Titin Myopathies
Titin Myopathy: Recessive, Fiber type size disproportion
1 year old female
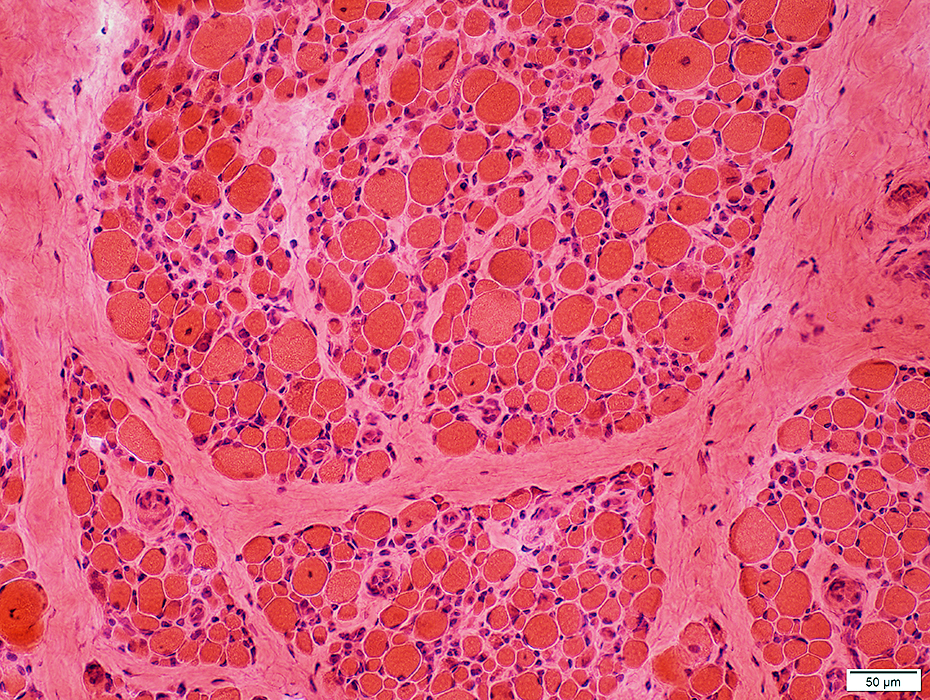 H&E stain Muscle fibers Size: Varied Internal nuclei |
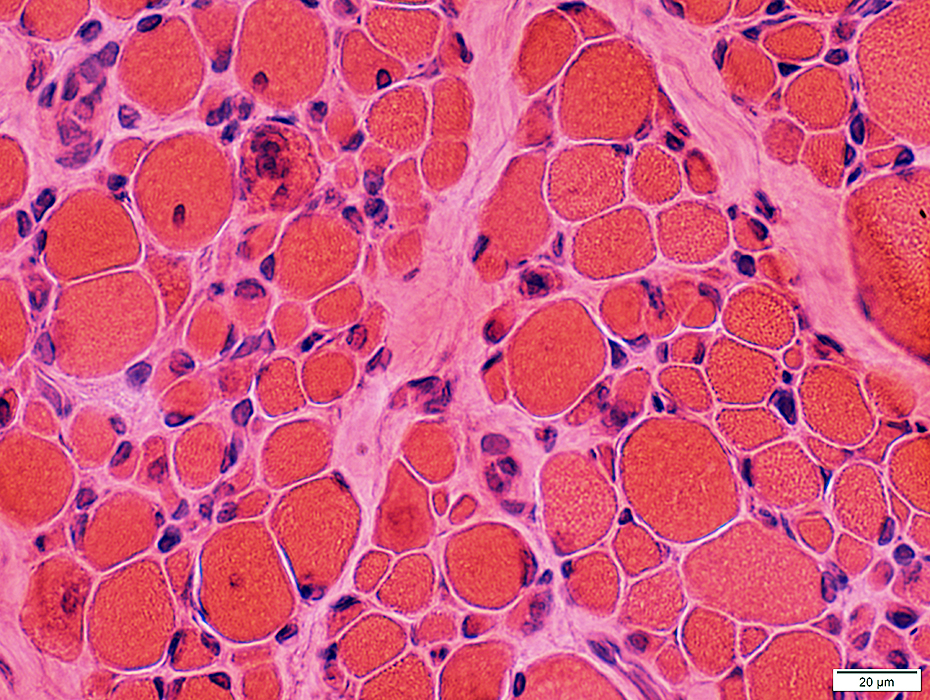 H&E stain |
Some are very small
A few have central nuclei
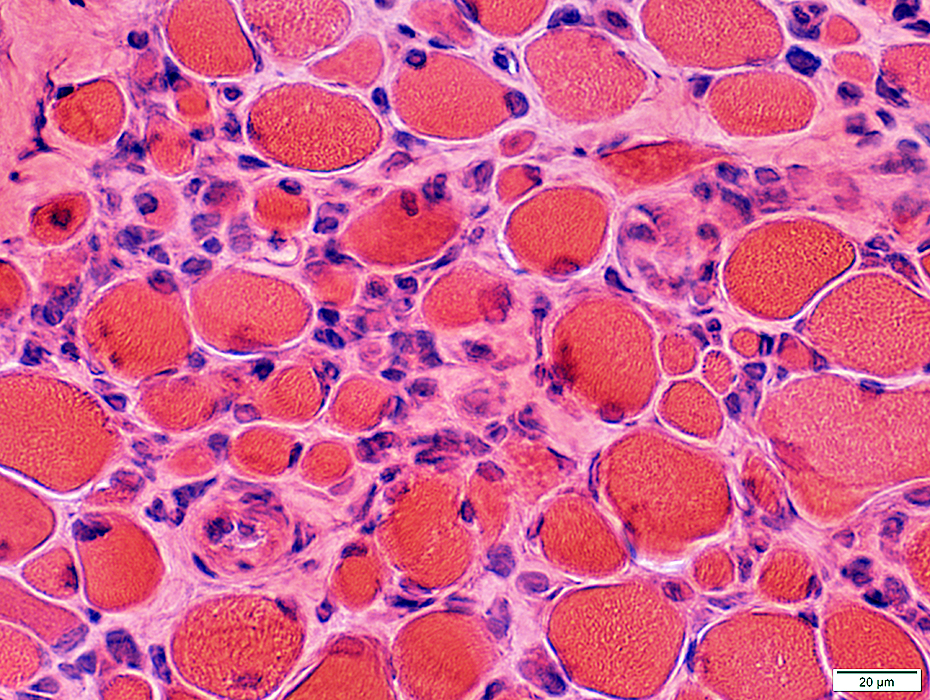 H&E stain |
Fiber size: Varied
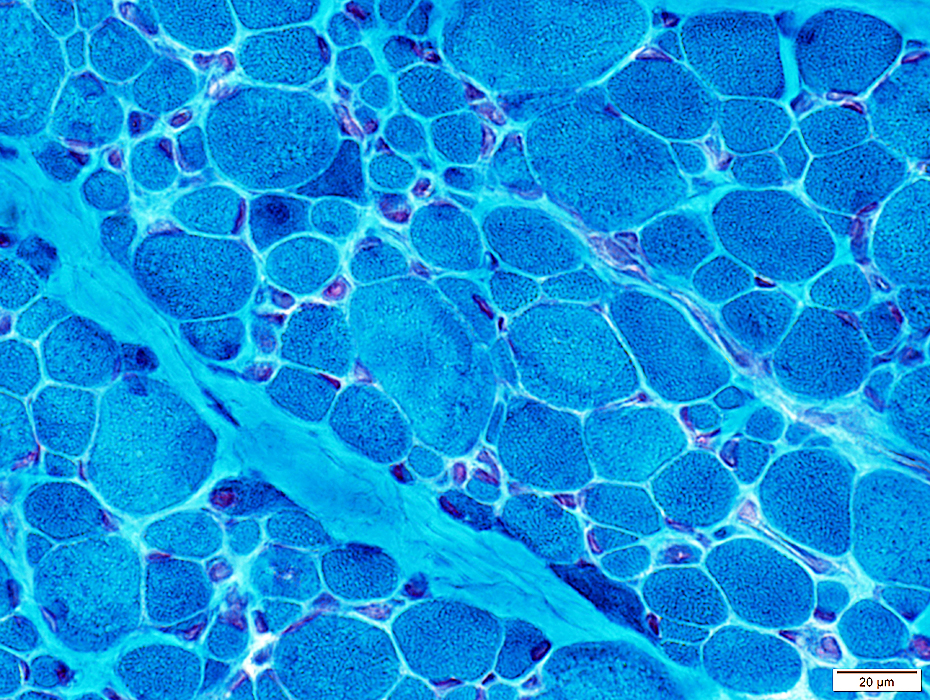 Gomori trichrome stain |
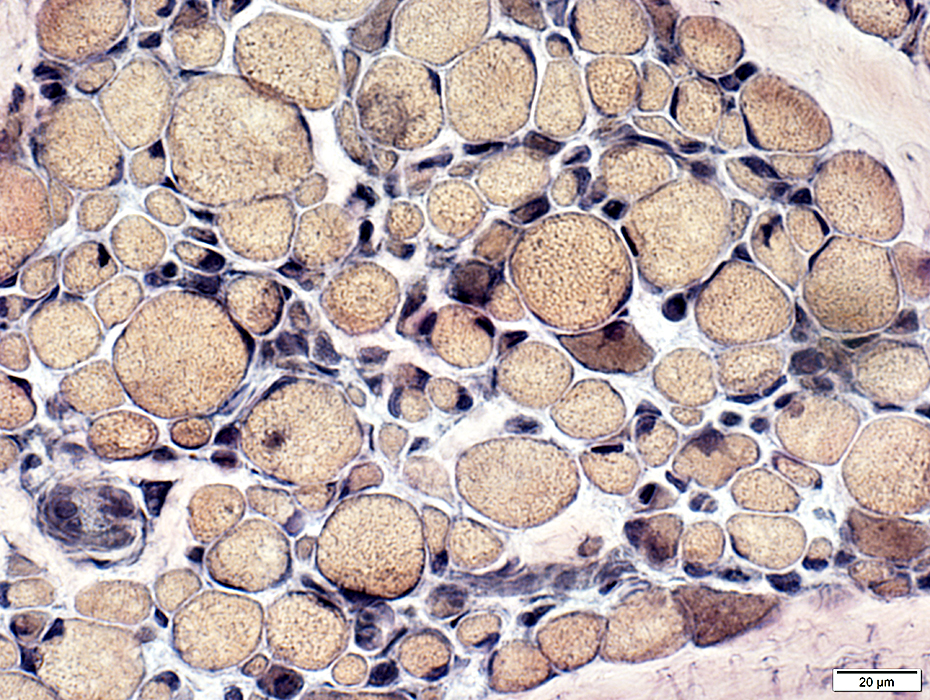 VvG stain |
Varied
Some regions have more very small fibers than others
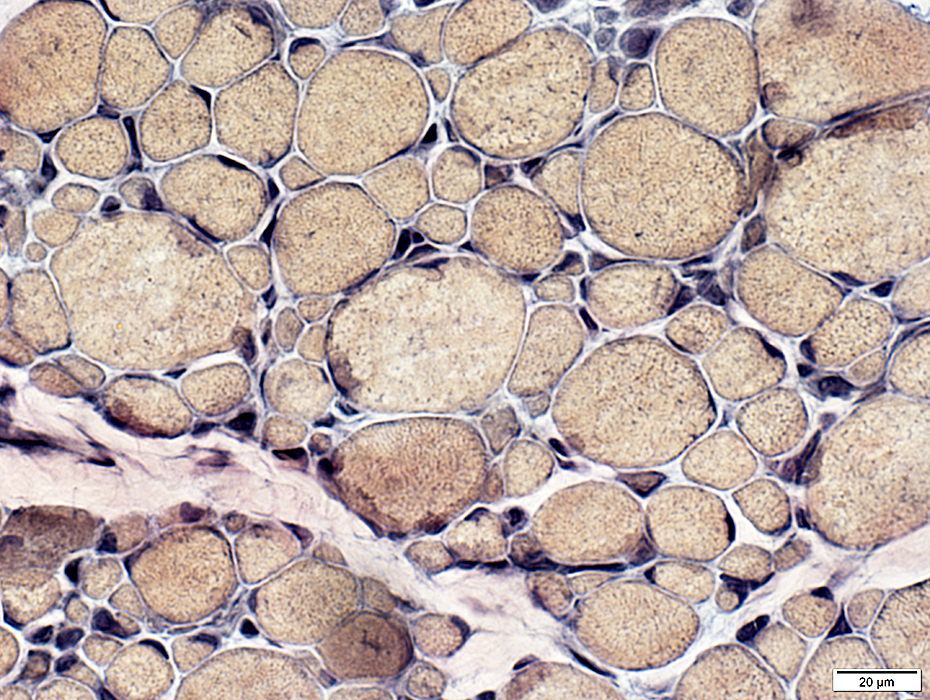 VvG stain |
Vessels: Normal structure
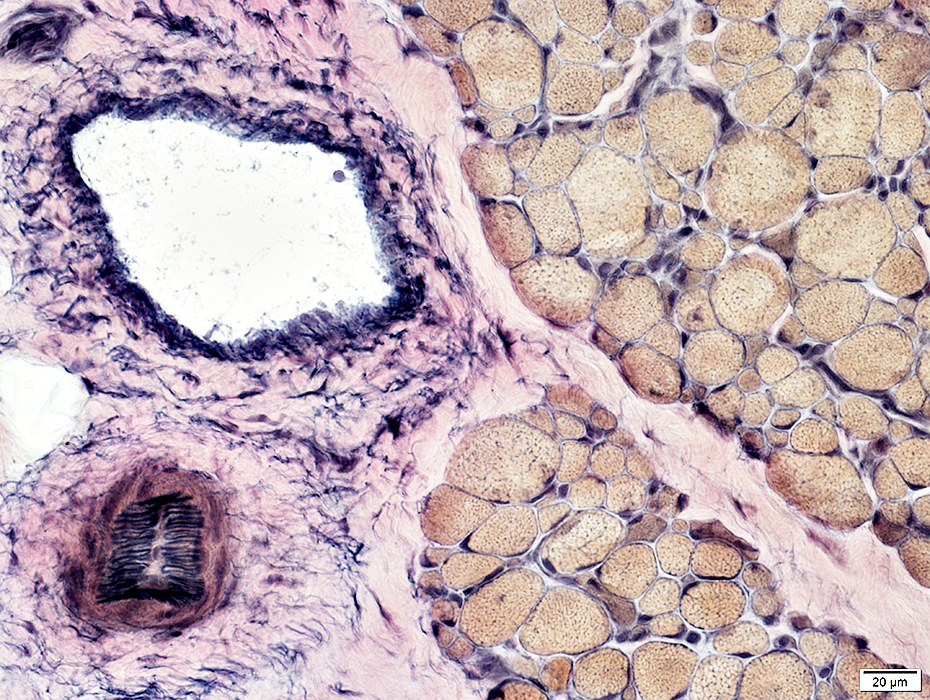 VvG stain |
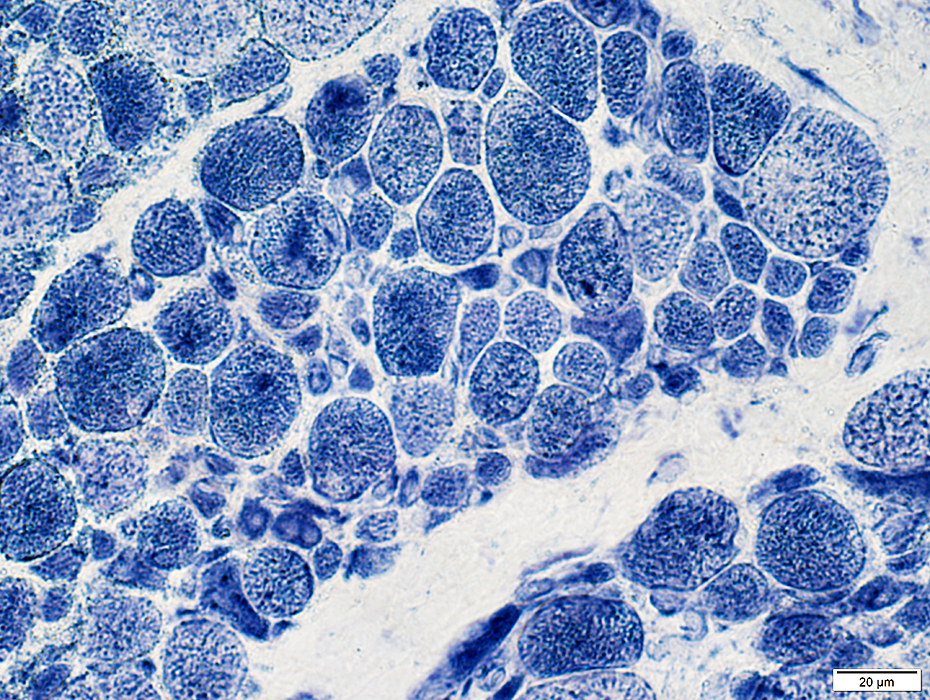 NADH stain |
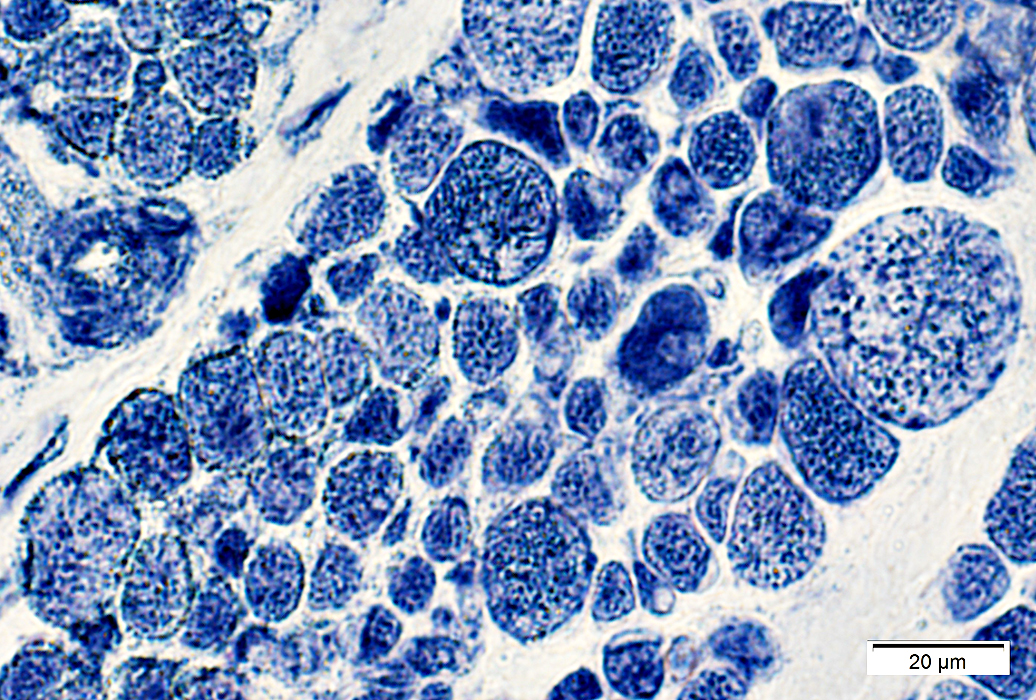 NADH stain |
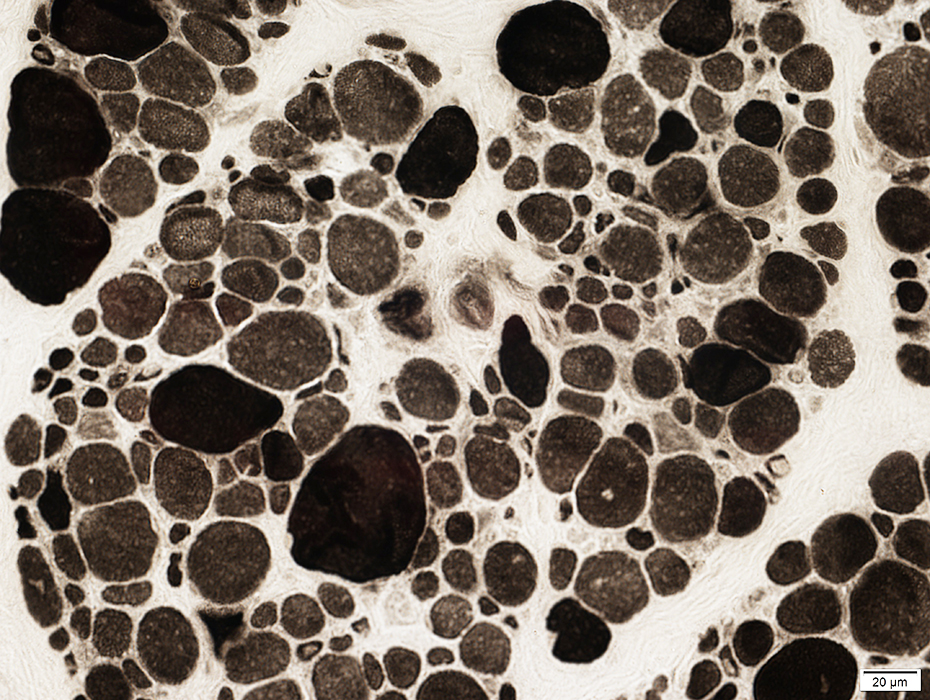 ATPase pH 9.4 stain Fiber types Type II: Are the largest Type I: Many very small Type IIC fibers: Few; Scattered |
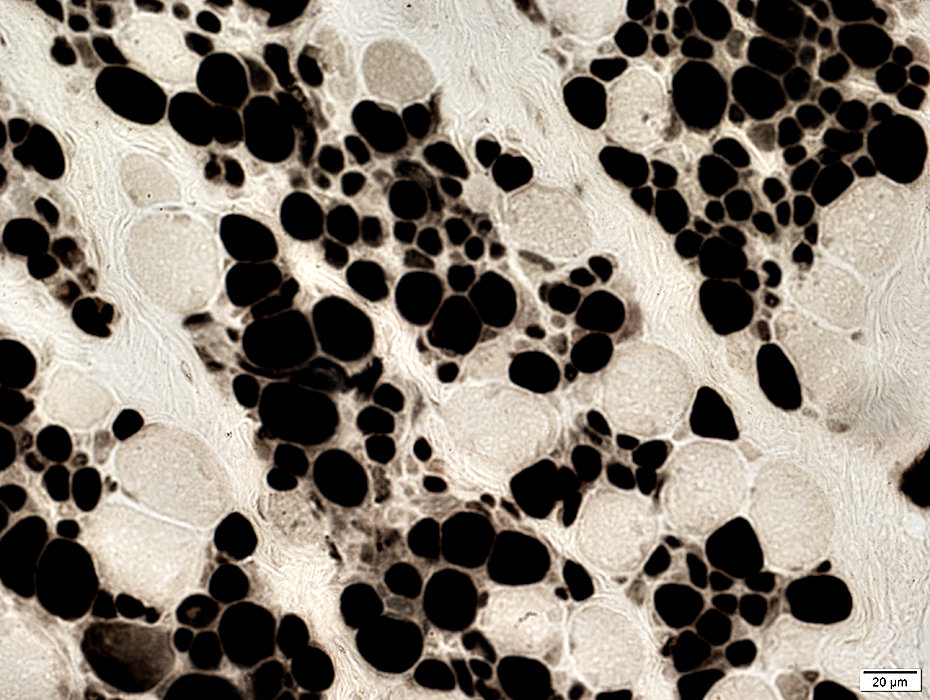 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Mitochondria: Normal
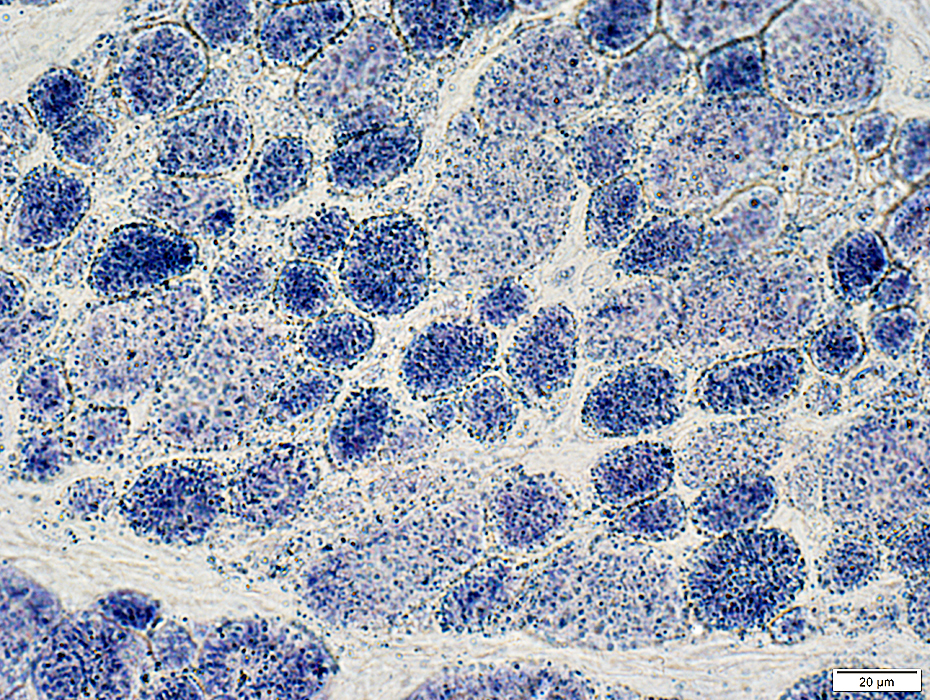 SDH stain |
Muscle fiber cytoplasm: Some muscle fibers have diffuse staining or small aggregates
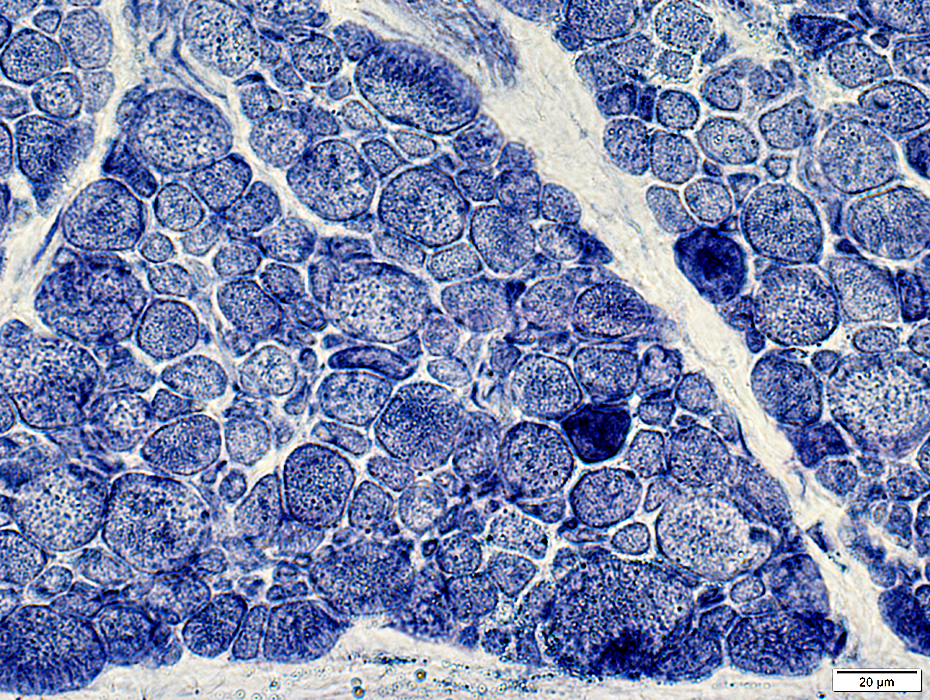 AMPDA stain |
Desmin: Small muscle fibers are darker stained
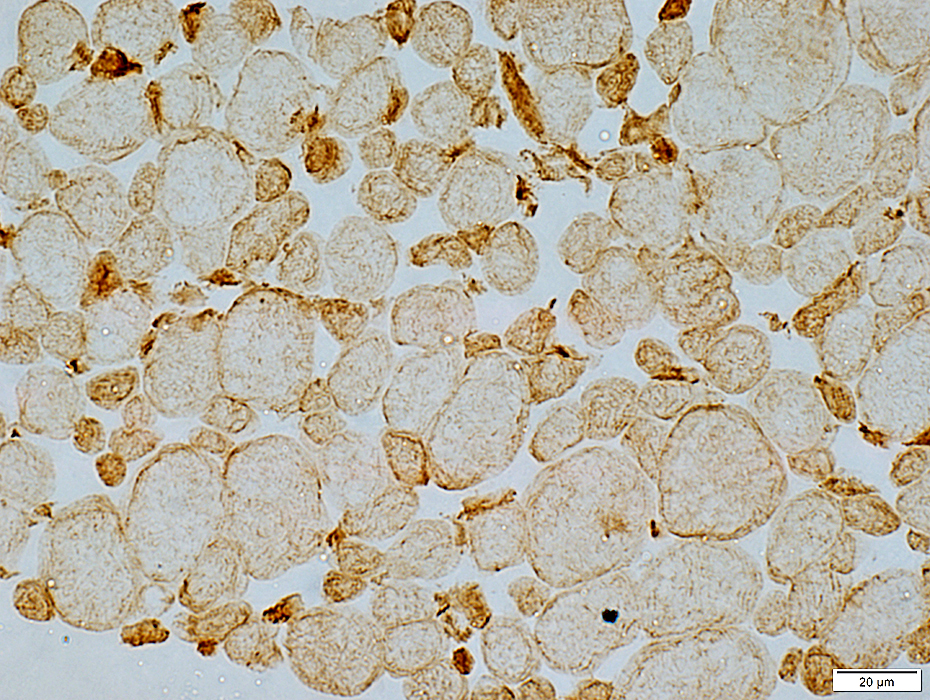 Desmin stain |
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Return to Titin disorders: Dominant; Recessive
10/15/2024