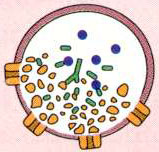
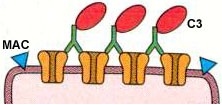
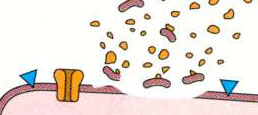
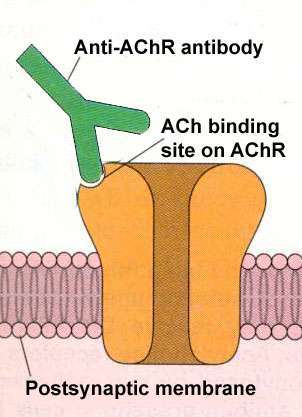
- Releases packets or quanta of acetylcholine
- Spontaneous release rate: 0.1-10 Hz
- Trigger: Increase in free Ca++ in nerve terminal
- Effect of release on post-synaptic membrane: Miniature endplate potentials (MEPPs)
- Single nerve impulse
- Causes release of 1-3 quanta from each presynaptic terminal bouton
- Release event at a given active zone: Occurs in response to one of ten nerve impulses
- Number of quanta released at a NMJ: Proportional to NMJ area
- Frog NMJs: Large; Release 100-200 quanta per impulse
- Human NMJs: 10x smaller; Release 20 quanta per impulse
- Each quantum consists of 5,000 to 10,000 molecules of ACh
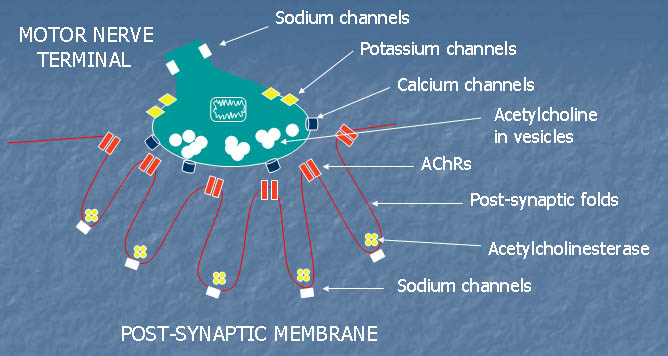
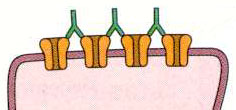
- Acetylcholine receptors (AChRs): High concentration
- AChRs are concentrated at peaks of, & 1/3 of way down, post synaptic folds
- Density: ~10,000/μm2; Form near crystalline array
- Voltage-gated sodium channels
- High density of Nav1.4

 in folded postsynaptic membrane
in folded postsynaptic membrane - Effect of transmission at human NMJs is amplified
- Concentrated at base of folds
- High density of Nav1.4
- Structrure
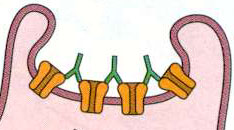
- Highly folded: Especially prominent in humans
- Opening of folds: Opposite active zones on nerve terminal