|
HEREDITARY MOTOR SENSORY NEUROPATHIES (HMSN; CMT)

|
CMT & HMSN: Demyelinating Dominant CMT 1A: PMP-22; 17p12 1B: P0 protein; 1q23 1C: LITAF; 16p13 1D: EGR2; 10q21 1E (Deafness) PMP-22: 17p12 P0 protein: 1q23 1F: NEFL; 8p21 1G: PMP2; 8q21 1H: FBLN5; 14q32 1I: POLR3B; 12q23 1J: ITPR3; 6p21 CMT1: c1orf194; 1p13 CMT: ATP1A1; 1p13 HNPP PMP-22 (Deletion or Point); 17p12 KARS; 16q23 HMSN 3 (Dejerine-Sottas) PMP-22; P0; 8q23; EGR2 Thermosensitive PCWH: SOX10; 22q13 Sensory PN + Deaf: GJB3; 1p34 SNCV: ARHGEF10; 8p23 CMT-DIF: GNB4; 3q26 ATXPC: SAMD9L HMSN: HARS; 5q31 HMSN: BAG3; 10q25 Recessive: CMT/AR-CMT1 4A: GDAP1; 8q21 4B1: MTMR2; 11q22 4B2: SBF2; 11p15 4B3: SBF1; 22q13 4C: SH3TC2 (KIAA1985); 5q32 4D (Lom): NDRG1; 8q24 4E: EGR2; 10q21 4F: Periaxin; 19q13 4G (HMSNR): HK1; 10q22 4H: FGD4; 12q12 4J: FIG4; 6q21 4K: SURF1; 9q34 HMSN 3 (Dejerine-Sottas) P0; PMP-22; EGR2; Periaxin HMSN + Juvenile glaucoma Cataracts (CCFDN): CTDP1; 18qter Cockayne's: 5 Congenital hypomyelinating P0, PMP-22 & EGR-2 Farber (FRBRL): ASAH; 8p22 CDG1a: PMM2; 16p13 Krabbe: GALC; 14q31 MLD: ARSA; 22q13 MNGIE PMP-22 point mutations Refsum's disease Child-Adult: PHYH; 10pter-p11.2 Adolescent-Adult: PEX7; 6q22 Infant: PEX1; 7q21 PHARC: ABHD12; 20p11 PBD8B: PEX16; 11p11 HMSN + CNS: Heterogeneous ACPHD: DNAJC3; 13q32 Mouse: TSG101 X-linked CMTX1: GJB1 (CX32); Xq13 CMTX3: Xq27 Pyramidal signs |
CMT & HMSN: Axonal
|
CMT + Intermediate NCV Dominant CMT-DIA: GBF1; 10q24 CMT-IB: DNM2; 19p13 CMT-DIC: YARS; 1p35 CMT-DID: P0; 1q22 CMT-DIE: INF2; 14q32 CMT-DIF: GNB4; 3q26 CMT-DIG: NEFL; 8p21 CMT-DI: c1orf194; 1p13 CMT-DI: EBP50; 17q25.1 CMT-DI: SARS1; 1p13 CMT-X (Semi-dominant): GJB1 CMT 1C: LITAF; 16p13 CMT 2E: NEFL; 8p21 CMT: RAB40B; 17q25 Hypomyelination: ARHGEF10; 8p23 PN: NOTCH2NLC; 1q21 Recessive CMT RIA: GDAP1; 8q21.1 CMT RIB: KARS; 16q23 CMT RIC: PLEKHG5; 1p36 CMT RID: COX6A1; 12q24 CMT XI: DRP2; Xq22 Other related names or disorders α-Methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR) Brachial plexopathy, Hereditary Childhood onset neuropathies CNS & Cranial nerve disorders COMNB Complex clinical syndromes Congenital Hypomyelinating EGR2: 10q21 P0: 1q22 PMP-22: 17p11 ARHGEF10; 8p23 Connective tissue: EMILIN1; 2p23 Cowchock: AIFM1; Xq26 Dejerine-Sottas (HMSN 3) Focally folded myelin sheaths CMT 4B: MTMR2; 11q23 CMT 4B2: SBF2; 11p15 CMT 4E: EGR2; 10q21 CMT 4F: Periaxin; 19q13 P0: 1q22 Juvenile glaucoma Hereditary Motor neuropathies Distal (dHMN) Sensory neuropathies (HSN; HSAN) Metabolic abnormalities Minifascicles & Gonadal dysgenesis HSN: DHH; 12q12 Myelin disorders; Recessive Recurrent Brachial plexopathy Pressure palsies (HNPP): PMP-22 Neuropathy: 21q21 SCA + Neuropathy SMARD SPG + Neuropathy Vertical talus: HOXD10; 2q31 |
Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) Features Associated Childhood Childhood CMT Comparative General Molecules NCV patterns Pathology Myelin proteins External links Mutations  |
OVERVIEW 119
Prevalence
Tissue & Functional involvement
|
|
Hereditary Neuropathies: Related Molecules
| |||||
|
Pathology in hereditary neuropathies: Differential diagnosis 120
Other hereditary motor-sensory neuropathies
|
 Bramwell 1907 |
Clinical CMT (HMSN): Differential Diagnosis & Associated Features
93
|
||||
Hereditary Neuropathy: Nerve Conduction Testing 220
- Uniform CV & Slowing
- Non-uniform CV & Slowing
- Metachromatic Leukodystrophy (MLD): Early 16
- HNPP
- MPZ: Some point mutations
- CMT1X: Especially female carriers
- CMT1C
- CMT4J
- MNGIE
- Adrenomyeloneuropathy
- Pelizeus–Merzbacher disease
- Refsum
- hATTR
Neuropathy: CMT Genes & Drugs 195
- Vincristine: May cause exacerbation of
- Paclitaxel
- Isoniazid (INH): May exacebate CMT2A
- Ethambutol: May exacebate CMT2A
- Thiopental anesthesia
- CMT1A: PMP-22
- Sensitive to low doses (Lower induction dose needed)
- Especially with severe motor & sensory involvement
- CMT1A: PMP-22
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
External links
Hereditary Motor-Sensory Neuropathy (HMSN) Syndromes
CMT IA

●
PMP 22
|
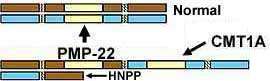
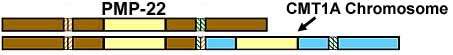
PMP-22 Gene mutations Clinical-Gene relations Duplication Contiguous gene (YUHAL) Triplication Homozygous (Duplication) Point Allelic disorders Recessive CMT 1E (Deafness) Protein Pathology Also see: HNPP |
CMT 1A
PMP-22 Duplication |
 Chaddock 1900 |
- CMT 1A: Epidemiology
- Prevalence: 10.5 per 100,000
- 60% to 70% of Demyelinating CMT
- 40% to 50% of all CMT
- Genetics
- PMP-22 Gene mutation types
- Duplication of one PMP-22 gene (3 total copies of PMP-22): Types
- Segmental duplication in gene area
- Duplication size
- Varies among patients
- Longer (Extended): 1%
- Shorter: 2%
- Trisomy of short arm on chromosome 17 (17p): Mosaic
- Contiguous gene syndrome (YUHAL): Duplication of one PMP-22 gene & neighboring genes
- Duplication of both PMP-22 genes (Homozygous) (4 copies)
- Point mutation
- Human
- Mouse: Trembler (G150D)
- Deletion: Most commonly associated with HNPP
- Recessive
- Nonrecurrent genomic rearrangements causing copy number variants
82
- Genomic deletions & duplications
- Complex rearrangements
- Exonic deletions: Small
- Duplication of one PMP-22 gene (3 total copies of PMP-22): Types
- PMP-22: Clinical-genetic correlations
- Chromosomal duplication containing PMP-22
- Identical to region deleted in HNPP
- Homozygotic twins
- Similar NCV but often dissimilar clinical severity
- "Sporadic" cases: 18%
- Paternal origin
- Common: 89%
- Due to unequal crossing over of homologous Chromosome 17 regions
- Most breakpoints: 700 bp region in complex low copy repeat sequence (24,000 bp) that flanks gene
- Also 'Mariner' insect transposon-like element (MITE) near break site
- ? Promotes DNA cleavage by transposase
- ? Cleavage leads to unequal cross-over
- ? Promotes DNA cleavage by transposase
- Maternal origin
- Rare: 11%
- Due to intrachromosomal rearrangement: Unequal sister chromatid exchange
- Breakpoint location
- Outside, but near, 700 bp interval containing most rearrangements of paternal origin
- Paternal origin
- Disease modifiers
- LITAF/SIMPLE 192V sequence variant
126
- Onset age
- 13 years earlier in CMT1A & HNPP adult-onset
- No difference in child onset patients with Ile92Val mutation
- Onset age
- miR-149 SNP (n.86T>C, rs2292832)
140
- TC & CC genotypes: Associated with late onset & mild symptom in asian patients
- SIPA1L2 (SPAR2)
 144
144
- SNP clinical association: Foot dorsiflexion strength
- SNPs: rs10910527, rs7536385, rs4649265, rs1547740
- Minor alleles: More severe weakness
- Expressed in peripheral nerve & growth cones
- Part of a myelination-associated co-expressed network regulated by SOX10
- Binding partners: MYH9; β-actin
- SNP clinical association: Foot dorsiflexion strength
- Other possible loci of modifiers
146
- Difficulty with eating utensils: rs4713376, Chromosome 6
- Hearing loss: rs7720606, Chromosome 5
- Decreased ability to feel: rs17629990, Chromosome 4
- CMT neuropathy score: rs12137595, Chromosome 1
- LITAF/SIMPLE 192V sequence variant
126
- Chromosomal duplication containing PMP-22
- Allelic disorders
- CMT1A
- Dejerine–Sottas-like
- Congenital Hypomyelinating Neuropathy
- HNPP
- Sensory ataxia, Recessive
- Davidenkow phenotype
- Yuan-Harel-Lupski syndrome (YUHAL): Contiguous gene duplication
- CMT 1E (Deafness)
- Sub-Acute polyneuropathy

- Mouse disorders
- Trembler (DSS-like)
- Trembler-J (CMT 1E-like)
- PMP-22 Gene mutation types
- PMP-22 protein
- 2 transcripts: Different 5' ends
- 1 predominantly expressed in Schwann cells
- Over expression → Reduced Schwann cell proliferation
- 2nd (GAS3) regulated in growth-dependent fashion in fibroblasts
- Over expression → Growth arrest & Apoptosis
- 1 predominantly expressed in Schwann cells
- Synthetic pathways
- Most wild type PMP-22 is retained in endoplasmic reticulum & degraded
- Some PMP-22: Transported to Golgi, Glycosylated & Incorporated into myelin
- Abundance: 2% to 5% of PNS myelin protein
- Location: Compact myelin
- Functions
- Structural: Myelination
- Mediates cholesterol trafficking (efflux) in Schwann cells
165
- CRAC domain in 4th transmembrane domain
- PMP22 KO mice: Elevated cholesterol in perinuclear area; No myelin
- PMP22 overexpression: Cholesterol sequestered in lysosomes
- Regulation of cell growth/differentiation
- Protein Family & Structure
- Immunoglobulin superfamily
- Membrane topology: 4 Hydrophobic transmembrane domains (4-TM)
- Other homologous neural 4-TM proteins
- Proteolipid protein
 : CNS
: CNS
- Connexin-32
- Plasmolipin

- Myelin vesicular protein (MVP17)

- Proteolipid protein
- PMP-22 protein expression altered in nerves in CMT1A & HNPP
- PMP-22 Duplication
- Increased PMP-22 protein Expression: At early disease stages
- Abnormal Schwann cell differentiation
- PMP-22 Point mutations & Deletions (HNPP)
- Reduced PMP-22 protein Expression
- Several PMP-22 mutations
- Some accumulation in Schwann cell cytoplasm: Adaxonal; Endoplasmic reticulum
- Reduced degradation
- Reduced Insertion into compact myelin
- Gly107Val: Strong staining of PMP-22 in onion bulbs
- Leu105Arg mutation: No PMP-22 staining in nerve; More severe disease
- PMP-22 Duplication
- 2 transcripts: Different 5' ends
- Duplication of PMP-22 gene

- Epidemiology
- Male: Female 1:1
- Sex: No effect on disabilty
- Family history +: 60%
- Most common CMT 1 type
- Range: 37.5% (Umea, Sweden) to 84% (Turku, Finland)
- Male: Female 1:1
- Mutation
- Segmental duplication in area containing PMP-22 gene on 1 chromosome 17
- Occurs with abnormal alignment during meiotic crossing over
- Leads to total of 3 copies of PMP-22 gene
-
- Extra gene produces: Overexpression of PMP-22 protein
- Neuropathy: Clinical features
- Neuropathy: Onset
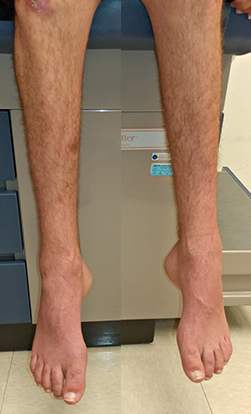
- Onset age: 1st decade in 75%; 2nd decade in 10%; Rare asymptomatic in 30's
- Initial symptoms: Gait disorder; Foot deformity
- Initial signs: 1st decade
34
- Leg areflexia (100%)
- Disordered heel walking (66%)
- Foot muscle atrophy (50%)
- Nerve enlargement (50%)
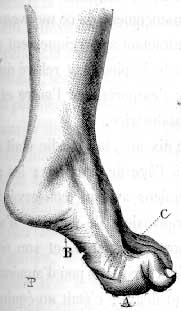
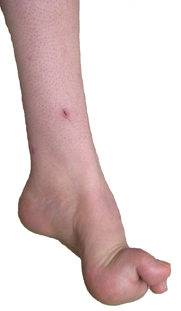
- Pes cavus (33%)
- Short Achilles tendon (25%)
- Severity: Similar or worse in males compared to females
- Weakness
- Related to degree of axon loss 51
- Distal muscles: Most patients
- Especially intrinsic muscles of Feet & Hands
- Most common muscles: Big toe & foot dorsiflexion
- May be normal at wrist, knee & more proximal muscles
- Proximal
- Rare at onset
- ~10% in late teens
- Leg weakness: Hips & thighs; Eventually in ~40%
- Arm weakness: Eventually in ~20%
- Rarely: Diaphragm or Bulbar
- Focal nerve lesions: 10%
- ? More disability in females
- Muscle size
- Wasting (Most common): Hands & Distal legs
- Calf hypertrophy: Occasional families
- Sensory loss
- Mild; Pansensory
- Occcasional patients with normal sensory exam
- No paresthesias or autonomic disorders
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or absent
- Enlarged nerves: ~20% clinically; 100% by ultrasound
- Cramps
100
- Location: Calf muscles
- Age: Onset in childhood (32%)
- More with: Increasing age; Stronger ankle; Hand tremor
- Sleep apnea
15
- With more severe neuropathy
- ? Related to pharyngeal involvement
- Progression
- Slow: Over decades
- Occasional exacerbations in pregnancy: Especially with earlier onset disease
- Penetrance: Nearly complete by 20 years; Earlier if nerve conductions performed
- Motor disability: Mild increase with concomitant diabetes
- Clinical variants
- More severe generalized weakness; Earlier onset
- Roussy-Levy Syndrome

- Neuropathy + Ataxia + Tremor
- Original RLS family has MPZ mutation
- Occasional: Transient recurrent palsies
- Drug interactions
- Vincristine: Produces severe exacerbation of neuropathy
- Thiopental anesthesia
- Sensitive to low doses: Lower induction dose needed
- Especially with severe motor & sensory involvement
- Neuropathy: Onset
- CNS
109
- Cognitive impairment: 70% by neuropsychological assessment
- White matter
- Volume reduced in 70%
- Creatine level: reduced in 28%
- Hypomyelination sparing U-fibers
- Brainstem auditory evoked potentials: Delayed wave I
- Electrophysiology
176
- NCV: Demyelinating Neuropathy + Axonal loss
- Conduction velocities
- Uniformly slow in all nerves
- Mean 17 to 21 M/s
- Range 5 to 34 M/s
- Time course of NCV slowing
- Clearly present by 2 years
- Onset before clinical signs appear
- Slower in earlier onset patients
- Stable after age 5 years
- Conduction block: Rare
- Compound motor action potential (CMAP): Small
- Due to axonal loss
- Degree of reduction: Correlates with
- Disease severity
- Slowing of NCV
- Nerve length
- May be progressively reduced over time
- Distal latency: Prolonged, Even in 1st months of life
- F-wave responses: Prolonged
- Sensory potentials
- Amplitude: Often absent or small
- Velocity: Slow
- Conduction velocities
- EMG: Denervation, Distal > Proxiomal
- NCV: Demyelinating Neuropathy + Axonal loss
- Laboratory
- CSF protein: High, Less in duplication patients
- Ultrasound: Nerve size enlarged, especially median & ulnar
- Pathology: Early excess myelin production
- Onion bulbs
- Small to moderate size & frequency
- Many develop > 6 years of age
- More prominent in nerves with less severe axon loss
- Myelinated axons
- Early: Myelin sheaths thicker than normal
- Late: Thinly myelinated axons
- Number: Large reduction, Especially with disease progression
- Tomaculae: Occasional patient
- Transgenic animals with PMP-22 overexpression: Hypomyelination
- Onion bulbs
- Epidemiology
- PMP-22: Triplications
121
- Genetics
- Triplication origin
- de novo from maternally transmitted duplications
- Nonallelic homologous recombination (NAHR): Especially intrachromosomal
- Mutatation rate from duplication: 1:550
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Triplication origin
- Clinical: Polyneuropathy
- Onset
- Age: Early childhood
- Gait: Waddling
- Weakness
- Distal
- Hands & Feet
- Symmetric
- More severe than: Other family members with duplication
- Muscle atrophy: Severe; Distal > Proximal
- Sensory loss: Distal; Feet & Hands
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Skeletal
- Onset
- Laboratory
- NCV: 8 to 16 m/S
- CMAP amplitude: Reduced or absent
- SNAP amplitudes: Reduced or absent
- EMG: Denervation, distal or diffuse
- Genetics
- PMP-22: Small mutations
 : Point & Other
: Point & Other
- Genetics
- Point mutations usually inherited as: Dominant
- Recessive: Arg157Trp
- Recessive or Dominant PMP-22: Thr118Met
192
- Present in controls: 1:75 in Europe; 1:120 general population
- Mutated protein
- Folding: Less stable; Similar configuration to Wild type
- Reduced traffic to cell surface: 4% to 6% vs normal of 20%
- Less likely to form large intracellular aggregates vs other disease mutants
- Heterozygous phenotypes
- Normal
- Neuropathy, Mild: Conduction velocities Normal or Mildly reduced
- HNPP, Mild
- Carpal tunnel syndromes: Chronic or Repeated
- Homozygous mutation: Axonal neuropathy, Severe
- Thr118Met/Null: More severe than WT/Null patients
- Locations
- Common: Transmembrane domain of PMP-22 protein, especially TM2
- Other: 1st extracellular loop; Asp37Val
- Missense or single base pair deletion occurs in
- Human CMT 1A
- Mouse models
- Trembler (G150D)
- Trembler-J (Leu16Pro mutation): Abnormal folding & Mis-assembly of PMP-22
- Cellular features
- Accumulate in swollen & fragmented ER + Golgi apparatus; Aggregate; Little reaches plasma membrans
- His12Gln, Leu16Pro (DSS phenotype); Ser72Leu, Ser79Cys, Leu105Arg, Leu147Arg
- Mistraffic to cell surface without aggregation: Thr118Met
- Accumulate in swollen & fragmented ER + Golgi apparatus; Aggregate; Little reaches plasma membrans
- Clinical features
- Variable
- Often more severe than duplication
- Mild subclinical forms: Some patients
- Variability within some families
- Axonal neuropathy: Few dominant or recessive point mutations
- Deafness
37 (CMT 1E
 )
)
- Clinical: Early onset; Severe
- Mutations
- Locations
- Base of first extracellular loop
- Transmembrane domains (1-3)
- Specific mutations
- Missense: Thr23Arg; Thr28Gln; Val65Phe; Ala67Pro (Severe phenotype); Leu71Pro;
Ser72Leu (Sporadic); Ser76Ile (Sporadic); Ser112Arg - Inframe deletion: del 115-118 (Later onset hearing loss)
- Missense: Thr23Arg; Thr28Gln; Val65Phe; Ala67Pro (Severe phenotype); Leu71Pro;
- Locations
- Sensory loss: Distal
- Weakness: Distal
- Vocal cord dysfunction: Some patients
- PMP22 point mutation: R159C
89
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Late onset: 5th decade
- Sensory loss: Distal; Trophic changes
- Weakness: Distal; Onset after sensory loss
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced, especially at ankles
- NCV: Axon loss
- Pathology: Axon loss; No demyelination; Mildly thin myelin sheaths
- PMP22 point mutation: Gly94fsX222
98
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Clinical
- Fixed distal weakness: Legs & Arms
- Episodes: Distal leg sensory
- NCV
- Demyelinating neuropathy
- Focal changes at entrapment sites
- Nerve pathology
- Tomaculae
- Demyelinating neuropathy
- Also see: CMT1A Recessive
- Variable
- Electrophysiology (Demyelinating types)
- Demyelinating Neuropathy
- More severe than duplication
- Slow NCV
- Long Distal latency
- Very slow NCV (15 to 20 m/sec): Asp37Val mutation
- Demyelinating Neuropathy
- Pathology: Early reduced myelin production
- Onion bulbs
- Large & on most axons
- Most develop < 6 y.o.
- Myelin sheaths thinner than normal
- Myelin uncompaction: Asp37Val
- Widening of intraperiod line
- Splitting of major dense line
- Tomaculae: Asp37Val; Gly94fsX222
- Onion bulbs
- Genetics
- Homozygotes for PMP-22 gene duplication
203
● PMP-22 duplication (4 copies); Chromosome 17p11.2-p12- Clinical features
- Most severe weakness
- Earlier onset: < 1 year to 10 years
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Nerve hypertrophy
- Pes cavus
- Some patients: Milder disease similar to patients with 3 PMP-22 copies
- Electrophysiology
- NCV: Very slow (11 to 19 M/s)
- Distal latency (Upper extremity): 6 to 12 msec
- Axon loss: CMAP amplitudes very low or absent
- Clinical features
- Autosomal Recessive CMT1A

● PMP-22 point mutations: Thr118Met; Arg157G; Arg157Trp- Mutant protein properties
- Aggregation tendency: Low
- Cellular transport: Reach cell surface
- Clinical: Dejerine-Sottas phenotype
- Onset: Infant
- Weakness: Distal
- Sensory loss
- Ataxia
- Also see: Sensory ataxia
- Deletion mutations
- Mutations: HNPP type + Exon 2 & 3 Deletion
- Clinical features: Severe phenotype
- HNPP: HNPP phenotype in parents
- CMT1A
- Dejerine-Sottas
- Mutant protein properties
- Contiguous PMP-22 gene duplication: Yuan-Harel-Lupski syndrome (YUHAL)

- Epidemiology: 23 patients
- Genetics
- Clinical: Variable features
- Onset age: Infancy
- Hypotonia
- Failure to thrive
- Global developmental delay: Walking, Speech delay, Behavior difficulties
- Dysmorphic features (50%)
- Face: Triangular
- Palpebral fissures: Downslanted
- Nose: Broad; Philtrum smooth or broad
- Upper lip: Thin
- Ears: Abnormal
- Polyneuropathy
- Onset age: Less than 5 to 10; Earlier than typical CMT-IA
- Weakness & Atrophy: Distal arms & legs
- Sensory loss: Distal arms & legs
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced at ankles
- Constipation
- Skeletal
- Foot deformities: Equinovarus; Pes planus or cavus
- Joint laxity
- Congenital heart disorder
- Laboratory
- Nerve conduction: Velocity reduced (15 to 24 M/s)
- Spine MRI: Syringmyelia (Some patients), Thoracic or Cervical
- Renal defects: Structural
- PMP-22 variant: Sensory Ataxia, Early onset
164
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Homozygous
- c.483A>G; p.[*161Trpext*10]),
- Sequence change: Loss of termination codon
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations
- PMP-22 protein
- Mutant protein: 9 amino acids larger
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 1 year
- Locomotor delay: Walking at 3 years
- Sensory ataxia: Gait ataxia; Pseudo-athetosis
- Strength: Near normal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced; Absent in Legs
- Skeletal: Varus posture in feet
- Laboratory
- NCV
- Patient: 2 to 3 m/Sec; SNAPs absent
- Parents: HNPP-like features
- CSF protein: Very high
- Brain MRI: Normal
- NCV
- PMP-22 variant: Congenital Hypomyelinating Neuropathy
- Genetics
- Inheritance: de novo Dominant > Recessive
- Mutations: Missense; Gain-of-function; Location in transmembrane domains
- Clinical
- Onset: Early infantile
- Weakness: Distal + Proximal
- Sensory: Pan-modal loss; Ataxia
- Cranial nerve involvement
- Disability: Severe
- Skeletal deformities
- Laboratory
- NCV: < 12 M/s
- Nerve pathology
- Axon loss
- Myelin sheaths: Thin or Absent
- BLOBs
- Endoneurial collagen: Surrounds axon
- Genetics
CMT IB + Other P0 Neuropathies
 61
61
●
Myelin Protein Zero (P0; MPZ)
|
P0: Genetic features Clinical-Gene correlations P0 protein P0 Clinical syndromes Myelin Δ CMT 1B: Dominant CMT 1B (Roussy-Levy): Dominant CMT 1B: Dominant; Pupils; Early onset CMT 1E: Dominant; Hearing loss CMT: Semi-Dominant Congenital: Rec or Dom; Hypomyelin Dejerine-Sottas: Dominant or Recessive Entrapment + Focal-folding Hypertrophic radiculopathy Increased P0 gene dosage: Dominant Roussy-Levy Steroid responsive, Late-onset Axonal CMT 2I: Dominant CMT 2J: Dominant; Pupil Δ; Hearing ↓ Adult onset Adult onset + Neuromyotonia Intermediate NCV CMT-DID: Dominant P0 variant syndromes Nerve pathology |
 P0 |
- Epidemiology
- Pooled prevalence: 18: 100,000
- P0 mutations in: 5% to 8% of CMT I; 2% to 5.7% of CMT
- Genetic features
- Different mutations identified: > 300
- Regions
- Exon 1: Signal sequence
- Exons 2 & 3: Extracellular domain; Immunoglobulin-like
- Exon 4: transmembrane domain
- Exons 5 & 6: Cytoplasmic domain
- Disease
- Mostly point mutations
- Exons 2 & 3 most common
- Corresponds to immunoglobulin-like extracellular domain
- 2 mutations in exon 4: Margins of transmembrane domain
- Mutations in transmembrane domain: Point or small tandem duplication
- Pathology with severely hypomyelinated axons
- Roussy-Levy (Original family)

- P0 autoantibodies: NOD.AireGW/+ mice
- Allelic disorders
- Clinical-genetic correlations
186
- Many mutations cause specific phenotypes
- Individuals in same family: Similar phenotype & NCV
- Onset age: May vary
- CMT 1B demyelinating neuropathy mutations
- Loss of function
- Mutations
185
- Null
- Ser34 deletion
- Tyr68Ter: Mild disease
- Asp104ThrfsX13: Mild disease; Neuropathic pain
- Other: Tyr53; Tyr68, Asp104
- Null
- Clinical
- Phenotype: Less severe neuropathy; Sensory > Motor; Tendon reflexes absent
- Exception: Ser233Argfs*18 with severe, early onset disease
- Mutations
185
- Missense mutations
- Mechanisms
- Disturb structure and function of MPZ
- Cause intracellular MPZ folding problems
- Mislocalize MPZ
- Asp35Tyr, Ile62Phe, Ser63del, Tyr68Cys, Gly93Glu, Arg98Cys, Val146Phe
- Mechanisms
- Mutations in single amino acids in extracellular domain
- Usual clinical: Typical CMT clinical syndrome
- Truncation mutations: Gly74frameshift; Tyr125stop; Tyr152stop
- Severe CMT; Ser34Cys; D61N; Arg69Cys; Trp72Cys
- Loss of function
- Dejerine-Sottas & other severe demyelinating neuropathy mutations
- Mutations producing aberrant protein
- Ser34Cys leads to free thiol group & disulfide aggregates
- ? Acts as dominant negative
- Ser34Cys leads to free thiol group & disulfide aggregates
- Homozygosity for P0 mutation
- Gly74frameshift; Phe35del
- Heterozygotes have typical CMT
- Mutations in cytoplasmic & transmembrane domain
- Transmembrane (DJS): Leu145frameshift; Ala192frameshift
- Transmembrane: Gln186stop (Congenital hypomyelination); Val203frameshift (Severe CMT)
- Mutations producing aberrant protein
- Axonal CMT2-P0
- Mutations
- Adult onset more common
- Other mutations
- Asn131Lys: CMT1B + Postural tremor in arms & ataxia.
- Ile135Arg & Lys138Glu: Optic atrophy; Severe phenotype
- Arg98Cys: Sensory > Motor
- Thr124Met: Pain; Pupil Δ; Hearing loss; Motor syndrome
- Same mutations may produce demyelinating or axonal neuropathies
- Mutations: Ser78Leu, Arg98Cys, Arg98His
- Italian clusters 211
- Many mutations cause specific phenotypes
- P0 Protein
168
- Size
- 28 kD
- Myelin protein: 219 amino acids
- Cells
- Myelinating Schwann cells
- Büngner band Schwann cells
- Most abundant protein in peripheral nerve myelin
- 50% of total peripheral myelin protein
- Present in myelin around most axons
- Myelin location
- Compact myelin: Around Large & small myelinated axons
- Associated proteins: PMP-22 & Myelin basic protein
- Absent from: CNS myelin
- Necessary for
- Normal myelin: Structure & Function
- Formation of intraperiod line
- Extracellular fold
- Domain similar to immunoglobulin variable chain
- Glycosylated: On extracellular domain
- Homophilic: Extracellular adhesion with similar P0 domains
- In same membrane: Interacts in cis to form homotetramers
- With apposing membranes
- Tetramers interact in trans with tetramers of P0 extracellular domains
- Necessary structures: Glycosylation; Cys21-Cys98 disulfide bond in Ig domain
- Similar in structure to single immunoglobulin variable region domain
- Other post-translational modifications: Acylation; Sulfation; Phosphorylation
- Aggregates as tetramers: Forms interperiod line
- Trans-membrane domain: 1; Amino acids 125-150
- Cytoplasmic domain
- Basic; Positive charge
- Necessary for mediationg adhesion by extracellular domains
- Interacts with - charged head groups of membrane phospholipids
- Holds together major dense line of myelin
- PKC-mediated phosphorylation: Important component of regulation of P0-mediated adhesion.
- Mutations in this domain may cause severe demyeinating neuropathy
- Schwann cells: Regulation
- Increased with: Axon contact
- Reduced by: Loss of axon contact; Turned off during Wallerian degeneration
- Present in some Schwann cells without axons: Büngner bands & Onion bulbs
- Node of Ranvier
- Interacts with: Neurofascins 155 & 186
- Mutation effects
- Common
- Gain of function
- Endoplasic reticulum stress
- Other
- Myelin structure disorders: Abnormal folding
- P0 hyperglycosylation + Myelin uncompaction: D61N mutation
- Endoplasmic retention + Activation of unfolded protein response
- Intercellular adhesion properties: Disruption
- Myelination: Altered radial axonal sorting
- Common
- Size
- CMT1B: Demyelinating polyneuropathy
- Inheritance
- Dominant: Common
- Sporadic presentation: May occur in 50% of cases
- Clinical features
- General
- Reach early milestones (walking) at the normal time
- Develop distal involvement (weakness) in 1st 2 decades
- Onset age
- Mean: 12 years
- Often in 1st decade: 30% to 40%; Delayed walking
- Some: 2nd decade
- Rare: > 30 years
- Earlier with NCV < 5 m/s
- Later onset
- Similar frequency in decades 2 to 7
- 30% > 30 years
- Weakness: Distal > Proximal
- Sensory loss: Distal; Mild; Vibration reduced
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Gait disorder: 2° distal weakness or foot deformities
- Nerve size
- ± Hypertrophic nerves
- Nerves not usually clinically enlarged
- Cauda equina syndrome due to nerve hypertrophy reported (Gly173Arg) 167
- Progression: Severe disability in some by 20 to 40 years
- Tremor (Roussy-Levy): Some patients
- Cranial nerves
- Gly163Arg mutation: Onset years after neuropathy onset
145
- Hemifacial spasm
- Trigeminal neuralgia
- Axonal neuropathy
- Pupil involvement
- Hearing loss
- Vestibular disorder (D121G) 174
- Gly163Arg mutation: Onset years after neuropathy onset
145
- General
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology
- Usual: Marked slowing of NCV < 20 M/s
- Earlier onset & more loss of ambulation with NCV < 5 m/s
- Adult onset: NCV, faster, often > 35 m/s
- Rare: Near-normal NCV
- CSF: High protein in 75%
- Electrophysiology
- Nerve Pathology
- Common
- Demyelinating
- 2 Myelin Patterns: Depend on site of mutation
- Uncompacted myelin
- 23% to 68% of myelinated fibers
- Onion bulbs
- Fewer demyelinated axons
- Mutations
- Amino acids 5, 34(del), 35(del), 69, 90(del), 98, 138, 186(stop)
- Myelin splits: Between dense lines
- ? Mutations interfere with homophilic adhesion function of P0
- Focal folding & Thickening of myelin
- Mutation types: Point mutations
- Amino acids 25, 34, 49, 61, 67, 101, 106 & 109
- Usually extracellular domain
- Folding locations: Outside or inside myelin sheath
- Onion bulbs
- Myelin: Thin sheaths; Tomaculae
- Axonal loss: Myelinated & Unmyelinated
- Myelin uncompaction: Rare
- Also seen in: CMT type 4B
- Mutation types: Point mutations
- Common
- Inheritance
- P0 mutations: Clinical variants
- P0 variant: CMT 1E
 : Demyelinating CMT + Deafness
: Demyelinating CMT + Deafness
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Mutation: Tyr145Ser
- Clinical
- Onset ages: Adult
- Sensory loss: Distal, Panmodal
- Weakness: Distal; Hands & Feet
- Hearing loss
- Adie's pupil
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- NCV: 23 to 43 M/s
- Nerve pathology: Axon loss
- Vestibular function: Reduced
- Auditory neuropathy
- Genetics
- CMT-DID (CMT DI3)
 :
CMT with Intermediate nerve conductions
:
CMT with Intermediate nerve conductions
- Epidemiology: 1 family
- Genetics
- P0 Mutation: Asp6Tyr
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Clinical
- Severity: Varied
- Weakness: Distal; Symmetric
- Sensory loss: Distal; Legs > Arms
- Laboratory
- NCV: Intermediate; 21 to 48 M/s
- Nerve pathology: Axon loss; Segmental demyelination; No onion bulbs
- CMT: Demyelinating; Semi-Dominant
- Epidemiology: 1 Italian family
- Genetics
- P0 Mutation: D195Y; Homozygous; Intracellular region
- Inheritance: Semi-Dominant
- Clinical
- Weakness: Distal; Hands & Feet
- Sensory loss: Vibration; Distal; Legs
- Skeletal: Pes cavus
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent
- Laboratory
- NCV: < 30 M/s
- Nerve pathology: Demyelination; Myelin outfoldings
- Mutation carriers
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Mutation: D195Y; Heterozygous
- Clinical
- Sensory loss: Distal; Legs; Vibration
- Strength: Normal
- Laboratory
- NCV: 41 to 44 M/s
- P0 variant: Axonal predominant neuropathy (Adult onset)
9
- Nosology
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- P0 mutations: Thr124Met (More common); Asp35Asn; His39Pro; Asp61Gly; Asp75Val; Ala76Val; His81Arg; Tyr119Cys; Lys130Arg; Gly167Arg
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Adult; Usually after 30 years
- Legs
- Paresthesias, Hypoesthesia (85%)
- Other: Weakness, Cramps, Photophobia
- Sensory loss (90% to 100%)
- Severe
- Panmodal
- Distal > Proximal
- Weakness (80% to 100%)
- Legs (80%) > Arms (35%)
- Distal
- Mild to Severe
- Deafness (29% to 45%)
- Pupil disorders: Adie's (35% to 70%)
- Deep tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent
- Cough
- Disability
- Moderate, or more
- More common than with demyelinating form of neuropathy
- Other associated features
62
- Restless legs: His39Pro
- Acute onset, painful neuropathy
- Mutations: Arg36Trp; His39Pro
- Pain: Distal legs; Burning & Shocklike
- Hyperalgesia: Hands & Feet; Pin & Temperature sensations
- Sensory loss: Vibration & Proprioception
- Intrafamilial variability
- Onset
- Laboratory
- NCV: Intermediate range of velocities
- Velocity: Usually > 20 m/s to Normal
- Often not clearly demyelinating
- CMAPs & SNAPs: Reduced amplitude or Absent
- Nerve pathology
62
- Axon loss
- Myelinated: Especially large axons
- Unmyelinated
- Length dependent
- Regeneration
- Subperineurial edema
- Segmental demyelination: Mild; Occasional patients
- Focal nerve enlargements
- Separation of axons from Schwann cells by inclusions in adaxonal portion of myelin
- Contents: MPZ; Ubiquitin; αB-crystallin; PGP9.5
- Location: Inner myelin intralaminar and/or periaxonal space
- Paranode
- Structure: Disordered
- Caspr: Asymmetric distribution
- Voltage-gated potassium channels (Kv1.2)
- Normal: Limited to juxtaparanodes
- MPZ mutations: Also present in internodal region, nondetectable
- Axon loss
- Serum CK: Mild elevation (47% to 75%); More frequent than in demyelinating form
- CSF protein: High in 75%
- NCV: Intermediate range of velocities
- P0 variant: Neuropathy with Neuromyotonia (Adult onset)
212
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- P0 mutation: Asp35Asn, Heterozygous
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Differential diagnosis
- Clinical
- Onset ages: 42 & 55 years
- Weakness: Legs ± Arms; Distal > Proximal
- Sensory loss: Distal; Panmodal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or absent at ankles
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: Mildly high
- NCV: Axon loss, Motor & Sensory
- EMG: Neuromyotonic & Myokymic discharges
- P0 variant: Polyneuropathy, Steroid responsive
10
- General
- Syndrome may be immune neuropathy in setting of CMT IB
- Similar Immune neuropathy-like disorders: CMT IA
- Genetics
- P0 Mutations: Ser63del; Arg98His; Ile99Thr
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Clinical
- Onset
- Adult: 28 to > 50 years
- Paresthesias
- Leg weakness
- Weakness: Legs > Arms; Distal > Proximal
- Sensory loss: Legs > Arms; Distal > Proximal; Panmodal
- Paresthesias
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Ophthalmoparesis: 1 patient
- Pes cavus
- Course & Progression
- Over 6 months to 10 years
- May be episodic or stepwise
- Treatment
- Steroid response: Best initially; May be reduced with time
- Immunomodulating drugs: Other
- Onset
- Laboratory
- NCV
- Slowed velocities: Variation among nerves
- Conduction block
- CSF: High protein
- Nerve pathology: Axon loss; Reduced myelin compaction
- NCV
- General
- P0 variant: Hypertrophic radiculopathy
79
- Epidemiology: 1 Italian family
- Mutation: Stop; c.306delA
- Clinical
- Laboratory
- MRI: Hypertrophic radiculopathy, C3-T1 & T11-S3
- NCV: 25 to 36 M/s; CMAP amplitudes relatively preserved
- P0 variant: Roussy-Levy (Original family)

- Genetics
- MPZ mutation: Asn131Lys
- Some families have PMP-22 mutations
- Allelic disorders
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Clinical
- Neuropathy
- Ataxia: Gait
- Tremor: Arms
- Genetics
- P0 variant: Entrapment neuropathies, multiple & Focally folded myelin
97
- Epidemiology: Japanese patient
- Genetics
- MPZ (p0) mutation: Asn131Ser
- Other mutation producing HNPP-like phenotype: Tyr145Stop
- Other mutation with focal folding: Val102Stop
- Clinical
- Onset: Slow running as child
- Distal Arms: Weakness; Wasting (Thenar); Dysesthesias
- Distal Legs: Sensory loss
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic
- NCV: Very slow
- Axon loss: Sensory & Motor
- Nerve biopsy
- Axon loss
- Myelination: Reduced thickness; Focal folding
- Electrodiagnostic
- P0 variant: CMT, Demyelinating + Increased P0 gene dosage
103
- Epidemiology: Taiwanese family
- Genetics
- Mutation
- Duplication: Includes entire MPZ gene
- Increased gene dosage: 5 MPZ copies
- Flanking genes: SDHC
 & c1orf192
& c1orf192

- Inheritance: Dominant
- Mutation
- Clinical: Intrafamilial variability
- Electrodiagnostic
- Median NCV: 9 to 47 M/s
- Temporal dispersion
- Nerve pathology
- Axon loss
- Myelin sheath: Thin
- Onion bulbs
- P0 variant: CMT 1E
CMT 1C
 20
20
●
Lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-α factor (LITAF; SIMPLE; EET1; PIG7)
- Epidemiology
- > 40 patients
- Locations: Irish, English, German
- Frequency: 0% to 1% of Dominant CMT
- Gene
- Mutations: All missense
- Missense: Ala111Thr, Gly112Ser, T115N, Trp116Arg, Leu122Val, Pro135Leu, Val144Met, Arg160Cys, Arg160His
- Gly112Ser mutation
- Adds potential new glycosylation site
- Phenotype: Mild; NCV mildly slow (25 to 30 M/sec)
- Location
- Near transmembrane domain
- Domain of the LITAF protein with role in peripheral nerve function
- LITAF polymorphisms
- Ile92Val: May be associated with early onset HNPP
- Thr49Met & Tyr80Cys: Probably not disease related
- Allelic disorders
- Sensory neuropathy, Hereditary
- HMSN digenic with EGR2
- Mutations: All missense
- LITAF protein
- Expression
- Normal: Many tissues; Abundant in Schwann cells
- Reduced expression: Cancer (Breast, Lymphoma, Leukemia, Thyroid)
- Increased expression: Obesity; Inflammatory bowel diseases
- Upregulated by: Estrogen; p53; Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
- Functions
- Regulation of endosome-to-lysosome trafficking & cell signaling
- Stimulator of monocytes and macrophages
- Causes secretion of tumor necrosis factor-α
 & other inflammatory mediators
& other inflammatory mediators - May play a role in protein degradation pathways: No E3-ligase activity
- Sort ubiquitinated substrates into multivesicular bodies
- Interacts with: WWOX; NEDD4; TSG101
- CMT IC mutations
- Abnormal function: Impaired endosomal trafficking & sorting
- Normal levels of LITAF protein in nerve & other tissues
- Expression
- Clinical
- Onset age: Mean 20 years; Range Birth to 58 years; Younger in males
- Weakness
- Distal
- Arms, Legs or Both
- Asymmetry: Few patients
- Wasting
- Sensory loss: Pan-modal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or absent in 90%
- Tremor (33%): Arms
- Feet: High arches
- Course: Progression slow; All remain ambulant
- Electrophysiology
- Nerve conduction velocities
- Demyelination (Intermediate velocities)
- Mild or Moderate
- NCV: Range 16 to 45 M/s; Mean 26 to 33 M/s
- F-wave latencies: Long
- Conduction block/Temporal dispersion: Some patients
- Axon loss: Reduced SNAP & CMAP amplitudes
- Demyelination (Intermediate velocities)
- EMG: Denervation
- Distal: Hands & Feet
- Motor unit potentials: Large, Polyphasic in distal limbs
- No spontaneous activity
- Nerve conduction velocities
- Nerve pathology
- Onion bulbs
- Mouse: Myelin infolding protruding into axons
- LITAF variant syndrome: Hereditary sensory neuropathy
- Epidemiology: May be in same family as HMSN phenotype
- Genetics
- Mutations: c.478C>T (p.Arg160Cys), c.334G>A (p.Gly112Ser)
- Clinical
- Pain: Transient; toes or Fingers
- Paresthesias
- Cramps
- Sensory loss: Distal legs
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced at ankles
- Feet: High arched
EGR2 mutations: CMT 1D
 & Other phenotypes
& Other phenotypes
●
EGR2 (Krox20)
- Genetics
- Inheritance: May be Dominant or Recessive
- Mutations
- > 30 described
- Types: Missense common
- Location: Zinc finger binding domain
- Predicted to alter DNA binding
- De novo mutations: Common
- Allelic disorders
- Dominant
- CMT 1D: Arg409Trp; Arg359Gln; Asp355Val; Arg381Cys; Arg381His
- Dejerine-Sottas (de novo): Arg359Trp; E412K
- Asymptomatic: Symptomatic after Vincristine treatment
- Recessive
- Dominant or Recessive
- Congenital Amyelinating Neuropathy
- Congenital Hypomyelinating (CHN): I268N; S382R/D383Y; Ile218Asn
- Digenic: HMSN
- Dominant
- Protein: Early growth response-2 (Krox-20)
- Family: Cys2His2 zinc finger
- DNA binding: 2 specific DNA sites in promoter region of Homeo box A4

- Regulates cellular proliferation
- Expression associated with myelination in peripheral nerve
- Transcription factor: Master regulator of myelin genes
- Role in PNS myelin development and maintenance
- Activated in Schwann cells before onset of myelination
- Disruption blocks Schwann cells at early stage of differentiation
- Activates transcription of several myelin-associated genes
- Directly: PMP22, Cx32 & PRX
- Via Egr2/Sox10 synergy: MPZ; MAG
- Maintenance of boundary between CNS & PNS
- See: EGR protein family
- Disease-Molecular correlation
- Severity of syndrome correlates with ability of mutant EGR2 to bind a cis-acting regulatory site
- Clinical syndromes
58
- CMT 1D

- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Mutations: Arg409Trp
- Clinical
- Onset: 2nd to 3rd decade
- Weakness: Distal, Legs & Arms
- Tendon reflexes: Absent or Absent distally
- Sensory loss: Distal; Arms & Legs; Mild
- Scoliosis: Progressive
- Nerve conduction velocities: Slow (9 to 42 M/s)
- Genetics
- Dejerine-Sottas

- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant, de novo
- Mutations: Arg359Trp; Glu412Lys
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 0 to 6 months
- Signs: Hypotonia; Hip dysplasia; Distal weakness
- Weakness: Distal; Hands & Feet
- Sensory loss: Legs
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Skeletal: Scoliosis; Hand contractures
- Onset
- Nerve conduction studies
- Velocities: Very slow (< 10 M/s)
- CMAPs: Small or absent
- Pathology: Onion bulbs; Thin myelin sheaths; Axonal loss
- Genetics
- Congenital Hypomyelinating Neuropathy

- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant, de novo, or Recessive
- Mutations, dominant: cis Ser382Arg & Asp383Tyr
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth
- Cranial nerve: Ptosis; Tongue fasciculation
- Walking age: 18 to 24 months
- Respiratory: Normal or restrictive disease
- Progression: Slow
- Motor nerve conduction velocity: 3 M/s
- Genetics
- Congenital Amyelinating Neuropathy: Recessive
- AR-CMT2, Late onset
141
- Epidemiology: 1 Spanish family, 5 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutation: p.R409Q
- Clinical
- Onset age: 20 to 50 years
- Weakness: Distal; Legs > Arms; Varied severity
- Sensory: Loss
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic
- Motor NCV: Usually > 40 M/s
- CMAP & SNAP amplitudes: Reduced
- EMG: Chronic denervation in distal arms & legs
- Leg MRI: Fatty replacement of foot muscles & posterior + anterolateral distal legs
- Electrodiagnostic
- Asymptomatic: Symptomatic after Vincristine treatment < 5 mg
102
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Missense; R353G
- Dominant
- Clinical
- Weakness: Distal
- Sensory: Paresthesias
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Progressive: Over weeks
- Electrodiagnostic
- Motor conduction velocity (MCV): 23 to 32 M/s
- MCV in mother: 38 to 50 M/s
- CMAP amplitude: Normal
- EGR2 variant: HMSN, Digenic
161
- Epidemiology: 1 family, 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: EGR2 (P397H); LITAF (T49M)
- P397H alone
- Asymptomatic
- Electodiagnostic: Demyelination in 1 patient also with diabetes
- Clinical: HMSN
- Onset age: Childhood to 5th decade
- Weakness: Distal; Hands & Feet; Gait disorder
- Tendon reflexes: Absent or Reduced
- Sensory loss: Pan-modal
- Pes cavus
- Laboratory
- NCV
- Velocities: Intermediate or Normal
- Axon loss: Sensory & Motor
- NCV
- CMT 1D
- Mouse disease: Krox20 knockout (Lethal) causes abnormal
- Hindbrain segmentation
- Bone formation
- PNS myelination
Hereditary Neuropathies
(CMT 1H or D-HMN) ± Macular Degeneration & Hyperelastic Skin (HNARMD)
 91
91
●
Fibulin-5 (FBLN5)
- Epidemiology: 23 families
- Genetics
- FBLN5 protein
- Location: Extracellular matrix
- Functions
- Role in elastic fiber assembly
- Endothelial cell adhesion
- Syndromes
- CMT 1 (Demyelinating; Dominant)
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 3rd to 6th decade; Earlier than D-HMN syndromes
- Neuropathy
- Weakness (80%): Distal; Legs & Arms
- Carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms
- Sensory loss: Distal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent
- Foot deformities
- Macular degeneration (10%)
- Not present
- Hyperelastic skin
- Course: Slow progression
- Onset
- Nerve conduction testing: Arms
- Motor conduction velocities: 22 to 38 M/s
- Distal latencies: 7 to 8.4 Msec
- Sensory conduction velocities: 28 to 30 M/s or absent
- Clinical
- D-HMN (Motor; Dominant)
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 1st to 9th decade
- Macular degeneration or Neuropathy
- Weakness: (70%): Distal; Legs & Arms
- Tendon reflexes: Normal or Reduced
- Sensory loss: Occasional
- Macular degeneration (50%): Exudative or Dry
- Hyperelastic skin (30%)
- Joint hypermobility (20%)
- Onset
- Nerve conduction testing: Arms
- Motor conduction velocities: Normal
- Distal latencies: 3 to 5 Msec
- SNAPs: Normal
- Clinical
- CMT 1 (Demyelinating; Dominant)
- Pathology
- Skin
- Dermis: Increased FBLN5 reactivity in some patients
- Elastin fibrils: Fragments; Short; Reduced in number
- Nerve & Muscle: Normal FBLN5 staining
- Skin
CMT 1G
 129
129
●
Peripheral myelin protein 2 (PMP2)
- Epidemiology: 8 families, 22 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Ile43Asn, Ile50del, Thr51Pro, Ile52Thr, M114T, V115A (Mild NCV Δ)
- PMP2 protein
- Basic P2 protein
- Major proteins of peripheral myelin
- Related to
- Transport of fatty acids
- Metabolism of myelin lipids
- Lipid-binding activity
- Organization of compact myelin
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1 to 18 years
- Pes cavus
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs: Severe at ankles
- Hands: With disease progression; May be median > ulnar
- Proximal: In few patients
- Early onset: Delayed walking
- Sensory loss: Pan-modal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Hand tremor: Some patients
- Laboratory
- NCV: Demyelinating neuropathy
- Tibial NCV: 15 to 22 M/sec
- Median CMAP: Reduced amplitude
- SNAPs: Absent
- EMG: Distal denervation
- Nerve pathology
- Demyelination
- Onion bulbs
- Myelin sheaths: Thin
- Axon loss (Large)
- Regenerating clusters
- NCV: Demyelinating neuropathy
CMT 1 150
● c1orf194- Epidemiology: 2 patients, 1 family
- Genetics
- Mutation: K28I (c.83A>T)
- Allelic disorder: CMT-DI
- c1orf194 protein
- Calcium regulator in neurons
- Clinical
- Onset age: 6 & 40 years
- Weakness
- Arms & Legs
- Distal
- Gait: Steppage
- Course: Progressive
- Sensory loss
- Distal
- Arms
- Modalities: Large & Small fiber
- Tendon reflexes: Absent in Legs
- Pes cavus
- Laboratory
- Nerve conduction
- Velocities: Demyelinating; Velocity 11 M/s
- SNAPs: Absent
- Nerve conduction
- c1orf194 variant: CMT-DI
- Epidemiology: 6 patients. 1 family
- Genetics
- Mutation: I122N (c.365T>A)
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Clinical
- Onset age: 20 to 33 years
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs
- Gait: Steppage
- Sensory loss
- Distal
- Legs
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent in Legs
- Laboratory
- NCV
- Motor NCV: 30 to 52 M/s
- Sensory NCV: 43 to 57 M/s
- Nerve pathology
- Axon loss
- Thinly myelinated axons: Regeneration
- Myelin folding irregularities
- Muscle fibers
- Grouped atrophy
- Hypertrophy
- NCV
CMT 1J
 170
170
●
Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor, Type 3 (ITPR3; IP3R3)
- Epidemiology: > 20 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Heterozygous
- Val615Met: Adult onset
- Met1064Val
- Thr1424Met: Recurrent; Multiple ethnicities; Varied phenotypes
- Arg2524Cys: Child onset
- Mutation mechanism: Dominant negative
- Allelic disorders
- Mutations: Heterozygous
- ITPR3 protein (IP3R3)
- Location in Schwann cells (Rat): Paranode
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Part of channel complex with itself & IP3R1 & IP3R2
- Transduces hormonal signals that regulate Ca++-dependent processes
- Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R)
- Apoptosis control
- IP3 signaling pathway
- IP3R3 Thr1424Met mutation: Channel gain of function
- ITPR3 knockdown: Altered Ca++ flux dynamics in response to GPCR agonist ATP
- Clinical
- Intrafamilial variability
- Onset ages: 1 to 27 years; Mean 21 years; Some clinically normal in 6th decade
- Weakness: Distal > Proximal; Symmetric
- Sensory loss: Distal; Panmodal except Joint position
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Pes cavus or planus
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- NCV: Demyelination + Axon loss
- Velocities (Arms): 20 to 52 M/s
- CMAP & SNAP amplitudes: Reduced or Absent in legs
- Asymptomatic carriers: Slow NCV
- EMG: Length dependent denervation
- Ultrasound: Irregularly large nerves
- MRI: Nerve roots large
- Muscle
- Chronic partial denervation
- Grouped atrophy
- Type grouping
- Type 1 fiber predominance
- Nerve
- Onion bulbs
- Axon loss: Large & Small
- Regenerating axon clusters
- NCV: Demyelination + Axon loss
CMT: X-linked
|
Type 1: GJB1 Variants Type 2 Type 3 Type 4 (Cowchock): AIFM1 Type 5: PRPS1 Pyramidal signs |
- CMT X-linked, Type 1 (CMTX1)

● Connexin-32 (GJB1)
 ;
Chromosome Xq13.1; Semi-Dominant
;
Chromosome Xq13.1; Semi-Dominant
- Genetics: Mutations
- Locations
- Numerous: > 400 identified; World-wide
- Most parts of Connexin-32 (GJB1) gene
- Mutations in noncoding DNA in 11% (3' & 5' UTR)
- Effects on Cx-32 protein: Normally located on cell surface membrane
- Markedly reduced abundance: 175 frameshift
- Cytoplasmic accumulation & none on surface
- G12S, R142W, E186K, E208K
- Cytoplasmic accumulation & some on surface
- R15Q, V63I, V139M, R220Stop
- "Dominant negative" effects on other connexins
- R142W reduces Cx-26 expression
- Locations
- Genetic-Clinical correlations
67
- Severity: General
- Many mutations produce same disease severity as GJB1 deletions
- ? Related to degree of protein function lost
- No clear relation: Ability of Cx32 mutants to form functional channels
- Mild phenotype: Rare
- Point mutations: Missense (e.g. Val84Ile)
- Mild electrophysiological changes: NCV > 40 M/s
- Moderate-Severe (Typical) phenotype
- Point mutations: Missense
- Mutation locations: Many
- Found in most regions of protein
- Not in 4th transmembrane domain
- Also in Promoter, or 5' untranslated region
- Many other missense & stop mutations
- Found in most regions of protein
- GJB1 Protein
- Some mutations: Present on plasma membrane ± cytoplasm
- Other mutations: Expressed in cytoplasm but not cell surface
- Clinical: Typical age-related progression
- Electrodiagnostic
- Mixed Axonal-Demyelinating Neuropathy
- NCV: Intermediate (30-40 M/s)
- Severe phenotype
- Mutations
- Out of frame deletion or insertion: 175 frame shift
- Stop codon: Arg22Stop
- Missense: Phe235Cys
- Causes abnormal leakiness of connexin hemichannels
- May be associated with severe or typical phenotype
- Protein: None or absent from surface membrane
- Earlier onset: < 10 years
- More disability
- Demyelinating Neuropathy (NCV: Slow (10-37 M/s))
- Mutations
- CNS involvement
- Females: Heterozygous carriers
- Severity: General
- Connexin-32 Protein

- Protein family: 4-TM; Homology to PMP-22
- Expression: Schwann cells
- Function
Gap junction formation
- Radial diffusion pathway: Between adaxonal & perinuclear Schwann cell cytoplasm
- Location: Myelinating Schwann cells
- Uncompacted myelin: May co-localize with MAG
- Para-nodal regions
- Schmidt-Lanterman incisures
- CMT 1X: Reduced expression of Connexin-32 & other myelin proteins
- Clinical features
- General: Intrafamilial variability common
- Onset
- Males: < 20 years
- Gait disorder
- Motor
- Weakness
- Distal
- Hands & Feet
- Split hand: Thenar > Hypothenar involvement
- Wasting: Legs > Hands
- Weakness
- Sensory loss (> 75%): Early proprioceptive loss
- Reflexes
- Ankle: Absent (100%)
- Knee: Males absent 90%; Females absent 50%
- Preserved elsewhere
- Extensor plantar: Some patients; Unilateral or Bilateral
- Hearing loss
- 2° changes in central auditory pathways
- Arg142Glu mutation
- May be asymmetric
- Tremor: Postural
- CNS
- Exercise related: White matter & corpus callosum lesions
- Transient encephalopathy at altitude
- Stroke-like episodes
- Dysarthria
- Weakness
- Other
- Few clinical features
- Slow conduction: Brainstem auditory evoked responses
- Exercise related: White matter & corpus callosum lesions
- Progression
- Slow
- Age-related: Relatively severe disability by 6th decade
- Nerve conductions
- Slow conduction velocities
- Moderate slowing
- Range in males: 25 to 35 M/s
- Most severe @ 22 to 25 M/s
- Range in females: > 35 M/s
- Non-uniform
- Asymmetric
- Among & Within nerves
- Moderate slowing
- Distal latencies: Prolonged
- Temporal dispersion: Prominent; Female & Male
- Axonal loss
- Length dependent
- Disability: Correlates with loss of motor units
- Absent SNAP in legs: 70%
- Intrafamilial variation
- Females
- Axon loss
- Temporal dispersion
- Less slowing of NCV (30 to 54 M/s)
- Slow conduction velocities
- Pathology
- Similar in most patients
- Not related to specific gene mutations
- Axons
- Myelin
- Thin sheaths
- Internodes: Short; Uniform on teased fibers; Poor relation to axon size
- Segmental demyelination: Some
- Nodes of Ranvier: Wide
- Onion bulbs: Few
- Similar in most patients
- CMT 1X: Variant syndromes
- Females
- Genetics: Heterozygotes
- Clinical
- Common: Mild signs or Asymptomatic (50%)
- Manifesting carriers
- More frequent than other X-linked CMT types
- More severe neuropathy: Phe235Cys mutation
53
- Pathophysiology
- Leaky Connexin-32 hemichannels
- Skewed X-inactivation: Chromosome with normal gene
- Manifest: Mutant proteins inhibit cell communications
- Onset: Early childhood
- Weakness: Face, Proximal & Distal; Progressive to severe
- Sensory loss: Distal
- Nerve pathology: Axonal loss; Onion bulbs; Thin myelin
- Family history
- Mother with same mutation, but much milder phenotype
- Pathophysiology
- Nerve conductions: Axonal or Less demyelination than males
- Episodic: Unusual GJB1 features
- Episodic weakness: C164T mutation
21
- Duration: 5 hours to 3 days
- Distribution of weakness
- Common: Extremities
- Other: Trunk & Head; Dysphagia; Dysarthria
- Transient encephalopathy
30
- Genetics
- Connexin-32 mutations
- CNS manifestations
- F51L, R75W, E102del, V139M, Arg142Trp,
R142Q, R164Q, Cys168Tyr - Mutated protein
- Unable to form gap junctions or junctional coupling
- F51L, R75W, E102del, V139M, Arg142Trp,
- PNS only manfestations
- Y151C, V181M, R183C, L239I
- Mutated protein
- Forms gap junction plaques
- Normal junctional coupling
- CNS manifestations
- Connexin-32 mutations
- Clinical features
- Triggers
- Exercise
- Altitude (> 8,000 feet)
- Illness
- Dehydration
- Hyperventilation
- Onset: 2 to 3 day delay
- Altered consciousness
- Ataxia
- Dysarthria
- Weakness: Bulbar; Proximal arms
- Course: Resolution over weeks
- Triggers
- MRI: White matter & corpus callosum lesions
- Nonenhancing, confluent, symmetrical
- More pronounced posteriorly
- Genetics
- Episodic weakness: C164T mutation
21
- Females
- Also see: Clinical pictures
- Genetics: Mutations
- CMT X-linked, Type 2 (CMTX2)

● Chromosome Xp22.2; Recessive- Epidemiology: 1 family, 5 patients
- Clinical
- Onset Infancy & 1st decade
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs > Arms
- Sensory loss (40%)
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Mental retardation (40%)
- Pes cavus
- Hearing: Normal
- Laboratory
- NCV: Slow; Axon loss
- EMG: Denervation
- CMT X-linked, Type 3 (CMTX3)
 63
63
● Chromosome Xq27.1; Recessive- Epidemiology
- Several families in Australia, New Zealand & US
- Probable Scottish founder mutation
- Genetics
- Mutation
- Large DNA interchromosomal insertion in CMTX3 locus.
- 78 kb insertion originates from chromosome 8q24.3: Produced trisomy of 8q24.3
- Possible effect of insertion: FGF13
 dysregulation
dysregulation
- Other Xq27.1 interchromosomal insertion syndromes: Hypoparathyroidism, Hypertrichosis, Ptosis, XX male sex reversal
- 1 original family reevaluated & not at this locus: HMN 5C (BSCL2 mutation)
- Mutation
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Birth to 13 years
- Fott deformities
- Pain & Paresthesias: Legs
- Weakness: Distal; Hands & Feet; Gait disorder
- Sensory loss: Distal; Arms & Legs; Pansensory or Small fiber
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or absent distally
- Skeletal: Pes cavus (60%); Hip dysplasia (20%); Scoliopsis (20%)
- Progression
- Arms involved with or after legs
- More rapiod than other CMT
- Some in wheelchair in 2nd or 3rd decade
- CNS
- Normal mentation & BAERs
- Spasticity: 1 family
- Carrier females: Asymptomatic
- Onset
- Electrophysiology
- NCV
- Axon loss
- Demyelinating features (90%)
- ≤ 23 M/s in 1 or more nerves (100%)
- Varied among nerves
- Conduction block (40%)
- EMG: Distal denervation
- NCV
- Female carriers
- Asymptomatic
- High arched feet
- Weakness: Foot dorsiflexion
- Epidemiology
- Cowchock Syndrome (Type 4; COWCK; CMTX4)

● Apoptosis-Inducing Factor mitochondrion-associated 1 (AIFM1) ;
Chromosome Xq26.1; Recessive
;
Chromosome Xq26.1; Recessive
- Genetics
- Allelic disorders
- Obligate heterozygous females: Asymptomatic
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth to 5 years
- Neuropathy, Axonal
- Weakness
- Distribution: Distal; Especially peroneal group
- Severe
- Sensory loss
- Areflexia
- Weakness
- Skeletal: Pes cavus & Hammer toes
- Mental retardation (60%)
- Deafness: Most by 5 years
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic testing
- Median motor conductions: 33 to 56 m/s
- Sensory conductions: Markedly abnormal
- Nerve morphology: Axon loss & regeneration
- Electrodiagnostic testing
- Genetics
- CMT X-linked, Type 5
 54
54
● Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase I (PRPS1) ;
Chromosome Xq22.3; Recessive
;
Chromosome Xq22.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: Korean & European families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Glu43Asp, Met115Thr; Ala121Gly
- Allelic with
- Arts syndrome
- Hyperuricemia, Mental retardation & Sensorineural deafness with PRPS1 superactivity

- Deafness, X-linked 1

- PRPS1 protein
- Ubiquitously expressed in human tissues, including cochlea
- Catalyzes phosphoribosylation of ribose 5-phosphate to 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate
- Mediates biochemical step in purine metabolism & nucleotide biosynthesis
- Mutation: Reduced enzyme activity
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Early
- Hearing loss
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs
- Onset age: 8 to 13 years
- Gait difficulties
- Hearing loss: Sensorineural
- Optic neuropathy: Onset age 7 to 10 years; Most patients
- Sensation: Normal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology: Axonal neuropathy ± Mild demyelination
- NCV: Normal or Mildly slowed
- SNAP amplitudes: Mildly reduced
- Pure tone audiogram: Bilateral sensorineural hearing loss, severe
- Nerve pathology: Loss of myelinated axons
- Electrophysiology: Axonal neuropathy ± Mild demyelination
- Nosology
- CMT X-linked, Type 6 (CMTX6)
 107
107
● Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isoenzyme 3 (PDK3; PDHK3)
 ; Chromosome Xp22.11; Semi-Dominant
108
; Chromosome Xp22.11; Semi-Dominant
108
- Epidemiology: 1 family
- Mutation: Missense; R158H
- PDK3 protein
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Tissues: Highest in heart & skeletal muscle
- Regulates pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC), by reversible phosphorylation
- Mutation effects
- Enzyme hyperactivity
- Binds with stronger affinity to inner-lipoyl (L2) domain of E2p chain of PDC
- Clinical
- Onset age: Mean 7 years; &le 13 years
- Foot deformity: Pes cavus, Bilateral; Clawed toes
- Gait disorder
- Motor: Wasting & Weakness
- Legs: Distal
- Hands: Reduced grip strength
- Ankle reflexes: Absent
- Sensory loss
- Distal
- Pan-modal
- Tremor: Hands
- Course
- Slow progression
- All remain ambulant
- NCV
- Axon loss: Motor & Sensory
- SNAPs: Often absent in arms & legs
- CMAPs: Reduced amplitude or absent in legs
- Carrier females: Mild features or asymptomatic
- Hands: Intrinsic muscle wasting
- Foot deformity: Onset in teens
- Ankle reflexes: Reduced
- Hand tremor: 5th decade
|
|
|
CMT 2
General features- Axonal Neuropathy (NCV: Axonal Loss)
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Prevalence: 4 to 12 per 100,000
- Onset: Peak in 2nd decade; Some as late as 7th decade
- Clinical
- Weakness: Symmetric; Distal in most
- Sensory loss: Distal; Panmodal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced most at ankles; Often preserved proximally
- NCV: > 38 m/s in Median nerve
- Associated with: Increased frequency of restless legs syndrome
- Characteristic clinical features
- CMT 2A (MFN2; 1p36): Distal leg weakness early in course; ? Anticipation
- CMT 2B (RAB7; 3q13): Severe sensory loss; Acrodystrophy
- CMT 2C (TRPV4; 12q24): Vocal cord & Phrenic involvement; Onset 1st decade
- CMT 2D (GARS; 7p15): Hand involvement early in course
- CMT 2E (NFL; 8p21): Legs > Arms; Ataxia worse with heat or fever
- CMT 2F (HSPB1; 7q11): Preominantly motor
- HMSN-P (3q13): Proximal weakness; Absent DTRs; Tremor; Diabetes mellitus
- CMT 2-P0 (P0; 1q22): Severe sensory loss; Deafness; Adie's pupil
- CFEOM3 (TUBB3; 16q24): Eye movement limitation
- HMN 5B (BSCL2; 11q13): Motor predominant; Early arm weakness
CMT 2A: General
- Clinical features
- Onset
- Age: 1 to 52 years; Variable in family; ? Anticipation
- Symptoms: Foot drop; Dysfunction in gait, running or climbing stairs
- MFN2: Moderate symptoms in early childhood
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs: Anterior & Posterior
- Sensory loss
- Mild: Variably present
- Distal
- Legs > Arms
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or absent in lower extremities; Absent at ankles
- Tremor: Intention; Up to 88%
- Pes cavus (100%)
- Leg pain: Some patients
- Hearing loss: 59% with MFN2 mutations
- Progression: Gait aids or wheelchair may be needed in 4th or 5th decade
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic: Axonopathy
- Median NCV
- Velocity: Slightly decreased; 38 M/s to 62 M/s
- CMAP amplitude: Reduced (< 4 mV)
- SNAP amplitude: Reduced (< 10 μV)
- EMG: Denervation in distal muscles
- Median NCV
- Sural nerve pathology
- Reduced numbers of myelinated axons, especially large
- Rare myelin changes: None on teased fibers
- Electrodiagnostic: Axonopathy
CMT 2A1
● Kinesin family member 1Bβ (KIF1B)
- Epidemiology with KIF1B mutation
- Families in Japan 13
- Patients also have MFN2 mutation
- Mutation
- Missense: Q98L
- Loss of function mutation in motor domain: ATP binding P loop
- May not be pathogenic in disease
- Kinesin family member 1Bβ protein (KIF1Bβ)
- Protein superfamily: Kinesin
- N-terminal-type microtubule motor protein
- Function: Anterograde transport of synaptic vesicle precursors
- Subcellular location: Normal KIF1B
- Cytoplasmic: Cell periphery
- Synaptic vesicle membranes
- Cofractionates with membranous organelles containing synaptotagmin, synaptophysin & SV2
- Mutant KIF1B (Q98L)
- Subcellular location: Aggregated in the perinuclear region
- Microtubule-activated ATP turnover rates reduced
- ? Functional loss of motor activity
- Kinesin mutations & disorders
- External link: Kinesin home page
|
CMT 2A2A
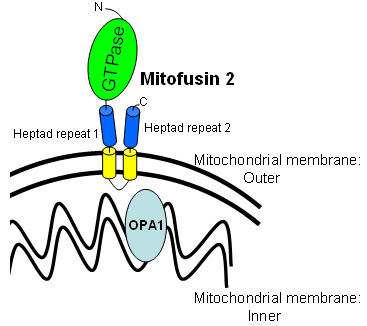
● Mitofusin 2 (MFN2; KIAA0214)
|
|
CMT 2B
● RAS-Associated protein RAB7 (RAB7; RAB7A)
- Epidemiology
- Families & Sporadic patients
- Genetics: RAB7 mutations
- Missense
- Specific mutations: Leu129Phe; Asp161Thr; Val162Met
- RAB7 protein
201
- Expression: Ubiquitous, including sensory & motor neurons
- RAB family of RAS-related GTP-binding proteins
- Regulators of vesicular transport & membrane trafficking
- May have a role in linking vesicles and target membranes to the cytoskeleton
- Localization: Late endosomes
- RAB7 functions
- Small GTPase
- Degradation pathways
- Transport between: Late endosomes & Lysosomes
- Interaction between: Mitochondria & Lysosomes
- Driven by: RAB7 GTP hydrolysis at contact sites
- Mediates: Lysosome regulation of mitochondria dynamics
- Locations: Axons & Soma
- Role in cellular vacuolation induced by cytotoxin VacA of Helicobacter pylori
- Autophagy pathway
- RAB7-effector protein RILP

- Induces recruitment of dynein-dynactin motors
- Regulates transport toward minus-end of microtubules
- Golgi targeting of glycosphingolipids
- Mutation effects
- GTP hydrolysis: Defective
- GTP binding: Increased
- Mitochondria-Lysosome contacts: Prolonged contact site tethering in axons
- Lysosome: Defective morphology; Increased size
- Clinical features
11
- Onset
- 2nd & 3rd decade
- Foot ulcers & Infections
- Weakness: Most patients
- Distal
- Legs (Most common) > Arms (50%)
- Symmetric
- Sensory loss: Severe
- Distal
- Symmetric
- Lower limbs > Upper
- Tendon reflexes: Normal, except reduced at ankles
- Foot deformities (100%)
- Pes cavus or planus; Hammer toes; Onset in childhood
- Acromutilation & Foot ulcers: Male > Female
- Pain: Unusual; Lancinating
- Autonomic dysfunction
- Light-headedness
- Hypohidrosis: Distal
- Abnormal skin innervation
- Phenotype variable within families: Severe in some, Mild in others
- CNS: Cerebellar atrophy & nystagmus reported in 1 patient
- Progression: Few need wheelchair
- Onset
- Electrodiagnostic
- Axonal loss: Absent sural potentials; Small CMAPs in legs
- Tibial H-reflexes: Preserved
- Mild slowing of NCV
- May detect disease carriers
- Nerve biopsy
- Axonal loss: Small & large myelinated axons; Unmyelinated axons
- Axon degeneration: Unmyelinated axons
- Axonal regeneration: May be abundant
- Occasional onion bulb
- Reduced staining for RILP (Rab interacting lysosomal protein)
- Skin axon loss: Length-dependent; Male > Female
- Variants
- Mutilating neuropathy not linked to chromosome 3p
- Ulcero-mutilating neuropathies
- Acromutilating sensory neuropathy without weakness: RAB7 mutation Asp161Thr
CMT 2C (HMSN 2C)
● TRPV4
- Epidemiology
- > 50 patients
- 0% to 7% of Axonal CMT in US, Europe & Australia
- Genetics
- TRPV4 mutations
80
- Ankyrin domain: Intracellular; N-terminal
- Arg232Ser; Arg232Cys; Arg269C; Arg269H, Arg315W, Arg316C,
- Missense
- Allelic disorders
- TRPV4 mutations
80
- TRPV4 protein
- Functions
- HMSN2C mutations
- Abnormal TRPV4-regulated Ca++ influx
- Higher basal intracellular Ca++ levels
- Brachyolmia mutation (V620I): Increased constitutively activated current & response to agonists
- HMSN2C mutations
- TRPV4 Protein distribution
- Normal: Cytoplasm
- Mutant: Increased perinuclear
- Functions
- Clinical features
- Onset
- Age
- Bimodal: Many < 2; Other up to 57 years
- Stridor
- Leg weakness
- Age
- Severity
- Variable within families
- Some patients with mutations may be normal
- Weakness
- Distal: Hands & Feet; Mild to Severe
- Proximal: With disease progression; Gait disorders
- Diaphragm & Intercostal paralysis: Shortness of breath
- Vocal cord
- Altered voice; Hoarseness
- Stridor
- May be only sign in mildly affected patients
- Scapula
- May progress to proximal & face muscles
- May be worse in cold
- Sensory loss: Asymptomatic; Reduced Vibration sense; Less with infant onset
- Tendon reflexes: Depressed or Absent
- Hearing loss: Sensorineural
- Urinary bladder: Urgency; Incontinence
- Skeletal
- Pes cavus (70%)
- Arthrogryposis: Some patients
- Scoliosis
- Dysplasia (20%)
- Course: Progressive, Less with infant onset
- Onset
- Electrodiagnostic
- Median NCV > 50 M/s
- CMAP amplitudes often reduced
- Phrenic CMAP: Reduced amplitude
- SNAPs: Normal or Reduced amplitude
- EMG: Chronic denervation
- Pathology
- Muscle: Chronic denervation
- Sural nerve
- Axon loss: Mild
- Myelin thickness: Normal
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: 2x to 3x high
CMT 2D
● Glycyl tRNA Synthetase 1 (GARS1)
- Epidemiology: 15 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; E71G, Glu125Lys, L129P, G240R, Ser265Phe, His472Arg, G526R
- Allelic disorders
- Hereditary Distal Motor Neuropathy V (dSMA-V)
- CMT2D
- SMAJ1
- ? Bulbar ALS: 1 patient 143
- Systemic & Cardiomyopathy syndromes: Recessive 328
- Related tRNA synthetase disorders
- Also see: Other ARS syndromes
- GARS protein
- Family: Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases
- Function: Charge tRNAs with cognate amino acid (glycine)
- Expression: Ubiquitous
- Location: Mitochondrial & Cytoplasmic
- Other disease association: Antibody target (EJ) in immune myopathy
- Clinical features
- Onset
- Age: 3 months to 59 years; Mean 9.5 years
- Hand weakness
- Weakness
- Distal
- Arms: Especially thenar & 1st dorsal interosseus; "Split hand"
- Legs
- Bilateral
- Gait disorder
- Respiratory & Feeding: Early onset
- Cramps: Distal
- Sensory
- Varied loss: Sensation normal in some family members
- Pattern: Distal; Arms & Legs; Pansensory
- Paresthesias
- Animal models: some pathology presenmt at birth
- Tendon reflexes: Absent or reduced arms; Decreased legs
- Skeletal: Pes cavus
- Progression: Slow over years
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic
- Axon loss: Hands
- CMAP amplitudes: Reduced more in median than ulnar
- Normal NCV
- Muscle MRI: Anterolateral & Superficial posterior leg involvement
- Skin biopsy: Reduced intraepidermal axons, non-length dependent
- Electrodiagnostic
- GARS1 variant: Spinal muscular atrophy, infantile, James type (SMAJI)

- Epidemiology: 7 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: de novo, Dominant
- Mutations
- Missense: Glu125Lys, Gly652Arg, Gly598Ala
- Especially in anticodon-binding & catalytic domains
- Clinical
- Onset: < 1 year
- Motor milestones: Delayed
- Weakness
- Distal > Proximal
- Arms > Legs
- Feeding difficulty
- Vocal cord
- Respiratory
- Skeletal
- Foot deformities
- Spine: Hyperlordosis, Scoliosis
- Contractures: Hip
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- EMG: Denervation
- NCV: CMAPs small
- Muscle biopsy: Grouped atrophy
CMT 1F
● Neurofilament light chain (NEFL)
- Epidemiology: <1% of CMT; ~70 families, 177 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense & Deletions; 35 described
- Head domain: Glu7Lys; Pro8Arg; Pro8Gln; Pro8Leu; Pro8Ser; P22T; Pro22Ser; Glu89Lys; E90K; N98S
- Coil 1A: Asn97Ser
- Coil 1B: A148V
- Coil 2B: Gln333Pro
- Tail: E397K; P440L; Glu528del
- Possible modifier mutation: E488K with more axon loss
- Mutation locations
- Most in exon 1
- NEFL protein head domain: More NCV slowing
- Coil 2B domain: Less NCV slowing
- De novo mutations: Pro8Ser, N98S
- Allelic disorders
- Mutations: Missense & Deletions; 35 described
- Neurofilament proteins
- Clinical: Variable
- Onset
- Less than 13 years
- < 3 years: 30%; P8L; E90K; N98S
- 2nd decade: Pro8Arg; Glu528del
- Early childhood: Other mutations
- Early: Delayed motor milestones or Gait disorder
- 6th decade onset: L311P
- Differential diagnosis: Dejerine-Sottas
- Gait disorder
- Less than 13 years
- Weakness
- Legs & Arms
- Distal > Proximal
- Proximal weakness with disease progression
- Face: Early onset disease
- May be severe
- Muscle atrophy
- Tendon reflexes: Often reduced or absent
- Sensory loss
- Large & Small fiber modalities
- Sensory ataxia
- CNS
- Tremor: Some patients
- Cerebellar: Ataxia, some patients
- Pyramidal tract signs: 20%
- Mutations: Y265C, Y389C, E396K, F439I, P440L
- Hearing loss
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology
- Motor NCV: 15 to 38 M/s
- SNAPs: Often absent
- F-waves: Normal or Slow
- Terminal latencies: Prolonged in some patients
- Nerve pathology (1 patient)
- Axon loss: Large & Unmyelinated
- Regenerating clusters
- Onion bulbs (Small)
- Thinly myelinated axons
- Neurofilaments may occur in masses
- Muscle: Neurogenic changes
- Brain MRI: Normal or Cerebellar atrophy
- Electrophysiology
- NEFL variant disorder: Charcot-Marie-Tooth, Dominant, Intermediate (CMTD1G)

- Epidemiology: 5 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Mutation: Missense; E396K
- Clinical
- Similar to CMT 1F
● Neurofilament light chain (NEFL)
- Epidemiology: Multiple families
- Taiwan: 17% of Han Chinese families with CMT 2
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Types
- Missense
- Deletion: In frame & frame shift
- Locations
- Usually in head & rod domains
- Thr21fs; Pro22Ser; Leu93Pro; Leu268Pro; del322Cys_326Asn; Gln333Pro; Leu334Pro; Glu396Lys
- Mutation effect: ? Alters self assembly of NFL 33
- Haploinsufficiency: Probably not pathogenic
- Types
- Allelic disorders
- CMT 1F
- AR-CMT (CMT 2B5)
- CMT + Intermediate NCV (CMT DIG)
- ?? Neuropathy vs Rod myopathy
- Mutations
- Neurofilament light chain protein
- Required for organization of neurofilaments
- Associated with radial axon growth
- Clinical features
- Onset
- Age: 1st to 5th decade
- Difficulty walking; Leg weakness
- Neuropathy
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs > Arms
- Sensory loss: Minor to Severe
- Distal
- Legs > Arms
- Pansensory, especially vibration
- Sensory ataxia (20%)
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent
- Progression: Slow over years; Some severe, others mild, disability
- Weakness
- Hearing loss (30%)
- Episodic ataxia: In childhood; Triggered by fever or heat
- Postural tremor (30%)
- Systemic features
- Pes cavus: 100% over 20 years of age
- Occasional patients with hyperkeratosis
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic: Nerve conduction studies
- Axonal loss: Small CMAP
- NCV: Normal or slightly reduced; Median - Range of 29 to 55 M/s
- Distal latencies: May be prolonged
- Brainstem auditory evoked potentials: Abnormal
- MRI of brain & spinal cord: Normal
- Nerve pathology
48
- Giant axons
- Focal swellings
- Filled with: Densely packed neurofilaments
- Surrounded by: Thin myelin sheath
- Not present with: Glu396Lys mutation
- Axon atrophy: Some regions with no neurofilaments
- Regenerating clusters
- Demyelination: Secondary; Few small onion bulbs
- Similarities to: Giant axonal neuropathy
- Giant axons
- Serum CK: May be high
- Electrodiagnostic: Nerve conduction studies
- ?? NEFL Variant syndrome: Neuropathy vs Nemaline rod myopathy
- Epidemiology: 1 family
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Mutation: R421X
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Congenital
- Hypotonia
- Weakness
- Face
- Legs, distal
- Arms, distal: 1 patient
- Respiratory
- Progressive
- Skeletal
- Contractures: Knees, Ankles, Hips, Fingers
- Scoliosis
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Grouped atrophy
- Rods: Possibly in some patients
- Endomysial connective tissue: Increased
- EMG: Denervation
- NCV: SNAPs & CMAPs small
- Muscle
● Neurofilament light chain (NEFL)
- Epidemiology: Palestinian & Japanese families
- Genetics
- Clinical: Severe phenotype
- Onset
- Age: Early childhood; Often < 2 years
- Hypotonia
- Weakness
- Degree: Severe in legs; Moderate in arms
- Distal > Proximal
- Slowly progressive
- Sensory loss: Pan-modal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Onset
- Electrodiagnostic
- NCV: 12 to 25 m/s
- SNAP amplitudes: Progressively reduced
- VER: Slowed
- Nerve pathology
- Myelinated axons: Marked loss
- Remaining axons
- Small size (< 3μM)
- No neurofilaments or intermediate filaments
CMT 2F/ Distal HMN
● Heat-shock 27-kD protein 1 (HSPB1; HSP27)
- Epidemiology: English, Indian, Pakistan, Russian (Voronezh) & Belgian families
- Genetics
- Mutations
- > 30 described
- Dominant CMT: Missense (Pro39Leu; G84R; V97L; S135F, R136W; R140G; Pro170Thr; C-terminal IXI/V (180-187); Stop (Glu186*)
- Recessive CMT: Homozygous; In α-crystallin domain; L99M; S135F, R136L
- Allelic disorders
- Distal motor neuropathy 2B (Distal HMN; HMND3)
- ALS-like disorder
- Mutations
- HSPB1 (HSP27) protein
- sHSP family
- Expression: Ubiquitous; Most in Nervous system, Heart, Muscle
- Chaperone
- Widely expressed sHSP
- Interacts with
- Intermediate filament proteins
- SQSTM1/p62: Autophagy mechanisms
- Misfolded proteins: Prevents aggregation
- Functions
- Protection against: Oxidative stress
- Promotes axon regeneration
- Regulation & maintenance: Cytoskeleton; Transport (Microtubule regulator)
- Mutant HSPB1
- Not transported in neurites of cortical neurons
- Forms intracellular aggregates
- Causes sequestration of NF-M & p150 dynactin
- Clinical
- Onset
- Ages: Range 6 to 66 years; Median 50 years
- Gait disorder
- Weakness
- Distal
- Proximal legs: Some patients
- Legs > Arms
- Legs: Early in disease course
- Arms: After 5 to 10 years of disease
- Symmetric
- May be severe with foot drop
- Early onset: More severe phenotype
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Increased
- Sensory loss: Some patients
- Mild
- Distal
- Feet & Hands
- Especially pain & temperature
- Fasciculations & Cramps: In elderly patients
- Cranial nerves: Normal
- CNS: Normal
- Progression
- Slow
- Disability in most after 15 to 20 years
- Some patients remain ambulant after 30 years
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic: Axon loss
- CMAPs: Small or Absent; 30% to 50% in hands; 10% of normal or unobtainable in feet
- NCV: 42 to 58 M/s
- EMG: Denervation, Distal or Diffuse
- SNAP amplitudes: Small in some patients
- Nerve pathology
- Axon loss
- Regenerative clusters
- Myelin sheaths: Thin
- Serum CK: Normal or Mildly high
- Muscle
- Vacuolar myopathy: Few patients
- Electrodiagnostic: Axon loss
- HSPB1 variant: ALS-like disorder
157
- Genetics
- Inheritance: de novo; No family history
- Mutations: Arg27Leu; c.570G>C (p.Gln190His), c.610dupG (p.Ala204Glyfs* 6)
- Clinical: ALS
- Bulbar onset: Dysarthria; Dysphagia
- Weakness: Arms, asymmetric; Respiratory
- Mild cognitive impairment
- Laboratory
- EMG: Diffuse denervation
- Serum CK: High
- Genetics
CMT 2L
● Heat-shock 22-kD protein 8 (HSPB8)
- Epidemiology: Chinese family; Korean patient; < 1% of CMT2/dHMN
- Genetics
- Mutation: Missense; Lys141Asn
- Allelic disorders
- HSPB8 protein
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 15 to 33 years
- Leg weakness
- Weakness
- Distal: 100%
- Legs: 100%
- Proximal: Occasional patient
- Hands: 30%
- Symmetric
- Sensory loss
- Distal
- Legs
- No painless injury or ulceration
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent
- Skeletal
- Pes cavus 80%
- Scoliosis 15%
- Course
- Progression: Slow
- Never wheelchair dependent
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology
- NCV: Normal
- SNAPs: Absent or Small amplitudes
- EMG: Chronic & active denervation
- Nerve pathology
- Axons: Loss & Regeneration
- Schwann cell pathology
- Electrophysiology
CMT 2N
● Alanyl-tRNA Synthetase 1 (AARS1)
- Epidemiology: > 30 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Asn71Tyr, Arg326Trp (North European), Arg329His, Glu337Lys
- Mutation locations: Most in catalytic domain; Some in editing & C-terminal domains
- Allelic with
- Other tRNA synthetase mutations
- ARS2 genes
- CMT
- AARS protein
- Cytoplasmic
- Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase: Aminoacylation of tRNAAla
- Ligase
- Protein biosynthesis
- Autoantigen: PL-12 immune myopathy
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Mean 28 yrs; Range 6 to 54 yrs
- Leg weakness
- Occasional asymptomatic patient
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs
- Arms: Some patients
- Asymmetry common
- Moderate to Severe
- Sensory loss
- Distal
- Legs
- Tendon reflexes
- Knees: Reduced
- Ankles: Absent
- Skeletal: Pes cavus; Hammer toes
- Deafness: Sensorineural; Variable
- Course
- Progression: Slow
- Cane: Occasional in 5th or 6th decade
- Never wheelchair dependent
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology: Axonal to Intermediate
- NCV: 32 to 50 M/s; CMAP amplitudes reduced
- SNAP amplitudes: Small
- EMG: Denervation
- Electrophysiology: Axonal to Intermediate
- Genetics
- AARS Mutation: Missense; D893N
- Allelic with: CMT 2N
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2 years to 6th decade
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs: Anterior & Posterior
- Tendon reflexes: Ankles absent; Knees reduced
- Sensory: Normal
- Foot: Deformities; Pes cavus
- Course: Minimal progression
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic
- EMG: Neurogenic; Large
- motor unit potentials
- SNAPs: Normal
- Motor NCVs: Normal velocity
- Muscle MRI: Abnormal gastrocnemius & vastus lateralis
- Electrodiagnostic
- Epidemiology: 3 patients, 2 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- AARS mutations: K81T, R751G
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy
- Microcephaly
- Failure to thrive
- Vertical tali
- Spasticity
- Myoclonic epilepsy, Refractory
- Extrapyramidal: Blepharospasm, Orobuccal dyskinesia, Dystonia, Chorea,
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced, ? Polyneuropathy
- Laboratory
- EEG: Slowing; Multifocal polyspike & slow-wave discharges; High-amplitude paroxysmal fast activity
- Brain MRI: Progressive diffuse cerebral atrophy; Hypomyelination
CMT 2O
● Dynein, cytoplasmic 1, heavy chain 1 (DYNC1H1)
- Epidemiology: British, Australian & Bulgarian families
- Genetics
- Mutations
- General location: Tail domain for neuromuscular disorders
- Missense: Arg264Leu; His306Arg; Arg598Cys
- CNS involvement: Motor domains
- Allelic disorders 204
- Mutations
- DYNC1H1 protein
- Features
- Adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase)-dependent motor protein
- C-terminal motor domain: 6 ATPase domains & Microtubule-binding stalk
- N-terminal tail domain: Assembly of structural & regulatory subunits & Docking of cargos & adaptors
- Dynein complex
- Location: Cytoplasmic
- Functions
- Multisubunit, microtubule-based motor
- ATPase-dependent movement along microtubules
- Recruitment of all other dynein components
- Retrograde axon transport
- Multisubunit, microtubule-based motor
- Associated with: Dynactin
- Disorders
- DYNC1H1
- Core of dynein complex
- Responsible for protein complex binding to & moving along microtubules
- Neuronal mitosis & migration
- Signaling affecting gene expression
- Mutations: Increase interaction with adaptor BICD2
- Axon transport: Other
- Features
- Clinical
- Onset: Early childhood to 59 years
- Motor milestones: Delayed
- Weakness: Distal; Legs > Arms
- Sensory loss: Distal; Pan-modal; Normal in some patients
- Tendon reflexes: Normal or Reduced
- Fatigue
- Tremor
- Autonomic
- Enteric neuropathy
- Dry eyes
- Bladder dysfunction
- CNS
- Learning difficulties
- Seizures
- Skeletal
- Pes cavus: Some patients
- Contractures: Multiple & Congenital
- More severe phenotype
- Legs > Arms
- Mutation: Arg264Leu
- Multi-system
- Immune deficiency
- Ophthalmologic
- Craniofacial dysmorphism
- Endocrine
- Pulmonary
- Skin
- Course
- May be deterioration with infections, puberty, pregnancy, menopause
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axon loss, Sensory & Motor
- EMG: Denervation
- Muscle
- Neurogenic atrophy
- Type 1 fiber predominance
- Mouse models
- Legs at odd angles (Loa)
- Cramping 1 (Cra1)
- Sprawling (Swl)
- DYNC1H1 deletion: Muscle spindle loss
CMT 2Q
● Dehydrogenase E1 & Transketolase domains-containing protein 1 (DHTKD1)
- Epidemiology: 4 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Heterozygous; Gly437X, Tyr485X, Pro790Leu, Arg834X
- Allelic disorders
- 2-Aminoadipic & 2-Oxoadipic aciduria (AMOXAD), Recessive

- Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) + Cognitive delay, Infant-onset, Recessive: 1 patient; Gly729Arg
- ALS, sporadic: Predisposition
- 2-Aminoadipic & 2-Oxoadipic aciduria (AMOXAD), Recessive
- DHKTD1 protein

- Location: Mitochondrial
- Encodes: Dehydrogenase E1 & Transketolase domain containing 1
- Thiamine diphosphate (ThDP)-dependent 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase
- 2-Oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (OADH) complex: Catalyzes conversion of
- 2-Oxoglutarate to succinyl-CoA & CO2
- 2-Oxoadipate to Glutaryl-CoA
- OADH Cofactors: ThDP; NAD+
- Reaction end products: Glutarylation, Glyoxylate detoxication
- Vitamin-related (B1, B6) CMT syndromes
108
- Clinical
- Onset age: 13 to 25 years
- Weakness: Symmetric; Distal; Legs & Arms
- Muscle wasting: Distal arms & legs
- Sensory loss: Pan-modal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Skeletal: Pes cavus
- Laboratory
- NCV
- CMAP amplitude: Small in arms & legs
- Conduction velocities: Normal
- Muscle: Angulated muscle fibers; Mitochondrial vacuoles
- NCV
- DHTKD1 variant: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
184
- Epidemiology
- More common in Germany
- Frequency: 4.4% of sporadic ALS; 2.9% of familial ALS
- Genetics
- Mutations
- > 10
- Heterozygous
- Missense > Nonsense
- Often characterized as pathogenic
- Mutations
- Clinical
- Onset age: Mean 71 years; Range 49 to 73 years
- Limb onset (80%): Especially arms
- Progression: More rapid
- Lower motor neuron predominant
- May have: Features of Neuropathy + ALS
- Sensory loss
- Laboratory
- 2-aminoadipate & 2-oxoadipate: Normal
- Muscle pathology
- Grouped atropy
- Small angular fibers
- Necrosis: Few fibers
- COX- fibers: Scattered
- NCV: Severe axon loss early in disease course
- Epidemiology
CMT2: Motor-Sensory Neuropathy 198
● Microdeletion containing TACC3
- Epidemiology: 1 family; 7 patients
- Genetics: Mutation
- Clinical: CMT2
- Onset age: Childhood to 3rd decade
- Weakness: Distal; Hands & Feet
- Sensory loss: Small fiber & Vibration
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- Nerve: Loss of most myelinated axons
- Skin & Sweat gland biopsy: Complete axon loss
- NCV: Axon loss; Motor & Sensory
- Autonomic functions: Often normal
CMT 2FF: CMT/Distal HMN
● Cell Adhesion Molecule 3 (CADM3)
- Epidemiology: 5 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Tyr172Cys, Gly368Cys
- CADM3 protein
- Adhesion molecule
- Expressed on axons
- Binds to CADM4 on Schwann cells
- Mutation: Activates unfolded protein response
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1 to 65 years; Mean 3rd or 4th decade
- Weakness
- Distal
- Arms ≥ Legs
- Gait disorder
- Sensory loss
- Distal or Normal
- Panmodal
- Tendon reflexes
- Varied: Absent at ankles to Brisk
- Skeletal: Foot & Hand deformities
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axon loss (CMAP amplitudes reduced); Velocities intermediate
- Nerve: Loss of myelinated axons; Tomaculae
- Brain & spine MRI: Normal
CMT 2GG/Distal HMN
● Golgi-specific brefeldin A-resistance guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1 (GBF1)
- Epidemiology: 5 families; 9 patients
- Genetics
- GBF1 protein
- Facilitates GDP-to-GTP exchange for ARF family of small GTPases
- Golgi: Maintenance of structure & function
- ARF1-GBF1 complex
- Formation of coatomer protein complex I (COPI) vesicles
- Lipid droplet metabolism
- Mitochondrial function & dynamics
- Location: Ubiquitous; Present in motor neurons: Soma & Growth cone
- Golgi disorders
- Clinical
- Onset ages: Childhood to 61 years
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs > Arms
- Gait disorder
- Early onset: Walking delay
- Sensory: Reduced vibration in legs or Normal
- Bulbar: Dysarthria in 1 patient
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced at ankles; May be increased at knees
- Skeletal: Pes cavus
- Laboratory
- EMG: Chronic neurogenic; Fibrillations or Positive sharp waves in some
- NCS: Axon loss, Motor ± Sensory
- Muscle MRI: Asymmetric; Distal fatty replacement
● Golgi-specific brefeldin A-resistance guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1 (GBF1)
- Epidemiology
- Italian family
- GBF1 protein
- Clinical
- Onset: 1st or 2nd decade
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs & Arms
- Symmetric
- More severe by 4th & 5th decade
- Sensory loss: Distal; Mild
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Cranial nerves: Normal
- Autonomic functions: Normal
- Progression: Slow over decades; More in 5th decade; Many never use wheelchair
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic
- CMAPs: Small or Absent
- NCV: 25 to 45 M/s
- SNAPs: Low amplitude
- CSF protein: Normal, or Mildly increased
- Pathology
- Loss of large myelinated axons
- Onion bulbs: Occasional on EM
- Electrodiagnostic
CMT 2/DI-CMT 202
● RAB40B, member ras oncogene family (RAB40B)
- Epidemiology: 1 family, 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Y83X
- RAB40B protein
- RAB family of small GTP-binding proteins
- Secretory vesicles
- Complexes with CUL5
- MMP2 & MMP9 trafficking during invadopodia formation
- Clinical
- Onset ages: 3 & 13 years
- Weakness: Distal; Legs > Arms
- Sensory loss: Distal; Panmodal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent in legs
- Skeletal: Scoliosis; Foot deformity
- Laboratory
- Motor & Sensory NCV
- Velocities: Mildly slowed
- Axon loss: Legs
- Motor & Sensory NCV
HMSN-P
CMT 2-P0
Hereditary Sensory-Motor Neuropathy with Ataxia (SMNA)
● Interferon-related developmental regulator gene 1 (IFRD1)
- Epidemiology: Single American family of Irish ancestry
- Mutation: Missense; Ile172Val 77
- IFRD1 protein
- Expression
- Early gestation: Brain, Spinal cord & Spinal ganglia
- Late gestation: Ubiquitous
- Trophic factor stimulation
- Upregulates Ifrd1 expression
- Results in translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus
- NucleIFRD1:
- Acts as a transcriptional corepressor
- Interacts SIN3 histone deacetylase complex
- Expression
- Clinical: Variable expression
- Onset
- Age: 13 to 27 years; No anticipation
- Gait disorder, especially in dark
- Ataxia: Dysmetria; Ataxic gait; Nystagmus
- Sensory loss: Vibration > Proprioception; Positive Romberg
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent
- Extensor plantar reflexes: 50%
- Weakness: Distal or Proximal; Legs or Arms; 70%; More at older ages
- Skeletal: Pes cavus; Hammer toes
- No dementia
- Progression: Slow; Normal life span
- Onset
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axonal neuropathy; Small or absent SNAPs; Occasional prolonged distal latencies
- EMG: Chronic denervation
- MRI: Cerebellar atrophy, mild, in older patients
CMT with Intermediate NCV (DI-CMT; CMT-DI) 17
DI-CMT, Type B (CMTDIB)
● Dynamin 2 (DNM2)
- Epidemiology
- Australian, Belgium & North America families
- DNM2 genetics
- Mutations
- Located in pleckstrin homology domain
- Reduce binding of DNM2 to membranes
- Allelic with
- Mutations
- DNM2 protein
- Family of large GTPases
- Part of cellular fusion-fission apparatus
- Onset age: 1st or 2nd decade
- Clinical
- Weakness: Distal; Legs & Arms; Symmetric
- Sensory loss: Distal
- Tremor
- Cranial nerves: Normal
- Autonomic functions: Normal
- Progression
- Slow over decades
- Many never use wheelchair
- Systemic: Neutropenia (Lys558 mutations)
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic
- CMAPs: Small or Absent
- NCV: 24 to 54 M/s
- SNAPs: Low amplitude
- CSF protein: Normal, or Mildly increased
- Pathology
- Loss of large myelinated axons
- Onion bulbs: Occasional
- Electrodiagnostic
- Variant: CMT2M; Axonal neuropathy ± Eye syndrome
70
- Genetics
- General DNM2 mutation location: Pleckstrin homology domain
- DNM2 mutation: K559del
- Other CMT 2 mutations: Gly533Cys; Leu566His
- Allelic with
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Congenital to 4th decade
- Cataracts: Early
- Neuropathy: Childhood
- Neuropathy
- Distribution
- Length-dependent
- Legs > Arms
- Sensory: Pan modal loss; Sensory ataxia; Paresthesias
- Weakness: Distal; Legs > Arms
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced at ankles
- Progression: Mild
- Distribution
- Eye
- Cataracts: Congenital
- Ophthalmoparesis
- Ptosis
- Pes cavus
- Onset
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axonal loss
- Neutropenia
- Pathology: Nerve
- Axon loss
- Axonal regeneration
- Internodes: Homogeneously short
- Onion bulbs: Rare
- Pathology: Muscle
- Muscle fibers: Scattered small angular
- No myopathy
- Genetics
DI-CMT, Type C (CMTDIC)
● Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase 1 (YARS1)
- Epidemiology
- 3 Families: Midwestern US (German); Bulgaria; Korea
- Genetics
59
- Mutations: Missense (G41R & E196K); Deletion (In frame 153-156delVKQV)
- Allelic disorders
- Cytoplasmic ARS syndromes
- AARS: CMT 2N; PL-12 antigen, Early-Onset Epileptic Encephalopathy with Persistent Myelination Defect, Recessive
- DARS: Leukoencephalopathy + Spasticity
- EPRS
 : Hypomyelinating Leukodystrophy
: Hypomyelinating Leukodystrophy
- FARSA: RILDBC2
 ; Zo antigen
; Zo antigen
- FARSB
 : RILDBCB1
: RILDBCB1

- GARS: CMT 2D; HMN 5A; EJ antigen
- HARS: Sensory-Motor neuropathy; Jo-1 antigen
- IARS

- KARS: CMT-RIB; DFNB89
 ; Encephalopathies
; Encephalopathies
- LARS
 : ? Liver failure, Infantile (ILFS1)
: ? Liver failure, Infantile (ILFS1)

- MARS1: CMT 2U; ILLD
 ; Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
; Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
- NARS1: Encephalopathy + Neuropathy
- QARS: Progressive Microcephaly, Cerebral-Cerebellar Atrophy & Intractable Seizures
- RARS1 (RARS)
 : Hypomyelinating leukodystrophy (HLD9)
: Hypomyelinating leukodystrophy (HLD9)
 124
124
- SARS
- VARS
 : Neurodevelopmental disorder + Microcephaly, Seizures, & Cortical atrophy (NDMSCA)
: Neurodevelopmental disorder + Microcephaly, Seizures, & Cortical atrophy (NDMSCA)

- WARS: HMN, Distal; Neurodevelopmental disorder + Microcephaly
- YARS: CMTD1C; Ha antigen
- AIMP1: HLD3
- AIMP2
 : HLD17
: HLD17

- Also see: Other ARS-related disorders
- Protein
- Cytoplasmic ARS: General
- aa tRNA synthetases: 37 different genes
- Form large 11-subunit multisynthetase complex (MSC)
- Function: Aminoacylation of ARS subunits; Channel loaded tRNAs to ribosome
- Normal YARS
154
- Functions
- Catalyzes aminoacylation of tRNATyr with tyrosine
- Transcriptional regulation network
- Expression: Ubiquitous, including brain & spinal cord
- Concentrated in granular structures in growth cone, branch points & distal neurites
- Functions
- Mutant
- Partial loss of activity
- May have dominant negative effect on function of normal protein
- Transcription factor E2F1 hyperactivation
- Other disease association: Target of antibodies in myositis-antisynthetase syndrome
- Cytoplasmic ARS: General
- Clinical
- Onset age: Range 7 to 59 years; Most in 1st or 2nd decade
- Weakness: Distal; Legs > Arms; Symmetric
- Sensory loss: Distal; Mild
- Cranial nerves: Normal
- Autonomic functions: Normal
- Progression: Slow over decades; Many never use wheelchair
- ? Less severe in females
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic
- NCV: 30 to 50 M/s
- Pathology
- Loss of large myelinated axons: More with increasing age
- Regenerating clusters
- No onion bulbs
- Electrodiagnostic
- YARS1 variant: Motor neuropathy, Proximal
191
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Mutation: Asp308Tyr; Loss of function
- Allelic disorders
- Clinical
- Onset age: 18 years
- Weakness
- Hands: Distal
- Legs: Proximal
- Cramps
- Fasciculations
- Tendon reflexes: Absent or Reduced
- Tremor
- Nystagmus: Rotary
- Kyphoscoliosis
- Sensory: Normal
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: 300 to 1,692
- EMG: Denervation, diffuse; MUPs large
- NCV: Normal velocities
- Muscle pathology: Gropuped atrophy
- YARS1 variant: Motor neuropathy, Distal
193
- Epidemiology: 4 patients; 1 family
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Mutation: c.587A>G, p.Glu196Gly
- Allelic disorders
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3rd decade
- Weakness: Ankle & 1st toe dorsiflexion
- Tendon reflexes: Absent at ankle
- Sensory: Normal
- Laboratory
- NCV
- Motor: CMAPs small amplitude in legs; Velocities 25 to 45 M/s
- Sensory: Normal
- EMG
- Legs: Distal MUAPs polyphasic, large amplitude; Fibrillations, few
- Arms: Distal reinnervation, Minor
- NCV
DI-CMT, Type E (CMT-DIE): CMT, Intermediate with Glomerulopathy
● Inverted formin 2 (INF2; c14orf173)
- Epidemiology: > 20 families
- Genetics: Mutations
- Heterozygous
- Mutation Locations
- Exons: 2 (3' end), 3 (Diaphenous-inhibitory domain; Nucleotides 300 to 500) & 4
- Amino acids: Leu57 to Glu184
- Mutation types: Missense; In-frame deletion
- Cys104Tyr
214
- Somatic mutation described
- May be associated with neuropathy without renal disease
- Mutation effects
- Disrupt cytoskeleton: Actin & Microtubules
- Abnormal mitochondrial & other organelle interactions
- Penetrance: Incomplete
- Allelic disorder
- Rare in CMT-I without renal disease
- INF2 protein
- Formin family: Involved in remodeling actin & microtubule cytoskeletons
- Endoplasmic reticulum: Cytoplasmic face
- Tissue locations
- Peripheral nerve: Present in Schwann cells (Perinuclear; Endoplasmic reticulum) & some axons
- Kidney: Podocytes
- Functions
- INF2-induced actin filaments: May drive initial mitochondrial constriction
- Promotes actin polymerization & filament severing + depolymerization
- Microtubules: Colocalize; Bind; Mediate bundling & stabilization
- Interacts with other diaphanous-related formins: MAL
- Cdc42
 effector: Actin filament nucleation, elongation & polymerization activities
effector: Actin filament nucleation, elongation & polymerization activities
- INF2 mutations: More protein in cytoplasm
- Clinical
- Family history: 50% sporadic
- Onset
- Ages: 5-28 years
- Pes cavus
- Cramps
- Proteinuria
- Weakness (100%)
- Mild to Severe
- Legs > Arms
- Distal
- Gait disorder
- Pes cavus
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced in legs or diffusely
- Sensory
- Loss (50%): Distal; Pain ± Large fiber; Legs ± Hands
- CNS: Cognitive impairment in some patients
- Hearing loss (30%): Sensorineural
- Renal: Progressive to end-stage
- Laboratory
- NCV: Intermediate (23 to 45 M/s in median); SNAPs reduced amplitude or absent in legs
- Nerve pathology: Axon loss; Onion bulbs; Irregular myelin folding; Schwann cell damage; Schwannomas reported
- Nerve imaging: Hypertrophy, multifocal, in proximal nerves & roots; Age > 30 years
- CNS MRI: White matter hyperintensity; Ventricles enlarged
- Renal: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; Proteinuria
DI-CMT, Type F (CMT-DIF)
● Guanine nucleotide-binding protein, β4 (GNB4)
- Epidemiology
- Taiwanese family + 4 patients
- CMT frequency: 0.8%
- Genetics
- Mutations: Gly53Asp, Lys57Glu, Lys89Glu, Gln220Arg
- GNB4 protein
- Functions: Cellular signal-transduction systems
- Nerve locations
- Axons & Schwannn cells
- Colocalized with neurofilament heavy chain & S100
- Not compact myelin
- Clinical
- Onset age: 5 to 70 years
- Weakness (80%)
- Distal
- Legs (80%) > Arms (20%)
- Symmetric
- Gait: Steppage
- Progression: 1 patient in wheelchair
- Sensory
- Loss (80%): Panmodal; Distal
- Dysesthesias: Limbs & Tongue
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Skeletal: Pes cavus; Scoliosis
- Laboratory
- NCV
- More severe motor changes in males
- SNAPs: Usually absent
- CMAPs: Legs reduced amplitude; Hands Normal or Mildly reduced amplitude
- NCV: 16 to 52 m/s; Demyelinating or Axonal range
- Nerve biopsy: Demyelinating
- Onion bulbs
- Myelinated axons: Loss; Regeneration
- NCV
DI-CMT 156
● Solute carrier family 9, Member 3, Regulator 1 (SLC9A3R1; EBP50; NHERF1)
- Epidemiology: 1 family, 3 patients
- Genetics
- SLC9A3R1 protein
- Co-localizes with: Actin; Ezrin
- PNS location: Schwann cell cytoplasm (S100); Nodes of Ranvier SC microvilli (Ezrin; Nav1.8)
- NRG1-induced AKT phosphorylation
- Functions
- Schwann cell migration & process extension
- Paranodal neurofascin expression
- May be overexpressed in tumors
- Clinical
- Onset age: 29 to 31 years
- Gait disorder: Steppage
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs then Arms
- Sensation: Pan-modal loss, especially Vibration & Joint position
- Tendon reflexes: Absent at Knees & Ankles
- Skeletal: Pes cavus
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- NCV
- CMAPs: Small amplitude or absent
- SNAPS: Small amplitude or absent
- Conduction velocities: Mildly reduced; 34 to 45 M/s
- EMG: Chronic denervation; Some fibrillations
- Muscle MRI: Fat replacement of hip, thigh & calf muscles
- Mouse model: Schmidt-Lanterman incisures increased; Paranode structure damaged
- NCV
Other CMT disorders with Intermediate NCV
- CMT-DI3 (CMT-DID): P0 mutations
- CMT-X
- CMT 2E
Recessive, Axonal CMT
|
AR-CMT2A: Lamin A/C; 1q22 AR-CMT2B: MED25; 19q13.3 AR-CMT2 + Hoarseness (CMT 2K): GDAP1; 8q21 AR-CMT2, Severe & Early onset: NEFL; 8p21 AR-CMT2/Distal HMN: HSPB1; 7q11-q21 AR-CMT2: LRSAM1; 9q33 AR-CMT2-Acrodystrophy AR-CMT2-Ouvrier: Early childhood onset AR-CMT2 + Neuromyotonia: HINT1; 5q31 Andermann (Corpus callosum Δ): 15q13 CMT X-linked HMSN + CNS: Heterogeneous Giant axonal neuropathy: Gigaxonin; 16q24 HMSN + Deafness HMSN + Optic neuropathy ± Deafness Lethal Neonatal Neuroaxonal dystrophy |
Axonal CMT (AR-CMT2A; CMT2B1) 1
● Lamin A/C
- Epidemiology: North African families
- Genetics
- Mutation: Arg298Cys; Homozygous
- Allelic syndromes
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 2nd decade; Mean 15 years; Range 4 to 24
- Signs: Distal weakness, especially legs
- Weakness
- Limbs
- Distal early
- Legs ≥ Arms
- Progresses to proximal involvement in legs (60%)
- Legs > Arms
- Symmetric
- Progression
- Rapid over 4 years
- Scapular weakness
- Distal to Proximal involvement
- Prominent disability
- Limbs
- Muscle wasting: Distal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced in lower extremities
- Sensory loss
- Distal
- Hands & Feet
- Modalities: Variable, especially large fiber
- Mild: Worse with disease progression
- Skeletal
- Pes cavus (80%)
- Kyphoscoliosis (30%): With proximal weakness; Mild
- CNS: Normal; No pyramidal or intellectual disorders
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Nerve conduction: Axonal loss
- Normal velocity
- SNAPs: Often absent
- Nerve biopsy
- Myelinated axons: Reduced, especially large axons
- Unmyelinated axons: Reduced
- Regeneration: Mild to Prominent
- Nerve conduction: Axonal loss
Axonal CMT (AR-CMT2B; CMT2B2)
● Polynucleotide Kinase 3' Phosphatase (PNKP)
- Epidemiology: Brazilian & Costa Rican families
- Genetics
- Gene mutated: PNKP
- Mutations: Gln517Ter; Thr408del
- Allelic disorders
- Initial incorrect gene identified: MED25 (Ala335Val; Homozygous)
 76
76
- Gene mutated: PNKP
- PNKP protein
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 1 to 42 years; Mean 32 years
- Weakness: Symmetric; Ankles ± Hands (66%)
- Weakness
- Distal
- Symmetric
- Legs (100%): Intrinsic feet; Peroneal; Calves; Anterior tibial
- Hands (80%): Intrinsic muscles; Finger extension; Wrist flexion
- Sensory loss
- Distal
- Feet & Hands
- Type
- Panmodal
- Large fiber modalities: Especially involved
- Sensory ataxia
- Tendon reflexes
- Often absent at ankles
- May be reduced or absent elsewhere
- Discomfort
- Cramps: Distal
- Paresthesias: Distal
- Autonomic: Normal
- Cranial nerves: Normal
- Course
- Progression: Slow
- Most remain ambulatory with or without cane
- Skeletal: Normal or Mild foot deformities
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Nerve conduction: Axon loss
- Motor
- Conduction velocity: Mildly reduced (30 to 65 M/s in arms)
- CMAP: Small or absent in legs & arms
- Sensory
- Absent sural SNAPs
- Reduced amplitude SNAPs in arms
- Conduction velocity: Reduced
- Motor
- EMG: Distal denervation
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar atrophy, mild
- Nerve conduction: Axon loss
- MED25 protein
- Subunit of the human activator-recruited cofactor (ARC)
- Expression levels correlate with PMP22
- Coactivator involved in regulated transcription of RNA polymerase II-dependent genes
- Mutated protein: Reduced binding specificity; Recognition of broader range of SH3 domain proteins
CMT 2K
● Ganglioside-induced differentiation-associated protein 1 (GDAP1)
|
GDAP1 CMT Variants Axonal Recessive (AR-CMT 2K) Recessive, Mild Dominant (CMT 2K) Intermediate Recessive, Type A (CMT RIA) Demyelinating Recessive, (CMT 4A) |
- Nosology
- Called CMT 2K by OMIM

- AR-CMT + Hoarseness
- CMT2H
- CMT4C4
- AR-CMT Ouvrier type
- Called CMT 2K by OMIM
- Epidemiology
- 1% of inherited peripheral neuropathies
- Brazil: 7% of recessive CMT
- Genetics
- Mutations: > 100 described
- Allelic disorders
- General: Recessive disorders are more severe & earlier onset
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, recessive with vocal cord paresis

- Other
- GDAP1 protein
52
- Expressed in: Neurons (DRG) > Schwann cells; CNS (Brain & spinal cord)
- Subcellular location: Mitochondria
- Outer mitochondrial membrane
- Localized by C-terminal transmembrane domains
- Protein type
- Structural family: Sequence similarities to Glutathione S-transferases but no GST activity
- Activities
- Membrane-remodeling activity
- Participates in mitochondrial fission processes
- Mitochondrial membrane contact sites (MCSs) with
- Plasma membrane
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Lysosomes: Interacts with LAMP1
- Clinical syndrome: CMT 2K, Recessive, Axonal (AR-CMT + Hoarseness; CMT2H)

- Genetics
- Mutations
- Stop codons, Nonsense; Some misasense
- S194X: Moroccan families
- L239F: Polish, German, Italian, Czech & Bulgarian; Milder phenotype
- A247V: Recessive; Japanese
- Glu222Lys: Recessive severe; Dominant mild
- Mutations
- Similar locus to AR-CMT with pyramidal involvement
- Same mutations may produce demyelinating or axonal phenotype : S194X
- Genetics
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Birth to 7 years; Typical 1 to 3 years
- Hypotonia
- Feet: Deformity; Weakness
- Vocal cord paralysis
- Onset: 2nd decade
- Hoarseness (80%)
- Not present in some families: S194X mutation; Czech families 68
- Other cranial nerves: Normal
- Weakness (100%)
- Distal
- Severe
- Feet > Hands: Hand onset later in 1st decade
- Proximal
- Moderate or None
- Legs > Arms
- Gait disorder: Onset in early childhood
- Distal
- Sensory
- Loss (100%)
- Distal
- Hands & Feet
- Large & Small fiber modalities
- Paresthesias
- Loss (100%)
- Tendon reflexes: Absent or Reduced
- Skeletal
- Club foot: Early onset
- Scoliosis: Mild
- Hip dysplasia
- Progression
- Disability by end of 1st decade
- Wheelchair: 4 to 16 years
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Nerve conduction testing
- CMAPs: Reduced amplitude or Absent
- NCV: Normal or mildly reduced in proximal nerves; 40 to 50 M/s
- SNAPs: Reduced amplitude or Absent
- CSF protein: Normal
- Nerve biopsy
- Loss of myelinated axons: Especially large, None > 7μM
- Axonal regeneration & atrophy, occasional degeneration
- No demyelination
- Occasional onion bulbs
- Unmyelinated axons: Increased; Probably regenerating
- Nerve conduction testing
- GDAP1 genetics
- Clinical
- General
- Milder phenotype than recessive syndromes with 2 GDAP1 mutations
- His123Arg mutation in Finland: Mild phenotype; Slow progression
- Onset
- Age: Late 2nd to 5th decade
- Gait difficulty
- Weakness
- Distal: Hands & Feet
- Proximal: Mild; Asymmetry
- Sensory loss
- Distal
- Arms & Legs
- Pan-modal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced at knees & ankles
- Pes cavus
- Progression: Very slow
- General
- Laboratory
- NCV
- Axon loss: Mild to Severe; Sensory before Motor
- Velocities preserved
- EMG: Denervation, Distal > Proximal
- NCV
- GDAP1 Mutations
- Homozygous
- 1-BP INS, 349T, IVS4DS, G-A, +1, Leu239Phe
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Early childhood
- Gait disorder
- Weakness
- Distal
- Arms & Legs
- Sensory loss
- Distal
- Arms & Legs
- Pan-modal
- Ankle & foot deformities
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Nerve conduction testing
- Velocities: 25 to 35 m/s
- CMAP & SNAP amplitudes: Reduced or Absent
- Peripheral nerve pathology: Axonal + demyelinating changes
- Axon loss: Especially large axons
- Regenerating clusters
- Demyelinated axons
- Onion bulbs: Small
- Nerve conduction testing
- Epidemiology: Polish, German, Italian, Czech & Bulgarian families
- GDAP1 mutations: L239F
- Homozygous
- Heterozygous with another missense mutation
- Clinical: Milder phenotype
- Onset age: 2 to 10 years
- Weakness: Distal; Arms & Legs
- Sensory loss: Arms & Legs
- Gait disorder: Falling
- Walking into 2nd decade
- Wheelchair in 2nd to 4th decade
- Club feet
- Electrodiagnostic: Axonal loss
Axonal CMT (AR-CMT): Ouvrier type
● Autosomal Recessive or Semi-Dominant
- Genetics: Several disorders
- AR-CMT with hoarseness (GDAP1)
- CMT 2A2 (MFN2)
- Clinical
- Onset age: Early childhood
- Weakness: Distal; Symmetric; Legs before arms
- Sensory loss: Mild
- Progression: Slow; Severe distal weakness by 20 years
- Pathology: Axon loss
Axonal CMT with pyramidal involvement (AR-CMT2C; CMT4C2; CMT 2H)
● Chromosome 8q21.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: Tunisian family
- Genetics: Similar locus to AR-CMT with hoarseness (GDAP1)
- Clinical features: Homogeneous in family
- Onset
- Age: 4 to 8 years
- Difficulty walking
- Weakness & Wasting: Distal; Legs then Arms
- Sensory loss: Distal
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk, except absent at ankles
- Other reflexes: + Hoffman & Palmo-mental
- Course: Progressive
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic: Axonal loss
- Nerve biopsy: Severe axonal loss; Occasional regeneration
HMSN with Intermediate NCV, X-linked (CMT XI) 128
● Dystrophin-related protein 2 (DRP2)
- Epidemiology: 9 males
- Genetics
- Mutations: Stop; Splice; Deletions
- DRP2 protein
- Schwann cell plasma membrane
- Periaxin-DRP2-Dystroglycan complex
- Maintenance of Cajal bands of myelinating Schwann cells
- Expression: High in brain & spinal cord; Also kidney, ovary, epididymus
- Homology: C-terminal region of dystrophin
- Clinical
- Onset age: 18 to 50 years; Mean 36 years
- Weakness: Distal; Legs then Hands
- Muscle size: Calf atrophy
- Sensory loss: Distal; Arms & Legs; Panmodal or Small fiber
- Tendon reflexes: Ankles absent; Others normal
- Pes cavus (60%)
- Course
- Slow or Intermediate progression
- Episode of unilateral brachial plexopathy
- Laboratory
- NCV
- Distal latencies: Long (60%)
- Conduction velocities: Intermediate; 36-52m/s; Non-uniform
- F-wave latencies: Prolonged in legs
- No conduction block or temporal dispersion
- Epidermal axons: DRP2 absent; Cajal bands absent
- Ultrasound: Patchy nerve enlargement
- CSF: Protein slightly high
- Nerve biopsy
- Axon loss
- Myelin sheath width: Varied; Thin, Thick & Tomaculae
- NCV
Hereditary Ulcero-mutilating Sensory > Motor Neuropathy, Recessive (HSAN IIC; HSN2C)
● Axonal transporter of synaptic vesicles (KIF1A; ATSV)
- Epidemiology: 5 families
- ATSV mutations
- Truncating & Missense (E239K)
- Commonly located in alternatively spliced exon 25b
- Motor domain mutations at KIF1A N-terminal: Linked to hereditary Peripheral neuropathy & Spastic paraplegia 208
- Allelic disorders
- Hereditary spastic paraparesis 30 (SPG30)
- Mutations in ATSV kinesin motor domain
- Inheritance: Dominant (SPG30A) or Recessive (SPG30B)
- Mental retardation, Dominant 9A (NESCAV)

- Hereditary Sensory > Motor Ulcero-Mutilating Neuropathy (HSN2C)
- Epilepsy, generalized: Ala397Asp, Dominant 158
- Similar to: Axonal CMT (CMT2) with Acrodystrophy, Recessive
- ALS associations
- Hereditary spastic paraparesis 30 (SPG30)
- ATSV protein
- Interacts with the domain Encoded by HSN2 Exon of WNK1
- Synaptic vesicle transport
- Clinical: Ulcero-mutilating sensory neuropathy
- Onset: 6 to 15 years
- Sensory loss: Feet & Hands; Vibration & Joint position
- Ulcero-mutilation: Amputations
- Progression: Slow
- Weakness: Distal; Hands & Feet
- Tendon reflexes: Absent in legs
- Developmental delay & Short stature: 1 patient
- Laboratory
- Nerve conduction
- SNAPs: Absent
- CMAPS: Small amplitude or Absent
- Conduction velocities: Normal or Mildly reduced
- EMG: Distal denervation; Large motor units
- ATSV variant syndrome: Hereditary Spastic Paraparesis, Recessive (SPG 30)
95
- Epidemiology: 1 Palestinian Muslim family; 3 brothers
- Genetics: ATSV mutation in kinsein motor domain; Ala225Val; Homozygous
- Clinical: Pure spastic paraparesis
- Onset age: Early Childhood; 2 years
- Spasticity
- Distribution: Legs; Gait
- Plantar responses: Extensor
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk in legs
- Normal: Lower limb sensation, Sphincters, Upper limbs, Intellectual functions
- Laboratory
- EMG: Normal
- NCV: Normal
- Brain MRI: Normal
Axonal CMT (CMT2) with Acrodystrophy, Recessive
● Recessive 8
- Epidemiology: Turkish family, consanguinous
- Similar to: Hereditary Ulcero-mutilating Sensory > Motor Neuropathy, Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset: 7 to 10 years; Painless ulcers on feet
- Weakness: Distal > Proximal; Symmetric; Hands & Feet
- Wasting: Distal
- Sensory loss: Distal; Symmetric; Hands & Feet; Panmodal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Acrodystrophy: Mutilation & Ulcers on feet & hands
- Course: Slowly progressive
- Laboratory
- NCV
- Normal velocity when obtainable
- Motor & Sensory amplitudes: Reduced
- EMG: Distal denervation
- Nerve pathology
- Myelinated axons: Reduced or absent
- Unmyelinated axons: Reduced (30% of normal)
- Endoneurial collagen: Increased
- NCV
Axonal CMT (CMT2P), Recessive
● Leucine-rich repeat- and sterile alpha motif-containing 1 (LRSAM1)
- Epidemiology: Canada, Rural Eastern family
- Genetics
- Mutation: Coding exon consensus splice acceptor AG to AA
- Allelic with: CMT 2P, Dominant
- LRSAM1 protein
- E3 ubiquitin ligase
- Regulates cell adhesion molecules
- Role in receptor endocytosis and viral budding
- RING finger protein
- Mutation: Causes loss of protein
- Nosology: TAL (TSG101-associated ligase); RIFLE
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2nd to 5th decade
- Weakness: Distal; Legs > Arms
- Cramps: Extremities & Trunk
- Sensory loss: Pan-modal; Distal; Legs > Arms
- Autonomic: Variable; Erectile dysfunction
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Skeletal: Pes cavus
- Course: Slow progression; Wheelchair in some
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: High; 1000-2000
- NCV: Axon loss; NCS >l 38 m/s; CMAPS small amplitude; SNAPs absent
- EMG: Denervation, Distal & Proximal
- CSF protein: Mildly high
- Variant LRSAM1 Syndrome: CMT 2P
 ; Axonal neuropathy, Dominant
; Axonal neuropathy, Dominant
- Nosology: Originally described as CMT2G on Chromosome 12q12–q13.3 46
- Epidemiology: Dutch, Sardinian & Spanish families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- LRSAM1 mutations
- p.Leu708Argfx28; Splice-site (c.2047-1G4A); p.Cys694Tyr
- Location: Truncate, Disrupt, or Abolish catalytic RING zinc finger domain
- Penetrance
- Some carriers: Asymptomatic; Only electrodiagnostic changes
- Family members with only pes cavus: May not be carriers
- Clinical
- Onset age: 9 to 76 years
- Weakness & Wasting
- Distal
- Legs > Arms
- Asymmetry: Some patients
- Gait disorder
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced, especially ankles
- Sensory
- Loss: Pan-modal; Legs > Arms; Distal
- Episodic: Numbness; Paresthesias; Cramps
- Autonomic: Occasional; Erectile dysfunction
- Skeletal: Foot deformity
- Course: Slowly progressive; Most remain ambulant
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic
- NCV: SNAP & CMAP amplitudes reduced, especially in legs
- EMG: Distal denervation in legs
- Pathology
- Axonal loss: Distal > Proximal; Regeneration
- Anterior horn cells: Reduced number
- Dorsal root ganglion cells: Reduced number
- Muscle MRI: Fatty atrophy of foot muscles
- Electrodiagnostic
Axonal CMT2, Recessive + Neuromyotonia (ARAN-NM; AR-CMT2 + Neuromyotonia; NMAN)
● Histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 (HINT1)
|
|
Axonal CMT2, Recessive, Early-onset
● Tripartite motif-containing protein 2 (TRIM2)
- Nosology: CMT2R
- Epidemiology: Finnish & Turkish patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Compound heterozygous; E227V; K567Rfs7X; D667A
- TRIM2 protein
- E3 ubiquitin ligase
- Role in axon specification during development
- Neurofilament light chains: Target of ubiquitination by TRIM2
- Mutations: Reduced TRIM2 in fibroblasts
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 6 to 8 months
- Poor growth
- Motor
- Hypotonia
- Respiratory insufficiency
- Vocal cord paralysis: 1 patient
- Hands & Feet: Small muscles
- Gait: Wide base
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Skeletal: Pes cavus; Contractures
- Onset
- Laboratory
- NCV
- Velocities: Slowed (20 to 30 m/s)
- CMAPs & SNAPs: Amplitude small or absent (Legs)
- Nerve pathology
- Myelinated axons: Reduced numbers
- Axons: Neurofilament accumulations, especially in mice with mutations
- Brain MRI: Normal
- NCV
AR-CMT2T: Axonal CMT2, Recessive, Adult onset
● Membrane metalloendopeptidase (MME; CD10; CALLA; Neprilysin; NEP)
- Epidemiology
- > 25 patients
- Common cause of AR-CMT
- Most frequent cause of AR-CMT2 in Japan
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Loss of function
- Nonsense, Missense, Splice site, Deletion
- Allelic disorders
- SCA43, Dominant
- CMT2, Dominant
- AR-CMT2T, Recessive
- dHMN, Recessive
- Neprilysin alloimmunization in neonatal glomerulopathies
- Mutations
- MME protein
- Neuro-Peptide processing
- Neutral endopeptidase
- Many substrates: Degrades atrial natriuretic factor, enkephalins, substance P & other peptides
- β-amyloid (Aβ)-degrading enzyme
- Locations: Brain (Neurons) & PNS; Proliferating B-cells
- Zinc dependent
- Neuro-Peptide processing
- Clinical: AR-CMT2T
- Onset age: Adult; Range Childhood to 73 years; Mean 47 years
- Weakness
- Distal > Proximal
- Legs > Arms
- Most common: Foot dorsiflexion
- Symmetric: Most patients
- Gait disorder: Steppage
- Sensory
- Loss
- Panmodal
- Distal
- More loss with disease progression
- Dysesthesias
- Pain (30%)
- Loss
- Cramps
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent
- Cognition: Normal
- Course: Progression; AFOs common
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axon loss
- CMAP: Low amplitude
- Conduction velocities: 31 to 54 M/s
- Nerve pathology
- Large myelinated axons: Reduced
- NEP/CD10 staining: Reduced around myelinated axons
- Brain MRI: Normal
- Leg MRI: Fat infiltration, Distal > Proximal
- Blood neprilysin levels: Low
- Serum CK: May be elevated
- NCV: Axon loss
- MME variant syndrome: SCA43
135
- Epidemiology: One 5 generation family, 7 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Missense; C143Y
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Allelic disorders
- Clinical
- Onset age: 42 to 68 years
- Ataxia
- Balance & Gait disorder
- Saccades: Hypometric
- Dysmetria
- Dysarthria
- Polyneuropathy
- Sensory loss: Distal; Legs > Arms
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced in legs
- Atrophy: Distal legs
- Pes cavus
- Course: Slow progression
- Cognition: Normal
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar vermis atrophy
- NCV: Axonal neuropathy
- Nerve biopsy: Axon loss, Large > Small
- MME variant syndrome: CMT2 Dominant, Late-Onset
136
- Epidemiology: 19 families, Austrian & German; 28 individuals
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant or Sporadic
- Mutations: Misense or Stop
- Age-related incomplete penetrance
- Allelic disorders
- MME protein
- Mutations cause: Decreased tissue availability (50%); Impaired enzymatic activity (Variable)
- Clinical
- Onset age: 30 to 80 years; Mean 55 years; Later than recessive syndrome
- Gait disorder
- Sensory loss: Legs > Arms; Distal > Proximal
- Discomfort: Pain, neuropathic; Cramps
- Weakness
- Toes & Ankles: Early
- Hands: Later in disease course
- Occasional patient: Motor predominant
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced with disease progression
- Course: Slow progression; Wheelchair in some
- Cognition: Normal
- Laboratory
- NCV: Small amplitude or absent CMAPs & SNAPs
- Nerve biopsy
- Axon Loss
- Large & medium myelinated axons
- Small axons: Mild loss; Collagen pockets; Skin biopsy normal
- Regenerating axon clusters
- Onion bulbs: Small
- No amyloid
- Axon Loss
- MME variant syndrome: Hereditary Motor Neuropathy, Distal, Recessive
153
- Epidemiology: 2 families; 3 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Stop & splice site; c.1342C>T; c.2071_2072delGCinsTT; c.1342C>T; c.2071_2072delGCinsTT
- MME protein in diseased nerve: Mild decrease
- Clinical
- Onset age: 16 to 50 years
- Weakness
- Legs > Arms
- Distal > Proximal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent in Legs
- Sensation: Normal
- Postural tremor, 2 patients
- Joints
- Pes cavus, 2 patients
- Contractures: Hands, 2 patients
- UMN features: None
- Laboratory
- NCV: CMAP amplitudes reduced; MNCV mildly reduced
- EMG: Distal denervation; Large amplitude, Long duration MUPs
- Sural nerve: Normal axon numbers; MME reduced in myelin
AR-CMT2 + Intellectual Disability (PNRIID)
● Minichromosome maintenance 3-associated protein (MCM3AP; GANP)
- Epidemiology: > 15 families; > 28 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense, Splice & Stop
- Null mutations: More severe phenotype & delayed walking
- Mutations outside Sac3 domain: Early-onset, Motor development delay, Cognitive Δ, More severe neuropathy
- Mutations within Sac3 domain: No GANP protein deletion
- MCM3AP (GANP) proteins
- Location: Nuclear envelope
- Scaffold for transcription export 2 (TREX-2) complex
- B cell antibody maturation
- Acetylates MCM3
- Inhibits cell cycle progression
- GANP protein
- Alternatively spliced protein
- Export of mRNAs from nucleus to cytoplasm: Through nuclear pores
- Clinical
- Onset age: Early childhood; 0.5 to 7 years
- Motor > Sensory Polyneuropathy
- Weakness
- Distal: Severe
- Proximal: Mild or None
- Motor development: Delayed
- Course: Progressive
- Independent ambulation: Lost between 10–24 years
- Atrophy: Hands & Feet
- Tendon reflexes: Often reduced in legs
- Sensory
- Loss: Distal; Pan-modal
- Hyperesthesia: Some patients
- Weakness
- CNS
- Intellectual disability (80%): Mld to Moderate
- Motor delay
- EOM Δ
- Laboratory
- Neuropathy features: Axon loss; Demyelination (20%)
- NCV: Arms 15 to 51 M/s; Legs 26 to 38 M/s
- CMAPs: Low amplitude
- SNAPs: Low amplitude
- Nerve biopsy: Loss of myelinated axons
- Brain MRI: Normal or Temporal lobe changes
- Neuropathy features: Axon loss; Demyelination (20%)
AR-CMT2 147
● AHNAK Nucleoprotein 2 (AHNAK2)
- Epidemiology: 1 Malaysian family
- Genetics
- Mutations: T40P, H915Y
- AHNAK2 protein
- Location: Nuclei; Muscle Z-bands; Myofibrillar aggregates
- Propeller-like protein
- Associates with calcium channel proteins
- Clinical
- Polyneuropathy
AR-CMT2 189
● Myosin IXB (MYO9B)
- Epidemiology: 4 patients, 2 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Tyr176His, Tyr63His, Asn18del; Located in structural domains
- Allelic disorder: Optic atrophy, non-syndromic (Arg991Gln, Ile1028Val)
- MYO9B protein
- Myosin, unconventional
- Expressed in CNS & PNS
- Single-headed
- Myosin motor protein
- Actin filament plus end-directed motor
- Processive
- Converts chemical energy from ATP hydrolysis into mechanical force
- RhoGAP domain
- Interacts with cytosolic region of Robo1
- Inhibits GAP activity
- Binds: Calmodulin
- Signaling properties
- Clinical
- Onset age: Childhood & Teens
- Weakness: Distal; Feet & Hands
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced at Knees & Ankles
- Sensory loss: Vibration; Pin
- Pes cavus
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- NCV
- CMAP & SNAP amplitudes: Reduced or Absent
- Velocities: Intermediate
- EMG: Chronic denervation, distal & proximal
- NCV
Episodic Axonal Neuropathy, Recessive 137
● Sphingosine 1-phosphate lyase (SGPL1)
- Epidemiology: 1 Serbian family, 2 patients
- Genetics
- SGPL1 protein
- Sphingosine-1-phosphate (SPP)
- Proliferative signal transduction pathways
- Lymphocyte egress from thymus & peripheral lymphoid organs
- SGPL1: Degradation of SPP
- Sphingosine-1-phosphate (SPP)
- Clinical
- Onset
- Ages: 11 & 12 years
- Weakness ± Pain: Distal legs
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs & Arms
- Symmetric or Asymetric
- Nerve involvement: Common peroneal; Tibial; Ulnar
- Episodes
- Onset: Subacute
- Recovery: Some
- Frequency: Few over decades
- Sensory loss (50%): Mild; distal legs
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent at ankles
- CNS
- Normal in this family
- Developmental delay: Other families
- Systemic: Other patients
- Endocrine: Adrenal insufficiency
- Immunodeficiency
- Sensory-Motor neuropathy described with CNS features in RENI syndrome
- Onset
- Laboratory
- NCV
- CMAPs & SNAPSs reduced amplitude
- Velocities: Normal of Mildly slow
- Sural nerve biopsy: Wallerian degeneration; Axon loss
- NCV
|
Hereditary Motor-Sensory or Motor Neuropathy (HMNR8; SORDDPN)
● Sorbitol Dehydrogenase (SORD)
|
|
Hereditary Motor-Sensory Neuropathy 187
● Neuregulin 1 (NRG1)
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Missense; Arg551Gln
- NRG1 protein
- Mutation: Partial loss of function
- Clinical
- Onset age: 20 years
- Weakness: Distal; Arms > Legs
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced at ankle
- Sensory loss: Pain; Distal; Arms & Legs
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axon loss, motor & sensory; F-wave latency normal
- EMG: Motor units large & Fibrillations in distal muscles
Hereditary Motor-Sensory Neuropathy + CNS disorders 217
● Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPR)
- Epidemiology: 2 siblings; 1 family
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Missense; P158A
- NAMPT protein
- Salvage pathway for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) biosynthesis

- Rate-limiting enzyme
- Secreted form: No enzyme activity; Cytokine & Adipokine
- Mutation: Possible mitochondral dysfunction
- Salvage pathway for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) biosynthesis
- Clinical
- Onset: Neonatal
- Weakness & Atrophy: Legs
- Deformities: Hands & Feet
- Upper motor neuron: Babinski sign+
- Speech: Indistinct
- Eye
- Mobility: Restricted; Strabismus, divergent
- Optic disc: Pale
- Retina: Thin
- Sensory loss: Panmodal; Legs
- Mental retardation: Mild
- Course: Progressive; Wheelchair in early teens
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Normal
- EEG: Normal
- NCV: Not reported
HMSN III (Dejerine-Sottas)
 32
32
|
General Clinical Types |
 Dejerine & Sottas 1893 |
- General
- Severe
- Infant onset
- Slowly progressive
- Genetic types: Dejerine-Sottas (DSS)
- General: Dominant are often sporadic
- DSS-A: PMP-22 point mutations
● Chromosome 17; Dominant
- Genetics
- Mutation locations
- Transmembrane domains
- Domains 1, 2, 3 & 4
- Transmembrane domain mutations also seen in CMT1A
- Hot spot for mutations: Ser72
- 26% of PMP-22 point mutations
- Mutations: Ser72Pro; Ser72Trp; Ser72Leu (Most frequent)
- Phenotype: Usually severe; Onset 1st year; Most never walk
- Transmembrane domains
- Mutation type: CG to TG transitions common (~ 40% of mutations)
- Mutation locations
- Genetics
- DSS-B: P0 point mutation

● Chromosome 1q22; Recessive or Dominant- Genetic disease mechanisms
- Dominant negative
- Missense mutations in membrane, intracellular, or extracellular domain
- 19 mutations identified
- Transmembrane mutations of P0 over-represented in DSS group
- Examples: Gly167Arg; Tyr82Cys
- Heterozygous
- May appear sporadically & then transmit as Dominant
- Missense mutations in membrane, intracellular, or extracellular domain
- Other mutaton patterns producing severe disease
- Mutations which disrupt the MPZ tertiary structure
- Most mutations that truncate the cytoplasmic MPZ domain
- Eliminate amino acids 198–201 (RSTK)
- Point mutation altering Ser204
- ? Phosphorylated via PKC binding to the RSTK domain
- Recessive: Absence, or loss of function, of P0 protein
- Mutations: Gly74 frameshift (1 bp deletion); c.306delA
- Heterozygotes: May have mild demyelinating neuropathy
- Dominant negative
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 1st 2 years
- Tone: Hypotonic prior to 9 months
- Walking: Usually after 18 months
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Course
- Walking
- Most patients able to walk at some time
- Most patients eventually need ambulation aids
- Wheelchair: Some patients
- Progression in weakness: Some patients
- Life expectancy
- Most normal
- Some early deaths due to respiratory failue
- Walking
- Nerve hypertrophy: Some patients
- Onset
- Laboratory
- CSF protein: 50 to 167 mg/dL
- Electrophysiology
- Motor nerve conduction velocities: < 15 m/s in arms
- No conduction block or temporal dispersion
- CMAP & SNAP amplitudes: Small
- Pathology: Irregular folding & redundant loops of myelin (Tomaculae)
- Teased fiber
- External link: EM
- Genetic disease mechanisms
- DSS-C
● Chromosome 8q23-q24; Dominant
- Epidemiology: Iowa family
- Clinical
- Onset: 2 years; Steppage gait
- Weakness: Progressive; Distal > Proximal; Hands & Feet
- Sensory loss: Distal > Proximal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Enlarged nerves
- Charcot joints
- CMT 4F
● Periaxin; Chromosome 19q13; Recessive - Dominant
- Hearing loss
- Unusual faces
- DSS-EGR2
● Early Growth Response 2 (EGR2) ;
Chromosome 10q21.3; Dominant, de novo
;
Chromosome 10q21.3; Dominant, de novo
- Mutation: Arg359Trp
- Clinical features: See EGR2
- Other EGR2 mutations
- CMT 1F
DSS-
A: PMP-22
B: P0
C: 8q23
Periaxin
EGR2
- Dejerine-Sottas: Clinical features
- Onset: < 3 years
- Weakness
- Diffuse; Distal > Proximal
- Delayed motor milestones: Walking 15 to 48 months
- Peak performance: 5 to 20 years
- Tone: Reduced
- Sensory loss: All modalities; Severe; Distal > Proximal
- Tendon reflexes: Areflexic
- Nerve enlargement
- Some patients: Gly138Arg mutation 31
- May be asymmetric & multifocal or symmetric
- Cranial nerve disorders: Occasional
- May be associated with cranial nerve enlargement
- Ocular
- Miosis
- Pupil: Reduced response to light
- Ptosis
- Nystagmus
- EOM limitation
- Hearing loss: Mild
- Morphology: Short stature, Coarse facial features & Full lips occur
- Skeletal: Kyphoscoliosis; Foot deformities (Club feet)
- Progression: Mild until teens; Severe disability may occur
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology: Demyelinating + Axonal loss
- NCV: Very Slow (< 12 M/s)
- Distal latency: Prolonged
- CMAPs: Reduced amplitude
- SNAPs: Absent
- CSF protein: Moderately high; 70 to 200 mg/dl
- Pathology
- Onion bulbs
- Enlarged nerves: Increased fascicular area
- Myelin sheaths
- Hypomyelination
- Long lengths of demyelinated axons
- Few macrophages with myelin debris
- Axons
- Large myelinated axons: Reduced number, especially distally
- Unmyelinated axons: Normal number; Mild reduction in size
- Electrophysiology: Demyelinating + Axonal loss
- Also see: Congenital hypomyelinating neuropathy
- Rule out: Childhood CIDP
Hereditary Liability to Pressure Palsies (HNPP)

|
PMP-22 mutations Clinical Genetics Biallelic deletions Laboratory Pathology Images KARS mutations |
HNPP: PMP-22 Genetics
● PMP-22
- PMP-22 Mutations
- Common mutation: Deletion in 80% to 85%
- Chromosomal deletion of region containing PMP-22
- Deleted region is identical to region duplicated in CMT IA
-

- Deleted region contains other genes including COX10
- Point mutations
18
- Types
- Nonsense (Stop codons): Leu7X, G183A (Trp61X), G372A (Trp124X),
- Frameshift: Premature termination (19-20delAG, 434delT); Longer transcript 281-282insG
- Splice site: 78+1G>T; 179+1G>C (Mild phenotype)
- Missense: Ser22Phe; Val30Met (May be asymptomatic); Cys42Arg; Ala67Thr; Thr118Met 65
- Usually cause loss of function of PMP-22
- Database of PMP-22 point mutations: IPNMDB
- Types
- Other mutations
- Deletion: Partial PMP-22 5’ region containing exons 1 to 3
- Homozygous missense
- Thr118Met: Associated with severe axonal loss with no demyelination 65
- Allelic disorders
- Common mutation: Deletion in 80% to 85%
- Clinical - Genetic Correlations
- Penetrance: Variable; Higher in males
- Family history
- 37% of patients with gene deletion have no family history
- "Sporadic" cases often have deletions of paternal origin.
- Due to unequal crossing over of homologous Chromosome 17s
- Rare maternal origin: Due to intrachromosomal rearrangement
- 20% of patients affected with HNPP & PMP-22 deletion have de novo mutation
- 16% to 30% of families with HNPP phenotype have no PMP-22 deletion
- Some have PMP-22 point mutation
- G-insertion in a stretch of six Gs at nt 276-281
- Small exon 5 deletion: Mild phenotype 110
- Some PMP-22 deletions can present as chronic demyelinating neuropathy mimicking CMT 1A
- Onset age < 18 years: Association with LITAF
 Ile92Val polymorphism
Ile92Val polymorphism
- PMP-22 Protein: Expression reduced in nerves in HNPP
- General
- Nerve palsies & Electrophysiological abnormalities more frequent in males 111
- Onset
- Age
- Mean: 19 to 26 years
- Range: 2 to 64 years
- Some patients asymptomatic
- Asymmetric weakness
- Age
- Episodes of nerve paresis
- Acute onset
- Sensation
- Paresthesias
- Numbness
- Usually painless
- Loss may occur without weakness
- Weakness: In distribution of nerve lesion
- Prodromes
- Mild trauma or compression: 40%
- Repeated local exercise
- Stretching
- On awakening: 10%
- Surgery: Occasional reports 45
- Number: 1 to 10
- Recovery
- Over days to months
- Complete 50%
- Severe long term motor defecit 9%
- Neuropathy features
- Motor: Weakness
- Related to nerve palsies: Commonly mild & transient
- Persistent: Ulnar hands (Mild); Foot drop (Asymmetric)
- Sensory loss
- Vibration & Pain commonly reduced: Distal; Symmetric; Legs
- Other regions related to nerve palsies
- Asymmetric
- Often
- Focal lesions (62%): Related to stretching, minor repetitive focal trauma or pressure
- Nerve size
- Enlarged: Diffusely; Visible by ultrasound
- Focal signs
- General
- Locations: At usual sites of nerve compression
- Variable among patients
- Radial: Spiral groove of humerus
- Ulnar: Elbow
- Median: Wrist; Isolated carpal tunnel syndrome rare
- Peroneal: Head of fibula
- Brachial plexopathy
- Not painful vs Hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy (HNA)
- May be recurrent
- General
- Tendon reflexes
- Normal in 62%
- Absent in some patients
- Ankle most often lost
- Cramps: 40%
- Skeletal
- Pes cavus: Some patientsl Less severe or common than with CMT1A
- Scoliosis: Occasional patient
- Course
- Episodic changes
- Some permanent weakness may develop
- Severe disability: Rare
- Progressive axon loss: Not prominent, except associated with nerve compression
- Occasional features
- Focal signs & sensory loss at
- Progressive generalized sensory-motor neuropathy
- May occur without pressure palsies
- CMT 1 + HNPP syndrome with frame shift G insertion in nt 276-281
- May have onset late in course: 5th & 6th decade
- Occasional cases rapidly progressive
- Tremor
- Variant: Davidenkow phenotype
- Motor: Weakness
- Differential diagnosis: Patients with multifocal neuropathies without a 17p11 deletion
- NCV: Diffuse sensory-motor polyneuropathy + Focal changes
28
- General
- Electrodiagnostic changes more severe in males
- Abnormalities not predictive of sites of symptoms
- NCV
- Sensory
- Diffusely reduced, especially in upper extremities
- More slowing in median & ulnar than sural
- More loss of ulnar sensory action potential in males
- Motor
- Minor slowing at regions other than compression sites
- More slowing in distal nerves
- Distal motor latencies: Prolonged
- Compression sites: Conduction commonly slow
- Slowing variable among nerves: Most median; Least tibial & proximal muscles
- Conduction block: Occasional (6% to 22%); ? Associated with transient episodes
- F-waves: Prolonged or absent in 80%
- Sensory
- Age changes
56
- Reduction in CMAP amplitudes in nerves vulnerable to compression
- Initially reduced, but little age-related change
- Asymptomatic carriers: Abnormal even in childhood
- Prolonged distal motor latency: Median or Peroneal
- Slow NCV: Sensory or peroneal
- QST: Abnormal vibration
- General
- Ultrasound
112
- Nerve enlargement at entrapment sites: Median wrist; Ulnar elbow; Tibial ankle
- CNS
64
- Electrophysiology
- Abnormal: Blink reflex, Jaw-opening reflex, Acoustic evoked potentials
- MRI: Subclinical abnormalities
- Bilateral T2-weighted signal alterations lateral to putamen
- Electrophysiology
- Muscle MRI: Fat replacement, More distal than proximal 163
- Pathology
50
- Myelin sheath: Focal thickening (Tomaculae) & Folding
- Location: Perinodal or Internodal
- Frequency: Most HNPP patients
- Present at 5% to ≥ 25% of internodes
- Differential diagnosis of tomaculae: Less frequent in other disorders
- CMT 1B
- MAG neuropathy
- CIDP: Rare
- Images
- Other myelin changes
- Demyelination: Segmental; Most patients
- Onion bulbs: Usually small
- Uncompacted myelin sheaths (20%)
- Hypomyelination
- Axons
- Loss
- Severity: Moderate to marked in 80%
- Large > Small axons
- Regenerating clusters: Common
- Axonal degeneration (25%)
- Loss
- Myelin sheath: Focal thickening (Tomaculae) & Folding
- Mouse models
- Heterozygous PMP22-deficient mouse
- PMP22-deficient mouse (Homozygous): Not reported to develop transient weakness or sensory loss
- Bi-Allelic, Large PMP-22 gene deletions
84
● PMP-22; Chromosome 17p11.2-p12- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics: 2 heterozygous deletion mutations
- Deletion of whole PMP-22 gene
- Deletion of PMP-22 exon 5
- Clinical features
- Dejerine–Sottas-like disease
- Onset: Neonatal
- Hypotonia
- Delayed walking
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Parents: Normal or HNPP phenotype
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology: Very slow NCV
- CSF protein: Mildly high
- Brain MRI: Normal
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, Recessive Intermediate B (CMTRIB)
● Lysyl-tRNA Synthetase 1 (KARS1)
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- KARS gene: Encodes both cytoplasmic & mitochondrial KARS
- KARS Mutations
- Heterozygous: Ile302Met
- Compound heterozygous: Leu133His; c.524_525insTT (Frameshift; Stop)
- Allelic disorders
- CMT-RIB
- Nonsyndromic Hearing Impairment DFNB89, Recessive

- Leukoencephalopathy
- Also see: ARS syndromes, Other
- Lysyl-tRNA Synthetase protein
- Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (ARS)
- Charges tRNA molecules with lysine
- Holoenzyme structure: Dimeric & Tetrameric
- Locations (Bifunctional)
- Dual: Mitochondrial matrix & Cytoplasmic
- Determined by alternative splicing of exons 1-3
- Clinical
- ? Distal weakness & Sensory loss
- Dominant Heterozygous mutation: Peripheral neuropathy
- Recessive Compound Heterozygote mutations
- Peripheral neuropathy
- CNS
- Developmental delay
- Self abuse
- Dysmorphic features
- Vestibular Schwannoma
- Laboratory
- NCV
- Dominant Heterozygote: HNPP type
- Conduction velocities: 30 to 40 M/s
- CMAP amplitudes: Normal or Reduced
- Distal latencies: Prolonged up to 2x
- Recessive Compound Heterozygote: CMT Intermediate type (CMT RIB)
- Conduction velocities: Mildly slowed (30 to 40 M/s in arms)
- Dominant Heterozygote: HNPP type
- NCV
- KARS1 variant syndrome: Ataxia, Deafness & Optic neuropathy
 148
148
- Nosology: Deafness congenital & Adult-onset progressive leukoencephalopathy (DEAPLE)
- Epidemiology: 4 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: c.683C>T (p.Pro228Leu); c.871T>G (p.Phe291Val)
- Clinical
- Onset age: Early childhood
- Motor delay
- Ataxia
- Deafness: Congenital
- Pyramidal syndrome: Arms & Legs
- Dystonia
- Optic neuropathy: Visual fields narrowed; Acuity reduced
- Cognitive decline
- Course: Progressive in 3rd decade; Death in 4th decade
- Laboratory
- Serum lacate: High
- Brain MRI: Dentate & White matter pathology in optic radiations & Corpus callosum
- NCV: Sensory axon loss in legs
- Muscle biopsy: COX- muscle fibers; Oxidative enzyme levels borderline
- KARS1 variant syndrome: Leukoencephalopathy
149
- Epidemiology: 4 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Heterozygous; All with 1 missense; Loss of function
- Clinical
- Onset age: 0.5 to 35 years
- Cognitive ability: Impaired
- Seizures
- Hypotonia
- Ataxia
- Spasticity
- Other: Ophthalmoplegia; Dystonia; Tremor
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: White matter pathology
- Serum lactate: High
- NCV: Neurogenic or Normal
- EEG: Slow or Normal
- KARS1 variant syndrome: Leukoencephalopathy, infantile-onset progressive ± Deafness (LEPID)

- Nosology: Mitochondrial encephalohepatopathy (MEH)
- Epidemiology: > 20 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Missense common
- Clinical
- Neurodevelopmental disorder
- Seizures
- Spasticity
- Microcephaly
- Retinopathy: Leopard spot
- Hearing loss: Sensorineural
- Systemic: Cardiac & Hepatic failure
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: White matter pathology; Brain atrophy & calcifications
- Pancytopenia: Sideroblasts
- Serum lactate: High
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, Recessive Intermediate D (CMTRID)
● COX6A1
- Epidemiology: 2 Japanese families
- Genetics
- Mutation: 5 bp deletion (c.247.10_247.6delCACTC) in splicing element of intron 2
- COX6A1 protein
- Mitochondrial
- Respiratory complex IV
- Inner membrane
- Required for the stability of COX holoenzyme
- Expression: Ubiquitous except muscle
- Mitochondrial
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1st decade
- Weakness: Distal; Arms & Legs
- Sensory loss: Pan-modal; Distal; Arms & Legs
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic
- EMG: Distal denervation
- Motor nerve conduction velocities: Mildly reduced
- SNAPs: Reduced amplitude or Absent
- Nerve pathology: Onion bulbs; Axon loss
- Electrodiagnostic
CMT 4
General features- Inheritance: Recessive
- Demyelinating
CMT 4A
● Ganglioside-induced differentiation-associated protein 1 (GDAP1)
- Genetics
22
- Mutations: Nonsense & Missense
- Allelic disorders
- Similar locus to AR-CMT with pyramidal involvement
- Same mutation may produce evidence of axonal loss & demyelination: S194X; Q163X
- Geographic segregation
- Q163X: Common in Hispanic & North African families
- S194X: Tunisian & Maghreb countries
- L239F: Polish, German, Italian, Czech & Bulgarian CMT families (Axonal neuropathy)
- GDAP1 protein
52
- Expressed in: Neurons (DRG) > Schwann cells; CNS (Brain & spinal cord)
- Subcellular location: Mitochondria, localized by C-terminal transmembrane domains
- Structural family: Sequence similarities to Glutathione S-transferases but no GST activity
- Clinical
- Onset: Childhood < 2 years
- Weakness
- Rapidly progressive
- Distal limb: Hands & Feet
- Legs > Arms
- Vocal cord: Left
- Respiratory
- Face: Occasional
- Severe
- Sensory loss: Distal
- DTRs: Absent diffusely or distally
- Scoliosis
- Course: Progressive; Wheelchair by 2nd decade
- Nerve conduction
- Velocity: Slow
- Motor & Sensory: Mean 30 M/s; Range 25 to 35 M/s
- CMAP & SNAP amplitude: Reduced or Absent
- Pathology: Demyelinating
- Myelin
- Hypomyelination
- Segmental demyelination
- Myelin folding: Mild or absent
- Onion bulbs
- Loss of myelinated axons: Especially large; At early age
- Myelin
HMSN + Focally-Folded Myelin Sheaths (CMT 4B)

|
CMT 4B1
● Myotubularin-related protein-2 (MTMR2)
|
CMT4B1 (AR-CMT-DM-MTMR2): Peripheral Nerve Ultrastructure Myelin: Remaining sheaths have many, aberrant myelin out-foldings Onion-bulbs: Irregular; Small Axon loss: Severe 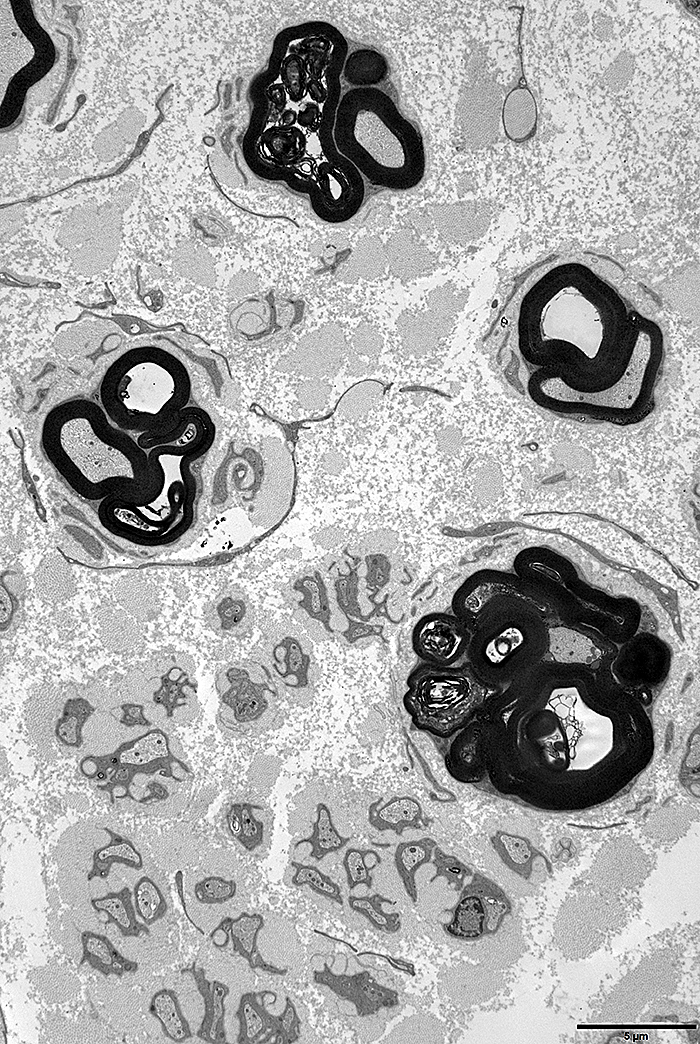 From: JM Vallat & M Tazir |
CMT 4B2
● SET binding factor 2 (SBF2) (MTMR13)
- Epidemiology: Families in Turkey, Tunisia, Japan, Italy
- Genetics
- Mutations: Homozygous inframe deletions
- Allelic disorders
- HMSN with glaucoma
- Taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy: More severe disease 183
- Protein
- Family: Myotubularins, pseudo-phosphatase branch
- General actions
- Phosphoinositide-mediated signalling events
- ? Associated with control of myelination
- Myotubularin family disorders
- Phosphinositide disorders
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 1st 2 decades
- No delayed motor development in childhood
- Weakness
- Onset: Distal legs; Intrinsic foot & anterior leg muscles
- Pattern: Legs > Arms; Distal; Symmetric
- Progression: Proximal weakness in some patients years after onset
- Loss of ambulation in some patients
- Sensory loss: Distal; Severe
- Tendon reflexes: Absent in legs; Reduced in arms
- Skeletal: Pes cavus; Hammer toes
- Eye: Juvenile-onset open-angle glaucoma in some patients
- Onset
- Electrophysiology
- Slow nerve conduction velocities (15 to 30 M/sec)
- Axonal loss: Motor & Sensory
- Pathology
- Irregular folding & redundant loops of myelin (Tomaculae)
- Segmental demyelination
- Onion bulbs
- Myelinated axon loss: Large > Small
● SET binding factor 2 (SBF2) (MTMR13)
- Geographic location: Japan family
- Allelic disorder: CMT 4B2
- Clinical
- Onset
- 1st decade
- Glaucoma
- Weakness; Difficulty running
- Weakness
- Distribution: Distal; Legs & Arms; Symmetric
- Progression: Slow
- Sensory loss: Distal; Arms & Legs; Panmodal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Skeletal: Pes cavus; Hammer toes
- Intellect: Normal
- Ocular
- Visual acuity: Reduced
- Intraocular pressure > 21 mm Hg
- Glaucomatous changes in optic disk
- Onset
- Laboratory
- CSF: High protein
- Electrophysiology
- Slow nerve conduction velocities (15 to 20 M/sec)
- Axonal loss: Motor & Sensory
- Pathology
- Irregular folding & redundant loops of myelin
- Segmental demyelination
- Thinly myelinated axons
- Onion bulbs
- Myelinated axon loss: Large > Small
CMT 4B3 with Focally folded myelin
● SET binding factor 1 (SBF1) (MTMR5)
- Epidemiology: Korean & Saudi families
- SBF1 genetics
- Mutations: Missense; M417V, D443N, T1590A
- SBF1 protein
- Expression: All tisues except testes
- May interact with MTMR2
- Myotubularin family disorders
- PIP phosphatase
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Infancy to 11 years
- Weakness: Distal legs
- Gait disorder
- Weakness
- Onset: 1st or 2nd decade
- Legs ≥ Arms
- Distal > Proximal
- Face in some
- Sensory loss: Pain ≥ Vibration; Distal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Skeletal
- Pes planus
- Scoliosis
- Syndactyly
- Course: Slow progression; Most continue to walk
- CNS: Saudi family
- Microcephaly
- Mental retardation
- Eye
- Ophthalmoplegia
- Strabismus: Exotropia
- Onset
- Laboratory
- EMG: Denervation; Large motor units
- Nerve conduction
- CMAP amplitudes: Reduced (Arms); or Absent (Legs)
- SNAPs: Absent
- NCV: 32 to 42 M/s
- Peripheral nerve pathology
- Myelin: Focally folded (Tomaculae); Onion bulbs, occasional
- Axon loss: Especially large myelinated
- Regenerating clusters
HMSN with focally folded myelin sheaths: Dominant
● P0 protein; Chromosome 1q23.3; Dominant
● Additional loci
- Focally folded myelin sheaths
HMSN + Focally folded myelin sheaths: Additional locus
● Recessive
CMT 4C
● SH3 domain and tetratricopeptide repeat domain 2 (SH3TC2; KIAA1985)
- Epidemiology
- Relatively frequent cause of AR-CMT
- Most common autosomal recessive demyelinating CMT
- Common (> 20% of AR demyelinating CMT): Italy; Czech Republic; Greece
- Less common (< 2%): Japan; Korea
- Sporadic patients identified
- Relatively frequent cause of AR-CMT
- Genetics
41
- Mutations
- > 230 pathogenic variants described
- Types: Truncation (Nonsense) most common (60%); Missense (20%); Large Deletions
- Some missense mutations involve splicing changes: Alter sequence of full length protein
- Hot spot: Exon 11
- European: Arg954X
- Spanish Gypsies: Arg1109X
- More severe disease: 2 truncation mutations
- Allelic disorders
- Cerebellar + Neuropathy syndrome
- Golden retriever dogs: Congenital hypomyelinating neuropathy
- Mutations
- SH3TC2/KIAA1985 protein
41
- Expression
- Neural tissues, including peripheral nerve Schwann cells
- Schwann cells: Plasma membrane; Endocytic vesicles
- Structure: Contains SH3 (2 N-terminal) & TPR (5 C-terminal) motifs
- Cellular location
- Plasma membrane
- Perinuclear endocytic recycling compartment
- Development: Interacts with ErbB2
- Function
- Myelination
- Endocytic/endosomal recycling: Associates with small GTPase, Rab11
- Axo-glial relations: Maintenance of node of Ranvier
- Influences transferrin receptor dynamics: Targets to intracellular recycling endosome
- Mutations
- Unable to associate with Rab11
- Mistargeting away from recycling endosome
- Hypomyelination
- Knockout animals
- Hypomyelination
- Node of Ranvier: Abnormal organization
- Expression
- Clinical
- Varied severity: Mild to Severe, childhood-onset phenotypes
- Onset
- Age
- Range: 1 to 73 years; 60% < 10 years
- Childhood (1 to 5 years) or Adolescence: Typical disorders
- Adults: Foot deformities; Scoliosis
- Early scoliosis: NCV may be relatively preserved
- Other patients with infantile neuropathy: Early loss of ambulation & respiratory problems
- Age
- Skeletal: Common presenting sign & disabling feature
- Scoliosis (75%)
- Course: Onset 3 to 9 years; Progressive; Surgery in teens
- Associated with: Respiratory insufficiency
- Pes cavus: Common; 85%
- Scoliosis (75%)
- Weakness
- Delayed walking: Normal to 30 months
- Distal: 100%
- Proximal: 40%; Late; Some patients
- Legs > Arms
- Face
- Course: Slowly progressive
- Atrophy: In regions of weakness
- Sensory loss
- Distal
- Cutaneous loss: Early in disease course
- Vibration & joint position loss: Later; Legs > Arms
- Sensory ataxia (70%)
- Areflexia: Most
- Deafness: Common; 40% to 70%
- Cranial nerve: Some patients
- Face weakness
- Pupils: Unresponsive
- Tongue atrophy: Unilateral
- Genitourinary: 6%; > 50 years
- No tremor or cerebellar ataxia
- Prognosis
- Very slow progression of neuropathy
- Mild gait disorder after 15 years disease duration
- Walking independently: 13% > 50 years
- Wheelchair: Some patients in 20's to 40's; 23% > 50 years
- Laboratory
- CSF: Protein probably normal
- Nerve conductions
- Velocities: Slow to Intermediate; 10 to 34 M/s; Mean 28 to 30 M/s
- Distal latency: Prolonged
- Conduction block: 50%
- CMAPs: Reduced amplitude, especially > 50 years
- Sensory potentials: Reduced or Absent
- Pattern: Length dependent
- Most affected nerve: Ulnar
- Nerve Pathology: Demyelinating neuropathy
- Severe depletion of large myelinated axons
- Myelin
- Hypomyelination
- Small & large focal thickenings
- Nodes of Ranvier: Wide
- Schwann cells: Membranous protrusions
- Cytoplasmic extensions, especially from around unmyelinated axons
- Surrounded by multiple basal membranes
- Onion bulbs
- Basal lamina onion bulbs
- Size: Small vs CMT1A
- Tomacula: Occasional
- Heterozygotes
- Increased frequency of: Carpal tunnel syndrome

- Increased frequency of: Carpal tunnel syndrome
- SH3TC2 variant: Neuropathy + Cerebellar syndrome
152
- Epidemiology: 5 Swedish patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutation: Arg954X; Homozygous; Probable founder effect
- Clinical
- Similarities to FRDA
- Onset
- Age: 1st decade
- Gait disorder
- Weaknees
- Legs > Arms
- Distal > Proximal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Sensory loss: Panmodal; Distal > Proximal
- Skeletal: Pes cavus; Scoliosis
- Hearing loss
- Eyes
- Nystagmus, Horizontal
- Saccadic dysmetria
- Optic disk: Normal
- Course
- Slow progression
- Wheelchair 50 to 70 years;
- Life expectancy: Normal
- Heart: Normal
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axon loss; Demyelination
- Face EMG: Spontaneous activity, Myokymia
- Brain MRI: Often normal
- Vestibular function: Reduced
CMT 4D: HMSN (Demyelinating) & Hearing loss (Lom type)
● N-myc Downstream-Regulated Gene 1 (NDRG1)
- Epidemiology
- Gypsies: Lom, Bulgaria, Slovenia, Spain & Italy
- Turkish family: 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Gypsies: Arg148X; Homozygous
- Turkish: Exon 6 to 8 duplication
- Bulgarian: IVS8AS-1G-A (intron 8), exon 9 skipping
- Bulgarian Muslim: c.538-1G>A, c.327-2A>G
- Carriers: Asymptomatic; Normal NCV
- Animal disease
- Greyhounds: 10 bp deletion 83
- Alaskan Malamute: Gly98Val
- stretcher mouse: Exon 10 to 14 deletion
- Mutations
- NDRG1 Protein
- Expression: Ubiquitous; High levels in Schwann cell cytoplasm
- Possible functions
- Growth arrest & Cell differentiation: Tumor suppressor
- Signaling protein shuttling between cytoplasm and nucleus
- Vesicle transport
- Schwann cells: Differentiation, Trafficking, Signaling, Myelin biosynthesis
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 1 to 10 years of age
- Motor milestones: Delayed
- Gait disorder
- Foot deformities
- Motor
- Weakness: Distal > Proximal; Legs > Arms
- Hand weakness: Onset 5 to 20 years
- Tongue: Atrophy
- Progression: Severe disability by 5th decade
- Sensory loss
- All modalities
- Distal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent in legs
- Skeletal: Pes cavus (50%); Scoliosis (20%); Claw hands
- Deafness
- Onset age: 1st to 3rd decade
- Speech perception: Reduced
- Auditory nerve lesion
- Vestibular dysfunction: Asymptomatic
- Intelligence: Normal
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology
- NCV
- Conduction velocities: Very slow (9 to 20 M/s)
- Distal latency: Prolonged
- Axon loss: Absent or reduced SNAP & CMAP amplitudes
- Hearing: BAEP
- Slow (Demyelination in VIII nerve)
- Prolonged I–V interpeak latencies: Involvement of central pathweays
- Hearing loss: Sensorineural type
- Blink reflex: Three-component response
- EMG: Denervation in distal legs
- NCV
- Pathology
- Demyelination
- Onion bulbs
- Especially younger patients
- Regression with increasing age
- Myelin sheaths
- Uncompacted myelin
- Thin or Absent
- Surrounded by elongated Schwann cell cytoplasm
- Older patients: Schwann cell processes in circular pattern; Fewer onion bulbs
- Onion bulbs
- Schwann cell inclusions: Adaxonal cytoplasm; Pleomorphic; Granulofilamentous
- Axon loss: Severe loss of Myelinated axons; Distal > Proximal
- Axonal inclusions: Curvilinear bodies; Similar to pathology in vitamin E deficiency
- Endoneurial collagenization: Vessels surrounded by multiple layers of basal lamina
- Unmyelinated axons: Preserved
- Demyelination
- Brain MRI: Normal or Subcortical white matter changes
- Electrophysiology
CMT 4F 3
● Periaxin (PRX)
- Epidemiology: Several ethnicities
- Lebanese Shiite Muslim; North American Hispanic; Northern European; Vietnamese
- PRX genetics
- Mutations: Nonsense, Frameshift & Missense
- Allelic disorders
- Adult onset demyelinating neuropathy: Recessive
- Heterozygous mutations: Susceptibility to toxic neuropathy
- Periaxin protein
- Membrane protein
- 3 locations during development
- Nuclear: Early
- Adaxonal: Plasma membrane
- Abaxonal: With myelin maturation; Schmidt-Lanterman incisure; Paranodal membranes
- Expressed by: Myelinating Schwann cells
- During myelination: L-periaxin located near adaxonal membrane
- Mature myelin sheaths: Localized close to abaxonal membrane (near basal lamina)
- Function
- Interacts with
- Dystrophin-related protein 2 (DRP2): Via PDZ domains
- Dystroglycan: Forms cluster at Schwann cell membrane
- PRX/Drp2/Dag complex
- Assembles connection between
- Myelin abaxonal surface
- Cytoplasmic surface of Schwann Cell membrane
- Forms & Stabilizes: Cajal bands; Myelin sheath
- Assembles connection between
- Interacts with: Basal lamina around Schwann cell
- Forms: Tight junction between myelin loop and axon
- Interacts with
- Isoforms contain PDZ motif & Nuclear localization signal
- Clinical: Dejerine-Sottas
- Onset age
- Early childhood; 4 weeks to < 7 years
- Variants with later onset
- Early development
- Gestation & Delivery: Normal
- Motor delay
- Sitting age: 12 to 18 months
- Walking & Talking: Delayed to 2 years
- Gait: Wide based; Ataxic
- Weakness
- Severe
- Distal legs at 9 to 10 years
- Hands at 14 to 15 years
- Progression: Slow
- Sensory loss
- More severe than other DSS or CMT
- Ataxia (80%)
- Pansensory
- Arms & Legs
- Cranial nerves: Normal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Skeletal: Mild kyphoscoliosis; Pes cavus (75%)
- Onset age
- Laboratory
- Nerve conduction studies
- Motor: Absent motor potentials or Severely slowed velocity (3 to 15 M/s)
- Sensory potentials (SNAPs)
- Usual: Absent
- May be preserved in childhood, especially milder syndromes
- Nerve pathology
- Axonal loss (Severe)
- Onion bulbs
- Hypomyelination
- Myelin folding, Abnormal: Occasional
- Nerve conduction studies
- Clinical variant: CMT phenotype with early sensory loss
- PRX Genetics: C715X mutation, Homozygous
- Onset: Childhood; Gait disorder
- Clinical features
- Scoliosis: Severe at 10 years
- Weakness: Distal; Legs & Arms; Symmetric
- Sensory loss: Severe; Distal; All modalities
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Progression: Very slow
- Laboratory
- NCV: Very slow; Severe axon loss
- Nerve biopsy: Axon loss; Onion bulbs; Focally folded myelin
- Clinical variant: Adult onset HMSN
- Epidemiology: Japanese patients
- PRX Genetics: Homozygous; R1070X or D651N
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3rd to 6th decade
- Weaknes
- Legs > Arms
- Distal
- Vocal cord paralysis: 1 patient
- Ambulation impaired
- Sensory loss
- Scoliosis
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Laboratory
- Nerve: Hypomyelination; Onion bulbs
- NCV: 20 M/s
HMSN-Russe (HMSNR; CMT 4G)
● Hexokinase 1 (HK1)
- Epidemiology
- Northern Bulgarian family (Russe): Kalderas
- Romanian & Spanish Gypsies: Similar haplotype to Bulgarian family
- Genetics
- Mutations
- -3818-195G-C in alternative untranslated exon (AltT2)
- G>A in adjacent intron
- Allelic disorders
- Hemolytic anemia, non-spherocytic, Recessive

- CMT 4G, Recessive
- Neurodevelopmental disorder with Visual defects & Brain anomalies (NEDVIBA), Recessive

- Retinitis pigmentosa 79, Dominant

- Hemolytic anemia, non-spherocytic, Recessive
- Mutations
- HK1 protein
- Ubiquitous expresssion: 5' splicing produces tissue specificity
- Catalyzes 1st step in glucose metabolism: Uses ATP for phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate
- Subcellular
- Cytoplasmic or
- Outer mitochondrial membrane: Interacts with porin (VDAC1)

- Patients: Normal activity & histochemistry
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 5 to 16 years; Mean 11 years
- Leg weakness
- Weakness
- Distal: Anterior & Posterior leg
- Symmetric
- Distal legs: Onset at 8 to 16 years
- Hands: Onset 10 to 43 years; Mean 22 years
- Progression
- Continuous
- Severe weakness
- Distal to knees & elbows by 4th to 5th decades
- Proximal legs
- Sensory loss: Distal; Hands & Feet; Panmodal; Prominent
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Deformities
- Foot: Pes cavus; Clawed toes; 100%
- Hands: Clawing; 80%
- Neuropathic joints: Occasional
- Cranial nerve involvement: Occasional ptosis, facial weakness or dysphonia
- Onset
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axonal loss
- SNAPs & Distal CMAPs: Absent
- NCV: Moderately reduced; 30 to 35 M/s
- Electical stimulation of nerves: Increased threshold
- Nerve pathology
- Axon Loss: Especially large myelinated axons
- Axon Regeneration: Abundant; Many small caliber axons
- Hypomyelination: Uniformly reduced thickness of myelin sheath
- NCV: Axonal loss
|
CMT 4H
● frabin/FGD4
|
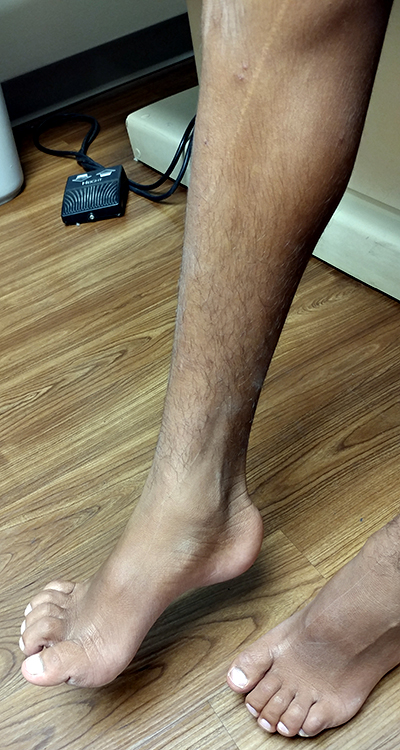 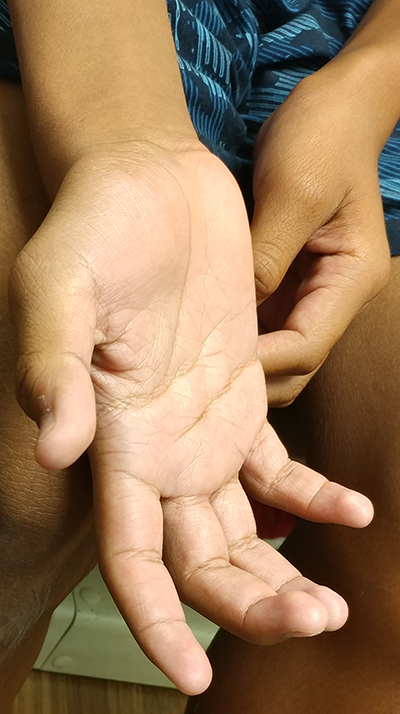
|
CMT 4J
● FIG4 phosphoinositide 5-phosphatase (FIG4; SAC3)
- Epidemiology: > 20 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation patterns
- Common: Compound heterozygous mutations
- Missense Ile41Thr (c.122T>C): Common to most European patients
- Truncation (F98fsX102 in exon 4) or nonsense as other mutation
- Common: Compound heterozygous mutations
- Homozygous Ile41Thr: Moderately severe disease; Possibly less progression 171
- Allelic disorders
- ALS 11: Dominant
- Yunis-Varón (Cleidocranial dysplasia, Digital anomalies, Neurological, Muscle vacuoles)
 : Recessive; 2 Null alleles
: Recessive; 2 Null alleles
- Polymicrogyria, bilateral temporooccipital (BTOP)

- Mutation patterns
- FIG4 protein
- Localization: Vacuolar membrane
- Biochemistry
- Functions
- Endolysomal trafficking
- Autophagy
- PI(3,5)P2 deficiency: Enlarged endolysosomal vacuoles
- Mutation effects
- Reduced intracellular concentration of PtdIns(3,5)P2
- Abnormal transport of intracellular organelles
- Phosphinositide disorders
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Congenital, Childhood or Adult (65 years)
- Weakness
- Asymmetric
- Distal & Proximal
- Legs > Arms
- Severe disease
- Course: Progression
- Over 5 to 10 years
- To Wheelchair confined & Quadriparesis
- Occasional rapid exacerbation
- Sensory: Mild loss
- Upper motor neuron signs: Uncommon
- CNS
159
- Frequency: 25%
- Features: Varied; Parkinsonism, Spasticity, Ataxia, Seizures, Cognitive
- Skeletal
- Scoliosis
- Foot deformities
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic
- NCV: Demyelination + Axon loss
- Velocities: 2–50 M/s
- Slowing: Non-uniform among nerves
- Conduction block (75%)
- Temporal dispersion
- Motor
- CMAP amplitudes: Reduced; Asymmetric
- Distal latencies: May be mildly prolonged
- SNAP amplitudes
- Reduced
- Absent with disease progression
- EMG
- Diffuse denervation:
- Proximal & Distal
- Fibrillations & Positive waves
- Motor unit potentials: Long duration; Polyphasic; Large amplitude
- Recruitment: Reduced
- NCV: Demyelination + Axon loss
- Nerve
- Axon loss: Especially large myelinated axons
- Demyelination
- Thinly myelinated axons: Scattered
- Onion bulbs: Small, Complex
- Collagen: Increased in extracellular matrix
- Fibroblasts
- LAMP-2 aggregates
- Vacuoles: May be associated with LAMP-2
- Impaired trafficking of intracellular organelles
- FIG4 reduced
- Brain MRI: Hypomyelination in some
- Electrodiagnostic
- Mouse disorder: "pale tremor"
- Multi-organ disorder
- Clinical: Impaired motor coordination, Muscle weakness, ‘Swimming’ gait
- CNS Neuronal degeneration: Cortex layers 4 & 5; Deep cerebellar nuclei
- Peripheral neuronopathy
- Neurons in sensory & autonomic ganglia: Loss; Contain cytoplasmic vesicles
- Sciatic nerve: Reduced numbers of large diameter myelinated axons
- Nerve conduction testing: Slow velocity; Small CMAP amplitude
- Pigmentation: Diluted
Demyelinating, Onion-bulb Neuropathy: Mouse 213
● Tumor Susceptibility Gene 101 (TSG101)
- Genetics: Deletion from Schwann cells
- TSG101 protein
- Nerve pathology
- Myelin sheath: Thin
- Onion bulbs
- Axons: Reduced number
- Develops during 3rd postnatal week
HMSN + CNS or Cranial nerve involvement
|
Dominant, Axonal Dominant, Demyelinating Recessive, Axonal Recessive, Demyelinating X-linked, Demyelinating Childhood onset |
HMSN + CNS or Cranial nerve: Dominant, Demyelinating
- Hearing loss, Bilateral high-frequency + Sensory polyneuropathy
16
● Connexin-31 (GJB3) ;
Chromosome 1p34.3; Dominant
;
Chromosome 1p34.3; Dominant
- Genetics
- Mutation: D66del
- External: Data bases
- Variable penetrance
- Allelic disorders
- Deafness: Non-syndromic (DFNA2B)

- Deafness digenic (GJB2, GJB3)

- Erythrokeratodermia variabilis

- Also occurs in: SCA34
- Deafness: Non-syndromic (DFNA2B)
- Protein
- Gap junction membrane protein
- Expressed in cochlea & sciatic nerve
- Clinical: Variable penetrance
- Hearing loss
- Middle & High frequencies
- Late onset
- Polyneuropathy
- Symmetric
- Often mild
- Predominantly sensory
- Weakness: Few patients; Distal
- Electrodiagnostic studies
- Motor & sensory NCV: Mild slowing
- SNAP & CMAP amplitudes: Mild reduction
- Nerve pathology: Demyelination in one patient
- Hearing loss
- Genetics
- Other CMT 1 with hearing loss in some patients
- HMSN IA: PMP-22 point mutation
- CMT 1X: Connexin-32
HMSN + Systemic, CNS or Cranial nerve Disorders: Dominant, Axonal
- HMSN + Pyramidal features (HMSN 5)
 7
7
● Chromosome 4q34.3-q35.2; Dominant- Genetics
- Some patients with
- MFN2 mutations: H165D
- KIF5A mutations
- Some patients with
- Clinical
- Onset: 2nd decade or later
- Weakness: Distal; Legs > Arms
- Upper motor neuron
- Extensor plantar responses
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk (60%)
- Spasticity: Some patients, but usually mild
- Sensory
- Loss: Distal legs; Symmetric
- Pain: Legs; Most patients
- Progression
- Slow
- Little disability in most patients
- Occasional patients in wheelchair by 10 years
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology: Axon loss
- Nerve pathology: Axon loss
- Also see: CMT + Upper motor neuron
- Genetics
- HMSN
129
● Serine palmitoyltransferase, long-chain base subunit 3 (SPTLC3) ;
Chromosome 20p12.1; Dominant
;
Chromosome 20p12.1; Dominant
- Epidemiology: 1 family
- Genetics
- Mutation: c.T448C; p.W150R
- SPTLC3 protein
- Subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT; EC 2.3.1.50)
- Catalyzes the rate-limiting step of de novo synthesis of sphingolipids
- Other SPTLC mutations: HSAN I
- Clinical
- Onset age: 4th decade
- Pes cavus
- Weakness: Distal
- Sensory loss
- Bulbar involvement
- NCV
- Motor NCV: 52 m/sec
- Median CMAP amplitude: Mildly reduced
- HMSN & Deafness
● Autosomal Dominant
- P0 mutation variants: Demyelinating CMT with deafness
- PMP-22 point mutations
- HMSN & Deafness
16
● GJB3 (Connexin 31) ; Chromosome 1p35.1; Dominant
; Chromosome 1p35.1; Dominant
- See: Connexin-31 Demyelinating neuropathy
- Genetics
- Mutation: D66del
- Clinical
- Deafness
- Peripheral neuropathy
- HMSN & Optic atrophy, Retinopathy, Deafness

● Autosomal Dominant- Clinical features
- Severe visual loss
- Onset age 7 to 10
- To light perception only by age 30
- Red-Green dyschromatopsia
- Other dominant optic atrophies: Blue-Yellow defects
- Onset age 7 to 10
- Asymptomatic sensory neuropathy
- Distal sensory loss
- Reduced tendon reflexes
- Hearing loss
- Severe visual loss
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic: Axonal Sensory-motor neuropathy
- Electrodiagnostic: Axonal Sensory-motor neuropathy
- Clinical features
- HMND10: Motor-Sensory Neuropathy & Connective Tissue Disorders
 130
130
● Elastin microfibril interfacer 1 (EMILIN1; gp115) ; Chromosome 2p23.3; Dominant
; Chromosome 2p23.3; Dominant
- Nosology: Distal Hereditary Motor Neuronopathy, Dominant 10
- Epidemiology: 3 families, 5 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Heterozygous; c.64G>A (p.A22T), c.748C>T [p.R250C], Asn658Seer
- Allelic disorders
- Arterial Tortuosity & Osteopenia, Recessive 205
- Intervertebral disk degeneration: Abnormal methylation-modified DEmRNAs
- EMILIN1 protein
- Tissue locations
- Extracellular matrix
- Sites of proximity of elastin & microfibrils
- Blood vessels, Skin, Heart, Lung, Kidney, Cornea
- Nerve: Co-localizes with S100; Epineurium
- Glycoprotein: Assembles into high molecular weight multimers
- Associated with: Fibrillin-1
- Functions
- Elastogenesis
- Blood pressure control
- Regulation of vessel assembly: Cell number & size of smooth muscle cells in arterial walls
- Adhesive ligand for α4β1 integrin
- Regulates TGF-β1
- Knockout mice: Lymphatic vessels large, lymphangiomas
- Tissue locations
- Clinical
- Onset ages: Childhood to 3rd decade
- Systemic
- Aortic aneurysms
- Bronchiectasis
- Polyneuropathy: May be predominant feature
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs
- Sensory loss: Panmodal; Some patients
- Course: Slow progression
- Weakness
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk in some patients
- CNS: Mental retardation in 2 patients
- Connective tissue
- General: Friable
- Joints: Arthropathy; Hypermobility, Pes cavus
- Skin: Elasticity increased
- Tendon ruptures
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic
- Axon loss: Motor & Sensory
- NCV: 42 to 55 m/s in Arms
- Demyelinating features: Few patients
- EMG: Distal denervation
- Skin: Apoptotic cells; Reduced extracellular EMILIN-1
- Muscle: Small angular fibers
- Nerve: Sensory myelinated axons mildly reduced
- CNS: Cingulate cortex gyrus defects
- Electrodiagnostic
HMSN + CNS or Cranial nerve: Recessive, Axonal neuropathy
- HMSN & Agenesis of Corpus Callosum: Andermann Syndrome (ACCPN)

● Solute carrier family 12 (Na+/Cl- transporter), Member 6 (KCC3; SLC12A6) ; Chromosome 15q14; Recessive
; Chromosome 15q14; Recessive
- Epidemiology
- French-Canadian: Charlevoix-Saguenay geographical focus; 1 in 2,100 live births
- KCC3 mutations also found in non-French-Canadian families
- Genetics
- Mutation type: Protein truncating
- Common mutations
- General: Arg1011X (Exon 22)
- French-Canadian: 2436delG
- Knockout mice develop similar syndrome
- Peripheral nerves have hypomyelination
- Normal corpus callosum: Other factors may be involved in agenesis
- Allelic disorders
- SLC12A6 protein
- Sodium-Potassium-Chloride cotransporter
- Location
- Brain & Spinal cord
- Cells
- CNPase positive oligodendroglia in white matter
- Basolateral membrane of choroid plexus epithelial cells
- Increased activity with cell swelling
- Family
- Diuretic sensitive cation-chloride cotransporters
- Other members
- Thiazide sensitive Na+-Cl- cotransporter (NCC)
- Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporters (NKCC 1 & 2)
- Glycoprotein: High mannose; May be complex
- Mutations
- Impair function of cotransporter
- Induce activity-dependent presynaptic terminal damage: ? Reversible with carbamazepine
- Clinical Features
- Cranial nerves: Symmetric or Asymmetric involvement
- Ptosis
- Facial weakness
- Ophthalmoplegia: Reduced upgaze; Other
- Neur(on)opathy
- Motor
- Early: Hypotonia
- Severe weakness: Distal & Proximal
- Progressive
- Rarely walk independently
- Sensory loss
- Areflexia
- Tremor
- Motor
- CNS
- Cognitive
- Mental retardation
- Atypical psychosis: Onset in teens; Episodic
- Seizures
- Optic atrophy
- Cognitive
- Dysmorphic features
- Face: Long; Hypertelorism
- Brachycephaly; High arched palate
- Toes: Syndactyly of 2nd & 3rd; Overiding 1st
- Scoliosis
- Pulmonary restriction
- Cranial nerves: Symmetric or Asymmetric involvement
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic: Axonal loss
- Absent sensory potentials
- Mildly reduced motor NCV
- CSF: Protein mildly increased
- Electrodiagnostic: Axonal loss
- Pathology
- Agenesis of corpus callosum
- Partial or complete (58%)
- Due to defect in axon migration across midline
- Cranial nerves: Axonal swellings with few neurofilaments
- Peripheral nerve
- Large myelinated axons: Reduced
- Axonal swellings with few neurofilaments
- Agenesis of corpus callosum
- KCC3 variant: Motor neuropathy
134
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- SLC12A6 mutation: c.2971A>G, T991A; Heterozygous; Gain-of Function
- Inheritance: Dominant or Sporadic
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 1 year
- Weakness
- Early: Distal; Legs
- With disease progression: Proximal legs; Arms
- Course: Progressive
- Cognition: Normal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Sensation: Normal
- Laboratory
- Nerve pathology: Axon loss
- Muscle: Atrophic & Hypertrtophic muscle fibers
- Nerve conduction
- CMAPs: Small amplitude or Absent
- SNAPs: Mildly small amplitude
- Conduction velocity: 14 to 44 M/s
- Brain MRI: Normal
- KCC3 variant: CMT 2II (HMSN), Dominant
 179
179
- Epidemiology: 15 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance
- Dominant or de novo: Most
- Recessive: 1 family
- Mutations: Missense, In-frame deletion; Arg207His (3 patients), Gly552Asp (Norway), Tyr679Cys, T991A
- Inheritance
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1 to 65 years
- Weakness: Distal; Legs > Arms
- Sensory loss: Panmodal; Some patients
- Tendon reflexes: Often reduced
- Gait disorder: Steppage; Falls
- Spasticity: 1 patient
- Skeletal: Contractures, Ankle; Pes cavus
- Intellect: Normal
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- NCV: Mixed Axonal/Demyelinating neuropathy
- CMAPs in Distal legs: Reduced amplitude
- SNAPs: Absent in legs
- NCV: Sensory-Motor axon loss in most, or Intermediate velocities
- Skin biopsy: Borderline axon loss or Normal
- EMG: Chronic denervation
- Brain MRI: Normal
- Serum CK: Mildly high
- CSF protein: High
- NCV: Mixed Axonal/Demyelinating neuropathy
- Epidemiology
- HMSN + Optic neuropathy (HMSN6C)
 151
151
● Pyridoxal Kinase (PDXK) ;
Chromosome 21q22.3; Recessive
;
Chromosome 21q22.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 5 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Asn75Lys; Thr148Met; Arg220Gln; Ala228Thr
- PDXK protein
- Conversion of vitamin B6 to pyridoxal-5-phosphate (PLP)
- PLP: Essential cofactor in the intermediate metabolism of amino acids & neurotransmitters
- Expression: High in nerve
- Other PLP disorders: Epilepsy common
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2 to 9 years
- Weakness
- Legs > Arms
- Distal
- Symmetric
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Sensory loss
- Early feature
- Distal
- Pan-modal
- Romberg+
- Pain
- Optic atrophy
- Onset: After neuropathy
- Pale optic disks
- Visual acuity reduced
- Skeletal: Pes cavus
- Cognition: Normal
- Seixzures, Neonatal: Some patients
- Treatment: PLP, oral, 50 mg/day
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Normal
- VEP: Reduced & Abnormal
- NCV: Axon loss, Sensory & Motor
- EMG: Denervation, Distal & Chronic
- Plasma PLP: Low
- HMSN, Optic neuropathy ± Hearing loss
● Recessive & X-linked forms
& X-linked forms

- Spastic paraplegia also reported in 1 family
- HMSN & Deafness

● Autosomal recessive
- Clinical
- Polyneuropathy
- Course: Early onset; Slowly progressive
- Weakness: Distal; Arms & Legs; Symmetric
- Sensory: Reduced proprioception in legs; + Romberg
- Sensorineural deafness: Congenital
- Mental retardation: Mild
- ± Pyramidal signs; Cerebellar atrophy
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Polyneuropathy
- Nerve conduction
- Slow motor velocity: Median < ulnar
- Absent sensory potentials
- Pathology
- Absence of α & β large myelinated axons
- Normal: δ & unmyelinated fibers
- Also see: CMT 2E; Hearing loss
- Clinical
- Also see: Childhood onset neuropathies
HMSN + CNS or Cranial nerve: Recessive, Demyelinating
- Congenital disorder of glycocosylation, Type 1a (CDG1A)
- HMSN (Demyelinating) & Hearing loss (Lom type; CMT 4D)

- Metachromatic Leukodystrophy (MLD)

● Arylsulfatase A (ARSA)

 ;
Chromosome 22q13.33; Recessive
;
Chromosome 22q13.33; Recessive
- Genetics
- Mutations: Many missense; Some splice & stop
- Late onset MLD common mutations: Pro426Leu; I179S
- Allelic disorders: Parkinson disease modifier
- L300S: Cognitive impairment; Early onset tremor
- N352S: Protective in dominant Parkinsonism
- Related to binding of cytosolic ARSA to α-synuclein
- Clinical features
- CNS
- Developmental delay & regression
- Optic Atrophy
- Spasticity
- Polyneuropathy
- Juvenile onset forms: Neuropathy may be presenting feature
- Weakness: Proximal & Distal
- Hypotonia
- Tendon reflexes: Decreased or absent
- Sensory loss: Mild; Distal
- Treatment: Corticosteroids may produce symptomatic benetfit for 2 to 3 years
- Laboratory
- NCV: Demyelination
- Slowing: Variable early; More uniform with progressive disease
- Prolonged F-waves
- No conduction block
- Nerve Pathology
- Hypomyelination
- Metachromatic inclusions in Schwann cells and macrophages
- Lamellar or dark ultrastructure
- CSF protein: High
- NCV: Demyelination
- CNS
- Rule out:
- Genetics
- Galactosylceramide Lipoidosis (Krabbe)

● Galactosylceramide β-galactosidase (GALC)
 ;
Chromosome 14q31.3; Recessive
;
Chromosome 14q31.3; Recessive
- Childhood
38
- CNS
- Mental retardation
- Irritability: Excessive crying
- Optic Atrophy
- Tone: Spasticity; Hypertonia (Occasional hypotonia)
- Polyneuropathy
- Onset: < 6 months
- Clinical
- May be presenting syndrome (Up to 25% of patients): Before CNS
- Motor delay
- Hypotonia
- Reduced movements
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent
- Other CNS features: Develop over months
- Electrophysiology: Demyelinating neuropathy
- Nerve conduction velocities: Slow
- Distal latency: Prolonged
- Conduction block: Occasional
- F-wave responses: Delayed or Absent
- CMAP: Mildly reduced amplitude
- Nerve biopsy
- Light microscopy: Often few features of myelin pathology
- Ultrastructure: Curved tubular inclusions in Schwann cell cytoplasm
- CNS
- Later-onset forms
29
- Onset
- Age: > 10 years; Range 13 to 47
- Limb weakness
- Gait disorder
- Spinal cord
- Spasticity: Legs & Bladder
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk or Absent
- Polyneuropathy: Predominantly motor
- May be asymmetric
- Weakness
- Early: Distal; Hands & Feet
- Later: Proximal; Respiratory failure; Tongue
- Pes cavus
- Fasciculations: Proximal muscles
- Course: Progressive over years
- Other CNS signs
- Dysarthria
- Optic atrophy
- Ataxia
- Dementia
- Genetics
- Most mutations in region coding for 50 kDa subunit
- Occasional mutations in 30 kDa subunit
- Onset
- Laboratory
- CSF: High Protein
- Electrophysiology: Demyelinating Neuropathy; Slow NCV
- MRI: Corticospinal tract & periventricular demyelination
- Nerve Pathology
- Nerve: May be hypertrophic without onion bulbs
- Myelin
- Hypomyelination of axons: Uniformly thin myelin sheath in most axons
- Demyelination & Onion bulbs: Some patients
- Inclusions
- Locations: Schwann cells; Histiocytes
- Structure
- Shape: Straight or Slightly curved, Crystalloid & Prismatic
- Contents: Clear & empty on paraffin & ultrastructure
- Axon loss
- Extracellular matrix deposition
- CNS
- Dysmyelination
- Remyelination: Defective
- Multinucleated cells: PAS+ inclusions from fusion of cerebral macrophages with unprocessed galactocerebrosides
- Childhood
38
REFSUM SYNDROMES (Peroxisome Biogenesis Disorders; Zellweger syndromes)
|
|
- Refsum disease: Adolescent or young adult (ARD)
 (Typical form)
(Typical form)
● PEX7 ;
Chromosome 6q23.3; Recessive
;
Chromosome 6q23.3; Recessive
- Genetics: PEX7 mutations 35
- Protein: Peroxin 7
- Function
Peroxisome Import
- Proteins with peroxisomal targeting signal type 2 (PTS2)
- Function
Peroxisome Import
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2nd to 4th decade
- CNS
- Ataxia
- Anosmia
- Cognitive impairment
- Polyneuropathy
- Sensory loss
- Weakness
- Nerve enlargement
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent
- Eye
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- Cataracts
- Skeletal
- Short 5th metacarpal
- Pes cavus
- Laboratory
- Plasmalogen synthesis: Deficient
- Refsum's: Infantile onset

● Peroxin-1 (PEX1) ;
Chromosome 7q21.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 7q21.2; Recessive
- Genetics
- Homozygous mutation (Gly843Asp) found in
- Infantile Refsum's & 1 patient with neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy (NALD)
- Heterozygosity for this mutation (? other mutation) found in
- Zellweger's; Neonatal Adrenal Leukodystrophy; Infantile Refsum's
- Homozygous mutation (Gly843Asp) found in
- PEX1 Protein
- Required for peroxisomal matrix protein import
- Peroxisome biogenesis
- Clinical
- Mental retardation
- Neuropathy: Demyelinating
- Deafness
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- GI: Hepatomegaly; Steatorrhea
- Skeletal: Facial dysmorphism; Growth failure; Osteopenia
- Biochemistry
- Hypocholesterolemia
- Accumulation of phytanic acid, pipecolic acid, very long chain fatty acids
- Pathology
- CNS: Leukodystrophy
- Peroxisomes: Reduced or Absent
- Genetics
- Refsum's: PBD5A
 ; PBD5B
; PBD5B

● Peroxisome biogenesis factor 2 (PEX-2; PXMP3) ;
Chromosome 8q21.11; Recessive
;
Chromosome 8q21.11; Recessive
- Genetics
- Mutations: Stop; Missense, Glu55Lys; Deletion
- Clinical
- Genetics
- Refsum's: Infantile onset 3

● Peroxisome biogenesis factor 26 (PEX-26) ;
Chromosome 2q11.21; Recessive
;
Chromosome 2q11.21; Recessive
- Genetics
- Clinical
- Peroxisome biogenesis disorder 8B (PBD8B)

● Peroxisome biogenesis factor 16 (PEX-16) ;
Chromosome 11p11.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 11p11.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 7 patients
- Genetics
- PEX16 protein: Peroxisomes
- Clinical: Mild peroxisome biogenesis disorder
- Onset age: 1 to 2 years
- Spasticity: Legs; Dysarthria; Dysphagia
- Ataxia
- Gait: Delayed walking; Frequent falls
- Course: Progressive, Wheelchair in 1st decade
- Eye: Optic atrophy, Cataracts
- Constipation
- Neuropathy: Demyelinating, Motor & Sensory
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: WHite matter pathology
- Muscle: Mitochondrial pathology
125
- COX+SDH stain: Reticular & punctate mitochondrial pattern
- Immature muscle fibers: 2C & Stain for fetal myosin
- Skin: Peroxisomes large
- Peroxisome biogenesis disorder 3A (PBD3A; Zellweger)

● Peroxisome biogenesis factor 12 (PEX-12) ;
Chromosome 17q12; Recessive
;
Chromosome 17q12; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 6 patients
- Genetics
- PEX12 protein: Peroxisomal
- Clinical: Severe or Mild phenotype
- Laboratory
- Muscle: Mitochondrial pathology
125
- COX+SDH stain: Reticular & punctate mitochondrial pattern
- Brain MRI
- Reduced white matter
- Corpus callosum: Hypoplasia
- Muscle: Mitochondrial pathology
125
- Refsum-like disorder
 71
71
● Abhydrolase domain-containing protein 12 (ABHD12)
 ;
Chromosome 20p11.21; Recessive
;
Chromosome 20p11.21; Recessive
- Nosology
- PHARC: Polyneuropathy, Hearing loss, Ataxia, Retinitis pigmentosa, Cataract
- Epidemiology: &ge 57 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations
- c.337_338 delGAinsTTT; Promoter & Exon 1 deletion; c.846_852 dupTAAGAGC ((p.His285fsX1); Arg352X
- Null mutations
- Mutations
- ABHD12 protein

- Highly expressed in brain
- Enriched in microglia
- Monoacylglycerol lipase
- Substrate: Main endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG)
- 2-AG functions: Synaptic plasticity; Neuroinflammation
- Interacts with: ABHD16A
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Childhood to late teens
- Hearing loss
- Polyneuropathy
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Sensory loss
- Ankle reflexes: Absent
- Ataxia
- Gait disorder
- Tremor
- Dysarthria
- Onset: Childhood to 5th decade
- Spasticity
- Some patients: Brisk reflexes or Extensor plantar response
- Eye
- Pigmentary retinopathy
- Cataract: Onset third decade
- Optic atrophy: Some patients
- Ear: Hearing loss in 1st to 4th decades
- Skeletal
- Pes cavus
- Tendoachilles contracture
- Skin: Normal
- Cardiac: Normal
- Progression: Slow over decades
- Cortical function: Usually normal
- No anosmia
- Carriers: Normal
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Normal
- Phytanic & Pristanic acid levels in plasma
- Peroxisomal function
- NCV: Demyelinating neuropathy
- Slow velocities
- Axon loss: Distal
- SNAPs: Absent
- Muscle biopsy: Normal
- MRI: Normal or Cerebellar atrophy
- Normal
- Nosology
- Diabetes Mellitus & Multisystem Neurodegeneration (ACPHD)
 127
127
DNAJ/HSP40 homolog, subfamily C, member 3 (DNAJC3) ;
Chromosome 13q32.1; Recessive
;
Chromosome 13q32.1; Recessive
- Nosology: Ataxia, combined cerebellar and peripheral, with hearing loss and diabetes mellitus (ACPHD)
- Epidemiology: 9 individuals or families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Loss of function
- Allelic disorder: Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia, Infancy
- DNAJC3 protein
- Cell location: Endoplasmic reticulum
- Immunoglobulin heavy-chain binding protein (BiP) co-chaperone
- All tissues, especially pancreas & liver
- Signaling: Endoplasmic unfolded protein response
- Other ER chaperone disorders
- Marinesco-Sjögren: SIL1
- DNAJ disorders
- Clinical
- Diabetes
- Juvenile onset
- No β-cell antibodies
- Hypothyroid
- Body
- Mass: Reduced
- Short stature
- Microcephaly
- Ataxia
- Gait disorder
- Upper-motor-neuron: Extensor plantar in 40%
- Polyneuropathy: Sensory loss
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Normal
- Hearing loss: Onset 2 to 27 years
- Cognitive: Mildly abnormal
- Diabetes
- Laboratory
- Nerve conduction
- Sensory NCV: 25 to 37 M/s
- Motor NCV: 16 to 33 M/s
- Sensory amplitudes: Reduced or Absent
- Neutropenia
- Nerve conduction
HMSN + CNS or Cranial nerve: X-linked, Demyelinating
HMSN with pyramidal signs & cerebral white matter lesions 40● Semi-Dominant
- Epidemiology
- Japanese family: 3 severe males, 2 mild females
- Genetics: No specific X-linkage defined
- Onset
- Age: Adult, 3rd decade
- Symptom: Gait disorder
- Clinical
- Weakness: Distal; Hands & Feet
- Wasting: Distal; Hands & Feet
- Upper motor neuron signs
- Spasticity: Legs > Arms
- Plantar responces: Extensor
- Tendon reflexes
- Ankles: Absent
- Other: Brisk
- Sensory loss: Distal; Panmodal
- Cranial nerves: Normal
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology
- NCV: 13 to 36 M/s
- CMAPs: Absent or reduced amplitude
- SNAP amplitude: Reduced or absent
- Evoked potentials: Abnormal central somatosensory & motor pathways
- Nerve biopsy: Non-diagnostic
- MRI: Hyperintense lesions inperiventricular white matter
- Electrophysiology
- Female heterozygotes: Milder than males
- Onset: Adult
- Clinical
- Wasting & Weakness
- Legs
- Distal
- Upper motor neuron
- Gait: Mildly spastic
- Plantar reflexes: Extensor
- Tendon reflexes
- Ankles: Absent
- Other: Brisk
- Wasting & Weakness
- Electrodiagnostic
- NCV: 22 to 48 M/s
Hereditary Neuropathies - Other
α-Methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR) deficiency● AMACR
- Epidemiology: Sporadic patients; 15
- Genetics
- AMACR: Enzyme function
- Location: Peroxisomal
- Metabolic: β-oxidation pathway of branched-chain fatty acids
- Racemize 2R-pristanic acid: Prepares substrate for β-oxidation
- Point mutations: Produce inactive proteins
- Clinical
24
- Onset
- Childhood to Early adult
- Encephalopathy
- Polyneuropathy
- Adult onset
- Weakness: Legs > Arms
- Sensory loss
- Electrophysiology
- Axonal loss
- Demyelination: Some patients
- Sensory & Motor involvement
- CNS: Variably present
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Late onset (5th decade)
- Gait, Appendicular & Speech
- Spastic paraparesis
- Developmental delay (Mild): Learning difficulties
- Seizures (80%)
- Encephalopathy
- Episodic (Relapsing)
- May be focal, localized or diffuse
- Static or Progressive
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Migraine
- Retinitis pigmentosa: Visual acuity reduced; Constricted visual fields
- Rhabdomyolysis: 2 patients
87
- Triggering factors: Neuroleptics; Infections; Anaesthesia
- Differential diagnosis: SCP2 deficiency
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Pristanic acid (a branched chain fatty acid) in plasma: Increased
- Phytanic acid: High
- Di- & Tri- Dydroxycopristanic acids (DHCA & THCA): High
- C27-bile-acid intermediates in plasma: Reduced
- Fibroblasts
- AMACR activity absent
- Peroxisomes (Catalase staining): Reduced number; Increased size
- Muscle
- Morphology: Normal
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Normal
- MRI: Suggestive of mitochondrial disorders
- Cortical edema: During episodes
- High T2 signal: White matter; Thalami; Brain stem; Cerebellar afferents & efferents
- Electroretinogram: Reduced rod responses
HMSN with Minifascicle Formation & 46XY Pure Gonadal Dysgenesis 25
● desert hedgehog (DHH)
- Genetics
- Mutation: DHH partial duplication
- Allelic disorder: Polyneuropathy with Minifascicles, 46,XY Gonadal dysgenesis & Mental retardation
HMSN + Congenital vertical talus
● HOXD10
- Epidemiology: Single Northern New York white family; Italian descent
- Genetics: Missense mutation; M319K
- Clinical
- Laboratory: Not available
Hereditary Recurrent Neuropathy 122
● Chromosome 21q21.1–q21.3; Dominant
- Epidemiology: 1 family
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2nd decade
- Numbness
- Episodic: Often after sleep
- Hands > Legs
- Post-Exercise: Patchy weakness, numbness & pain in 1 patient
- Course: Resolution to normal examination
- Laboratory
- NCV: Motor & sensory axonal neuropathy
- SNAP amplitudes: Reduced
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: Some patients
- NCV: Motor & sensory axonal neuropathy
CMT 2W: Peripheral neuropathy, Hereditary
● Histidyl-tRNA synthetase 1 (HARS1)
- Epidemiology: 24 patients; 5 families
- Genetics
- Mutation: Missense; Loss of function; Arg137Gln, Thr132Ile, Pro134His, Asp175Glu, Asp364Tyr
- Penetrance: 2nd patient with same mutation has no neuropathy
- Allelic disorders
- Usher syndrome type 3B (USH3B)
 (Recessive)
(Recessive)
- Hearing loss
- Vestibular dysfunction
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- Ataxia, Multisystem, Recessive
- Usher syndrome type 3B (USH3B)
- HARS protein
- Amino-acyl tRNA synthetase: Cytoplasmic
- Catalyzes covalent ligation of histidine to its cognate tRNA
- Molecular chaperone
- Expression: Ubiquitous
- Mutated protein: Loss of function allele; Toxic in experimental models
- Jo-1 antigen
- Clinical: Variable phenotype
- Onset age: Childhood to 62 years
- Sensory
- Loss: Distal legs; Vibration or Panmodal
- Pain: Shooting
- Paresthesias
- May be normal in some patients
- HMN or SPG syndrome: Gait disorder
- Age < 40 years
- Asp364Tyr mutation
- Weakness
- Distal > Proximal
- Gait disorder
- Normal in rare patient
- Tendon reflexes
- Ankles: Absent
- Knees: Brisk
- Plantar reflex: Flexor
- Muscle bulk: Normal or Distal atrophy
- Skeletal: Pes cavus
- Course: Slow progression
- Nerve conduction studies
- Sensory: Sural SNAP amplitude progressively reduced
- Motor: Peroneal CMAP reduced or absent amplitude
- NCV
- Usual: Normal or slightly reduced (> 40 M/s in arms) velocities
- More severe, childhood onset, disease
- More slowed (24 to 39 M/s in arms) velocities
- Pro134His mutation
- HARS1 variant syndrome: Ataxia, Multisystem
160
- Epidemiology: 2 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Stop, Duplication & Missense; 1 Missense in each patient
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth
- Microcephaly
- Psychomotor development: Delayed; Intellectual disability
- Oculomotor apraxia
- Ataxia: Gait; Dysarthria; Dysmetria; Nystagmus
- Spasticity: Legs
- Extrapyramidal: Athetoid movements; Dystonia
- Weakness: Distal in 1 patient
- Skeletal deformities
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: T2-signal in Upper cerebellar peduncles & Subthalamic nuclei; cerebellar atrophy
- NCV: Motor velocity slow with increased latency
CMT 2U: Peripheral neuropathy, Sensory-Motor
● Methionyl-tRNA synthetase 1 (MARS1)
- Epidemiology: 4 families, 9 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; R199Q, Arg618Cys, Pro800Thr
- Penetrance: Incomplete; 2 patients with mutation not affected
- Allelic disorders
- SPG 70
- Infantile liver failure syndrome 2 (Interstitial lung & liver disease)

- Trichothiodystrophy 9, nonphotosensitive

- MARS protein
- Amino-acyl tRNA synthetase: Cytoplasmic
- Clinical
- Onset ages: Childhood to 67 years
- Weakness: Distal arms; Proximal & Distal legs; Foot drop
- Sensory loss: Distal; Panmodal; Arms & Legs
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Course: Slowly progressive; Some ambulation preserved
- Laboratory
- EMG: Denervation distal arms & legs + proximal legs
- NCV: Axonal neuropathy
- SNAP amplitudes: Reduced or Absent
- CMAP amplitudes: Reduced or absent in legs
- Velocities: Normal or Intermediate
- Sural nerve pathology
- Axon loss: Large & Small
- Onion bulbs in some patients
- Variant syndrome: SPG 70

- Epidemiology: 6 patients, 2 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations
- Compound heterozygous
- Missense: V5M; C389Y; R625W; R702W
- MARS protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth to 6 months
- Developmental Delay: Motor; Intelligence
- Spasticity
- Gait disorder
- Tendon reflexes: Increased in legs ± arms
- Plantar reflex: Extensor
- Amyotrophy
- Contracture: Ankles
- Laboratory
- Brain imaging: Normal
- NCV: Normal
CMT 2Z: Peripheral neuropathy, Sensory-Motor
● MORC family CW-type zinc finger protein 2 (MORC2)
- Epidemiology: > 20 familes
- Genetics
- Mutations: Arg252Trp (Common); Ser25Leu (Infant onset); E236G; Ala406Val; Tyr394Cys
- MORC2 allelic disorders
- CMT 2Z
- Developmental disorder, de novo mutations (DIGFAN)
- Motor neuropathy, Proximal, Adult onset
- Cockayne-like syndrome 194
- MORC2 protein
- Cell location: Nucleus & Cytoplasm
- Locations: Axons & Schwann cells
- Fatty acid metabolism: Binds & Regulates ATP-citrate lyase (ACLY)
- Transcriptional gene repressor: Gastric cancer cells
- Chromatin remodeling
- DNA repair
- ATPase family: Epigenetic silencing through chromatin modification
- Disease mechanisms
- ? Deregulation of DNA damage response pathway
- Hypermethylation of DNA in promoter regions
215
- Transcriptional repression of target genes: ERCC8, NDUFAF2, FKTN
- MORC2 dysfunction
181
- Axon swellings
- Neurotransmitter receptor abnormalities
- Neuron: DNA damage
- Apoptosis
- Clinical
- Onset ages: Congenital to 2nd decade
- Motor
- Early onset
- "SMA-like" weakness
- Hypotonia
- Later onset
- Weakness: Distal
- Cramps
- Weakness
- Asymmetric
- Legs & Arms
- Distal > Proximal
- Proximal: Later in course
- Neck flexion: Some patients
- Pelvic & Shoulder girdle
- Some patients: Scapuloperoneal
- Sparing: Intermediate muscles
- Atrophy
- Early onset
- Sensory loss
- Large & Small fiber modalities
- Distal > Proximal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Increased
- Other: Some patients
- Spech: High pitched
- Retina: Pigmentary changes
- Pyramidal signs: Some families
- Learning difficulties
- Course
- Slow progression
- Vincristine: May produce exacerbation 173
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axon loss, Motor & Sensory
- CMAP & SNAP amplitudes: Reduced
- Velocities normal
- More prominent with increased age
- EMG: Myokymia; Fasciculations
- Nerve pathology
- Axon loss: Multifocal
- Axon Regeneration
- Onion bulbs: Few
- Unmyelinated axons: ? Reduced numbers
- Brain MRI: White matter changes in some patients
- NCV: Axon loss, Motor & Sensory
- MORC2 variant: Neurodevelopmental disorder (DIGFAN)
 166
166
- Epidemiology: > 20 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: de novo Dominant mutations
- Mutations: Missense; Glu27Lys (Common), Ser87Leu, Arg132Cys, Tyr394Cys, Val413Phe
- Mutation locations: ATPase module of MORC2
- Neuropathy features: Ser87Leu, Tyr394Cys
- Developmental delay: Glu27Lys, Arg132Cys; Hyperactivate HUSH-mediated silencing
- Clinical
- Onset age: Childhood
- Skeletal: Microcephaly; Face dysmorphism; Short stature; High arches
- CNS: Motor delay; Intellectual disability; Seizures
- Sensory: Hearing loss; Retinopathy, pigmentary
- Neuromuscular: Weakness (50%); Hypotonia; Gait disorder
- Tendon reflexes: Increased or Decreased
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: White matter Δ; Leigh-like lesions
- EMG/NCS abnormal (60%)
- MORC2 variant: Motor neuropathy, Adult onset
188
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant or de novo
- Mutations: Missense; Gly444Arg, His446Gln
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Adult; 20 to 30 years
- Hand weakness
- Tremor
- Weakness: Distal + Proximal; Arms & Legs
- Cramps
- Tremor: Hands
- Tendon reflexes: Absent at ankles or diffusely
- Course: Slow progression
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle MRI: Soleus & Gastrocnemius
- EMG: Denervation
- Serum CK: Mildly high
CMT 2: Peripheral neuropathy, Early onset + Sensory Ataxia 132
● Diacylglycerol O-Acyltransferase 2 (DGAT2)
- Epidemiology: 1 family
- Genetics
- Mutation: de novo; Missense; Y223H
- DGAT2 protein
- Endoplasmic reticulum: Lipid droplet-ER contact
- Mitochondrial-associated
- Membrane protein
- Catalyzes final step of triglyceride biosynthesis pathway
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 1st decade
- Falling
- Weakness: Distal; Legs > Arms
- Muscle atrophy: Distal legs
- Gait: Unsteady; Broad based
- Tremor: Hands
- Sensory loss: Vibration & Position > Pain; Sensory ataxia
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Serum triglycerides: Low to 50%
- Serum CK: 348
- NCV: Axonal neuropathy
- CMAPs: Absent in Legs
- Distal motor latencies: Long in arms
- EMG: Denervation
- MRI: Distal muscle atrophy
- Nerve biopsy
- Axon loss
- Myelin thickness: Usually normal
- Collagen pockets with no axons
- Subperineurial edema
CMT 2: Peripheral neuropathy, Dominant de novo 197
● DExH-box helicase 9 (DHX9)
- Epidemiology: 20 patients; 3 with CMT2
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Features: Heterozygous; de novo; Missense or Loss of Function
- CMT2: Arg837Thr; Asp846Gly; Ala1255Thr
- Mutations
- Allelic disorders
- Neurodevelopmental disorders
- CMT2: Axonal; Dominant, de novo
- RNA helicase: Play roles in transcription, RNA processing, translation & RNA replication
- Localization: Nucleus,
- Regulates transcription
- Unwinds nucleic acid structures: R-loops (3-stranded with DNA-RNA hybrid & displaced single-stranded DNA
- Repairs DNA breaks: Through homologous recombination (HR) via recruitment of BRCA1 to DSBs
- Mutations
- Abnormal DHX9 cell distribution: More in cytoplasm
- Altered Helicase ATPase activity
- CMT2 mutants: Missense; Aberrant nucleolar DHX9 accumulation
- DHX disorders
- Onset age: Adolescent or Adult
- Weakness: Distal; Symmetric
- Sensory loss: Distal
- Pain (67%)
- Tendon reflexes
- Foot deformities: Pes cavus; Hammer toes
- Axonal neuropathy
CMT 2DD: Peripheral neuropathy, Motor + Sensory
● ATPase, Na+/K+ transporting, alpha-1 polypeptide (ATP1A1)
- Epidemiology: > 10 familes
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Missense: 11 identified
- Hotspot: Helical linker region (Residues 592 to 608)
- Most missense CMT mutations: Axon loss phenotype
- P600R: Demyelinating neuropathy
- L48R: Mild phenotype; Varied onset age; Incomplete penetrance
- Y148*: No phenotype
- Mutations with disease effects
199
- Haploinsufficiency +
- Malfunctioning gene product
- Allelic disorders
- CMT 2DD
- de novo germinal mutations
- Hypomagnesemia, Seizures & Mental retardation 2 (HOMGSMR2)

- Spastic paraplegia, complex
- Demyelinating neuropathy: P600R mutation; NCV < 30 M/s 200
- CMT, Intermediate
- Hypomagnesemia, Seizures & Mental retardation 2 (HOMGSMR2)
- Somatic mutations
- Adrenal adenoma
- Primary aldosteronism: Aldosterone-producing cell clusters
- Mutations
- ATP1A1 protein
- Membrane protein
- Tissue expression: Ubiquitous
- α1 subunit of Na+/K+ ATPase
- Predominant paralog in peripheral axons: Axolemma
- Schwann cells, Myelinating: Non-compact myelin areas; Paranodal loops & Schmidt-Lantermann incisures
- Thr339-Leu772 fragment: Binding site for E3 ubiquitin ligases; ZNRF1; ZNRF2
- Na+/K+ (αβ) pump functions
- ATP hydrolysis: Transport 3 Na+ out in exchange for 2 K+ in, at expense of 1 ATP
- Establish transmembrane electrochemical gradients of Na+ & K+
- Electrical signaling & Cell survival
- α2 subunits: Skeletal muscle; Glia
- α3 subunits: Neurons
- &beta subunit: Targets Na+/K+ ATPase to plasma membrane
- Clinical
- Onset age: Varied; Childhood to Adult, 5 to 50 years
- Weakness: Distal; Arms & Legs
- Sensory loss: Distal; Legs > Arms
- Skeletal: Pes cavus
- Hearing loss: Some patients
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axon loss
- Nerve biopsy
- Axon loss: Large myelinated axons; Regeneration; Thin myelin
- ATP1A1 variant disorder: Spastic paraplegia, complex
177
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Inheritance: de novo; Dominant
- Mutation: Missense; L337P
- Clinical
- Onset: Early childhood
- Developmental delay
- Spastic paraparesis: Legs > Arms
- Sleep disorder
- Laboratory
- CNS imaging: Normal
- NCV: Normal
- EEG: Normal
CMT 2HH: Polyneuropathy with Vocal Cord Involvement
● JAGGED 1 (JAG1)
- Epidemiology: 2 families, 5 patients
- Genetics
- JAG1 protein
- Ligand of: Notch receptor

- Clevage of Notch receptor
- Release of intracellular part of Notch receptor from membrane
- Translocation to nucleus
- Activates transcription factors
- Ligand of: Notch receptor
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth or Childhood
- Vocal cord paresis: Stridor; May need trachiostomy
- Strength: Normal or Distal weakness, mild
- Sensory: Normal or Mild loss
- Tendon reflexes: Often reduced or absent
- Scoliosis: 1 patient
- Laboratory
- EMG: Chronic denervation in larynx & distal limbs
- NCV: Velocities Normal or Mildly slow
- Mouse nerve pathology: Folded myelin, mild
Also see: Childhood onset neuropathies
Patient information
Support groups
Return to Polyneuropathy Index
Return to Neuromuscular home page
References
1. Am J Hum Genet 1999;65:722-727, Neuromuscular Disorders 2003;13:60–67, Brain 2007 Mar 8
2. Genomics 1999;62:344-349, Human Molecular Genetics 2003;12:349–356
3. Am J Hum Genet 2001;68:325-333
4. Am J Hum Genet 2000;67, Brain 2007;130:394–403, JAMA Neurol 2014; Online Sep
5. Am J Hum Genet 2000;67:664-671, Ann Neurol 2001; Online Aug 7, European Journal of Human Genetics 2009; Online June
6. Neurology 2000;55:392-397, Am J Hum Genet 2003;72 Online April3
7. Neuromuscular Disorders 2000;10:497-502
8. J Neurol 1999;246:107-112
9. JNNP 2000;69:806-811, Brain 2003;126:134-151
10. JNNP 2000;69:799-805, J Clin Neurosci 2020;75:228-231
11. Neurology 2000;55:1552-1557
12. Am J Hum Genet 2001;68:269-274, Neuromuscular Disorders 2004;14:301–306. Neurogenetics 2018;19:215-225
13. Neurology 2001;56:100-103
14. Neuromuscular Disorders 2001;11:27-34
15. Lancet 2001;357:267-272
16. Hum Mol Genet 2001;10:947-952
17. Neurology 2001;56:A315, Neuromuscular Disorders 1998;8:392–393, Am J Hum Genet 2001;69:000–000
18. Neuromuscular Disorders 2001;11:400-403, J Neuromuscul Dis 2020 Jun 12
19. Eur J Hum Genet 2001;9:646-650, Neurology 2008; Online October, J Neurol Sci 2020 Mar 27;413:116809, Biomolecules 2022;12:1382
20. Am J Hum Genet 2002;70:244-250, Neurology 2003;60:22-26, Eur J Neurol 2017;24:530-538
21. Neurology 2001;57:1906-1908
22. Nature Genet 2002;30:21-22, Neurology 2002;59:1865–1872
23. Nature Genet 2002;30:22-24, Arch Neurol 2003;60:598-604, Brain 2003;126: August, Brain 2007 Mar 8
24. JNNP 2002;72:396-399
25. Ann Neurol 2002;51:385–388
26. Am J Hum Genet 2002; On-Line April
27. Neuromuscular Disorders 2002;12:399–404, J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2002;73:762–765, Neurology 2003;60:1151–1156, BMC Neurol 2023;23:250
28. Neurology 2002;58:1769–1773
29. Neuromuscular Disorders 2002;12:386-391
30. Ann Neurol 2002;52:429–434, Pediatr Neurol 2008;38:293-295
31. J Neurol 2002;249:1298-1302
32. Muscle Nerve 2002;26:608–621
33. J Cell Sci 2002;115:4937-4946
34. Muscle Nerve 2003; Online December 2002
35. Am J Hum Genet 2003; On-Line January
36. J Neurol 2002;249:1629-1650, Semin Neurol 2010;30:373-386
37. Neurology 2003;60:506–508
38. Pediatr Neurol 2003;28:115-118
39. Brain 2003;126:590-597, J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2017 May 13
40. Muscle Nerve 2003;28: 623–625
41. Am J Hum Genet 2003;73:1106–1119, PNAS 2009; Online September 29, N Engl J Med 2010 Mar 10, Hum Mol Genet 2010;19:1009-1018, Front Genet 2024;15:1381915
42. Neurology 2003;61:1154-1155
43. Am J Hum Genet 2003; Online November
44. Muscle Nerve 2004;29:205-210, Acta Neurol Scand 2003;108:352-358, Neuromuscul Disord. 2003;13:827-829
45. Neurology 2003;61:1457-1458
46. J Med Genet 2004;41:193–197
47. Human Genet 2004;114:527–533, Human Genet 2004; Online November
48. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2004;9:124
49. Am J Hum Genet 2004; Online May
50. J Neuropath Exp Neurol 2004;63:1167-1172
51. J Neurol 2004;251:1491-1497
52. Hum Mol Genet 2005; Online March, Am J Hum Genet 2007; Online March, Neurology 2009;72:617–620
53. Ann Neurol 2005;57:749–754
54. Neurology 2005;64:1964–1967
55. J Cell Sci 2005 Jun 28, Hum Mol Genet 2005;14:1405-1415
56. JNNP 2005;76:1109-1114
57. Neurology. 2005;65:197-204, Neurology. 2005;65:496-497
58. Neuromuscul Disord 2005 On line Sep 27, Neurogenetics 2007 Aug 24
59. Nature Genetics 2005; Online Jan 22
60. Ann Neurol 2005;59:276–281
61. J Neurol Sci 2005; Online
62. JNNP 2006;77:963-966, J Comp Neurol 2006;498:252-265, Neuromuscul Disord 2006;16:308-310
63. Neurology 2006;67;2016-2021, Neurogenetics 2008;9:191-195, Muscle Nerve 2012; Online Nov, PLoS Genet 2016 Jul;12(7):e1006177, Neurology 2018 Apr 6
64. Neurology 2006;67;2250-2252
65. Ann Neurol 2006;59:358–364
66. Otol Neurotol 2005;26:405-414
67. Neurology 2007;68:849–855
68. Neuromuscul Disord. 2007 Apr 10
69. Nature 2007; Online June 17, Brain 2008;131:1990-2001, Ann Neurol 2018 Mar 8
70. Neuromuscul Disord 2008;18:334-338, Neurology 2007;69:291-295
71. Neurology 2009;72:20-27, Am J Hum Genet 2010 Online August, Acta Neurol Belg 2025 Mar 11
72. Neurology 2008;70:2010-2011
73. Neurology 2008;71:1959–1966
74. Neurology 2008;71:1678–1681
75. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2008;67:1097-1102
76. Neurogenetics 2009 Mar 17
77. Am J Human Genet 2009; Online April 30
78. Journal of Human Genetics 2009;54:94–97, Ann Neurol 2009; Online May
79. Neuromuscular Disorders 2009; Online November
80. Nature Genetics 2009; Online Dec A, B, C
81. Am J Hum Genet 2009; Online Dec, BMC Neurol 2022;22:299, Neurol Genet 2022;8:e200019
82. Am J Med Genet 2010; Online May
83. PLoS One 2010;5:e11258
84. J Human Genetics 2010; Online August
85. J Obes 2011;2011. pii: 482021. Epub 2010 Sep 1
86. Surv Ophthalmol. 2010 Sep 16
87. Neurology 2010;75:1300-1302, Eur J Neurol 2020 Oct 12
88. American Journal of Human Genetics 2010;87:560–566
89. Muscle Nerve 2011; Online February
90. PLoS Genet 2010 Aug 26;6
91. Brain 2011; On-Line May
92. Neurology 2011;77:168–173
93. Neuromuscul Disord 2011;Jul 6
94. Am J Human Genet 2011; Online Aug
95. Genome Research 2011;21:658–664
96. Am J Human Genet 2011; Online Aug, Hum Mutat 2014 Dec 16
97. Neuromuscular Disorders 2011; Online Sept
98. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2011;16:113-118
99. Human Molec Genet 2011; online October
100. Neurology 2011; Online November
101. NEJM 2011; 365:2377-2388, Sci Rep 2023;13:12003
102. Neurogenetics 2012; On line Jan
103. Ann Neurol 2012;71:84–92
104. Neurology 2012;78:1644–1649
105. Hum Mutat 2012 Aug 28, Brain 2015 Jun 13
106. Nature Genetics 2012; Online September, Brain 2016 Dec 21, Front Neurol 2023;14:1084335
107. Neuromuscular Disord 2012;22:806-807, Hum Molec Genet 2103;22:1404-1416
108. Am J Human Genet 2012; Online November, Biology (Basel) 2023;12:897
109. JNNP 2012; Online December
110. Muscle Nerve 2012;45:135-138
111. Neurol Sci 2012; Online Dec 4
112. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2012;17:391-398
113. Am J Human Genet 2013; Online Feb, Eur J Med Genet 2017 Jun 19
114. Neurogenetics 2013; Mar 3
115. Human Molecular Genetics 2013; Online April, Hum Genet 2015 Apr 17
116. JNNP 2013; Online June, Neuropathology 2022 Jun 20
117. Neurology 2013:81 Online June
118. J Neurol Sci 2013; Online August
119. Nat Rev Neurol 2013; Online Sep, GeneReviews 2019, Nat Rev Dis Primers 2026;12:3
120. Clin Neuropathol 2012;31:7–23
121. Am J Hum Genet 2014; Online Feb
122. Neuromuscular Disorders 2014; Online May
123. Am J Human Genet 2014; Online August
124. Ann Neurol 2014;76:134-139
125. Eur J Pediatr 2014 Oct 7
126. Neurogenetics 2014: Online Oct
127. Am J Human Genet 2014; Online Nov
128. Neuromuscular Disorders 2015, Neurology Genetics 2018;4:e220, Neurology 2024;102:e209174
129. Cell Rep. 2015;12:1169-1183, PLoS Genet. 2016;12:e1005829
130. Hum Mutat 2015 Oct 14, Neurobiol Dis 2020 Jan 21, Cureus 2025;17:e89357
131. Brain 2015; Online Oct, Ann Neurol 2015; Online December, Eur J Neurol 2021 Jun 30
132. Hum Mutat 2016 Jan 20
133. Ann Neurol 2016; Online March, J Med Genet 2018 Nov 10, Neurology 2020 Nov 3, J Peripher Nerv Syst 2024 Jun 11
134. Sci Signal 2016;9(439):ra77
135. Neurology Genetics 2016;2:e94
136. Am J Hum Genet 2016;99:607-623
137. Neurology 2017 Jan 11
138. Brain 2017 Online June, Front Genet 2024;15:1405644
139. Am J Hum Genet 2018;102:505-514, Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2021 Jul 7
140. Neuromuscular Disorders 2018; April
141. Eur J Neurol 2015;22:1548-1555
142. Exp Neurol 2018 Apr 28
143. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener 2019 Jan 20:1-3
144. Ann Neurol 2019; Jan
145. Muscle Nerve 2019; March
146. J Neuromuscul Dis 2019 Apr 3
147. Neurogenetics 2019 Apr 22
148. Hum Mutat 2019 May 22
149. Neurology Genetics 2019;5:e565
150. Brain 2019; Online June
151. Ann Neurol 2019; Online July
152. Cerebellum Ataxias 2019 Jul 15;6:9
153. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2019 Aug 20
154. Nat Commun 2019;10:5045
155. J Clin Invest 2020 Feb 17
156. Glia 2020 Feb 20
157. Hum Mutat 2016;37:1202-1208
158. Front Genet 2020;11:61
159. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2020;74:6-11
160. Hum Mutat 2020 Apr 25
161. Neurol Genet 2020;6(2):e407
162. Nat Genet 2020 May 4, Front Neurol 2021;12:733926, Brain 2025 Feb 13
163. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2020;7:15-25
164. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2020 May 15
165. Glia 2020 Jun 8
166. Am J Hum Genet 2020 Jul 15
167. Neuromuscul Disord 2016;26:837-840
168. Cells 2020;9:E1832
169. Am J Hum Genet 2020 Sep 10, Genes (Basel) 2024;15:1556
170. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2020 Sep 19, Brain 2024 Jun 28
171. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2021 Jan 6
172. Brain 2020;143:3589-3602, Front Neurol 2021;12:757518
173. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2021 Apr 12
174. Neurol Clin Pract 2021 Apr;11(2):e129-e134
175. Brain 2021 Apr 23, Brain Commun 2023 Sep 5
176. Eur J Neurol 2016;23:1566-71
177. Clin Genet 2020;97:521-526
178. J Mol Med (Berl) 2021 Sep 18
179. Neuromuscul Disord 2021;31:149-157, J Med Genet 2020;57:283-288, Brain 2022 Dec 21
180. Front Mol Neurosci 2021;14:727552
181. Dis Model Mech 2021 Oct 1
182. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener 2021 Nov 9
183. PLoS Genet 2022;18:e1009968
184. Genes (Basel) 2021;13:84
185. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2021;26:177-183
186. Eur J Neurol 2021;28:2913-2921
187. Hum Mutat 2022 Apr 29
188. Hum Mutat 2022 Jul 29
189. Eur J Neurol 2022 Oct 19
190. Transl Neurodegener 2022 Oct 26
191. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud 2022 Oct 28
192. J Biol Chem 2022 Dec 26;102839
193. Muscle Nerve 2023 Jan 11
194. Pediatr Neurol 2023;141:79-86
195. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2023 May 30
196. Brain 2023;146:1844-1858
197. Am J Hum Genet 2023 Jul 13
198. Neurol Genet 2023;9:e200078
199. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2023 Aug 31;119572
200. J Neurol 2023;270:2576-2590
201. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2023;120:e2313010120
202. Exp Neurobiol 2023;32:410-422
203. Ann Neurol 1997;41:104-8
204. Brain 2024 Jun 8, Epilepsia 2024 Jul 2
205. Am J Hum Genet 2022;109:2230-2252
206. Eur J Neurol 2024 Jul:e16416
207. Int J Mol Sci 2024;25:8170
208. Front Aging Neurosci 2024:16:1421841
209. Int J Mol Sci 2024;25;9047
210. Hum Genet 2024;143:1281-1291
211. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2025;96:47–53
212. Neurol Sci 2025 Feb 26
213. MicroPubl Biol 2025:10.17912/micropub.biology.001406
214. Genes Genomics 2025 Apr 21
215. Brain 2025 Apr 30
216. Eur J Neurol 2025;32:e70313
217. Sci Adv 2025 Sep 26;11(39)
218. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci 2023;6:1310-1322
219. medRxiv 2025:2025.10.01.25336578
220. Muscle Nerve 2025 Dec 3
Illustration by J Kwon, MD
1/24/2026