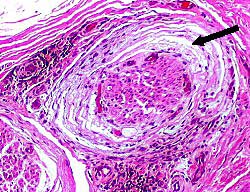
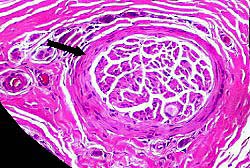
Perineurium
|
Normal Description Images Disorders |
Perineurium: Disorders
- Perineurium
- Damage & Abnormal structure
- Trauma
- Minifasciculation
- Neuroma
- Calcification
- Inflammation & Immune
- Perineuritis
- Subperineurial edema
- Spanish toxic oil
- Leprosy: "Onion-skinning"
- Behçet
- Other: Cryoglobulinemia; Sarcoid; Lyme; Lymphoma
- Inclusions
- Fabry's
- Xanthomatous neuropathy
- Neoplasm & Proliferation
- Perineurioma
- Perineuriosis (Proliferation of perineurial cells in endoneurium)
- Also see: Perineurium components
Perineurium: Normal
 Toluidine blue stain |
Structure: Lamellar
Fewer fascicles in distal, smaller nerves
Outer layers may merge with epineurial connective tissue
Location: Surrounds all peripheral nerve fascicles
Cells
Basal lamina: Surrounds perineurial cells; Thicker than Schwann cell basal lamina
Cytoplasm contents
Filaments
Pinocytic vesicles: More in outer perineurial layers
Tight junctions: Link adjacent perineurial cells; More in inner perineurial layers
Origin: May be endoneurial fibroblasts
Molecular
Stained by
C5b-9 antibodies
Epithelial Membrane Antigen
Contains: Collagens I & III
Function
Part of Blood-Nerve barrier
Regulates endoneurial melieu
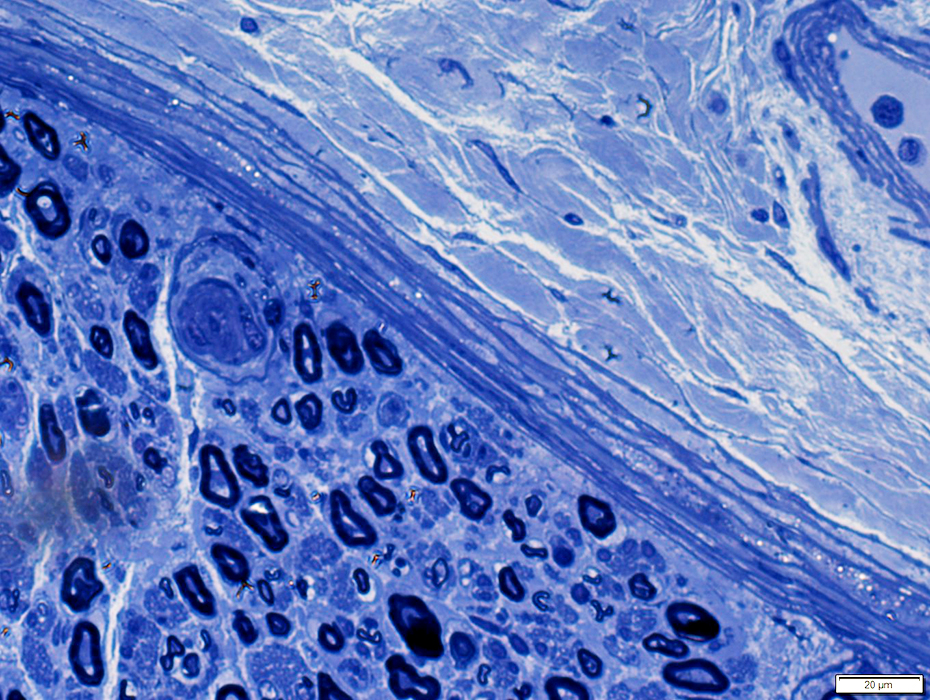
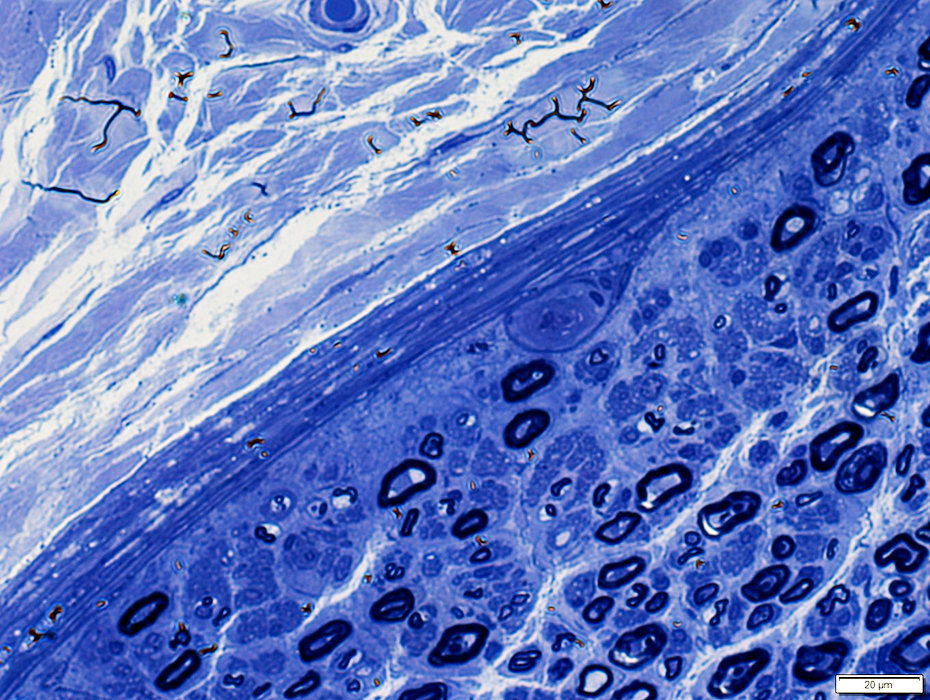 Toluidine blue stain |
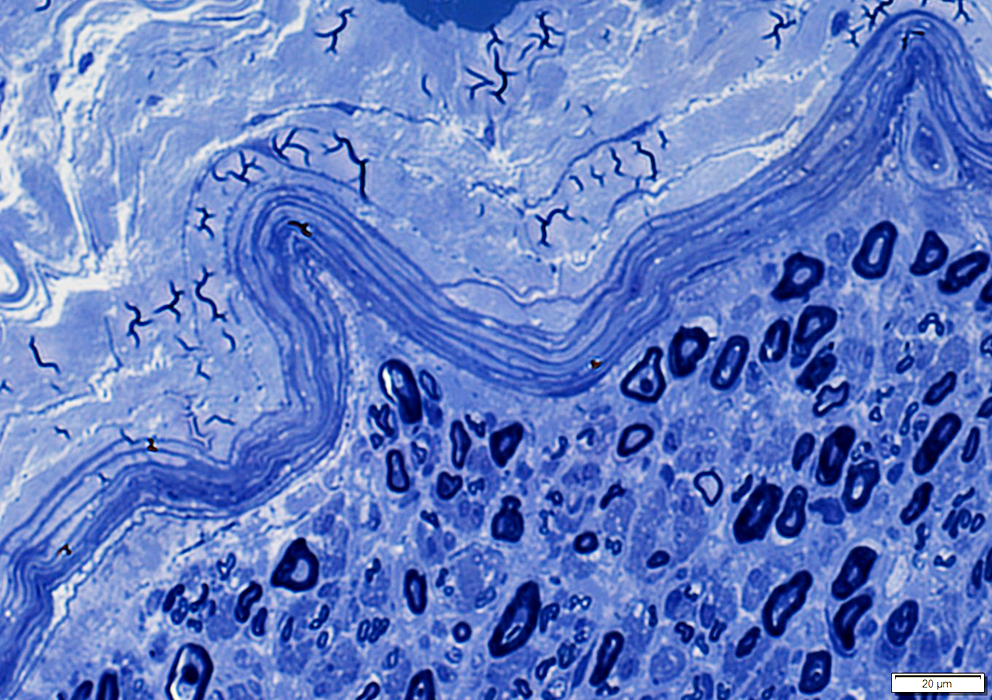 Toluidine blue stain |
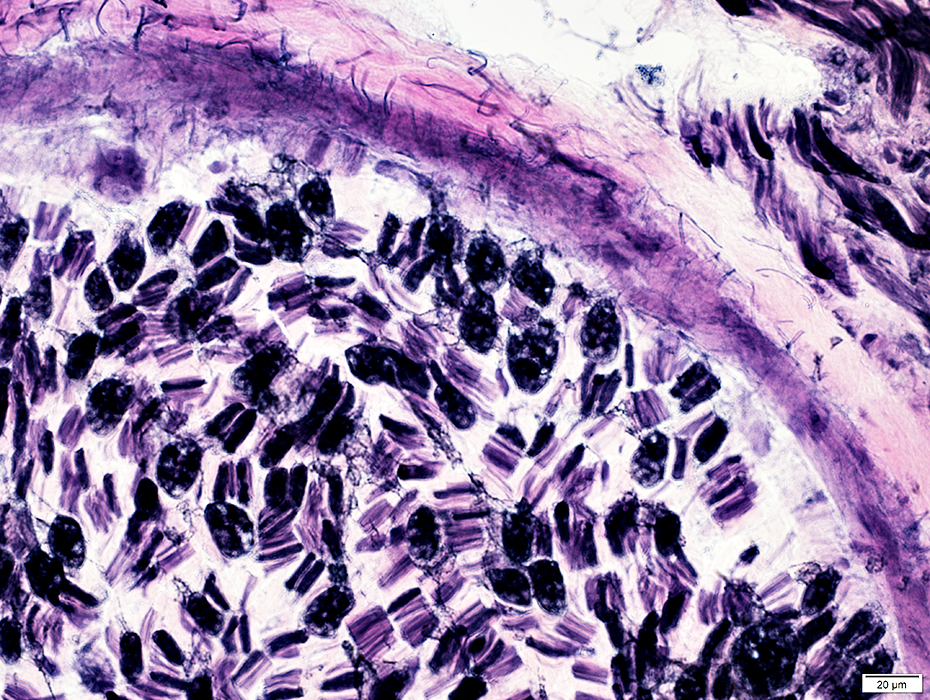 VvG stain |
Vessel within Perineurium
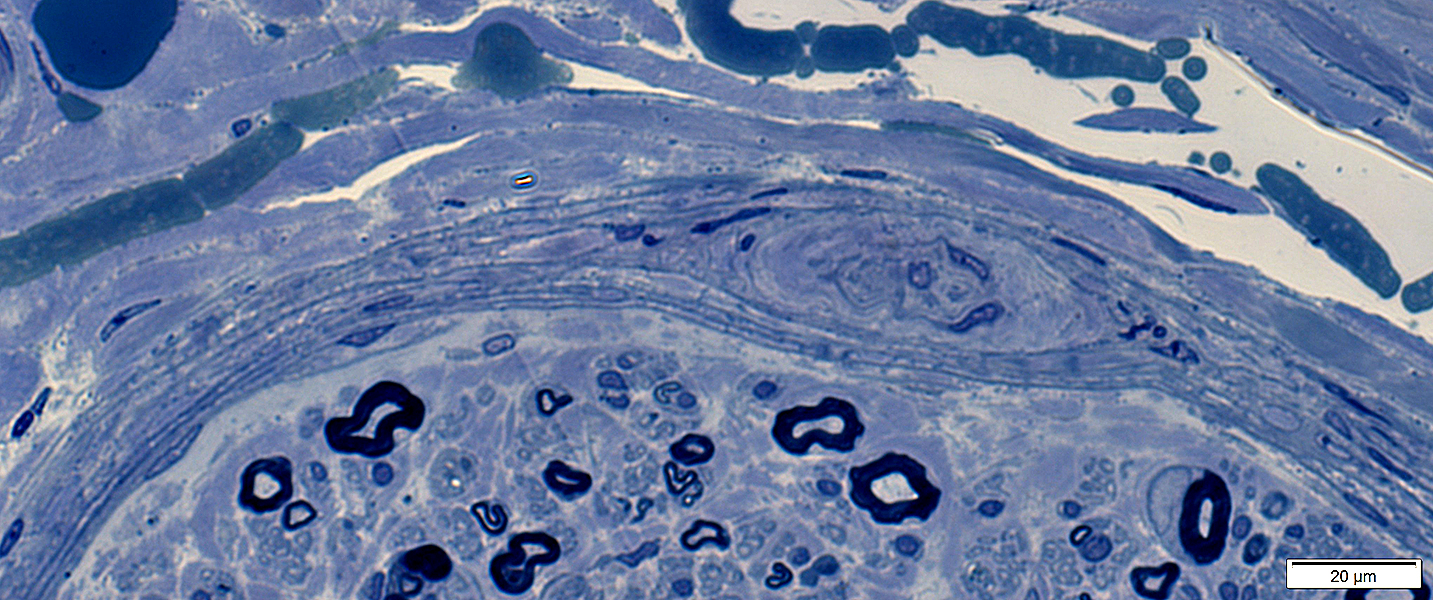 Toluidine blue stain |
Perineurium: Thin
Perineurium: Thin & Narrow
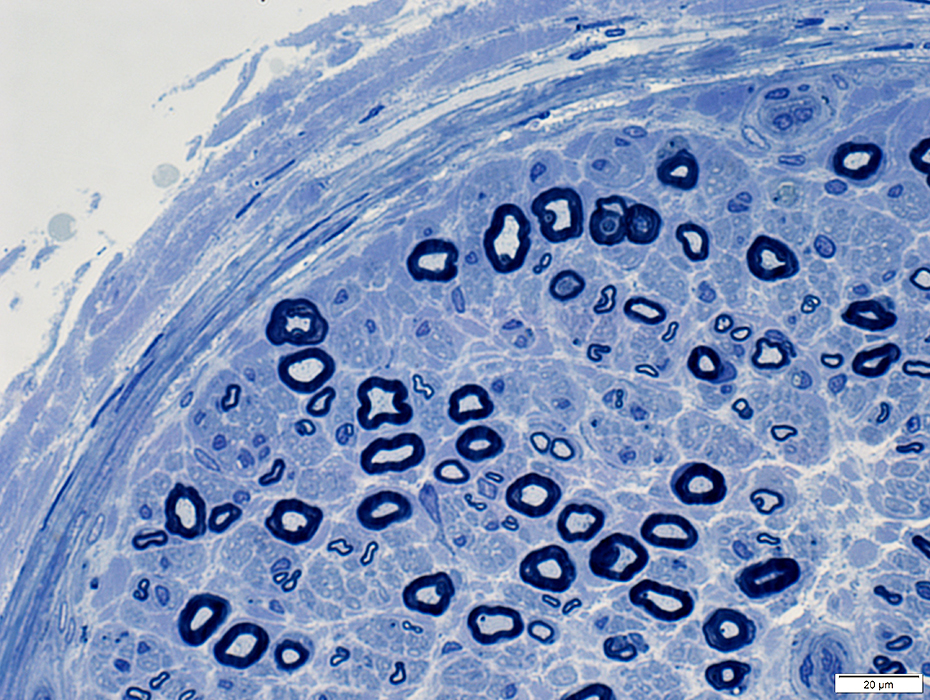 Toluidine blue stain |
Perineurium: Indistinct connective tissue layers
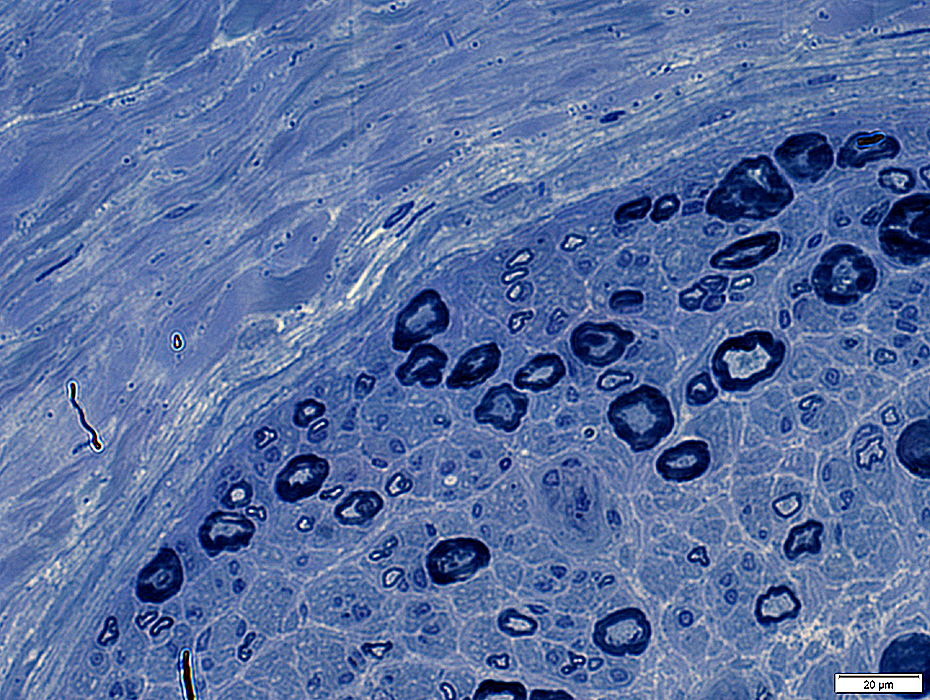 Toluidine blue stain |
Perineurium: Narrow; Few fibrils
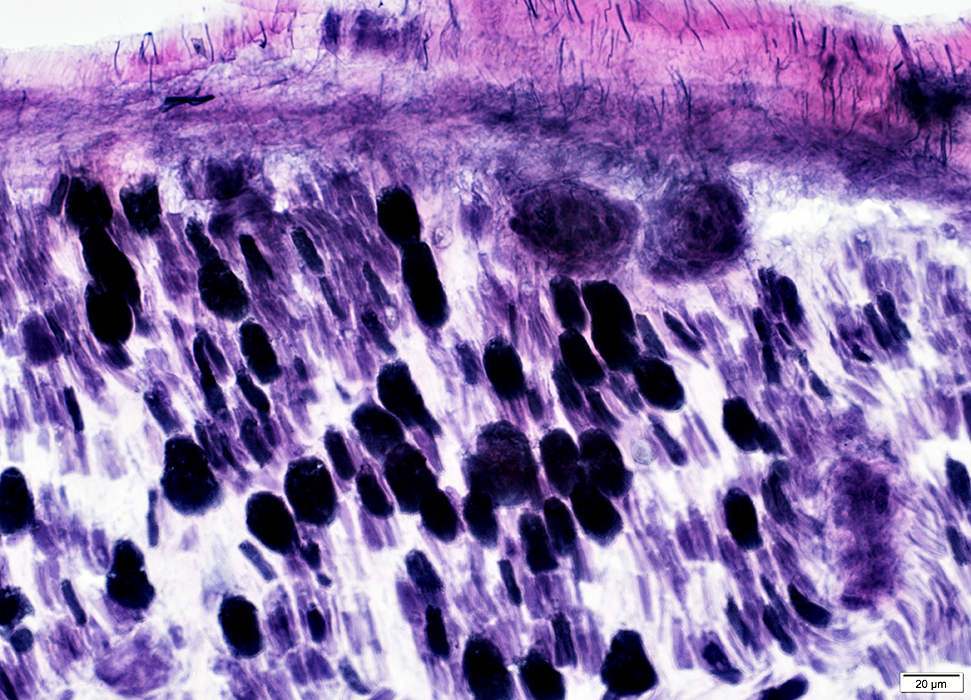 VvG stain |
Perineurium: Wide & Thickened
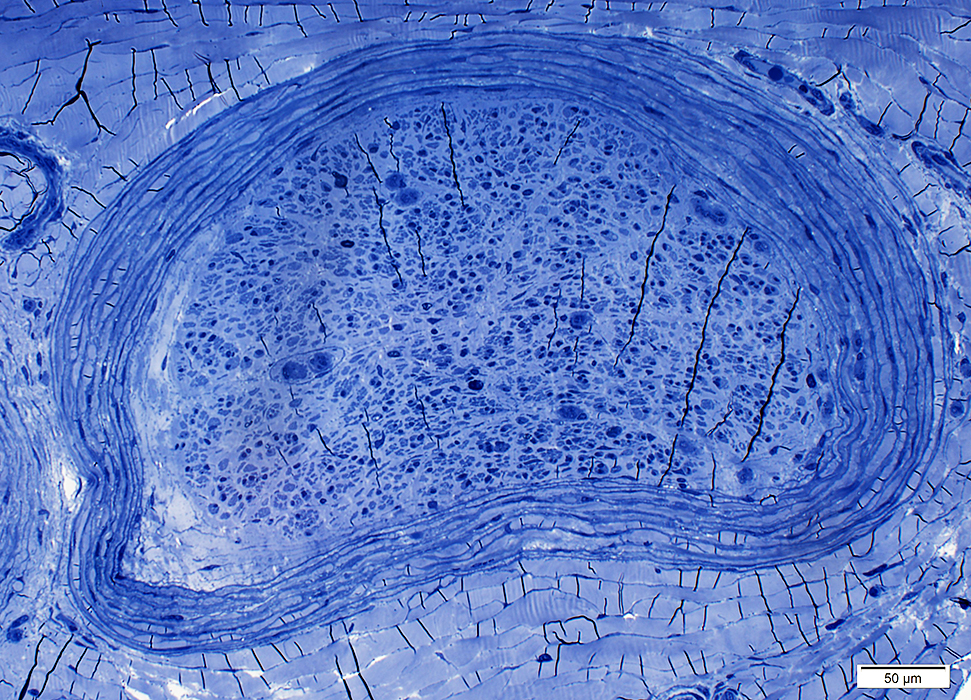 Toluidine blue stain |
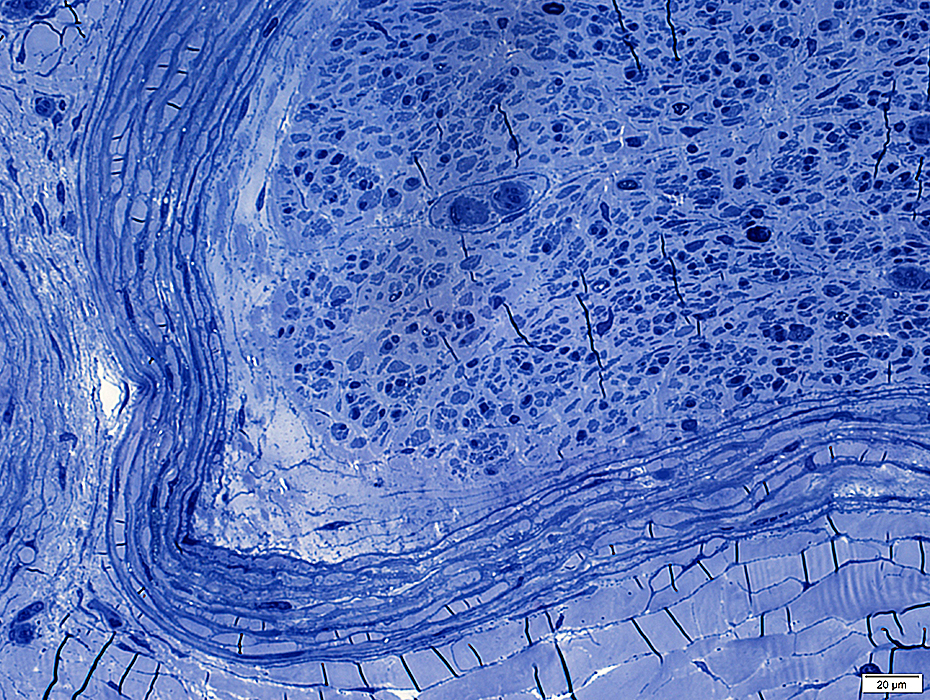 Toluidine blue stain |
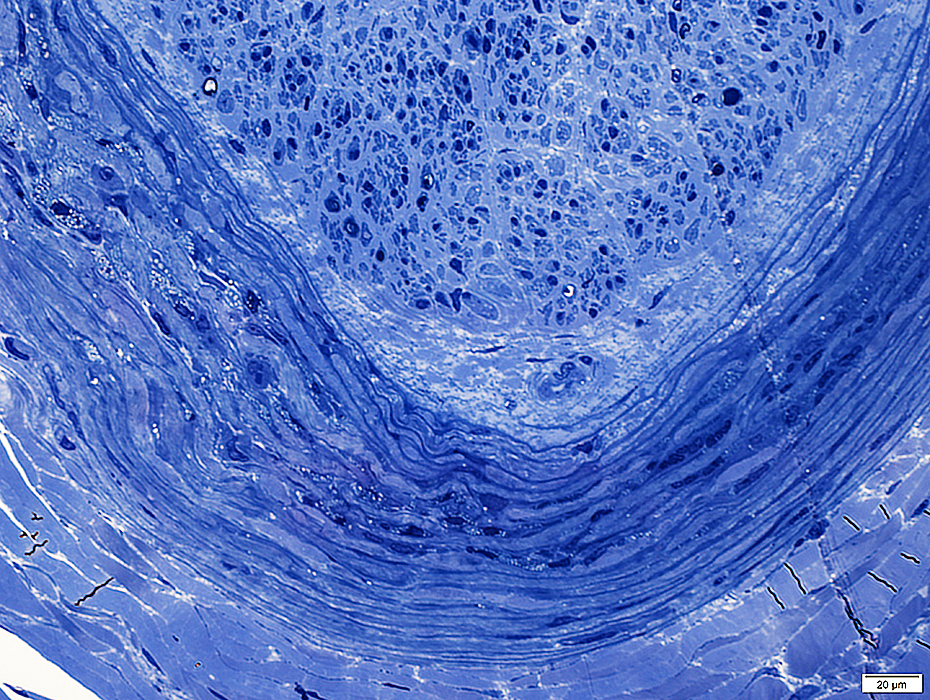 C5b-9 stain |
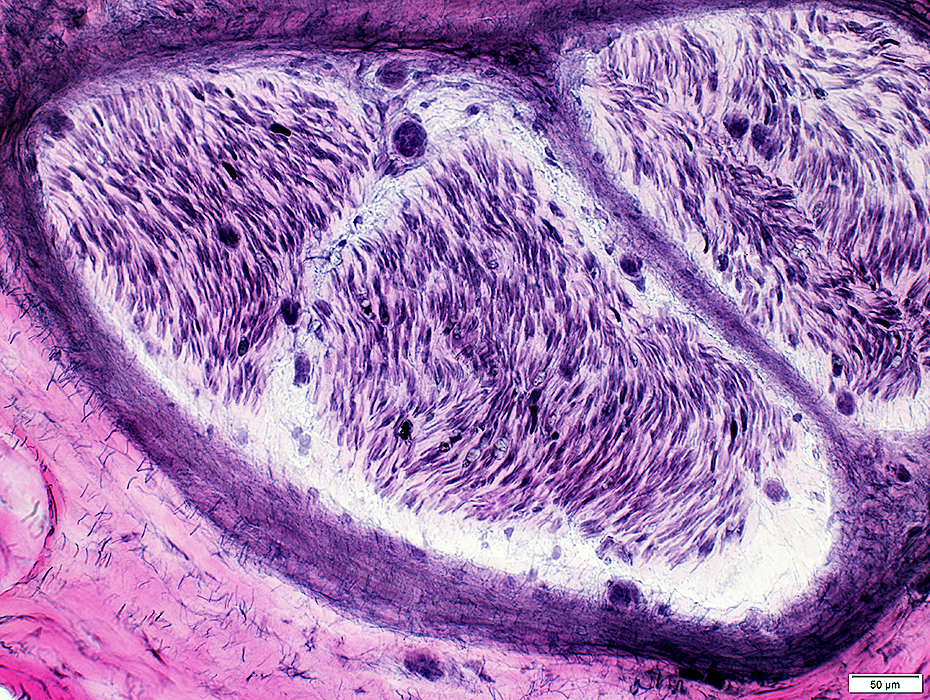
|
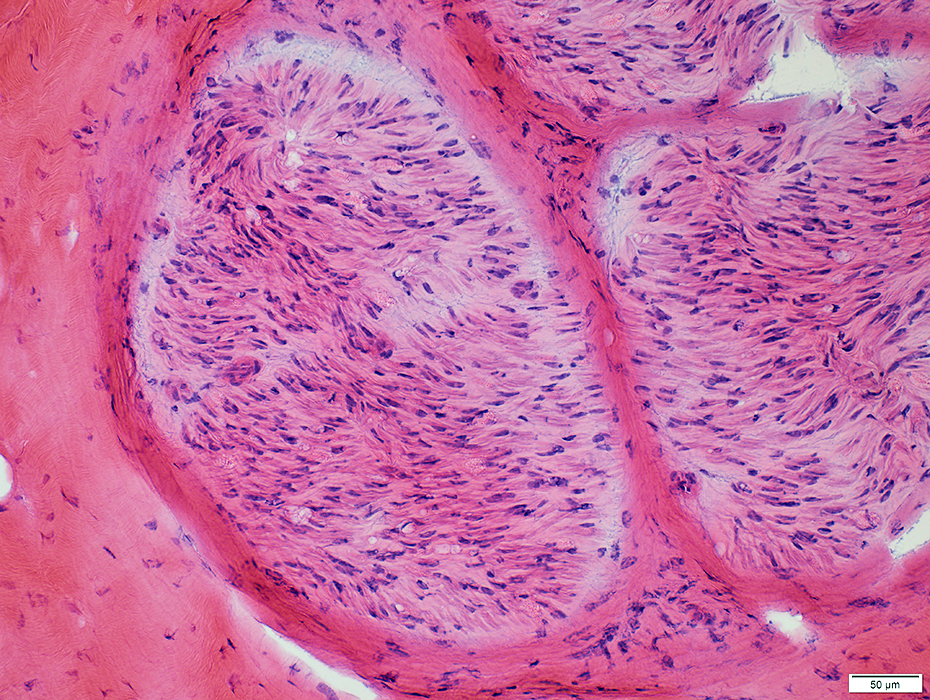
|
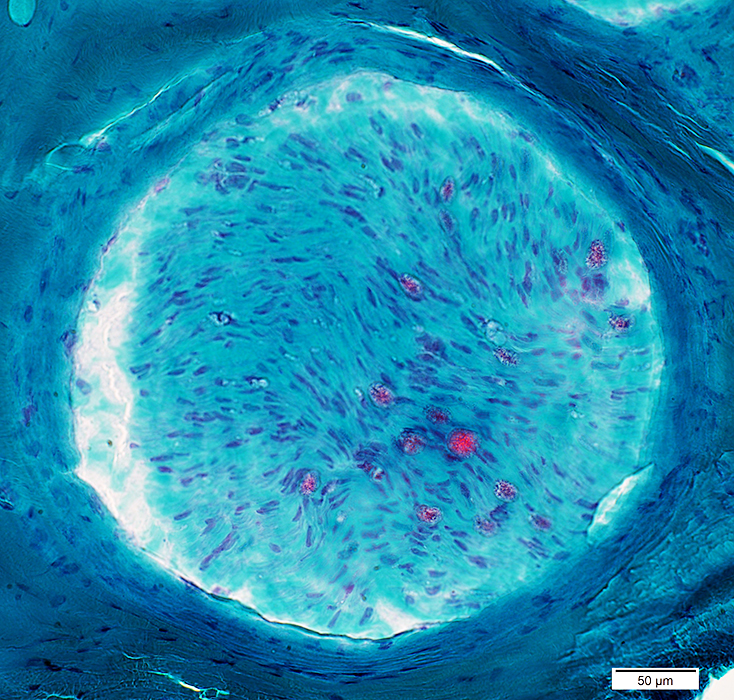
|
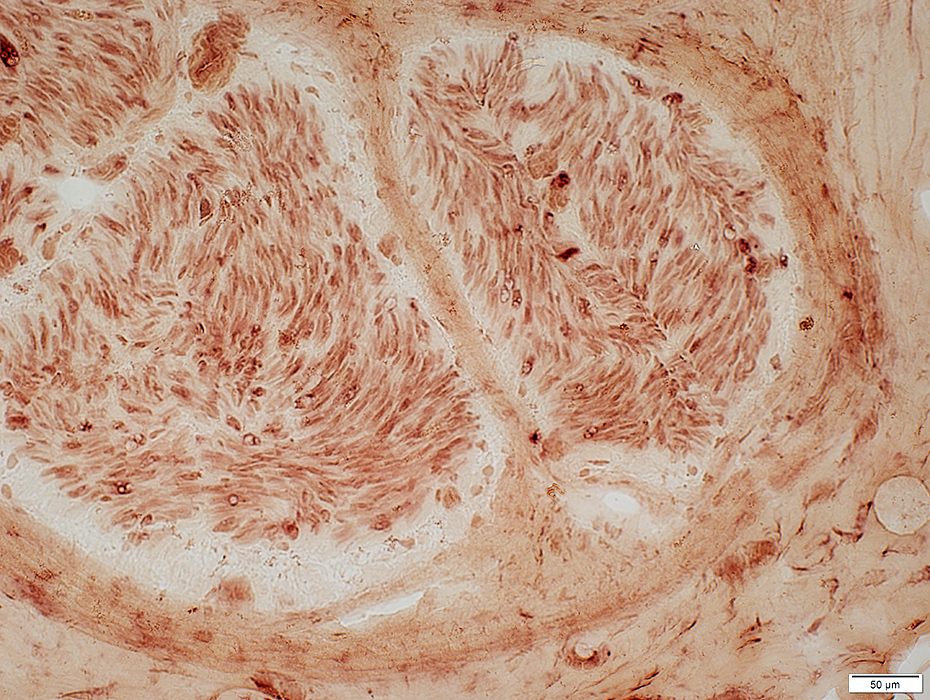
|
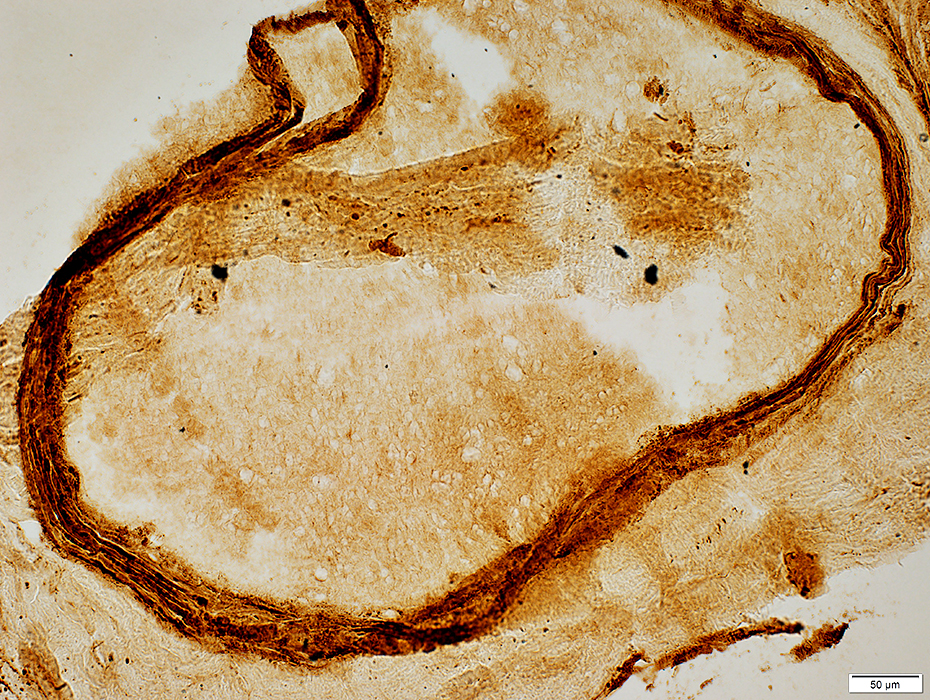 C5b-9 stain |
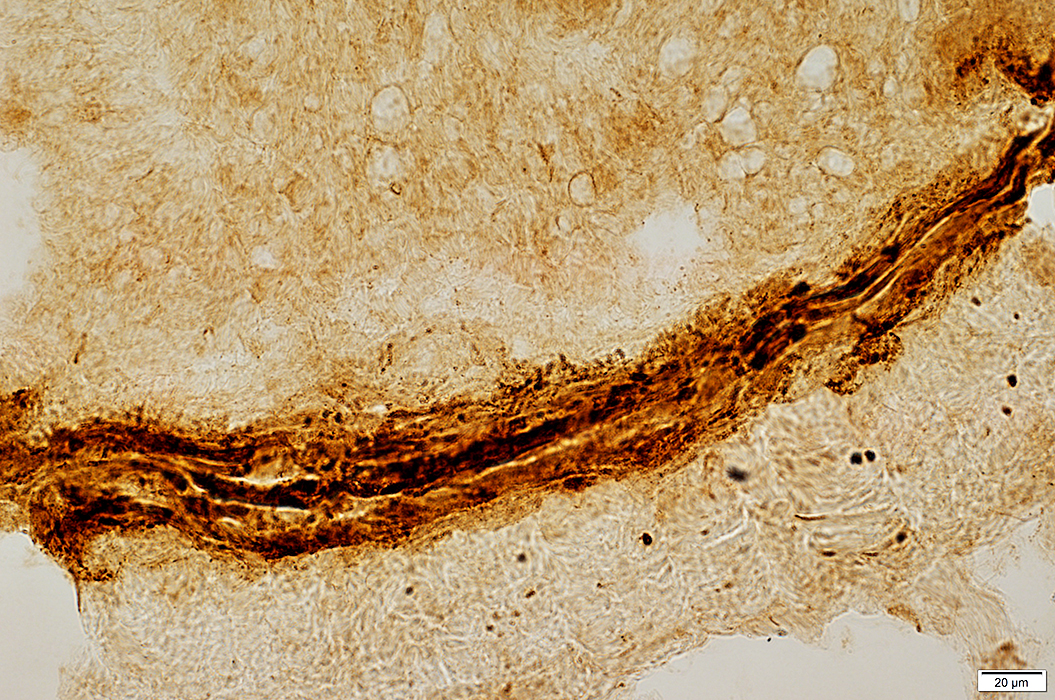
|
Perineuritis 1
|
Anatomic Pattern Axon involvement Differential fascicular Wallerian degeneration Connective tissue Inflammation Perineurial Damage Behçet ICI Vessels Endoneurial inflammmation Epineurial |
Perineuritis: Anatomic Pattern in Nerve
General: Varied involvement among fascicles
Perineurial Connective Tissue Damage
Several fascicles with perineurial acid phosphatase staining (Arrows)
Wallerian degeneration with scattered Histiocytes (Larger fascicle; Right)
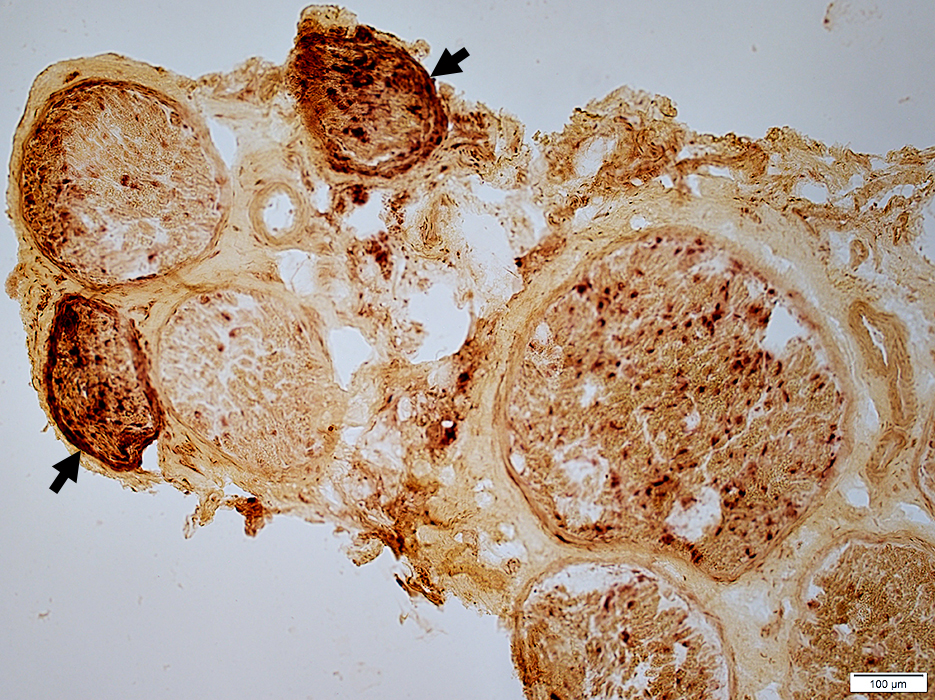 Acid phosphatase stain |
Perineurium: Structural Damage, Varied patterns
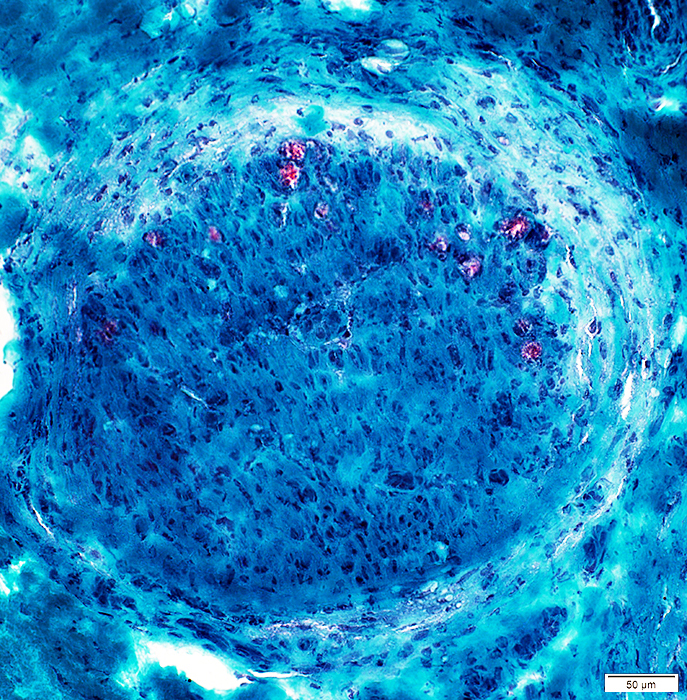 Gomori trichrome stain Perineurium Widened around fascicle Some areas are pale |
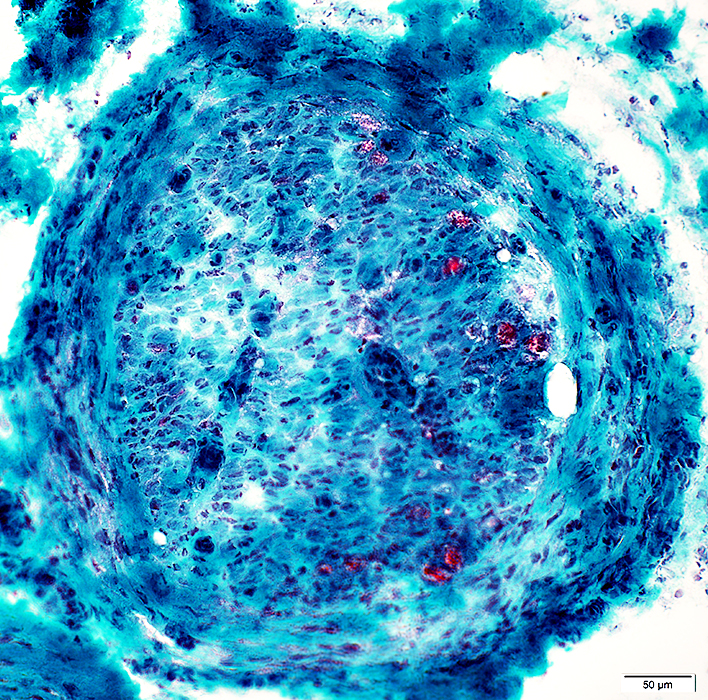 Gomori trichrome stain Perineurium Widened around fascicle Some areas are more dense or dark-stained |
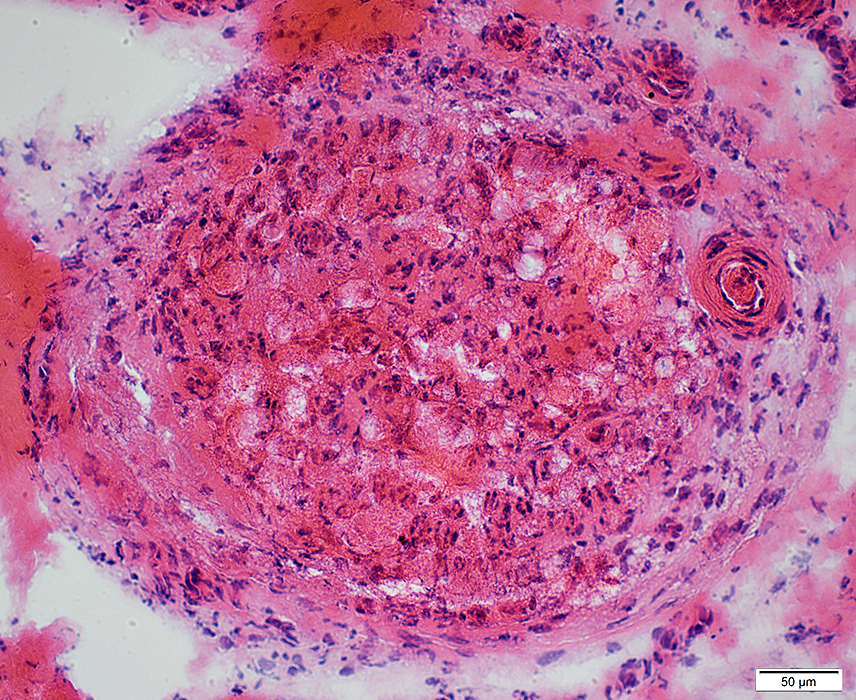 H&E stain |
|
Widened around fascicle
Some areas are light- or dark-stained
Cellularity: Increased
Endoneurium
Microvessels: Large; Darker stained
Axons: Reduced numbers
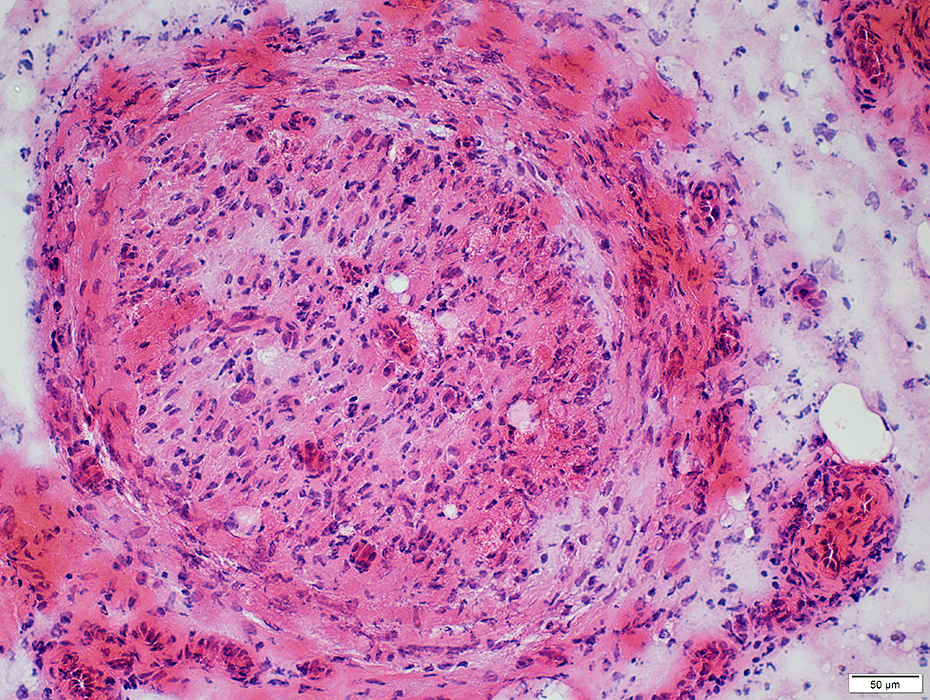 H&E stain |
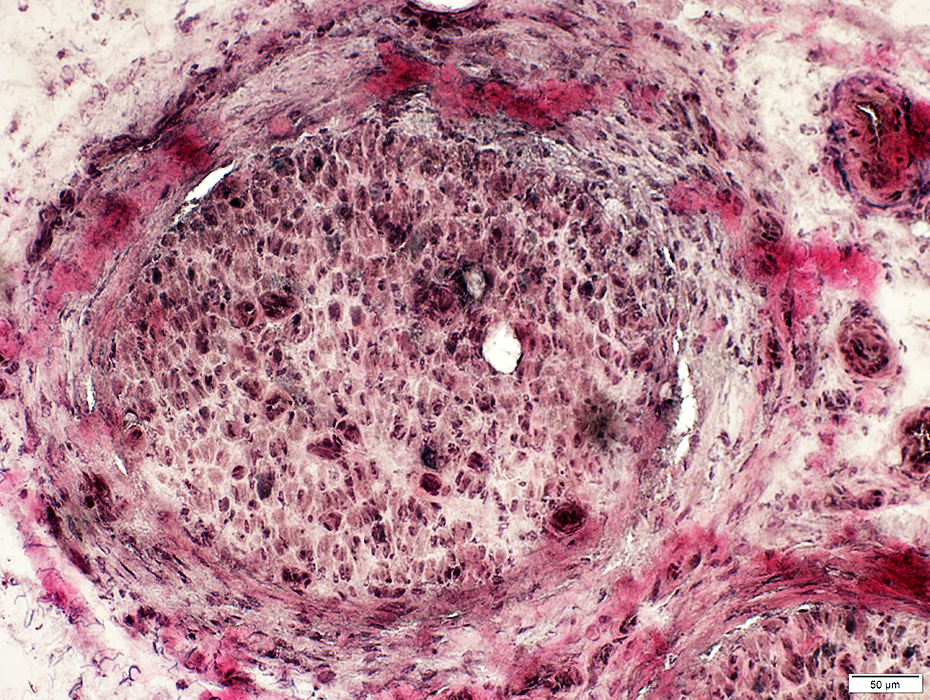 VvG stain |
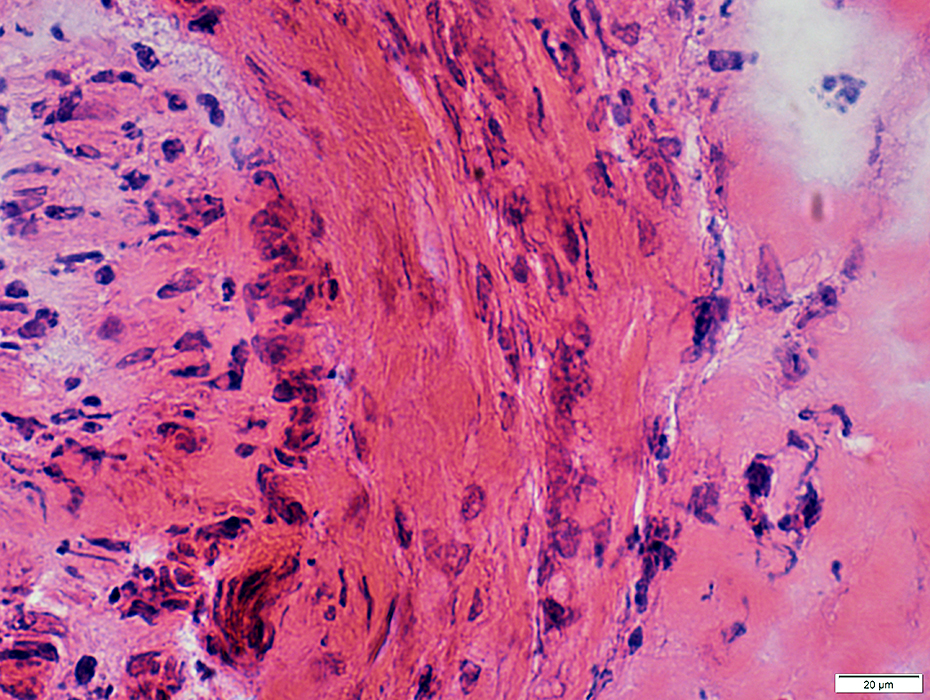 H&E stain |
Connective tissue staining
Increased (Above)
Reduced (Below)
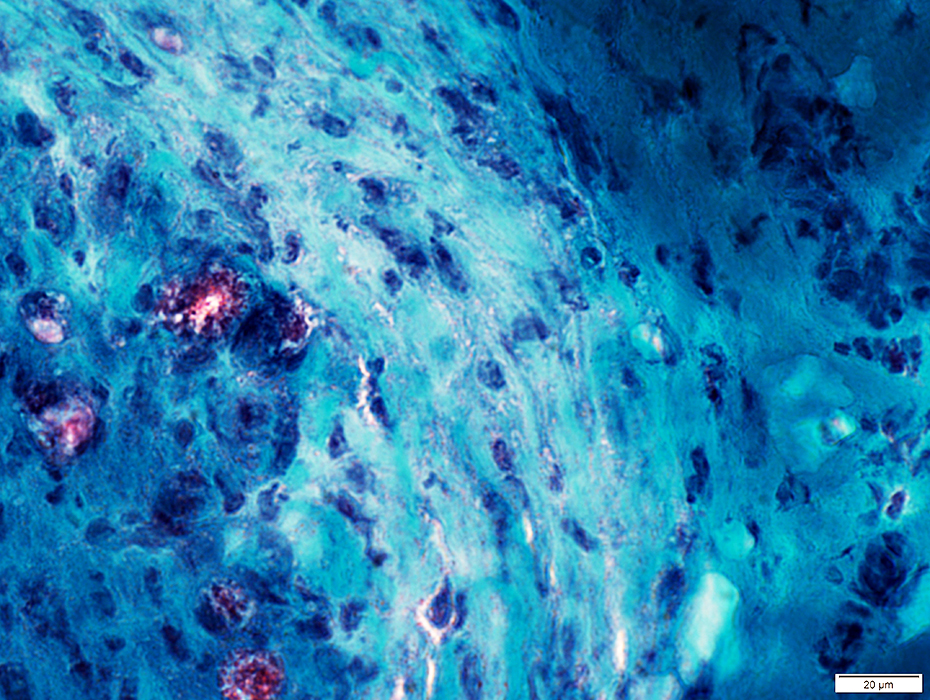 Gomori trichrome stain |
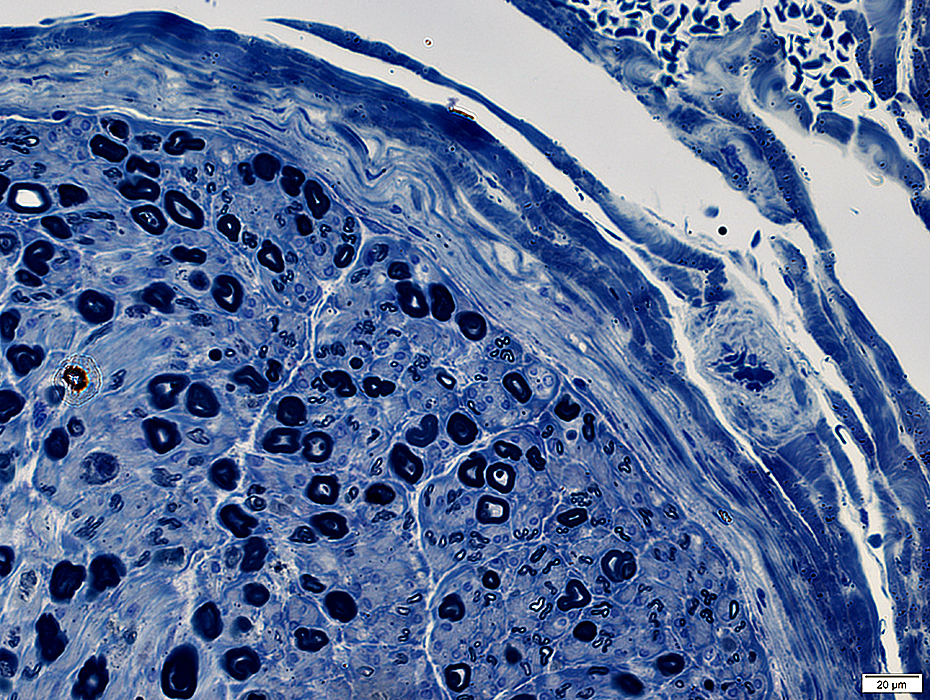 Toluidine blue stain |
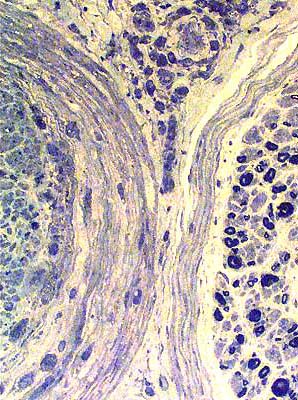 Toluidine blue stain |
Perineuritis: Perineurial structure is Abnormal
Layers: Widened or Condensed (Above)Cellularity within layers is increased (Below)
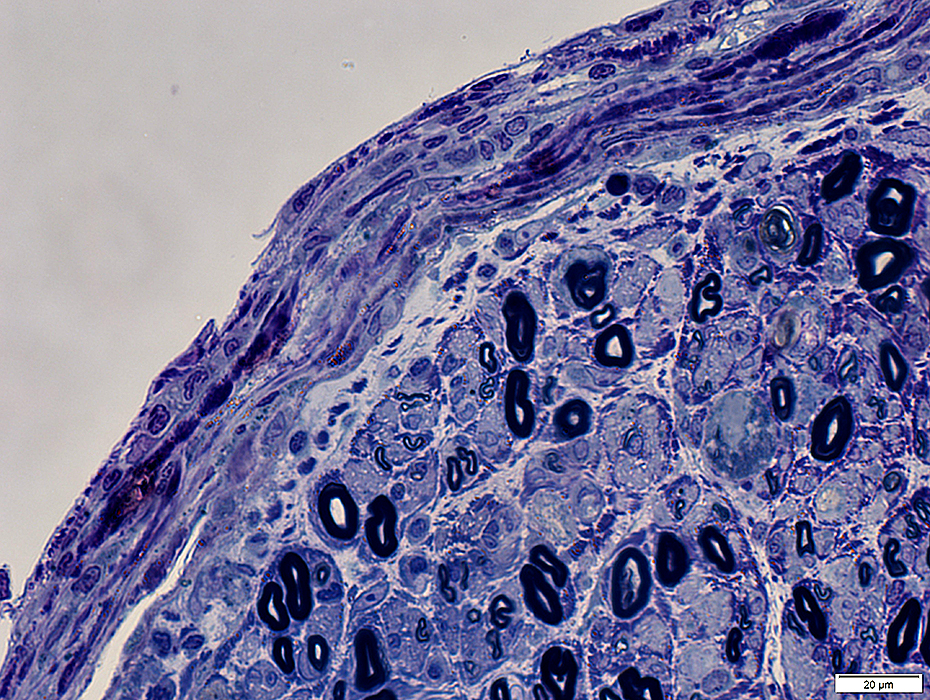 Toluidine blue stain |
Perineuritis: Inflammation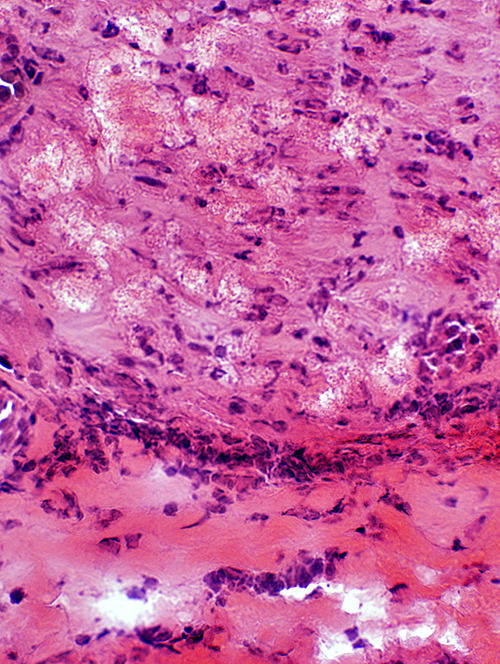 H&E stain |
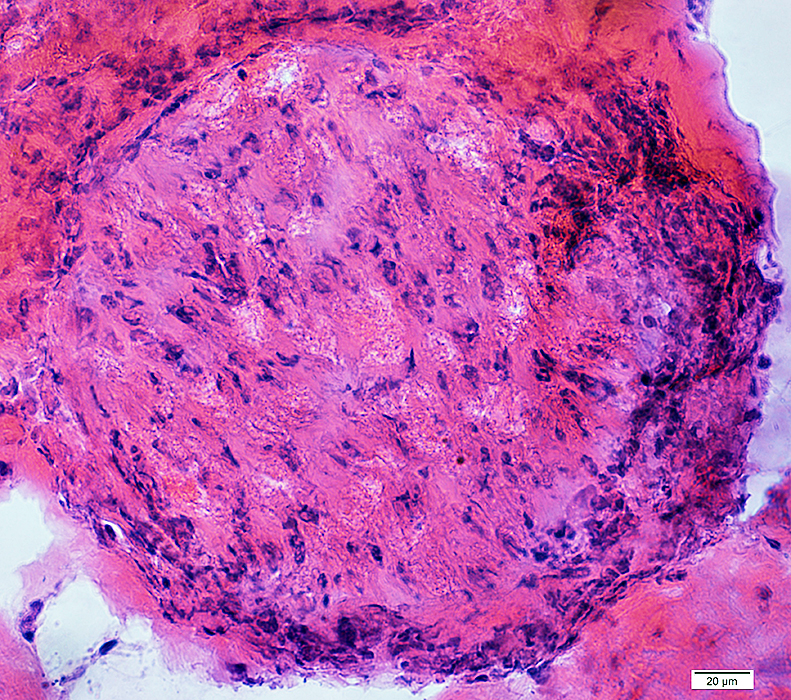 H&E stain |
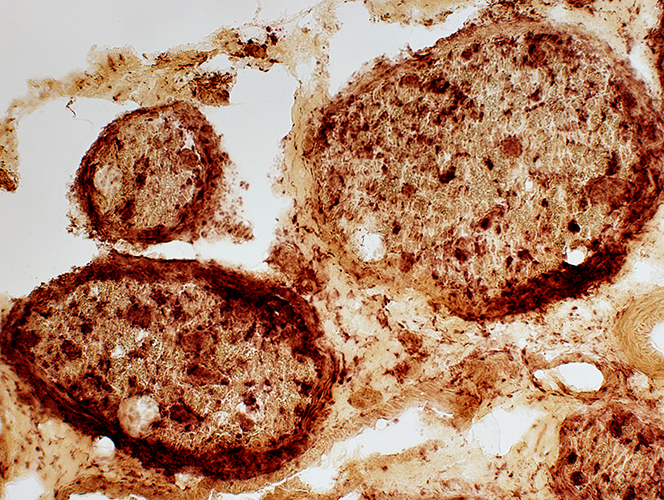 Acid phosphatase stain |
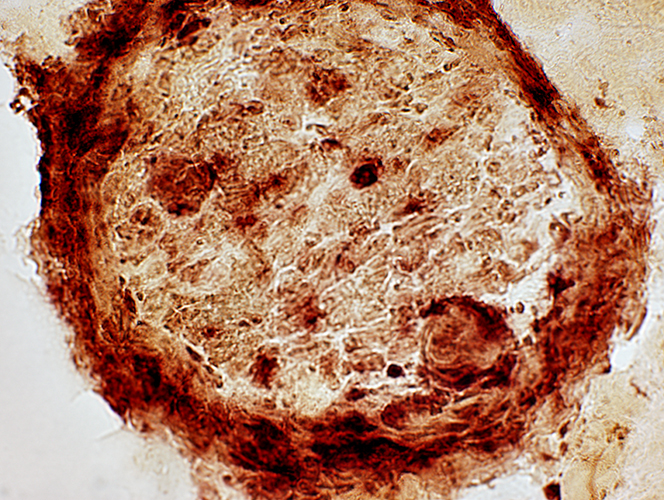 Acid phosphatase stain |
|
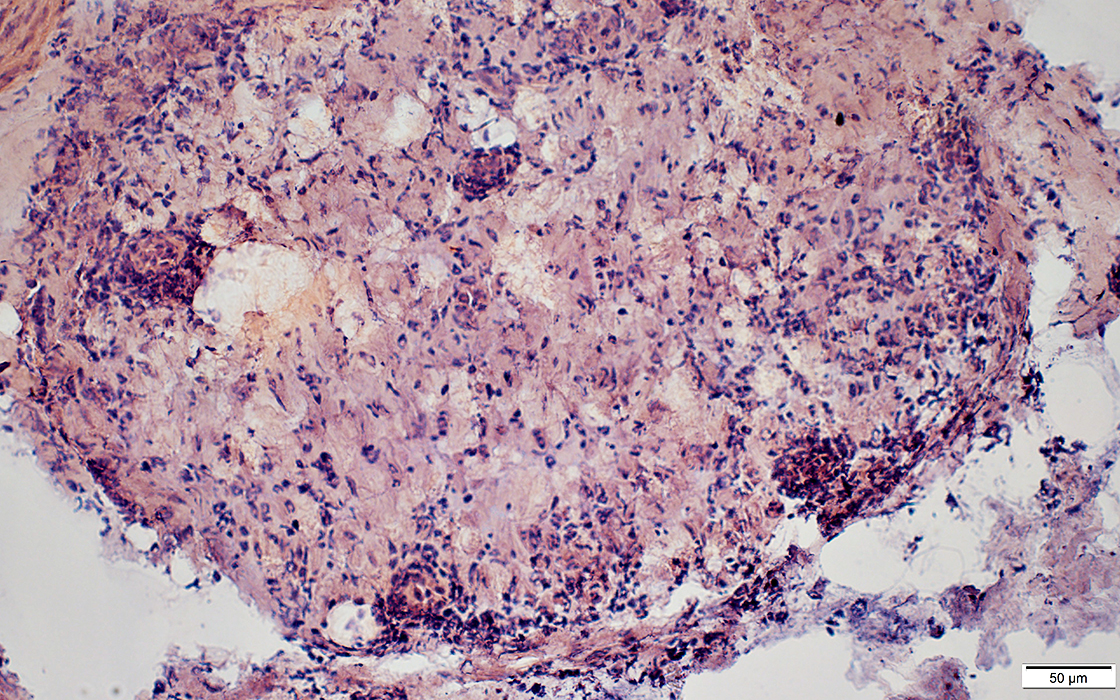
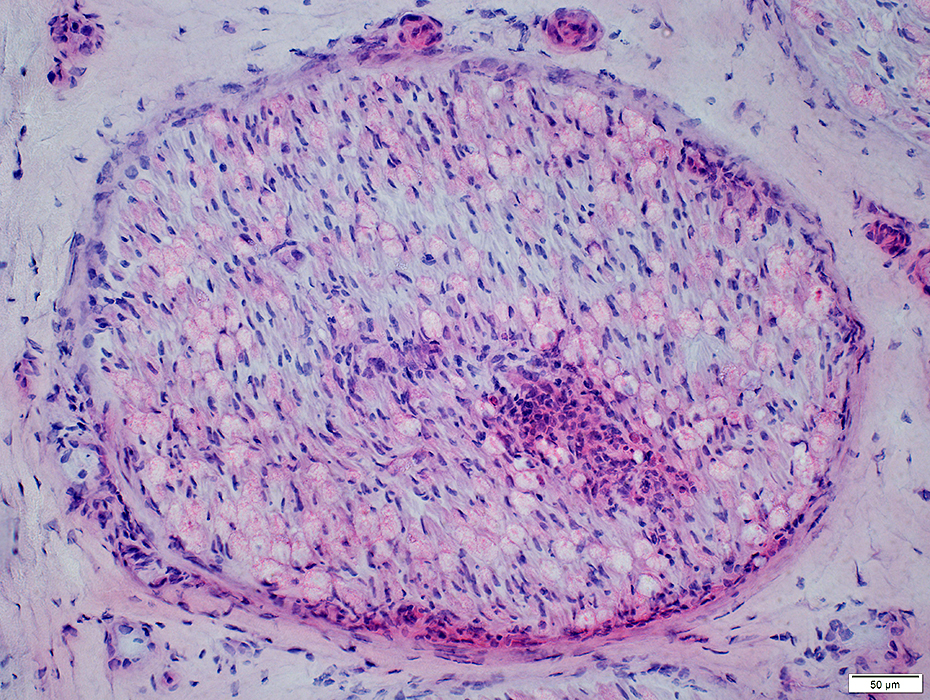
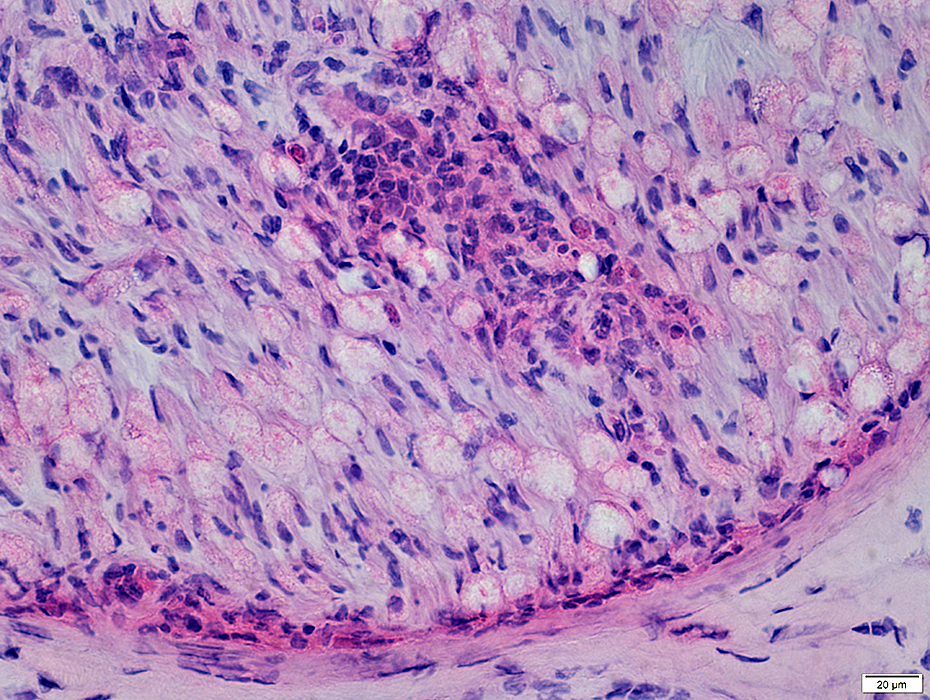
Perineuritis: Histiocytic cells In perineurium & endoneurium Confluent red stained histiocytes, mainly in perineurium Endoneurial cells: May reflect Wallerian degeneration |
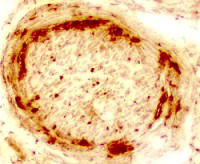
|
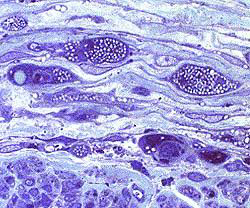
|
Perineuritis: Cells around Endoneurial microvessels
|
|
|
Perineuritis: Abnormal Epineurial & Endoneurial vessels
Epineurial VesselsArtery, Large: Damaged structure; Interrupted internal fibril layer
Smaller vessel (Botton right): Perivascular inflammatory cells
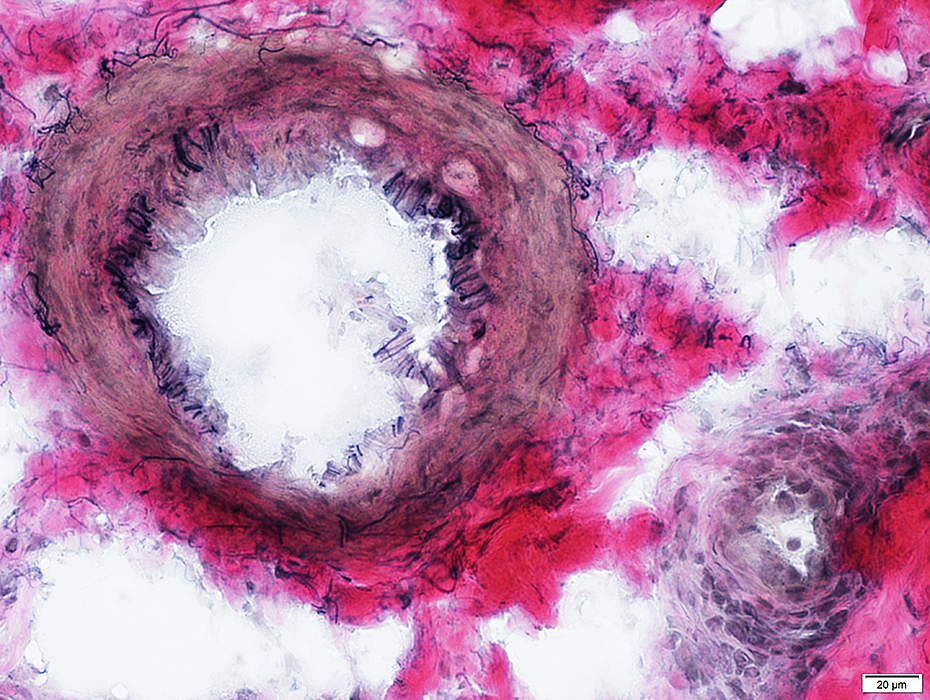 VvG stain |
Endoneurial Microvessels
Size: Moderately large
Endothelial cells: Prominent
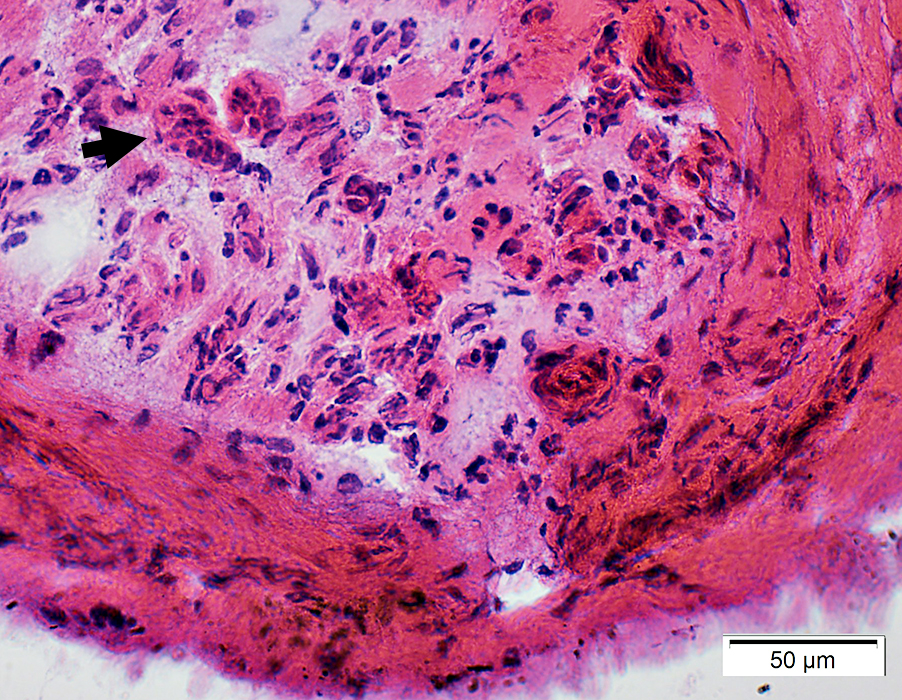 H&E stain |
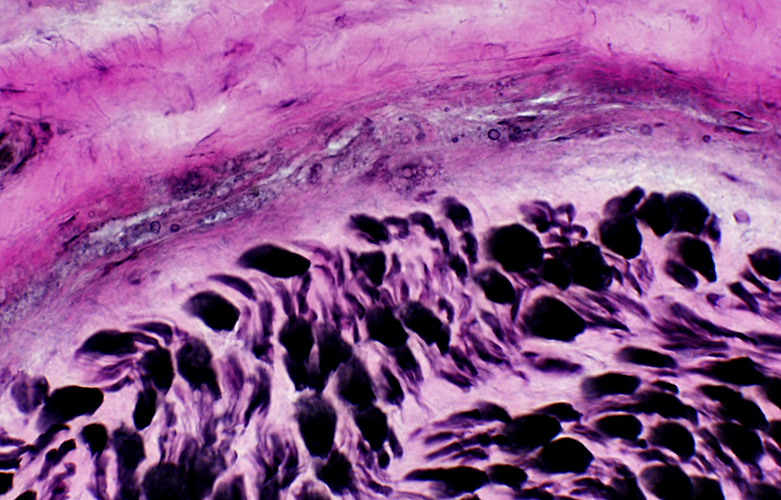
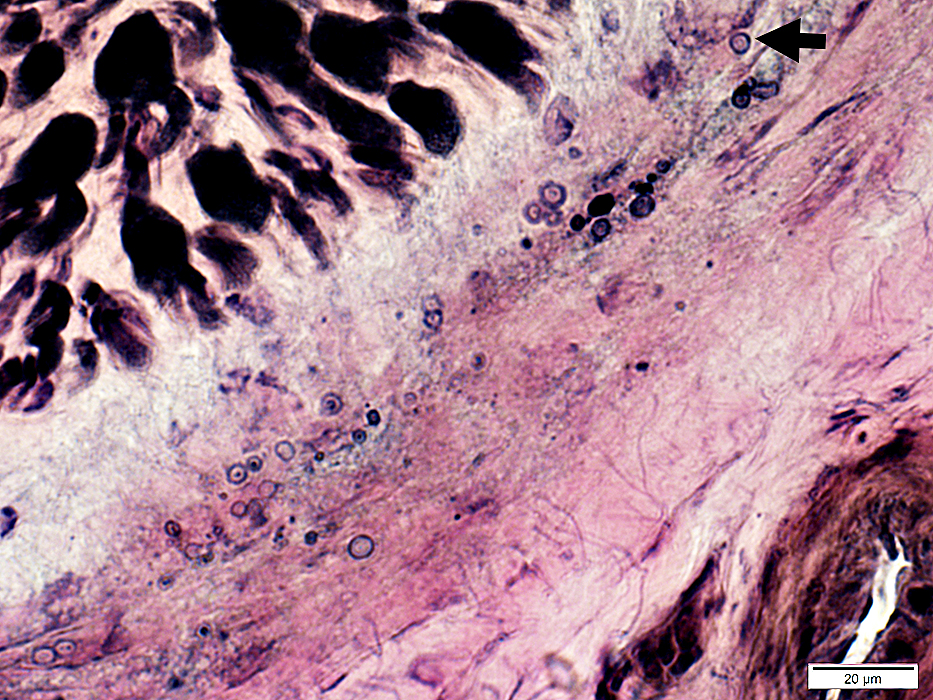
Perineurial Calcification
- Occurs in some chronic neuropathies
- Location: Between perineurial lamellae
- Causes
- Amiodarone
- Calciphylaxis
- Diabetes
Perineurial Calcification: Dark-stained regions on Gomori trichrome
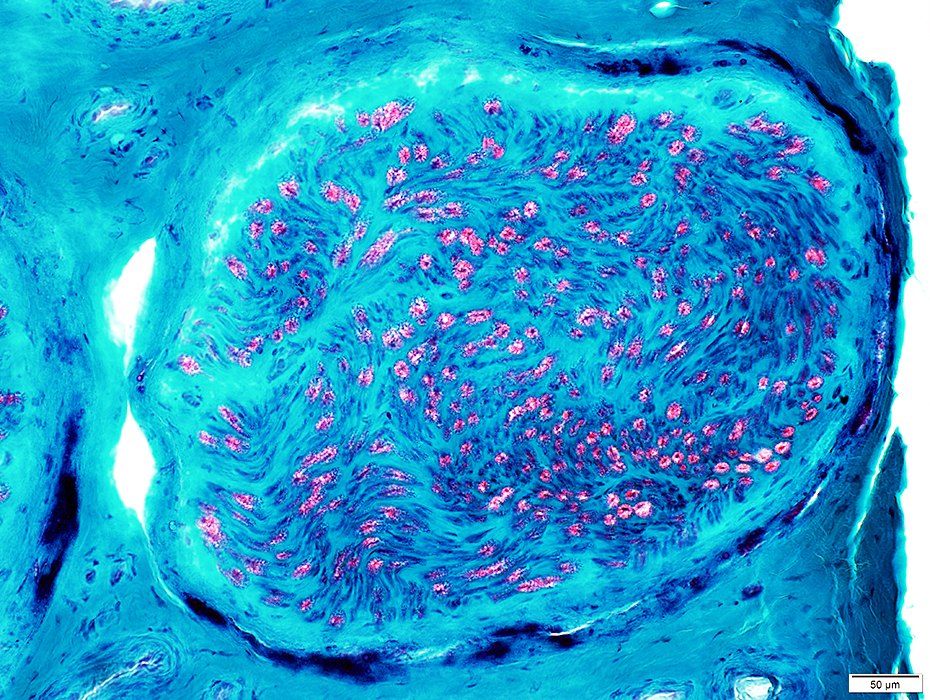 Gomori trichrome stain |
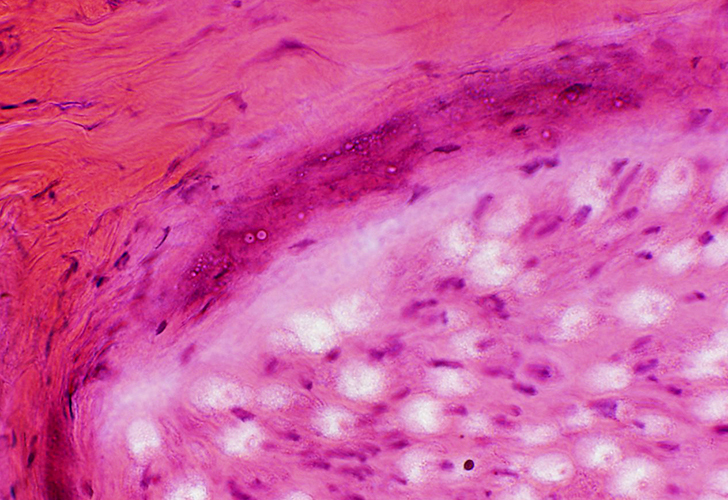 H&E stain |
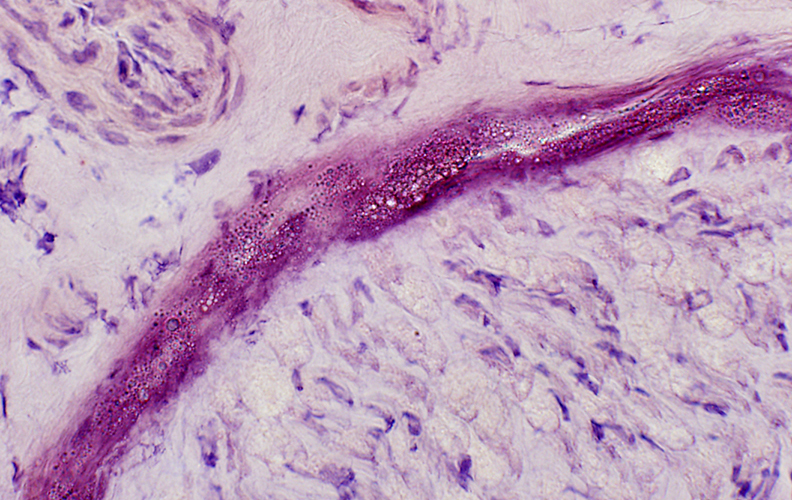 Congo red stain |
Irregular, lucent regions in perineurium
Calcium granules may be free or within histiocytic cells
 VvG stain |
 VvG stain |
Perineurial Calcification: Ultrastructure
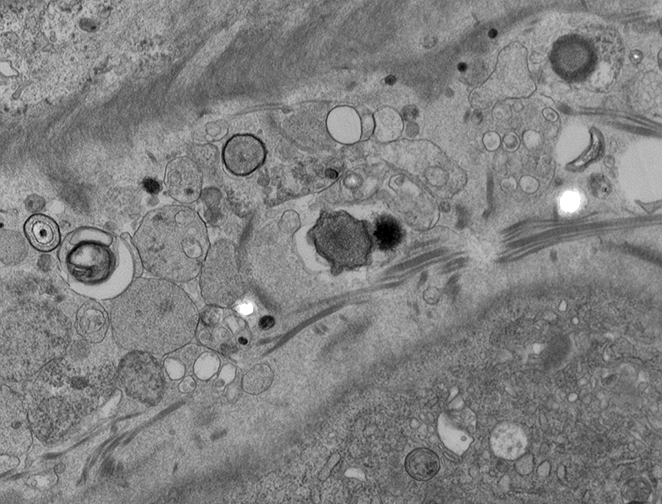 From: R Schmidt |
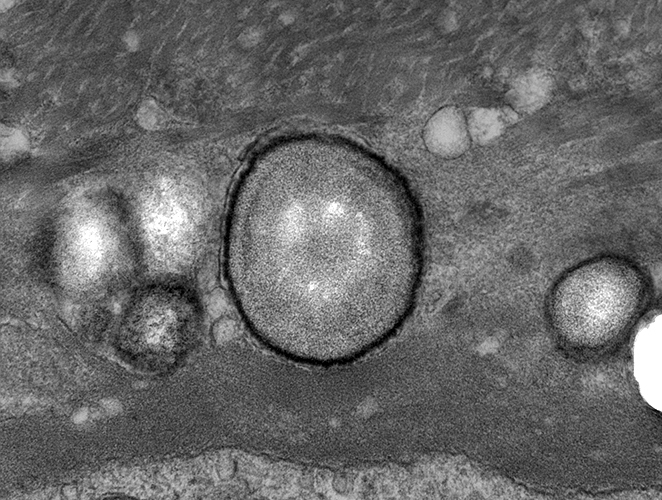
|
Rounded or irregular bodies
Layered (Targetoid): Some layers are osmiophilic
Location: Between perineurial connective tissue layers
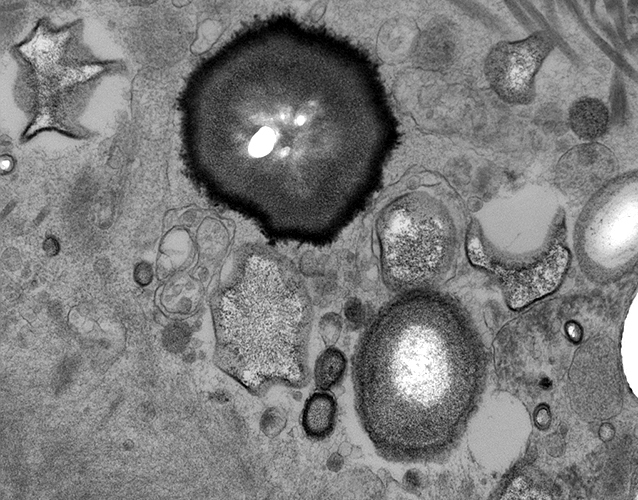 |
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Return to Perineuritis
References
1. Muscle Nerve 2023 Aug 21
7/16/2024