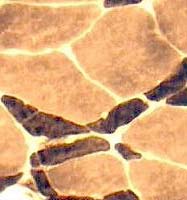
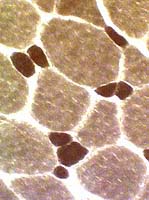
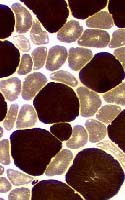
Myosin ATPase, pH 9.4
What is the differential diagnosis in adults (Left)?
Answer: Disuse, Aging, Weight loss, Systemic disease & Paraneoplastic disorders
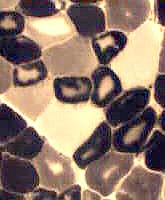
What is the differential diagnosis in children (Right)?
Answer: Severe type 2 atrophy is common in congenital myasthenia.
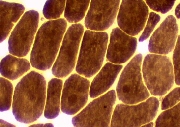
ATPase, pH 9.4
What is the differential diagnosis?
Answer Central core
Large fiber type grouping
Demyelinating neuropathies
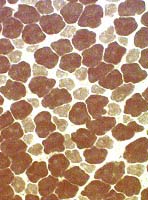
ATPase pH 9.4 stain
What is the differential diagnosis?
Image: Type I muscle fibers are selectively small,
Answer: Very small type I muscle fibers are common in congenital myopathies such as
Centronuclear
Nemaline rod
Fiber type disproportion, congenital.
Rigid spine syndromes
NOTE: Type 2 muscle fibers can be selectively enlarged with exercise.
Myosin ATPase, pH 9.4 stain
Answer: Some muscle fibers have focal or diffuse loss of myosin.
Some muscle fibers have staining that is less intense than Type I fibers.
Some muscle fiber have a focal loss of myosin staining.
What are likely clinical features in this patient?
Answer: Severe proximal > distal weakness and respiratory failure.
The syndrome is variously called Myosin-loss, Acute quadriplegic, ot Critical illness myopathy.

ATPase pH 9.4 stain
Answer: Fiber type grouping without muscle fiber atrophy
There was denervation and reinnervation of the muscle in the past
What does this pattern of ATPase staining suggest about the disease course?
Answer: Non-progressive course; Strength may be reduced or normal in this muscle.