Behçet Syndrome: Neuropathy
History
41 year old female, 22 weeks pregnant, with onset of oral ulcers & motor sensory neuropathy during prior 8 weeks
Sural Nerve: Skip serial sections
Behçet Nerve Pathology
Varied loss of Axons among fascicles
Severely damaged fascicle with loss of axons & endoneurial cells (White Arrow)
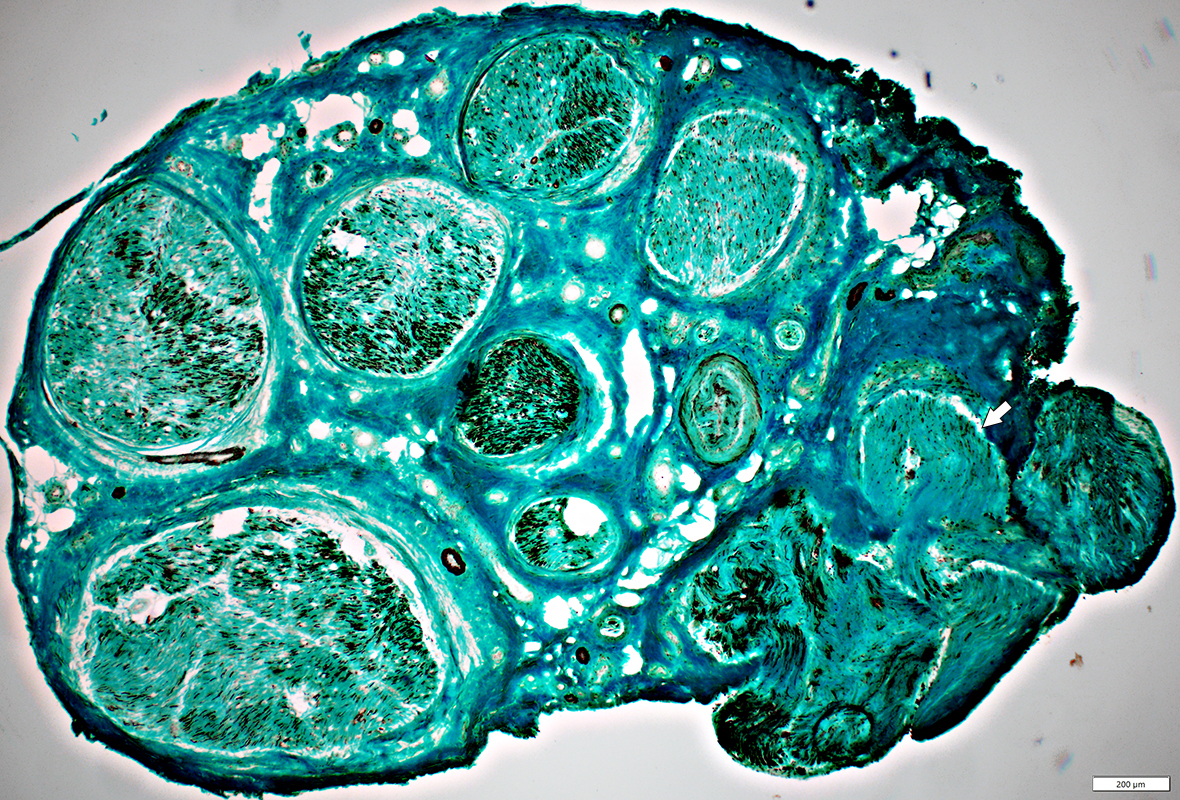 Neurofilament stain |
Behçet Nerve Pathology
Perineurial Damage (Yellow Arrows)
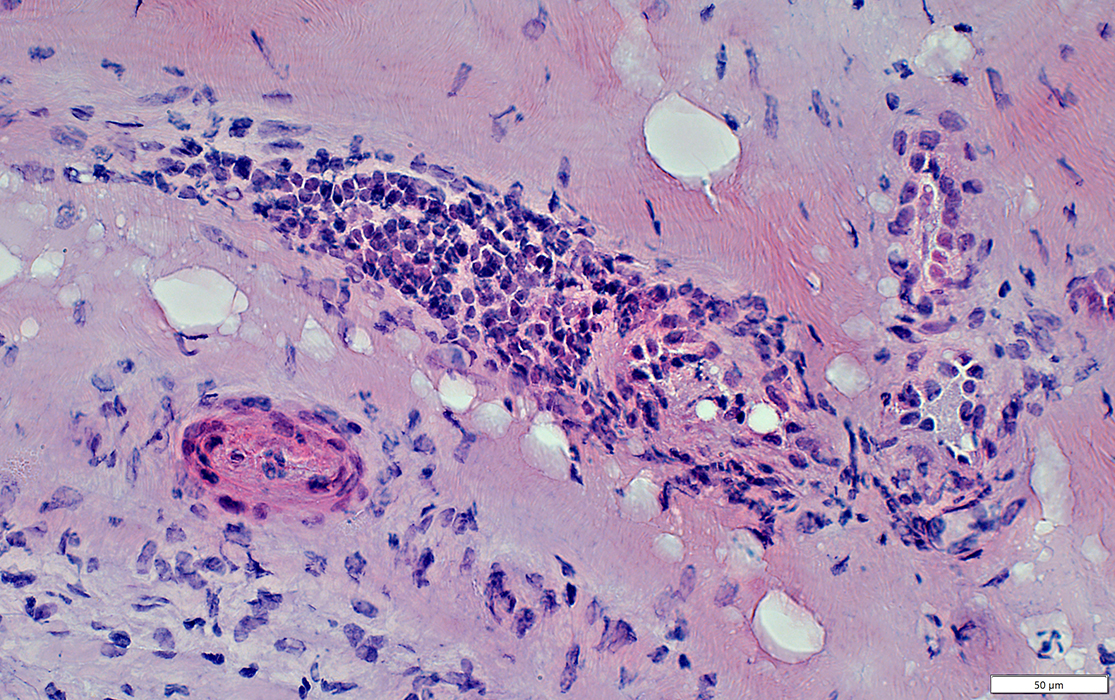
Lymphocytic inflammation around a small epineurial vessel (Black Arrow)
Vein & Artery Damage (White Arrow)
Endoneurial Pallor (Blue Arrow)
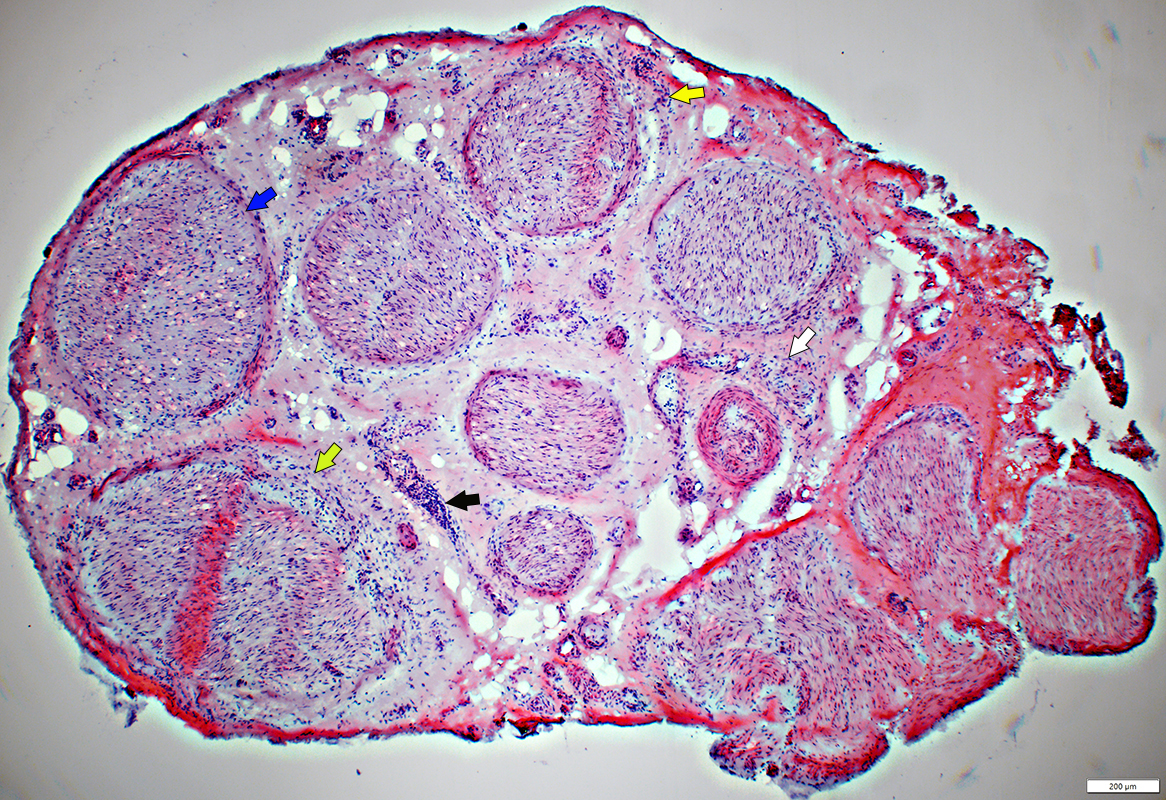 H&E stain |
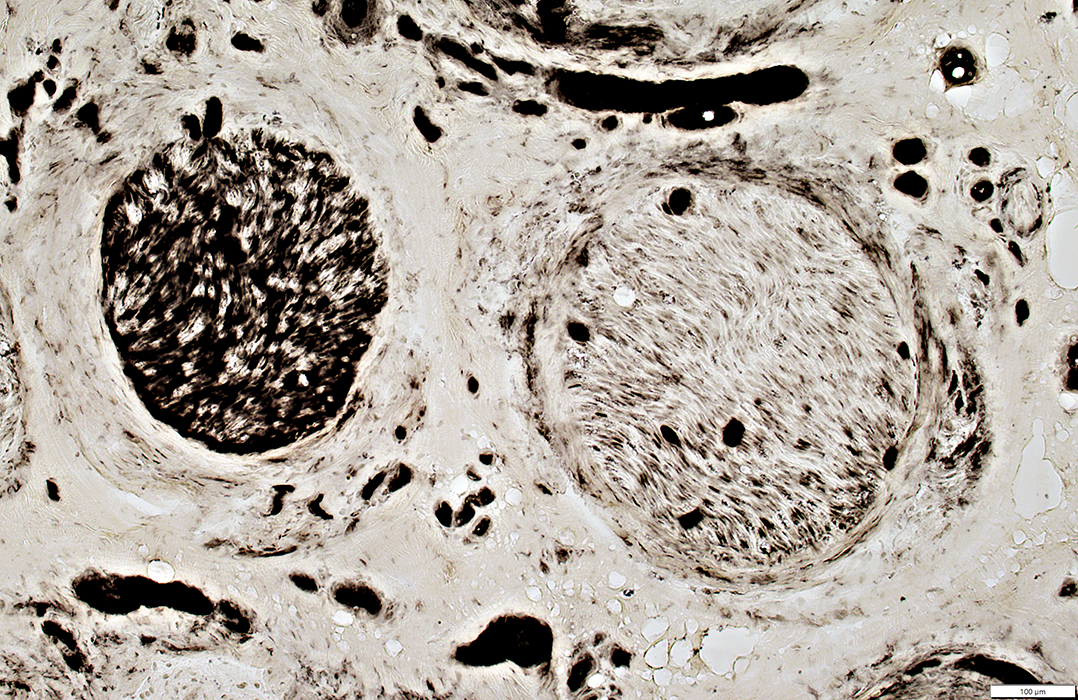
Behçet Nerve Pathology
Varied loss of Axons among fascicles
Severely damaged fascicle with loss of axons & endoneurial cells (White Arrow)
Perineurial Damage (Yellow Arrows)
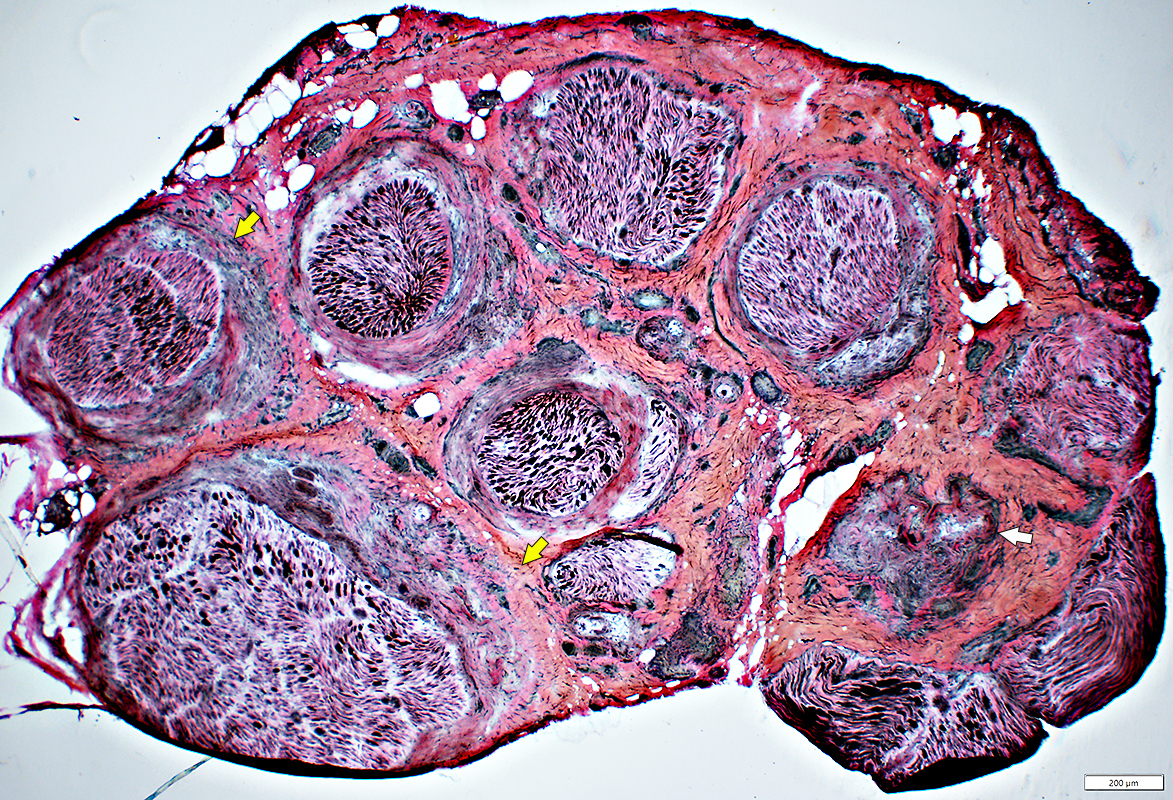 VvG stain |
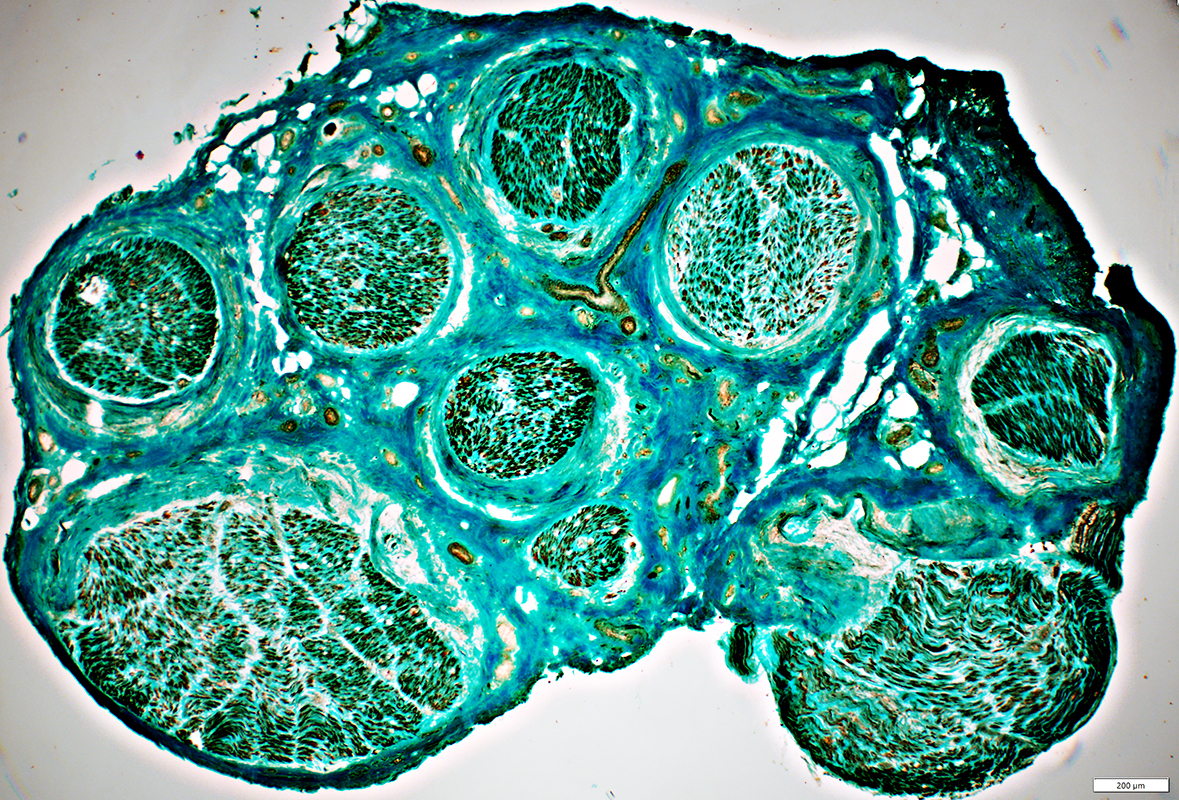
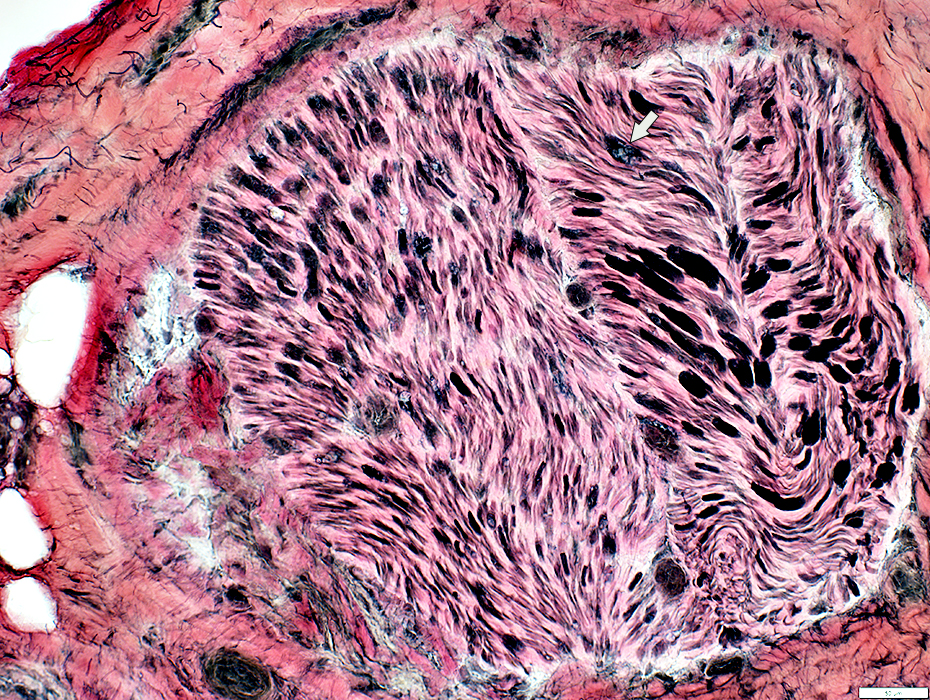
Behçet Nerve Pathology
Varied loss of Axons among fascicles
Severely damaged fascicle with loss of axons & endoneurial cells (White Arrow)
Perineurial Damage (Yellow Arrows)
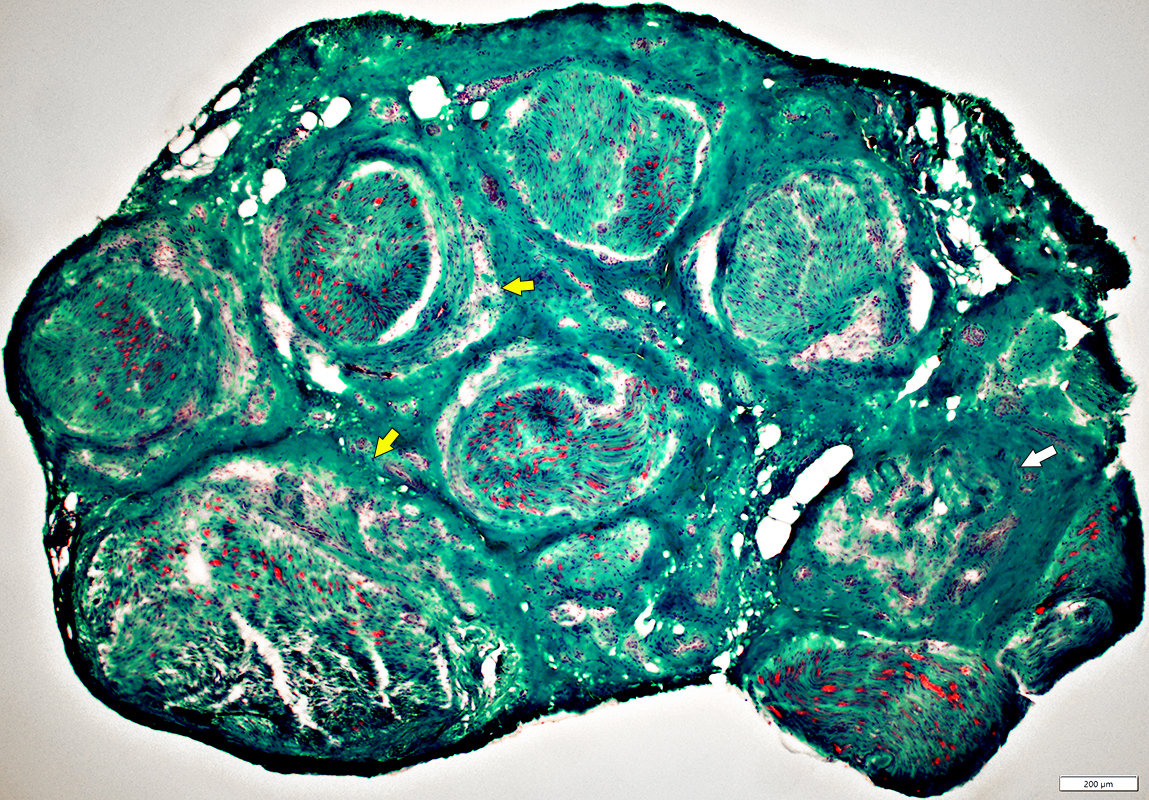 Gomori trichrome stain |
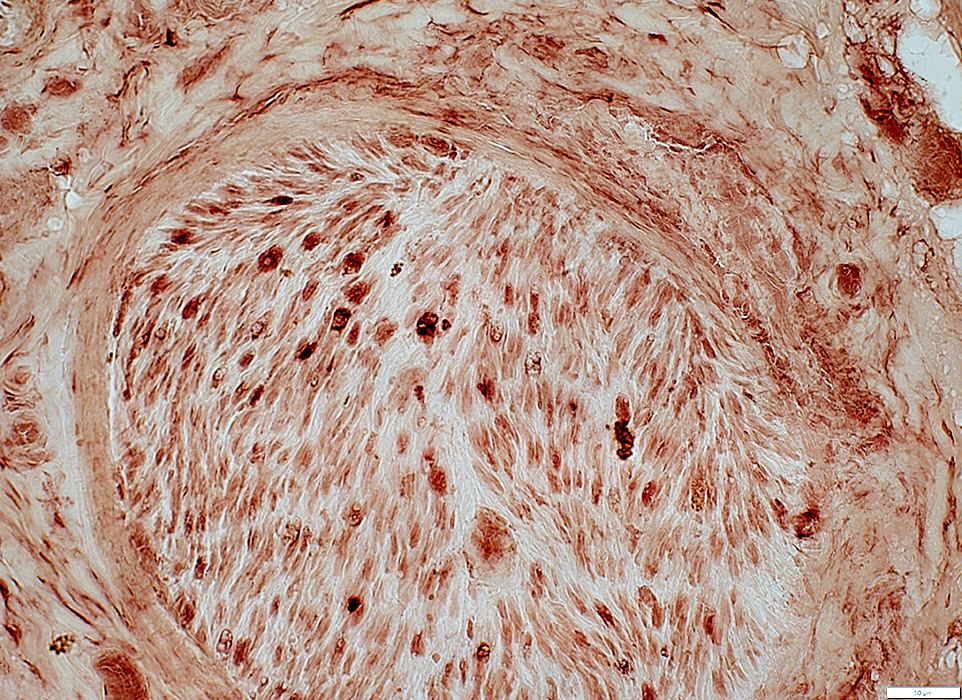
Behçet Nerve Pathology
Local Infarction: Varied loss of Non-myelinating Schwann cells among fascicles
 NCAM stain |
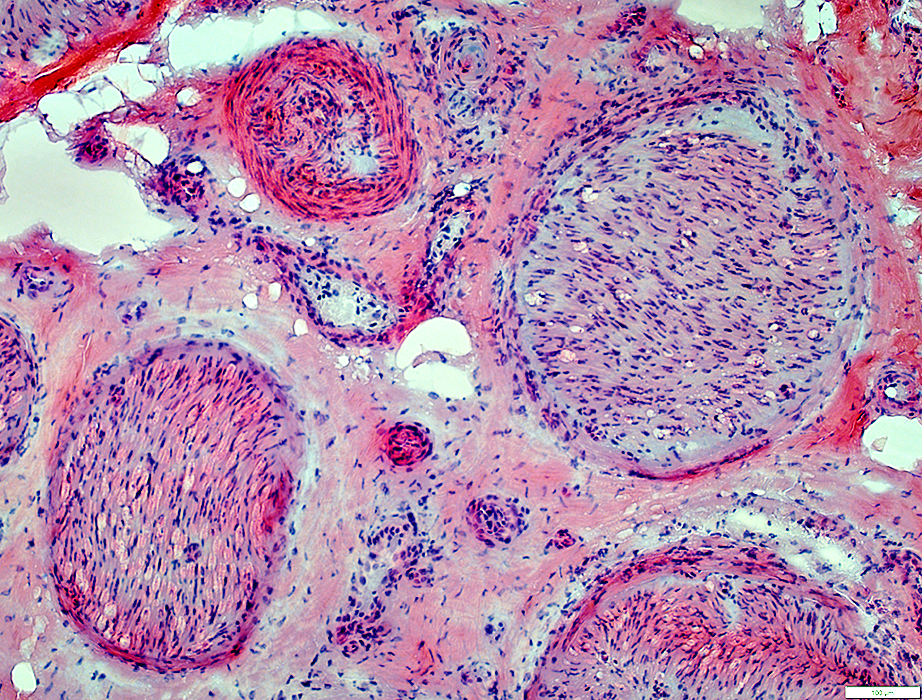
Vessel Pathology
Epineurial Veins: Damaged or Occluded
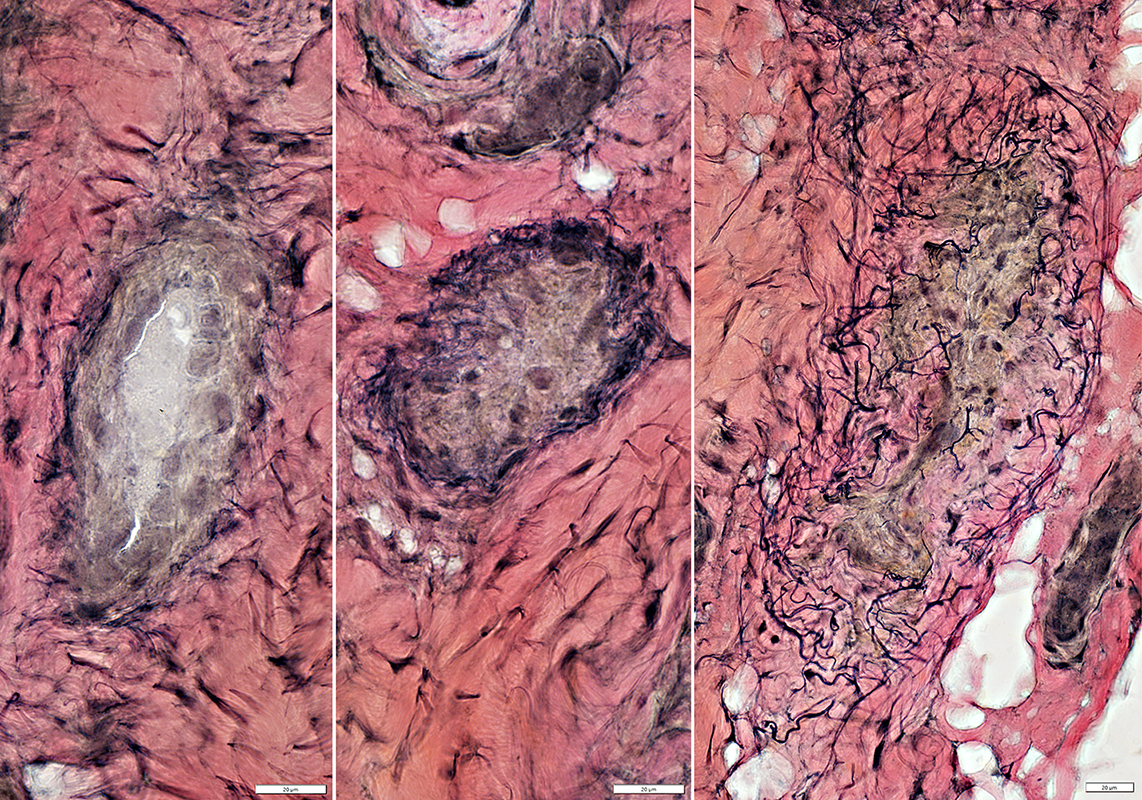 VvG stain |
Epineurial Artery: Occluded
 H&E and Neurofilament stain |
Lymphocyte Inflammation
 H&E stain |
Associated with: small epineurial vessel
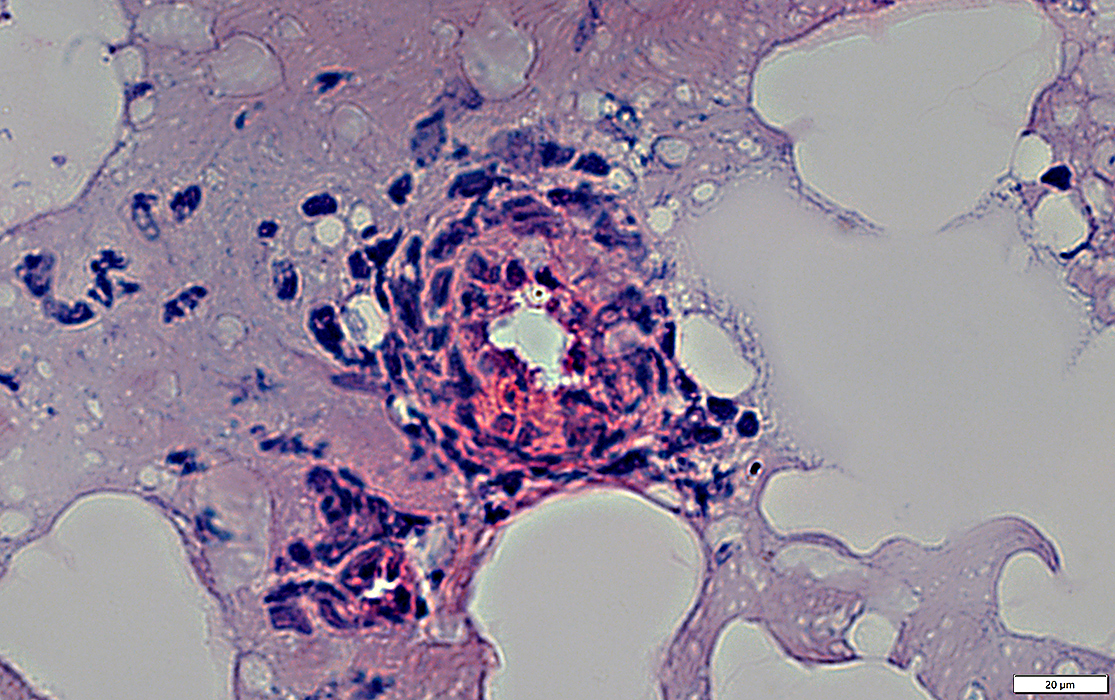 H&E stain |
Epineurial Neovascularization
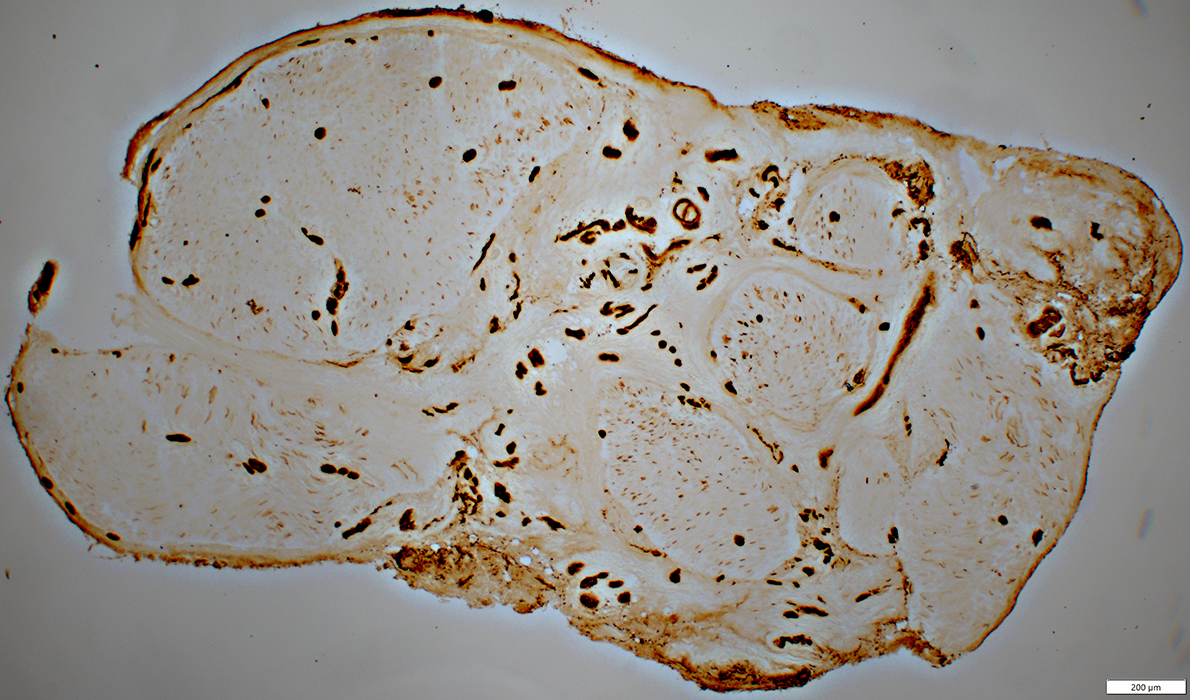 UEA I stain |
Multiple, Small vessels
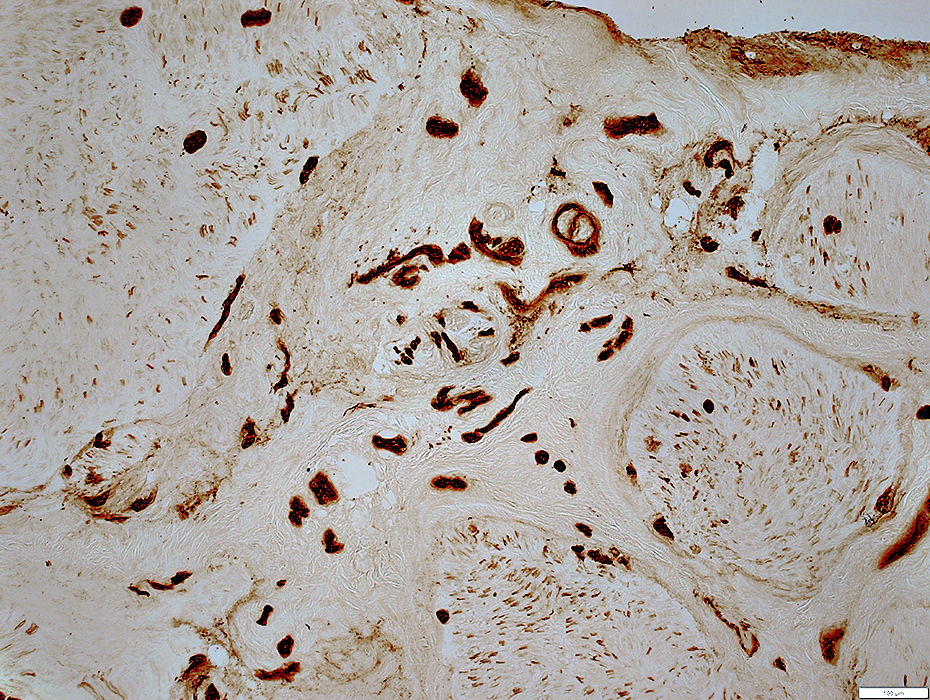 UEA I stain |
Epineurium
Multiple, Small vessels
MCH-I upregulation by Epineurial connective tissue
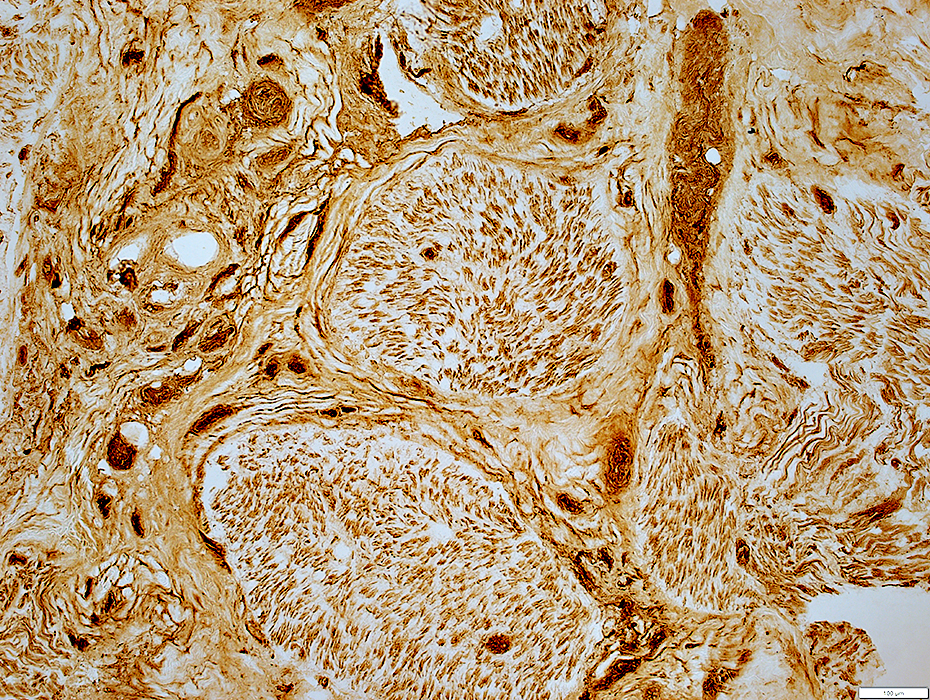 MHC Class I stain |
Endoneurial Microvessels: Dilated
 Toluidine blue stain |
Size: Large
Lumen: Large; Filled with RBCs
Wall: Thin
Axons
Loss of large & small Myelinated axons
Remaining axons: Small
Wallerian degeneration: Scattered ovoids
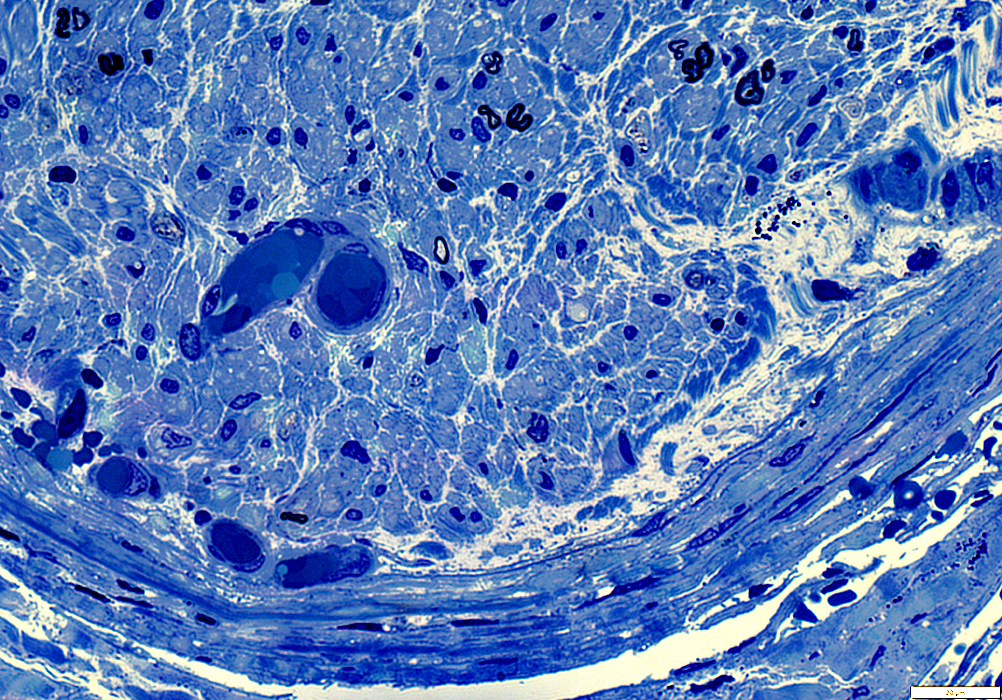 Toluidine blue stain |
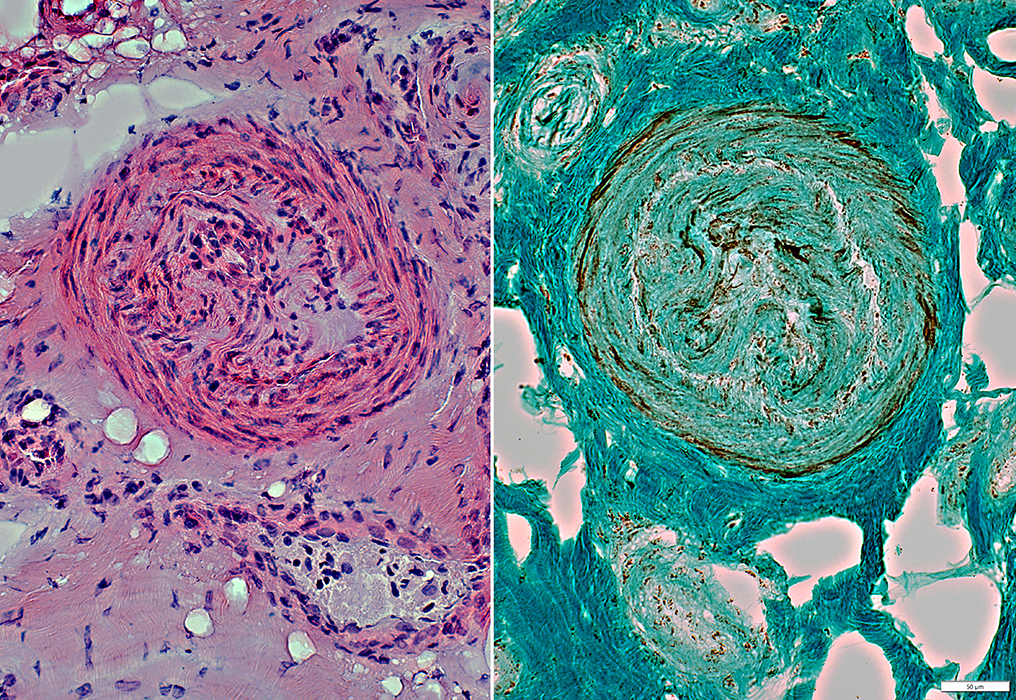
Behçet: Perineurial Pathology
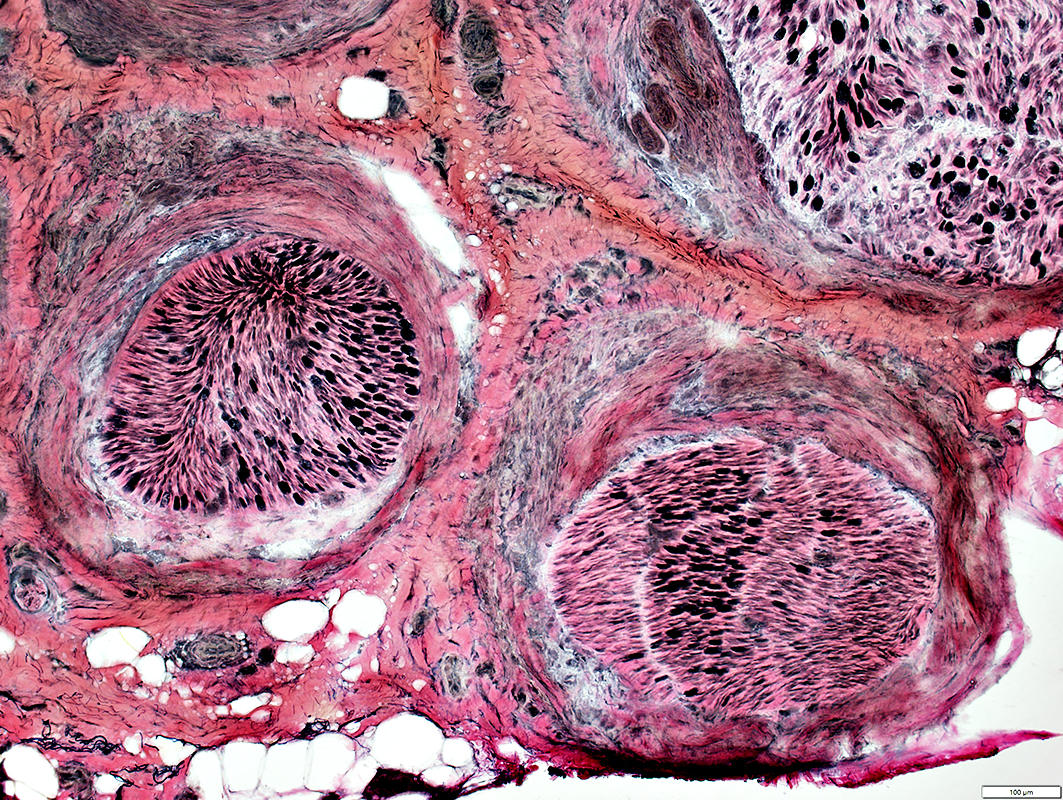 VvG stain |
Axon loss: Intrafascicular variation
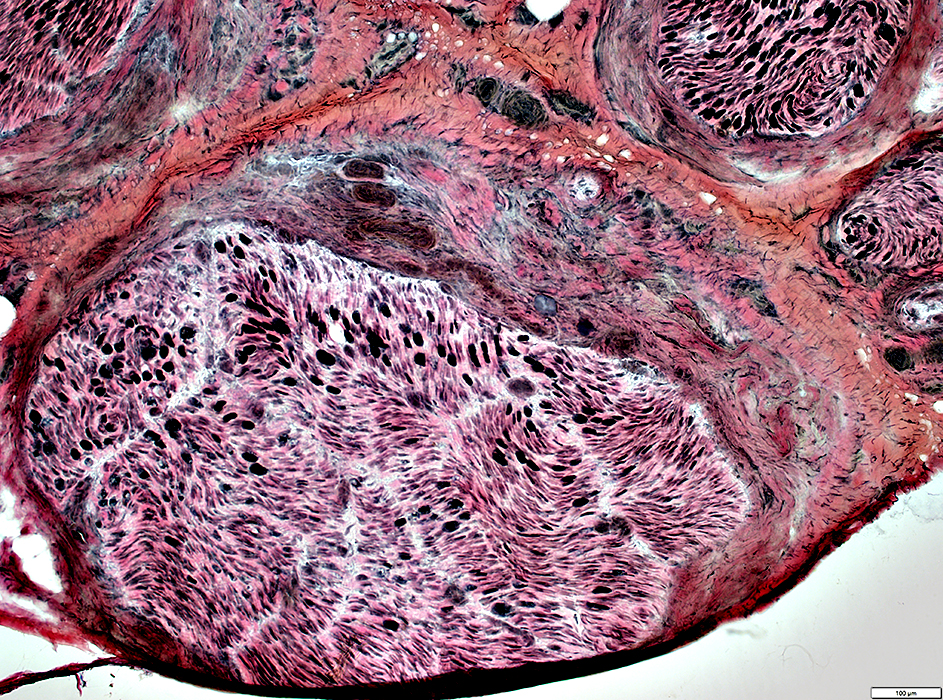 VvG stain |
Fascicles with Non-uniform, Irregularly-stained Perineurium
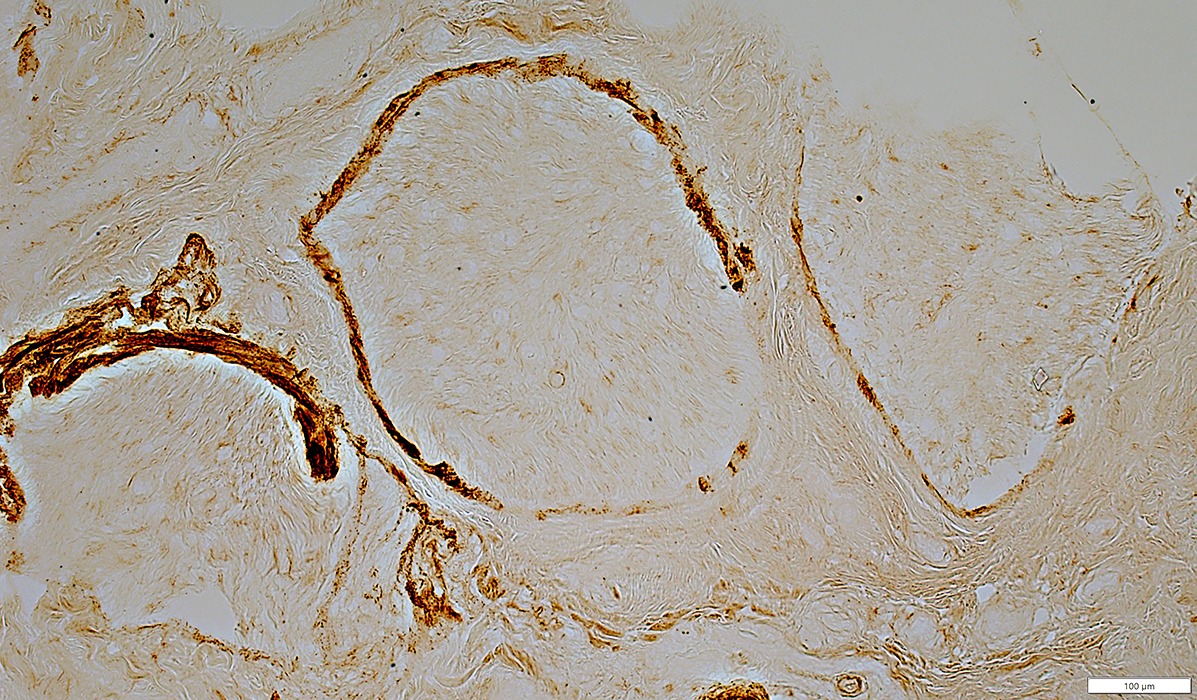 C5b-9 stain |
Wallerian Degeneration
 VvG stain |
Pale, Irregularly-stained Myelin (Above; Arrow)
Acid phosphatase stains a few degenerating myelin sheaths (Below)
 Acid Phosphatase stain |
Nerve Ischemia, Local: Varied involvement of Cells in Different Fascicles
Also see: Rheumatoid Vasculitis
 H&E stain |
Left: Normal background staining of endoneurium
Right: Endoneurial Pallor with mild subperineurial edema
Wallerian Degeneration: Staining of myelin sheaths is lost
Vessels
Occluded artery & Damaged veins
 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Left: Normal to dark background staining of endoneurium
Right: Endoneurial Pallor
Epineurium
Neovascularization: Many small, ATPase+ vessels
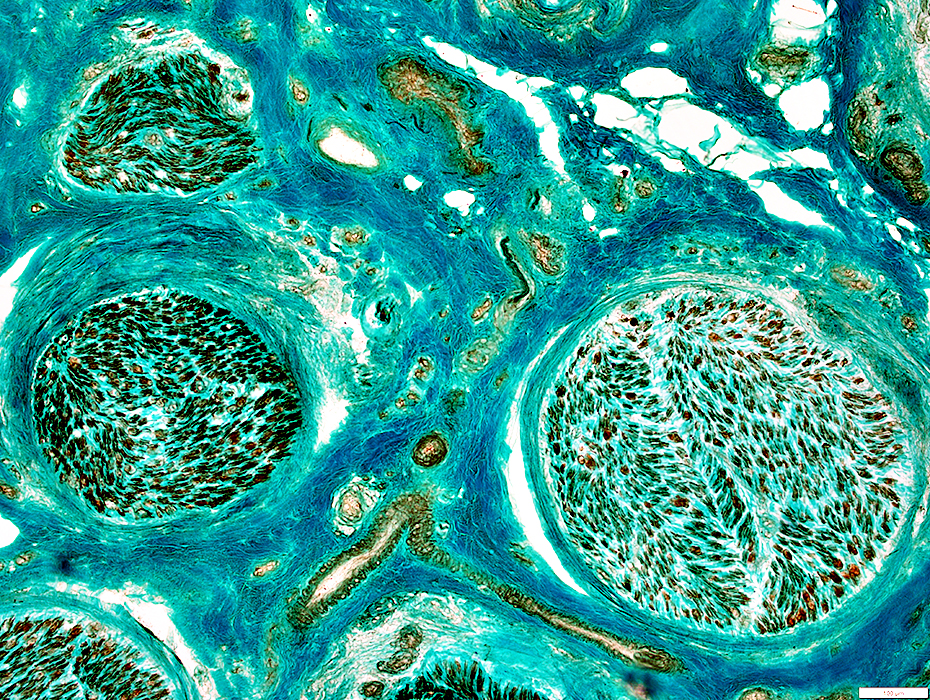 NCAM stain |
Left: Diffuse distribution of non-myelinating Schwann cells in endoneurium
Right: Reduced numbers of non-myelinating Schwann cells in endoneurium
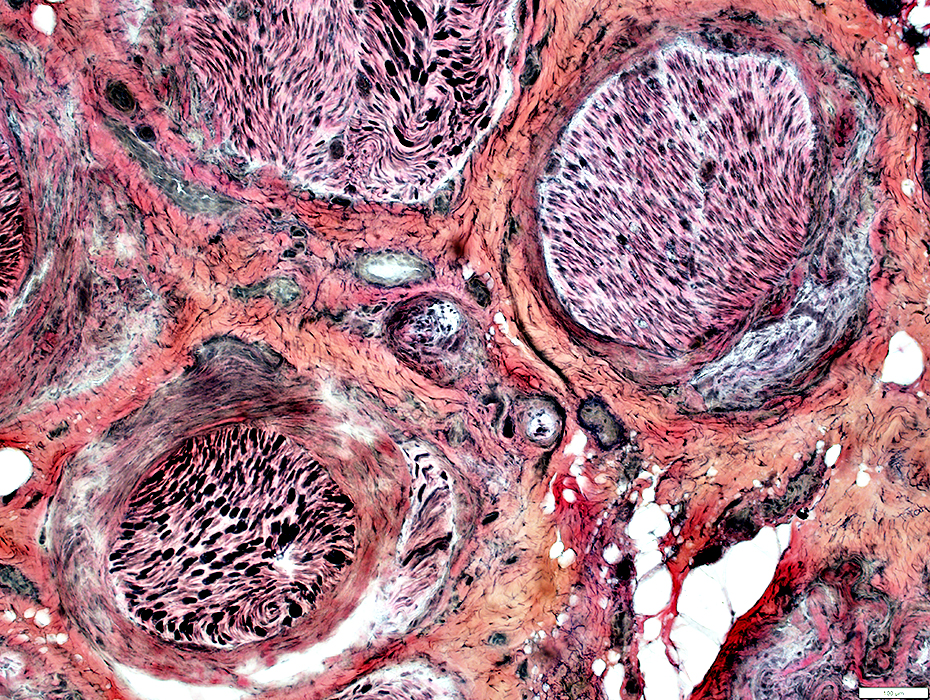 VvG stain |
Left: Mild loss of myelinated axons
Right: Severe loss of myelinated axons
Above: Intrafascicular variation in loss of myelinated axons
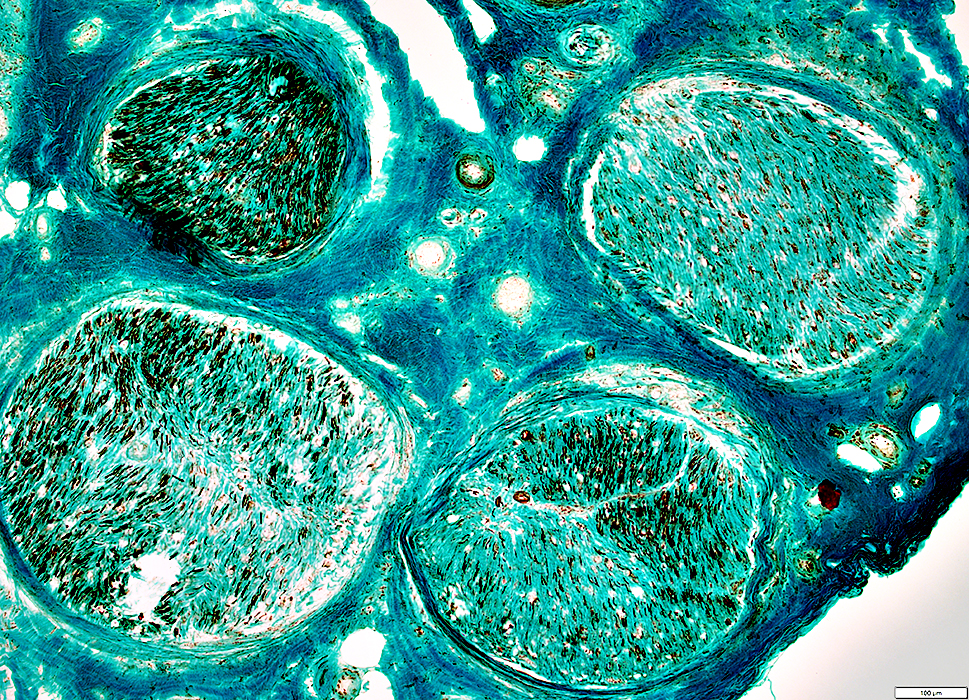 Neurofilament stain |
Left, Above: Mild loss of myelinated axons; Normal numbers of small axons
Right, Above: Severe loss of all axons
Below: Fascicles with intrafascicular variation in loss of axons
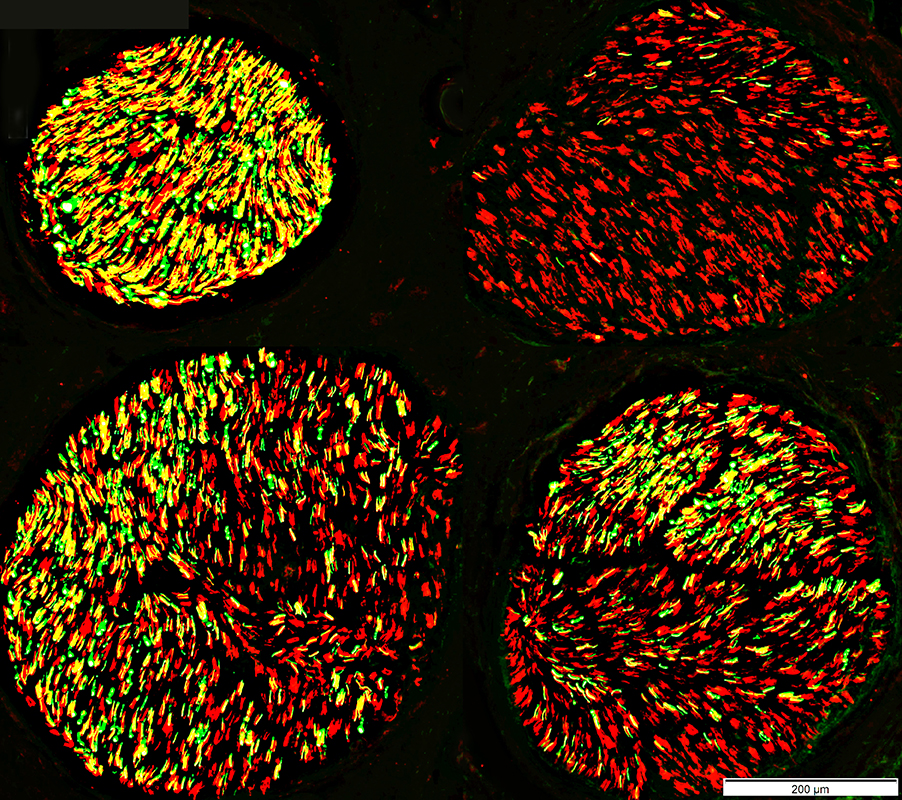 Neurofilament (Green) + NCAM (Red) stain |
Damaged Fascicle
Endoneurium: Collapsed & Lost
Perineurium: Wavy & Irregular shape
Surrounding Epineurium: Neovascularization
Compare to: Other fascicles in nerve
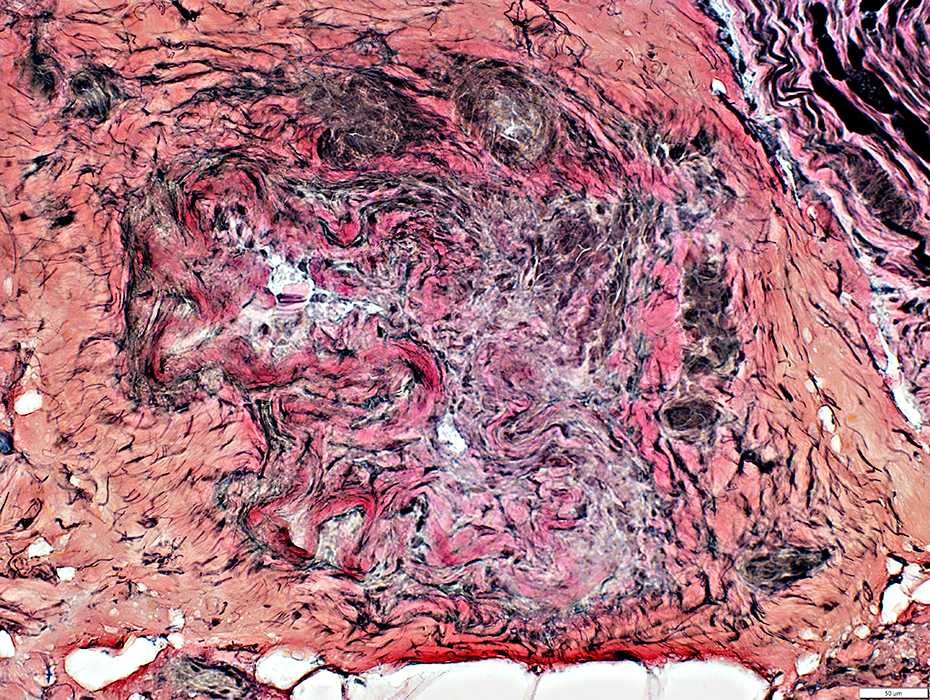 VvG stain |
Schwann Cell Populations
P0(r)sm.jpg) NCAM (Green), P0 (Red) |
Little co-staining of P0 & NCAM in Schwann cells
MBP(r)sm.jpg) Neurofilament (Green), Myelin Basic Protein (MBP) (Red) Immature Schwann cells on many remaining axons MBP stains on smaller axons with no myelin |
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Return to Immune Axonal Neuropathies
1/9/2025