Statin Myopathy: Toxic 61
|
Muscle pathology Necrosis Early Membrane damage Cytoplasm pathology Ongoing Muscle fiber properties Alkaline Phosphatase ATPase PAS Also see Necrosis: General features |
Myofiber Necrosis: Statin Toxicity Muscle Membrane Damage 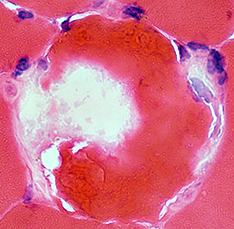 Muscle Fiber Cytoplasm 2 regions of staining Pale "C" or Δ Lesion Dark Regional Hypercontraction |
 H&E stain |
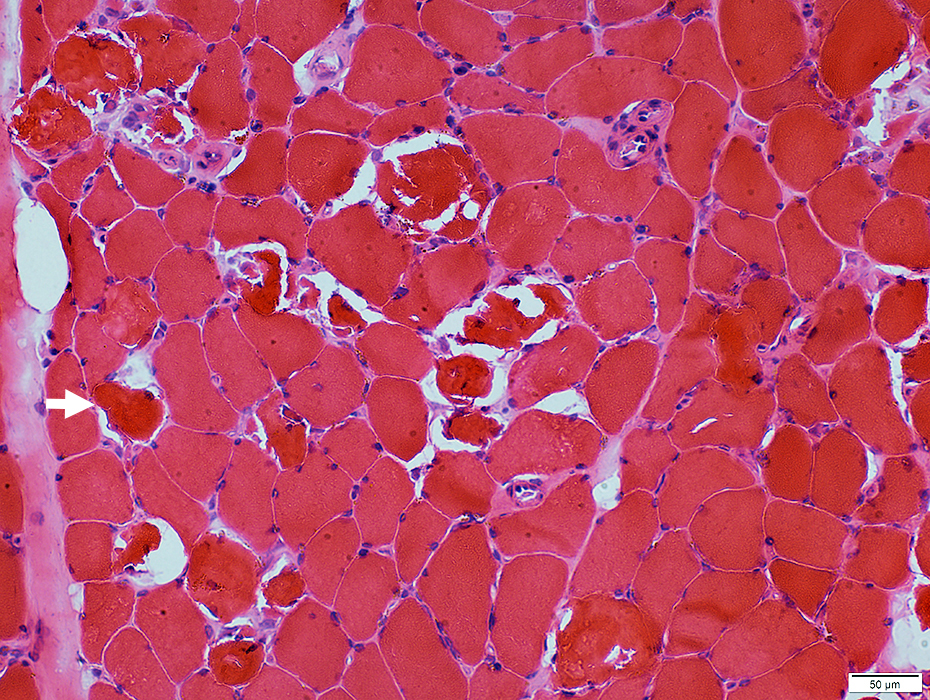
Dark: Gomori trichrome & H&E (Arrows) stains
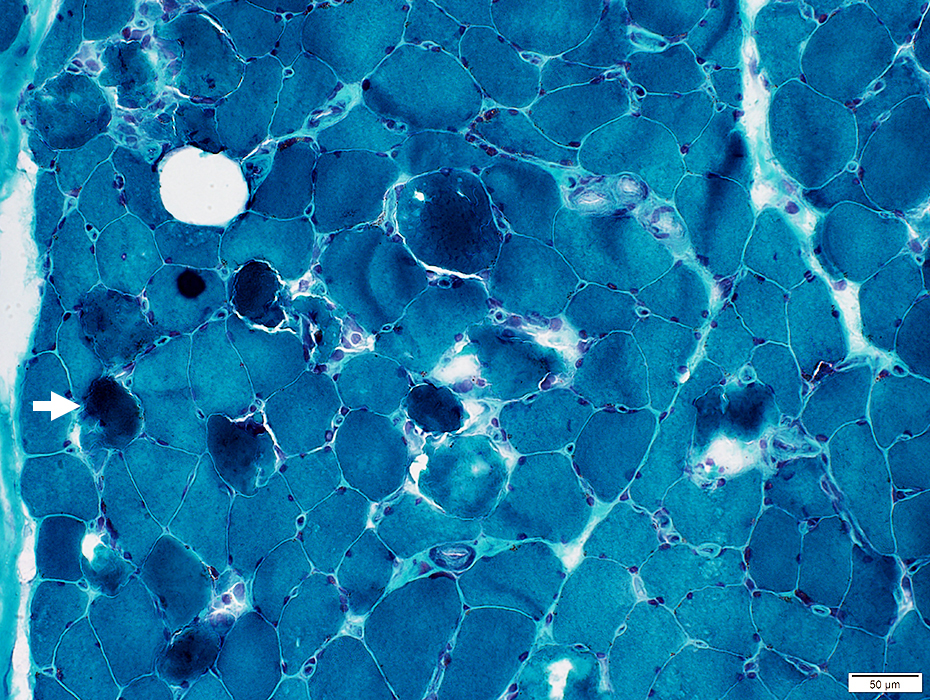
Pale: NADH stain
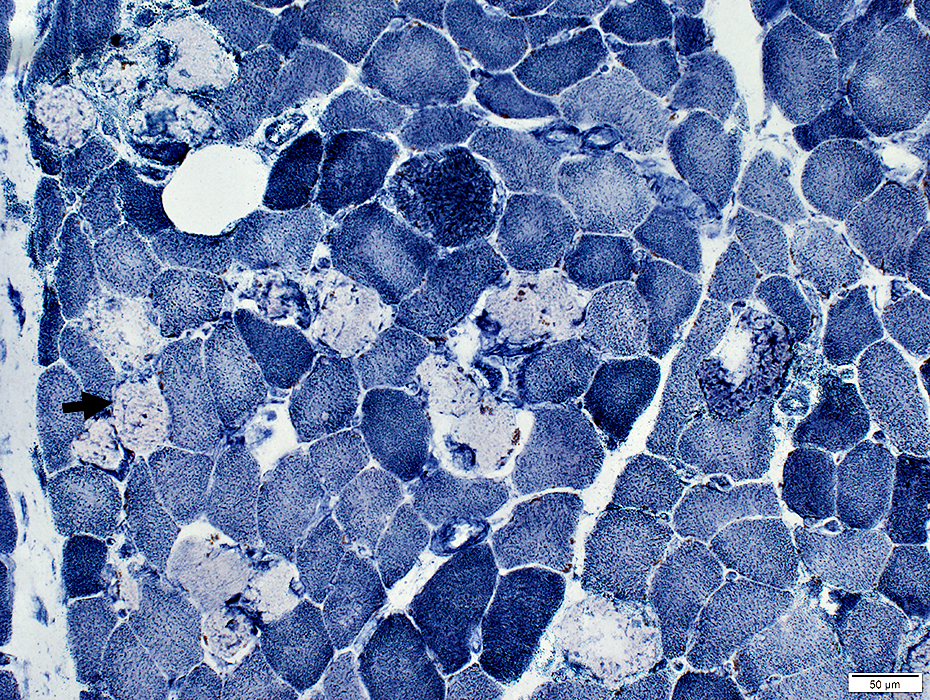
Gomori Trichrome stain |
 NADH stain |
Pale stained by NADH (Arrow)
Dark-stained on H&E & Gomori trichrome
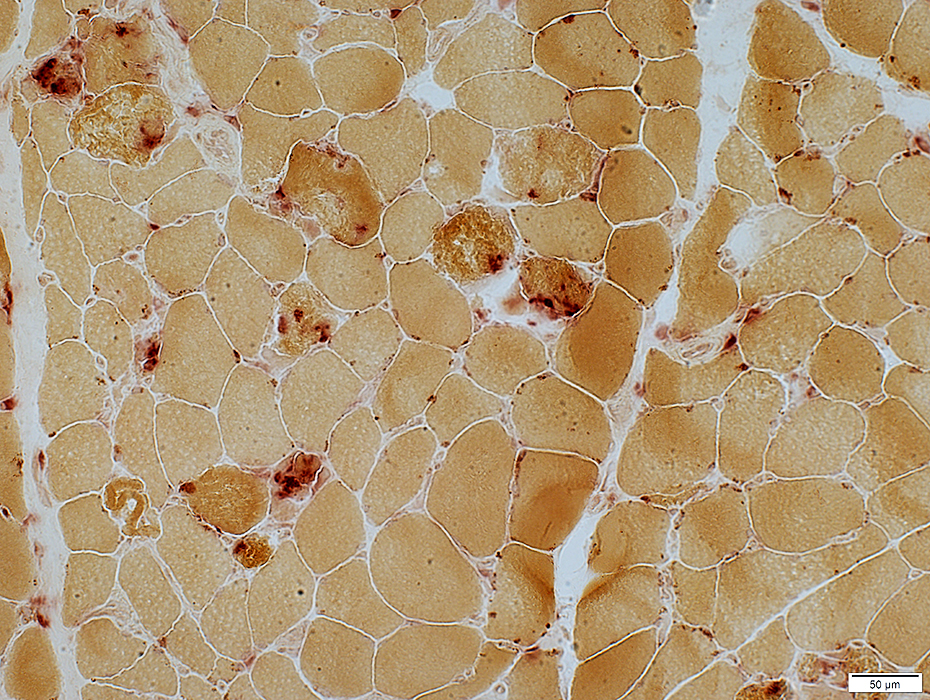 Acid phosphatase stain |
Few histiocytes associated with necrotic muscle fibers
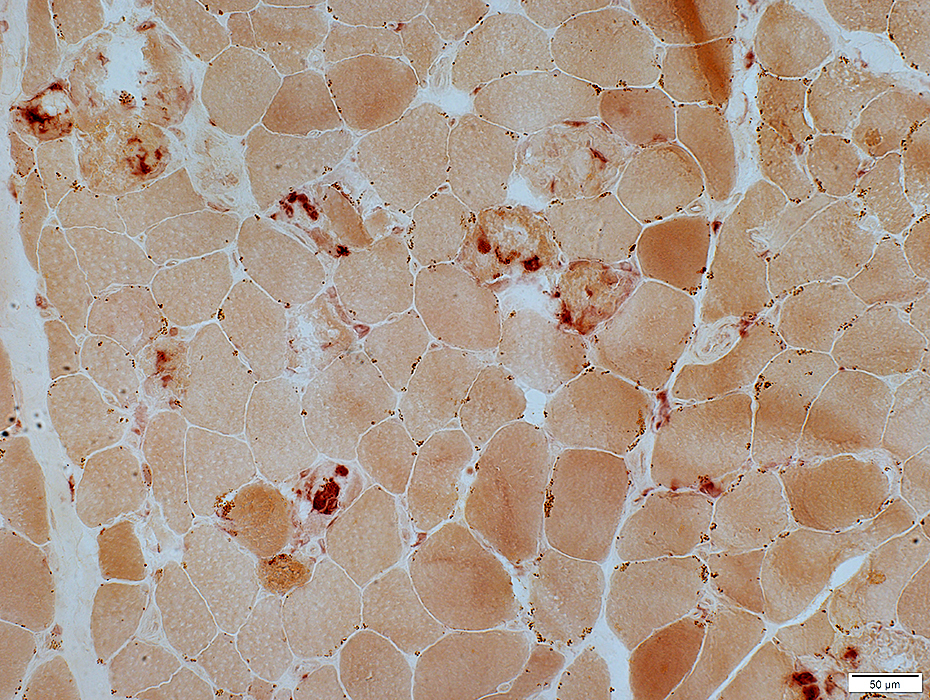 Esterase stain |
Necrosis: Active
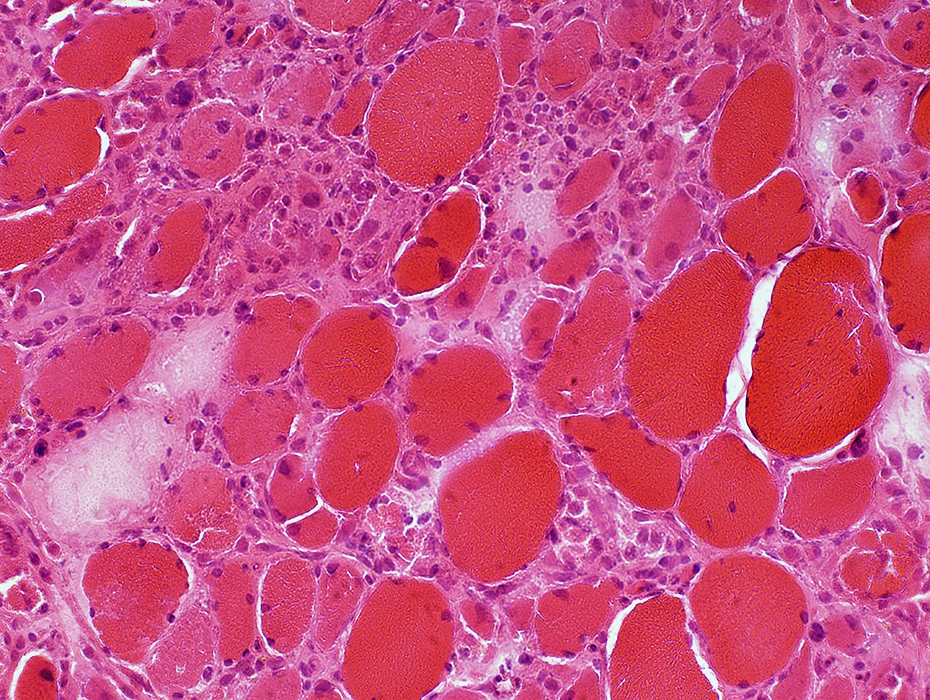 H&E stain |
Muscle fibers in varying stages of necrosis (Dark arrow), phagocytosis & regeneration (Light arrow)
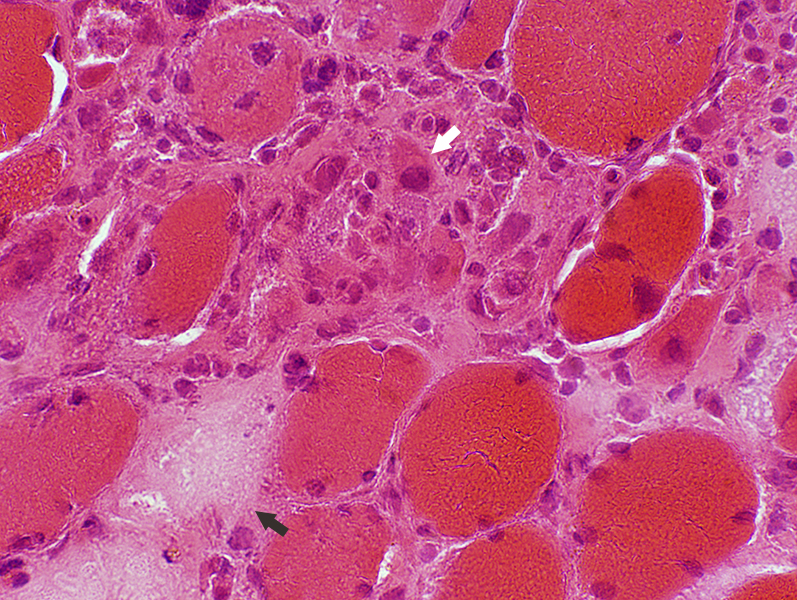 H&E stain |
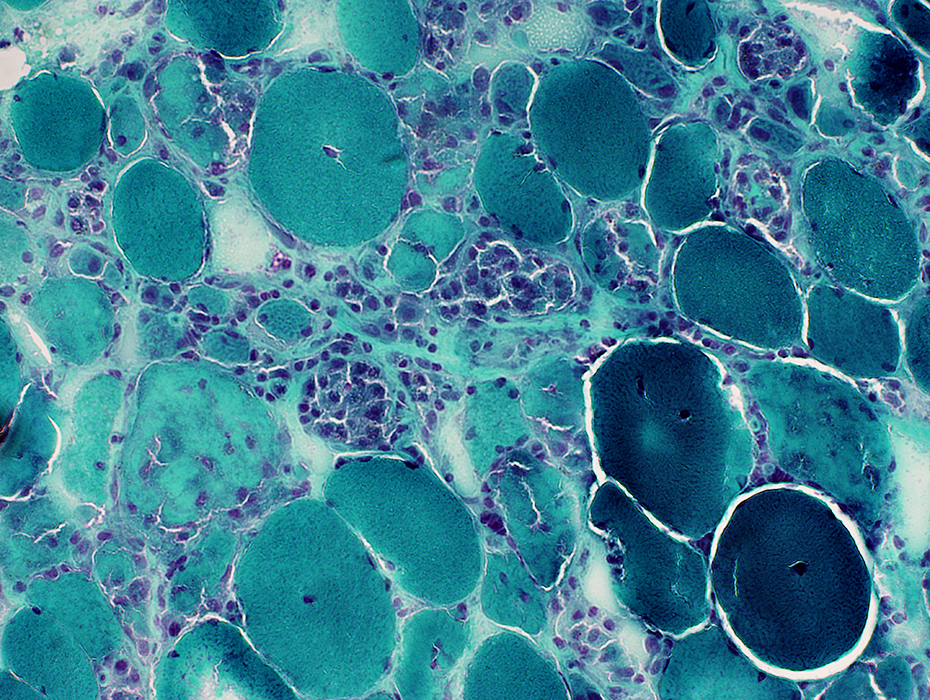 Gomori trichrome stain Sub-acute myopathy, Very active: Muscle fibers in varying stages of necrosis, phagocytosis & regeneration |
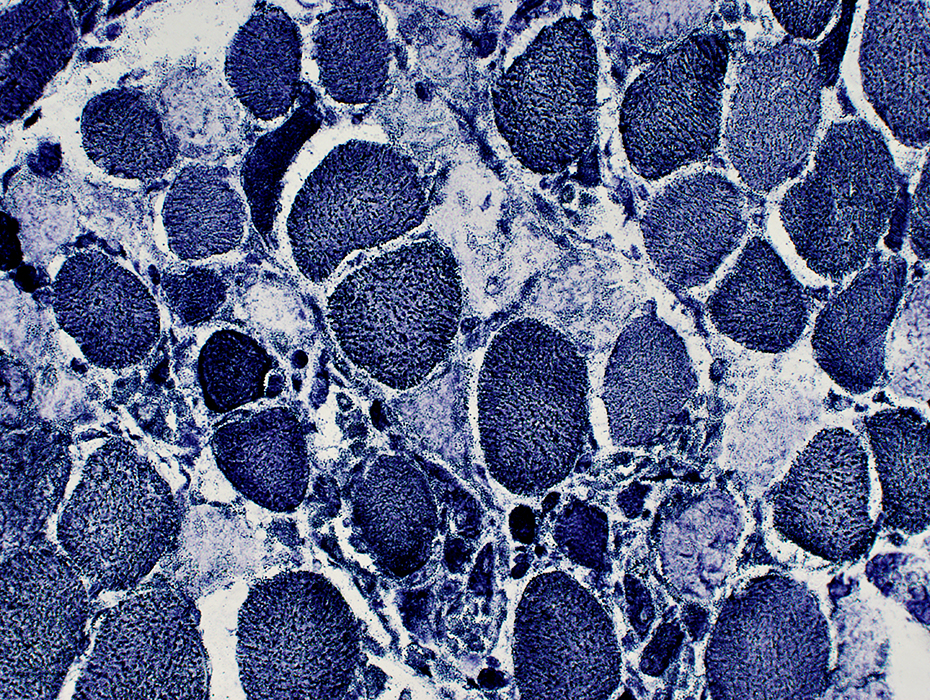 NADH stain Sub-acute myopathy, Very active: Large muscle fibers: Coarse internal architecture Small, regenerating muscle fibers: Dark-stained |
 Acid phosphatase stain Sub-acute myopathy, Very active: Muscle fibers invaded, or replaced, by phagocytic cells Histiocytic cells are also scattered in the endomysium near capillaries (Arrow) |
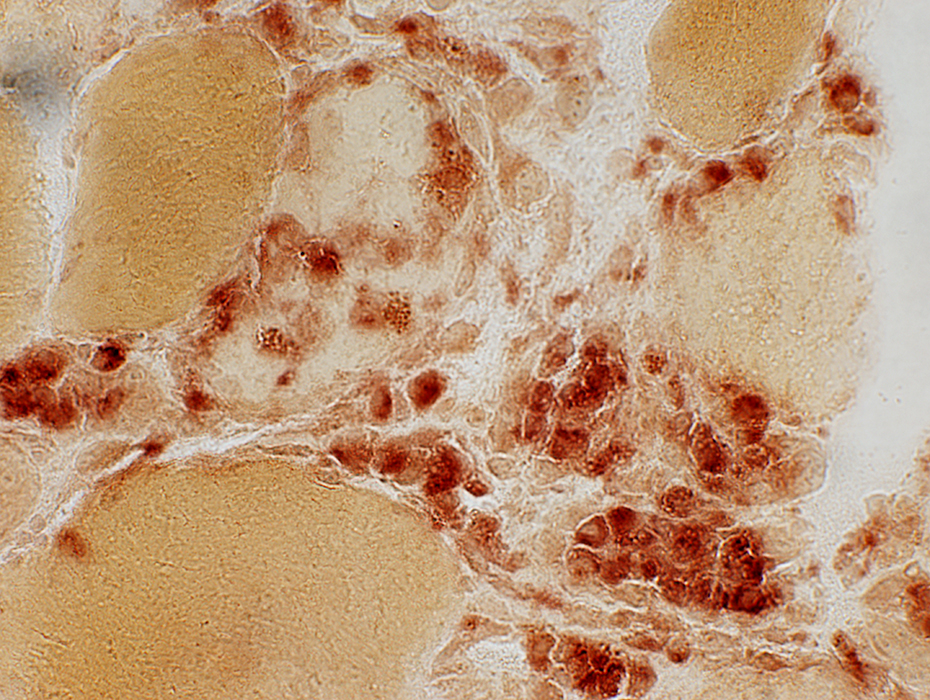 Acid phosphatase stain |
Statin myopathy: Muscle fiber properties
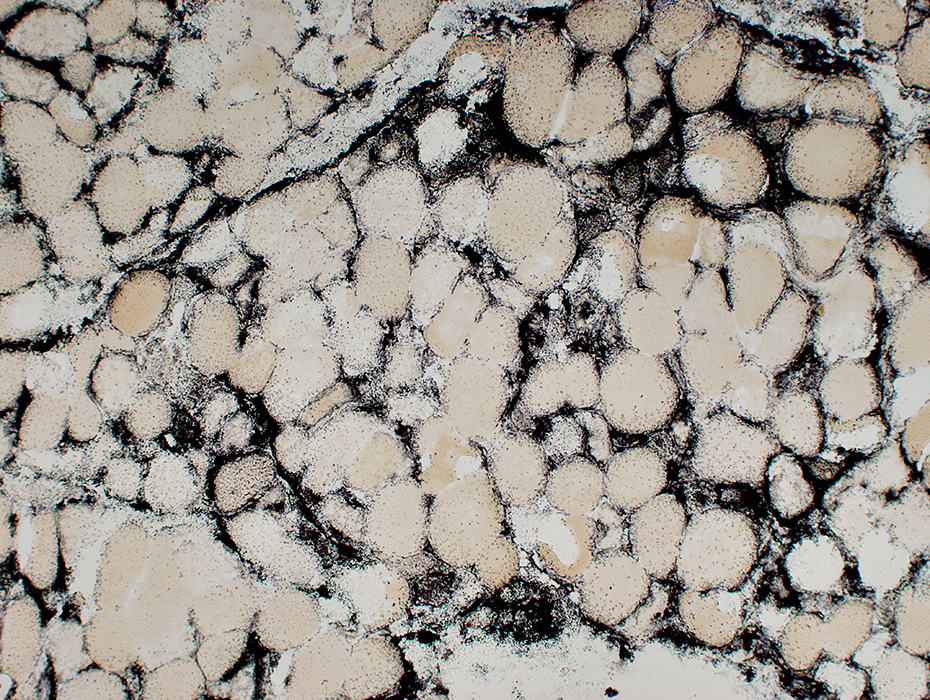 Alkaline phosphatase stain Sub-acute myopathy, Very active: Muscle fibers are surrounded by alkaline phosphatase stain |
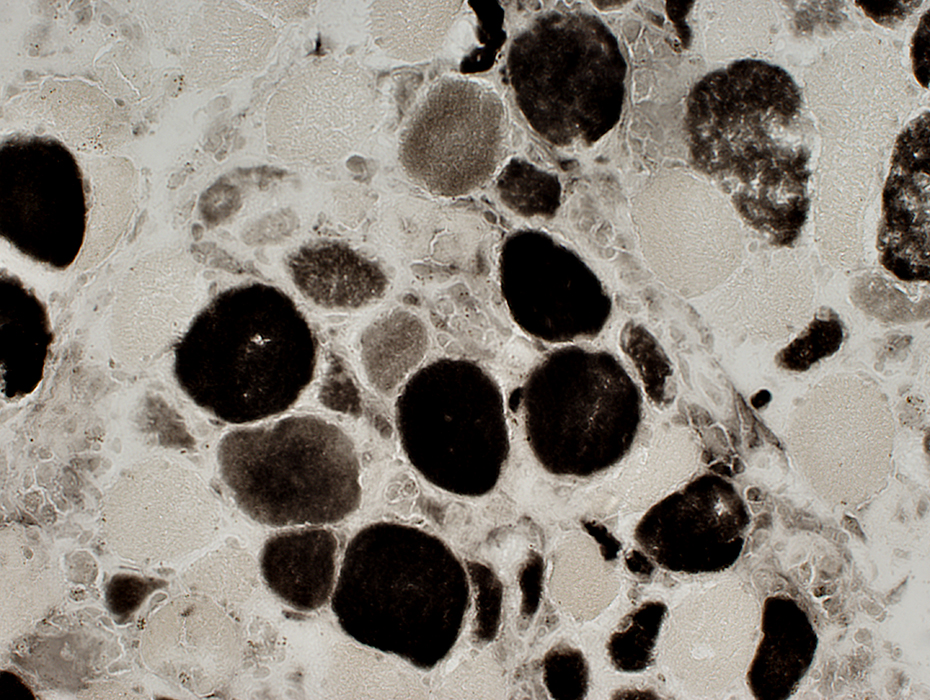 ATPase pH 4.3 stain Sub-acute myopathy, Very active: Scattered intermediate stained muscle fibers: Type 2C or Necrotic |
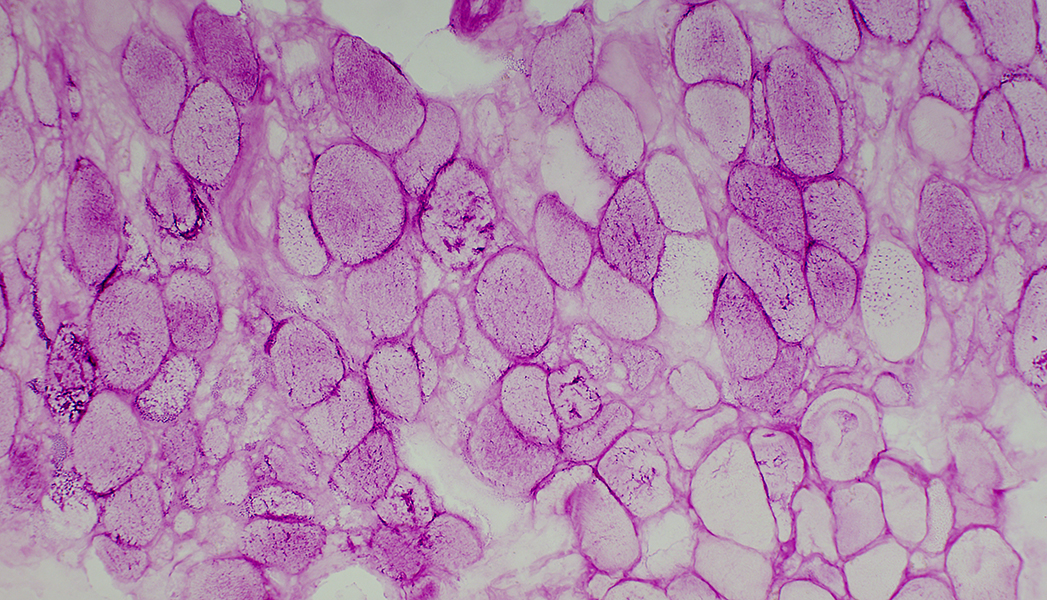 PAS stain Sub-acute myopathy, Very active: Unlike some other patterns of rhabdomyolysis, glycogen is still present in muscle fiber cytoplasm |
Return to Necrosis
Return to Pathology & Illustrations
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
11/6/2022