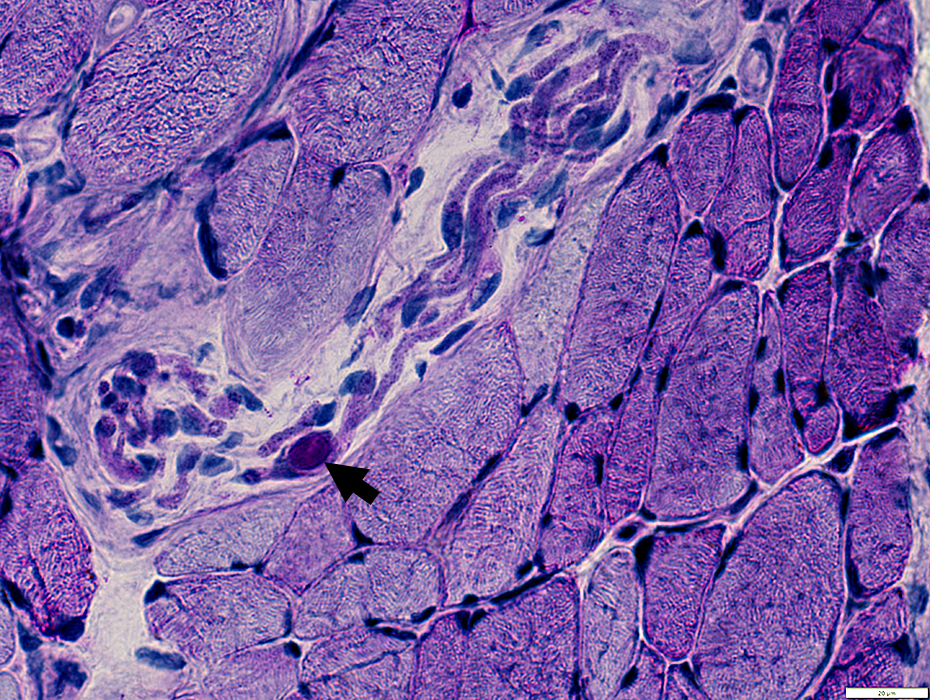
 VvG stain Intramuscular axons: Focal swellings |
 VvG stain |
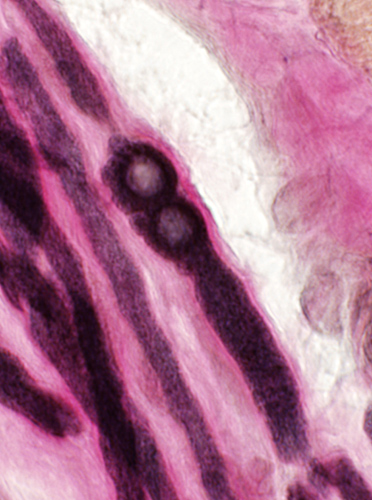
 VvG stain Intramuscular axons: Focal swellings |
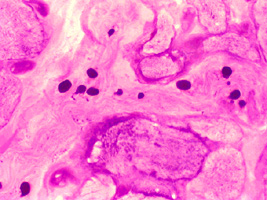 PAS stain Intramuscular nerve: Polyglucosan bodies |
 PAS stain |
 PAS stain |
 |
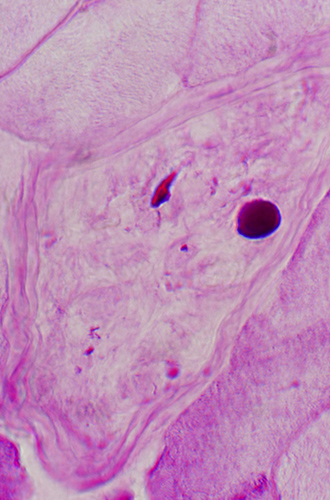 |
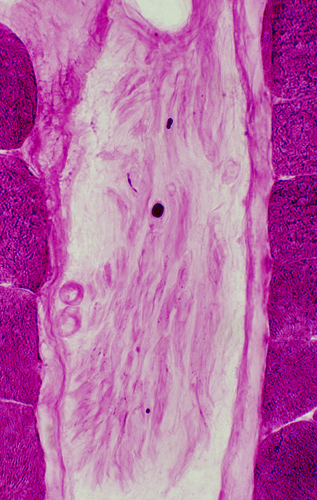
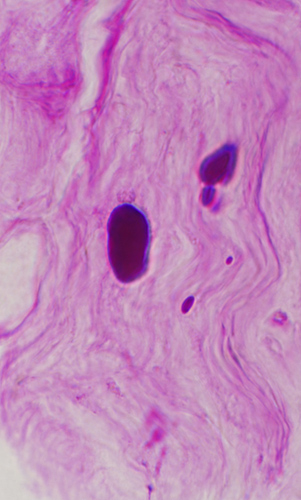
Polyglucosan Bodies: Swellings in Peripheral nerve axons
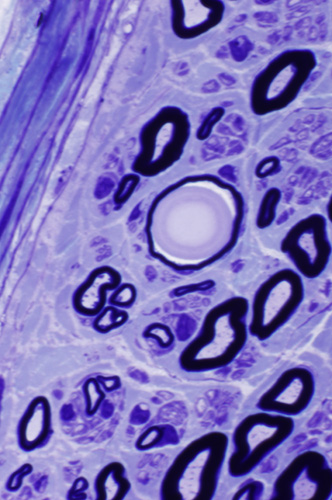 Toluidine blue stain |
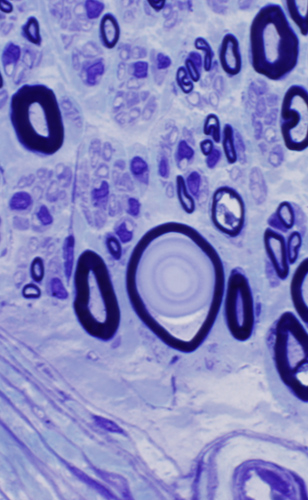 |
Intra-axonal, cytoplasmic round structure
Composed of concentric bands with varied density
Contains: Short filaments
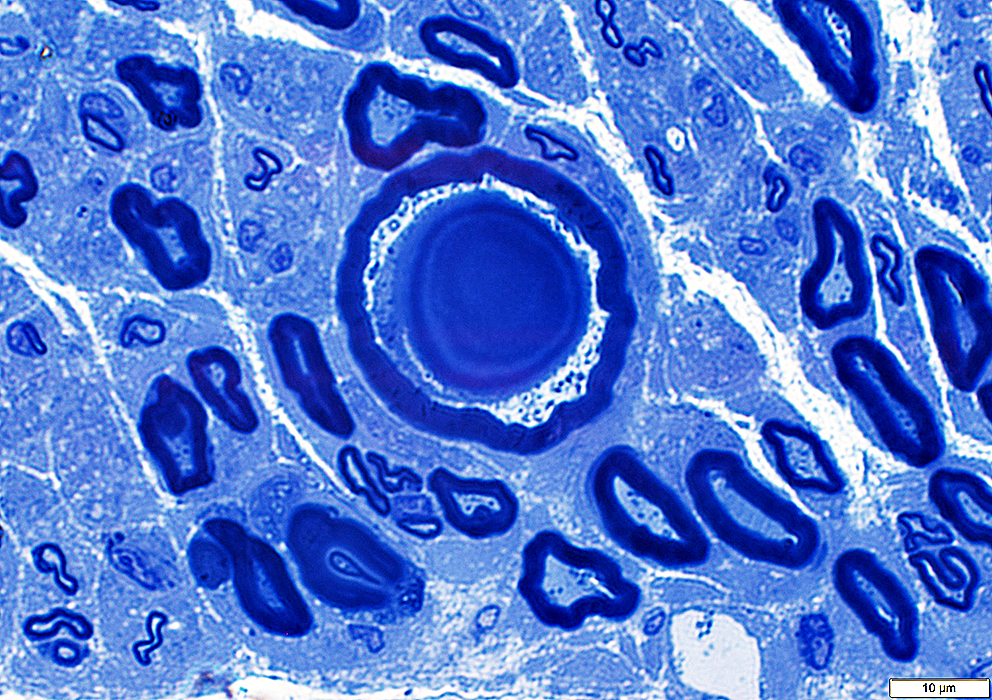 Toluidine blue stain |
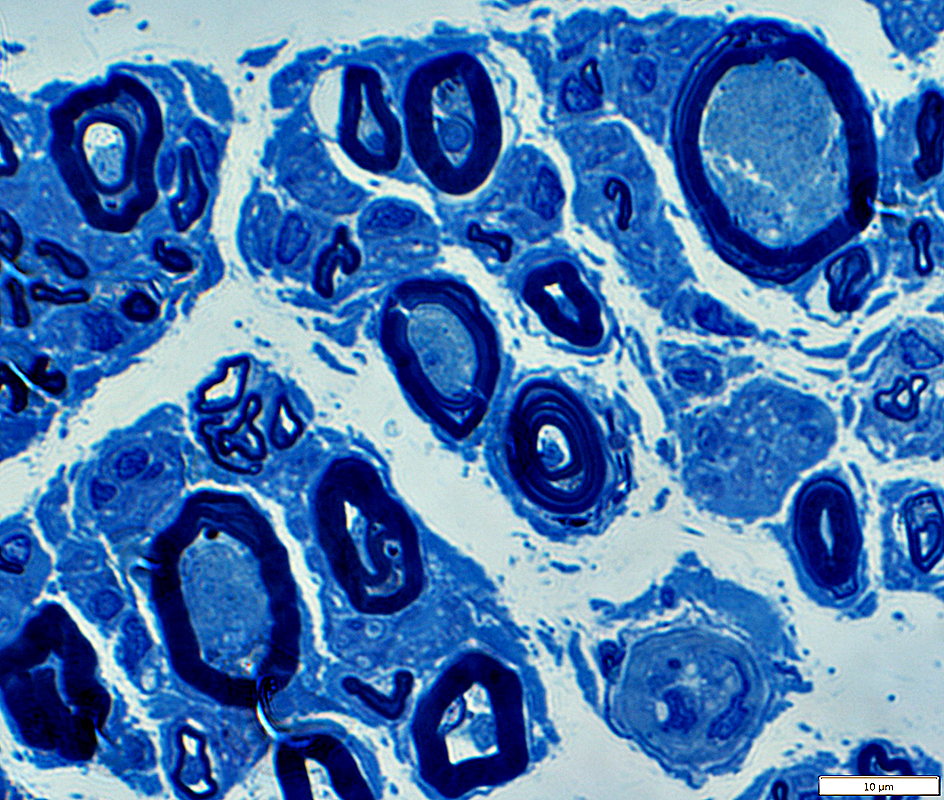 Toluidine blue stain |
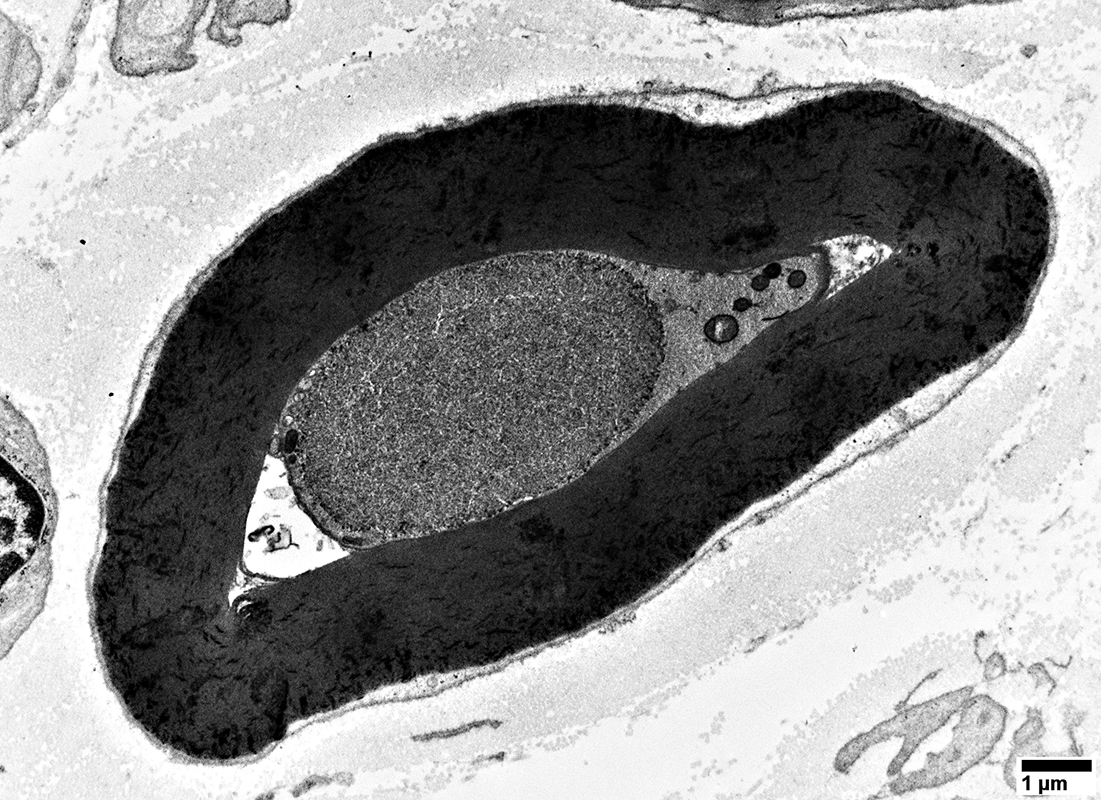 Ultrastructure: From Robert Schmidt |
Location: Intra-axonal
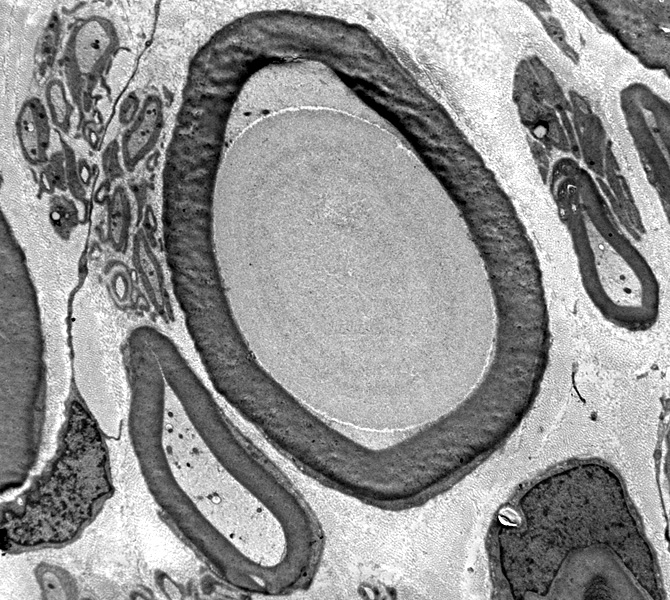 Ultrastructure: From Robert Schmidt |
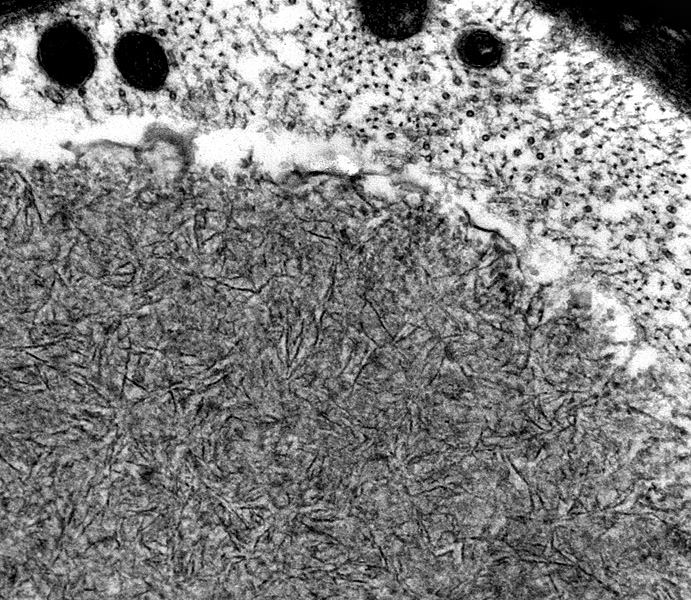 |
Contains: Filaments
Random orientnation
Short
Tightly packed
Polyglucosan Body Disease
 |
Anatomic types
Corpora amylacea
Lafora bodies
Bielschowsky bodies
Contents: Abnormally branched glycogen (Amylopoectin)
 |
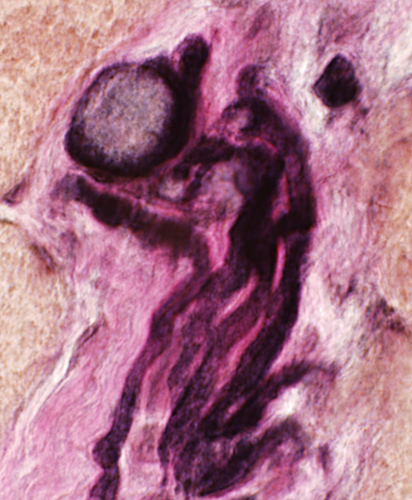
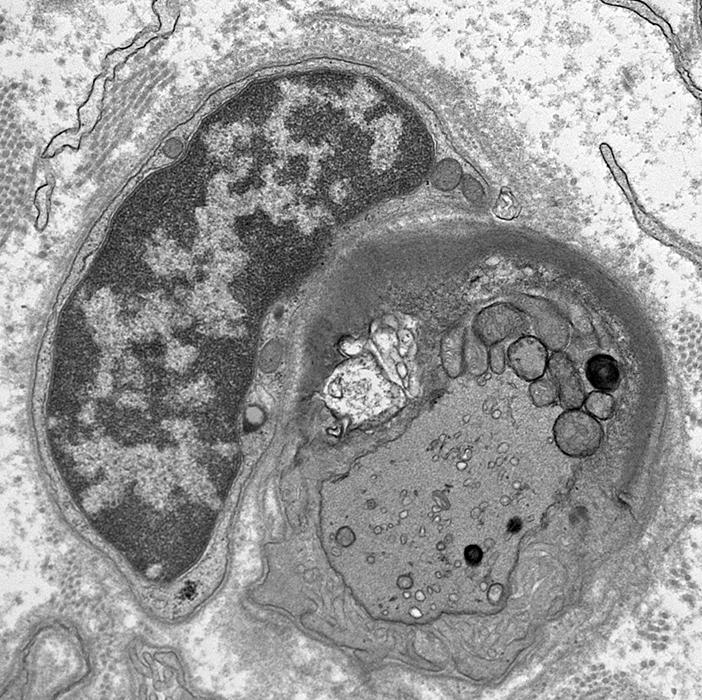
Axon Swellings: Enlarged Unmyelinated axons, or Axon sprouts
|
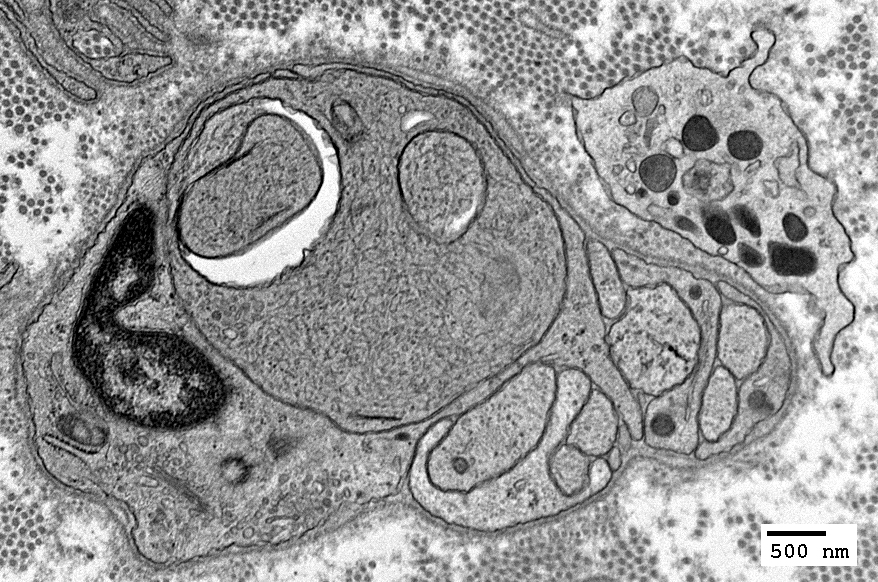
|
Axon, Intermediate-sized, Probably regenerating, within a set of Büngner band Schwann cell processes
With many mitochondria in axoplasm
Surrounded by multiple Schwann cell processes (? Büngner band)
Fibroblast process outside of Schwann cell processes (Upper left)
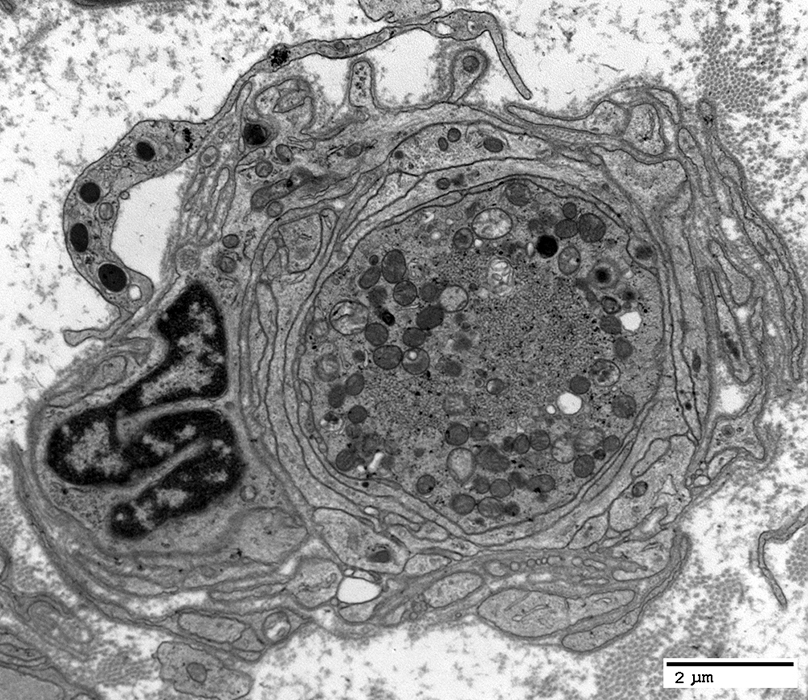
|
Enlarged axon: Contains organelles & tubulovesicular profiles
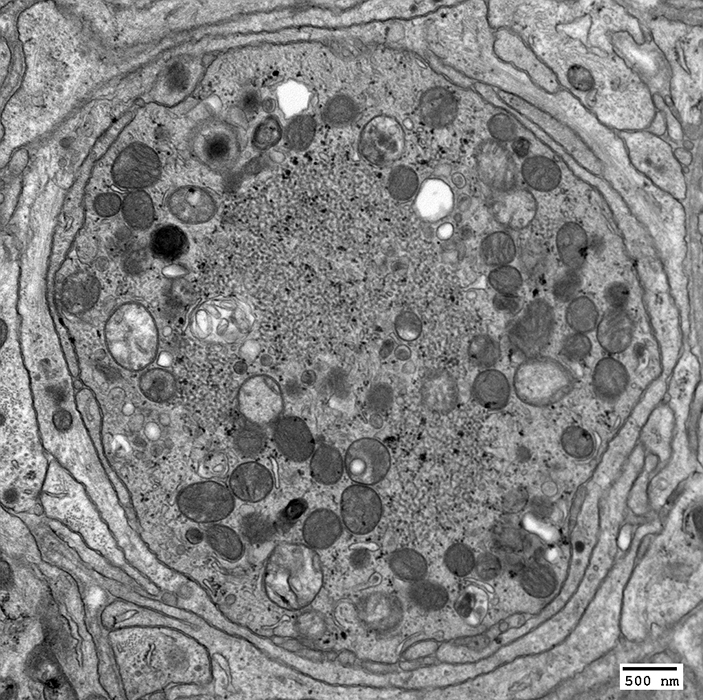
|
Enlarged axon: Contains tubulovesicular profiles
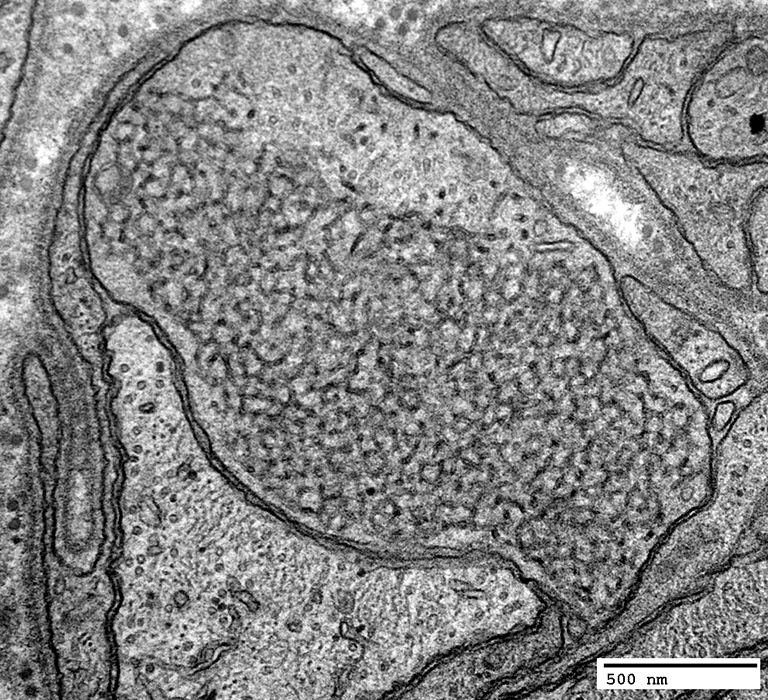
|
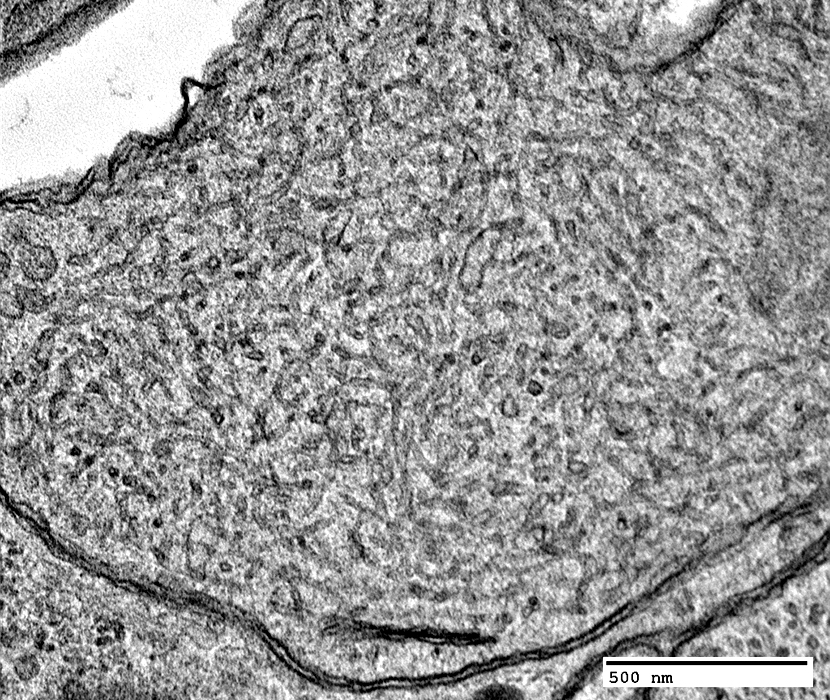
|
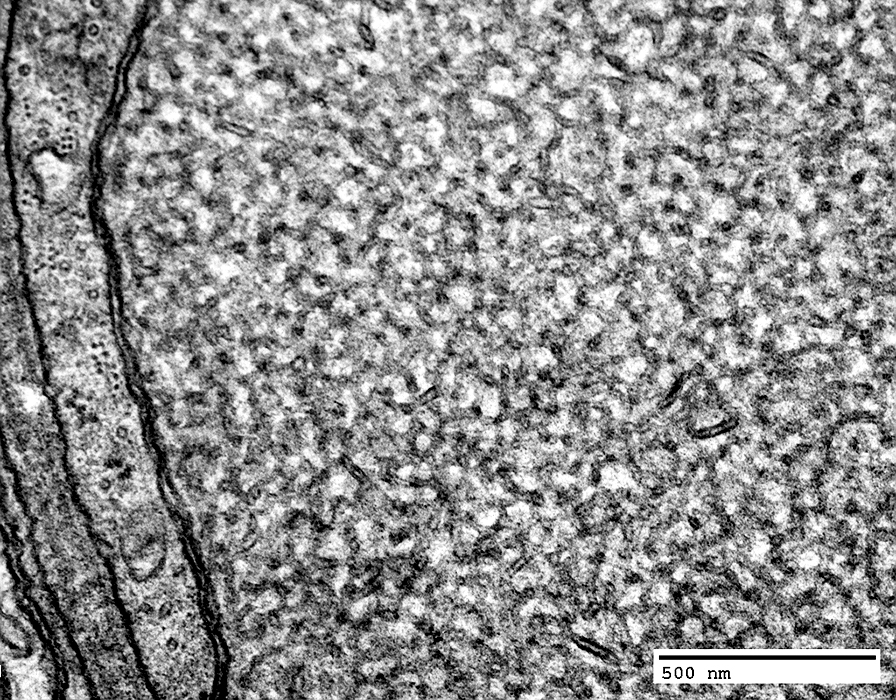
|
Tubulovesicular profiles & Peripheral organelles
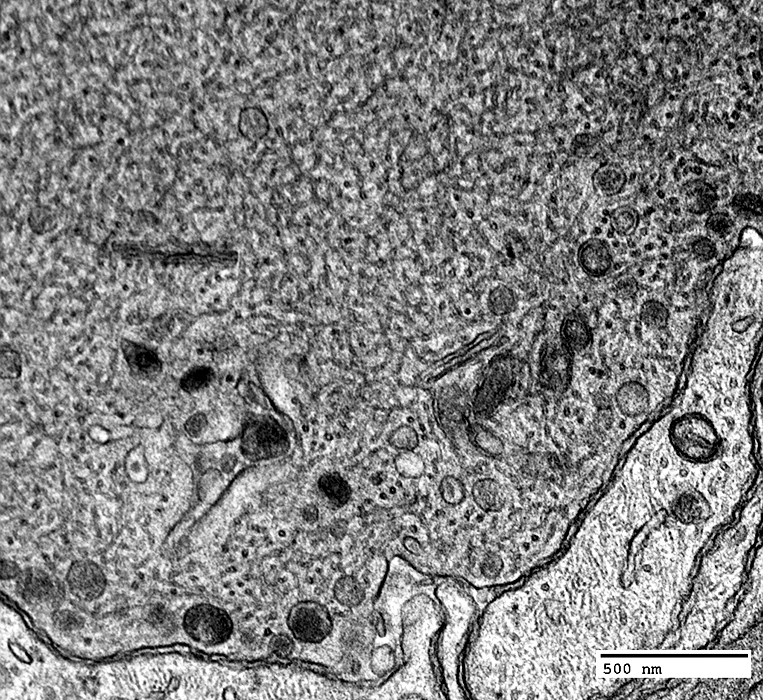
|
Axons: Beaded appearance
|
Neurofilament stains Ultrastructure Axoplasm Neurofilaments Tubuloreticular Dark filaments Schwann cells Processes near axon Few axon-related SC processes No Büngner bands |
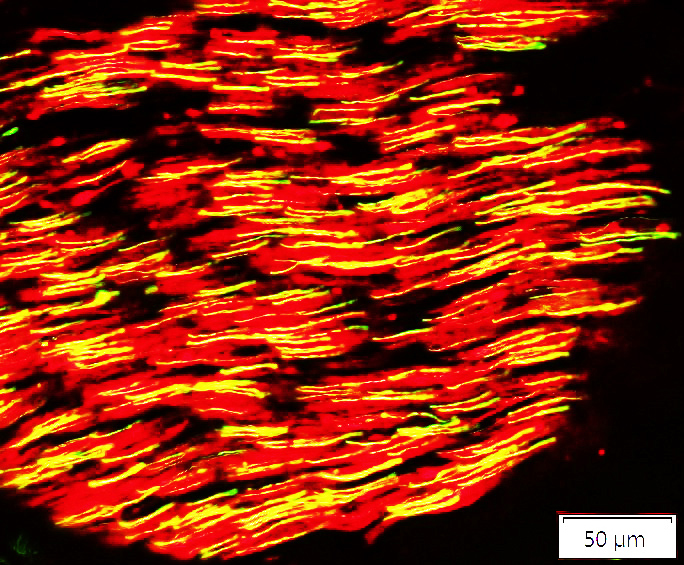 Neurofilament (Green/Yellow) + NCAM (Red) |
Axon loss is apparent
Small axons are often visualized individually, rather than in clusters
Empty Schwann cells (Red) with no axons are present
Remaining axons
Most axons have associated NCAM, either co-staining or surrounding them
Many remaining axons have a beaded appearance
There are no large axons in this nerve fascicle
See: Control nerve
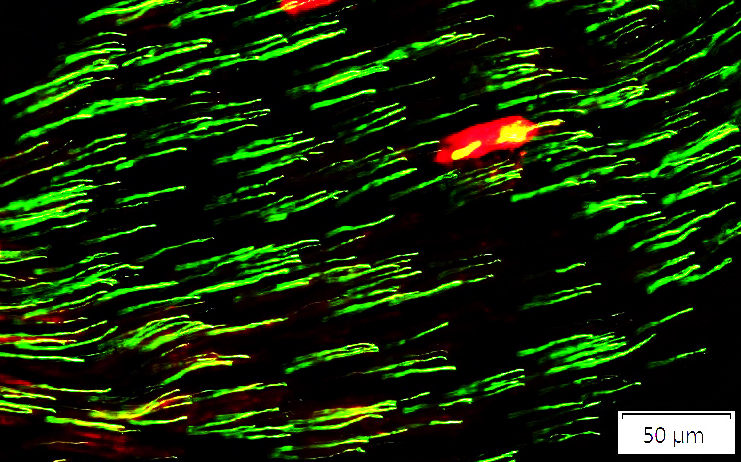 Neurofilament (Green/Yellow) + P0 (Red) |
Most of these axons have no associated P0
There are rare large myelinated axons in this nerve.
See: Control nerve
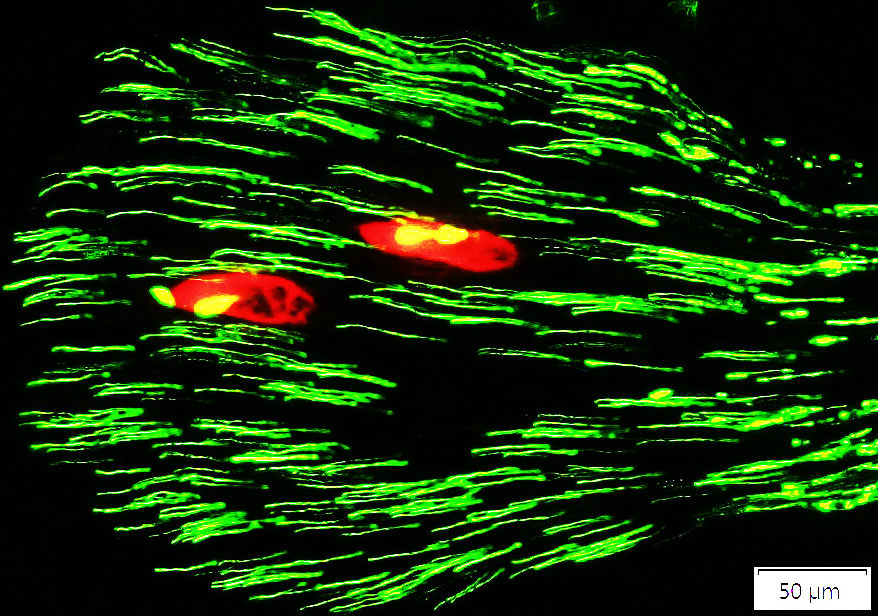 Neurofilament (Green/Yellow) + MBP (Red) |
Most of these axons have no associated MBP
There are rare large myelinated axons in this nerve.
See: Control nerve
Axons with multiple neighboring Schwann cell processes, but not surrounded by them
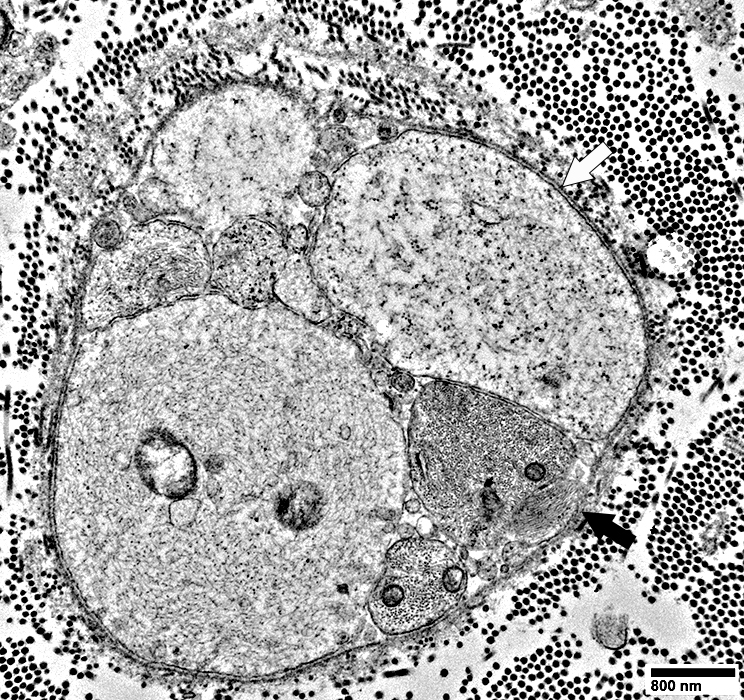 From: R Schmidt |
Axon (Above; Black Arrow) is associated with multiple Schwann cell processes, but not surrounded by them
Schwann cell processes & axons are surrounded by a layer of basal lamina (Above; White arrow)
Small axon: Contains neurofilaments (Below)
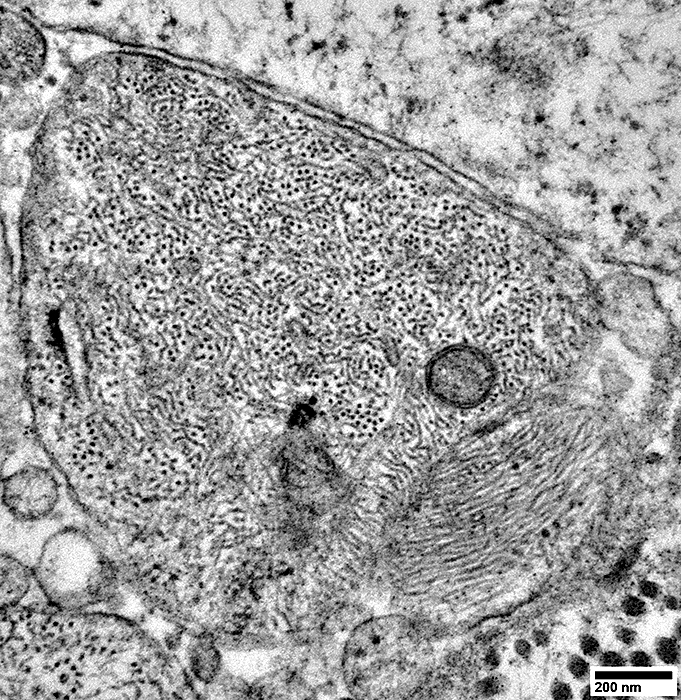 From: R Schmidt |
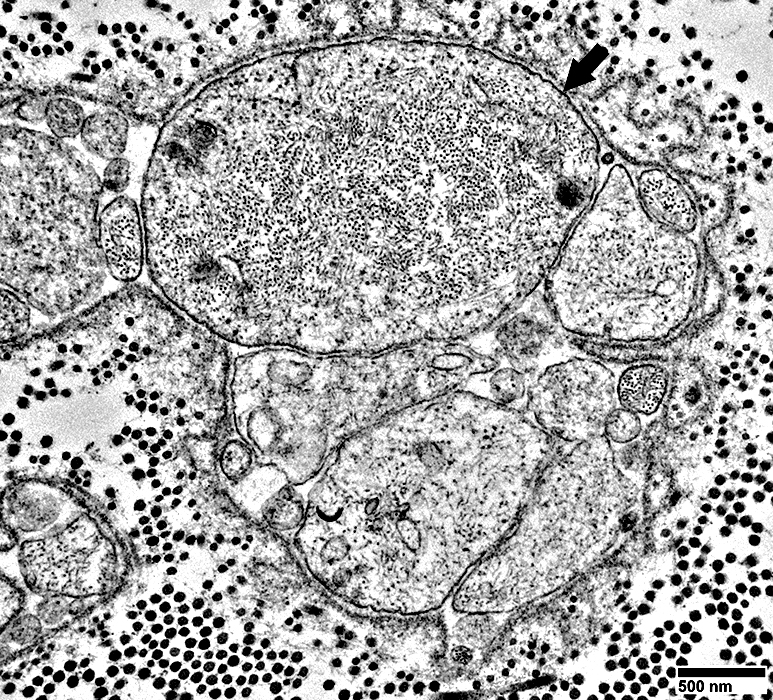 From: R Schmidt |
Associated with multiple Schwann cell processes on one side, but not surrounded by them (Above)
Schwann cell processes, & axon above them, are surrounded by a layer of basal lamina (Above)
Upper region of axon: Is covered by Schwann cell basal lamina but No Schwann cell processes
Small axon: Contains neurofilaments (Below)
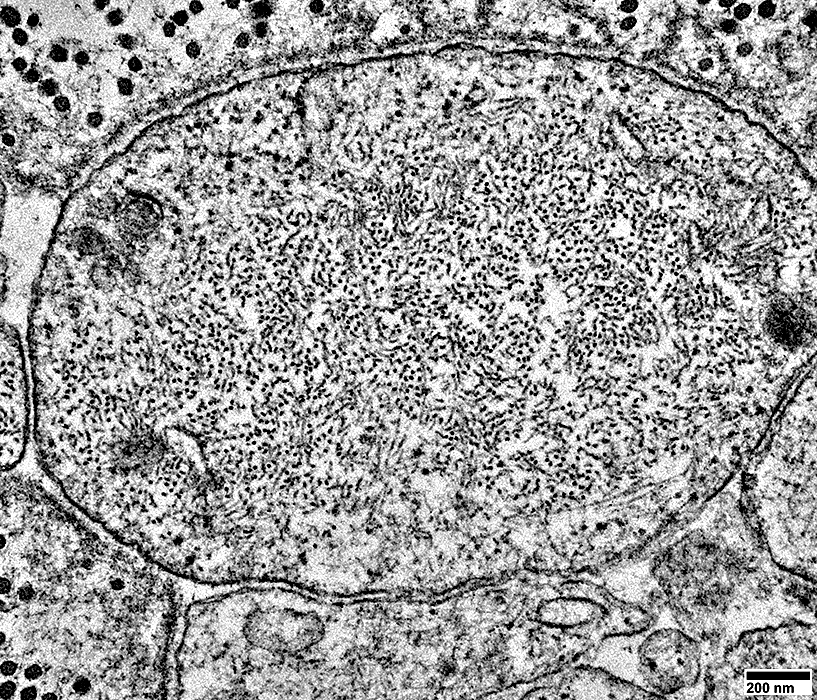 From: R Schmidt |
Abnormal, axon with dark, punctate cytoplasm: Surrounded by several different thick Schwann cell processes
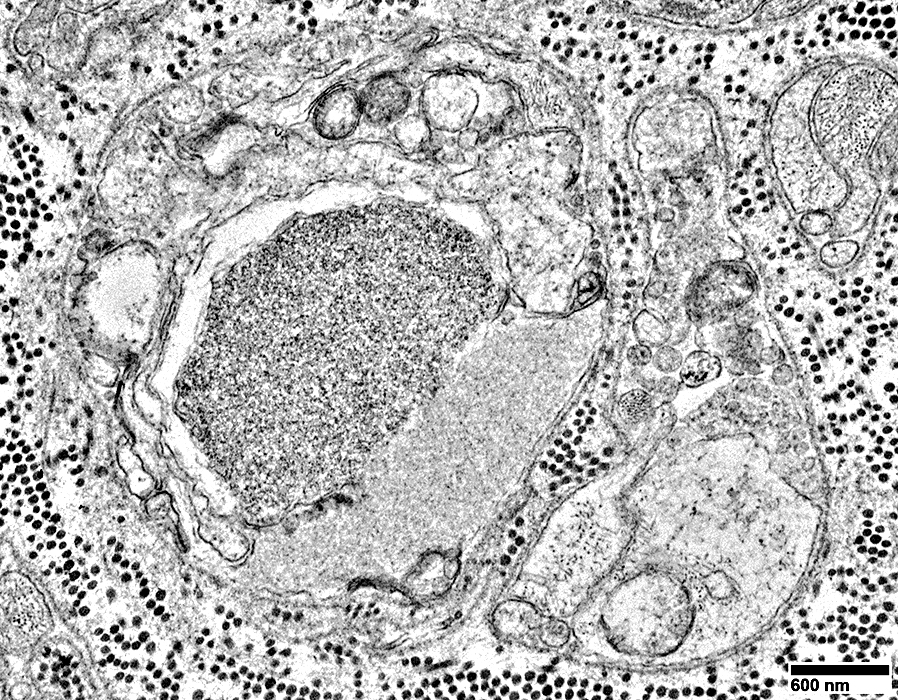 From: R Schmidt |
Contains: Dark tubulo-reticular material
Surrounded by: 3 Different types of Schwann cell processes
No associated myelin
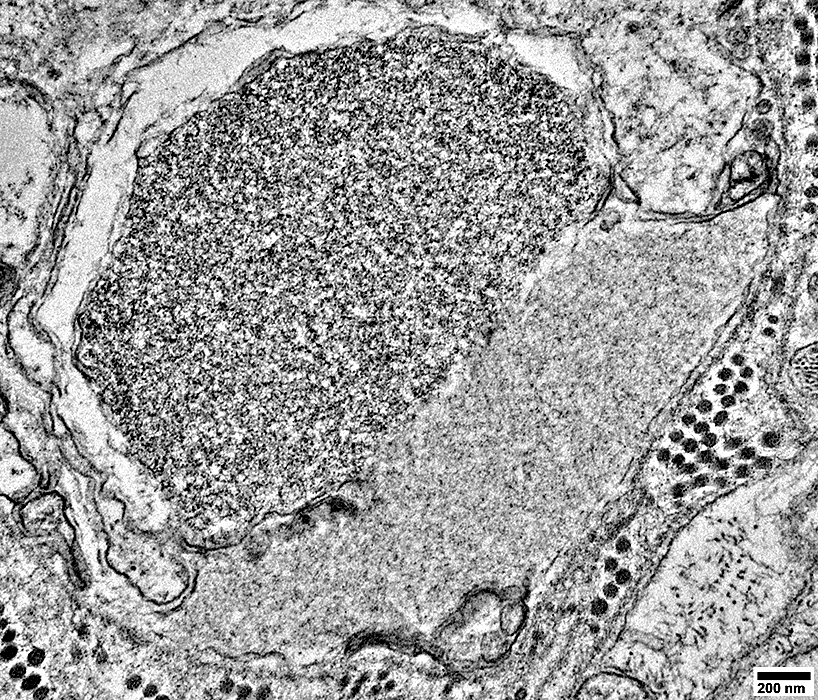 From: R Schmidt |
Axon associated with a few small round Schwann cell processes
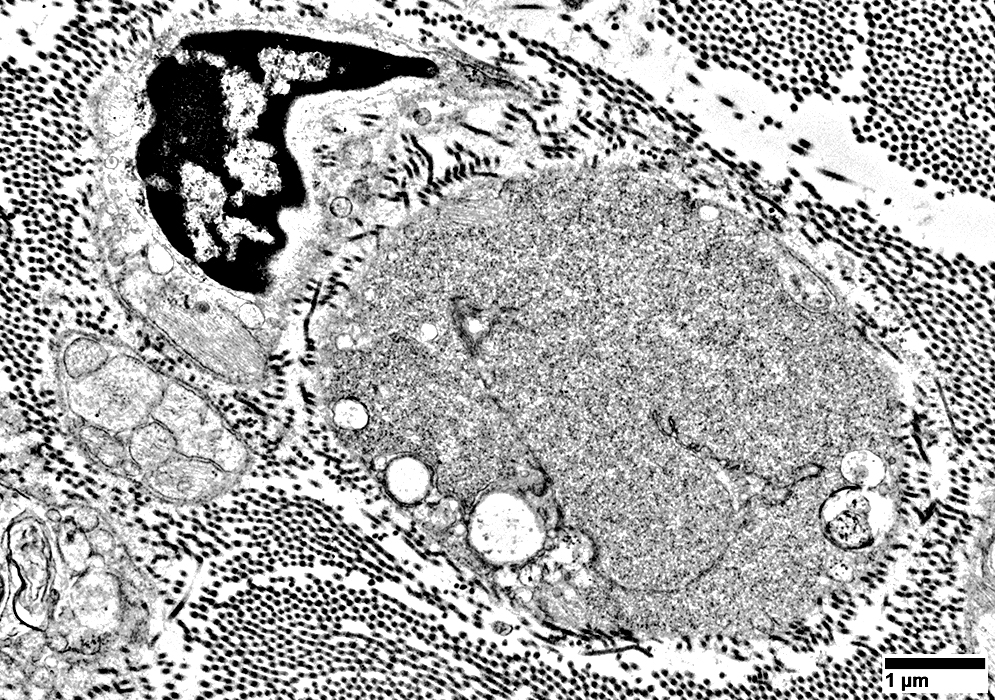 From: R Schmidt |
Associated with a few small, round Schwann cell processes (Above)
No associated myelin
Axon cytoplasm: Contains probable tubuloreticular profiles, but few neurofilaments (Below)
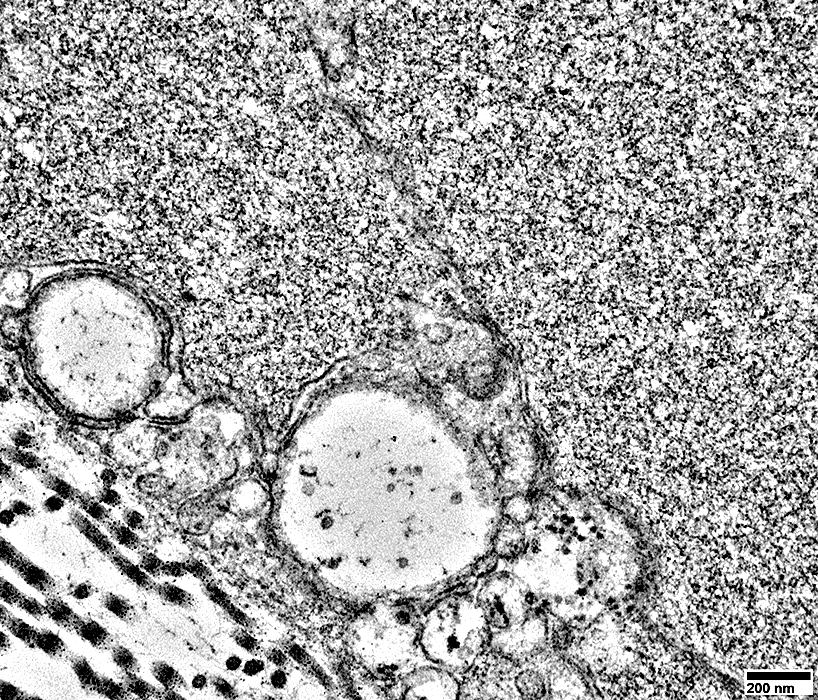 From: R Schmidt |
Axon associated with almost no Schwann cell processes
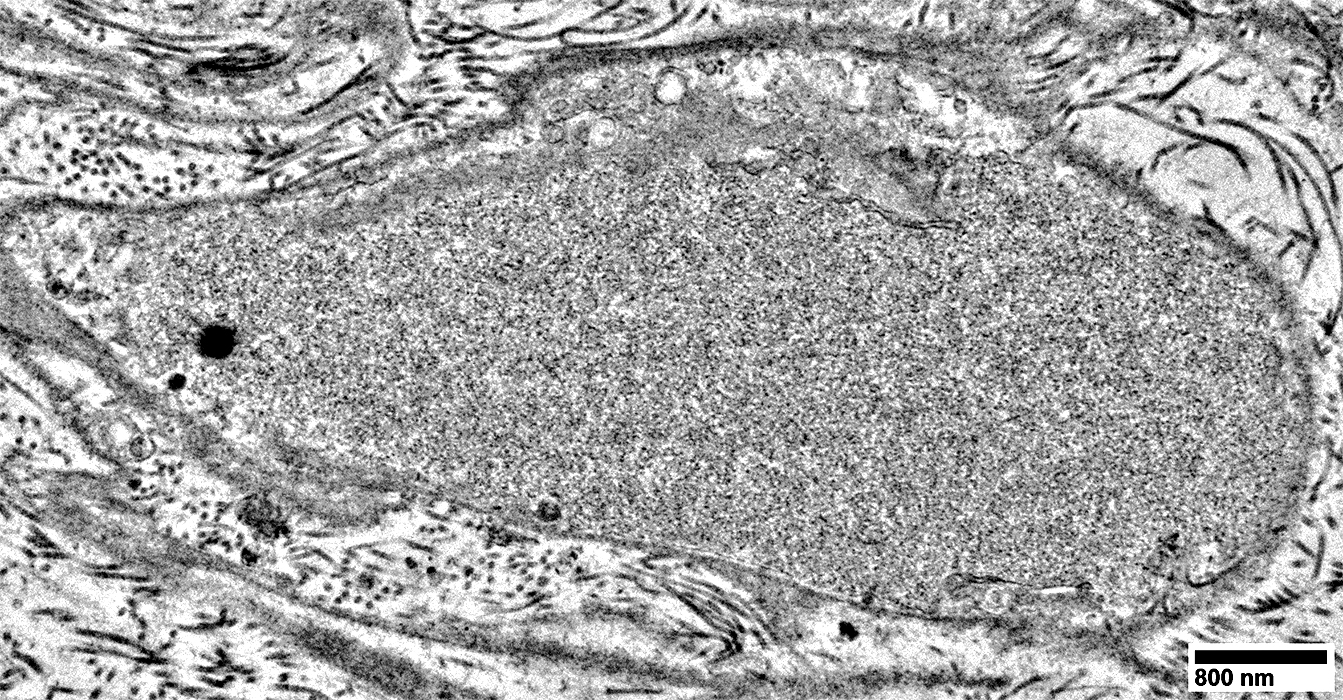 From: R Schmidt |
Associated with few Schwann cell processes (Above)
No associated myelin
Axon cytoplasm: Contains probable tubuloreticular profiles, but few neurofilaments (Below)
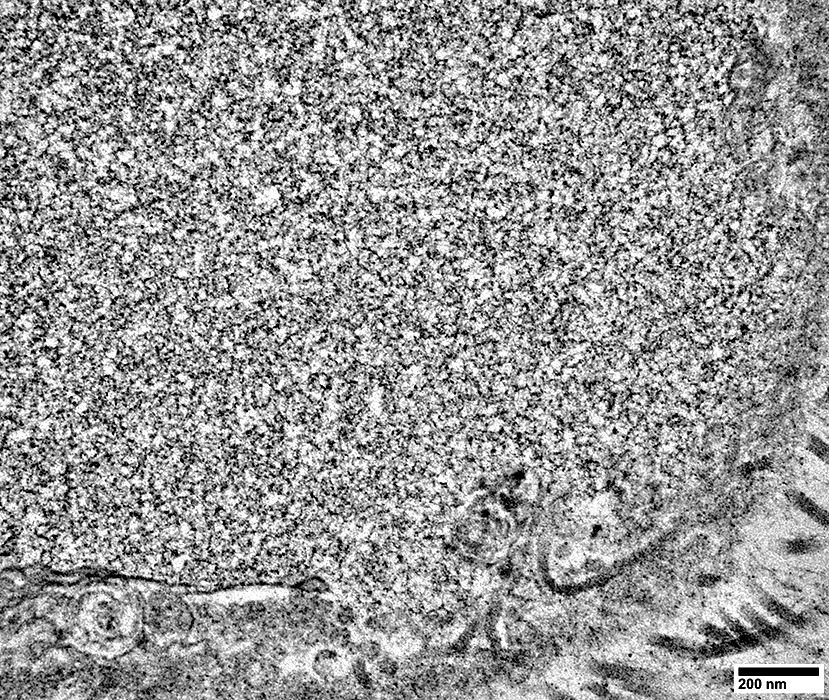 From: R Schmidt |
Denervated Schwann cells with No Büngner band formation
|
Ultrastructure Immunohistochemistry |
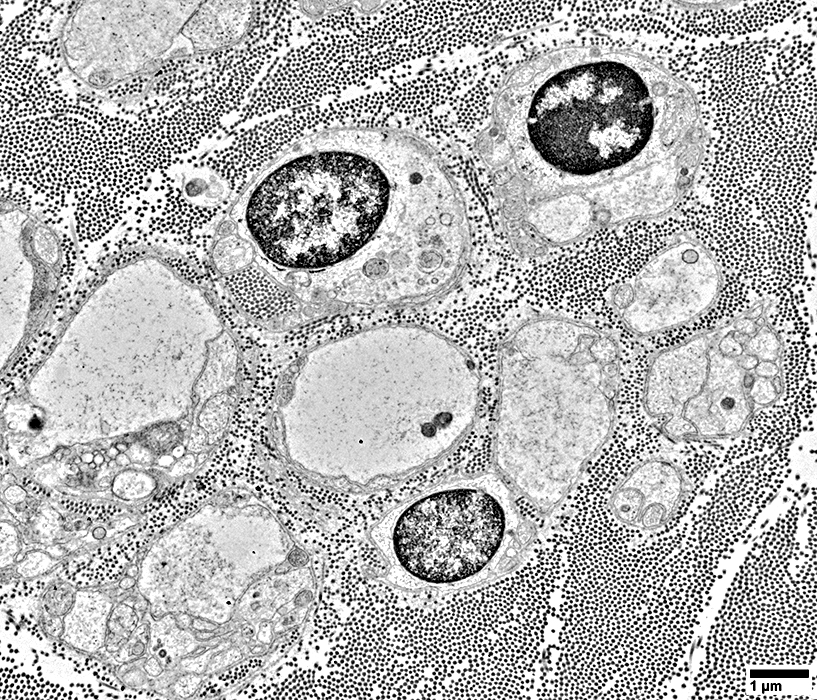 From: R Schmidt |
Associated with marked axon loss
Individual Schwann cells & their processes
Are surrounded by a layer of basal lamina
No associated axons
No Büngner bands (Clusters of multiple Schwann cells & their processes)
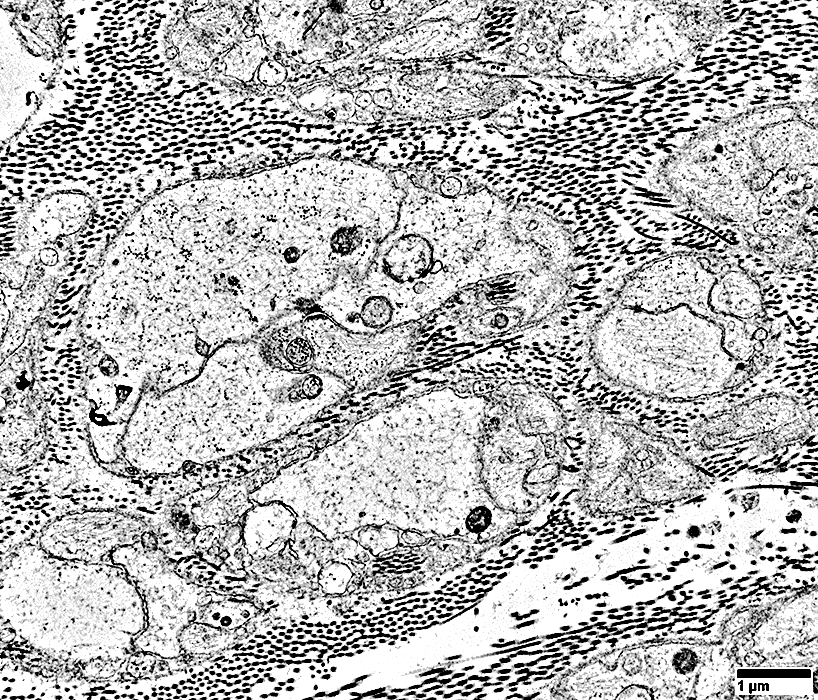 From: R Schmidt |
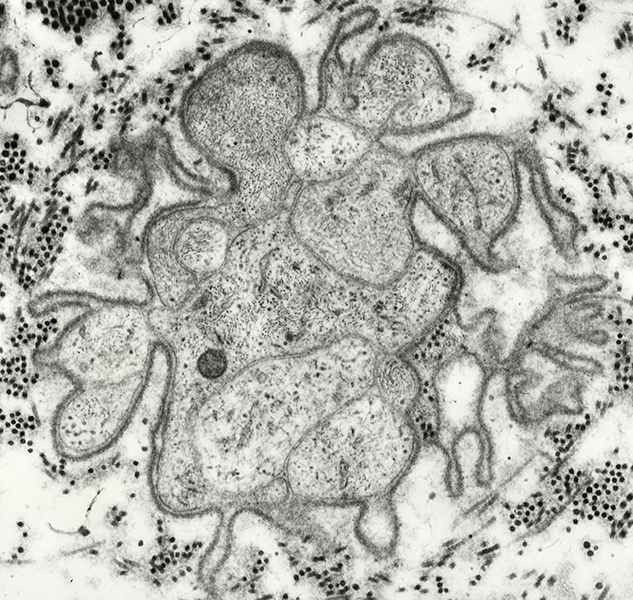 From: R E Schmidt MD |
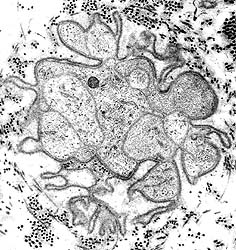
|
Associated with marked axon loss
Individual Schwann cells & their processes
Are surrounded by a layer of basal lamina
No associated axons
No Büngner bands
Clusters of closely spaced processes: Only arise from individual Schwann cells
Typical Büngner bands: Clusters of processes from multiple Schwann cells
Clusters of multiple Schwann cells & their processes)
No Büngner band cells (No cells that contain both NCAM & P0) (Below)
Denervated Schwann cells contain NCAM but not P0
P0 (Red) is only present in myelin around 2 larger axons
See
Control nerve
Nerve with Büngner band cells
Immunohistochemistry
Ultrastructure
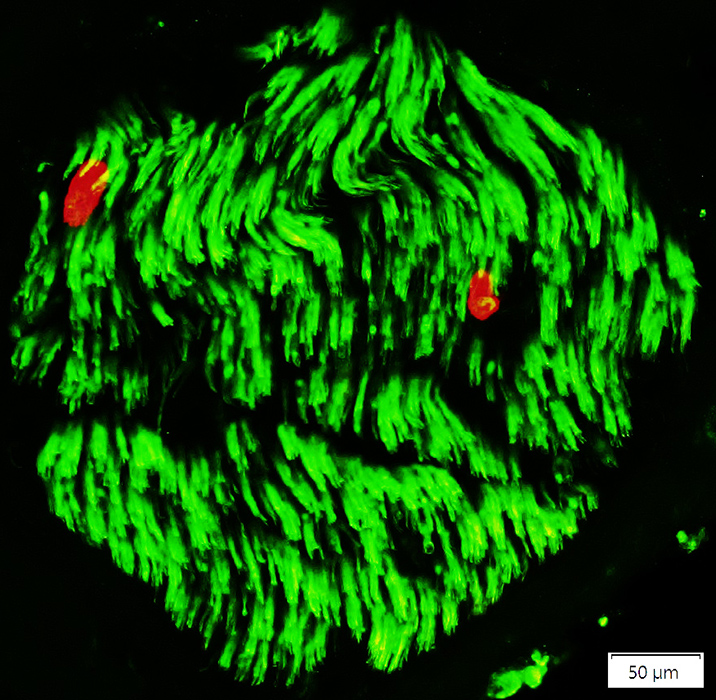 NCAM (Green) + P0 (Red) |
Teased Fibers
TopNormal myelinated axon: Long myelin internodes & Node of Ranvier (Black Arrow) at center
Middle
Axon loss, Chronic: Multiple nuclei along teased fiber comprise Büngner Schwann cell bands
Bottom
Wallerian Degeneration: Fiber contains myelin fragments (Ovoids; Blue Arrow)
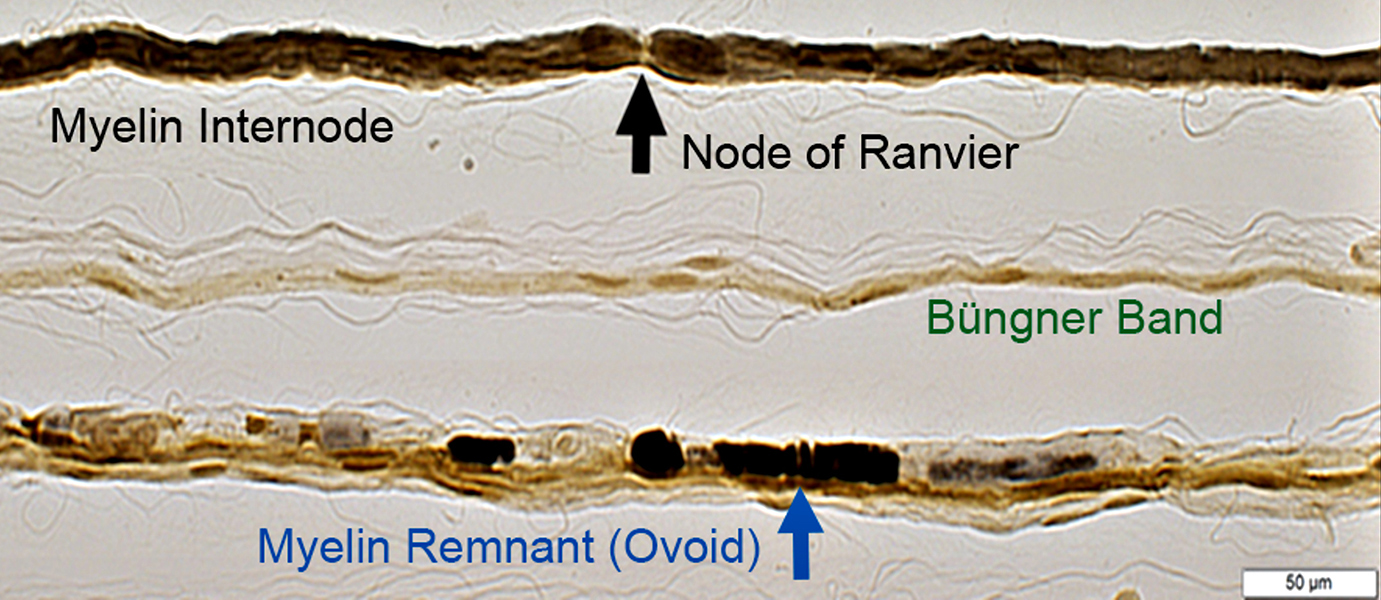
|
Segmental demyelination
Tomaculae
Return to Giant axonal neuropathy
Return to Muscle biopsies
Return to Biopsy illustrations
Return to Neuromuscular home page
Return to Polyneuropathy Index
5/25/2025