Histiocytic Arteritis: Rheumatoid Disorder/Cryoglobulinemia
82 year old female with rapidly progressive mononeuritis multiplex & Multi-organ failureRheumatoid factor = 616; ANCA-; NfL 777; C4<4; IgM M-protein; Cryoglobulins, borderline
|
Vessels Epineurial: Artery Occlusion Also see pANCA Perimysial: Histiocytic Vasculitis Nerve Fascicle: Focal Infarction |
Nerve: Occluded Artery; Focal infarction
Focal nerve infarction: Also see BehçetEpineurial Vessel (Artery): Chronic Pathology, Occlusion
Vessel StructureDamaged wall: Elastin layer interrupted & irregular
Lumen: Absent or Contains large cells, possibly endothelium
Neovascularization
Abnormal staining for NCAM
Size: Large at some levels
Calcification: In some regions of vessels wall
Hemosiderin: Present in Epineurium
Epineurial connective tissue Surrounding vessel: Scattered histiocytes
See: Epineurial vessels, control
 Gomori trichrome stain |
 H&E stain |
 VvG stain |
 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
 VvG stain |
 Neurofilament (Green) + NCAM (Red) |
 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
 Neurofilament stain |
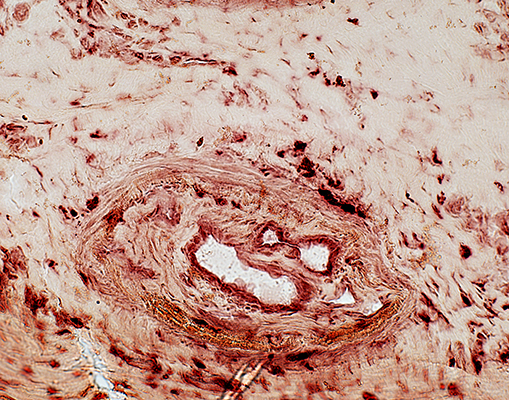 Acid phosphatase stain |
 Acid phosphatase stain |
Cryoglobulin/Rheumatoid Vasculitis: Nerve Infarction
 H&E stain |
Endoneurial vessels: Large size & lumen
Epineurium: Increased numbers of small vessels (Above)
Myelin sheaths: Many are abnormally pale-stained (Below)
 Gomori trichrome stain |
Endoneurial Vessels: Enlarged with large lumen
 Toluidine blue stain |
Histiocytes with Lipid droplets: Scattered in endoneurium
Myelin remnants (Ovoids): Scattered in endoneurium

|
Axon Loss
Myelinated Axons: Marked lossEndoneurial Microvessels: Often large; Some dark stained
 VvG stain |
Axons, Large & Small: Nearly complete loss
Perineurium: Thick & Irregular structure
 Neurofilament stain |
Axon & Myelin Degeneration
Myelin sheaths: Abnormal, strong acid phosphatase stain
 Acid phosphatase stain |
Nerve Infarction: Schwann cell loss in focal regions
Schwann cells, Non-myelinating: Reduced in region of endoneurium
 NCAM stain |
 Neurofilament (Green) + NCAM (Red) |
Axons: Complete loss in fascicles with loss of Schwann cells
 Neurofilament (Green) + NCAM (Red) |
Schwann cells (Green & Yellow)
Reduced numbers in region of endoneurium (Left)
"Denervated"" type: Most co-stain for P0 & NCAM (Yellow)
 NCAM (Green) + P0 (Red) |
Endoneurial Damage: C5b-9 staining of Endoneurium
C5b-9 stainsEndoneurium: Cells & Connective tissue
Perineurium: Irregular structure; Thick
 C5b-9 stain |
Endoneurial Damage: Hemorrhage
 Toluidine blue stain |
Endoneurial Cells after Axon loss
 From: R Schmidt |
Schwann cells: With myelin & lipid debris
Mast cell
Fibroblast processes
Schwann cells
With Myelin & Lipid debris
Büngner band components
 From: RSchmidt |
Epineurial Damage
 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Stains: Connective tissue around nerve; Epineurium
 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Cryoglobulinemia/Rheumatoid Disorder: Muscle
Vessel Structure: DamagedSee: Perimysial vessels, control
 H&E stain |
Size: Very large
Wall Structure
Inner layer: Fibrinoid necrosis
Outer layer: Replaced by large, "palisaded" cells
Lumen: Large cells, possibly endothelium, adherent to inner wall
 H&E stain |
 Gomori trichrome stain |
Large cells: Replace wall structure
 Congo red stain |
 AMPDA stain |
Fibrinoid Necrosis: Inside fibril layer
Fibril layer of vessel wall: Irregular
Outer layer: Replaced by large cells
 VvG stain |
Fibrinoid Necrosis: C5b-9 stain
 C5b-9 stain |
Histiocytic Arteritis
 Acid phosphatase stain |
Replace vessel wall
Nearly all cells are stained
 Acid phosphatase stain |
Esterase stains
Clusters of cells in vessel wall
? Early granulomatous change
 Esterase stain |
Arterial Smooth Muscle Layer: Incomplete & Damaged
 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Perimysial Connective Tissue: Alkaline phosphatase stain around damaged artery
 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Perimysial connective around, & extending away from, damaged artery
 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Vessel Endothelium: Strong stain by NADH
 NADH stain |
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Return to Pathology index
2/8/2024