PHOSPHORYLASE DEFICIENCY (McArdle Disease)
|
Vacuoles No vacuoles Rhabdomyolysis Muscle fibers: Dark necrosis Post-Rhabdomyolysis Ultrastructure |
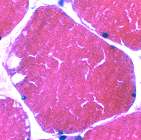
McArdle Disease: Vacuoles
Often subsarcolemmal
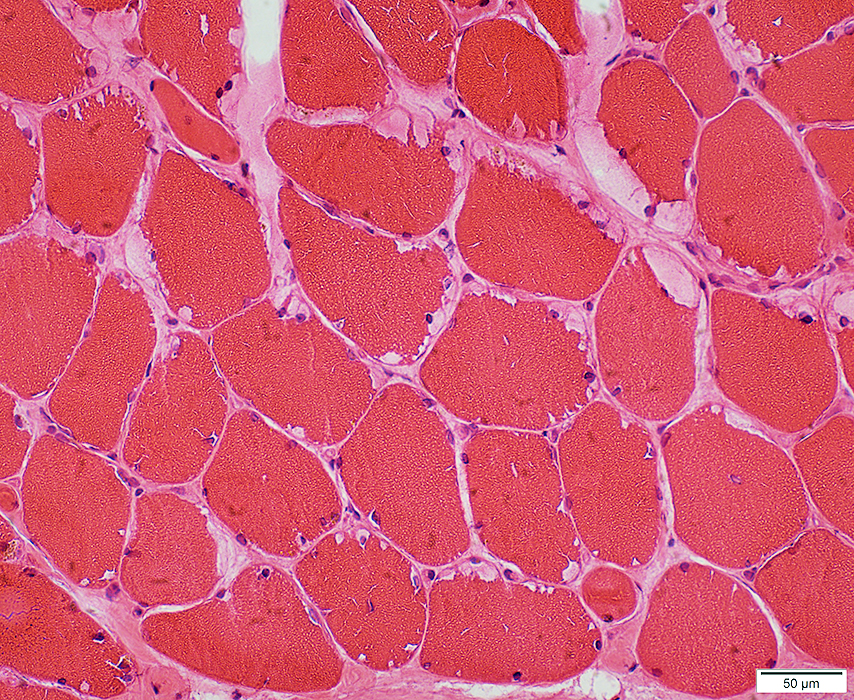 H&E stain |
|
Subsarcolemmal cytoplasmic vacuoles (Blebs) Most contain diffuse pale-staining material May contain myonuclei 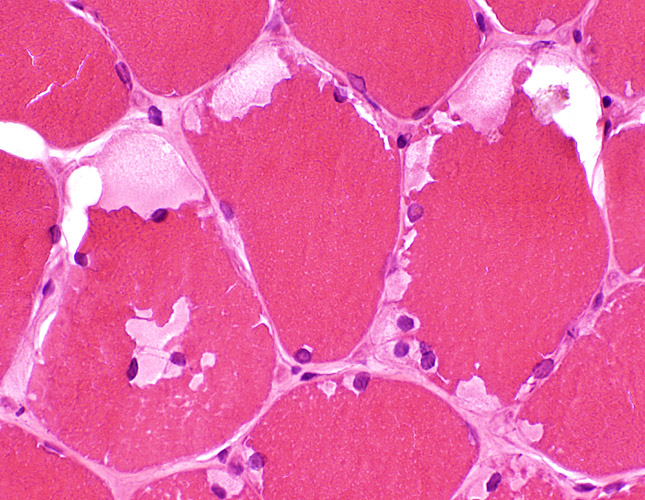 H & E stain |
   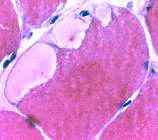 |
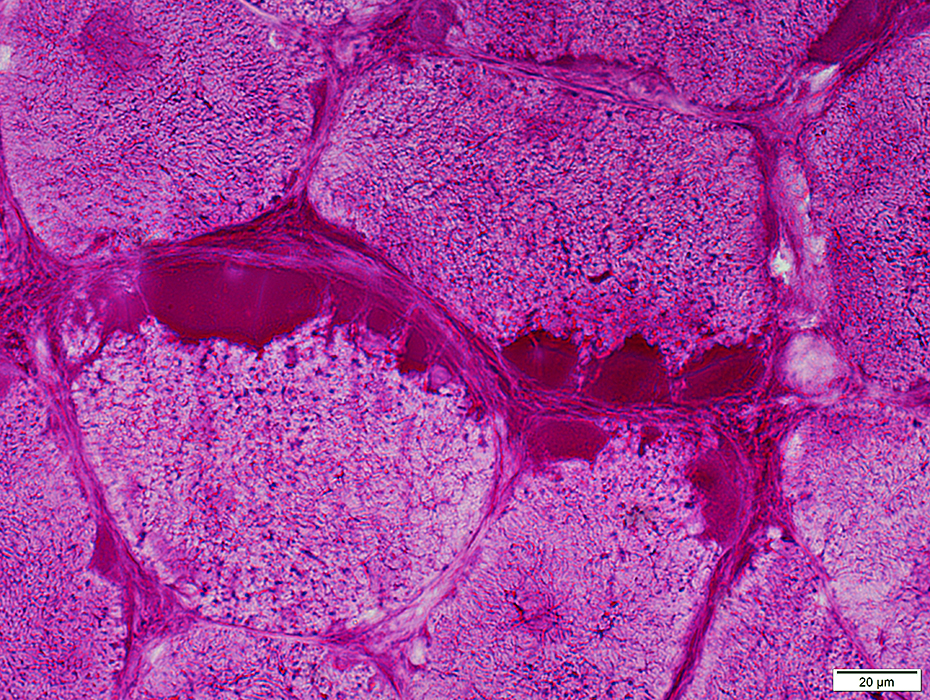
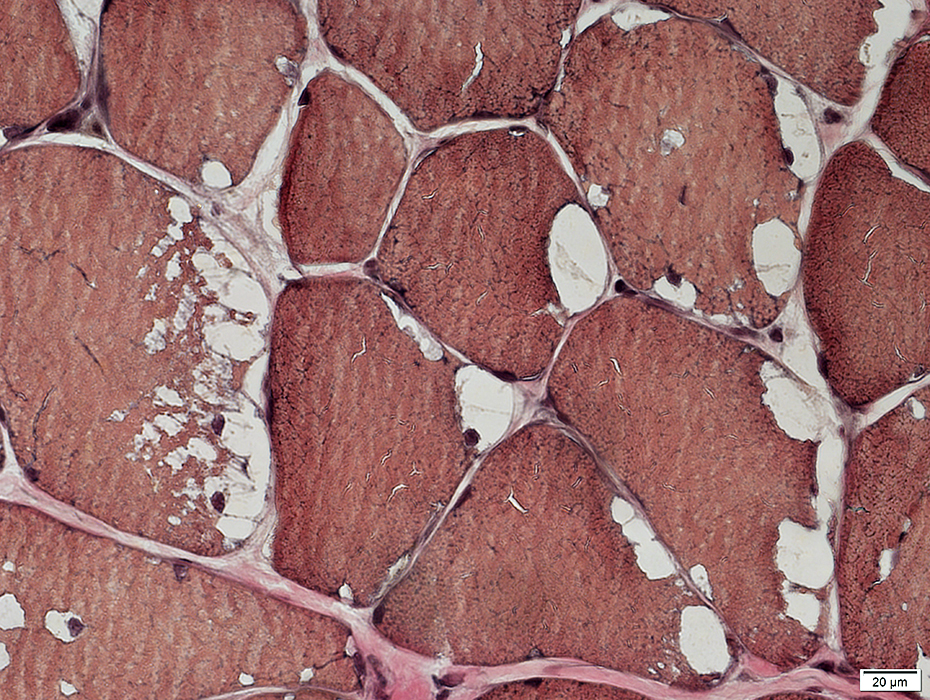 VvG stain |
Pale staining of contents on Gomori trichrome
May contain myonuclei
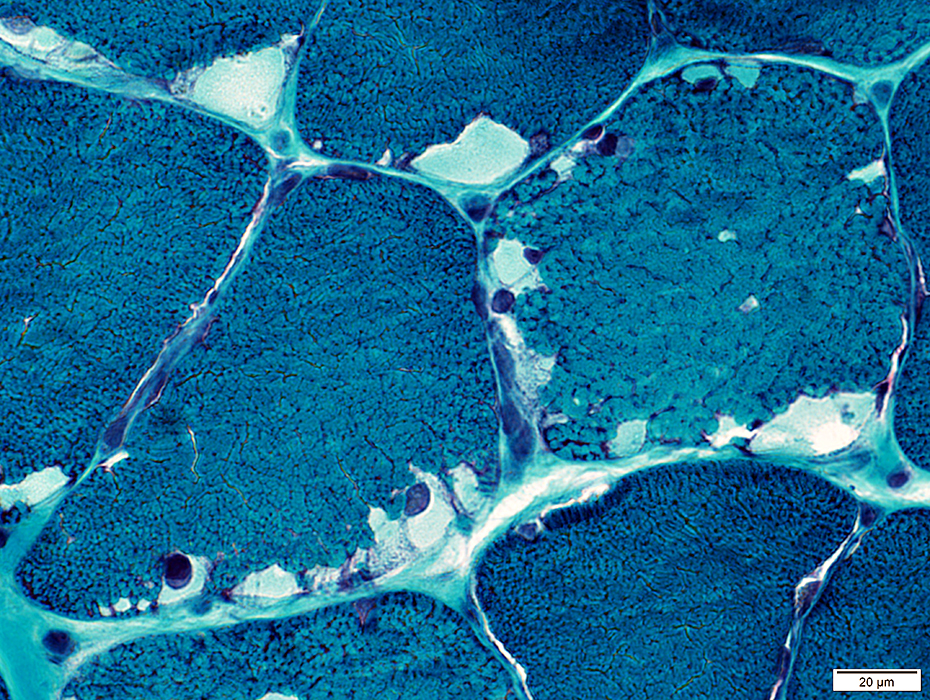 Gomori trichrome stain |
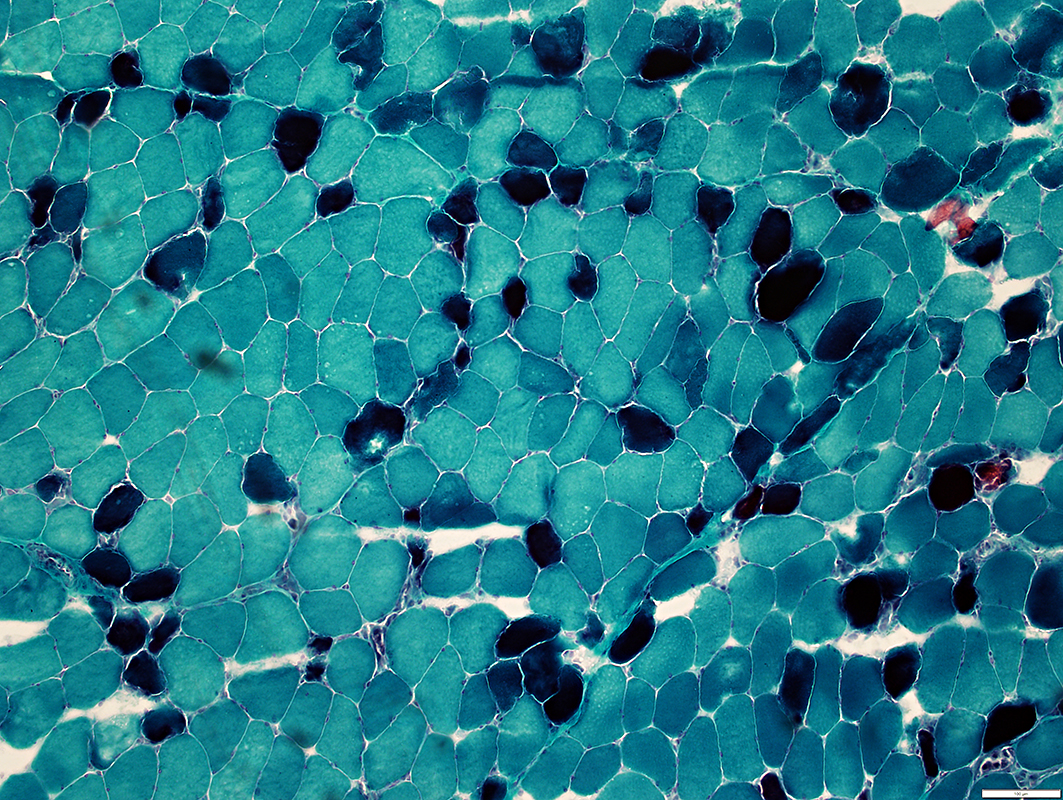
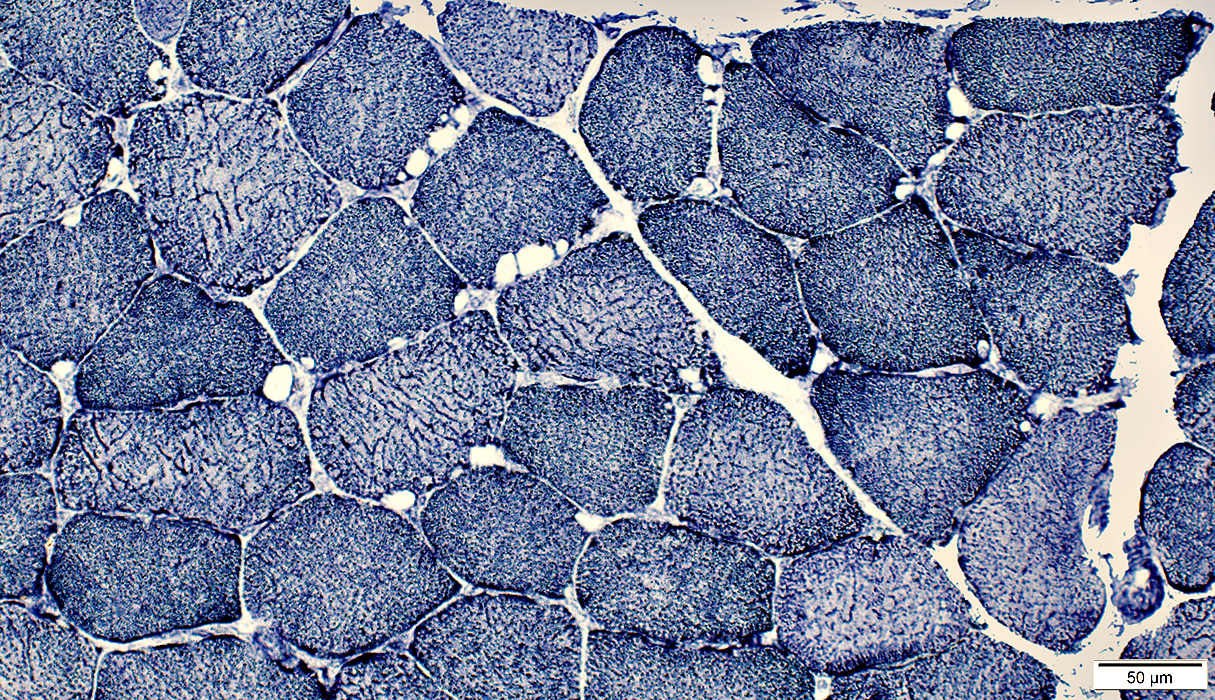 NADH stain |
Subsarcolemmal vacuoles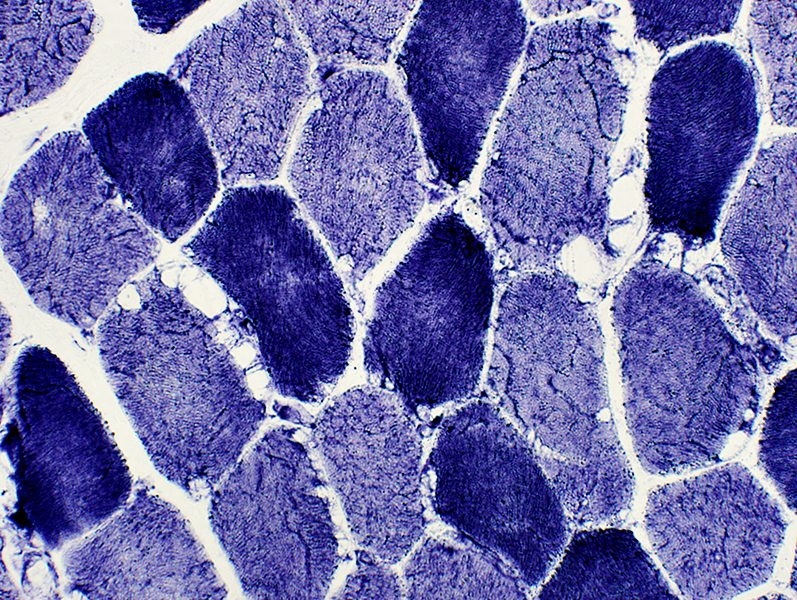 NADH stain |
|
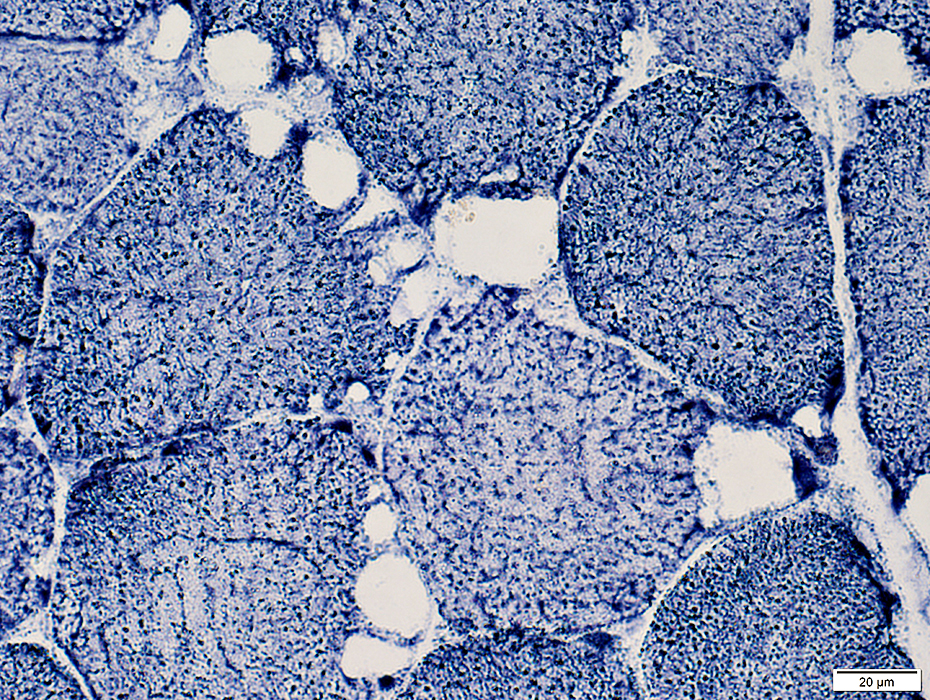 NADH stain |
PAS: May stain contents of sub-sarcolemmal blebs, or be diffusely increased in sarcoplasm
 PAS stain |
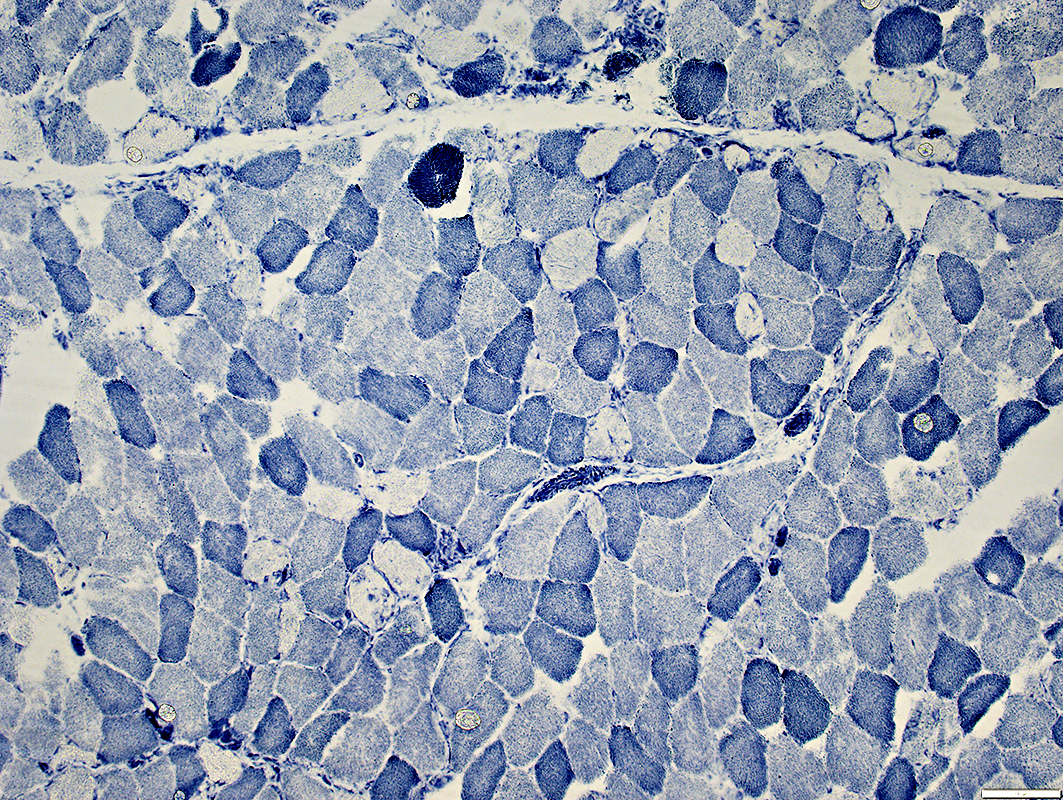
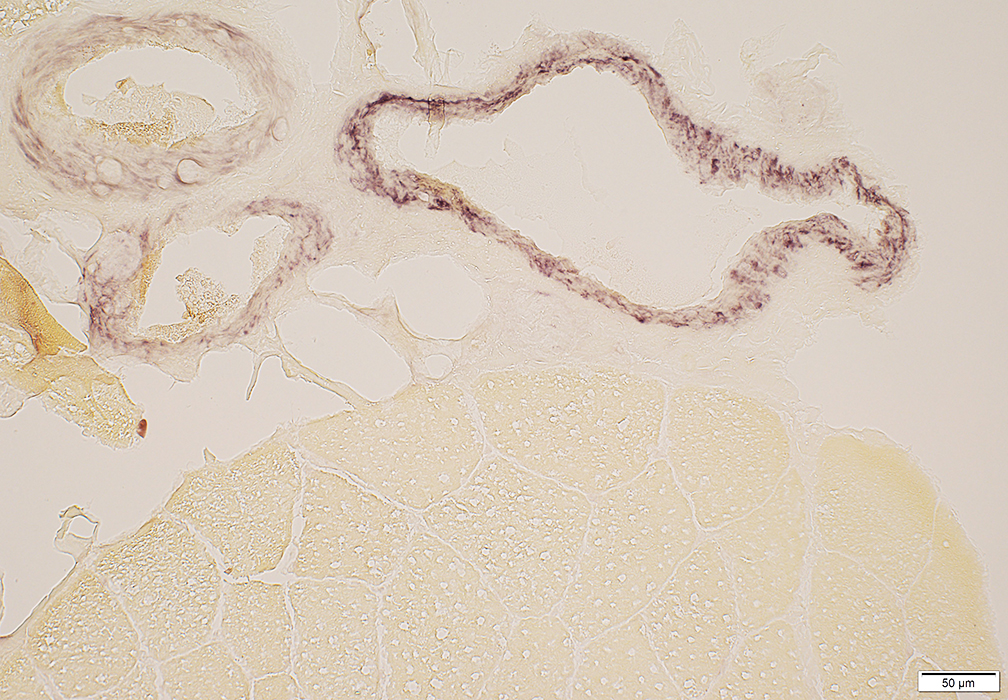 Phosphorylase stain |
Absent in muscle fibers
May be residual activity in vessels
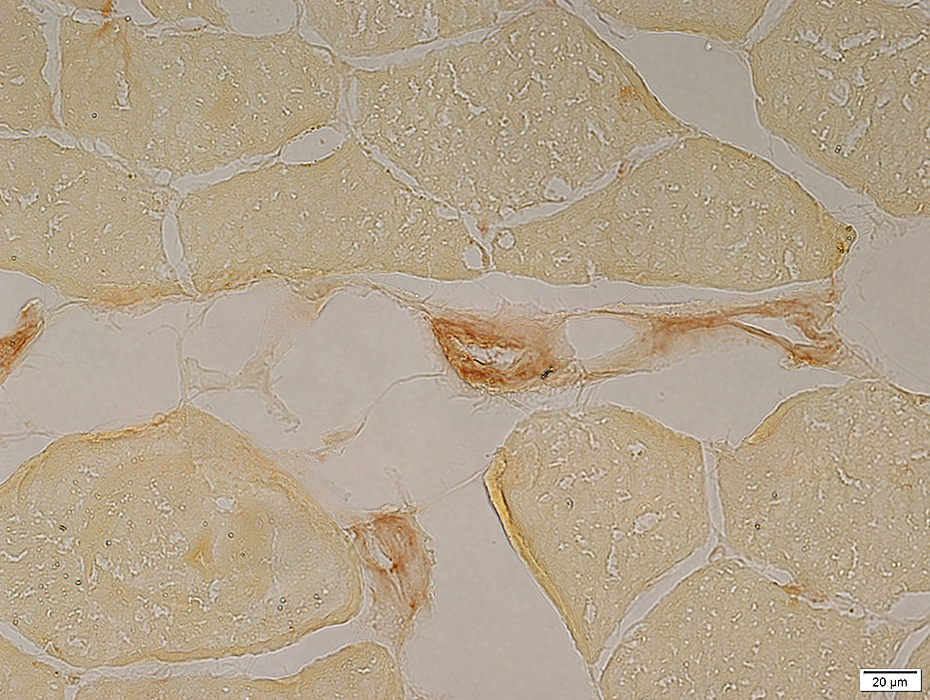 Phosphorylase stain |
Normal
Phosphorylase in muscle fiber cytoplasm
More in type II muscle fibers
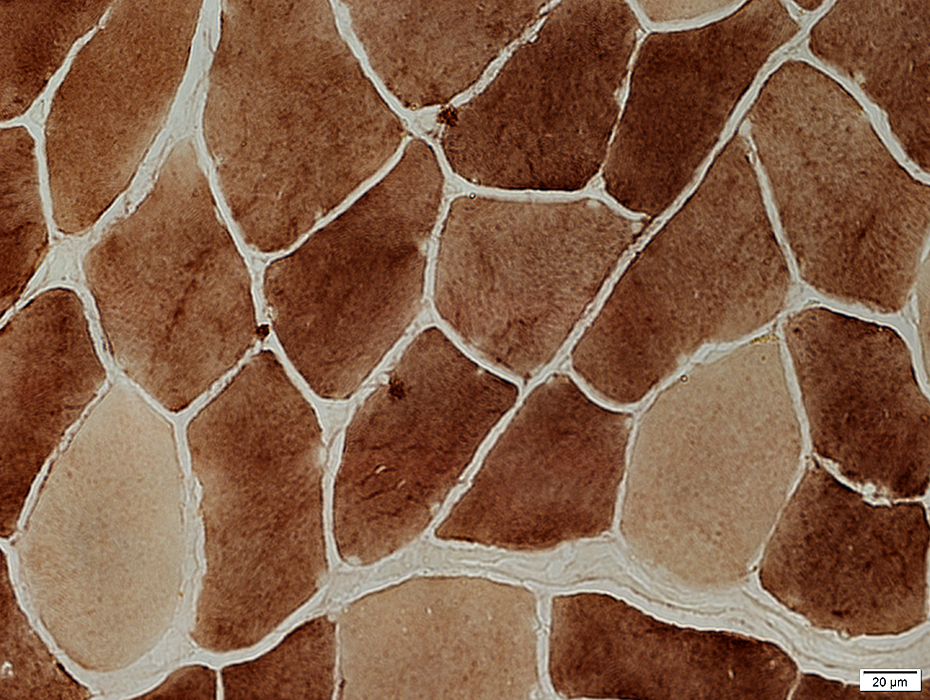 PAS stain |
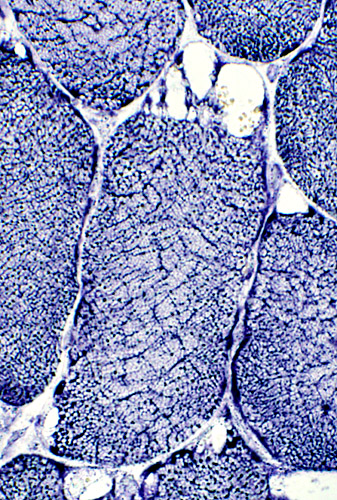
McArdle disease: Muscle fibers in regions with few blebs
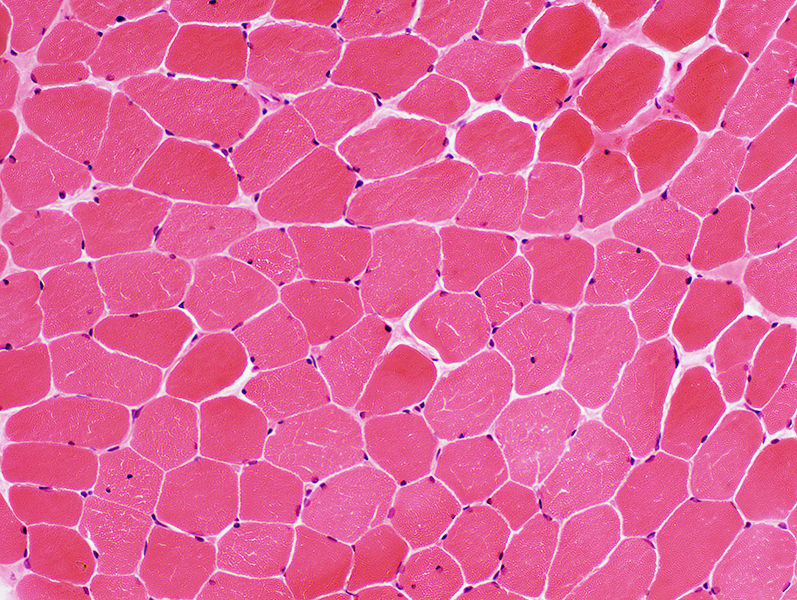 H&E stain Linear "cracks" in muscle fibers |
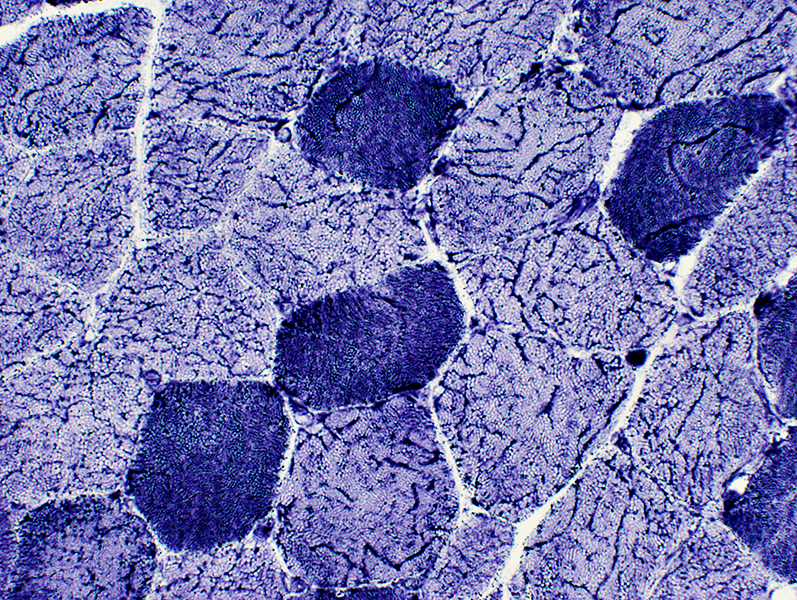 NADH stain Linearized pattern of internal architecture: Type 2 > Type 1 |
 |
Phosphorylase Deficiency
Internal nuclei: some muscle fibers
Prominent internal architecture
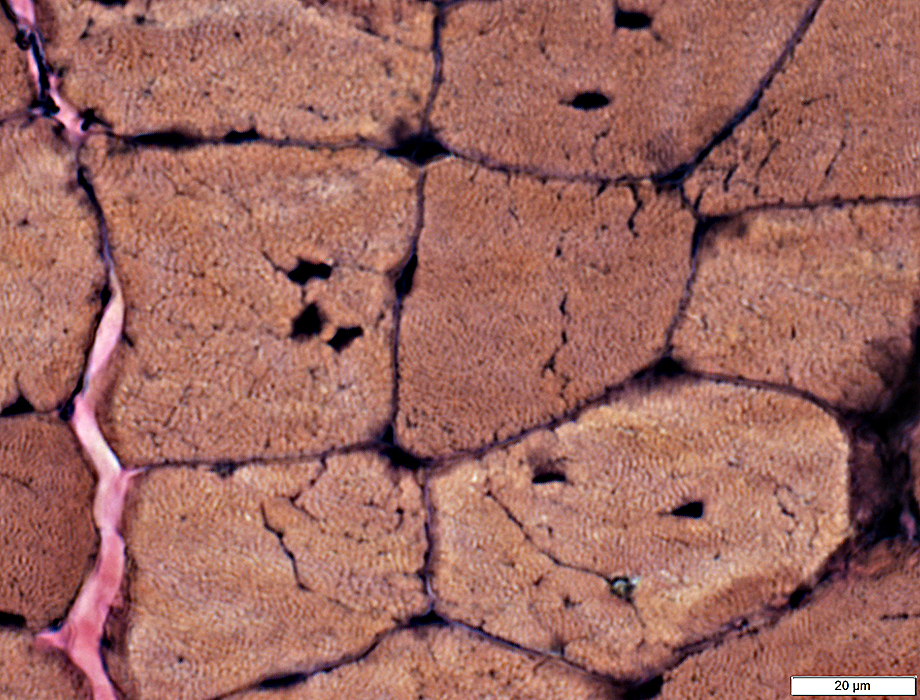 VvG stain |
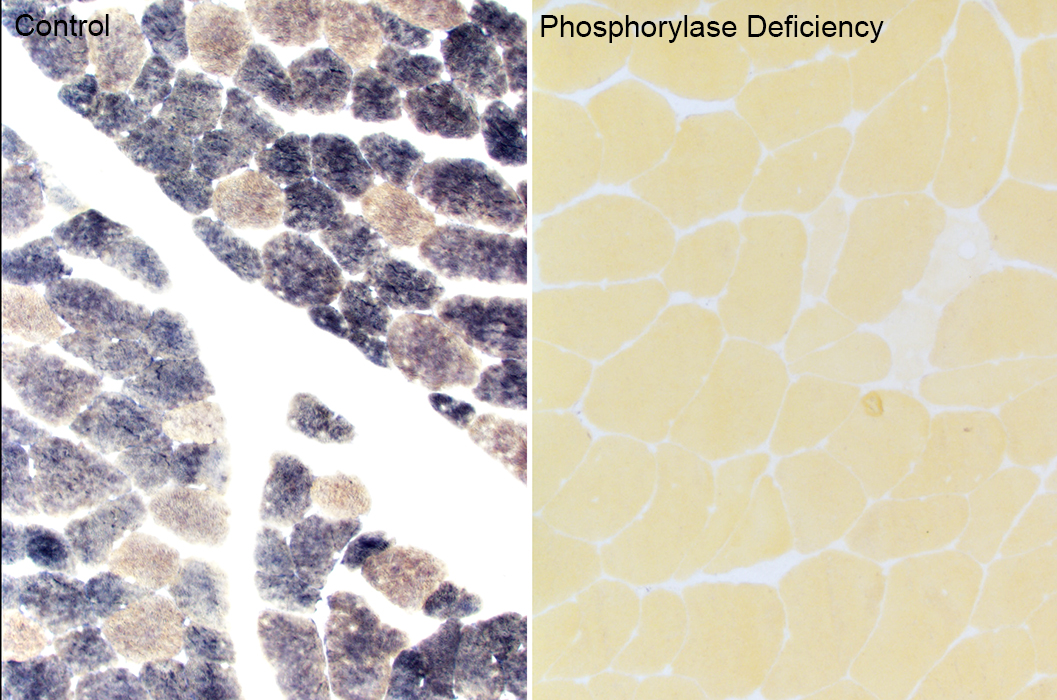 Phosphorylase stain From: S Moore |
Phosphorylase stains |
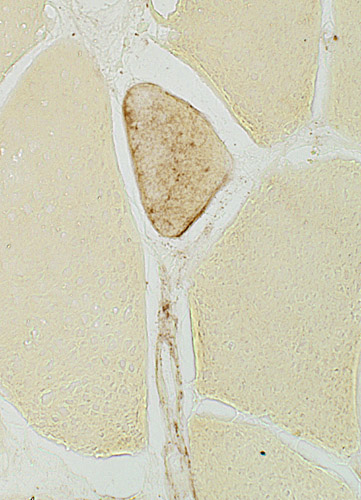 McArdle disease Some phosphorylase staining is present in vessels & regenerating muscle fibers |
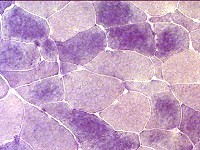 Phosphorylase stain: Normal Type II fibers: Darker than type I |
|
 Phosphorylase stain: McArdle disease Myophosphorylase deficiency Muscle fibers stain yellow |
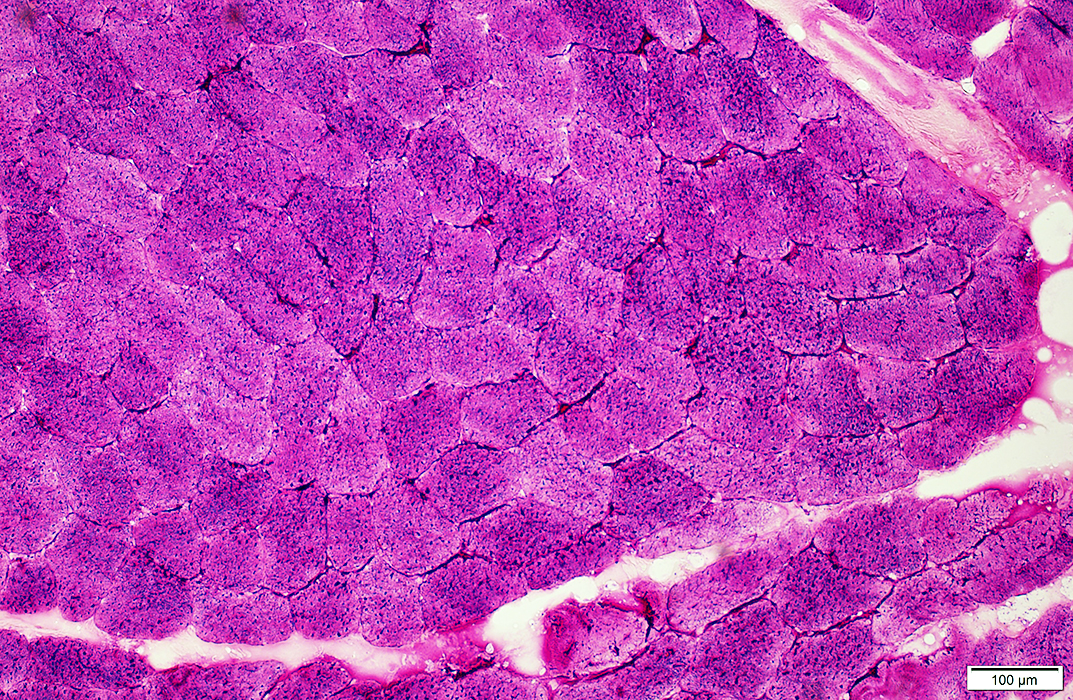 PAS stain: McArdle disease |
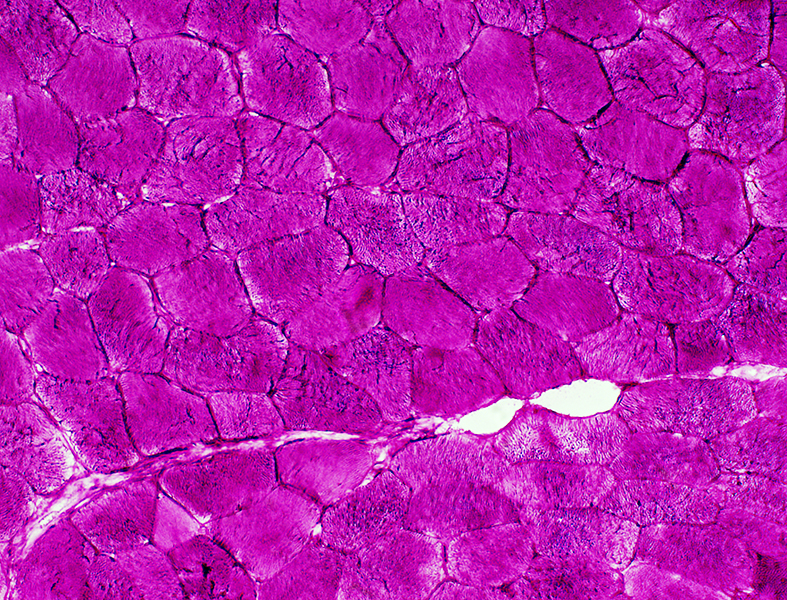 PAS stain: McArdle disease |
|
Glycogen: PAS stain Increased: Diffusely in cytoplasm Slightly metachromatic blue color in some areas May also stain contents of blebs |
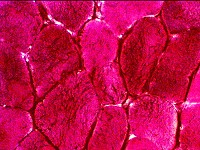 PAS stain: McArdle's disease |
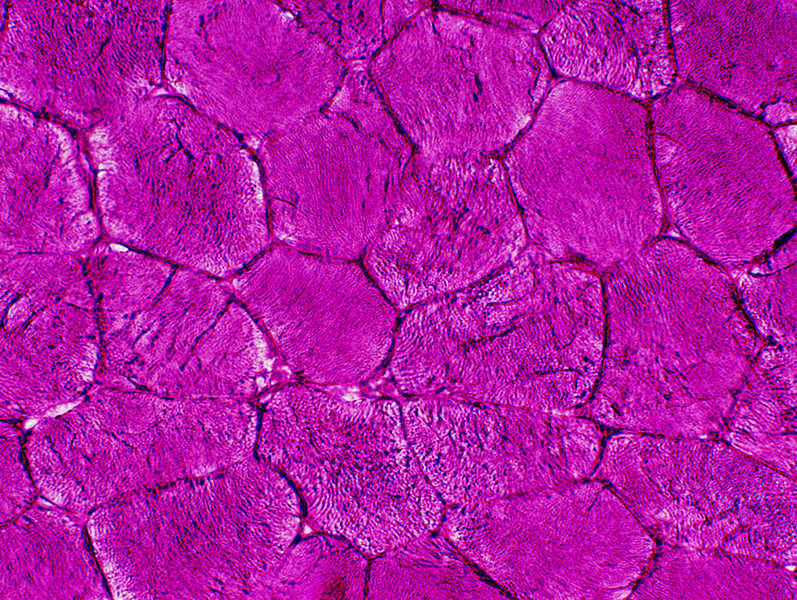 PAS stain: McArdle's disease |
|
Fiber types Vacuoles: May be in type I or type II muscle fibers 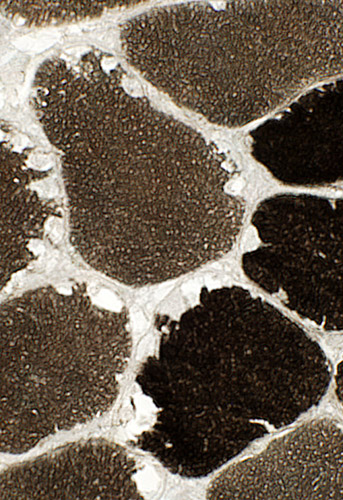 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
|
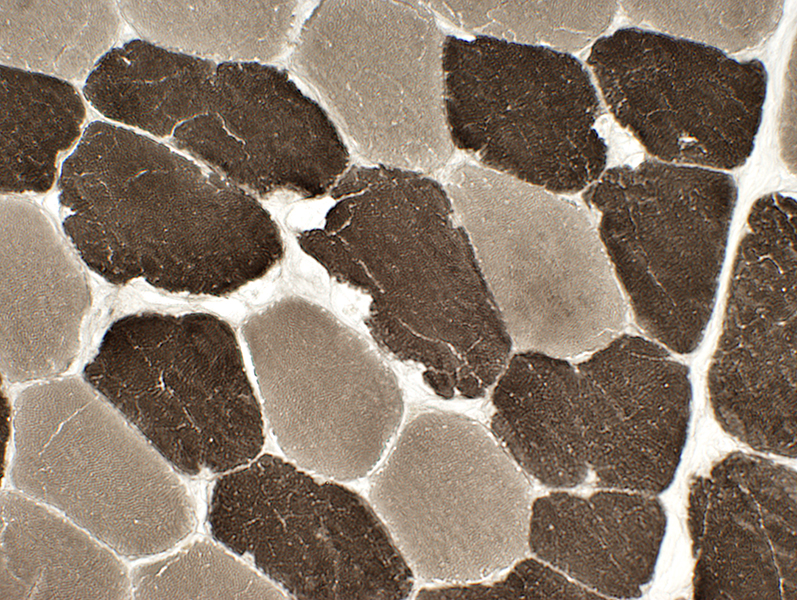
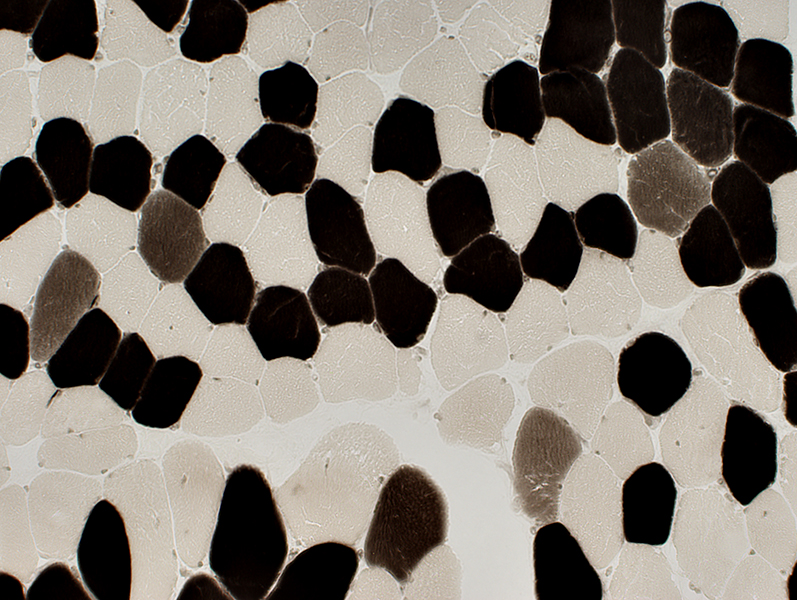 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
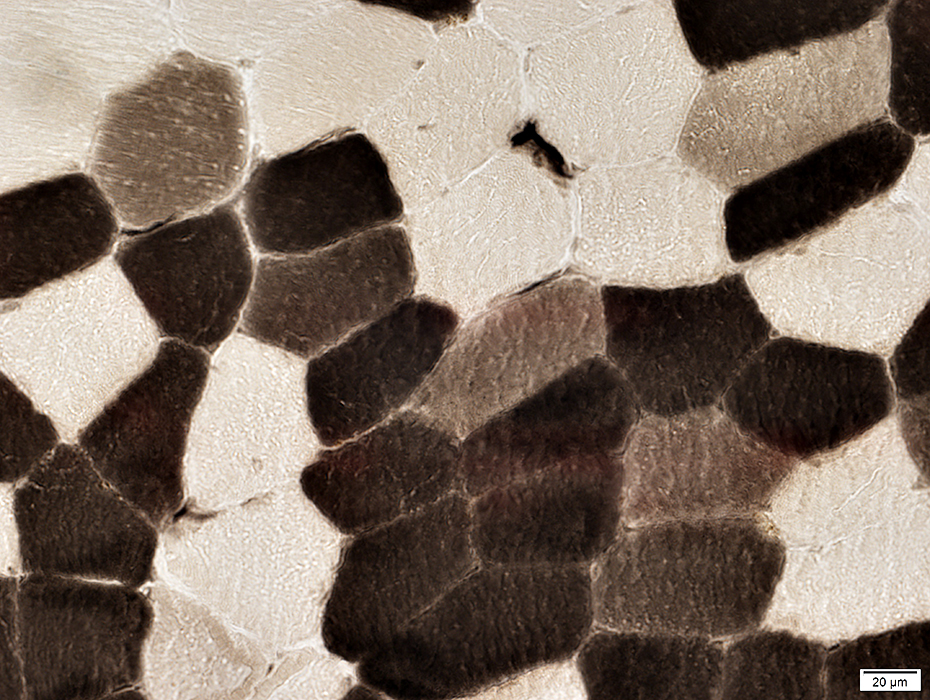 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Phosphorylase Deficiency: Rhabdomyolysis
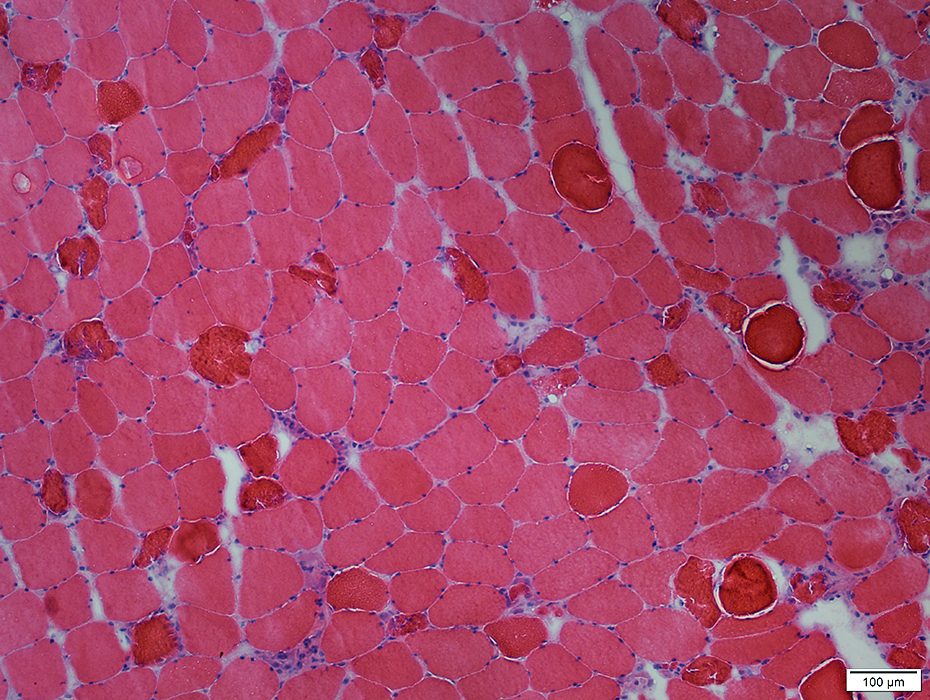 H&E stain |
Contrast: Pale necrotic fibers with Alcohol toxicity
 Gomori trichrome stain |
Phosphorylase deficiency: Necrotic muscle fibers
Pale on NADH: Despite dark stain on H&E & Gomori trichrome (Above)
 NADH stain |
Necrotic Muscle Fibers: Varied stages
Dark
Pale: Few fibers
Replaced by histiocytic cells
 H&E stain |
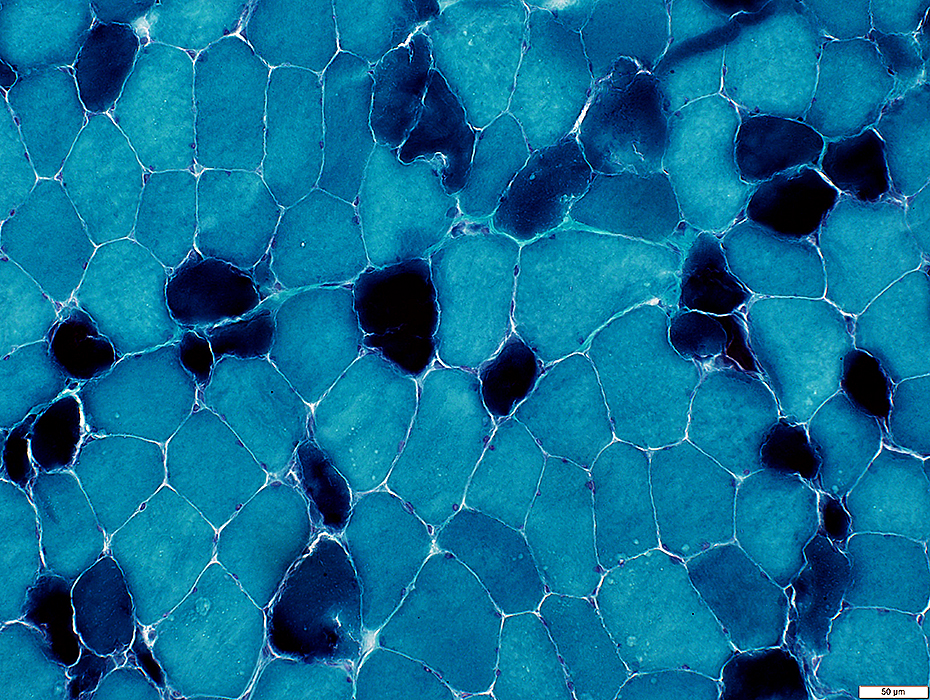 Gomori trichrome stain |
Cytoplasm
Early
Most necrotic fibers: Diffusely Dark stained; ? Hyper-contracted
Intermediate
Disintegrated fibers (Dark Arrow): Pale with irregular cytoplasm remnenats
Late
Replaced by histiocytic cells (White Arrow)
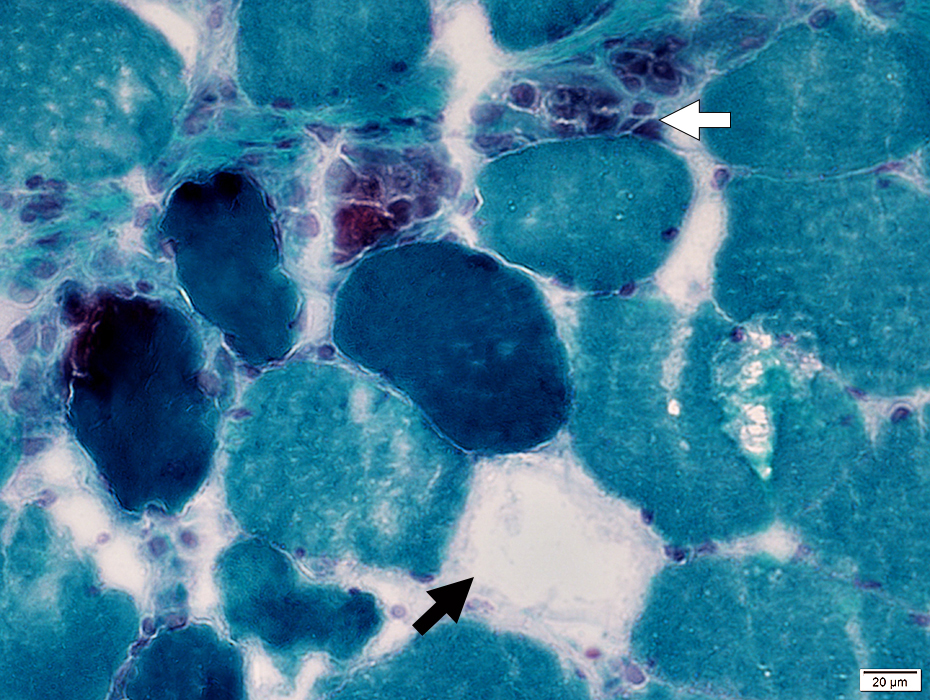 Gomori trichrome stain |
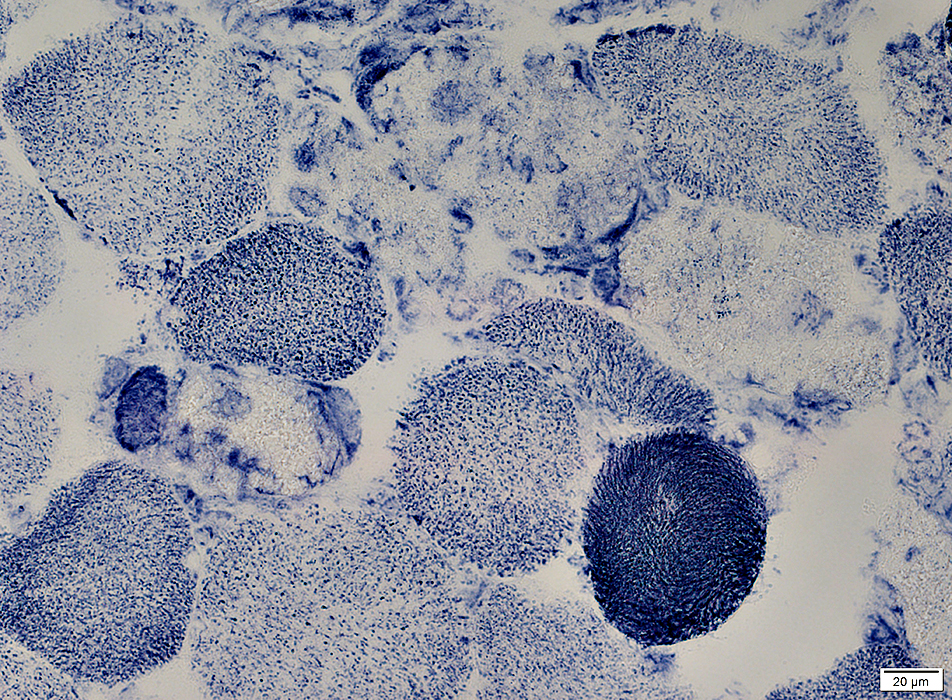 NADH stain |
Pale: Reduced NADH staiining of cytoplasm
Replaced by histiocytic cells: NADH+ cells in cytoplasm
Hyper-contracted: Dark-stained cytoplasm
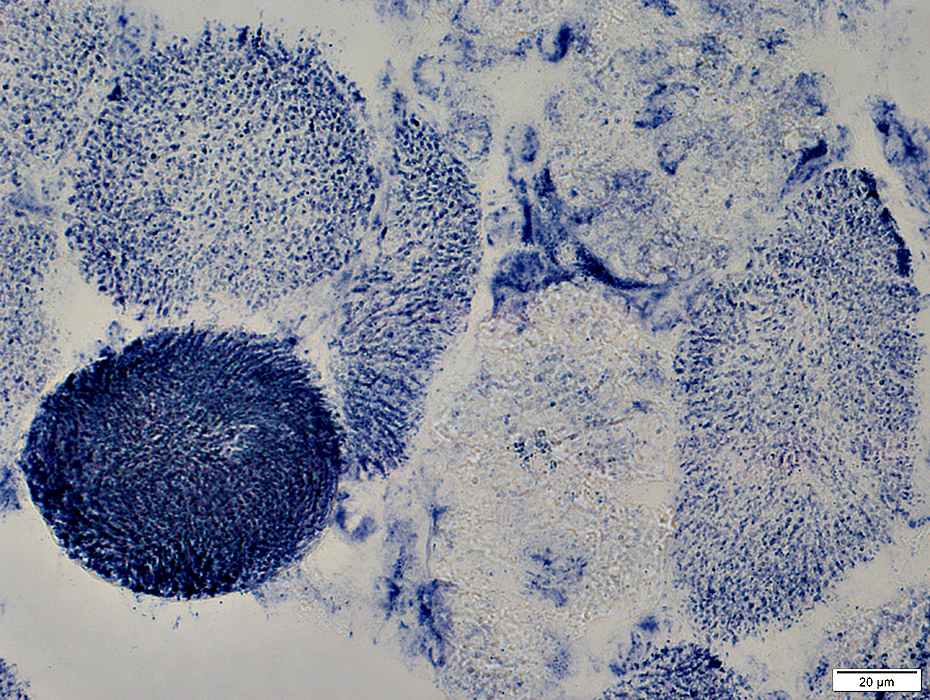 NADH stain |
Glycogen in muscle fibers
Reduced or absent during rhabdomyolysis
 PAS stain |
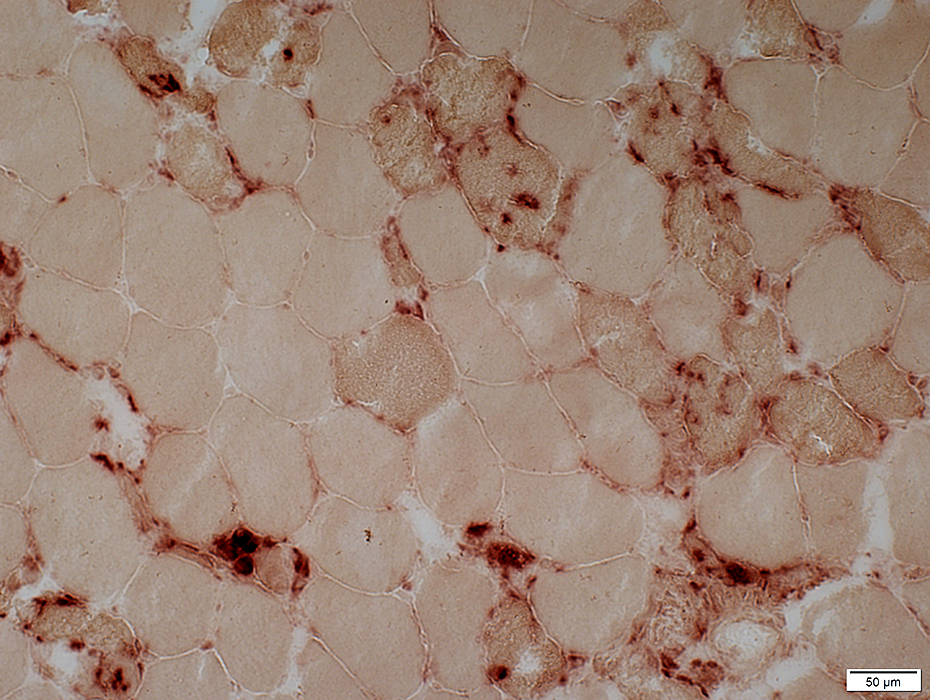 Acid phosphatase stain |
Acid phosphatase positive cells invading or replacing scattered muscle fibers
A few necrotic muscle fibers with pale cytoplasm are not invaded by histiocytes
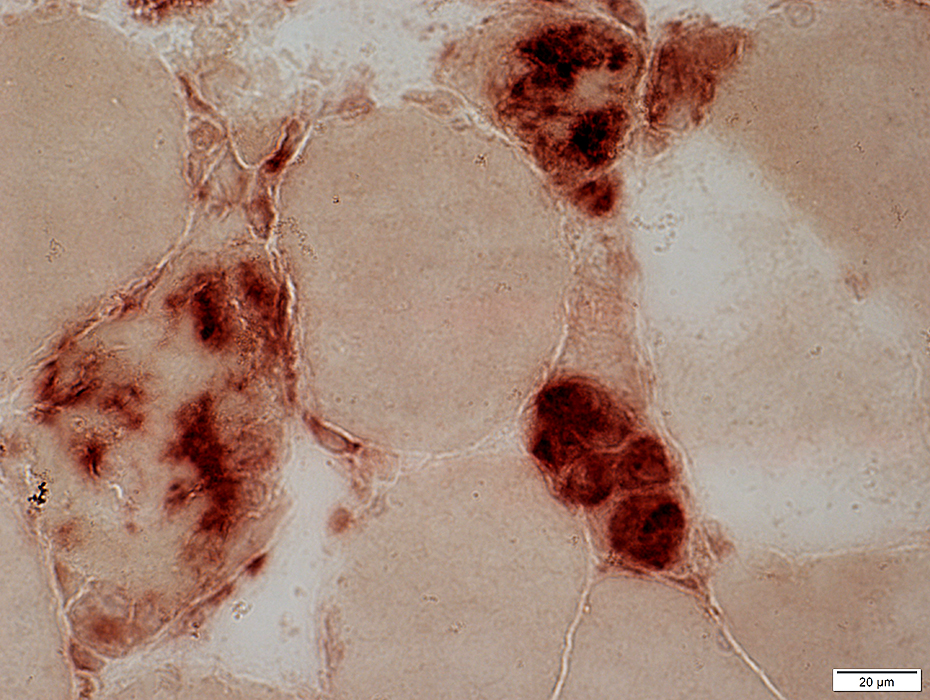 Acid phosphatase stain |
Necrotic muscle fibers: Characteristic pattern of irregular alkaline phosphatase stain around fibers
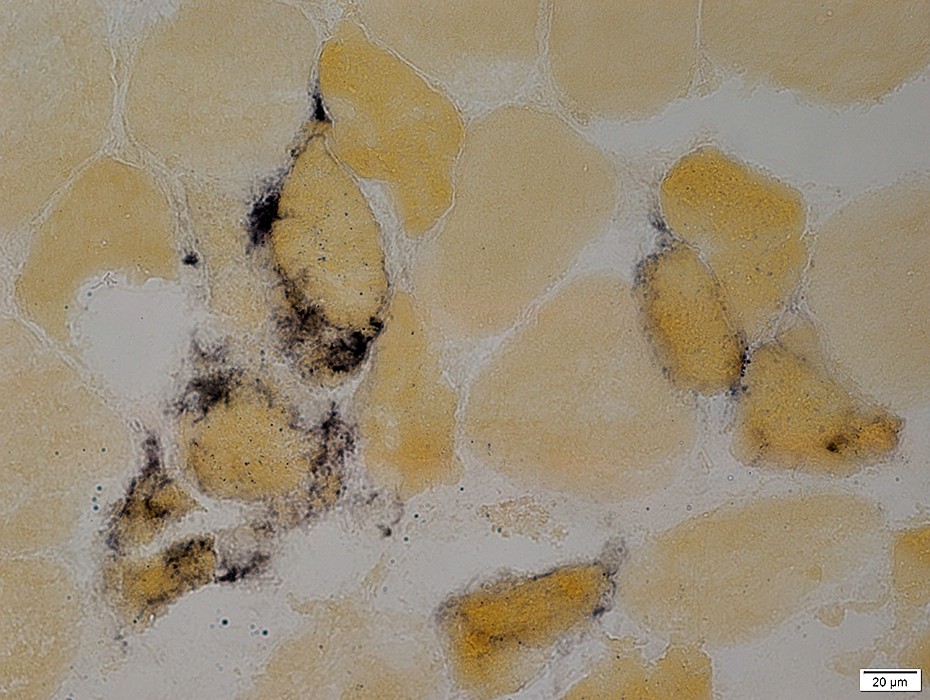 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
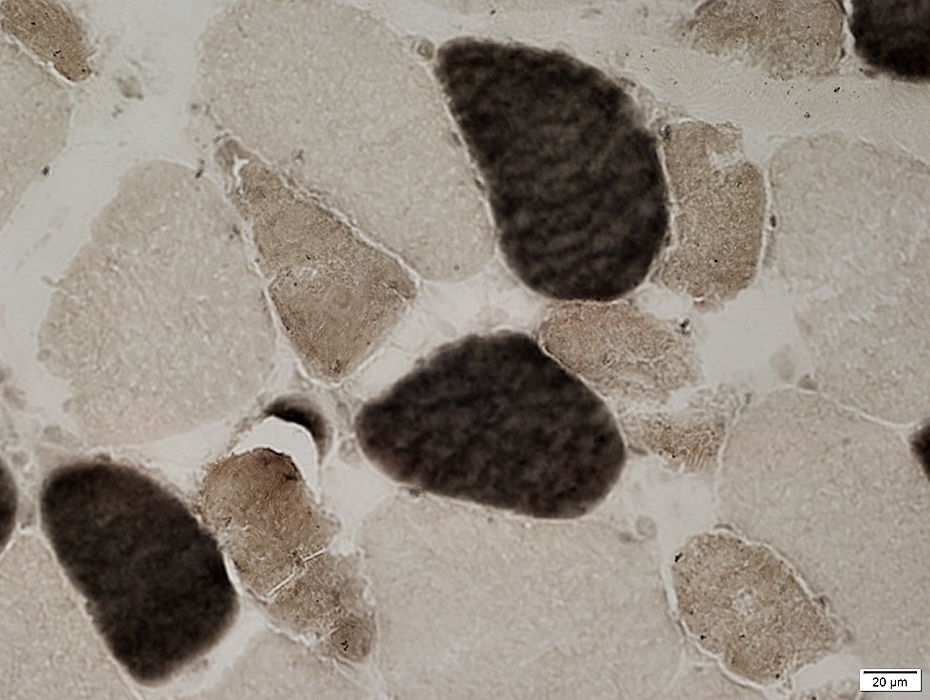 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
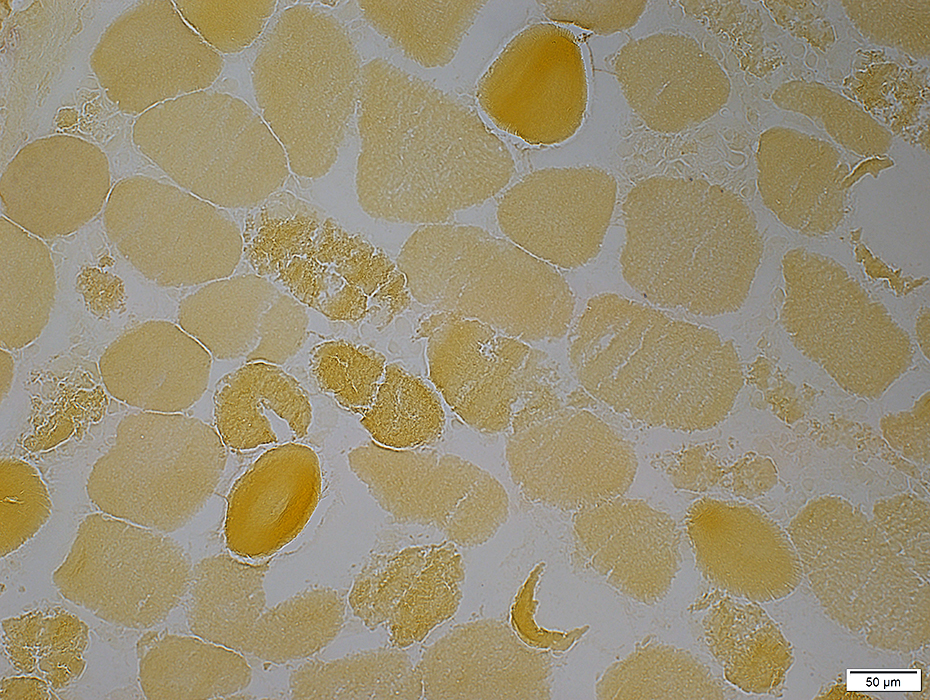 Phosphorylase stain |
Absent in large regions of muscle (Above)
Other isozymes upregulated in scattered muscle fibers (Below)
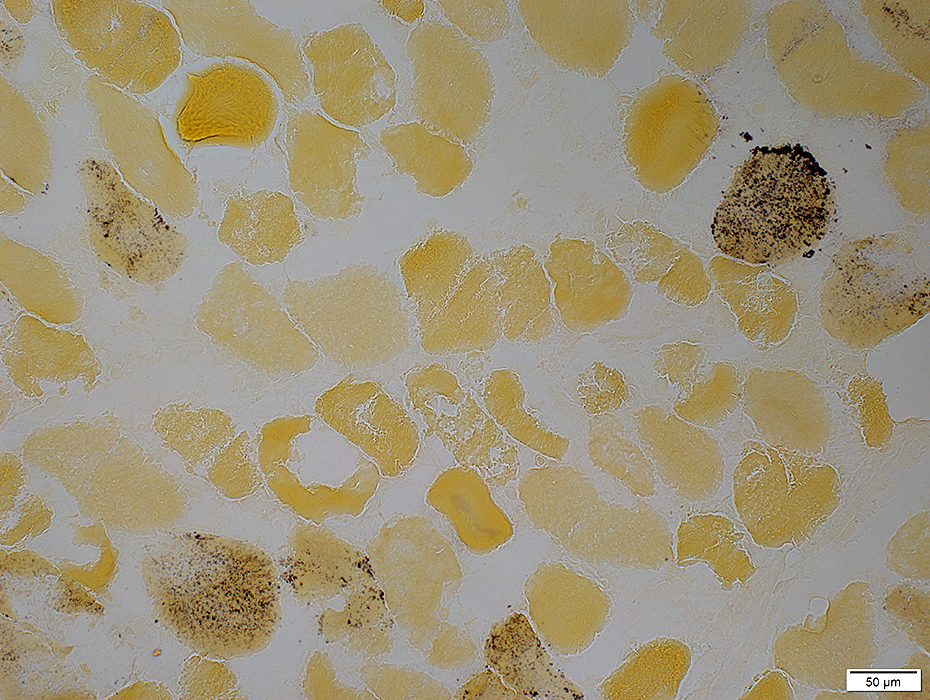 Phosphorylase stain |
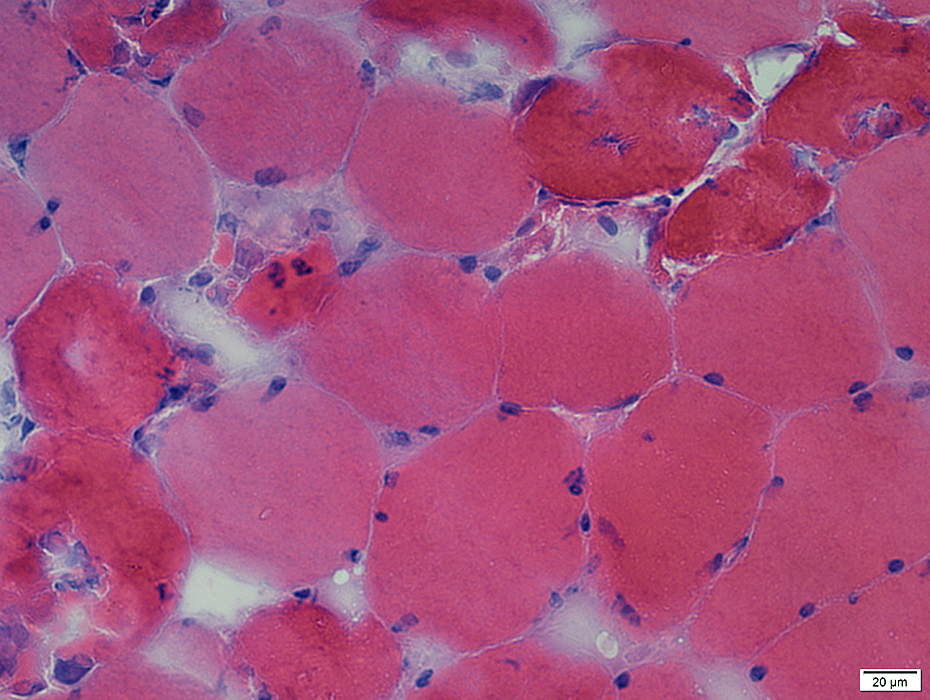
Phosphorylase Deficiency, Early Rhabdomyolysis: Dark Necrosis of Muscle Fibers
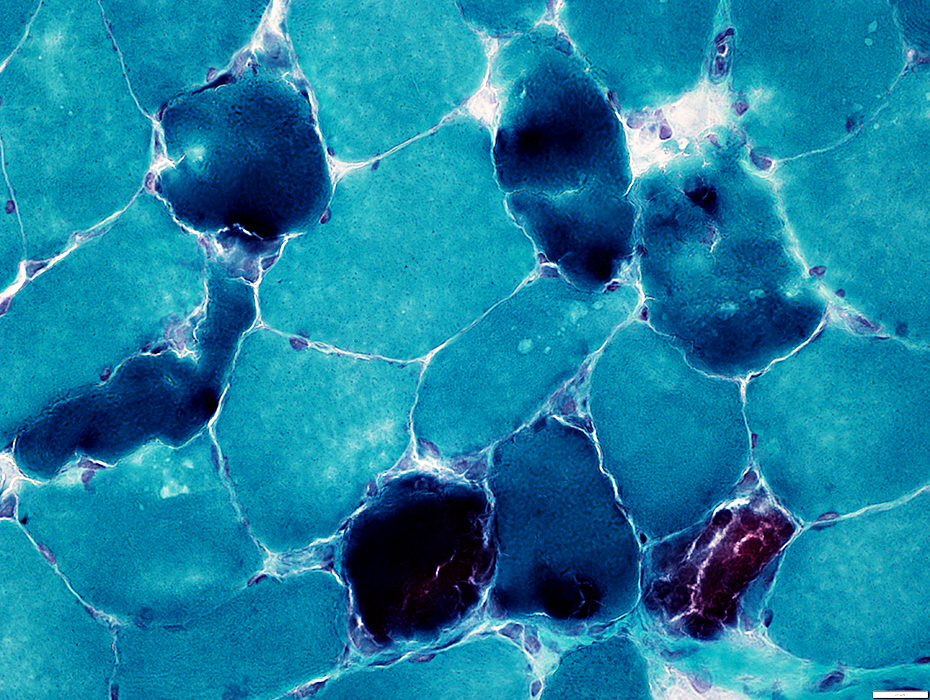 Gomori Trichrome stain |
Scattered muscle fibers have feature-less dark-stained cytoplasm
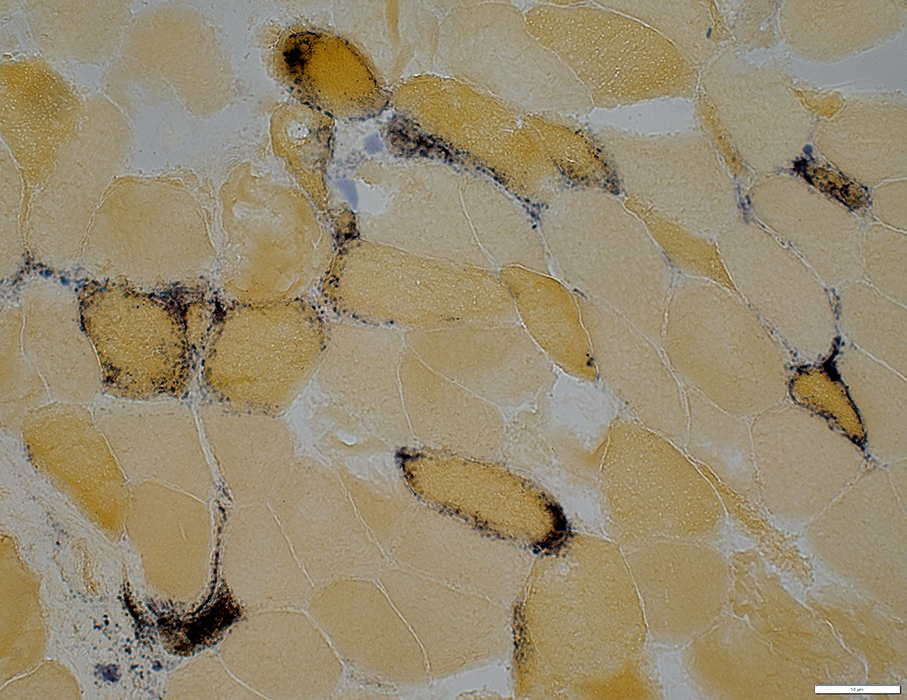 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Surrounded by alkaline phosphatase stain
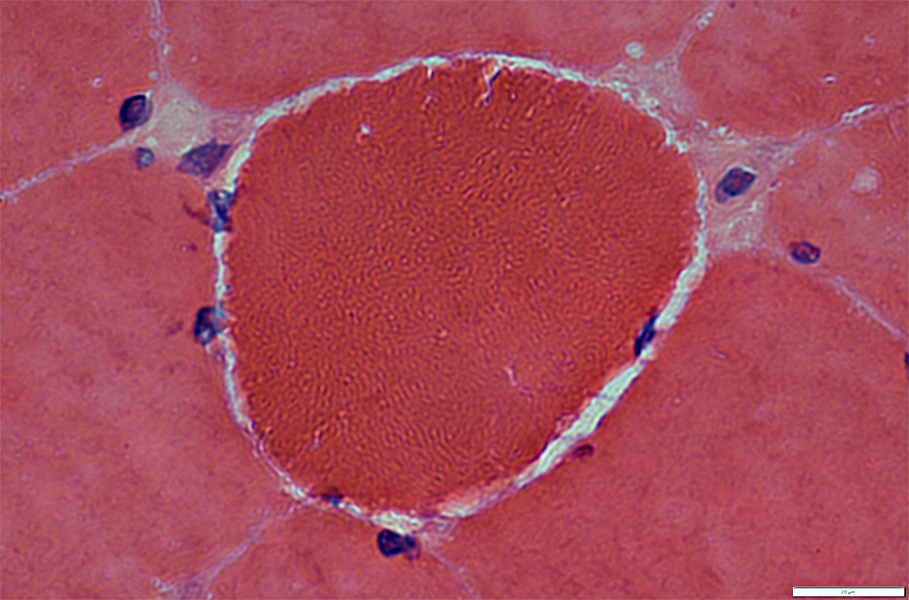 H&E stain |
Cytoplasm is diffusely dark stained
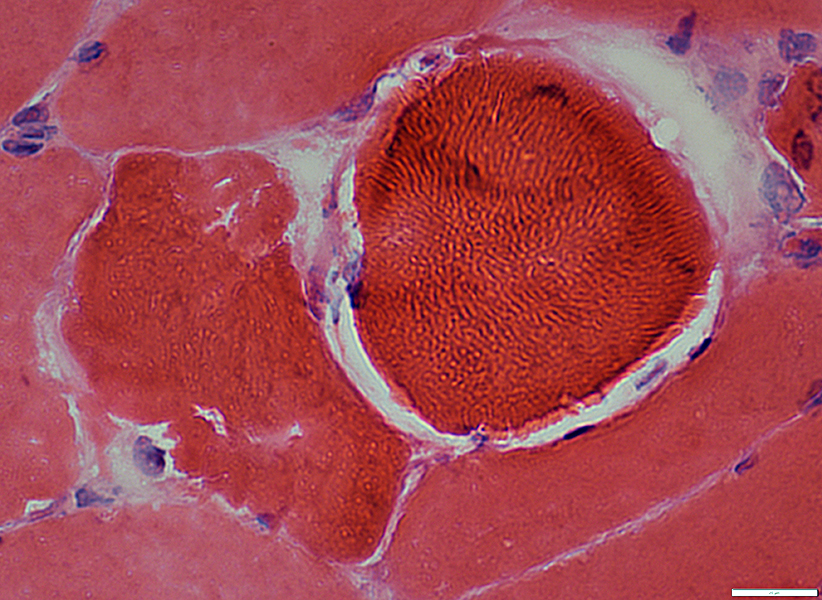 H&E stain |
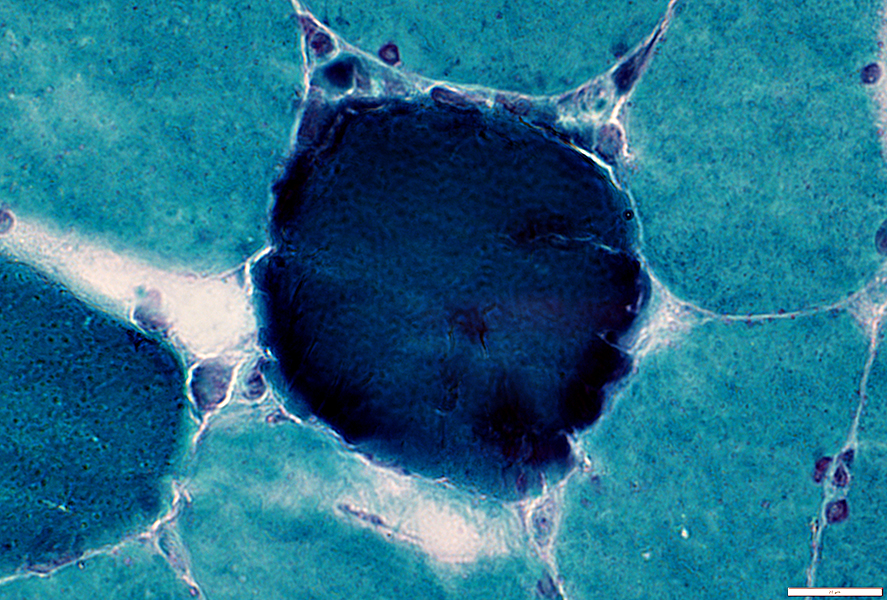 Gomori Trichrome stain |
Cytoplasm is diffusely dark stained
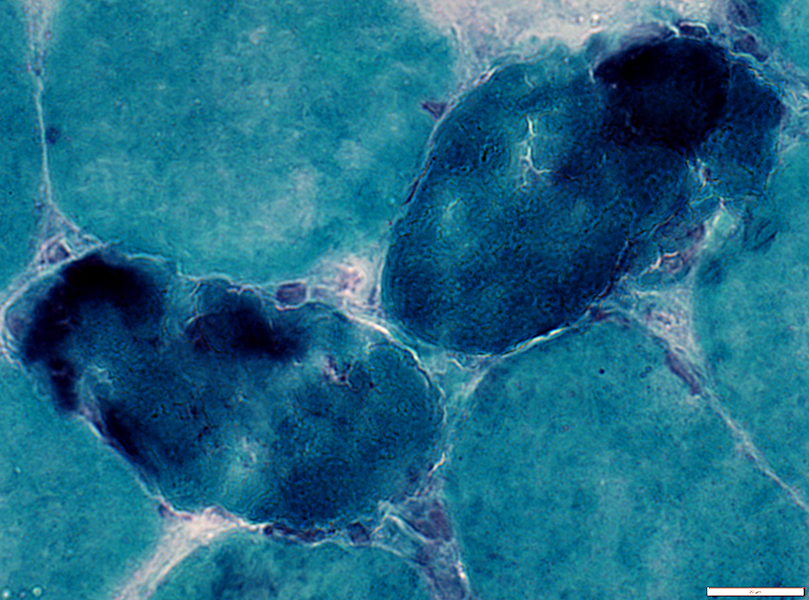 Gomori Trichrome stain |
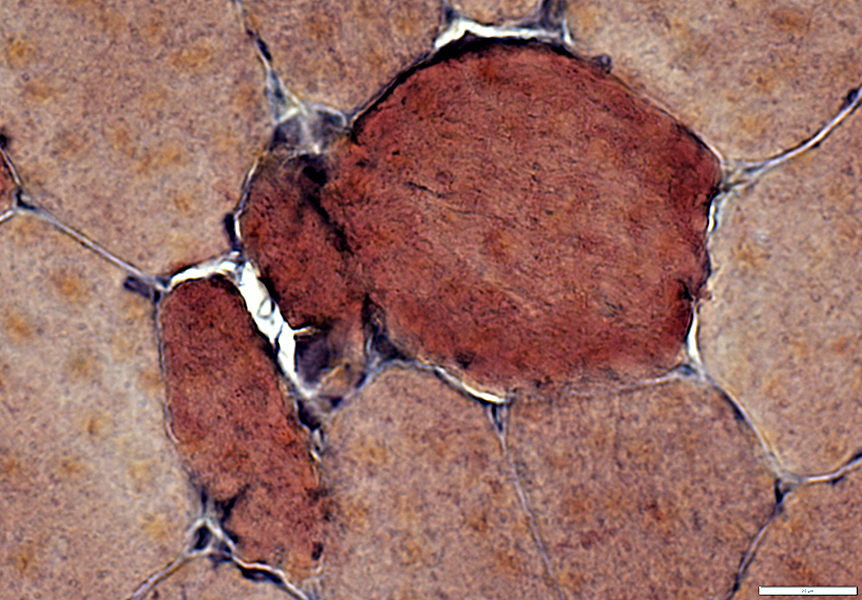 VvG stain |
Cytoplasm is diffusely dark stained
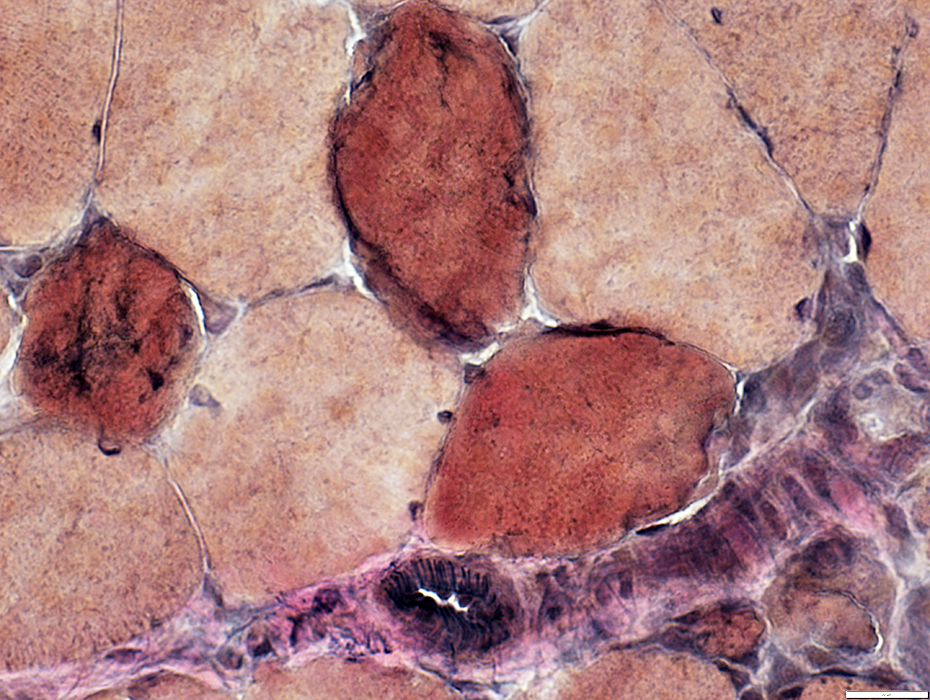 VvG stain |
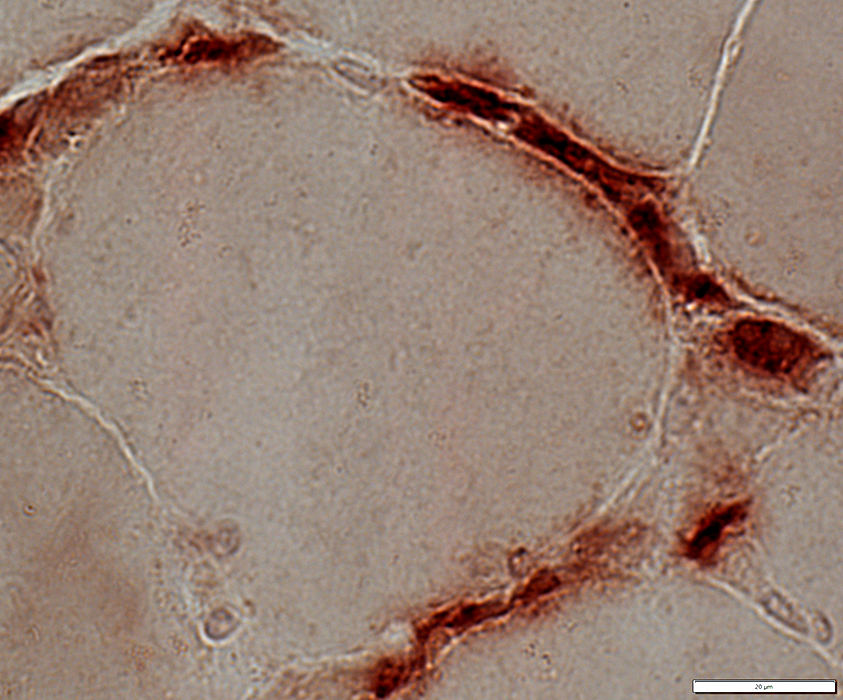 Acid Phosphatase stain |
May be surounded by histiocytes
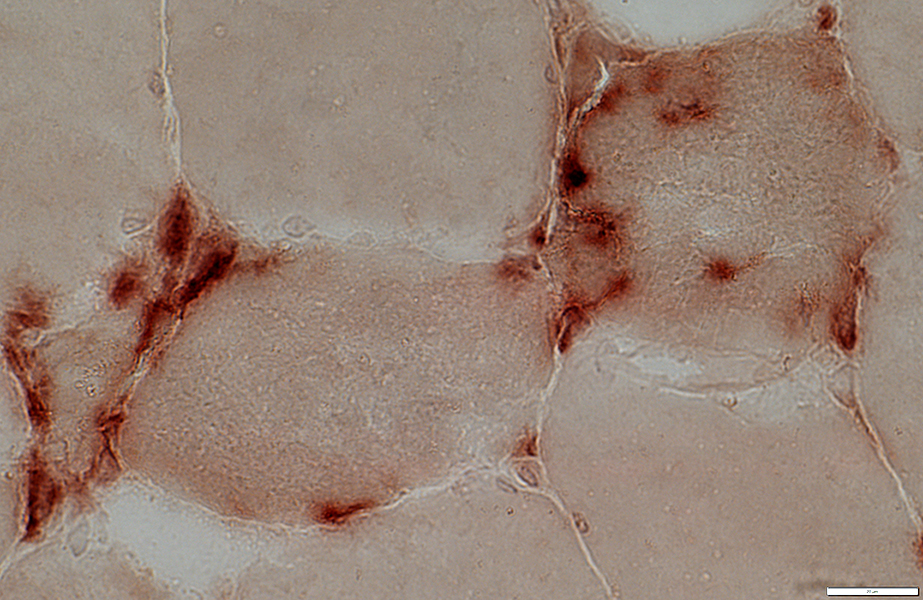 Acid Phosphatase stain |
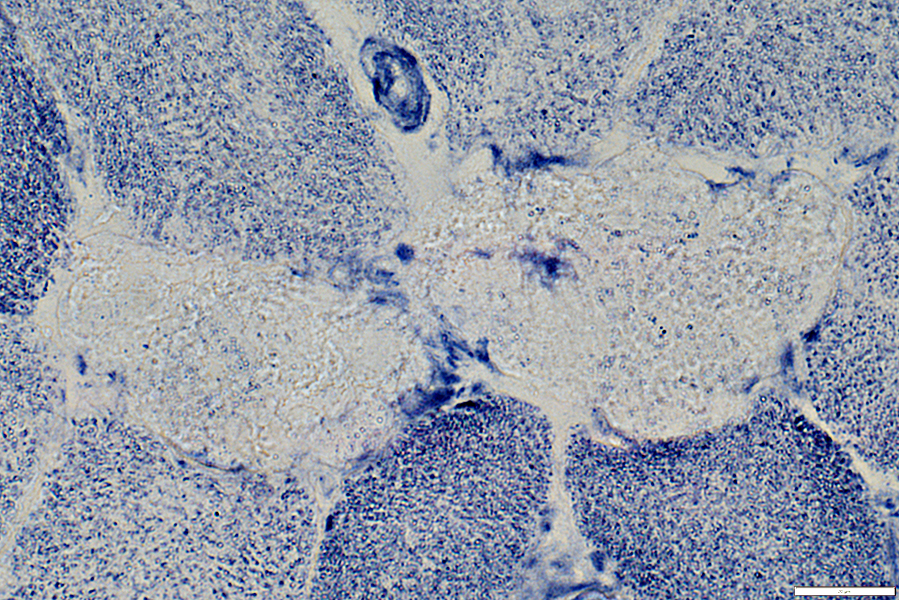 NADH stain |
Pale stain on NADH: Typical of all types of muscle fiber necrosis
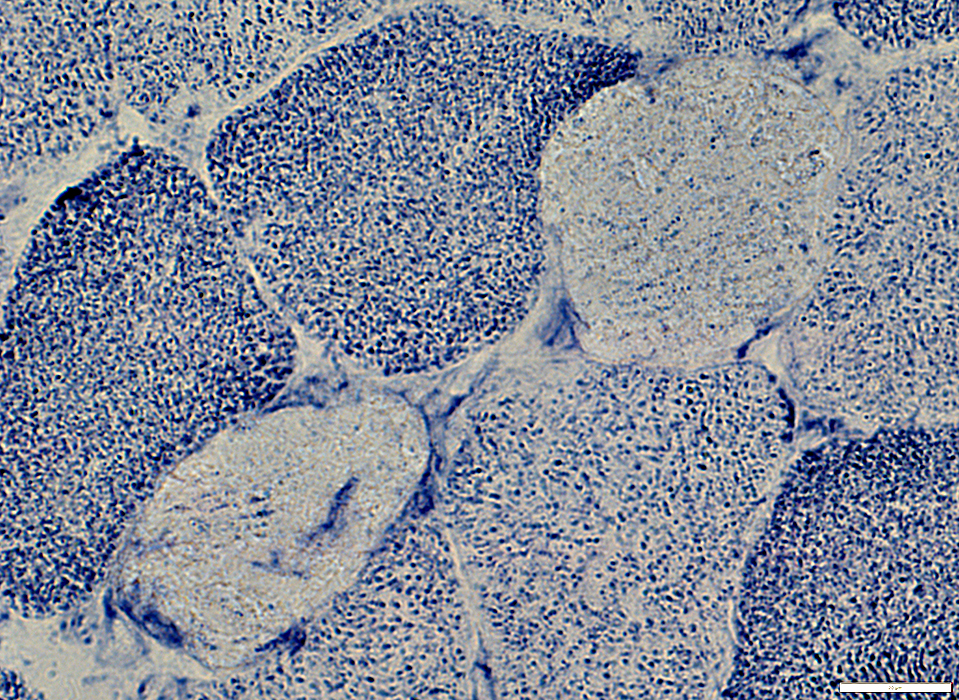 NADH stain |
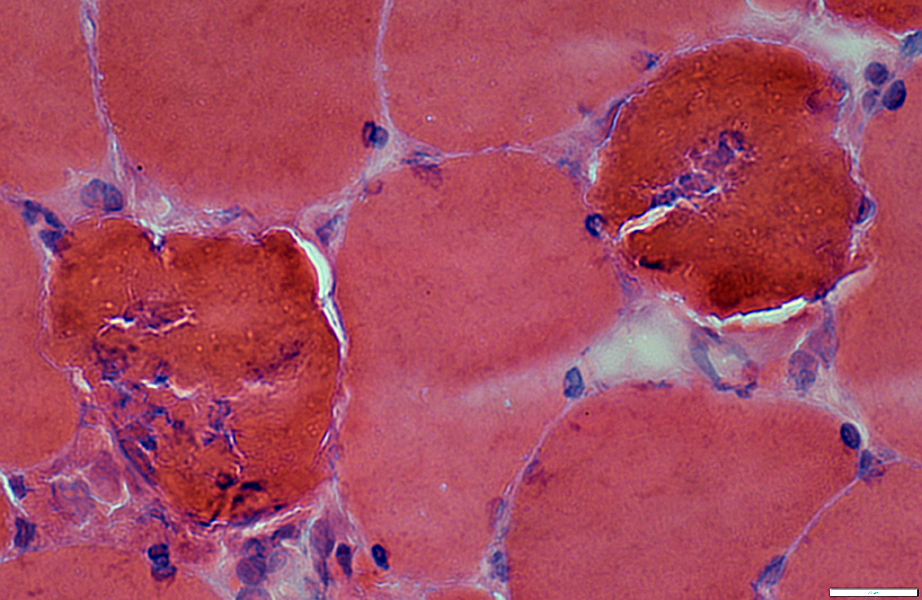 H&E stain |
Dark necrotic fibers may become
Invaded by histiocytes (Above & Below)
Degenerated with pale, fragmented cytoplasm but no associated histiocytes
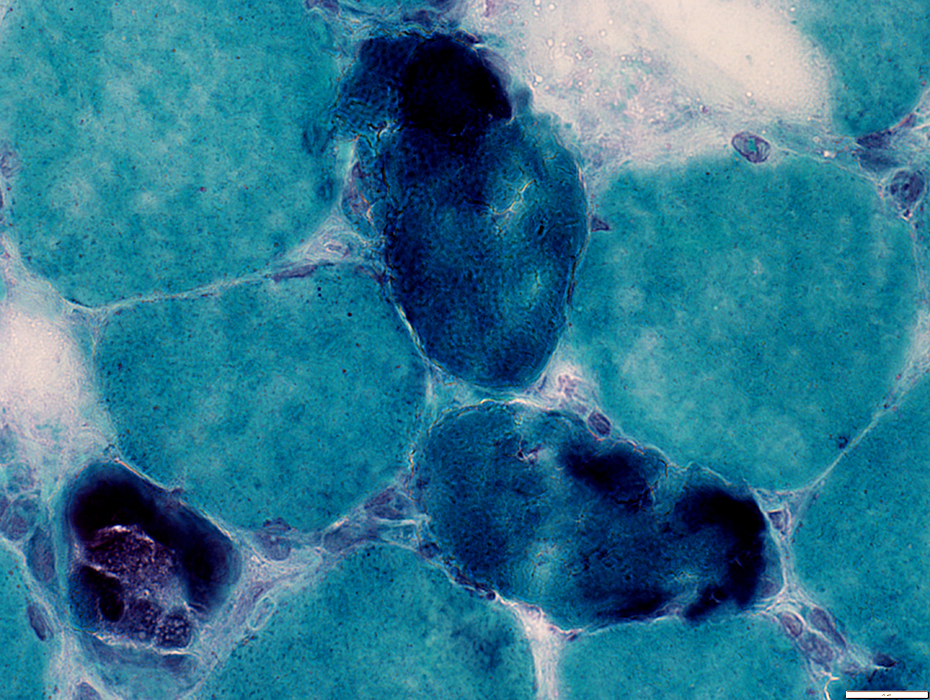 Gomori trichrome stain |
Dark necrotic muscle fibers: Slightly later stage
Dark necrotic fibers may become
Invaded by histiocytes
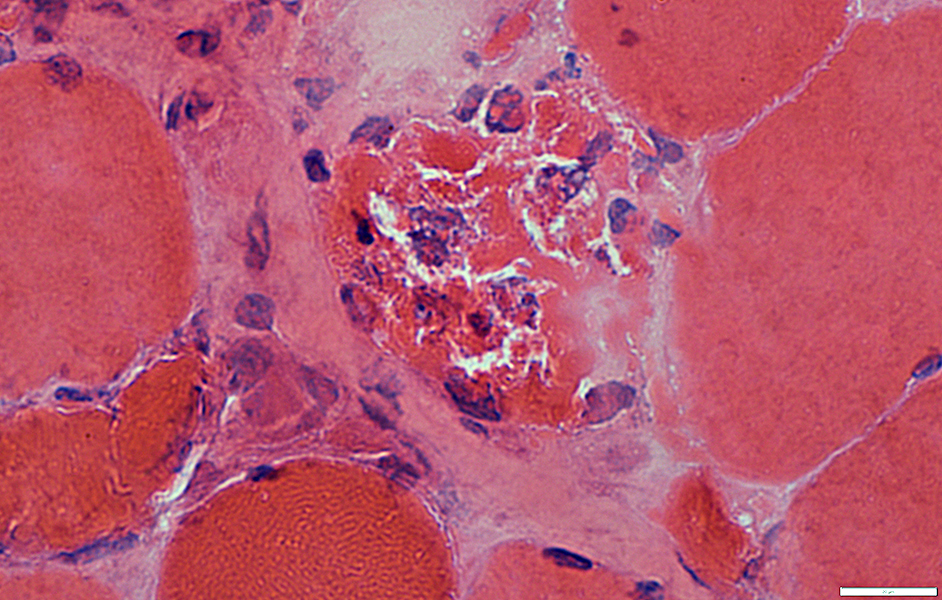 H&E stain |
Phosphorylase Deficiency: Post-Rhabdomyolysis
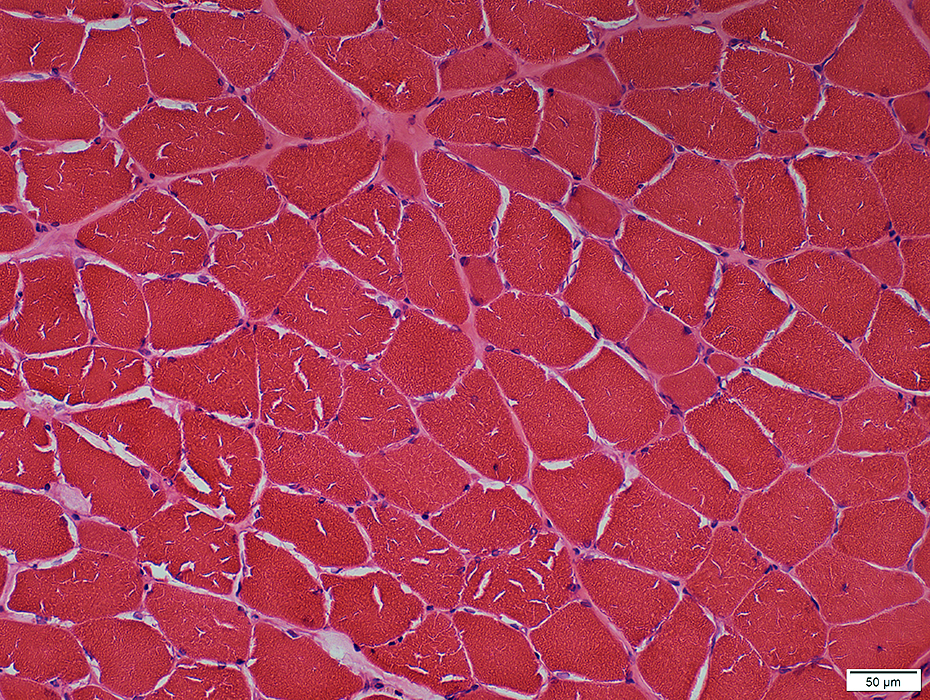 H&E stain |
Internal architecture: Cracks & Clefts
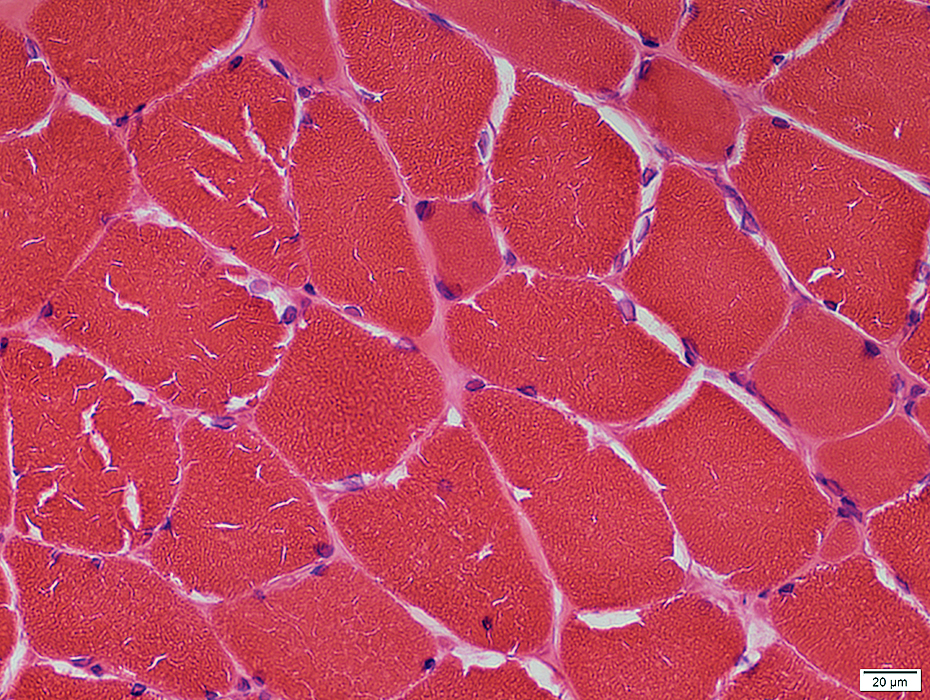 H&E stain |
Subsarcolemmal Blebs
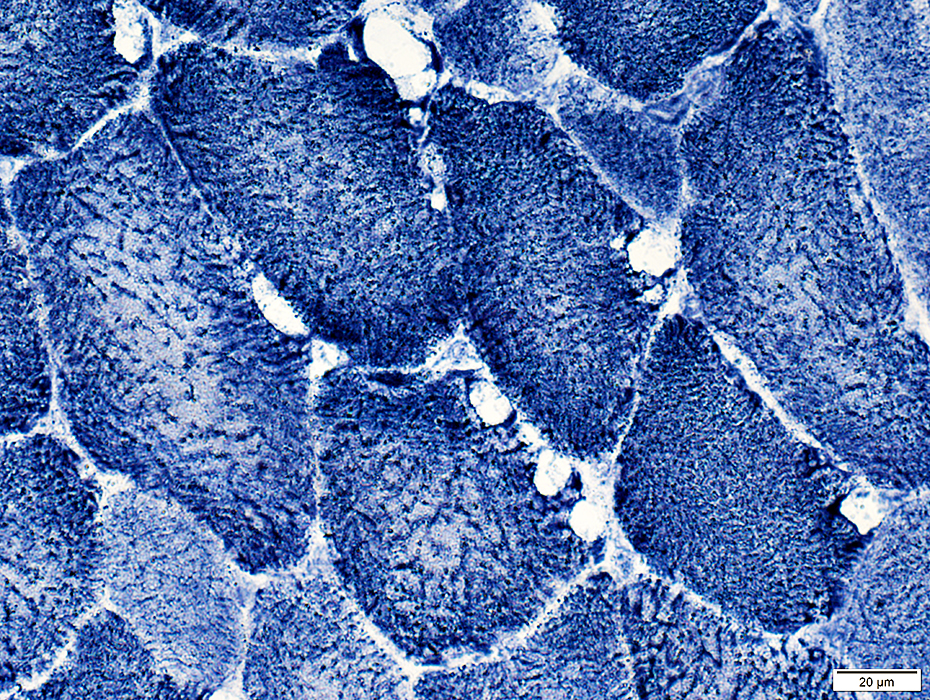 NADH stain |
Post Necrosis
Residual histiocytic, Acid phosphatase-positive, cells scattered in endomysium
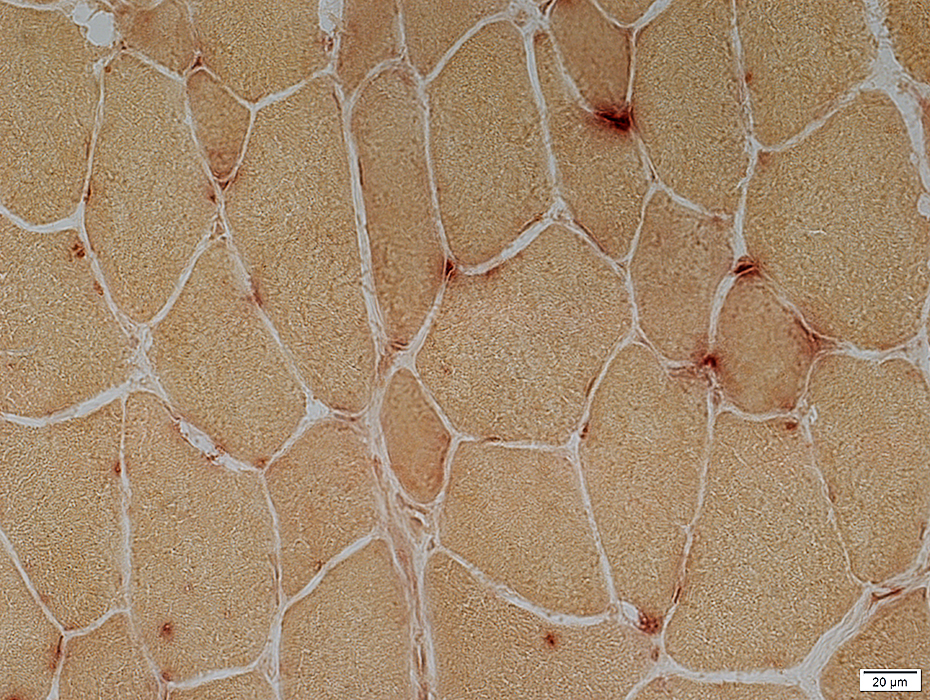 Acid phosphatase stain |
Glycogen: PAS positive areas in muscle fiber cytoplasm
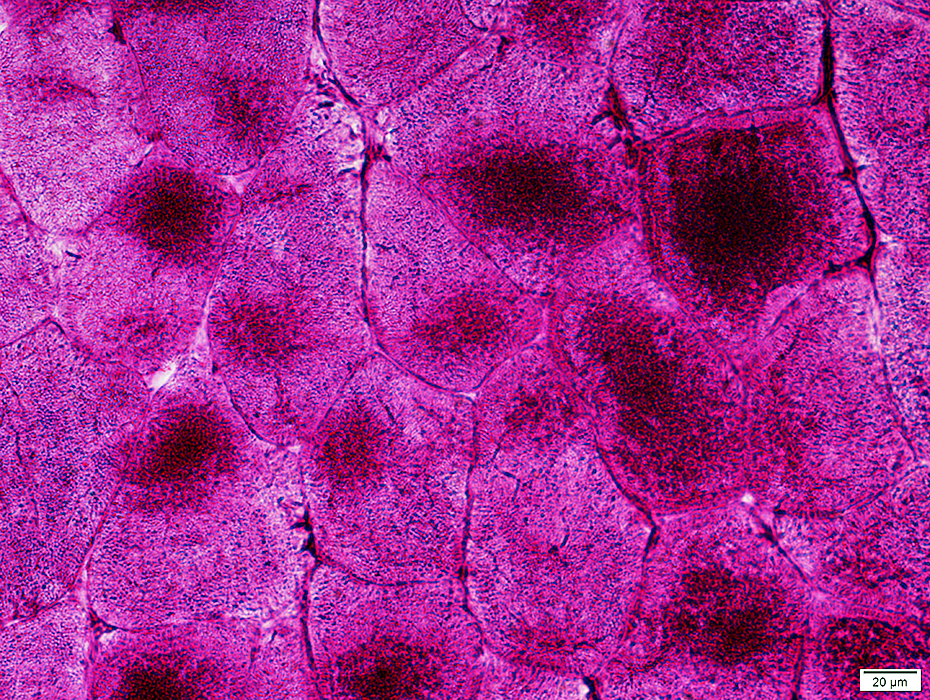 PAS stain |
Immaturity: Many intermediate-stained (Type 2C) fibers
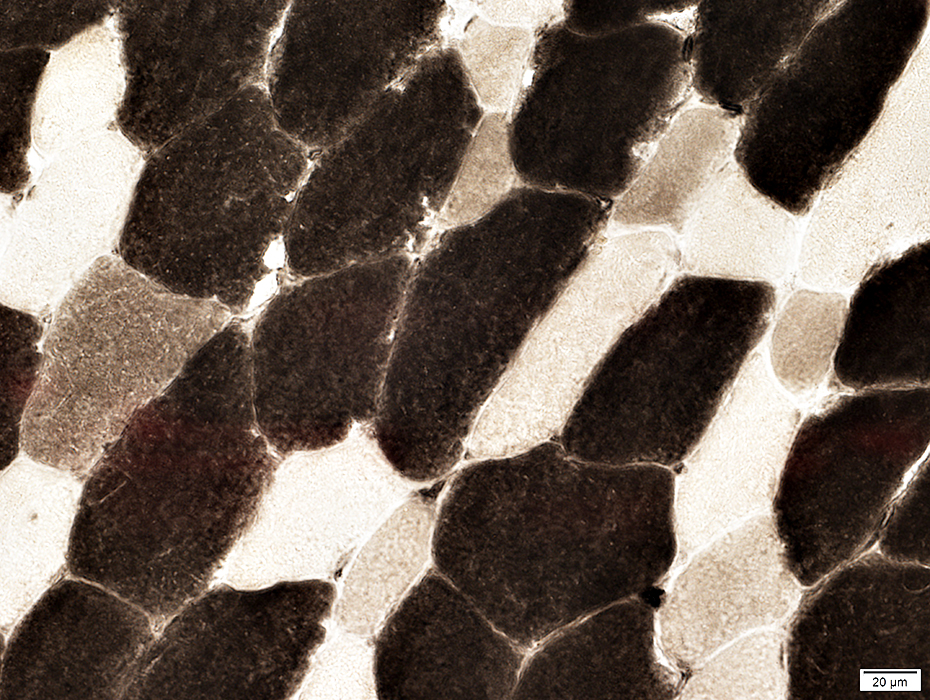 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Phosphorylase: Many immature or small muscle fibers express an immature form of phosphorylase
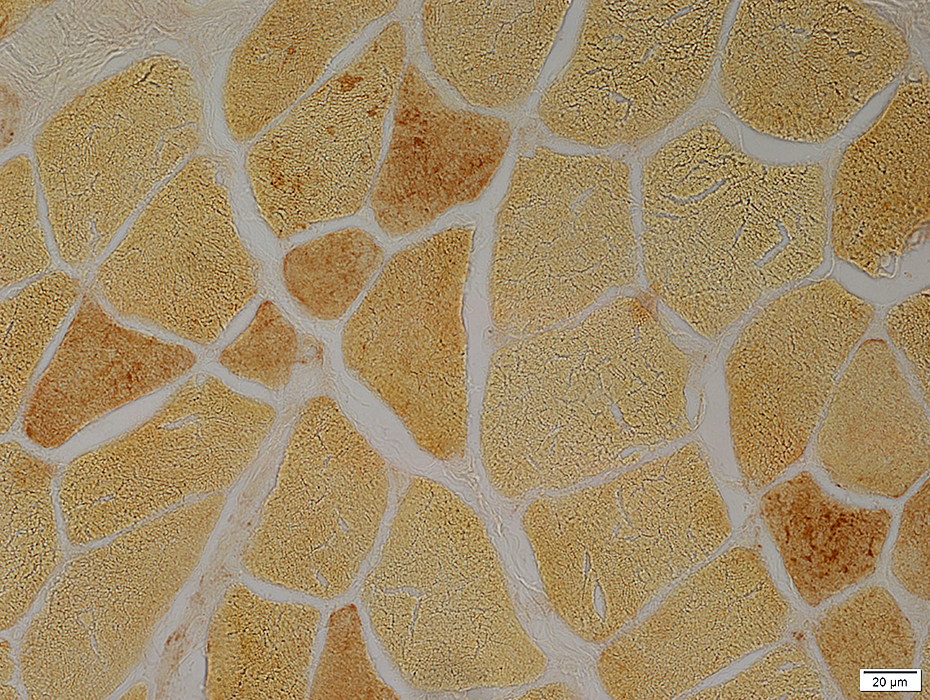 Phosphorylase stain |
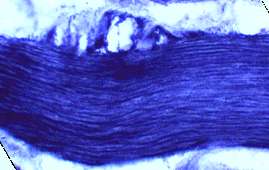
Phosphorylase Deficiency: Fixed muscle & Ultrastructure
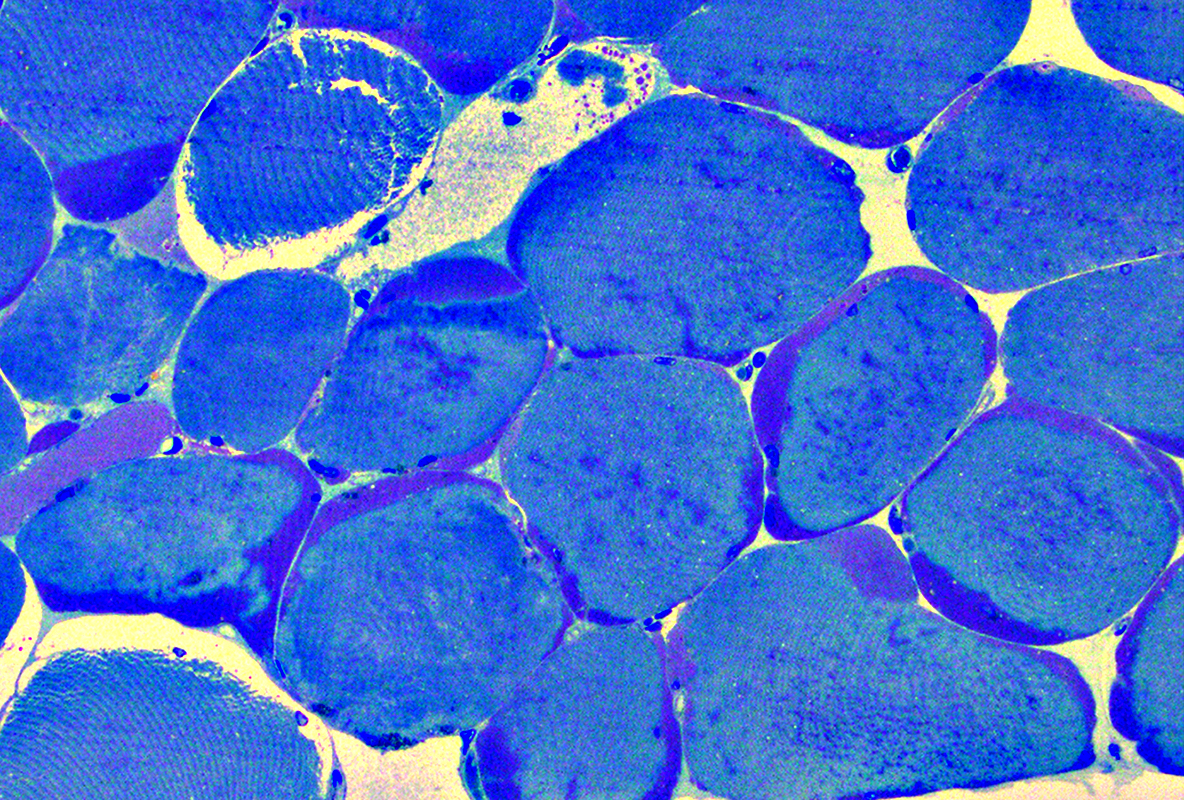 Toluidine blue-stained plastic section From: Mari Perez-Rosendahl |
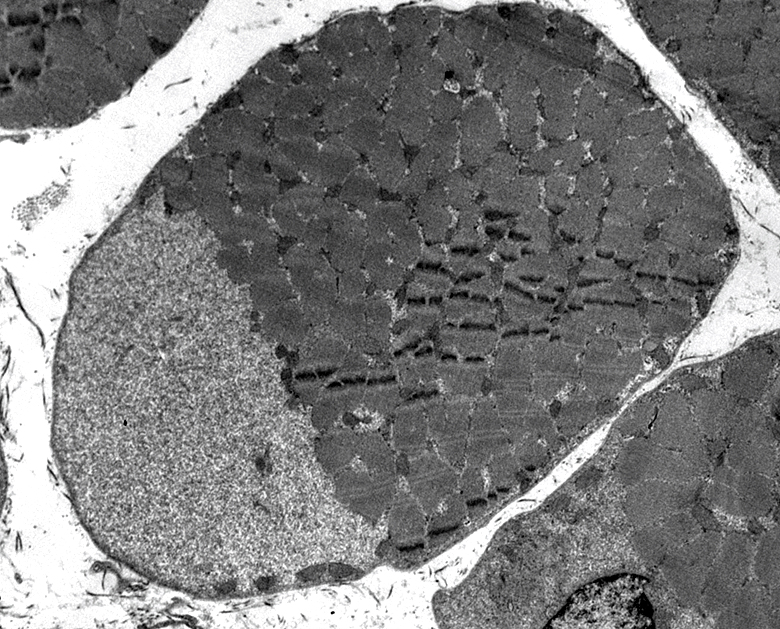 From: S Moore |
Contain Glycogen granules
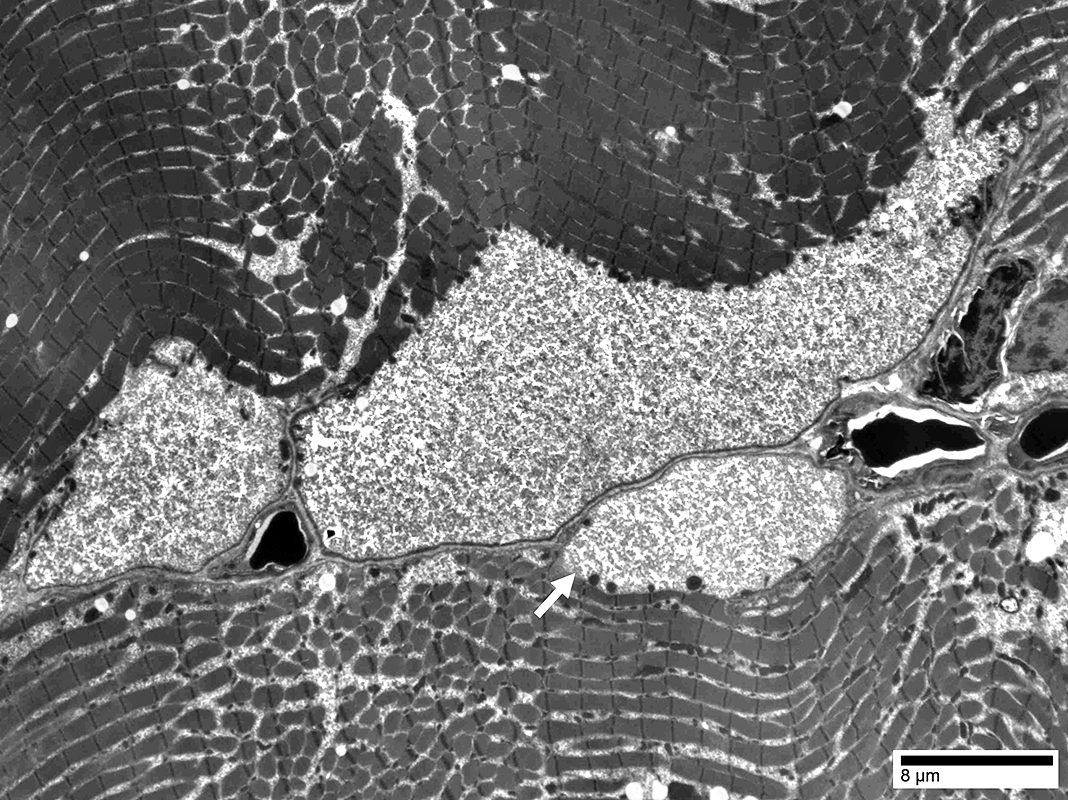 From: Chunyu Cai |
Some contain Glycogen granules (Arrow)
Others have no contents (below)
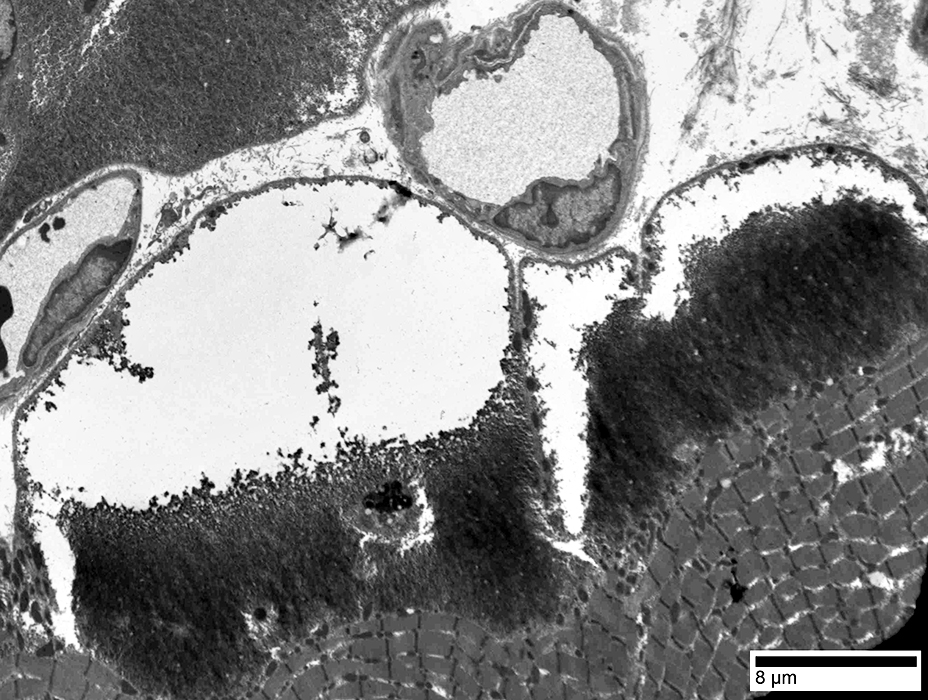 From: Chunyu Cai |
Glycogen granules in Bleb
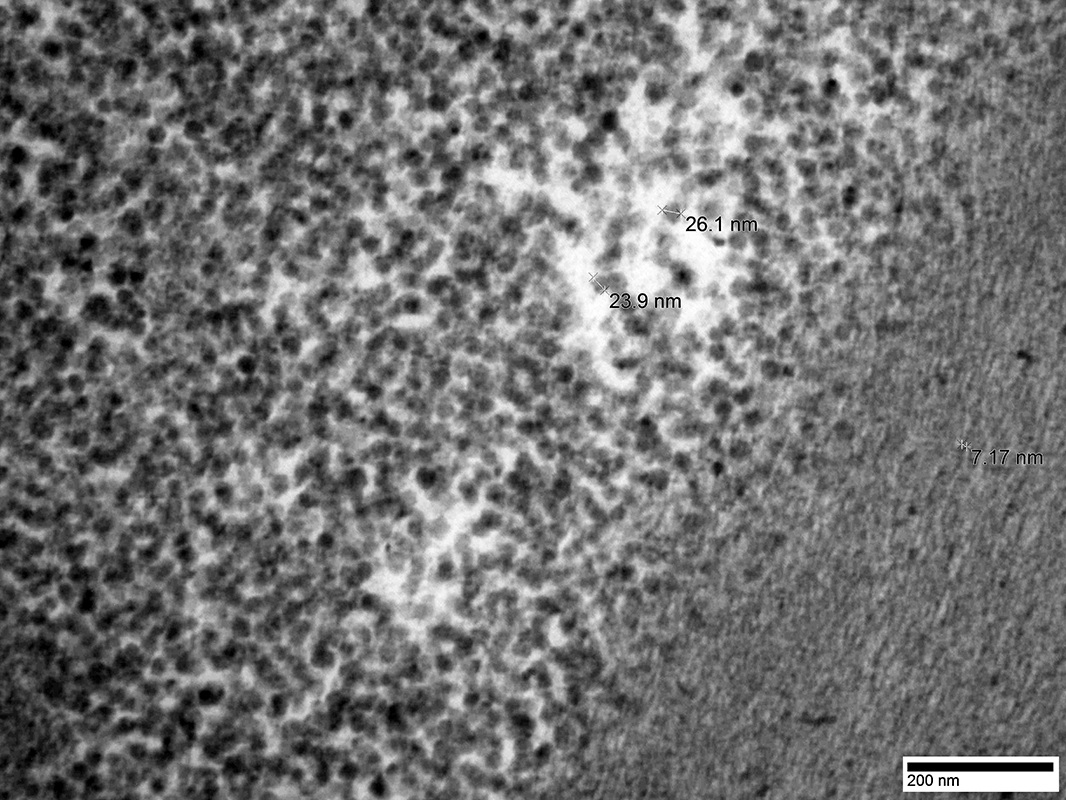 From: Chunyu Cai |
Phosphorylase Deficiency: Spindle
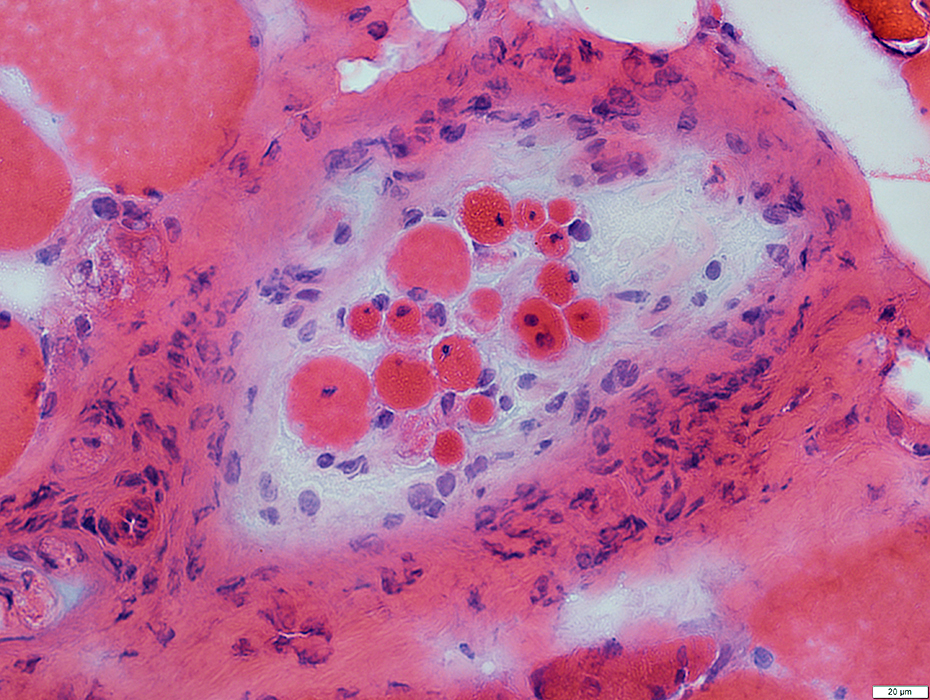 H&E stain |
Also see: Acid maltase deficiency: Adult; Child
Return to Glycogen storage disorders
Return to Muscle biopsies
Return to Pathology images
11/7/2022