Cylindrical Spirals 3
- General
- Reported in 29 patients
- Male > Female
- Adult > Children
- Pathology
- Derive primarily from sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Location
- Subsarcolemmal > Central: Parallel to long fiber axis
- Type 2B fibers
- Histochemical Staining: Similar to Tubular aggregates
- Gomori trichrome: Red
- AMPDA: Dark
- NADH: Mild
- Menadione α-glycerophosphate
- Negative: SDH & COX
- Protein contents 2
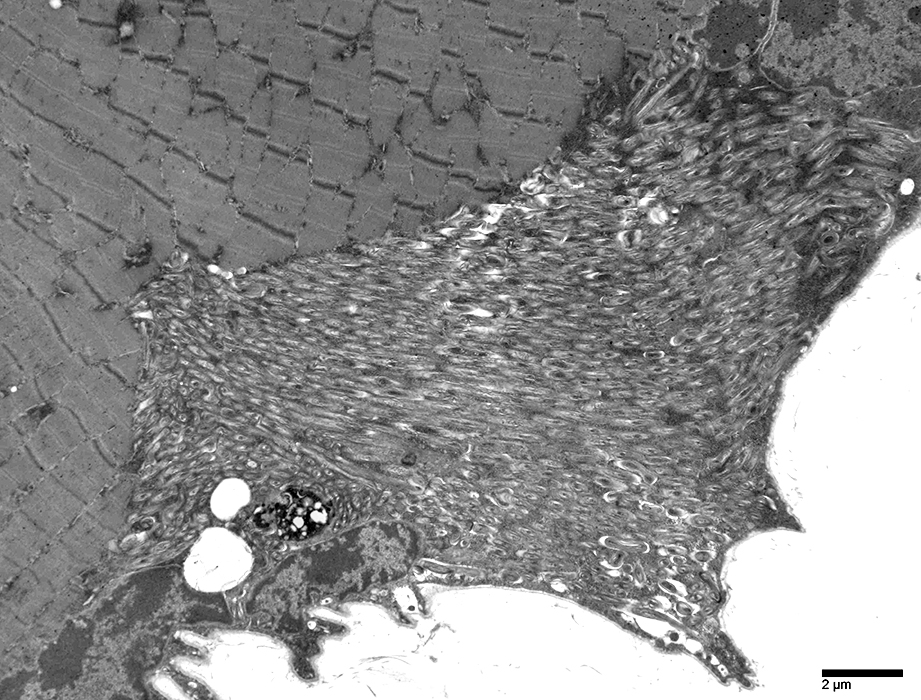
- Ultrastructure
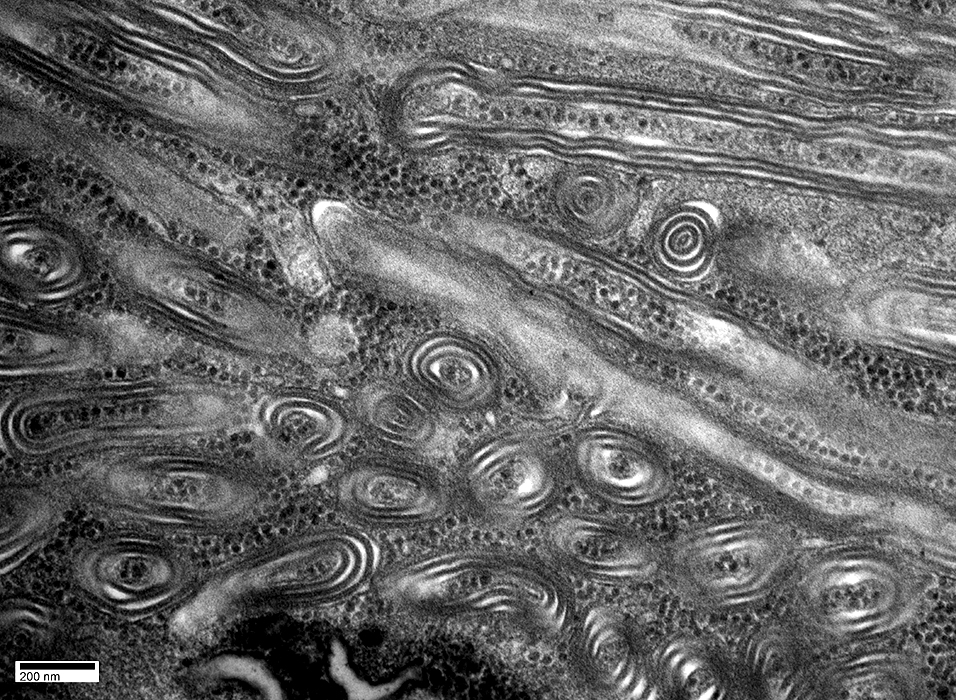
- Spiral membranous lamellae
- Parallel arrays
- Tightly packed
- Cylinders
- Trilamellar
- Form multiple layers: 3 to 35
- Location: Sarcoplasm, Subsarcolemmal
- Central cytoplasmic core
- May be
- Continuous with: Tubules or Vesicles
- Associated with: Tubular aggregates
- Different from
- Disease associations: Not specific
- Myotonia, Cramps, Myalgias

- Epidemiology: 1 family
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Clinical
- Percussion myotonia
- Cramps
- Stiffness: Posteffort
- Myotonic lid lag
- Laboratory
- Muscle: Cylindrical spirals
- Congenital weakness & Epileptic encephalopathy
1
- Epidemiology: 2 French-Antillean & Moroccan sisters
- Clinical
- Birth: Hypotonia
- Weakness
- Psychomotor delay
- Epilepsy
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: Mildly high
- Muscle: Cylindrical spirals
- Denervation: Most cases
- Melorheostosis

- Behr syndrome
- Mitochondrial myopathy
- Myalgias
- Asymptomatic high CK
- Myotonia, Cramps, Myalgias
Images from: Chunyu (Hunter) Cai
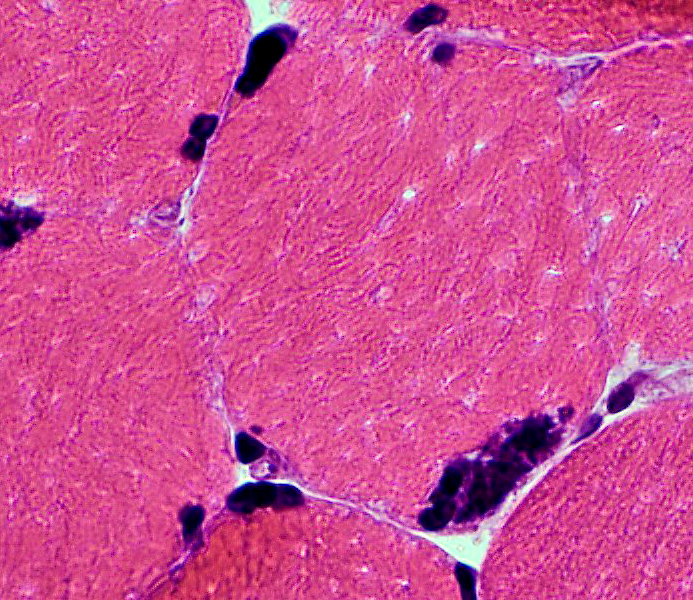 H&E stain |
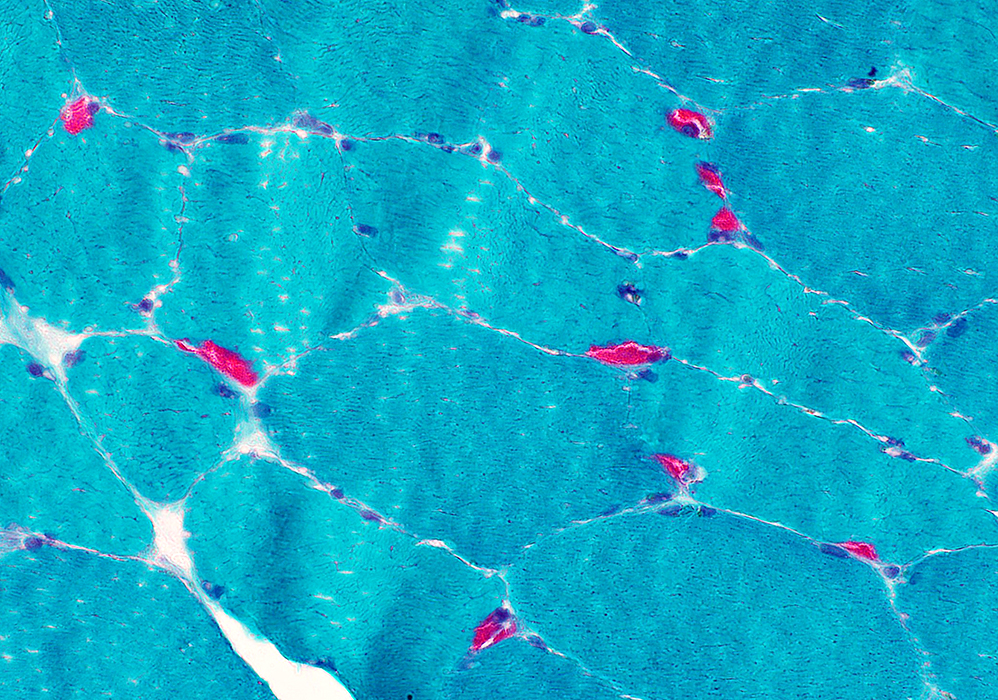 Gomori trichrome stain |
 AMPDA stain |
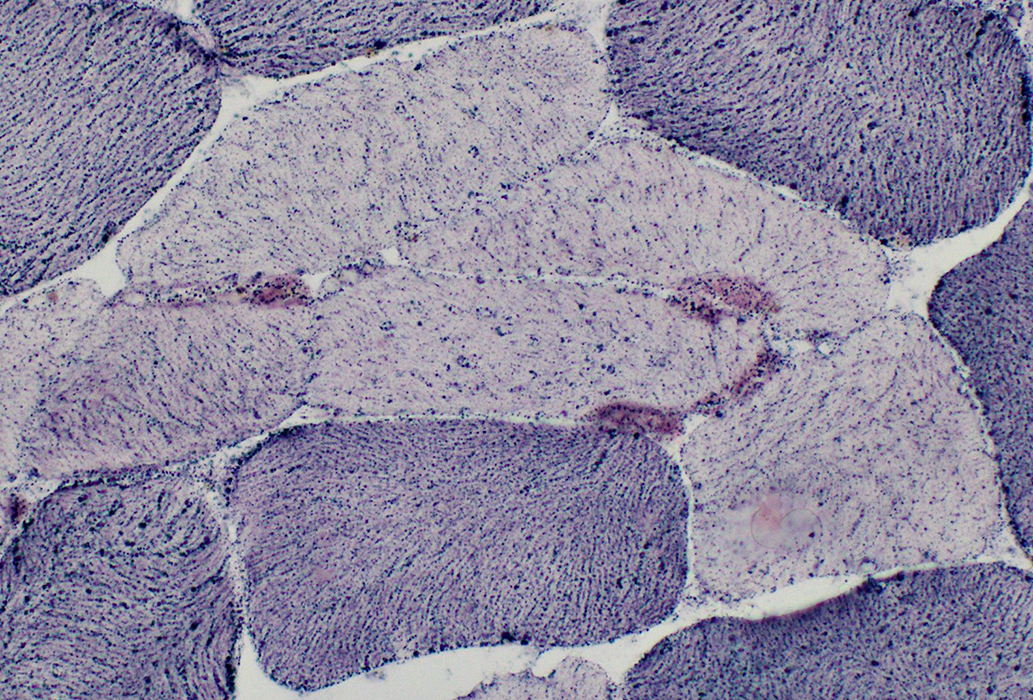 NADH stain |
 |
 |
 |
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Return to Pathology index
References
1. Muscle Nerve 2015;52:895-899
2. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2016;75:1171-1178
3. J Neurol Sci 2023;451:120734
7/23/2023