|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
Dysferlin Deficiency (LGMD 2B)
|
Amyloid Chronic Differential diagnosis Immune features MRI Myopathy Ultrastructure Vessels |
Dysferlinopathy Pathology: Distinctive Features
1
|
LGMD 2B: Myopathy
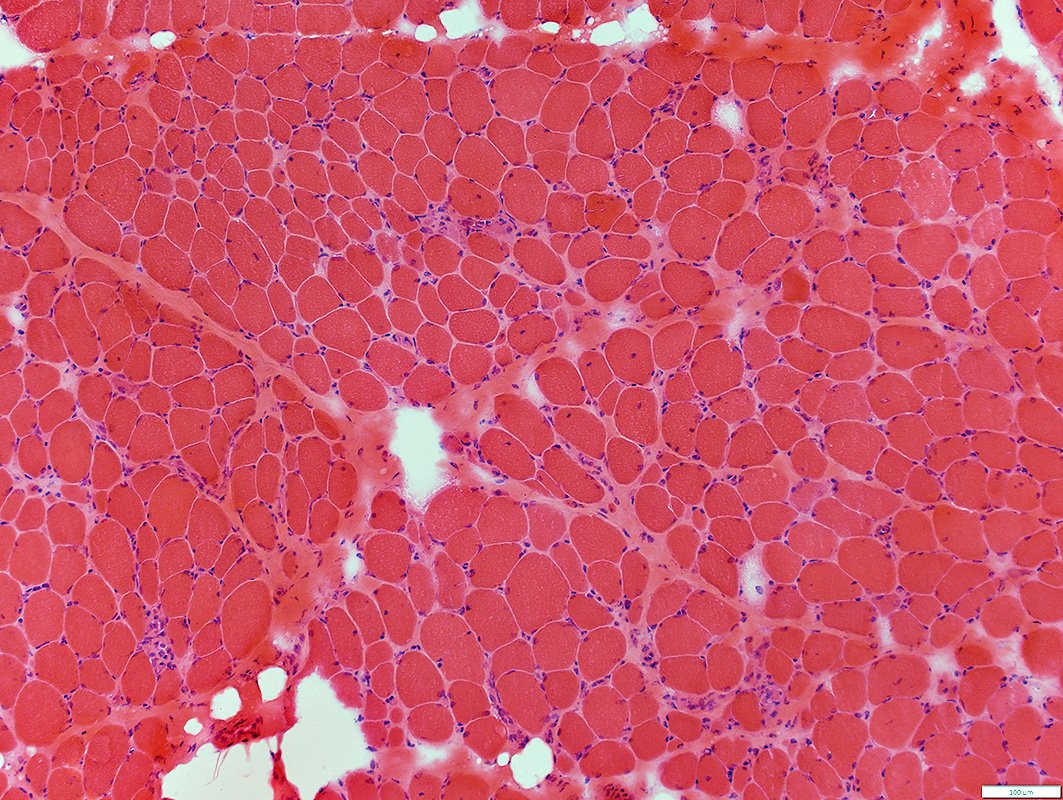 H&E stain |
Muscle fibers
Necrosis & Regeneration: Scattered
Sizes: Varied
Replacement of perimysium by fat: Varied Degrees
Connective tissue
Endomysial: Increased
Perimysial: Replaced by fat
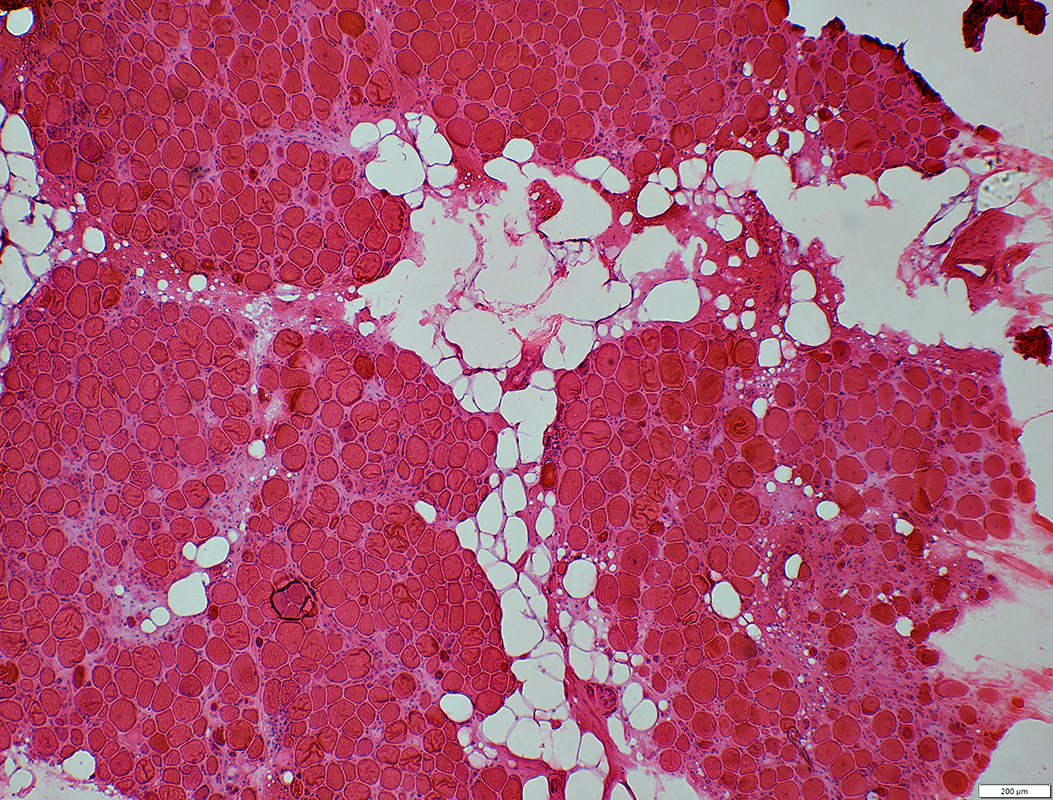 H&E stain |
Myopathy: Varied Degrees & Patterns of Pathology in same muscle
|
Myopathy, Mildly active Varied fiber size Immature fibers scattered 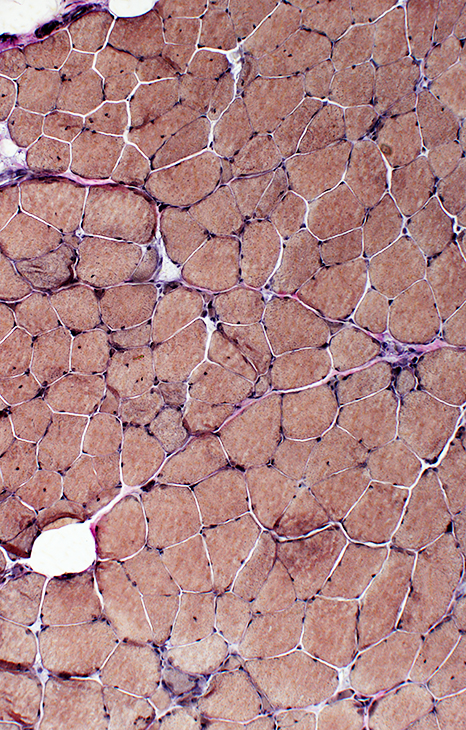 VvG stain |
Severe pathology Pyknotic nuclear clumps Replacement of muscle by fat 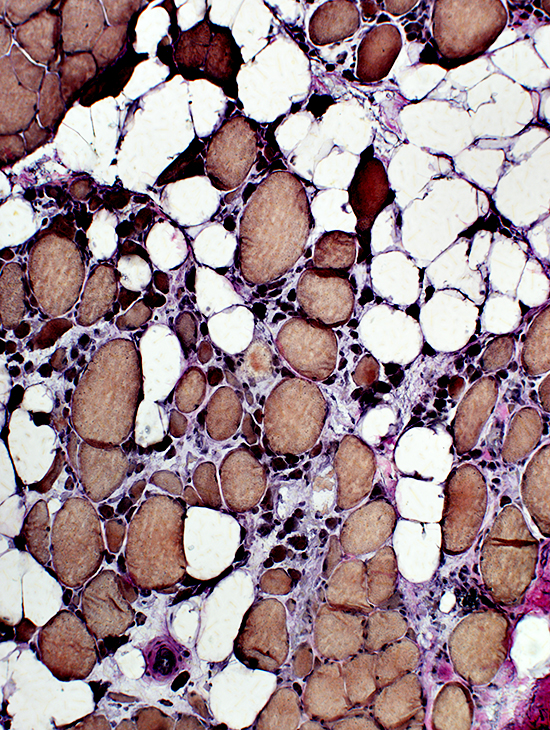 VvG stain |
Active Myopathy
Necrotic Muscle Fibers (Blue Arrow)Immature Muscle Fibers (Red Arrow)
Myopathic Grouped Small Muscle Fibers (Black Arrow)
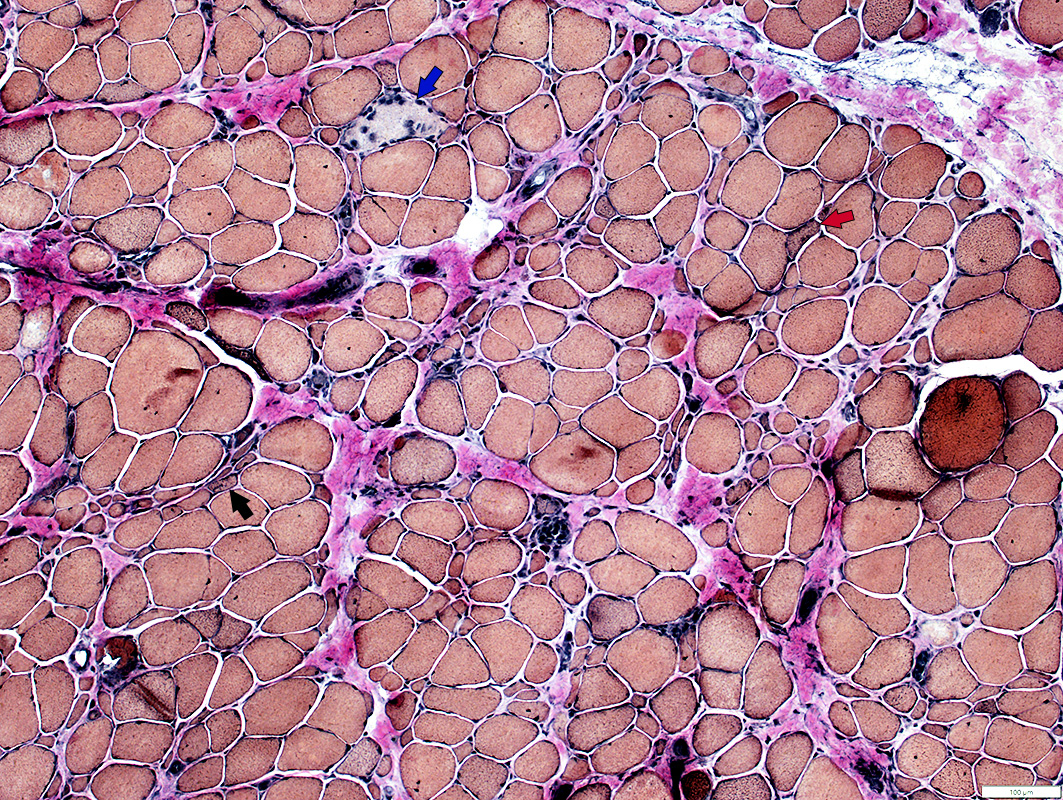 VvG stain |
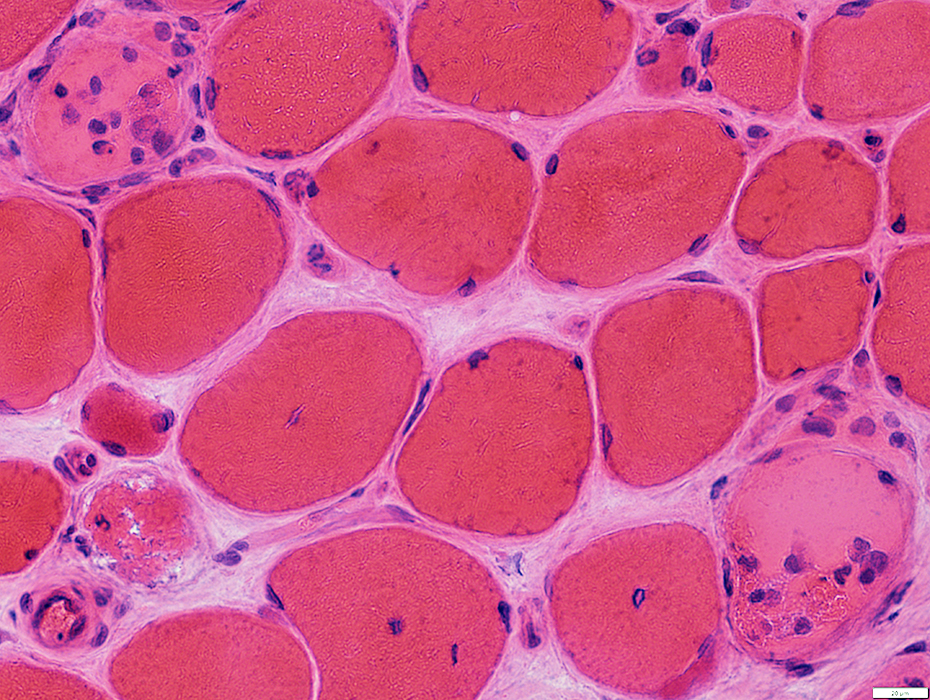 H&E stain |
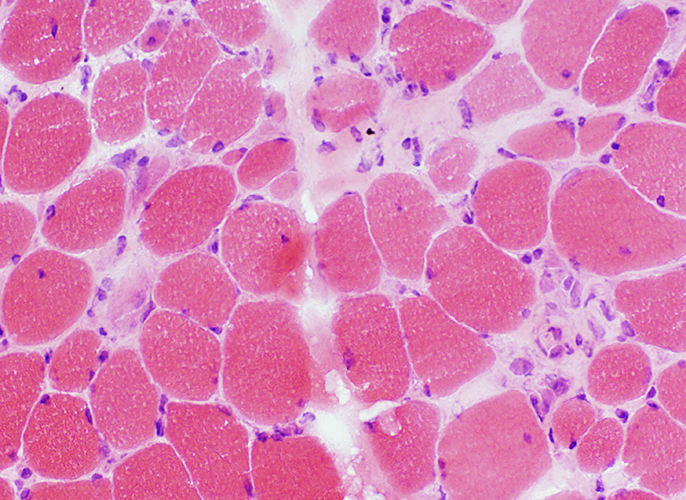
|
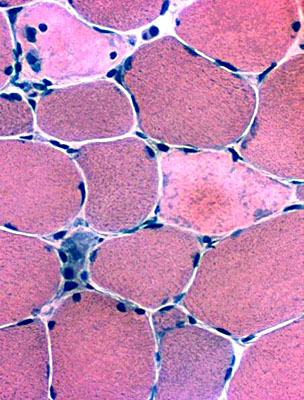 H&E stain |
Necrosis (Pale fibers)
Regeneration (Basophilic, smaller fibers)
Fiber size: Varied
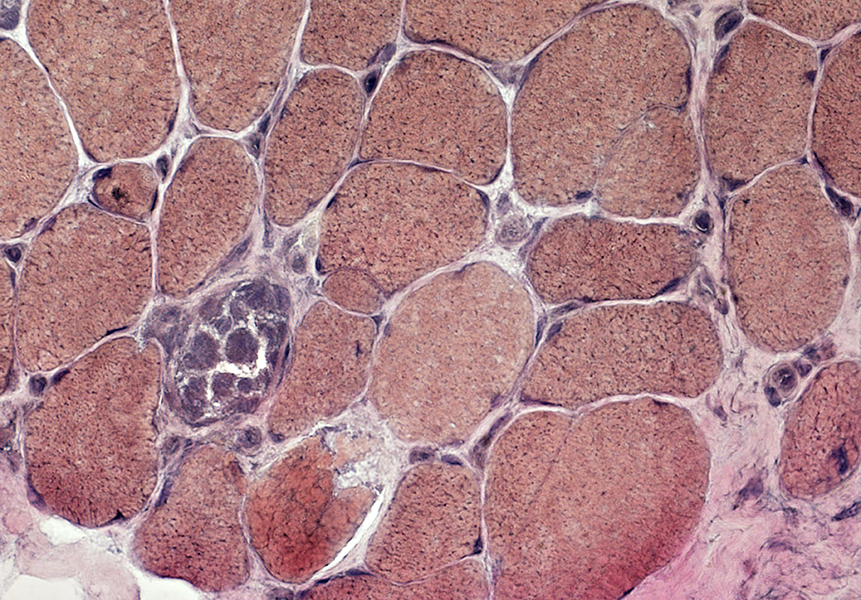 Necrotic muscle fibers 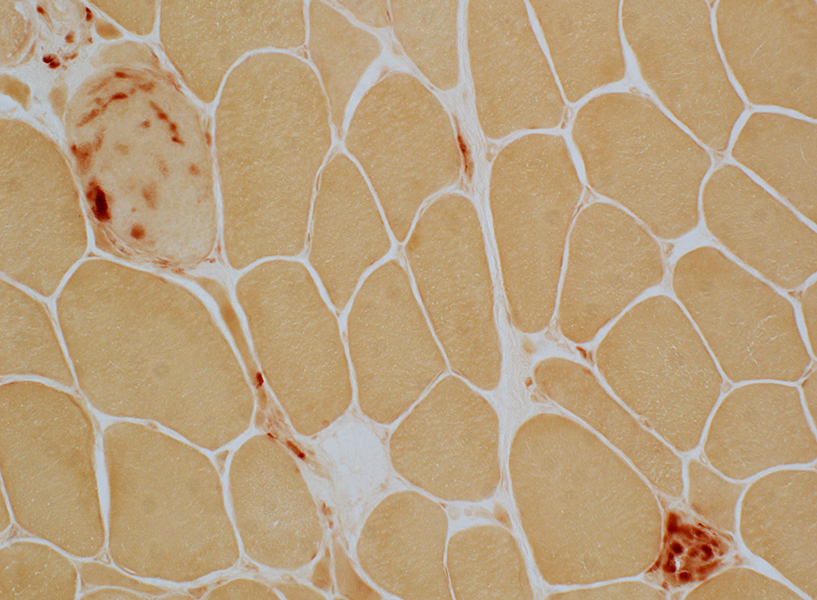
|
Necrotic muscle fiber replaced by phagocytic cells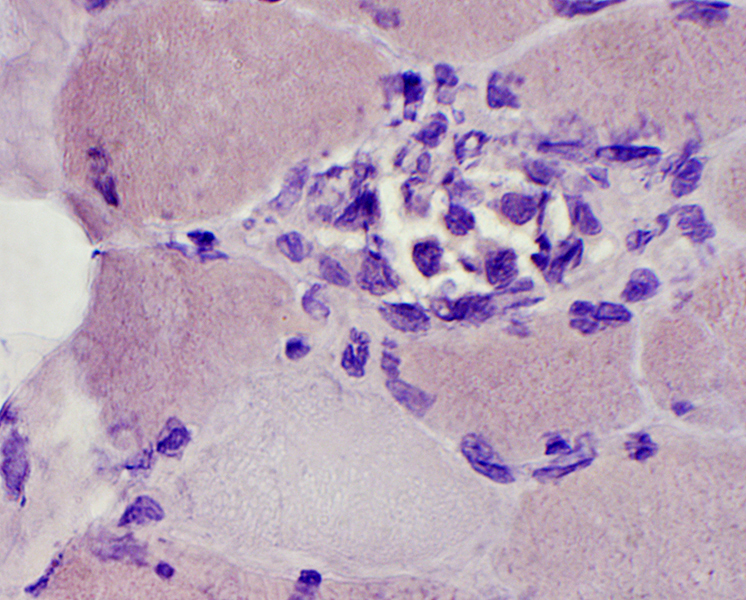 Congo red stain |
Necrotic & Regenerating muscle fibers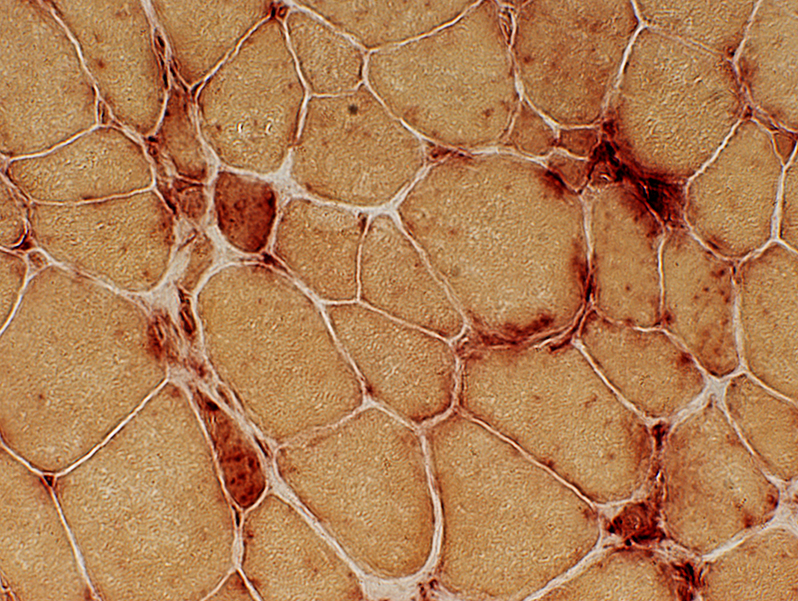 Acid phosphatase stain |
Immature Muscle Fibers: Type 2C, Intermediate color (Black Arrow)
Capillary Pathology: ATPase staining (Blue Arrow)
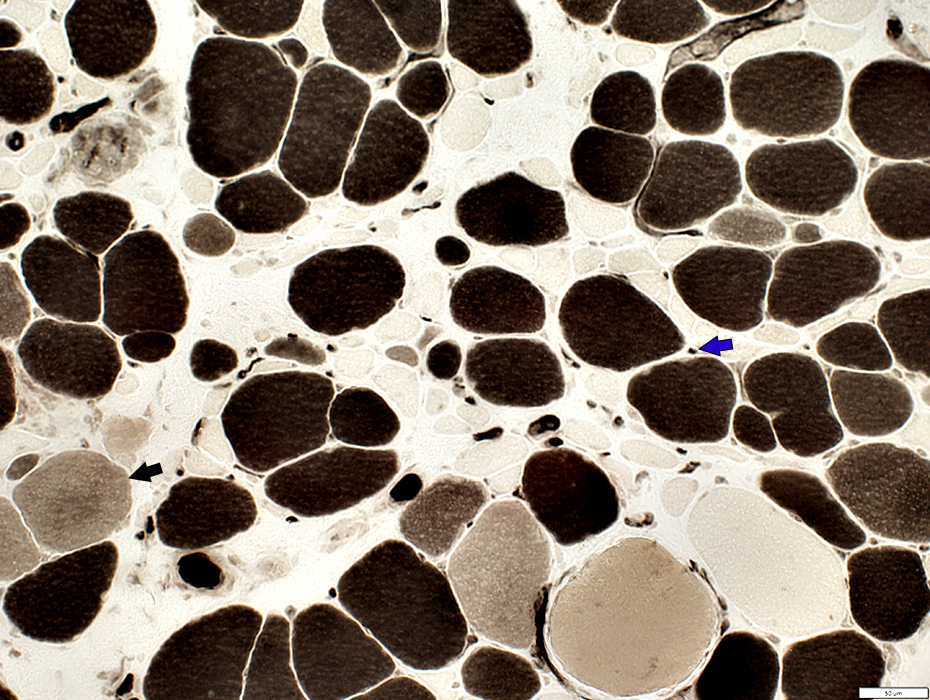 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Immature Muscle Fibers: Irregular internal architecture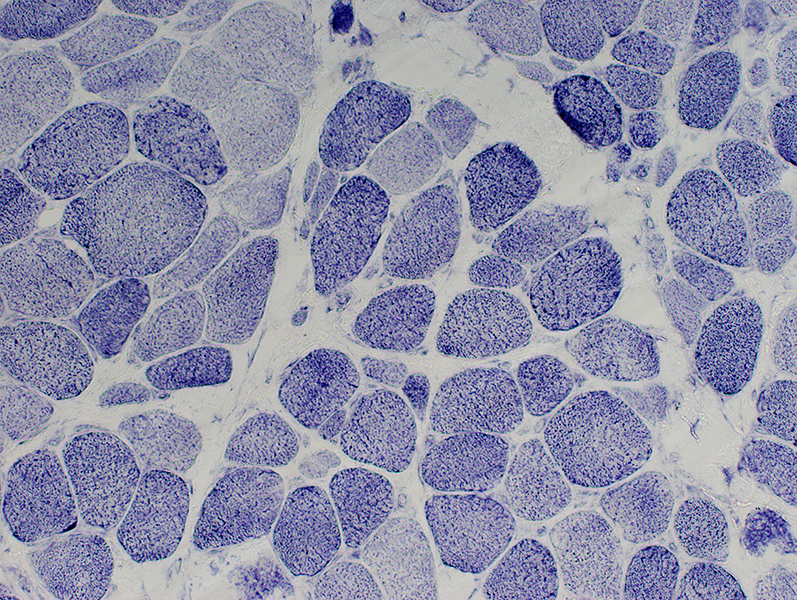 NADH stain |
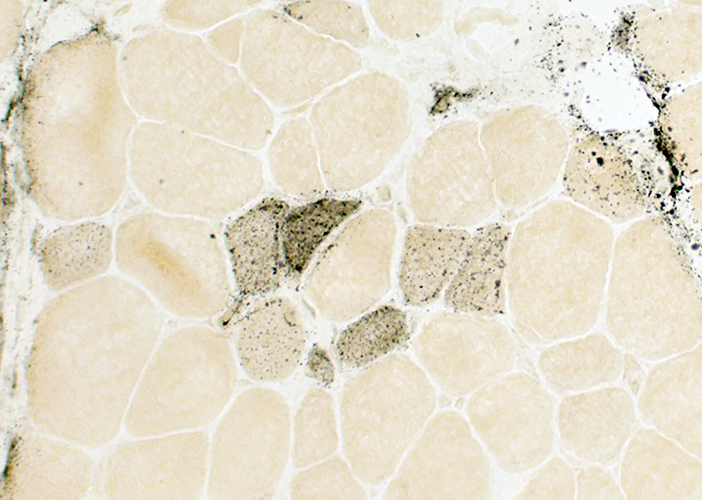 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
| Immature smaller muscle fibers Alkaline phosphatase positive cytoplasm (Above) Type 2C fibers (Intermediate staining; Below) |
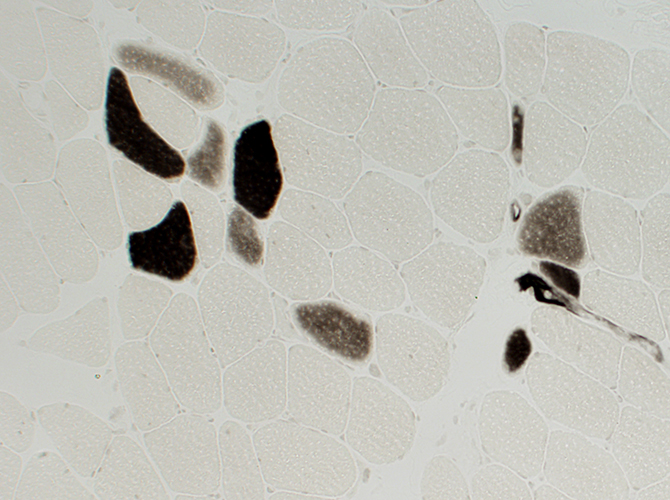 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
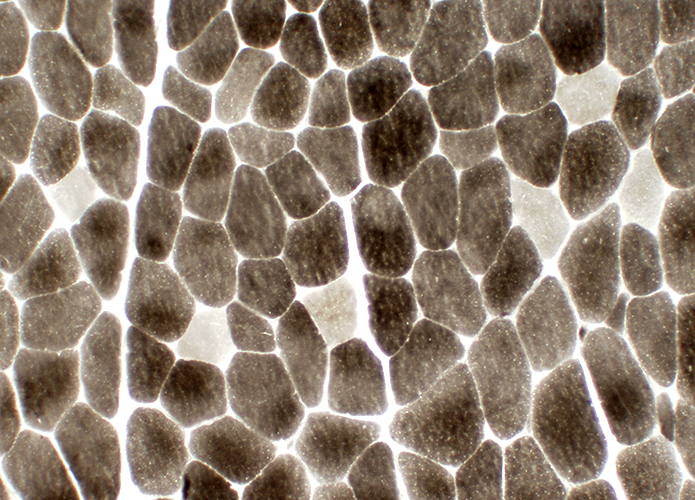 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
|
Type 2 muscle fiber predominance Most fibers are dark stained with ATPase pH 9.4 |
Dysferlinopathy: Immune features
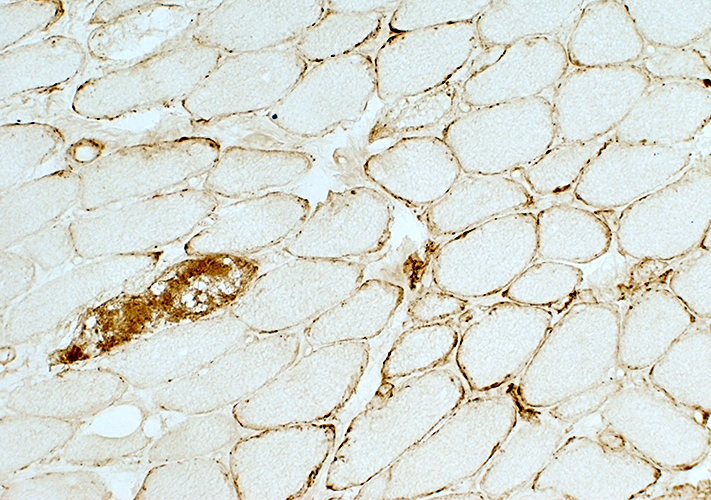 C5b-9 stain |
|
C5b-9 Complement deposits Muscle fiber surface membranes: Irregular, Punctate Muscle fiber cytoplasm: Necrotic fiber |
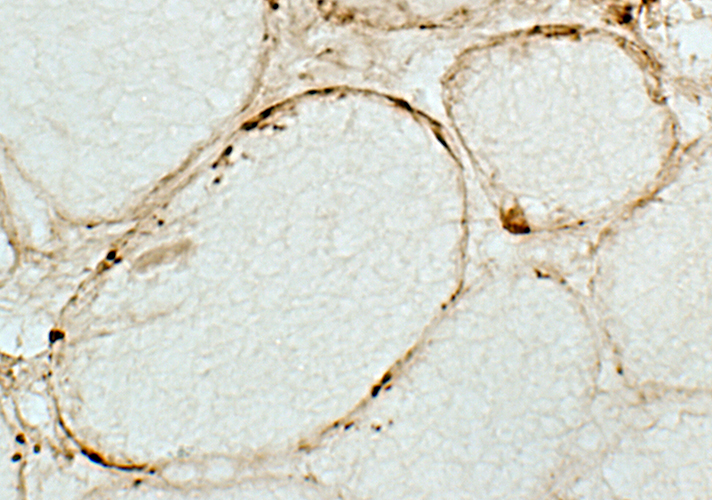 C5b-9 stain |
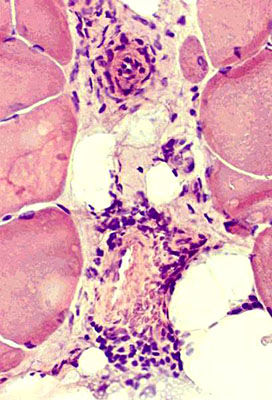
Inflammation, Lymphocytic: Found in some biopsies
May reflect superimposed immune disorder
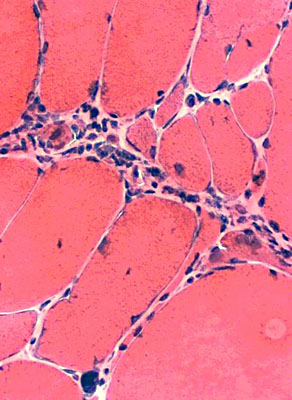
|
|
| Perimysial inflammation Cells in connective tissue between fascicles |
Perivascular inflammation Cells around intermediate-sized vessels |
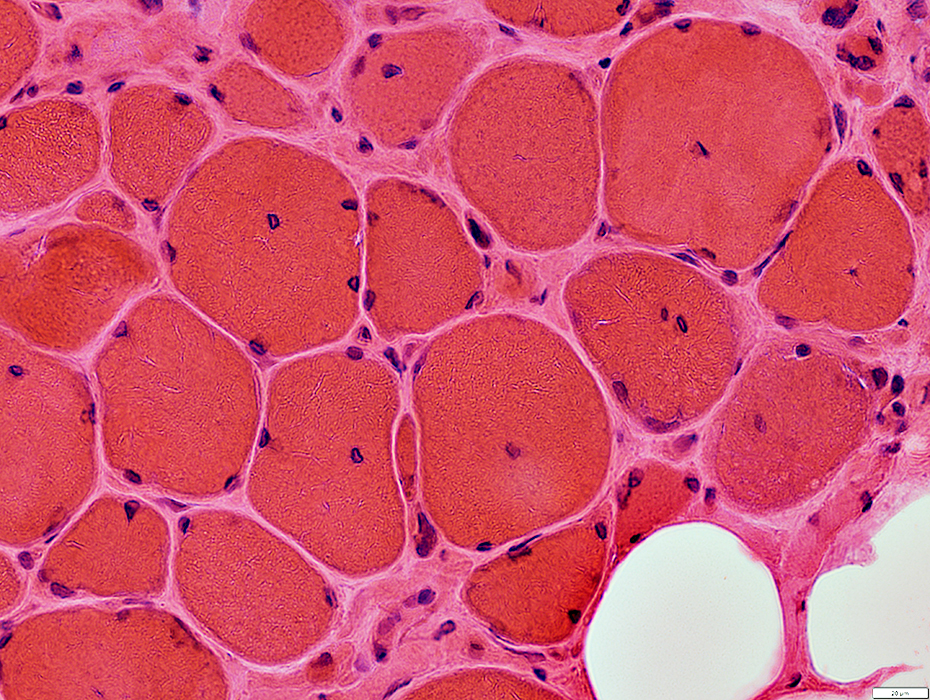
Myopathy
Muscle fibers
Sizes: Varied
Internal nuclei
Endomysial connective tissue
Increased between muscle fibers
 H&E stain |
|
 H&E stain |
|
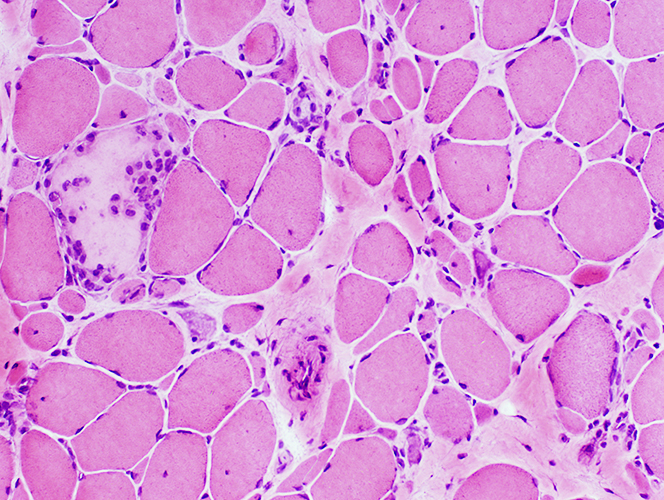
Small muscle fibers Rounded Some with basophilic cytoplasm & Large nuclei Often in Myopathic Groups Larger muscle fibers Often hypertrophic Occasionally necrotic |
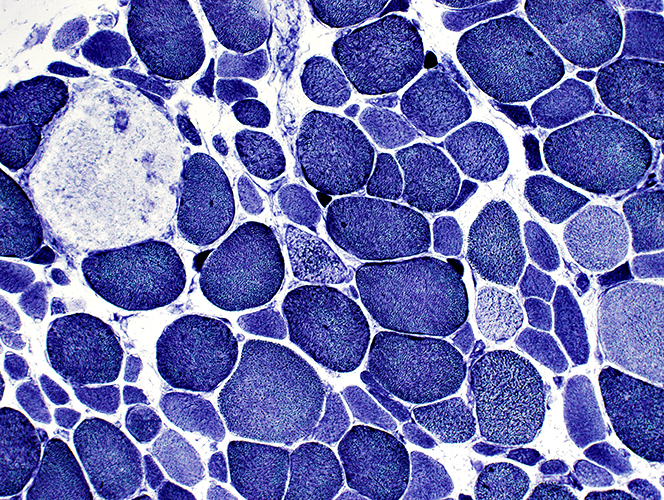 NADH stain Muscle fiber internal architecture Coarse staining in scattered muscle fibers Necrotic fiber shows only pale staining Pyknotic nuclear clumps: Very small, dark-stained muscle fibers |
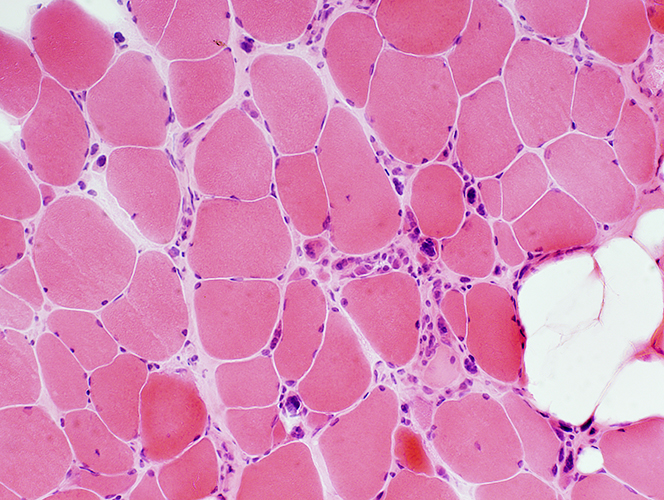 H&E stain Varied muscle fiber size Pyknotic nuclear clumps: Some muscle fibers are very atrophic and composed mainly of nuclei |
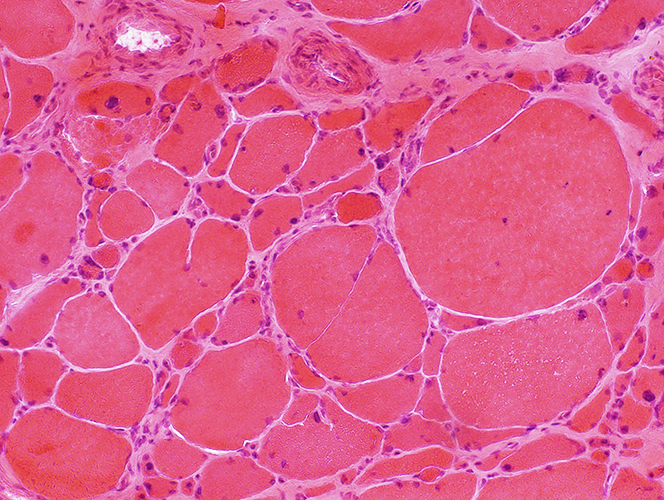 H&E stain |
|
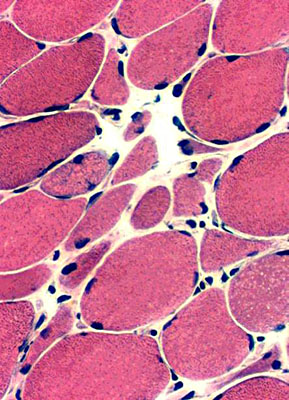
Size changes Small muscle fibers: Rounded; Often in Myopathic Groups Larger muscle fibers: Often very hypertrophic Muscle fiber splitting Endomysial connective tissue: Increased |
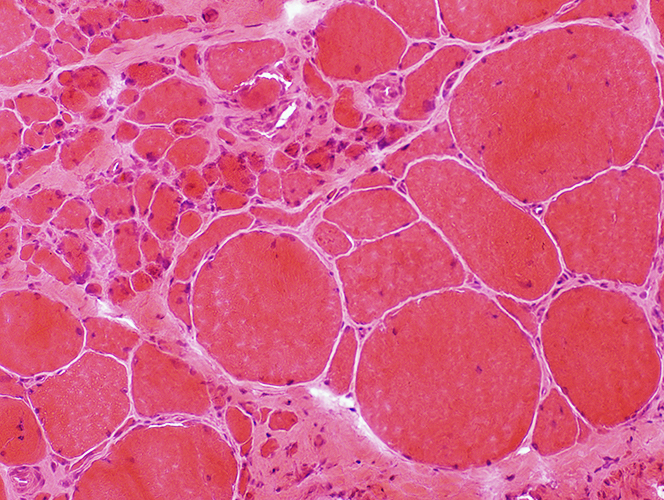 H&E stain |
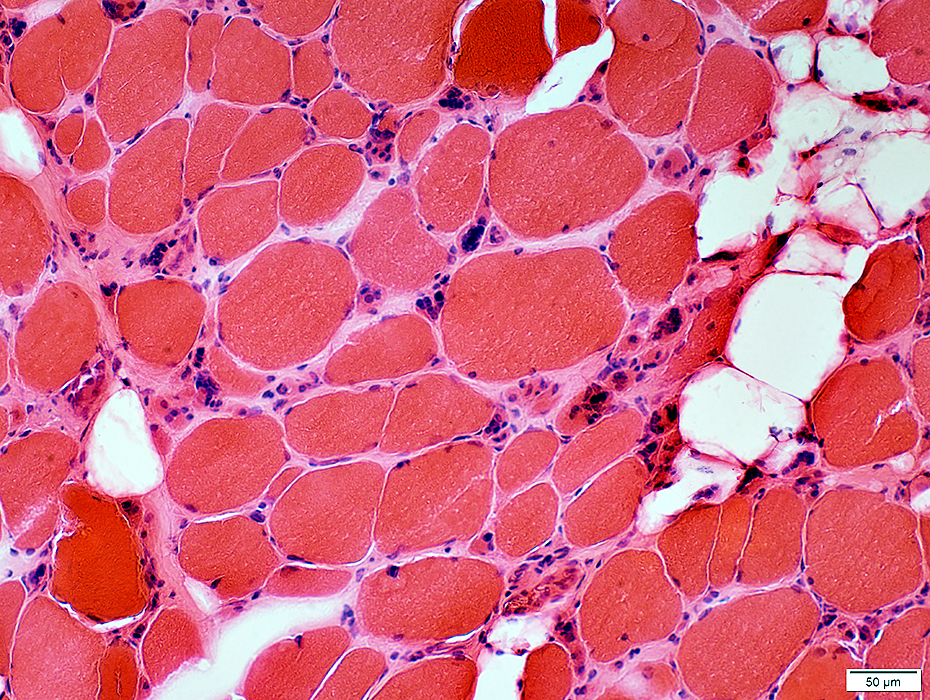
|
Pyknotic nuclear clumps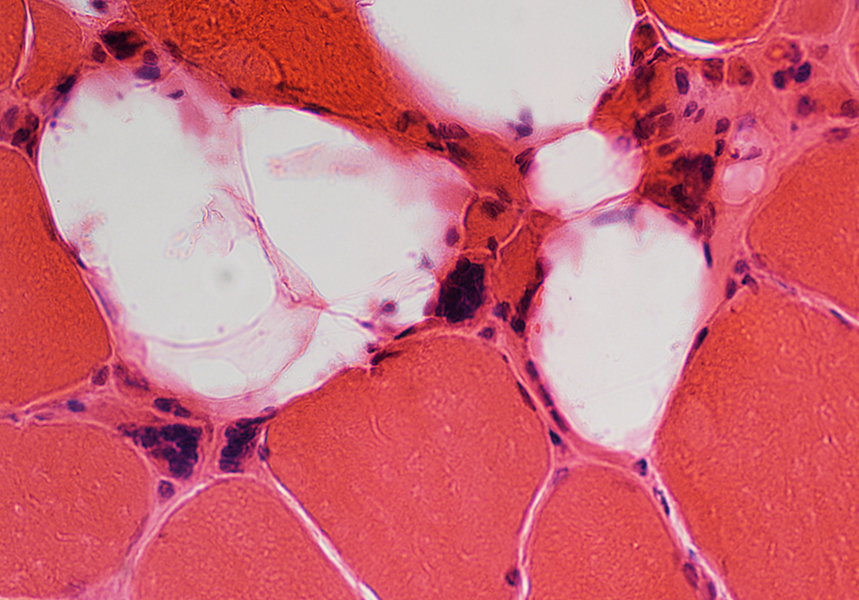
|
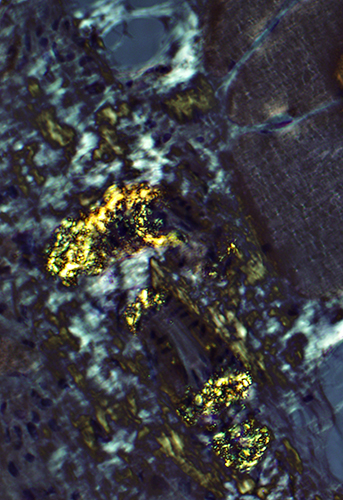
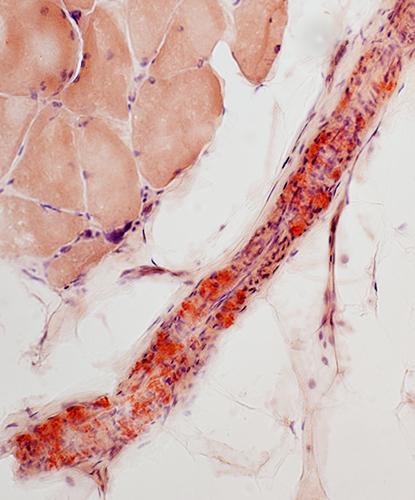
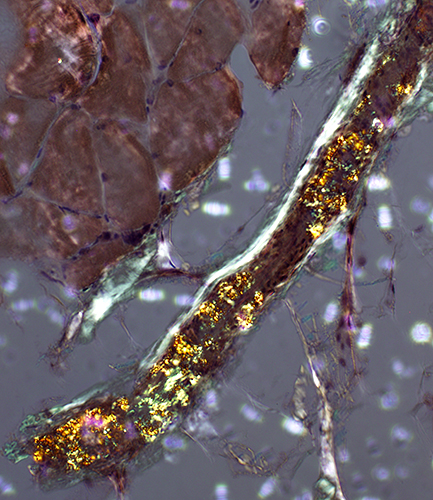
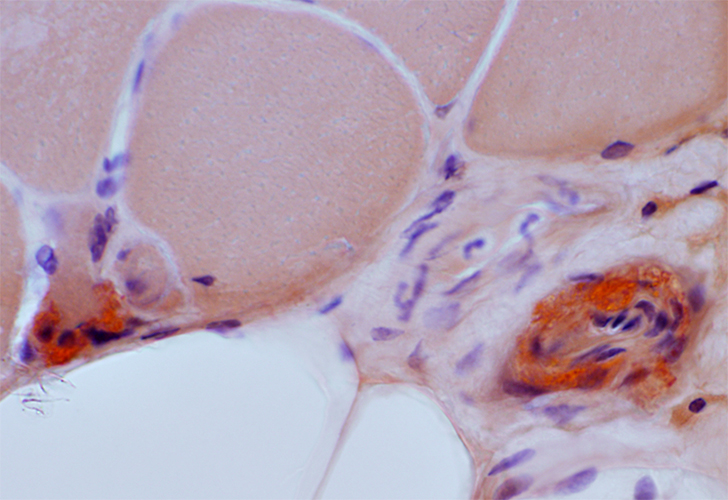
Amyloid (LGMD 2B): Commonly in vessel walls
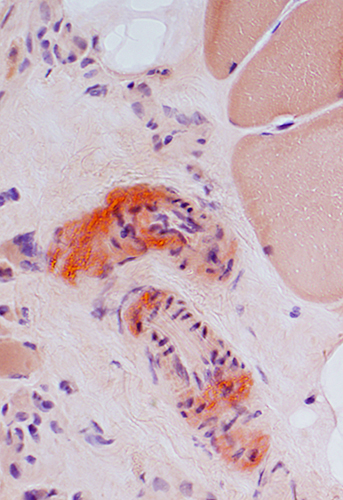
|
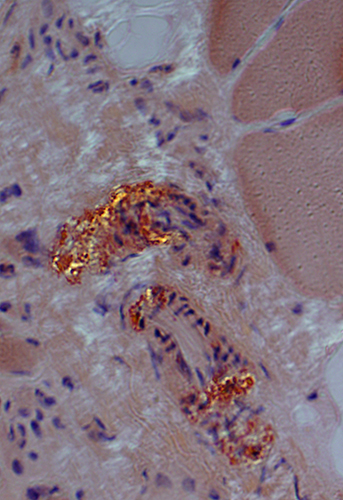
|
|
| Red-Green birefringent amyloid in vessel walls | ||
|
|
|
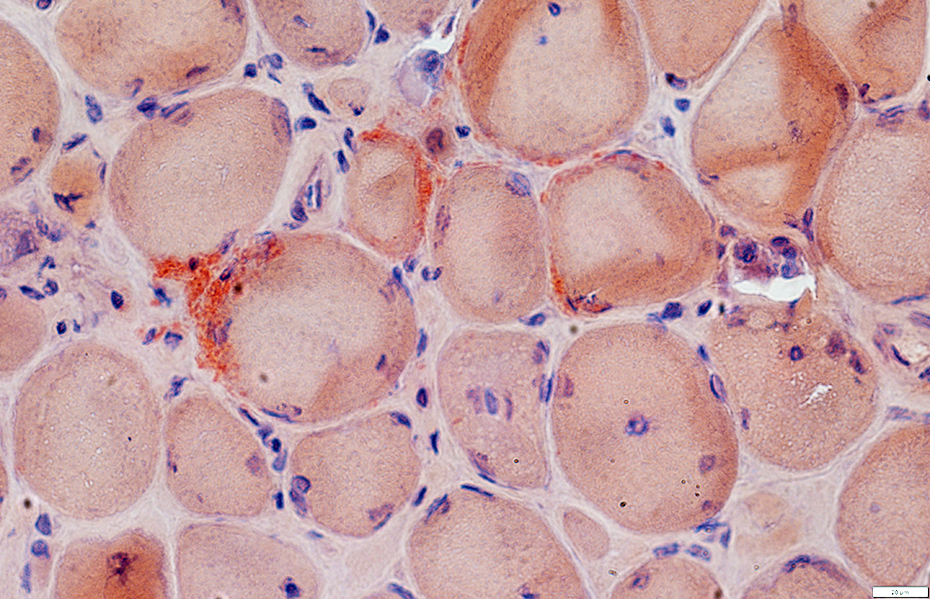 Congo red stain |
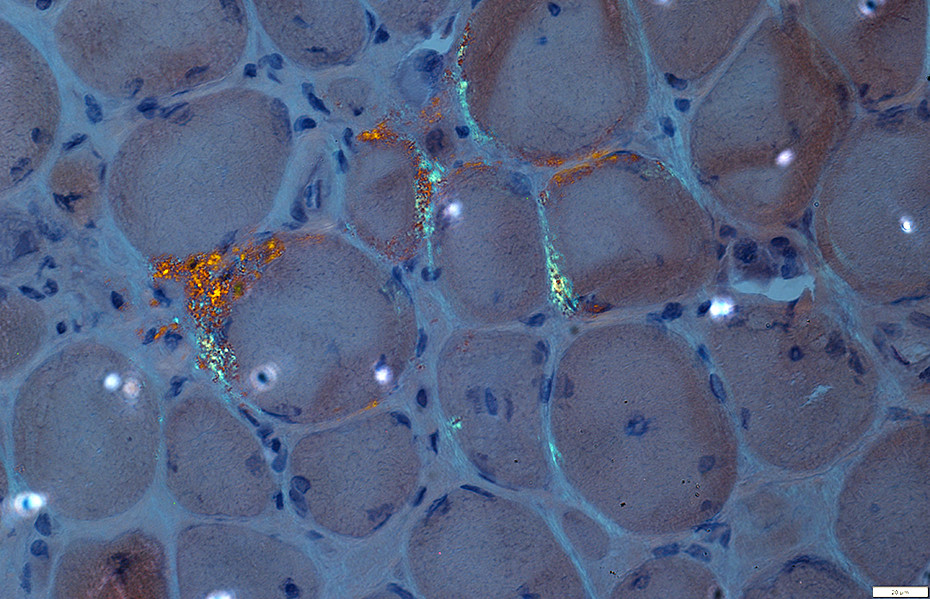 Congo red stain |
Dysferlin staining of muscle fibers
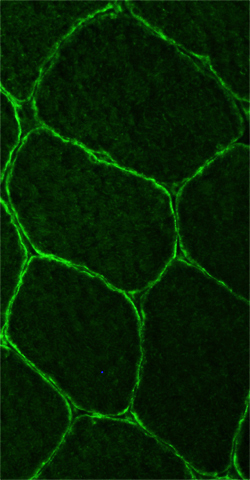
|
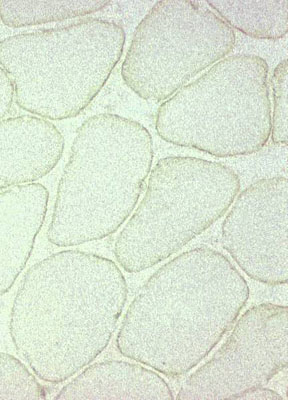
|
|
| Normal: Dysferlin on surface of muscle fibers | LGMD 2B: Absent dysferlin on muscle fiber surface |
|
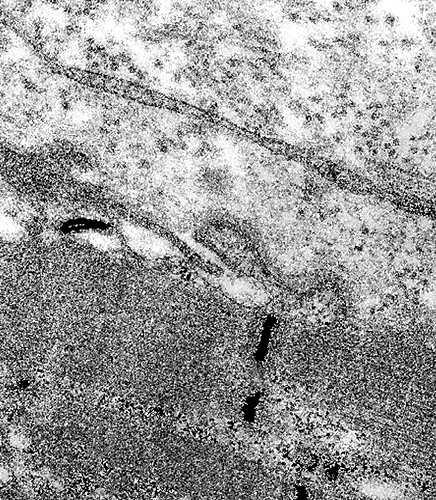
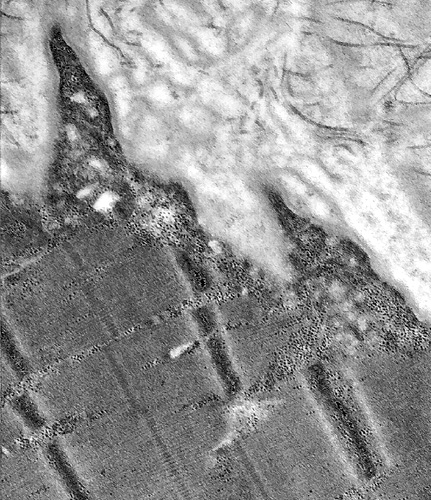
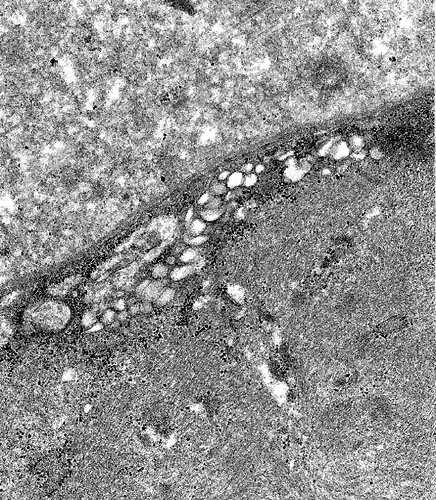
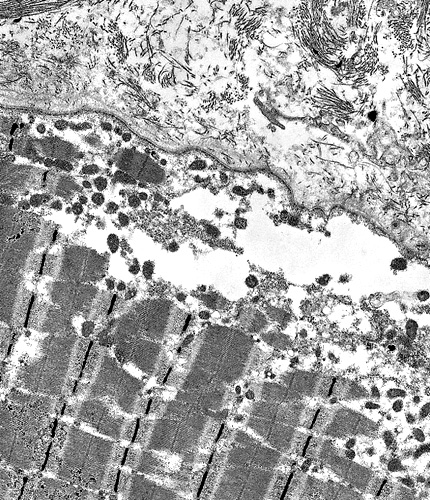
Dysferlin mutations: Ultrastructure
From: C Angelini
|

|
| Sarcolemma: Focal lesion | Sarcolemma: Focal projections |
|
|
| Subsarcolemmal region: Vacuoles | Subsarcolemmal region: Disrupted internal architecture |
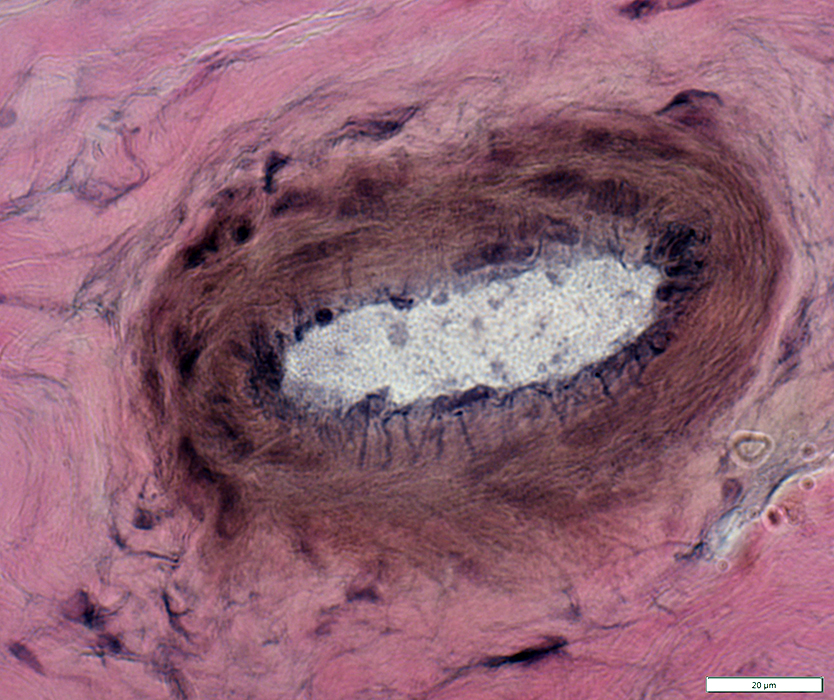 VvG stain |
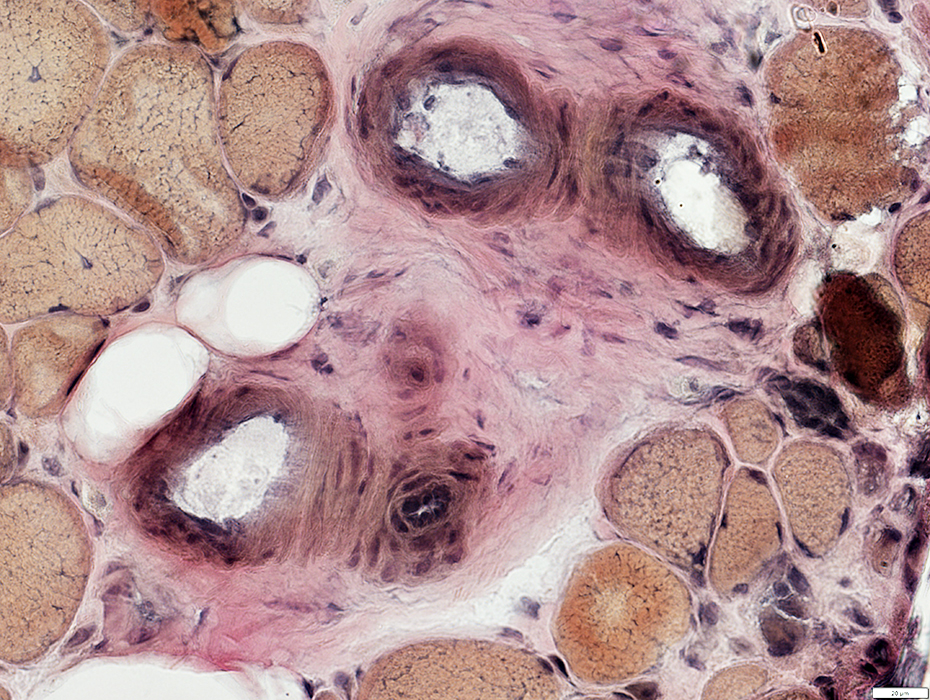 VvG stain |
Dysferlinopathy: Muscle Image
From: C Angelini
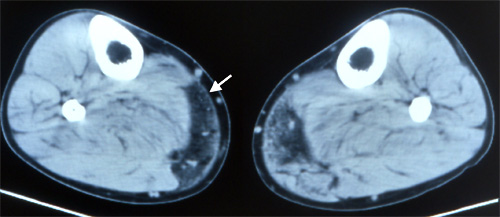
Leg: Involvement of posterior-medial gastrocnemius
|
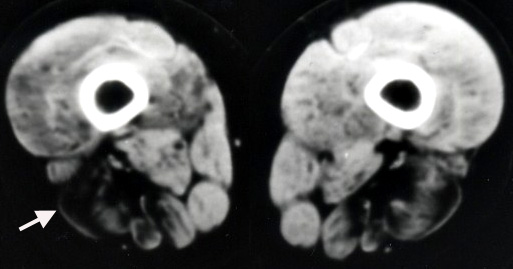
Thigh: Involvement of posterior muscles
|
Return to Pathology Index
Return to LGMD 2B
References
1. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:17
5/6/2025