SQSTM1: Distal Myopathy - Digenic - Welander Phenotype
Mutations: SQSTM1 c.1165 G>A; TIA1 N357S|
Myopathy Internal Architecture Vacuoles Aggregates Other |
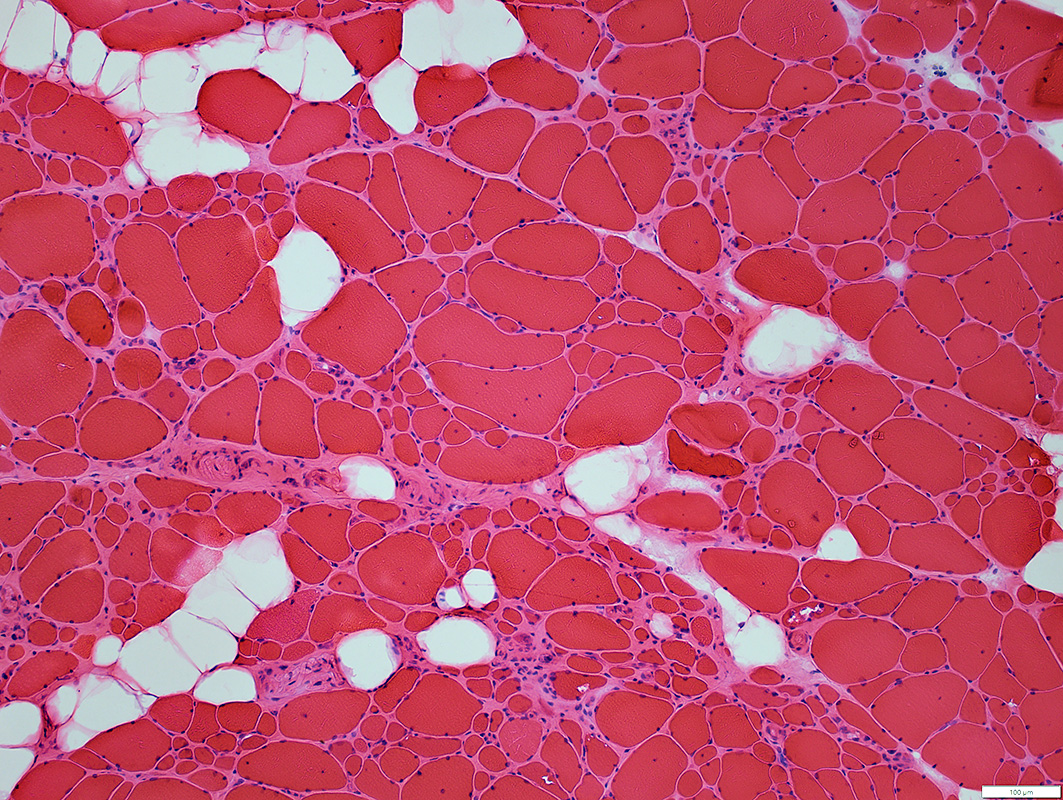
H&E stain |
Fiber sizes
Varied from Small to Hypertrophic
Small fibers: clustered
Pyknotic nuclear clumps
Perimysium & Endomysium: Replaced by fat
No necrosis or regeneration
Vacuoles: In some smaller muscle fibers
Chronic myopathy, Late stage
Perimysium: Wide; Replaced by fat
No necrosis or regeneration
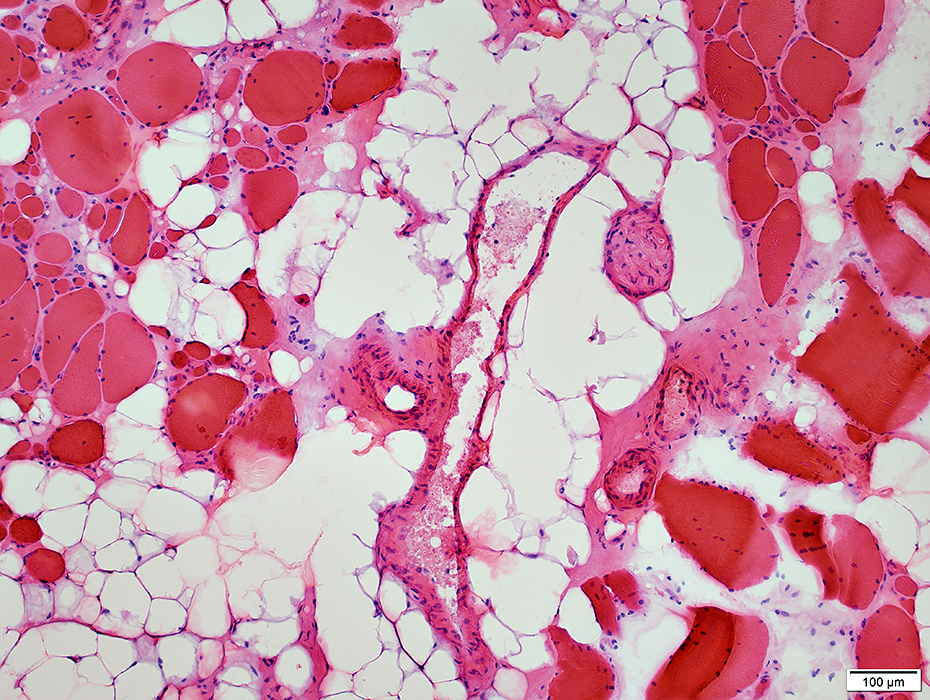 H&E stain |
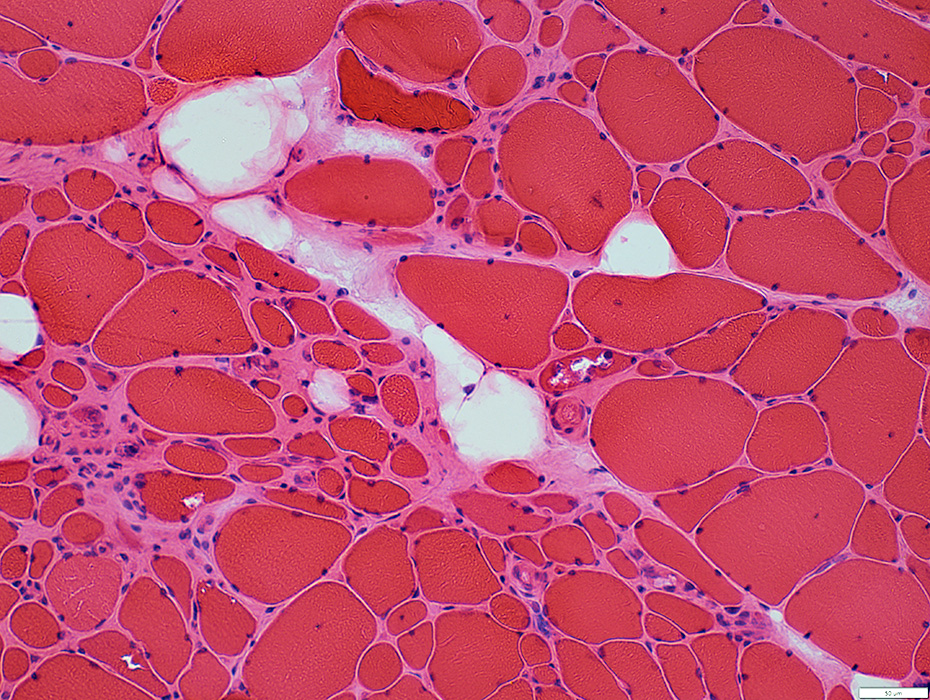 H&E stain |
May occur in clusters or groups
Some have
Basophilic cytoplasm & large nuclei
Vacuoles
Endomysial connective tissue
Increased between muscle fibers
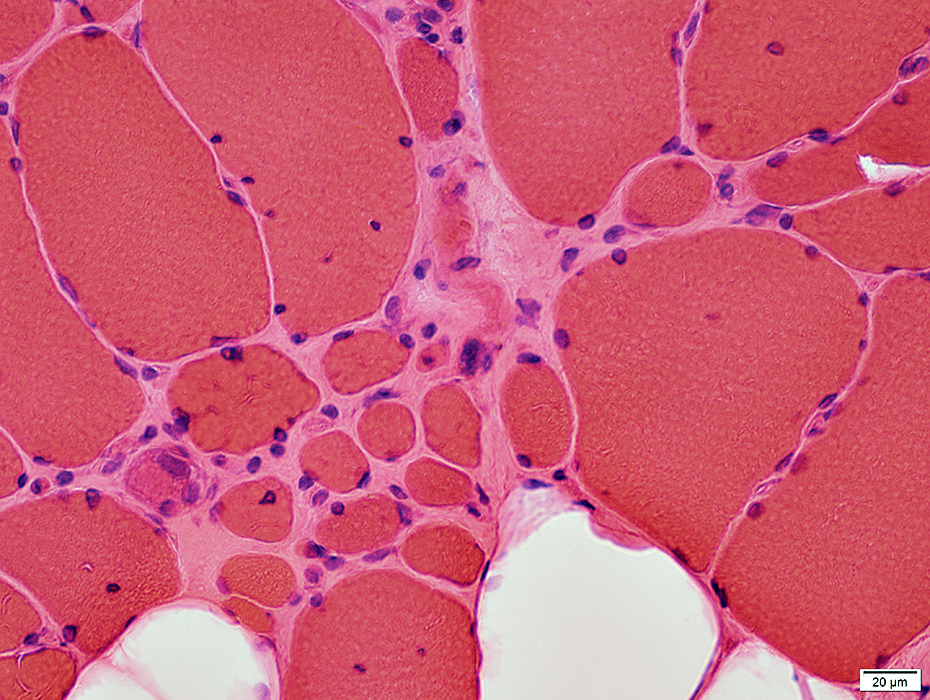 H&E stain |
Internal Architecture
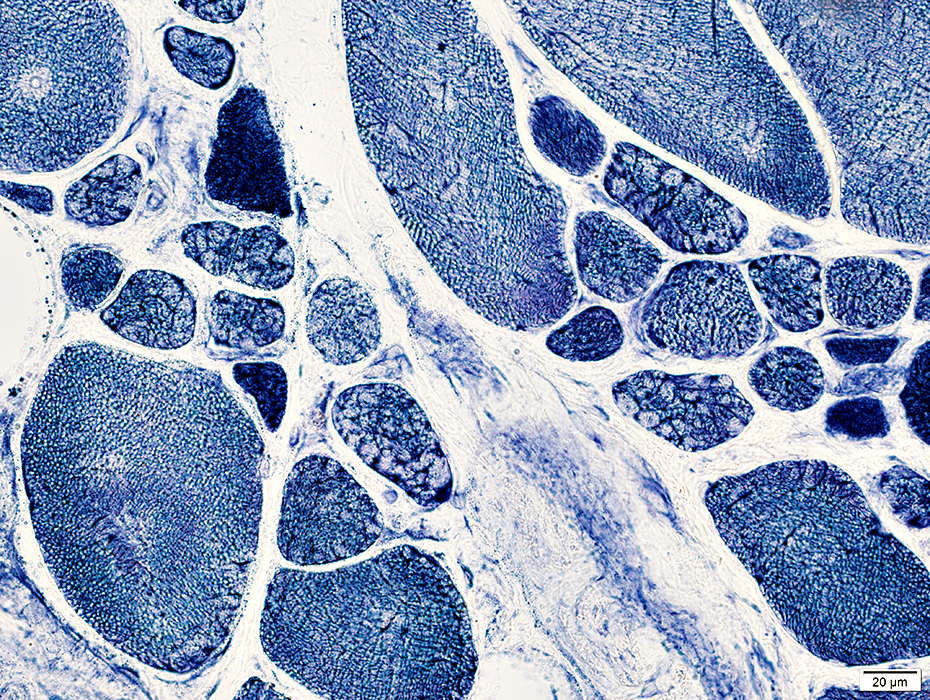 NADH stain |
May occur in clusters or groups
Irregular internal architecture or Dark staining
Endomysial connective tissue
Increased between muscle fibers
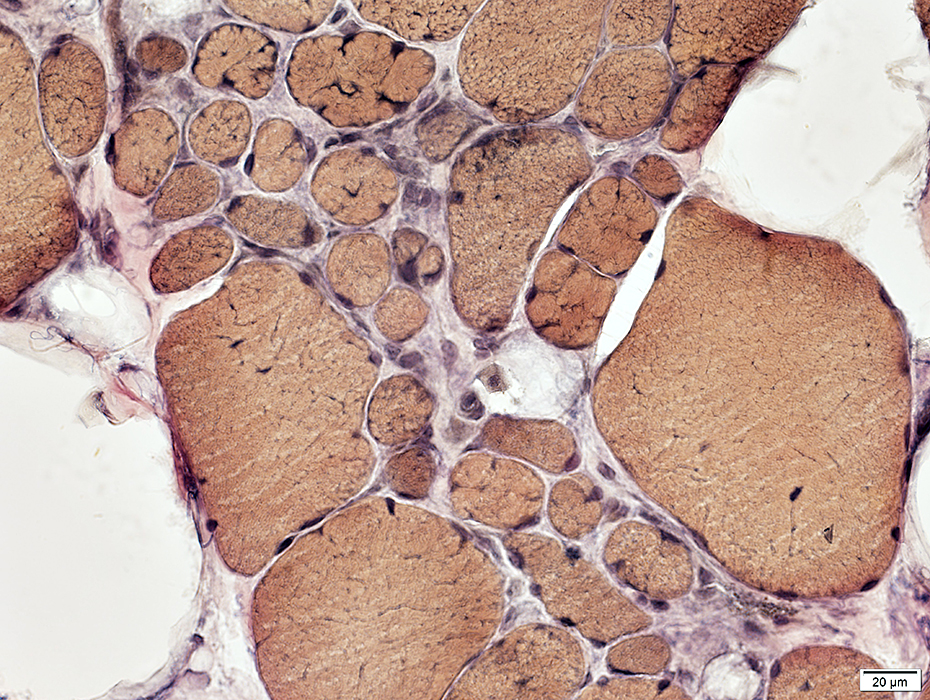 VvG stain |
Internal architecture
Irregular esterase-stained cytoplasm in scattered muscle fibers
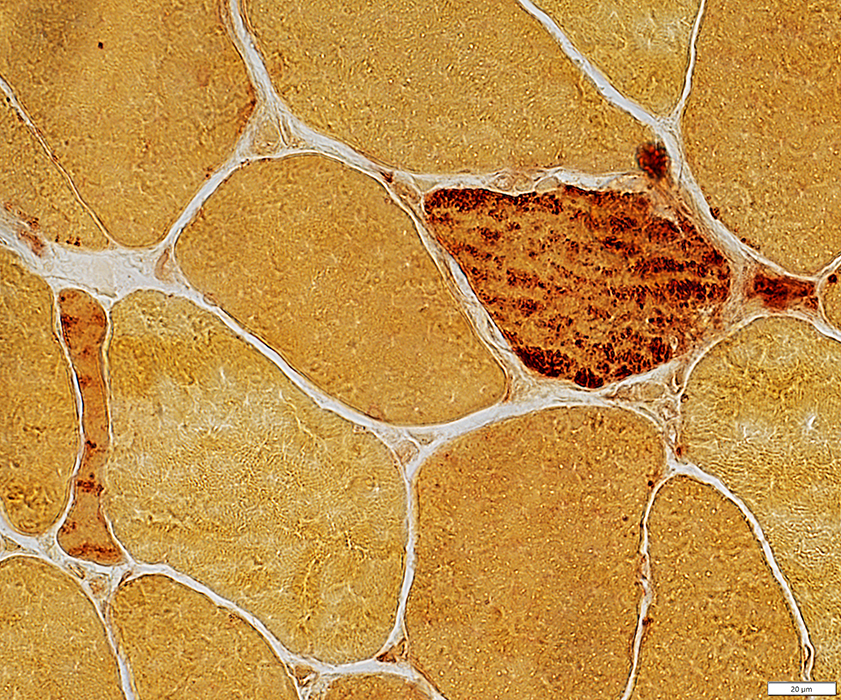 Esterase stain |
Vacuoles
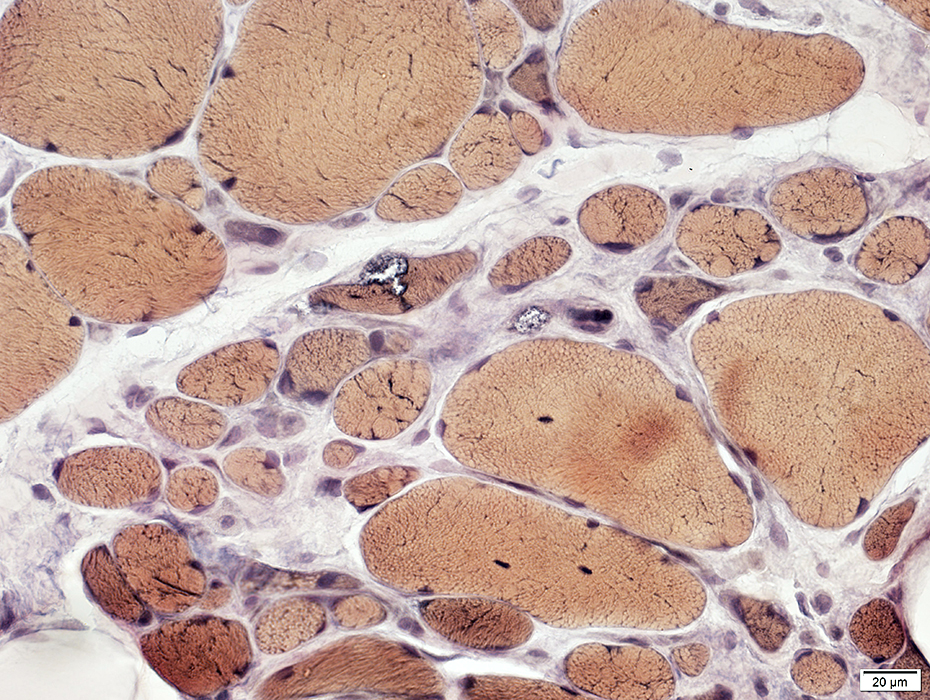 VvG stain |
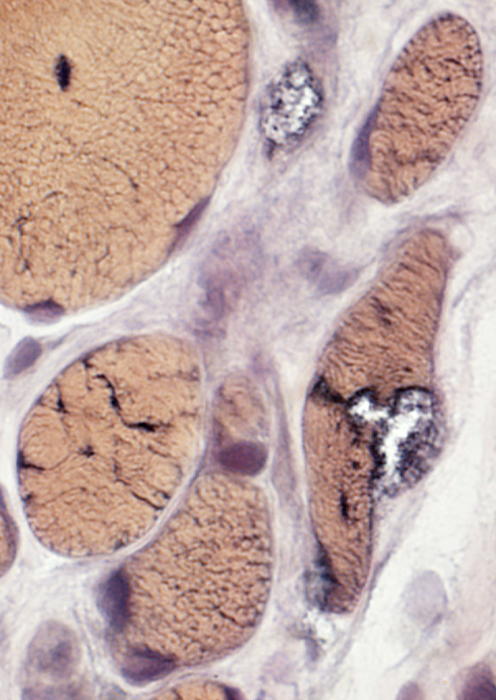 VvG stain |
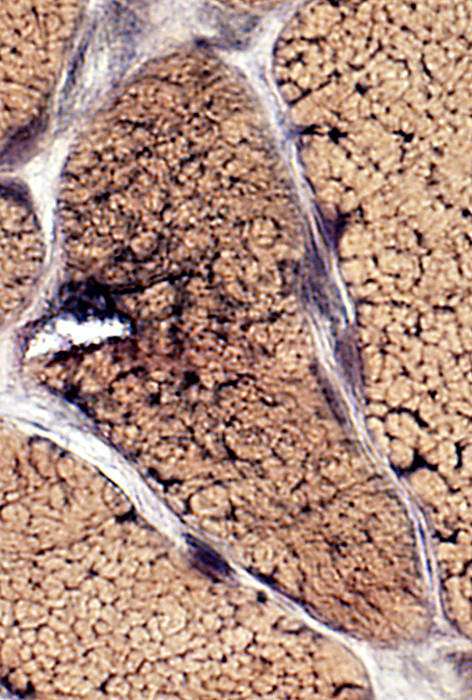 VvG stain |
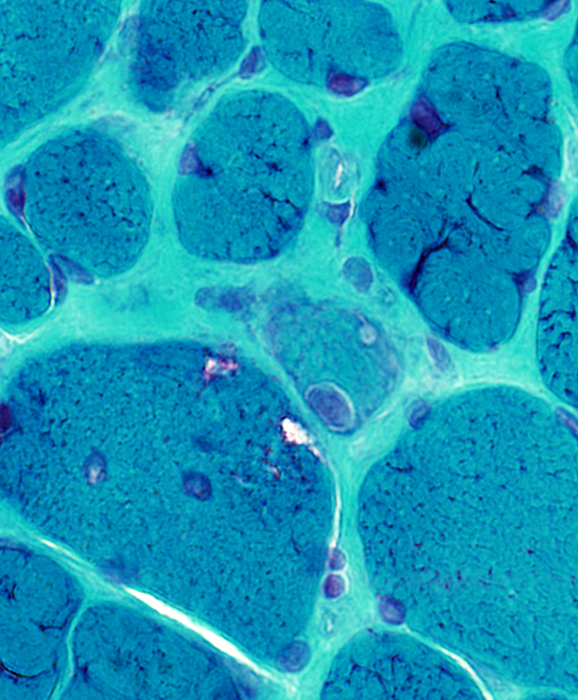 Gomori trichrome stain |
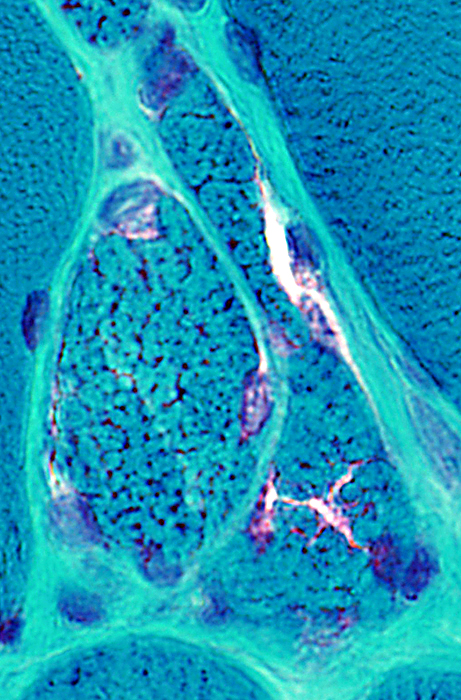 Gomori trichrome stain |
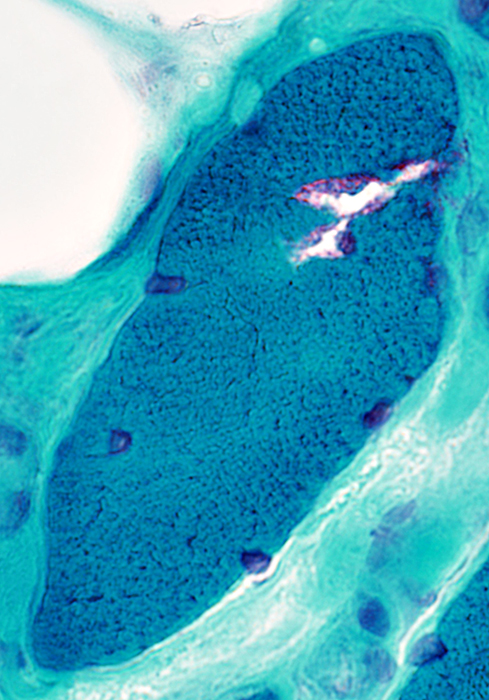 Gomori trichrome stain |
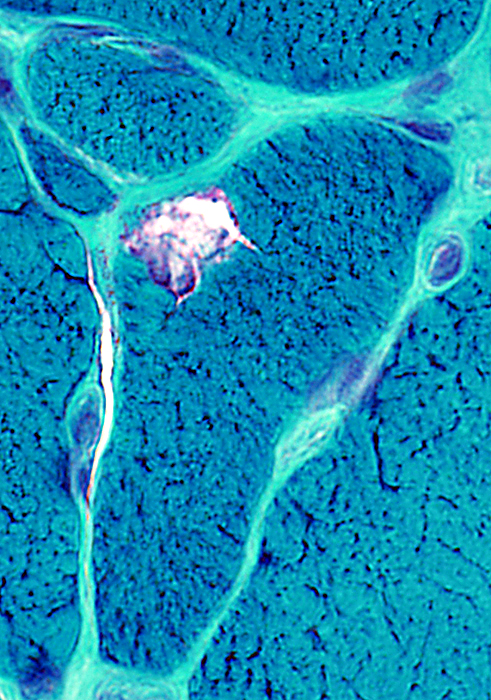 Gomori trichrome stain |
Vacuoles
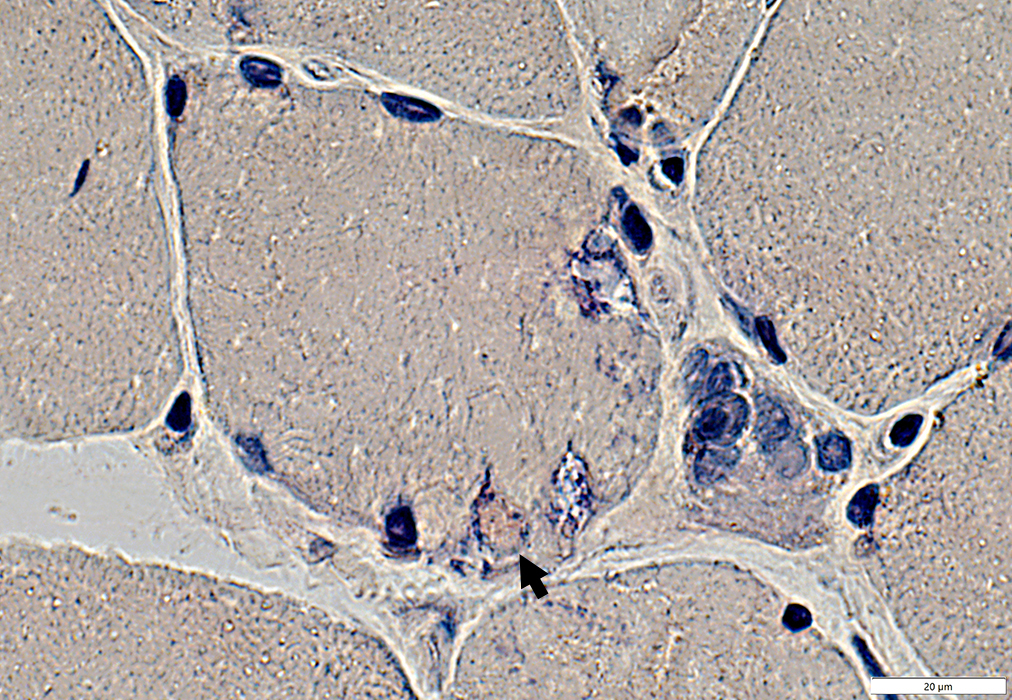
Red staining material (Amyloid-like; Arrow) around edge of vacuoles
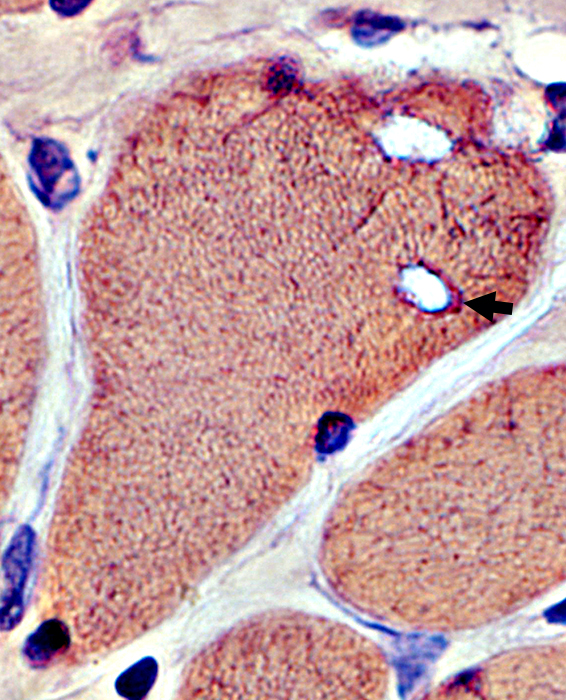 Congo red stain |
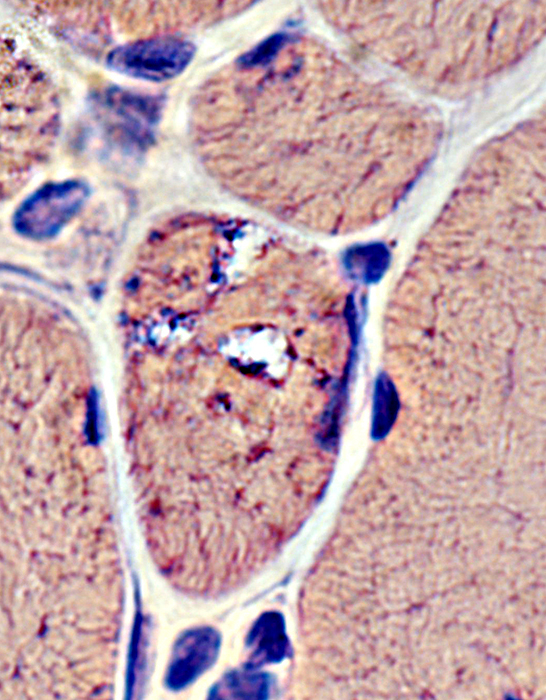 Congo red stain |
Vacuoles & Aggregates
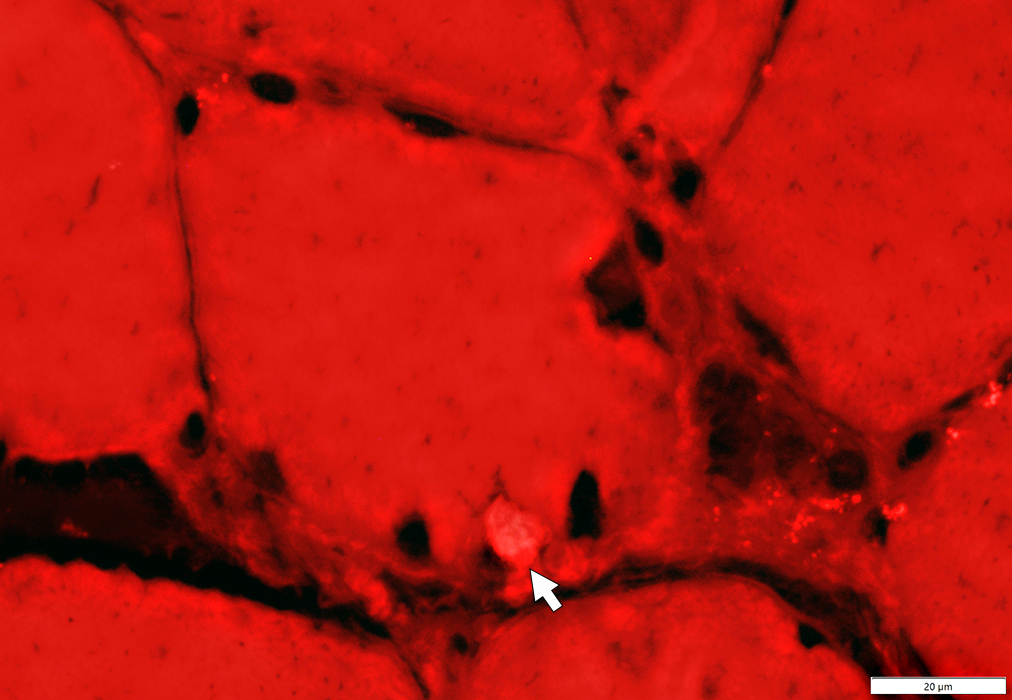
 Congo red stain |
 Congo red stain |
Nuclei: Aggregates & Vacuoles
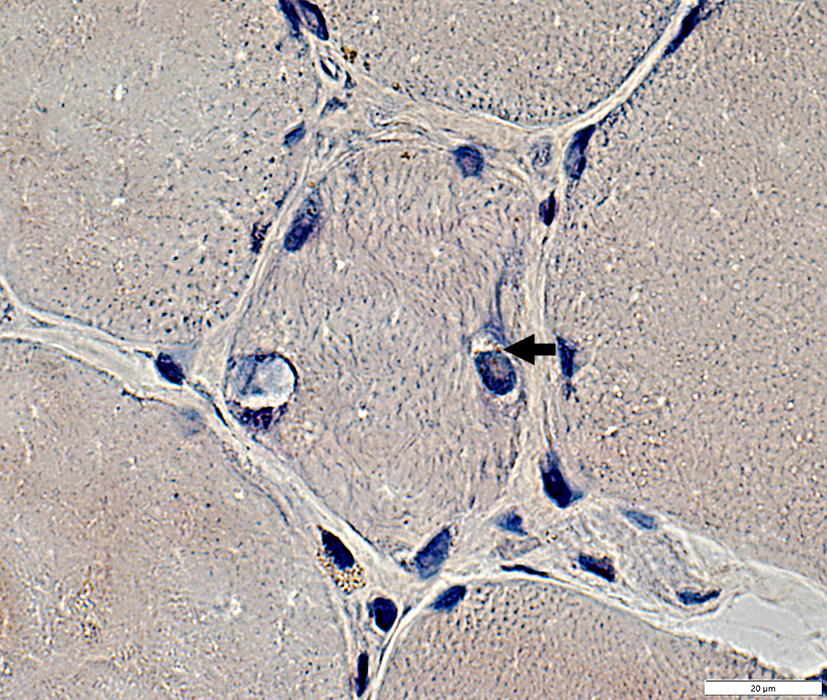 Congo red stain |
Congo red: Red-Green, birefringent (Above)
Rhodamine positive (Below)
Cytoplasmic
Rhodamine-positive irregular aggregate surrounds large nucleus on left side of fiber
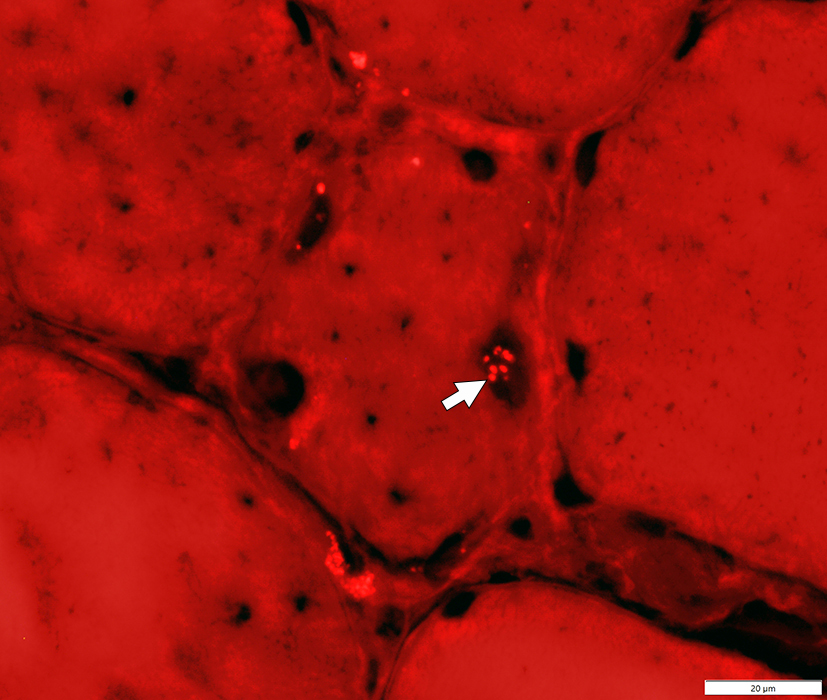 Congo red stain |
Aggregates
AMPDA granules at edge of vacuole & in fiber cytoplasm
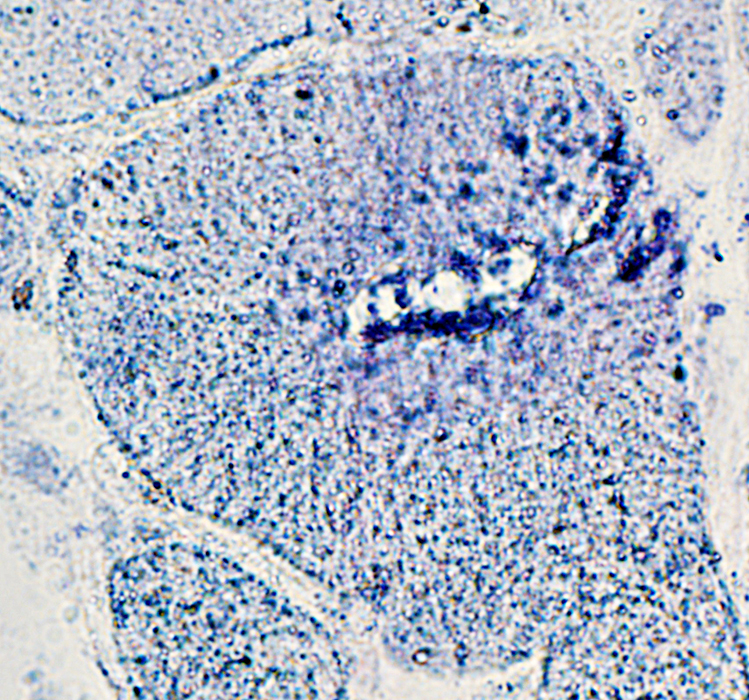 AMPDA stain |
Fiber types
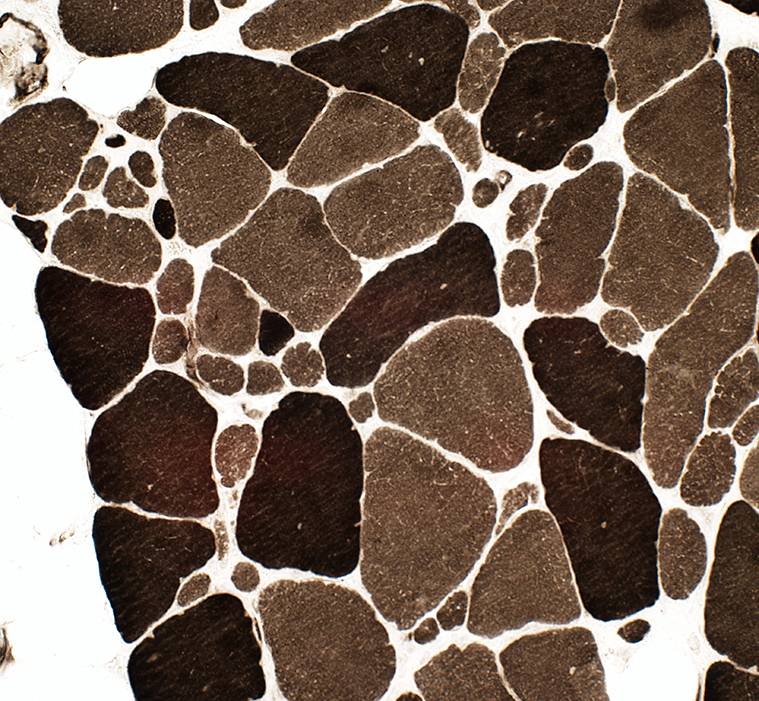 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
Intermediate-stained muscle fibers at ATPase pH 4.3
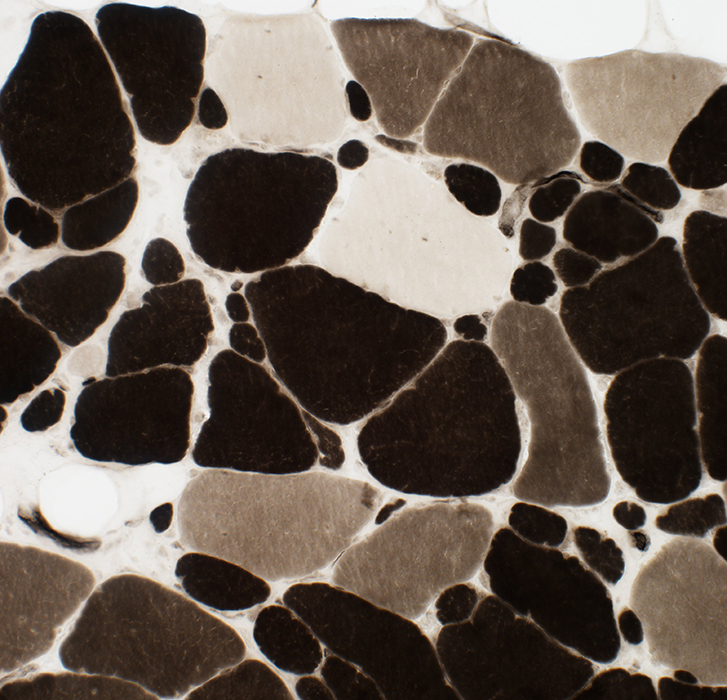 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
MHC Class I: Upregulated on muscle fiber surface
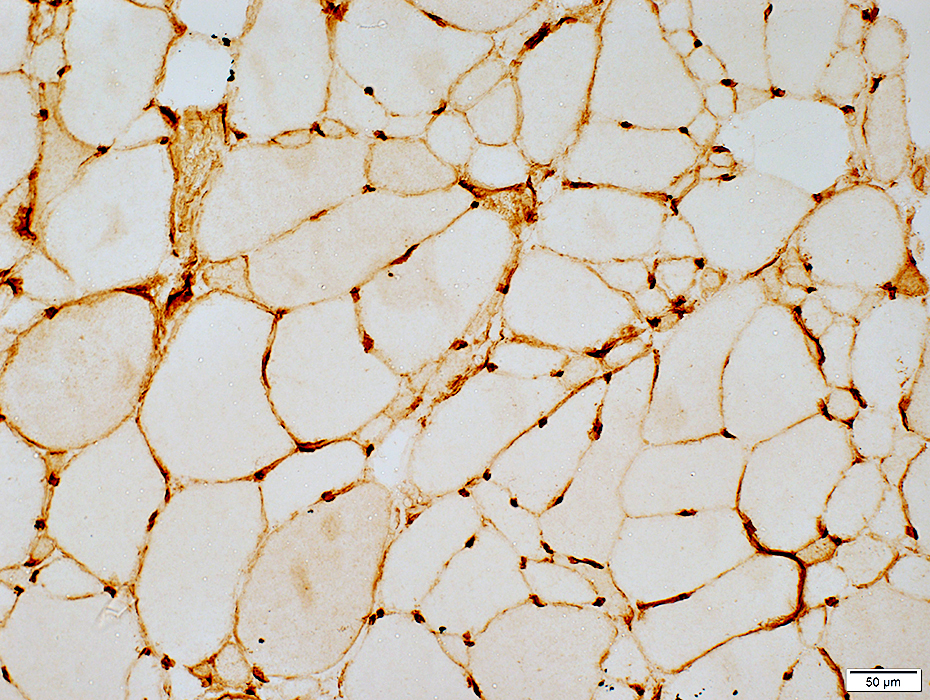 MHC Class I stain |
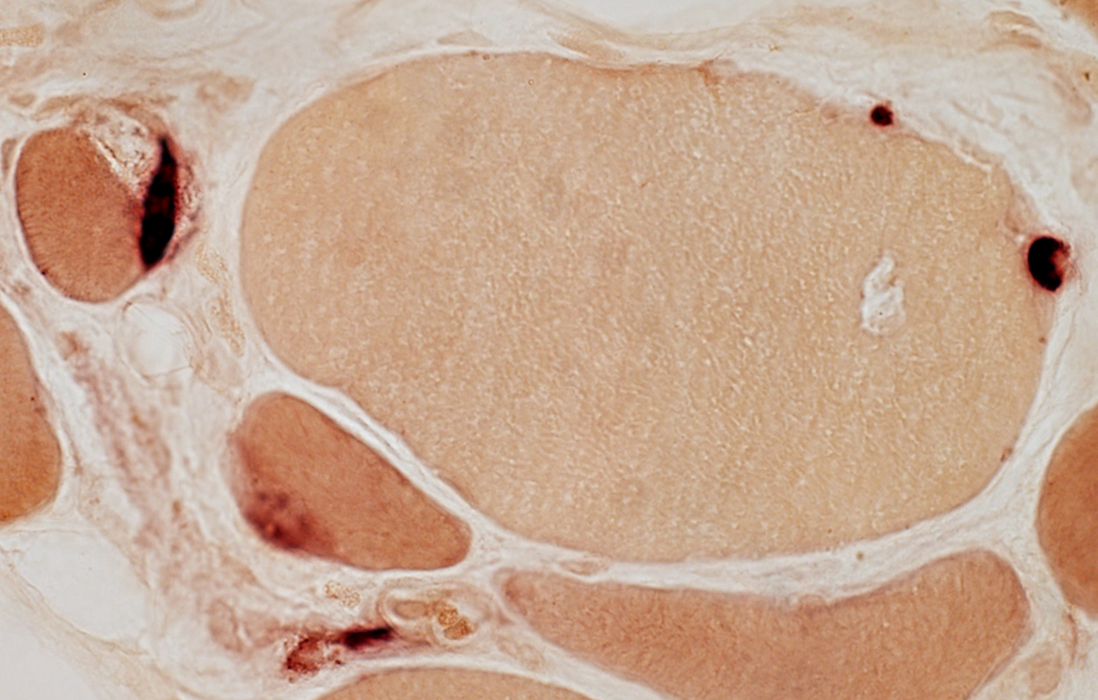 Esterase stain |
Most appear normal
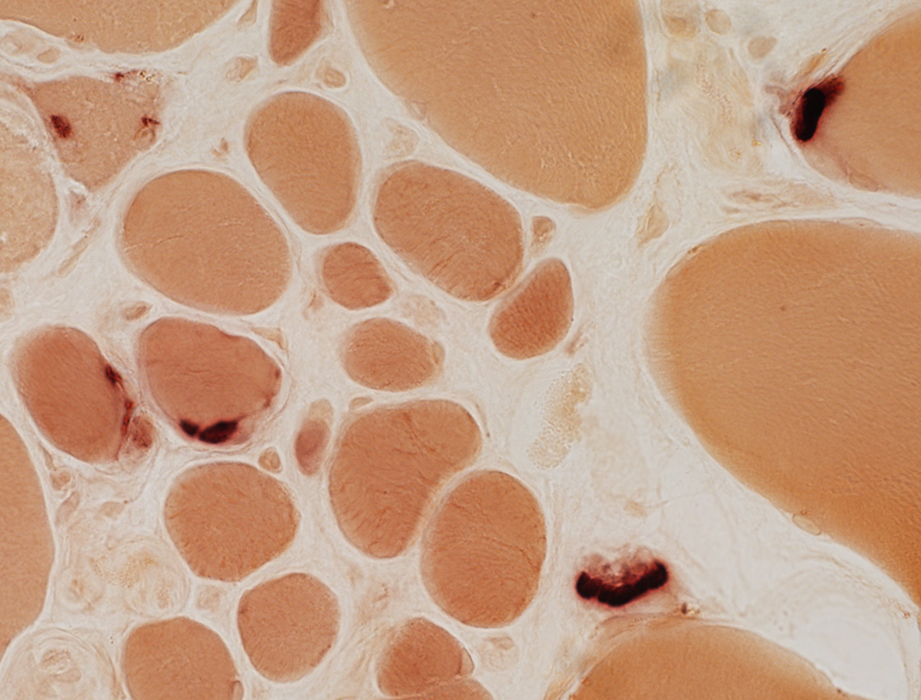 Esterase stain |
Return to Distal myopathy
Return to SQSTM1 myopathy
Return to Muscle biopsies
Return to Biopsy illustrations
Return to Neuromuscular home page
6/4/2024