Hereditary Inclusion Body Myopathy: Type 2
|
Myopathy Early Late Vacuoles Granules Internal architecture Small fibers |
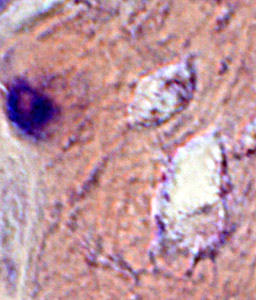 Congo red stain |
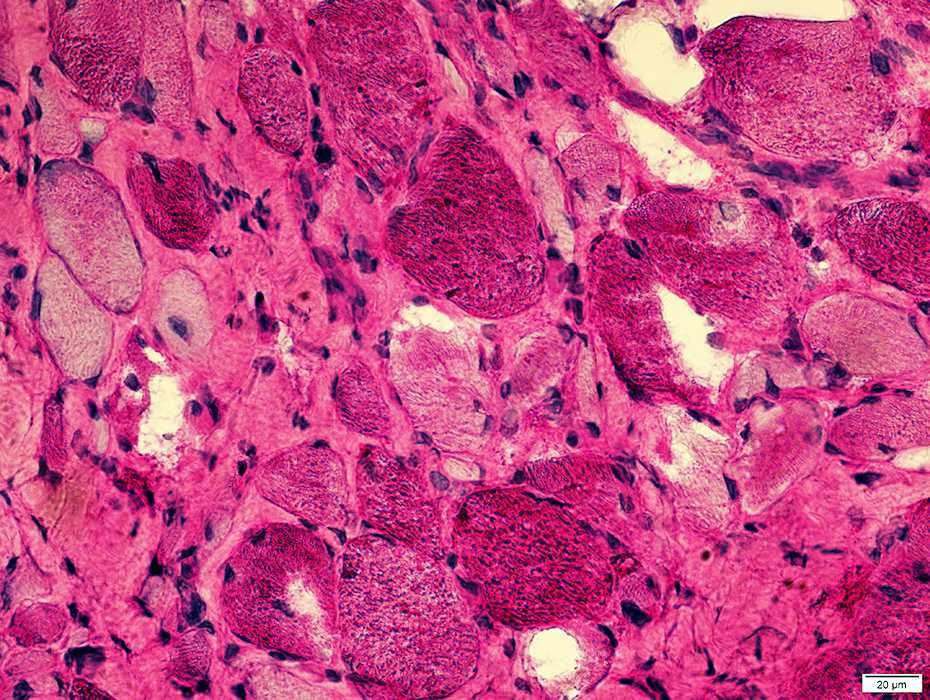
Muscle: General features
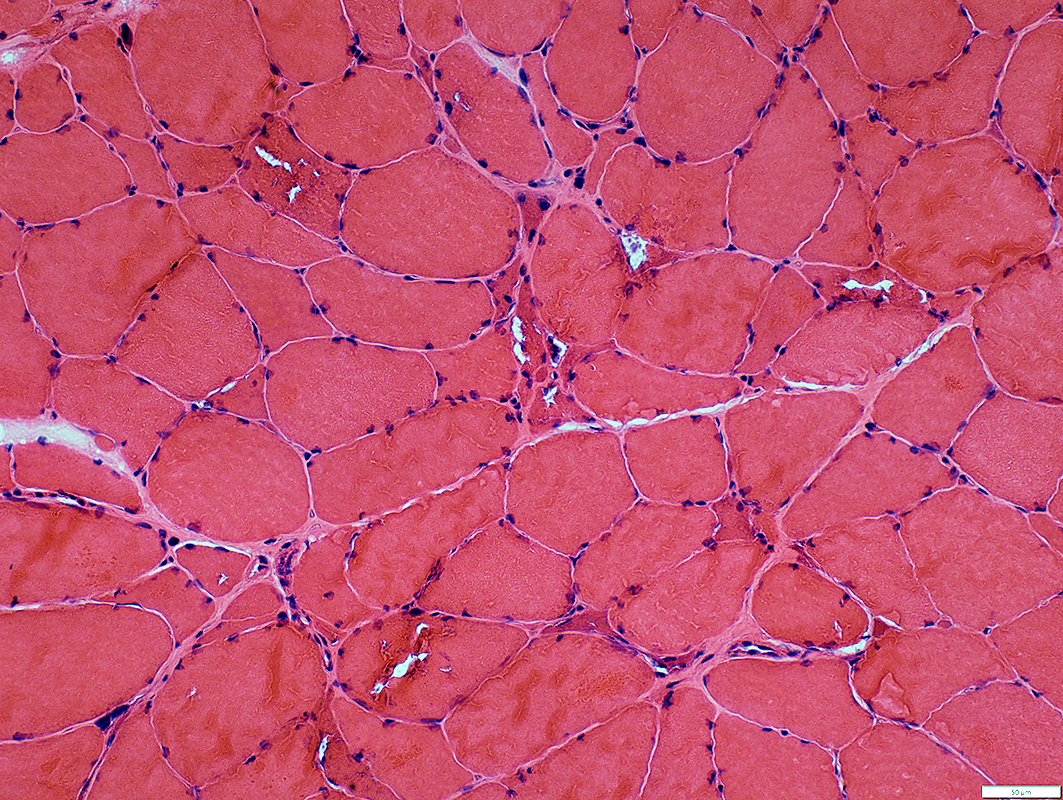 H&E stain |
Muscle fiber size: Varied
Smaller fibers: May be angular clustered
Endomysial connective tissue:
Not prominently increased
Vacuoles: Irregular shapes
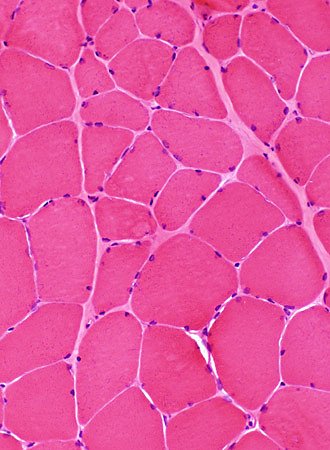 H&E stain Myopathic features Muscle fiber size: Varied Smaller fibers: May be clustered Endomysial connective tissue: Not prominently increased |
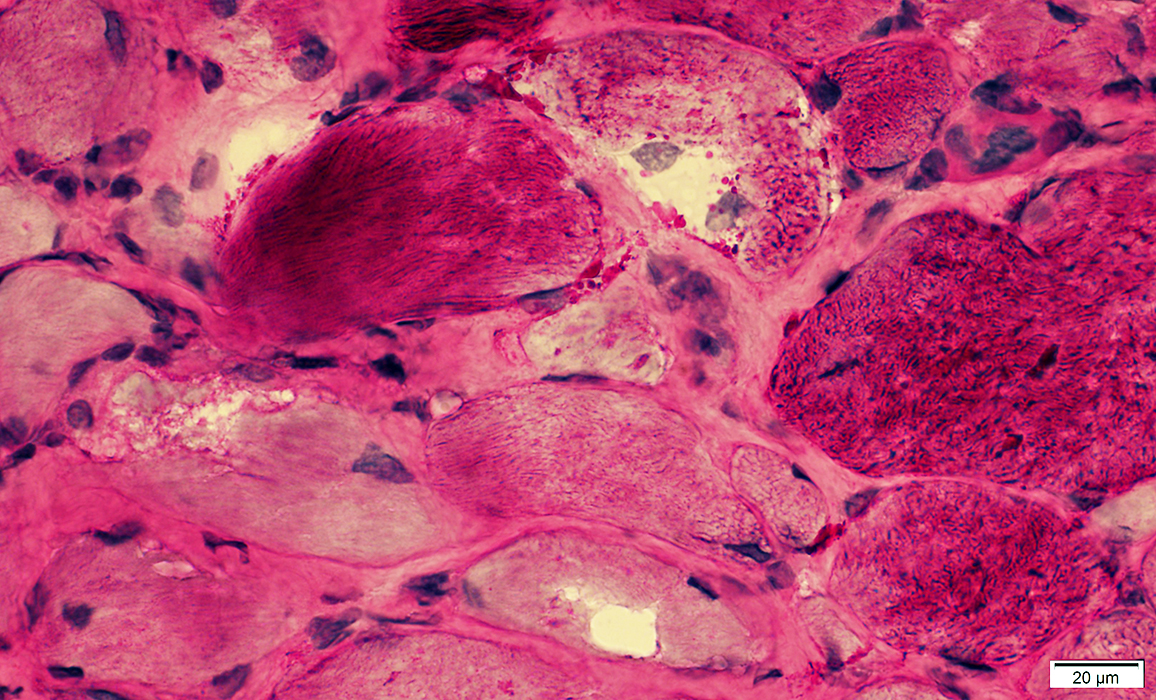
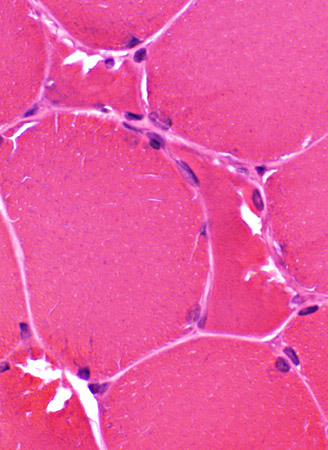 H&E stain Vacuoles In Small, polygonal muscle fibers |
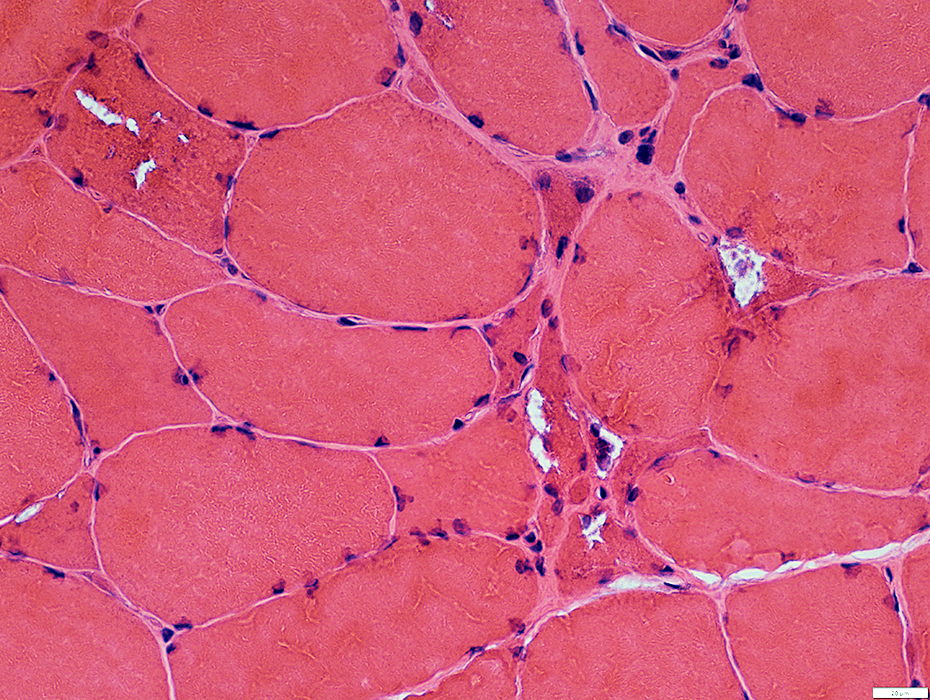 H&E stain |
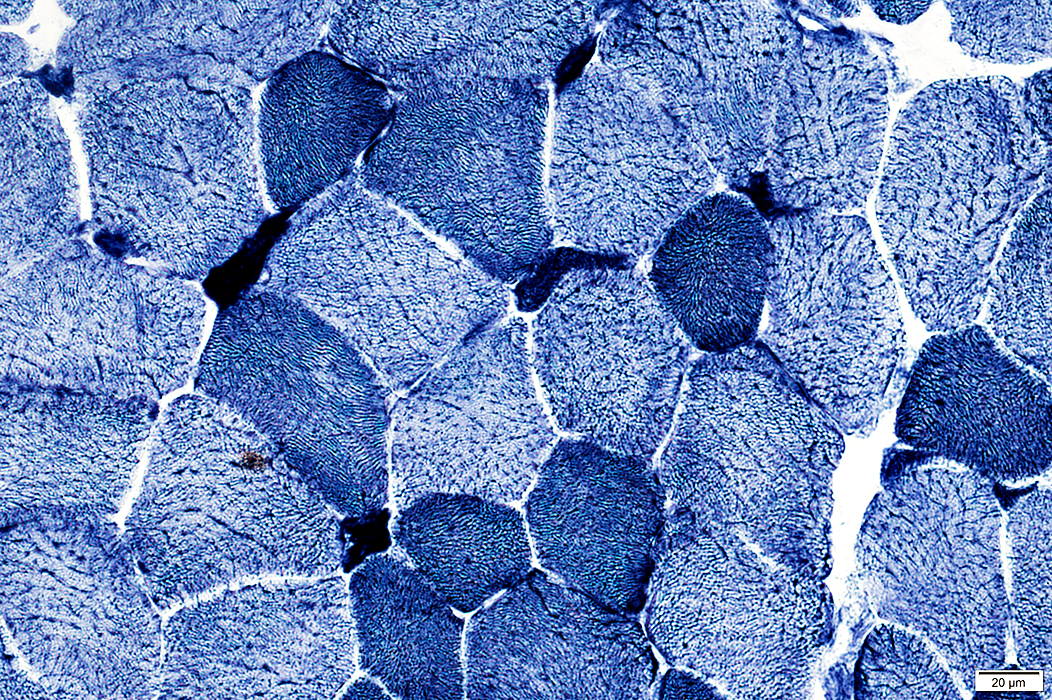
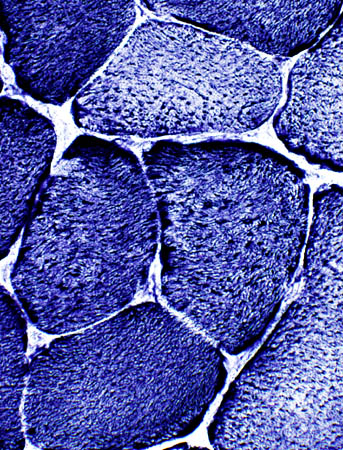 NADH stain Scattered muscle fibers with coarse internal architecture or dark staining |
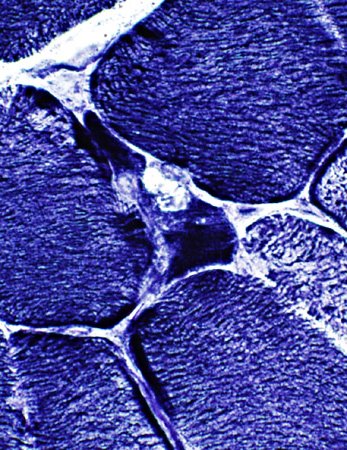 NADH stain |
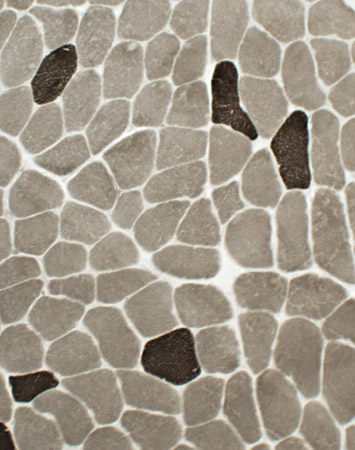 ATPase pH 9.4 stain Type 1 muscle fiber predominance |
Vacuolated muscle fibers
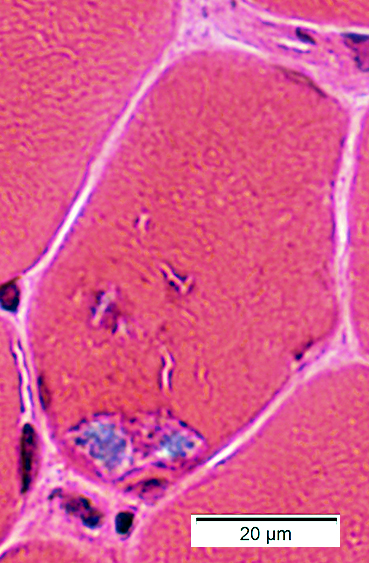 H&E stain |
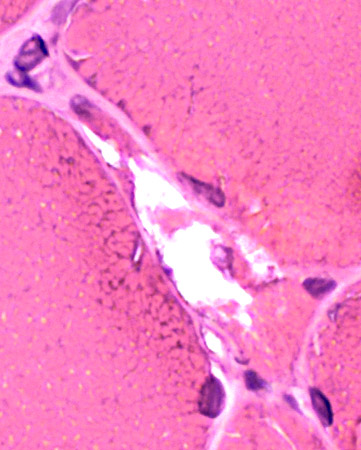 H&E stain |
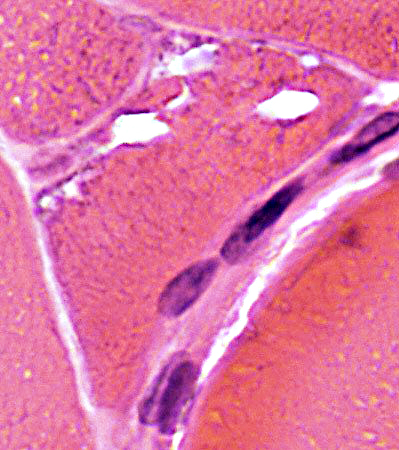 H&E stain |
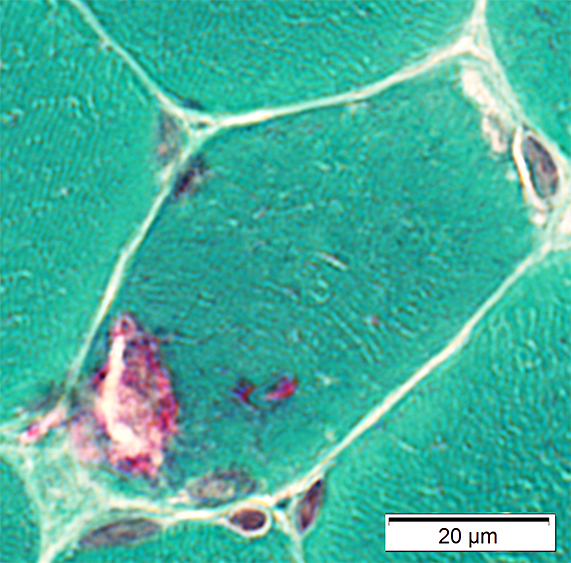 Gomori trichrome stain |
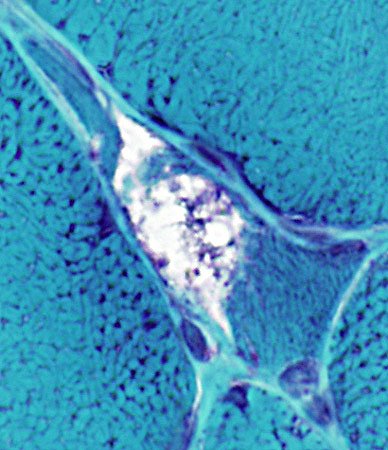 Gomori trichrome stain |
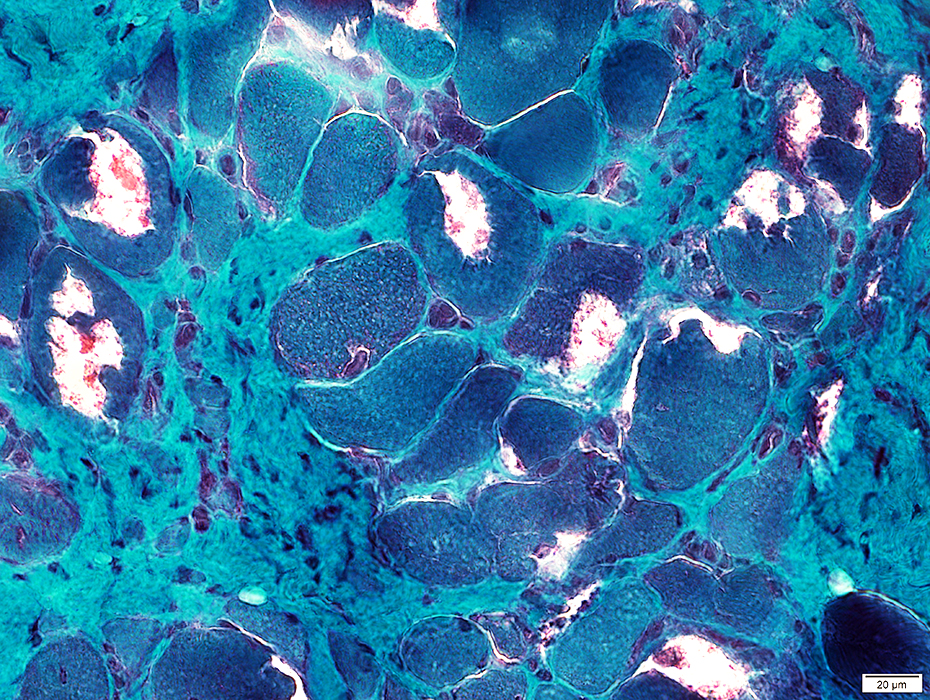
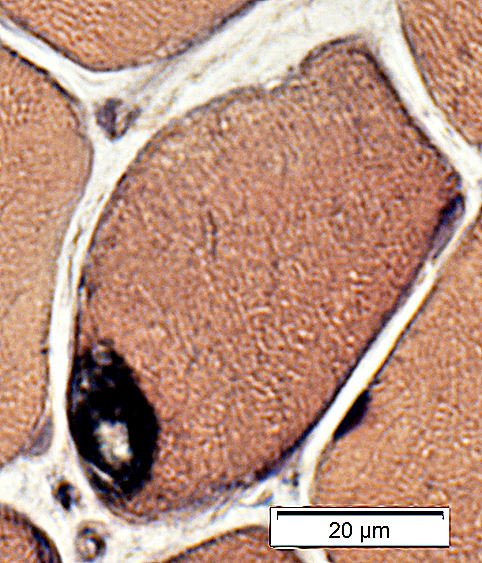 VvG stain |
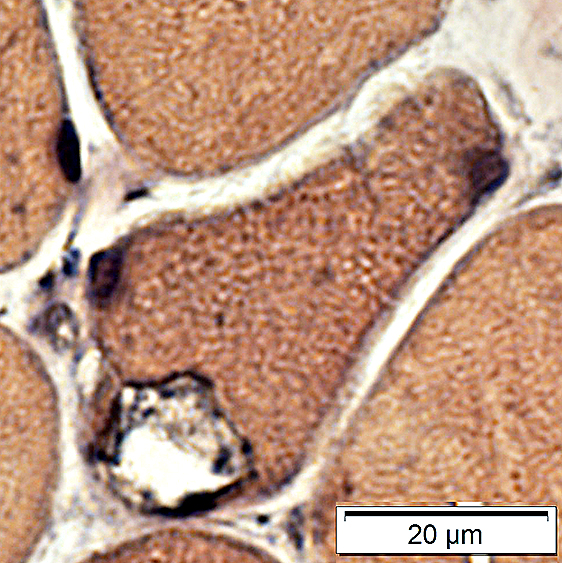 VvG stain |
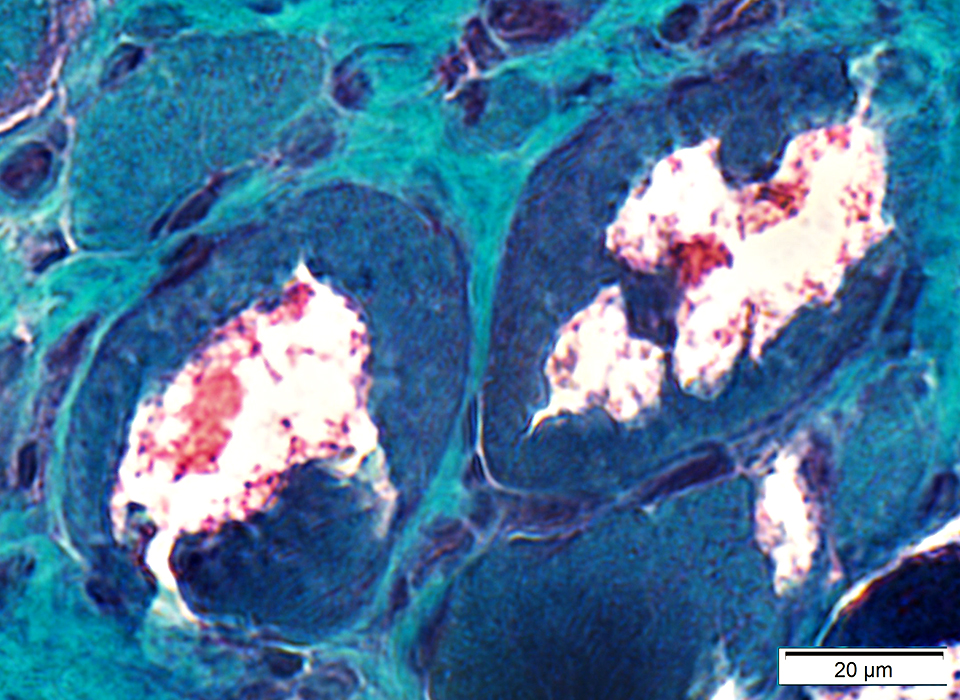
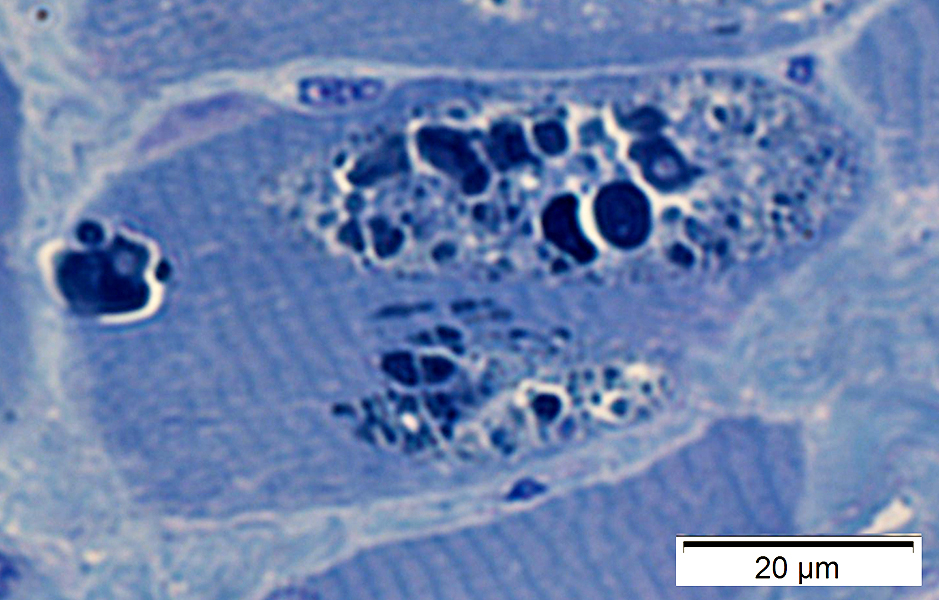
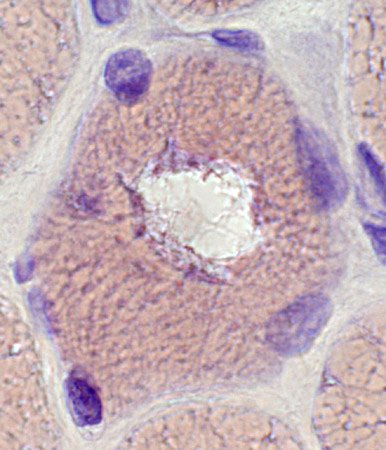 Congo red stain |
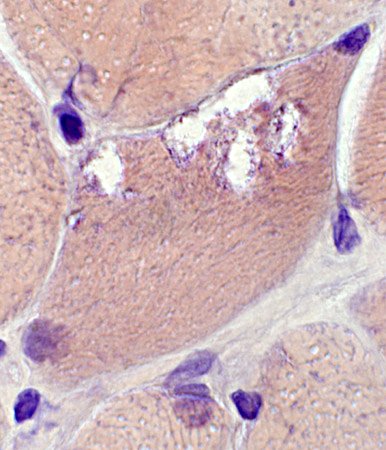 Congo red stain |
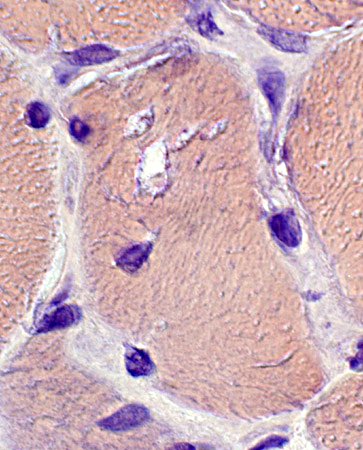 Congo red stain |
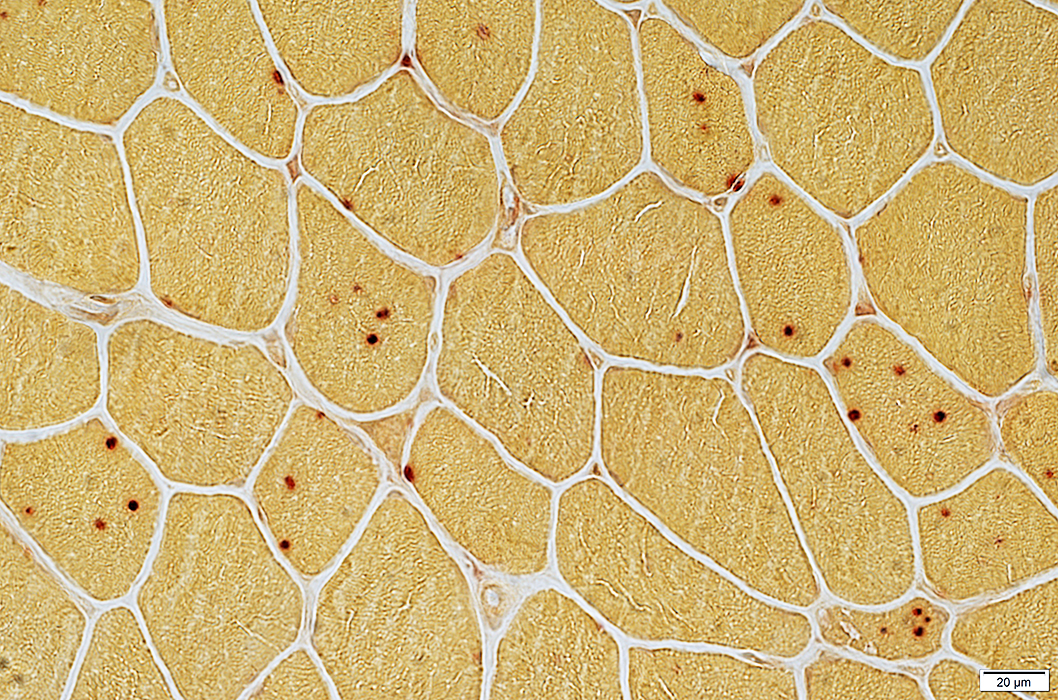
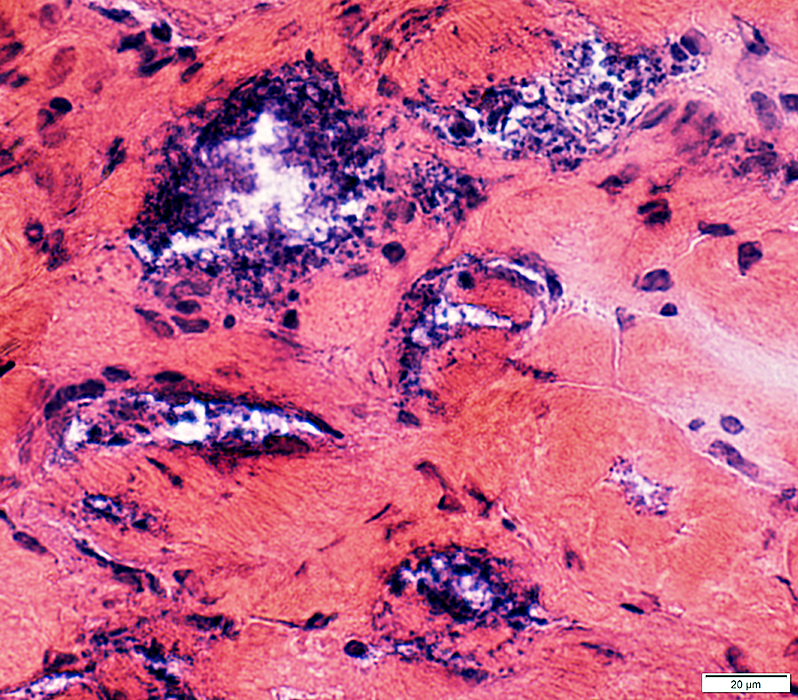
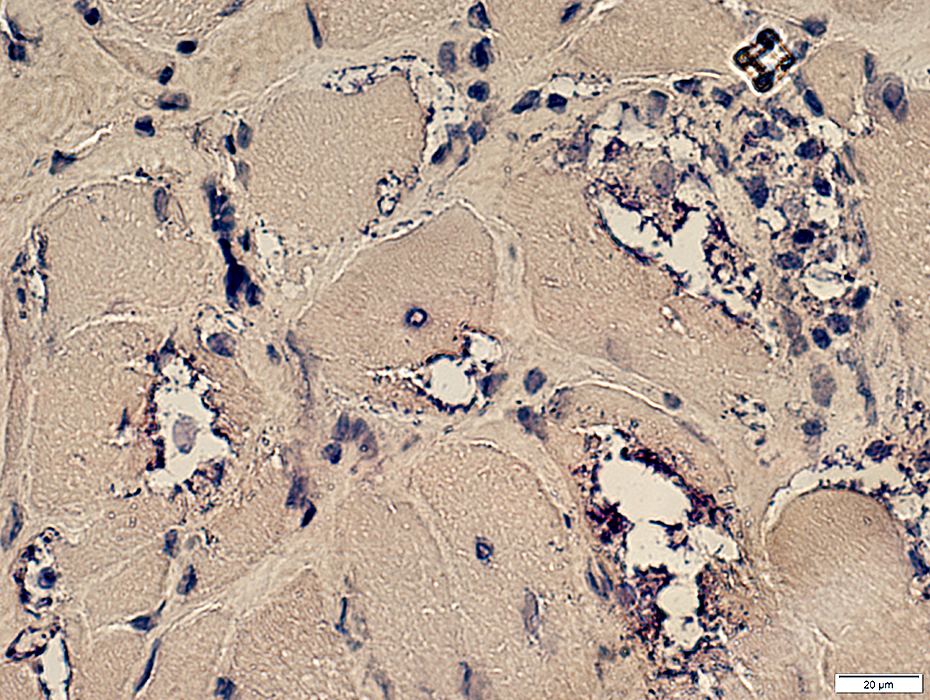
Acid phosphatase positive granules Cytoplasmic aggregate
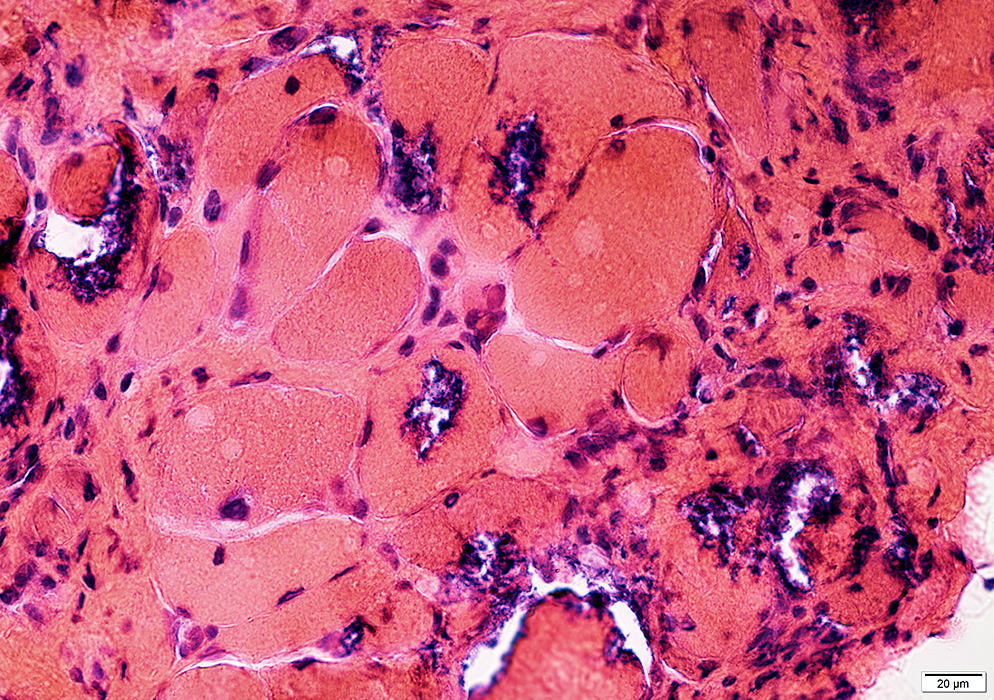
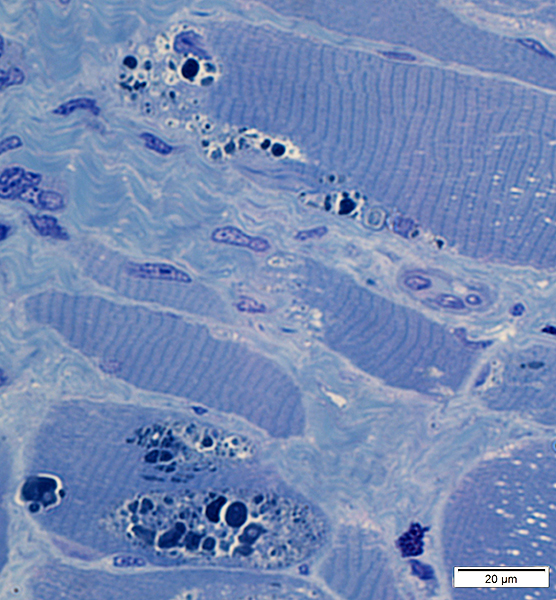
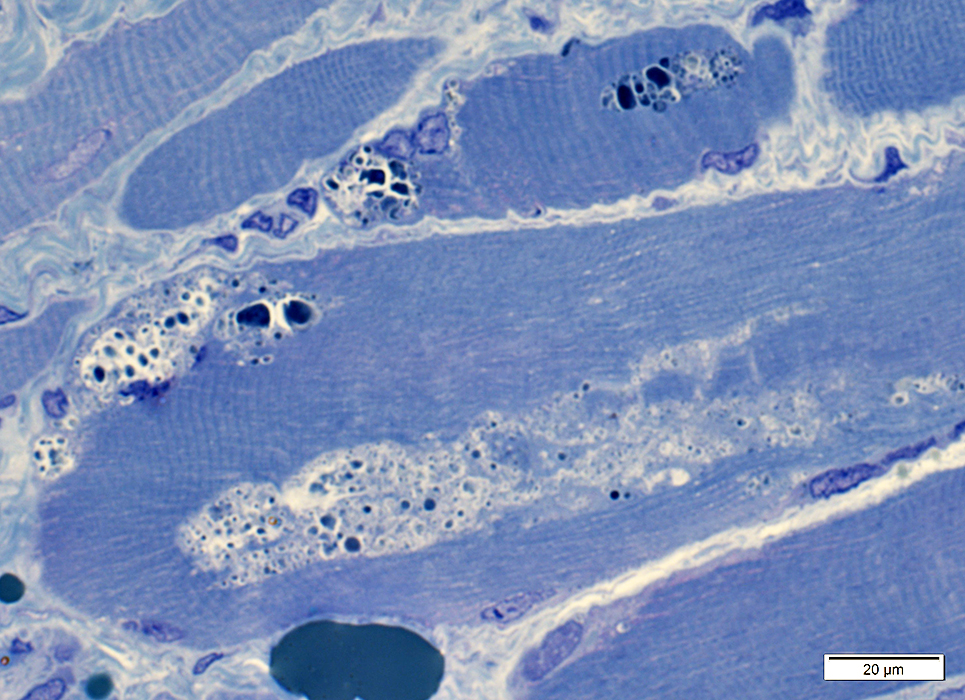
HIBM2 (GNE) Myopathy: Later pathology
Vacuoles: Cytoplasmic with granular, dark-stained contents; Irregular shapes Endomysial connective tissue: Moderately increased
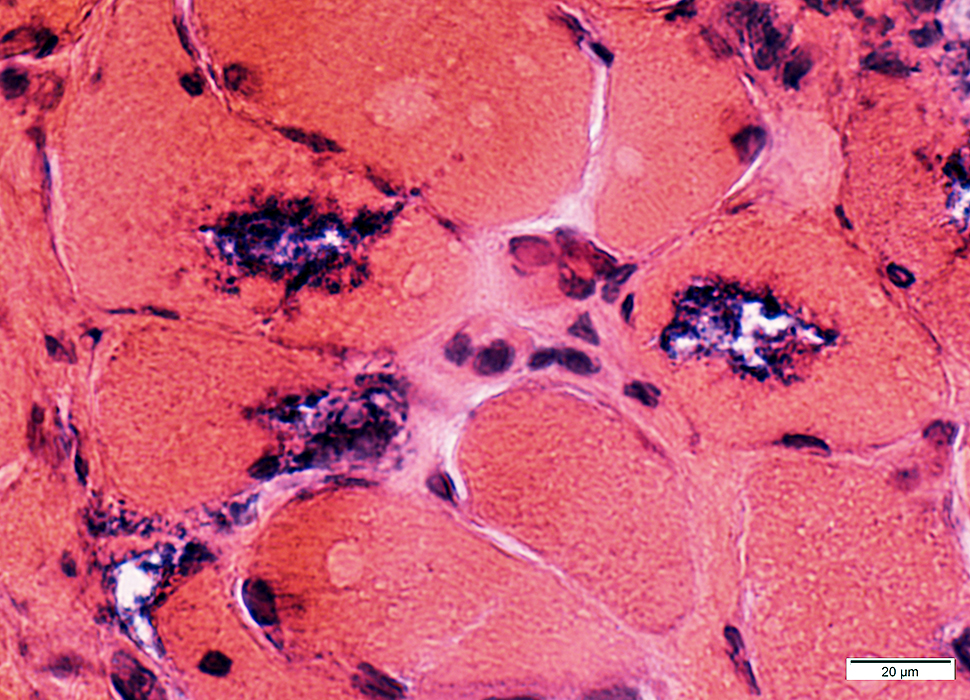
Vacuoles: Granular, dark-stained contents, more at rim
Some muscle fibers have increased cytoplasmic glycogen Some debris near & in vacuoles contains PAS-positive material
Some aggregated material may stain for SMI31 (phosphorylated proteins) or p62
Also see: Distal myopathies Return to Neuromuscular Home Page Return to HIBM 2 4/13/2020 |