ACID MALTASE DEFICIENCY: INFANT & EARLY CHILDHOOD ONSET
|
Adult pathology Child pathology 1 year 1 year, Post treatment 1 month |
Acid Maltase Deficiency: 1 year-old Child
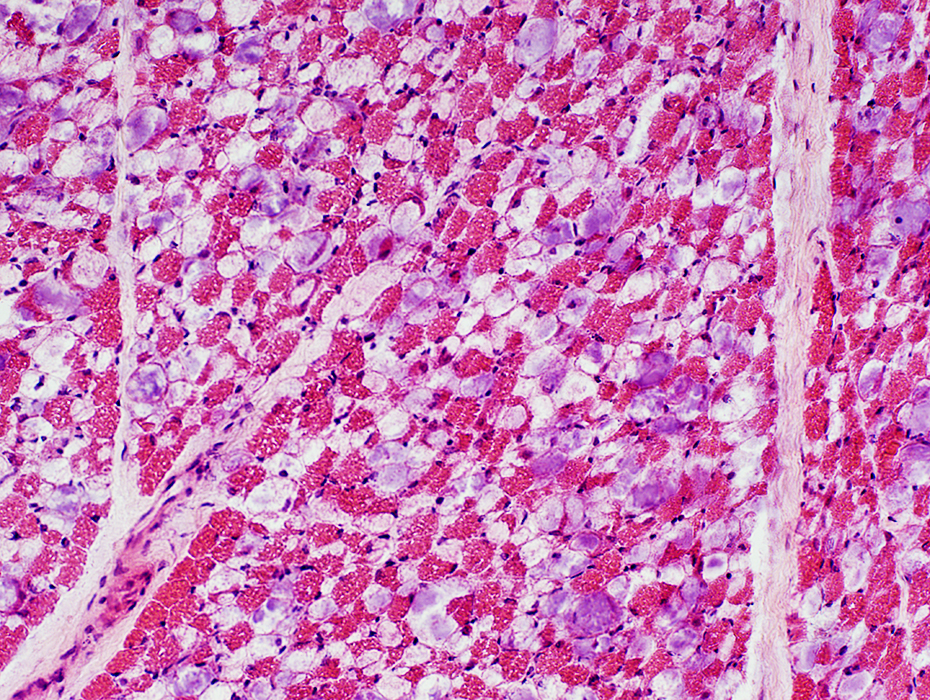 H & E stain Storage material in many muscle fibers |
- Storage material & Vacuoles in many muscle fibers
- Cytoplasm is replaced by
- Storage material: 2 types; Clear or Purple
- Vacuoles: Moderate-sized, Clear, Round
- Post treatment
- Clear storage material is reduced in amount
- Most storage material is purple
- Some muscle fibers are enlarged
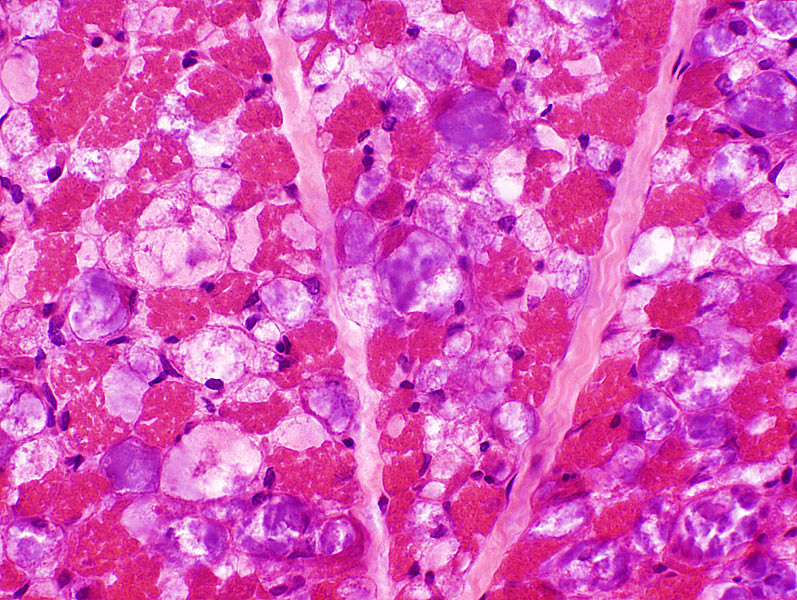 H & E stain |
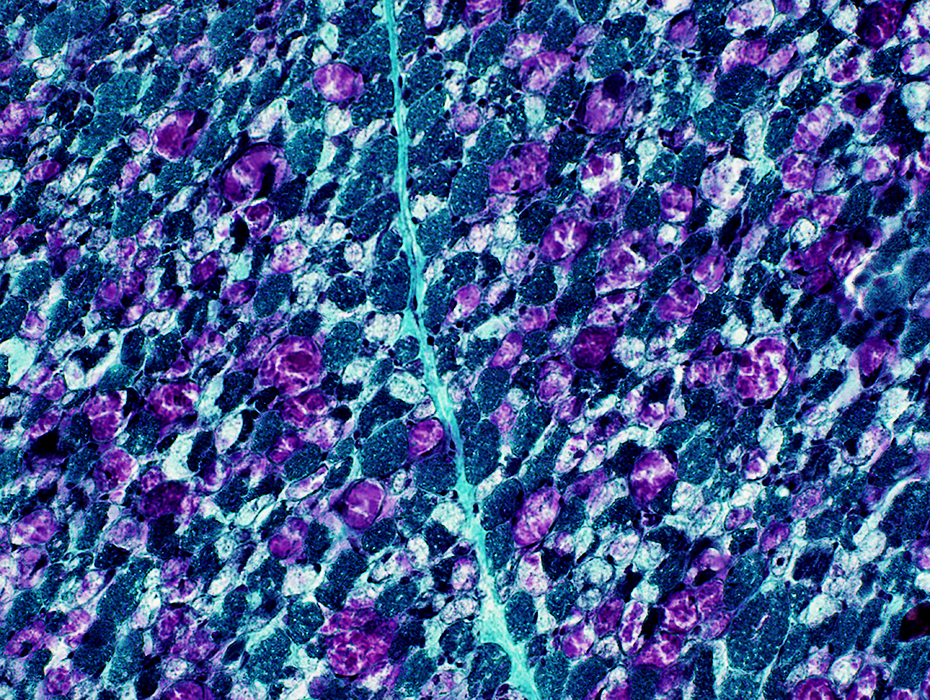 Gomori trichrome stain |
- Cytoplasm is replaced by
- Storage material & Vacuoles in many muscle fibers
- Storage material: 2 types; Clear or Purple
- Vacuoles: Moderate-sized, Clear, Round
- Post treatment
- Clear storage material is reduced in amount
- Most storage material is purple
- Some muscle fibers are enlarged
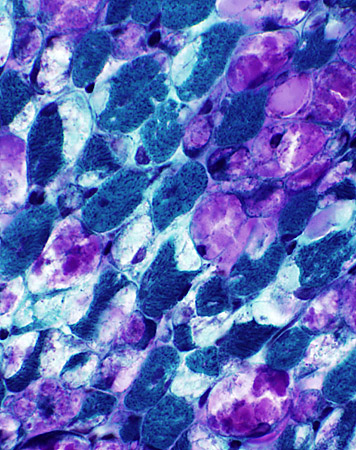 Gomori trichrome stain |
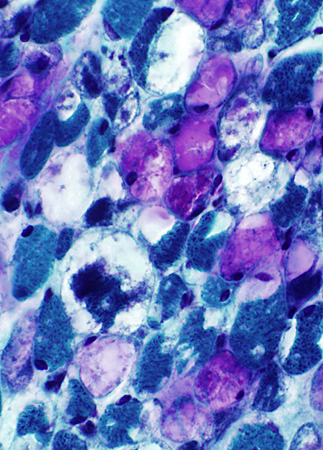 Gomori trichrome stain |
Cytoplasmic membranes (NADH+ Endoplasmic reticulum): Displaced by storage material
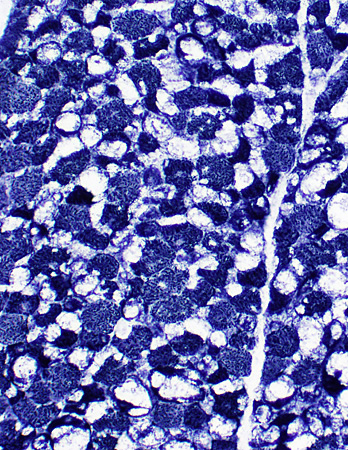 NADH stain |
 NADH stain |
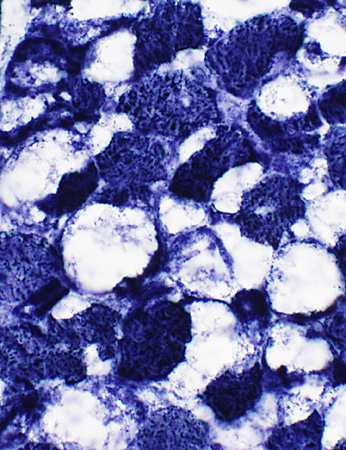
 PAS stain |
Glycogen: Diffusely increased staining in fibers
 PAS stain |
|
PAS-stained muscle fibers Diffusely increased staining in fibers |
ATPase stained muscle fibers Remaining intact fibers are mostly type 2 |
 PAS stain |
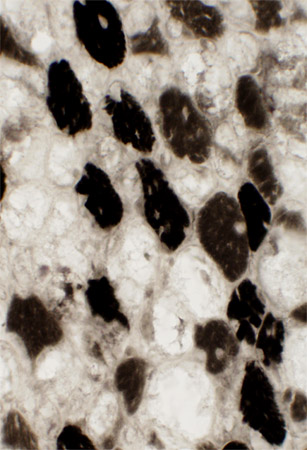 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
Acid phosphatase-stained muscle fibers
Location: Muscle fiber cytoplasm
Frequency: Scattered muscle fibers
Pattern: Diffuse; Few acid phosphatase positive granules
Compare to: Post treatment
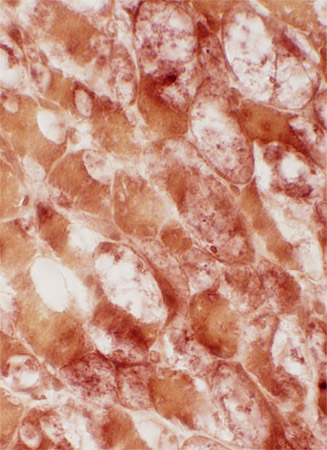 Acid phosphatase stain |
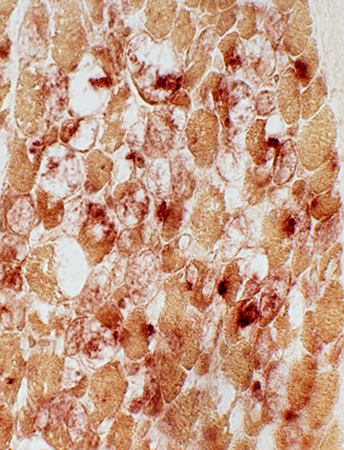 Acid phosphatase stain |
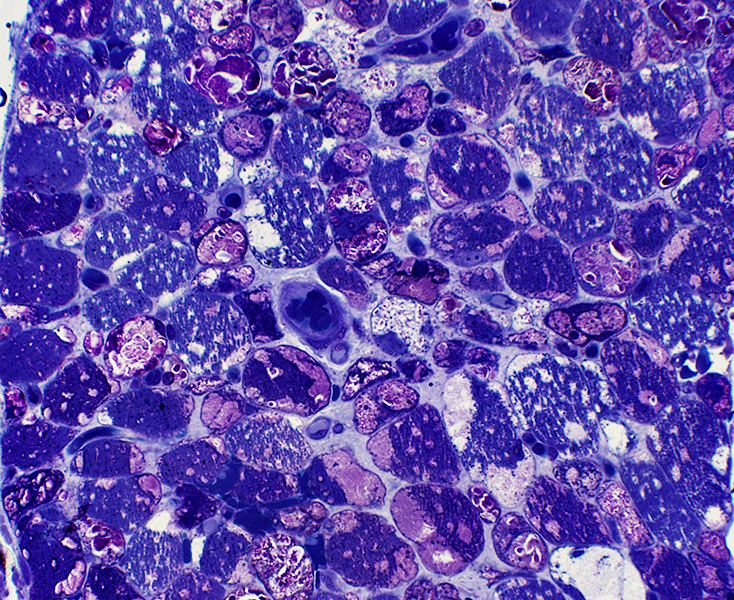 Toluidine blue stained plastic sections |
Replaces regions of cytopasm in many muscle fibers
May be free in cytoplasm or membrane-bound
Autophagic Vacuoles
Present in muscle fiber cytoplasm (Below; Left)
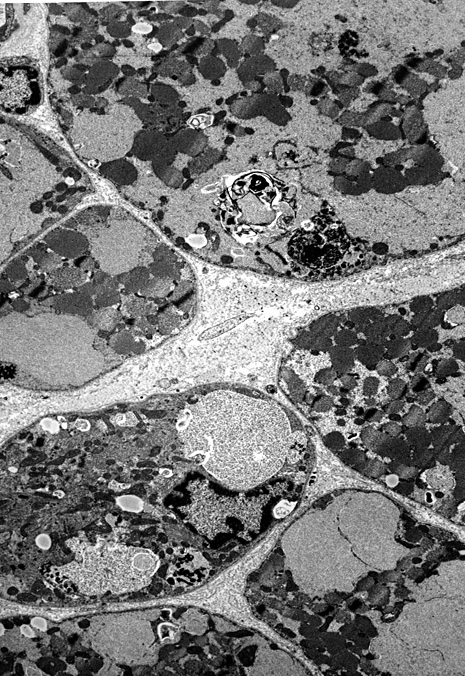 Earlier stage: Most glycogen storage is in membrane bound structures |
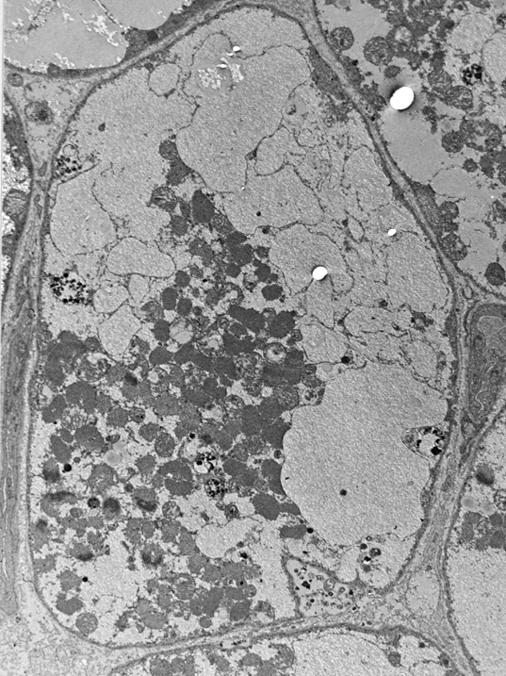 Later stage: More glycogen storage is in cytoplasm |
Acid maltase deficiency: Glycogen accumulation in other tissues
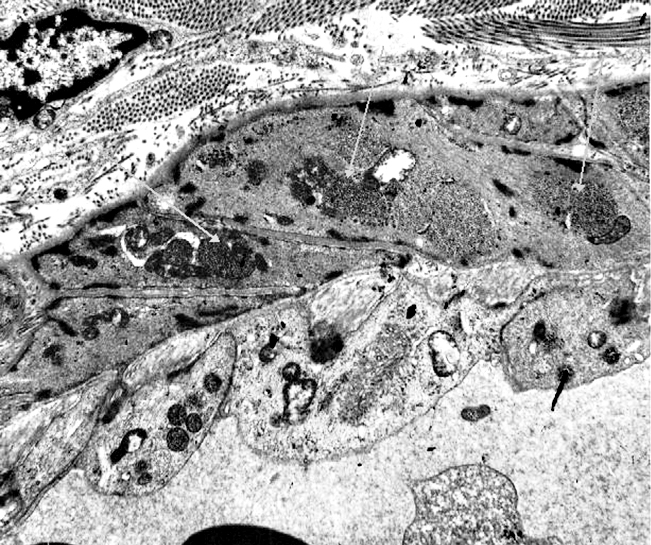 From L Gutmann Acid maltase deficiency: Glycogen deposits (Gray arrows) in smooth muscle cells in vessel walls |
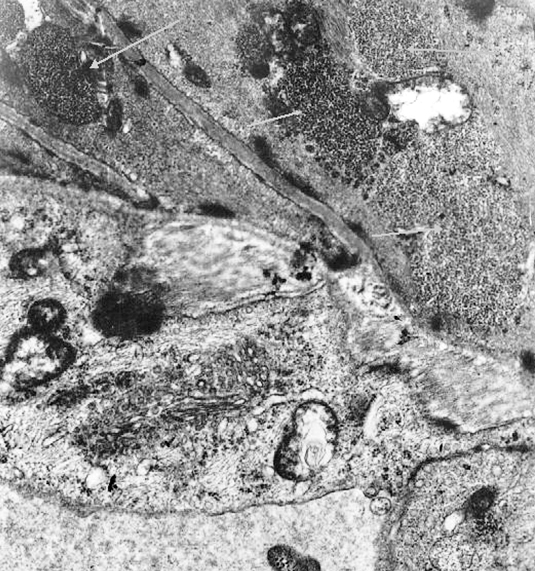
|
Acid maltase deficiency: Glycogen deposits in CNS neurons
Cortex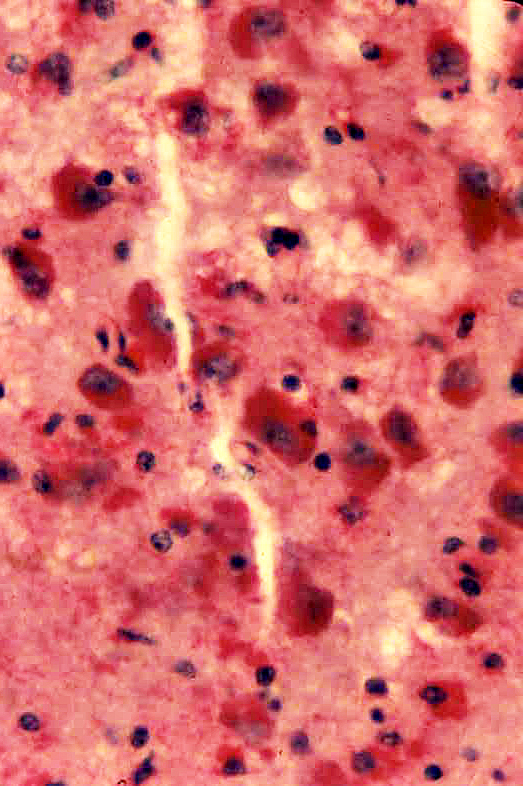
|
Motor neurons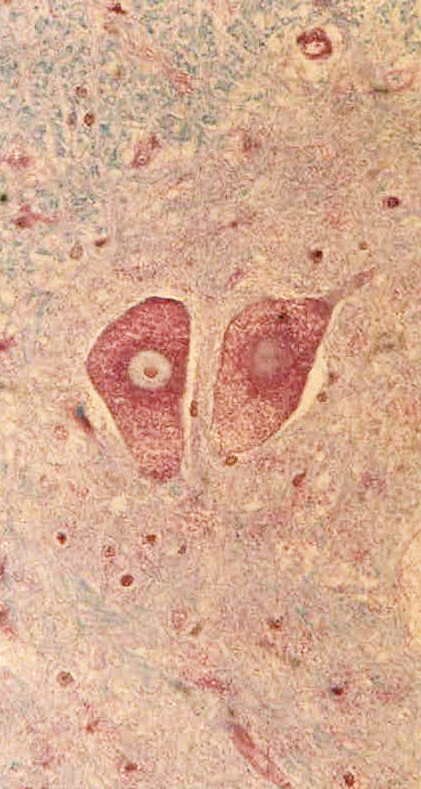
|
Acid Maltase Deficiency: 1 year-old Child, Post Treatment
 H&E stain |
- Storage material replaces cytoplasm in many muscle fibers
- Cytoplasm is replaced by
- Storage: Mostly Purple; Few fibers with clear-stained material
- Compare to: Untreated patient
- Some muscle fibers are enlarged
 H&E stain |
 H&E stain |
 H&E stain |
 H&E stain |
 H&E stain |
 Gomori trichrome stain |
- Storage material replaces cytoplasm in many muscle fibers
- Cytoplasm is replaced by
- Storage: Mostly Purple; Few fibers with clear-stained material
- Compare to: Untreated patient
 Gomori trichrome stain |
 Gomori trichrome stain |
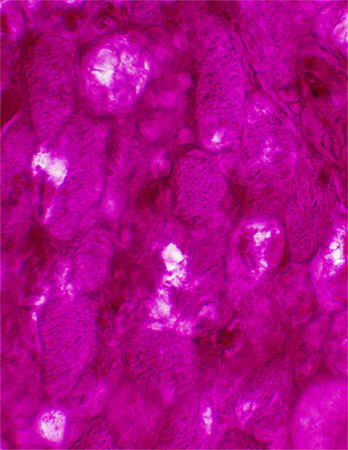
 Congo Red stain |
- Storage material replaces cytoplasm in many muscle fibers
- Cytoplasm is replaced by
- Storage: Mostly Purple; Few fibers with clear-stained material
- Compare to: Untreated patient
 Congo Red stain |
 Acid phosphatase stain |
- Cytoplasm: Most fibers diffusely stained by Acid phosphatase
- Compare to: Untreated patient
 Acid phosphatase stain |
 Acid phosphatase stain |
 PAS stain |
 PAS stain |
 PAS stain |
 VvG stain |
 VvG stain |
 Esterase stain |
 Esterase stain |
|
NADH stain |
 NADH stain |
 NADH stain |
 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Acid Maltase Deficiency: 1 month-old Child
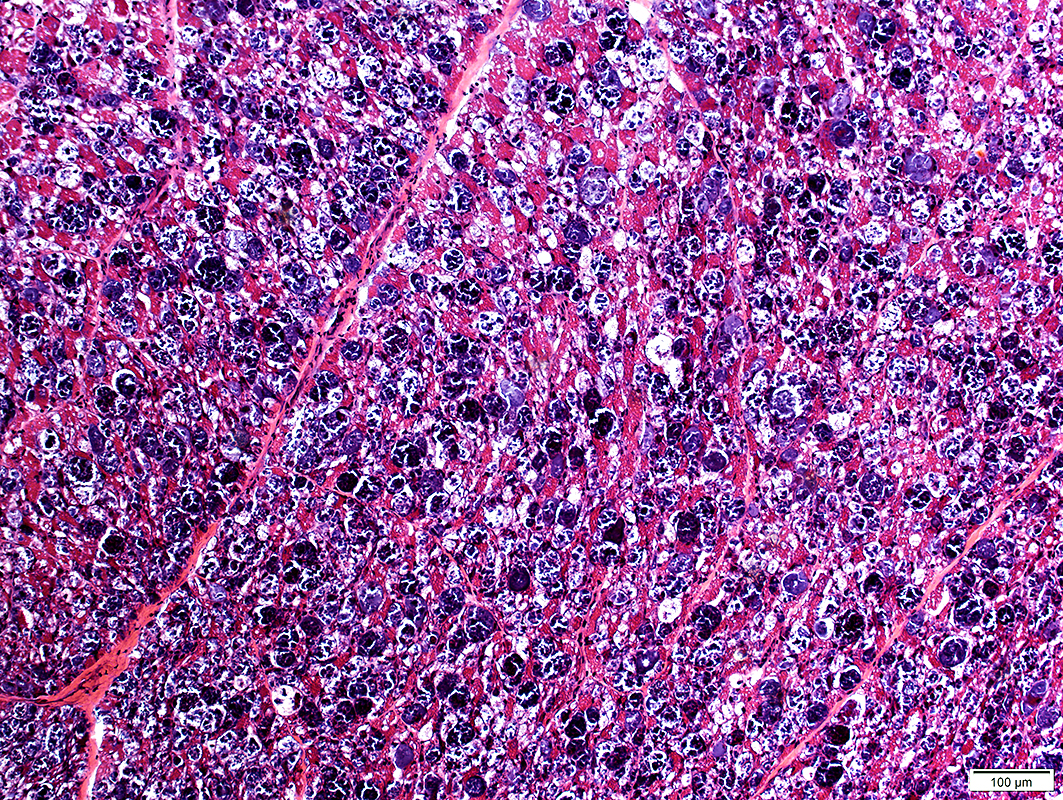 H&E stain |
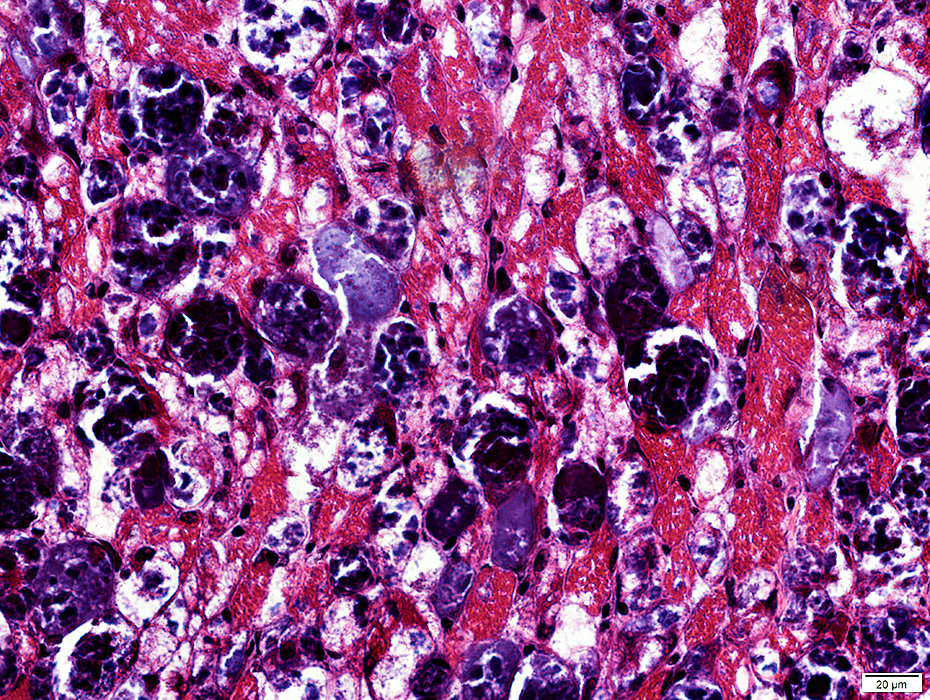 H&E stain |
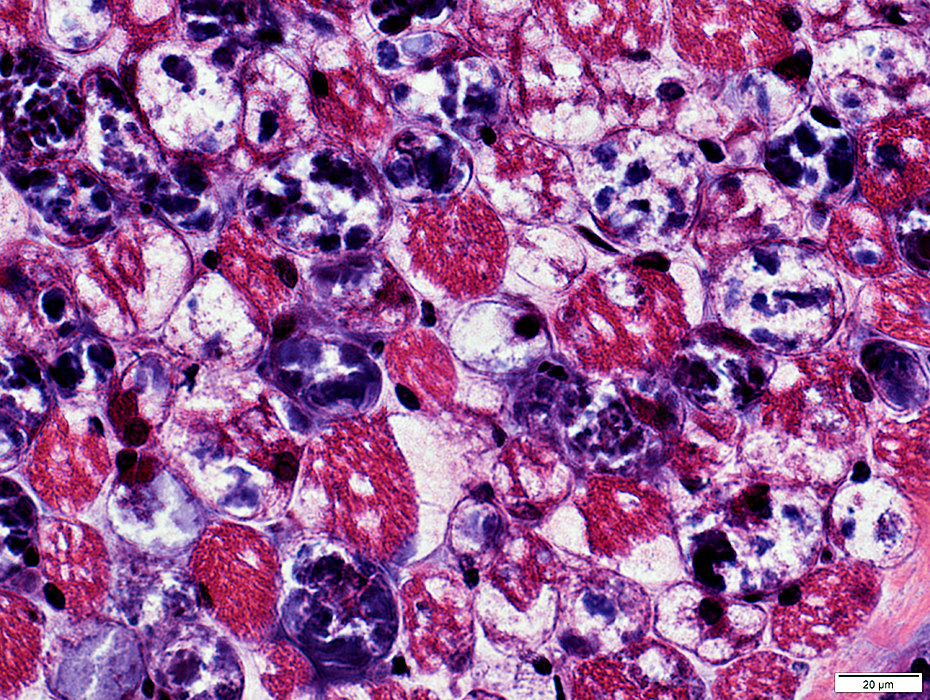 &E stain |
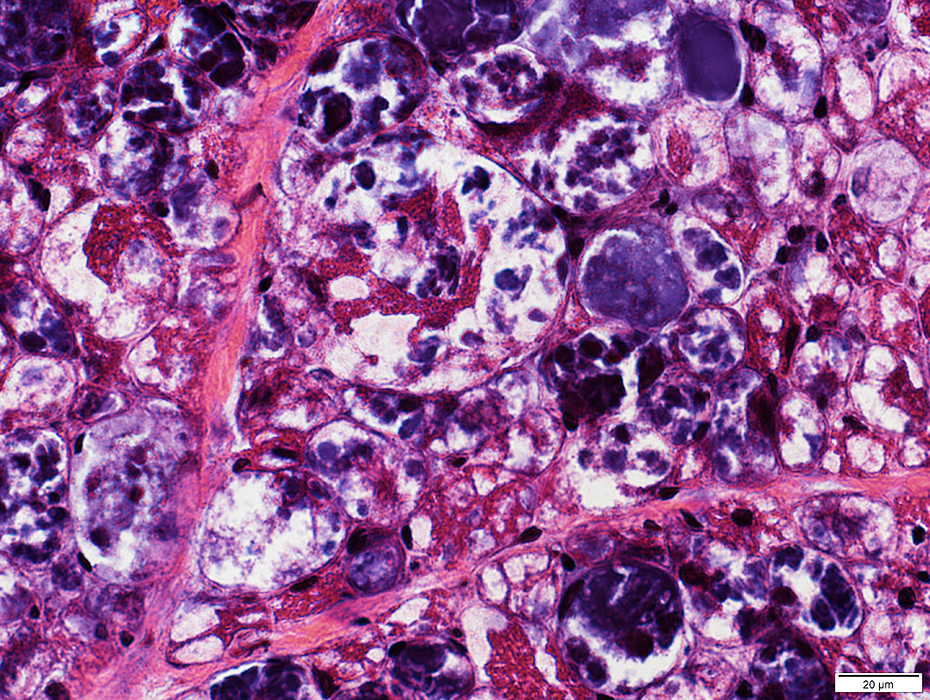 H&E stain |
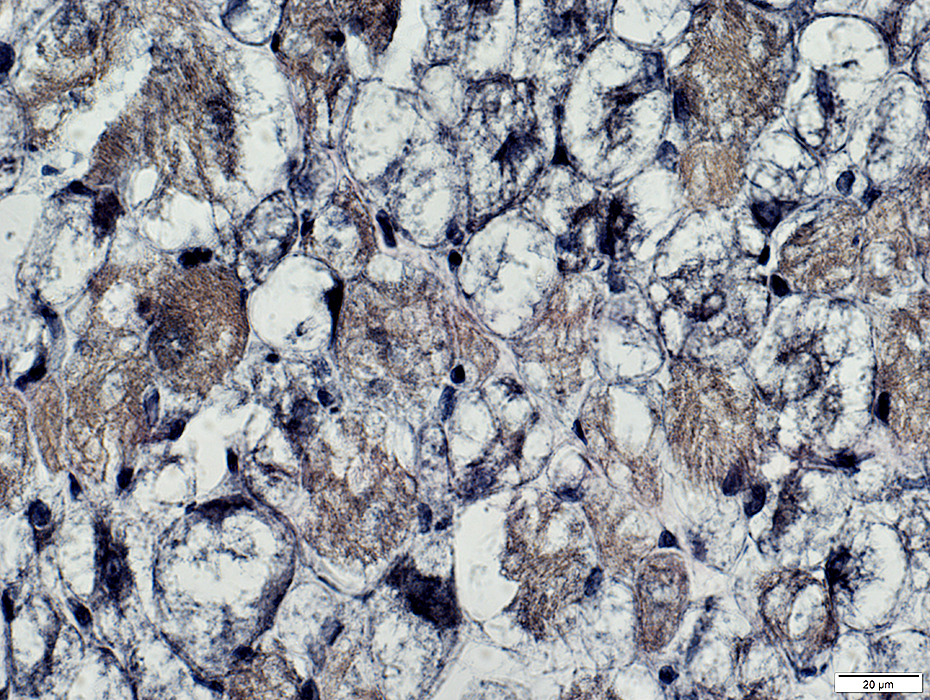 VvG stain |
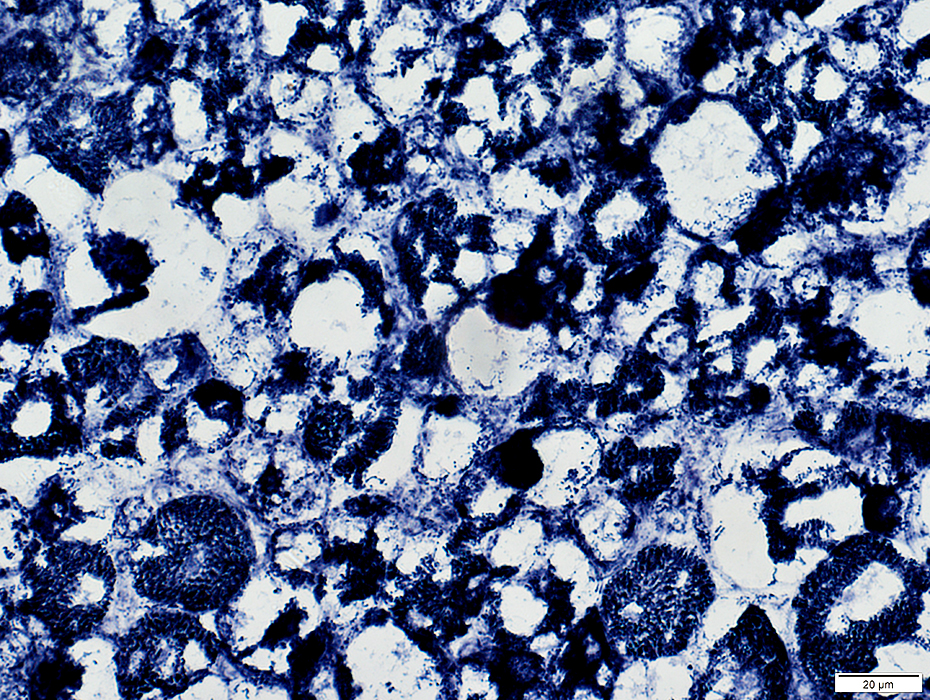 NADH stain |
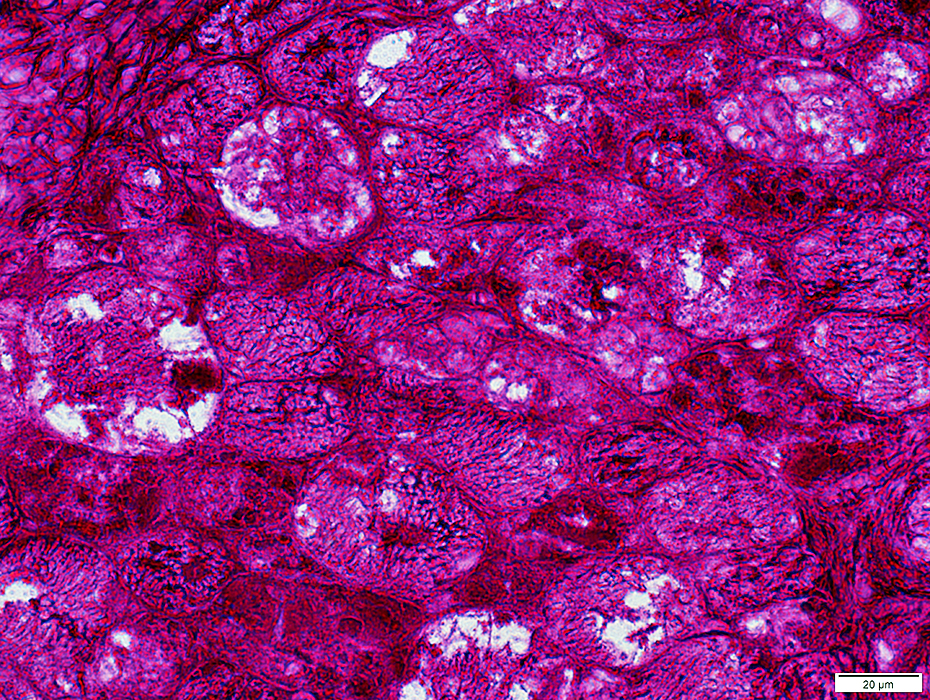 PAS stain |
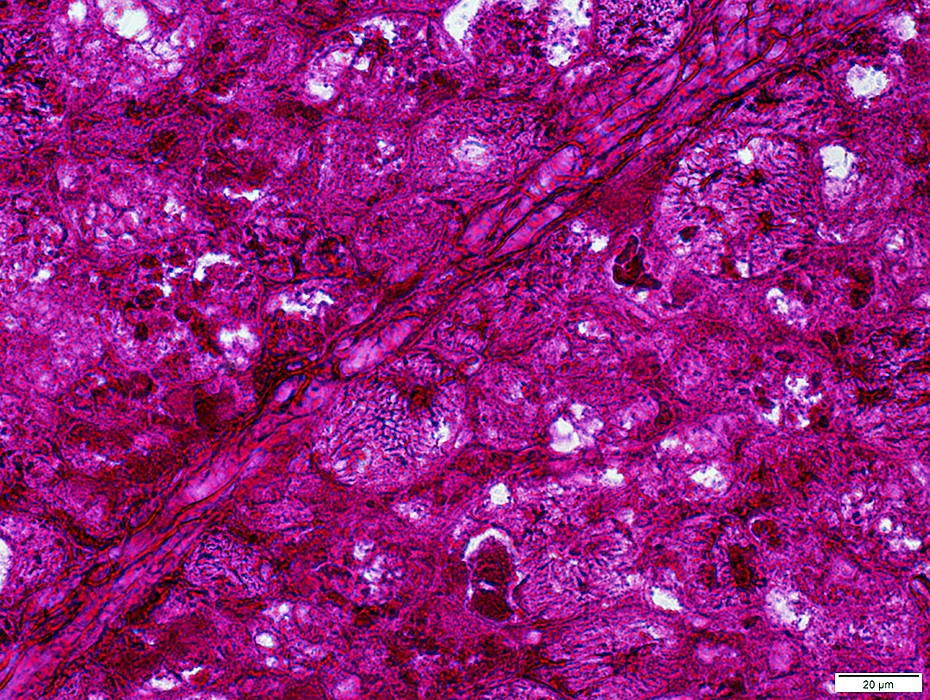 PAS stain |
Acid maltase deficiency: Neonatal
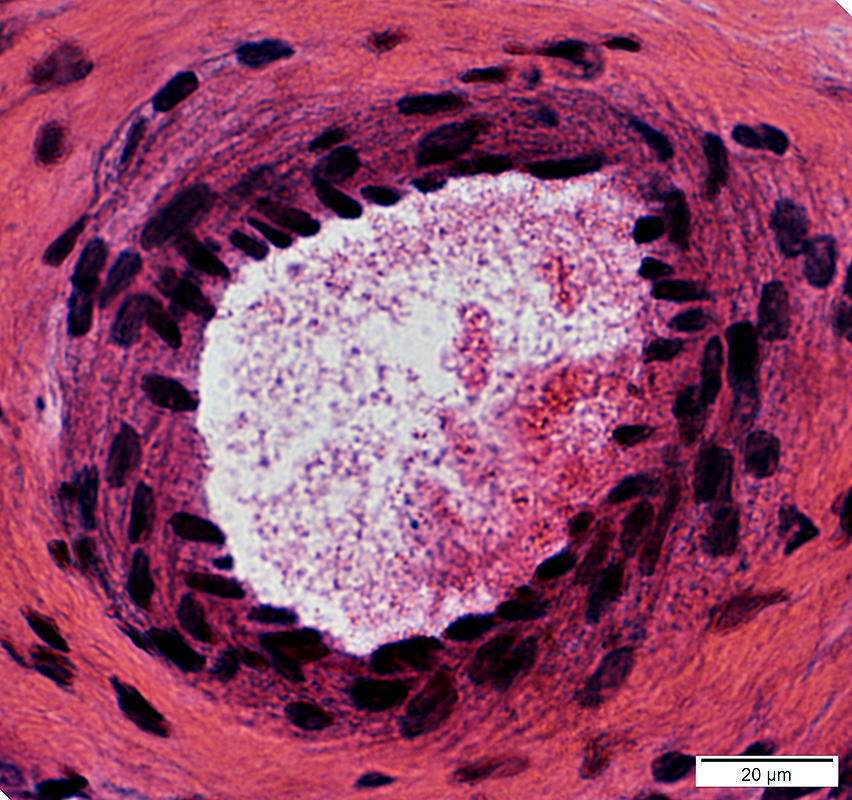 H&E stain |
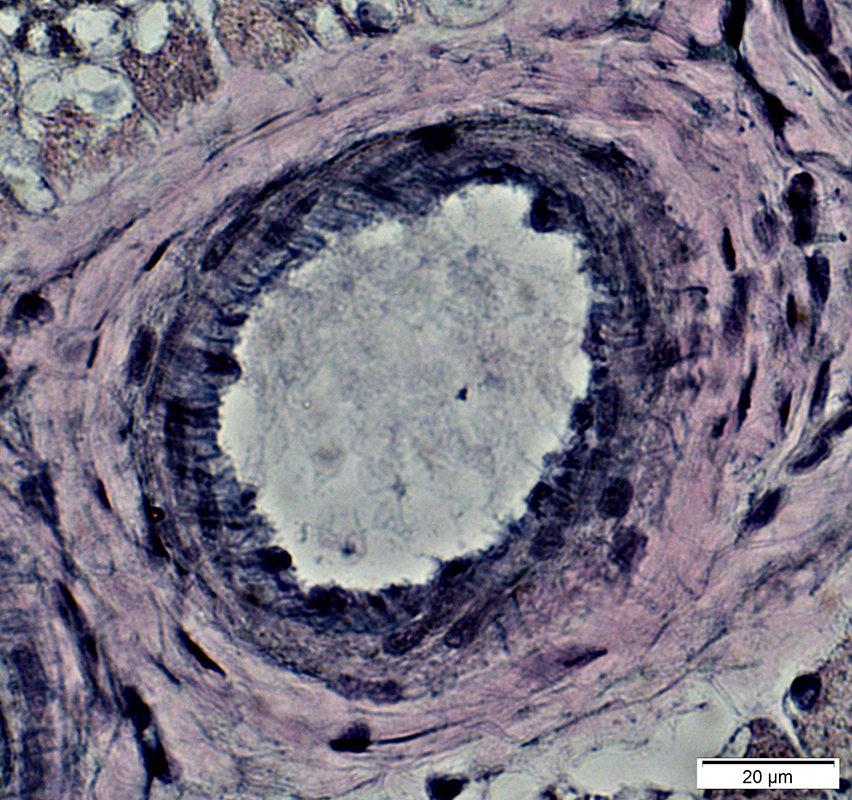 VvG stain |
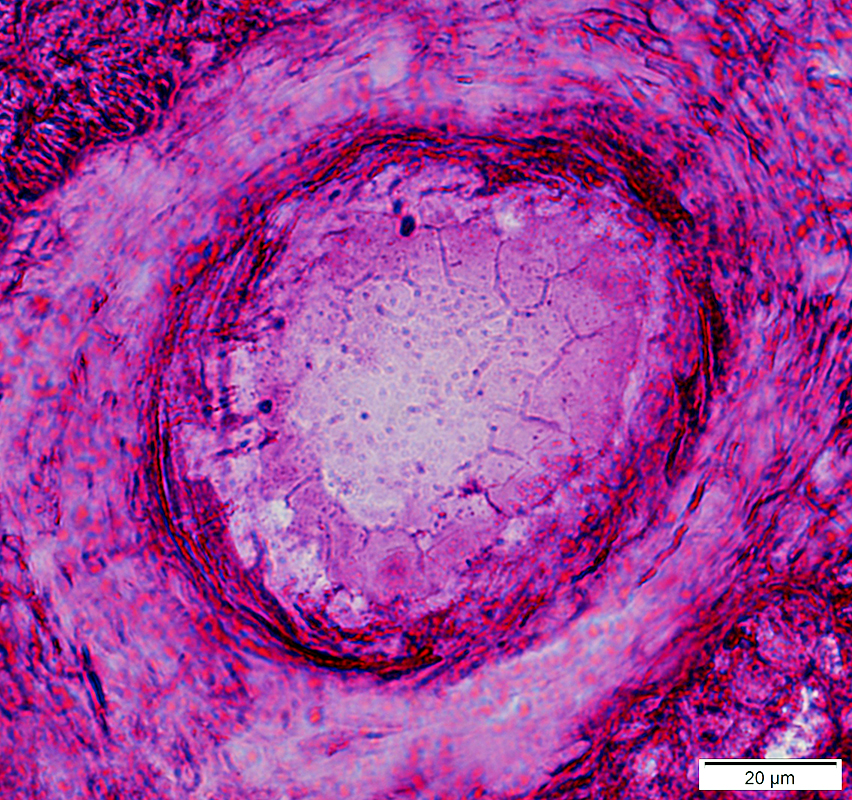 PAS stain |
Normal artery: PAS stain
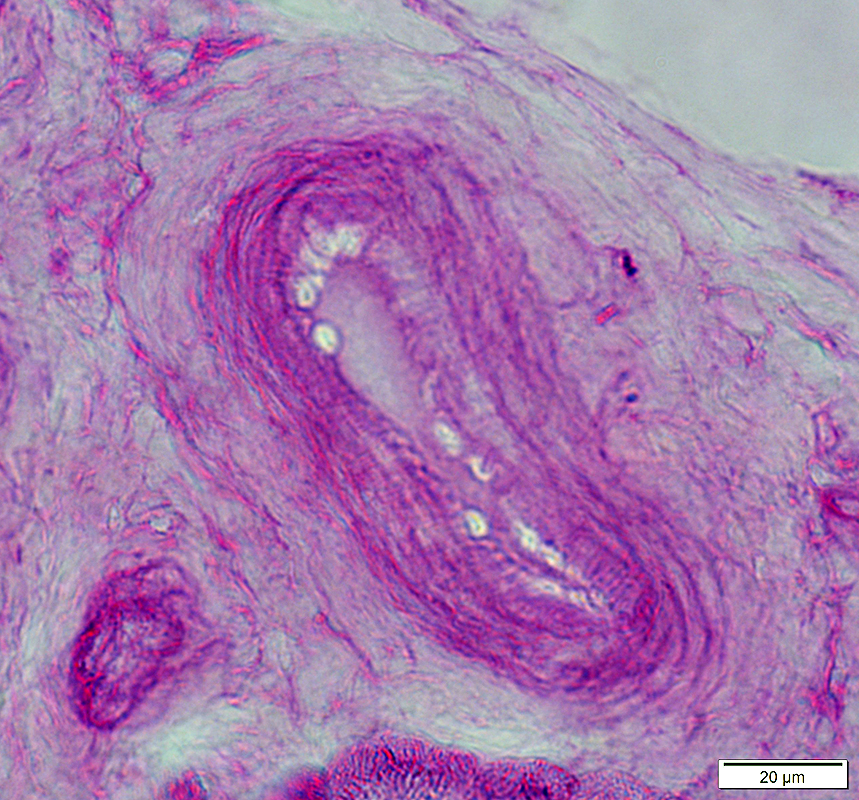 PAS stain |
Also see
Acid maltase deficiency: Later onset
Phosphorylase deficiency
Return to Glycogen disorders
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
9/8/2024