Centronuclear (Myotubular) Myopathy
|
General features Ultrastructure Adult MTM1, Missense Titin Juvenile DNM2 mutations Myopathic Muscle fibers Ultrastructure Necklace fibers Abnormal fiber types Punctate, Small fibers Childhood Infant MTM1, Stop |
|
General: Pathologic differential diagnosis
- Central nuclei
- Central muscle fiber staining
- Radiating sarcoplasmic strands (NADH): DNM2
- Necklace fibers
- Connective tissue pathology: DNM2
- Endomysial connective tissue: Increased
- Perimysium: Replaced by fat
- Type I fiber predominance/smallness: MTM1; DNM2, Bin1, TTN
- Core-like regions: RYR1; TTN
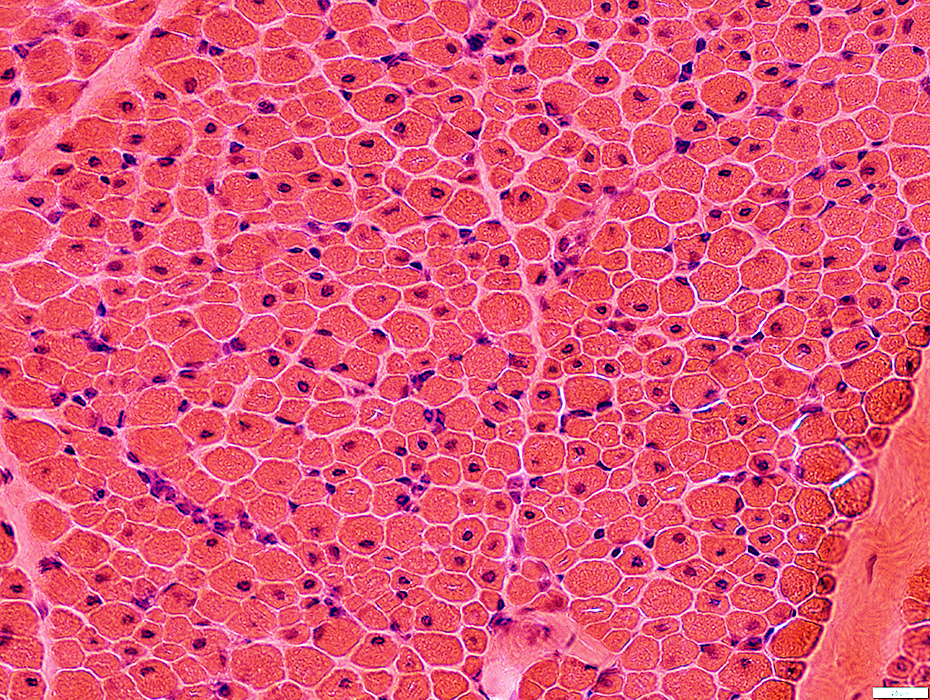
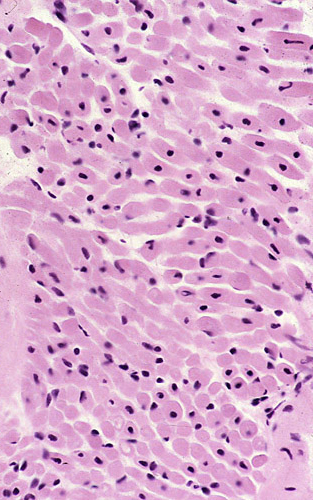
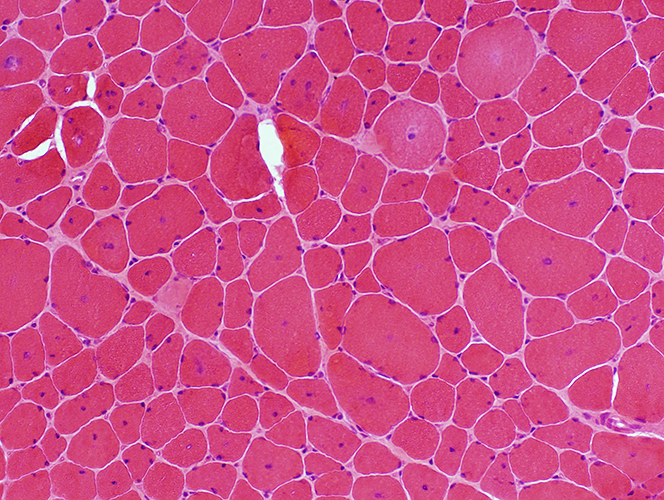
Centronuclear myopathy: Infantile
A single central nucleus is present in many muscle fibers
 |
 |
 From: T Mozaffar
|
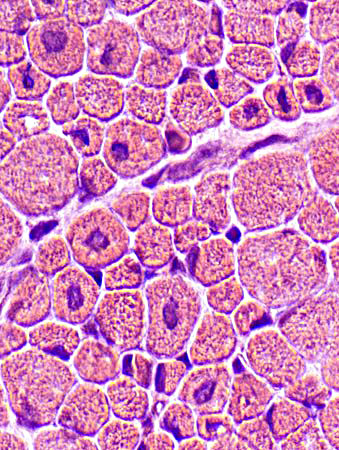 H&E stain |
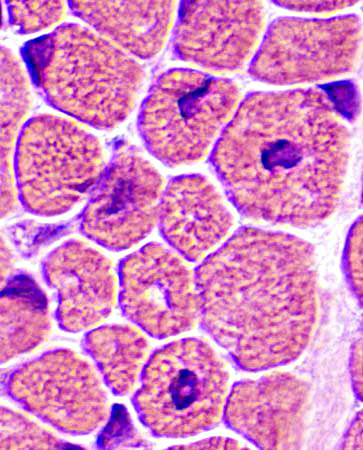 H&E stain |
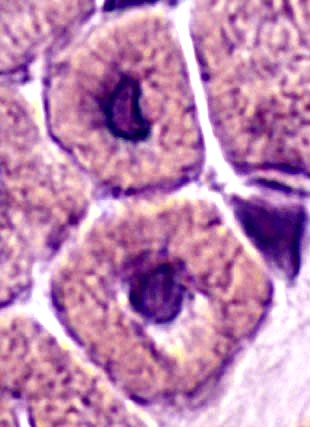 H&E stain |
 H&E stain |
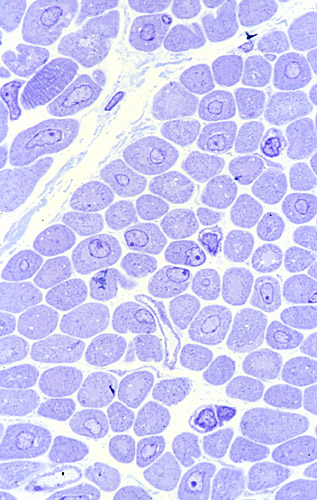
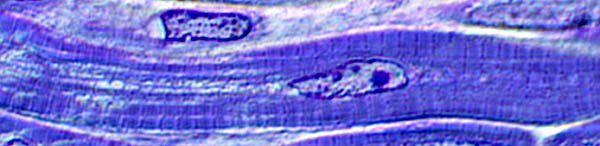 Toluidine blue stain |
Central nuclei & abnormal internal architecture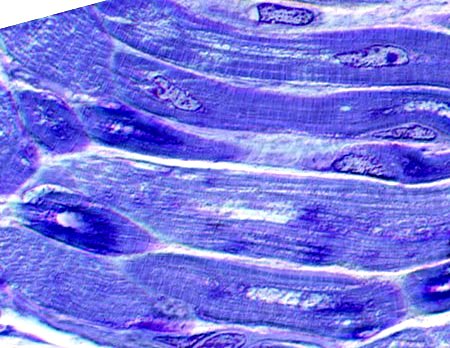 Toluidine blue stain |
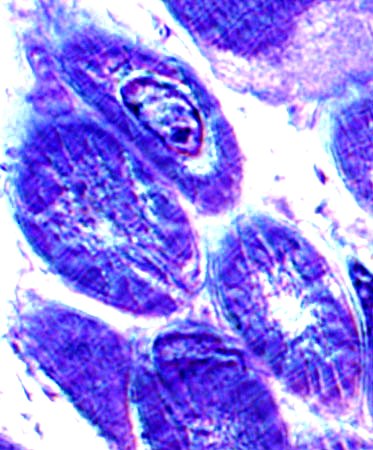 Toluidine blue stain |
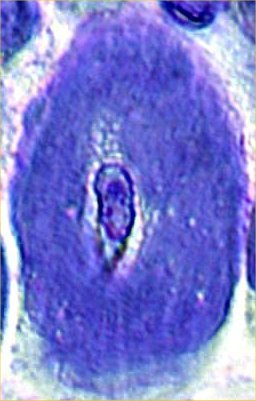 Toluidine blue stain |
A single central nucleus is present in many muscle fibers
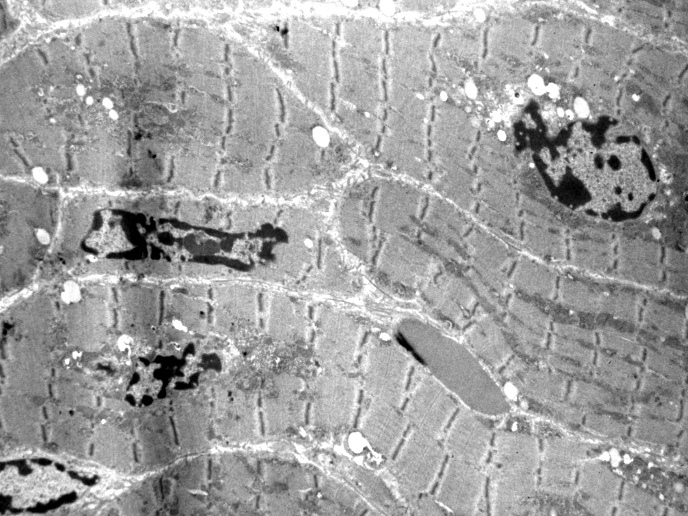
|
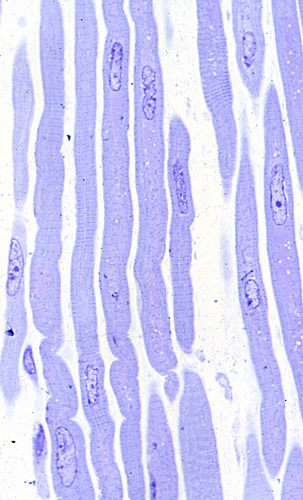
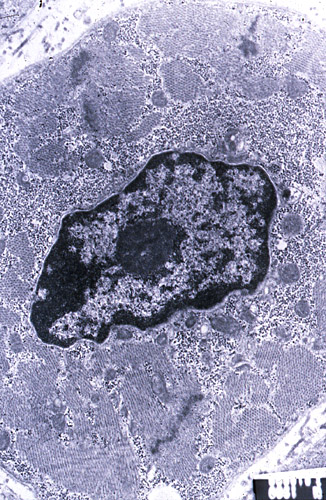 Electron microscopy from T Mozaffar |
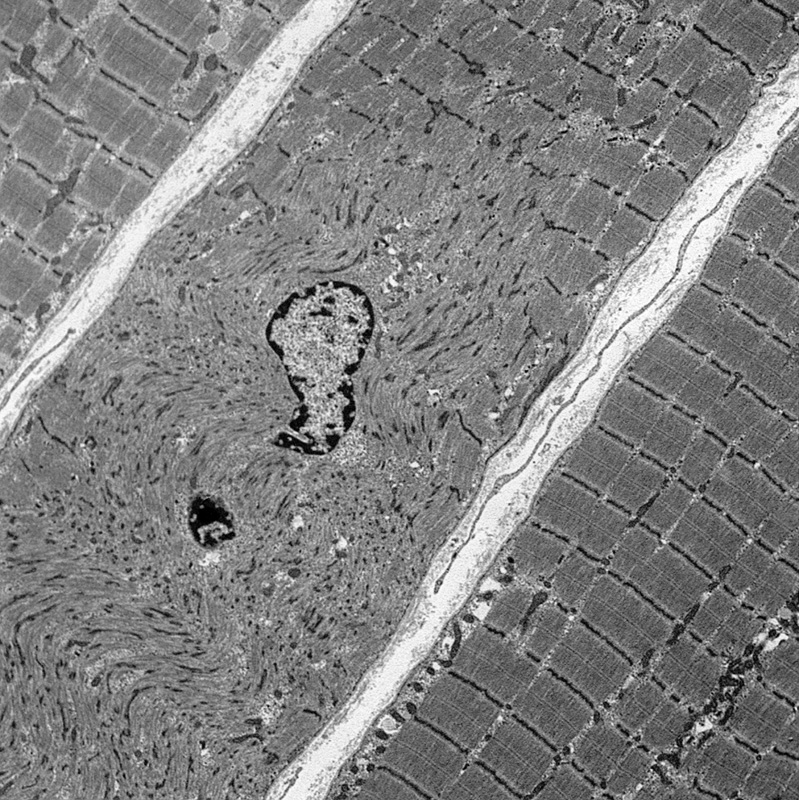
|
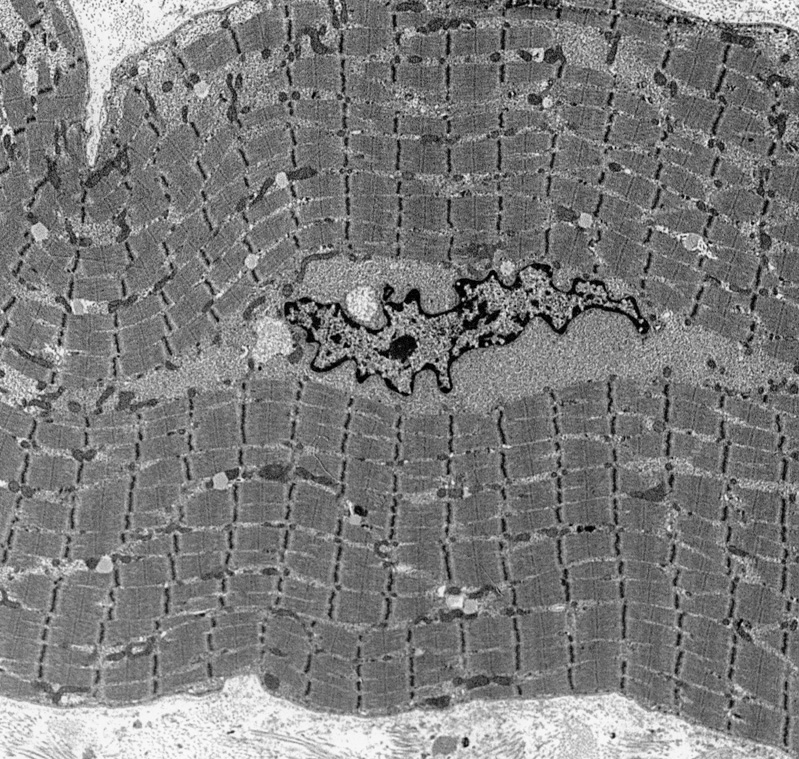
|
Type I (light) muscle fibers tend to be smaller than type II.
Clear regions occur in center of some fibers.
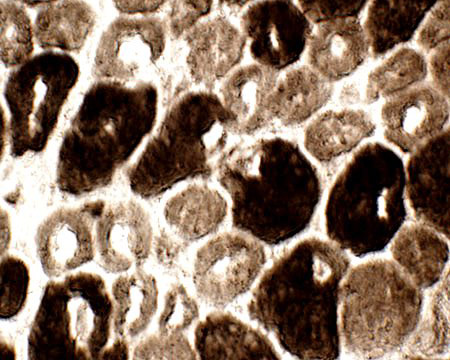 ATPase stain, pH 9.4 |
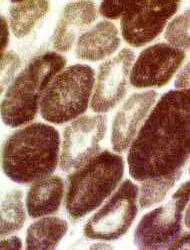 ATPase stain, pH 9.4 |
Internal architecture: Small "Halo" muscle fibers.
Darker staining: Central regions
Clear rim around edge
Common in MTM1 mutations
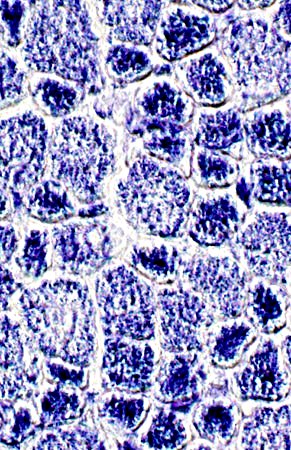 NADH stain |
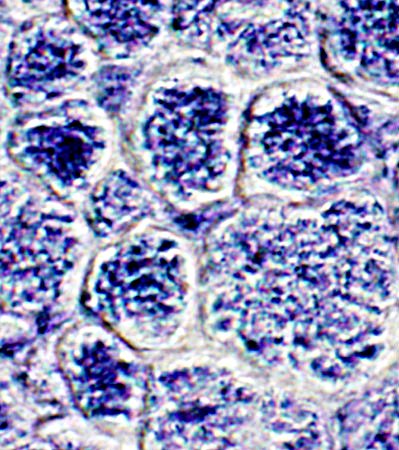 NADH stain |
   NADH stain |
Centronuclear myopathy: Childhood
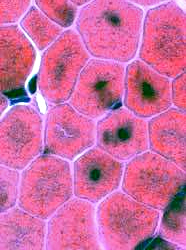 H&E stain |
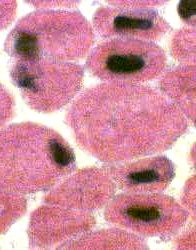 H&E stain |
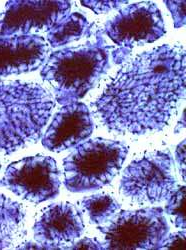 NADH stain |
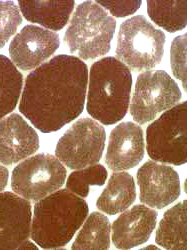 ATPase stain, pH 9.4 |
|
Some smaller muscle fibers Central nuclei Other muscle fibers Central regions are basophilic. |
Abnormal internal architecture. Central dark staining. Coarse Radial strands |
Type I (light) muscle fibers Smaller than type II Clear central regions |
|
|
Muscle fibers with abnormal internal architecture, including "radial" strands and necklace fibers 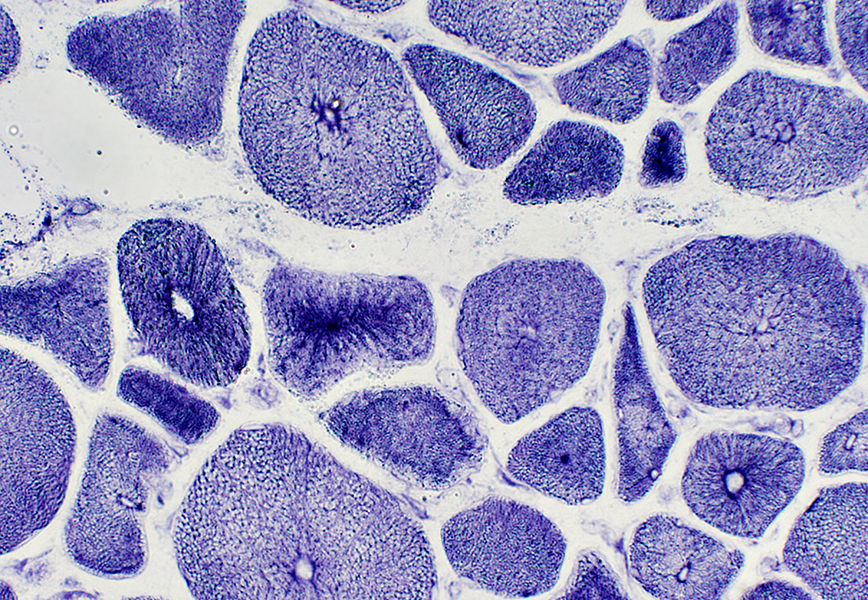 NADH stain |
Centronuclear myopathy: Juvenile with Necklace fibers |
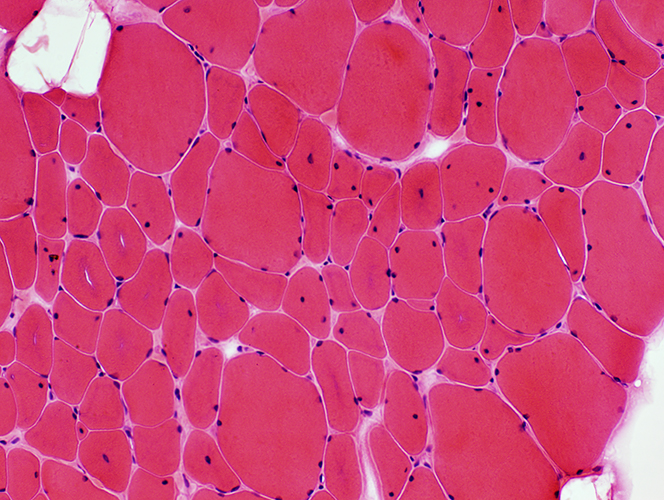 H&E stain |
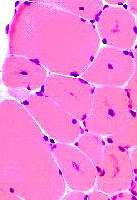 H&E stain |
|
Muscle fiber sizes: Bimodal distribution Central nuclei: Especially in smaller fibers Clefts: In center of other muscle fibers 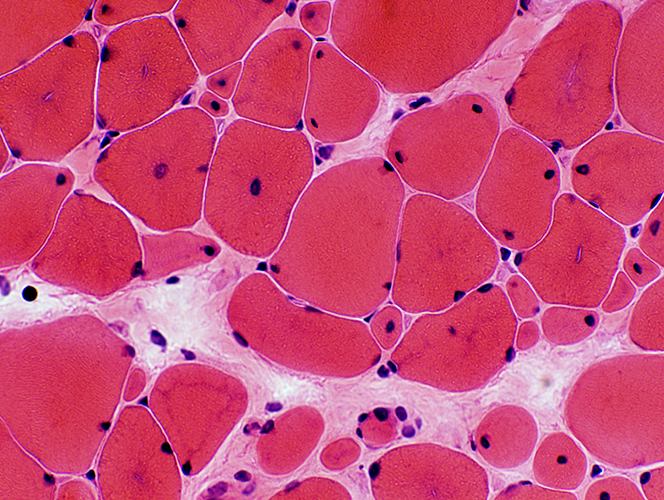 H&E stain |
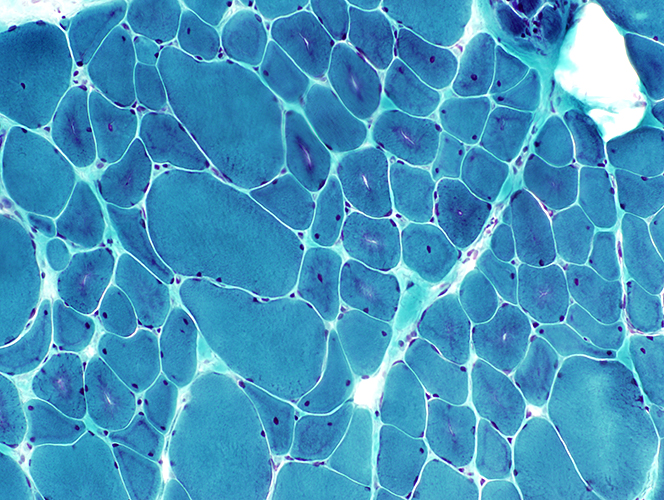 Gomori trichrome stain |
|
Central nuclei: Especially in smaller fibers Clefts: In center of other muscle fibers Rings (Necklaces): In some muscle fibers 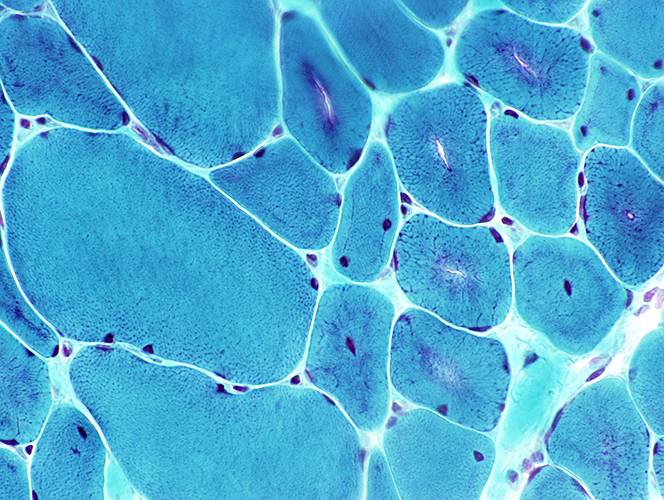 Gomori trichrome stain |
|
Necklace fibers Dark fibers: Rings Light fibers: Irregular internal architecture 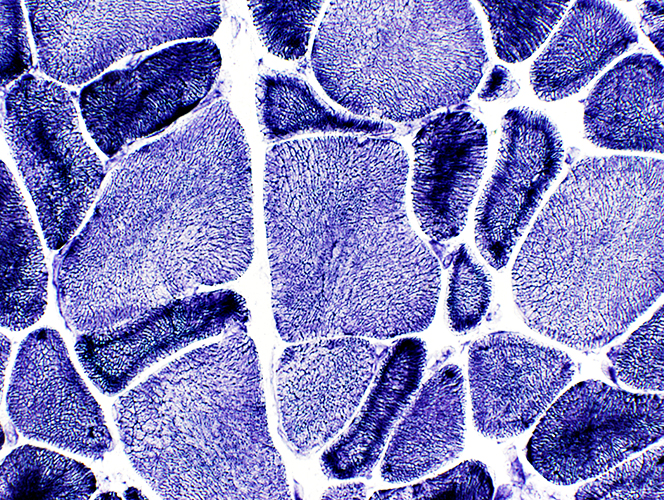 NADH stain |
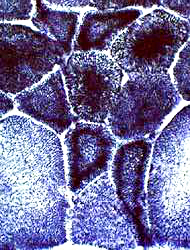 NADH stain |
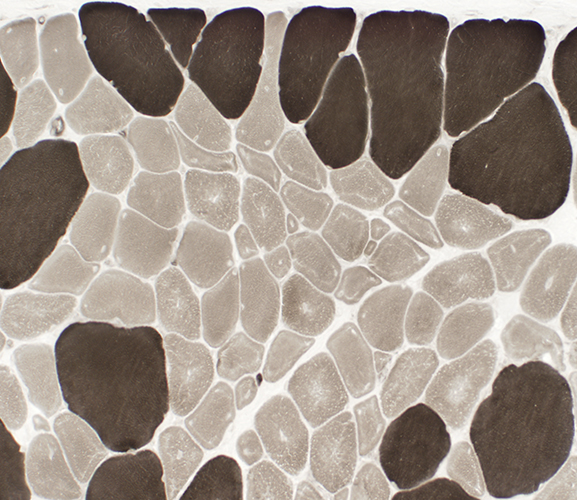
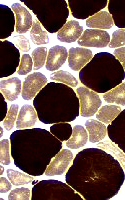 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
|
Small muscle fibers Most are type 1 Contain central clear regions 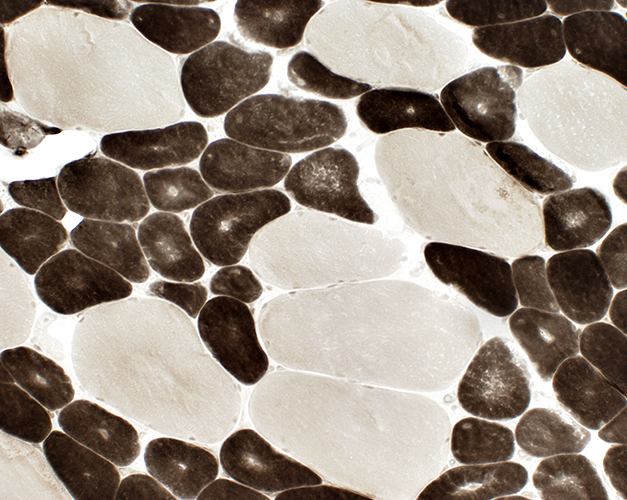 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
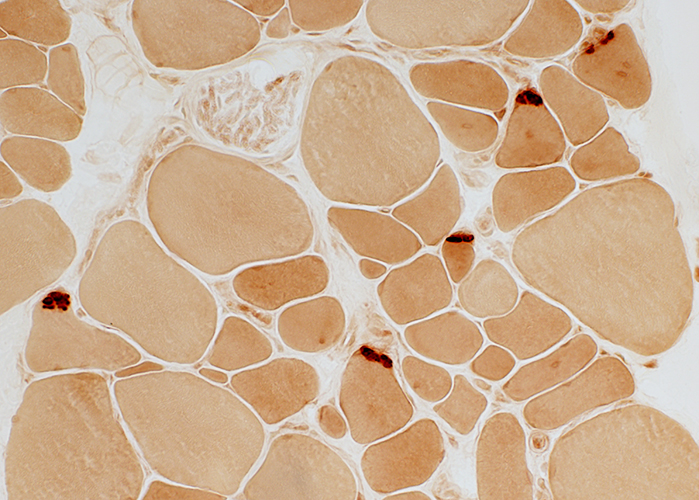 Esterase stain |
Centronuclear myopathy: Juvenile with many Central nuclei & Type 2C fibers |
 H&E stain |
Many muscle fibers have single central nuclei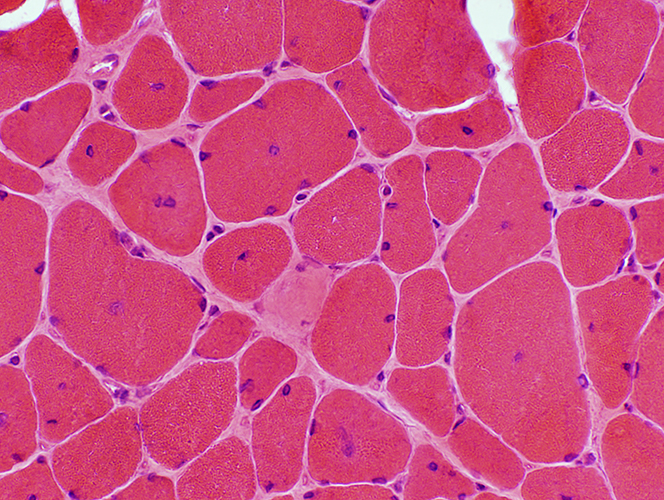 H&E stain |
 VvG stain |
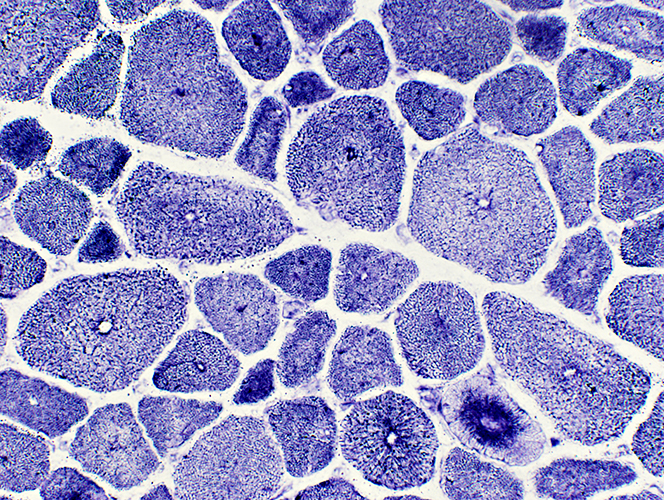 NADH stain Abnormal internal architecture around central nuclei |
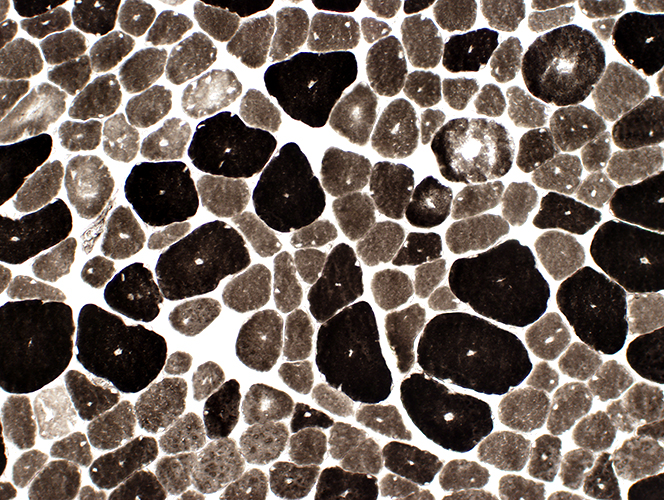 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
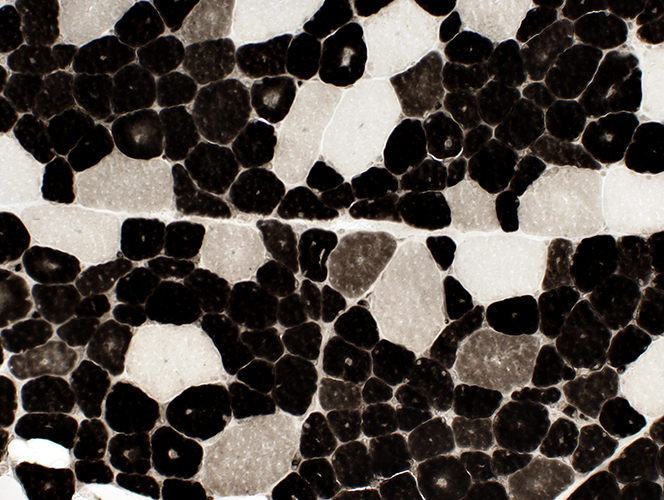 ATPase pH 4.3 stain Many abnormal, intermediate-staining (type 2C), muscle fibers |
Centronuclear myopathy: Juvenile with Small muscle fibers & Punctate central NADH stain |
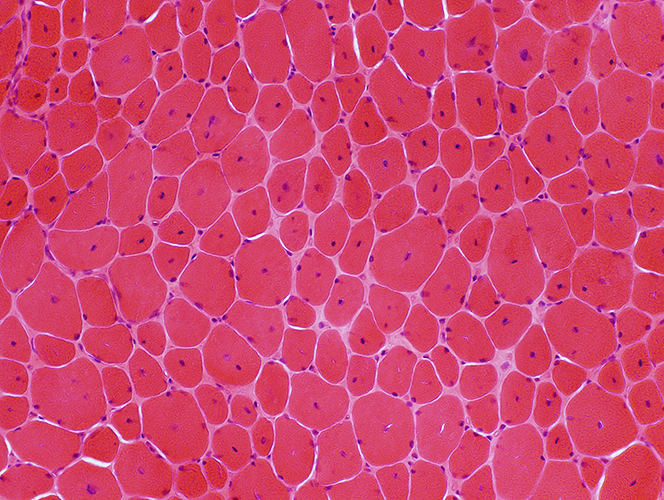 H&E stain |
Many muscle fibers have single central nuclei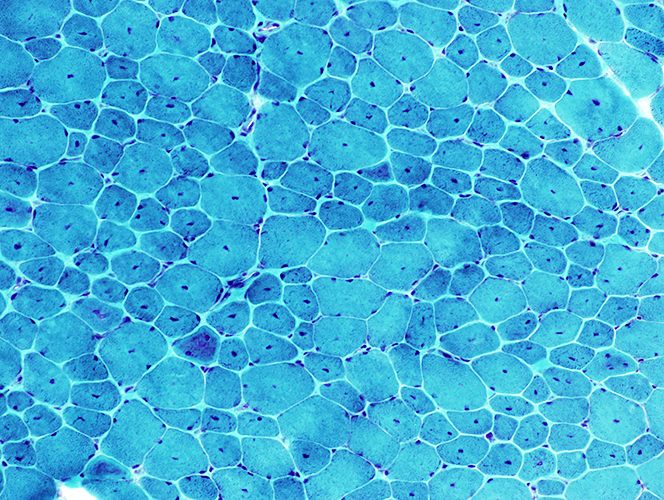 H&E stain stain |
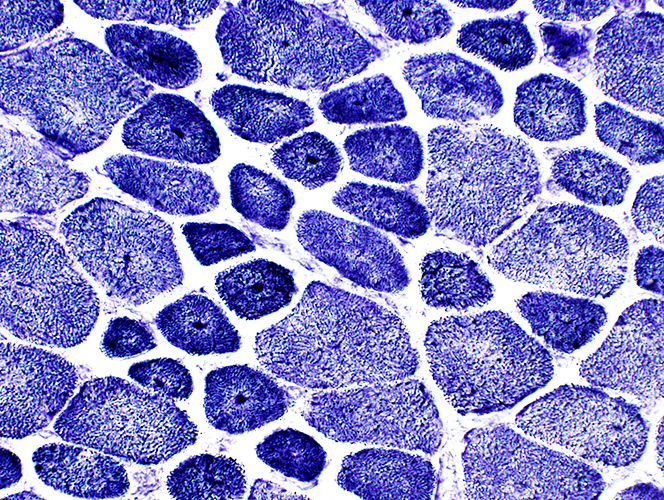 NADH stain Punctate central staining in many muscle fibers |
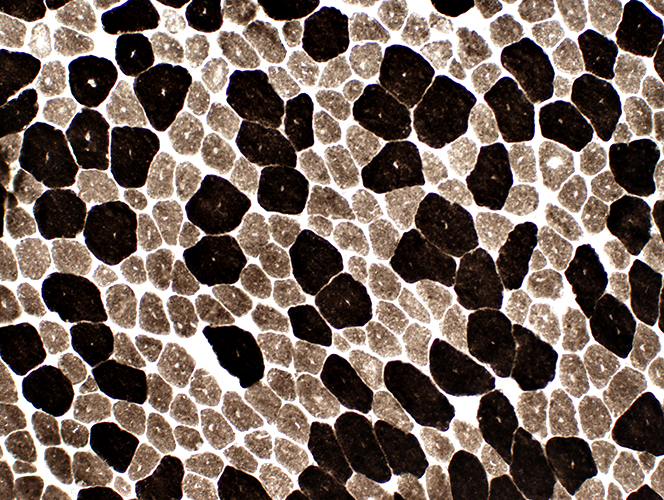 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
Type 1 muscle fibers are smaller than type 2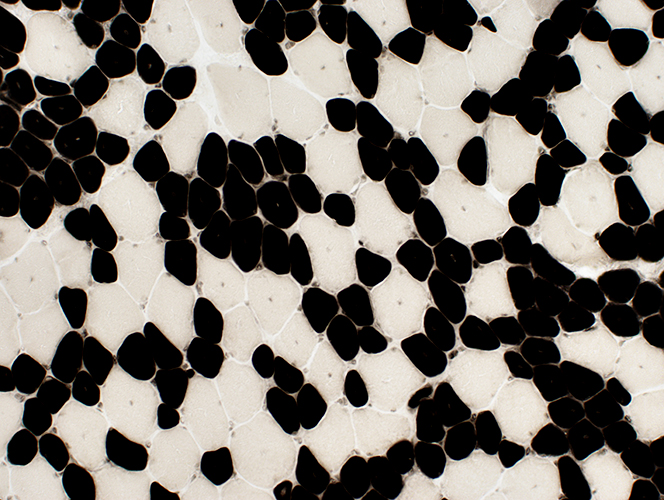 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Centronuclear myopathy: Teenage, DNM2 mutation
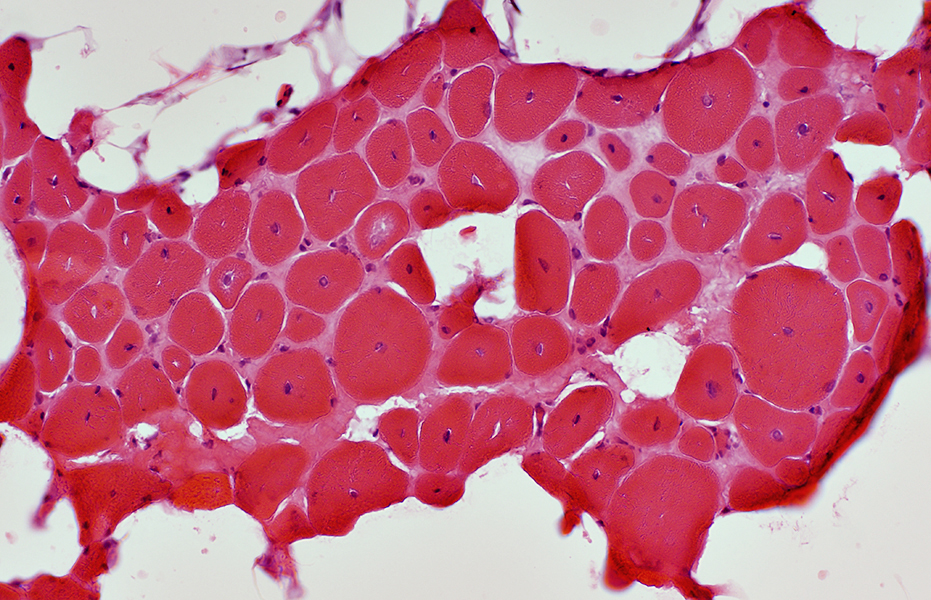 H&E stain |
|
|
Myopathic muscle Central nuclei: Single; In most muscle fibers Endomysial connective tissue: Increased between muscle fibers Fat: Replaces perimysium and some muscle 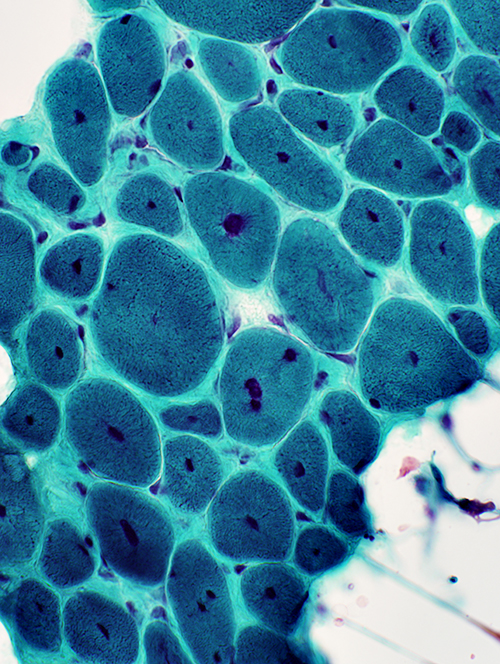 Gomori trichrome stain |
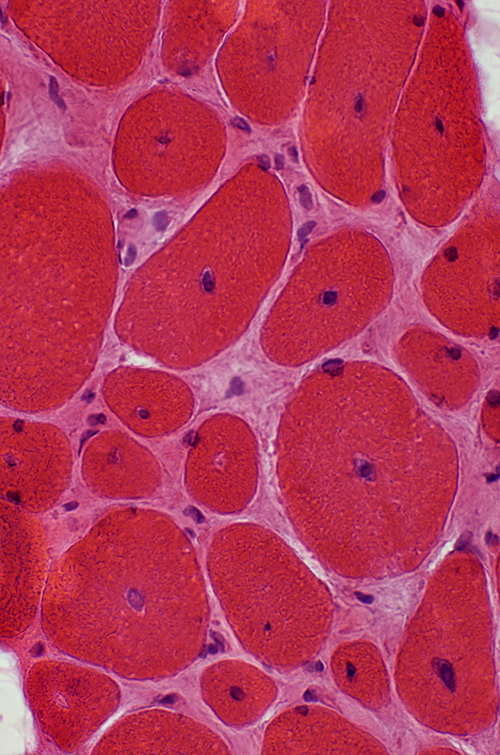 H&E stain |
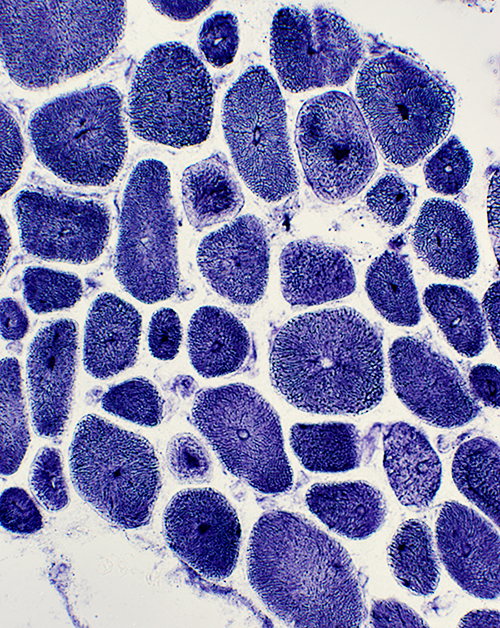 NADH stain Abnormal internal architecture Muscle fibers may have radial strands, necklace formations or central "dots" |
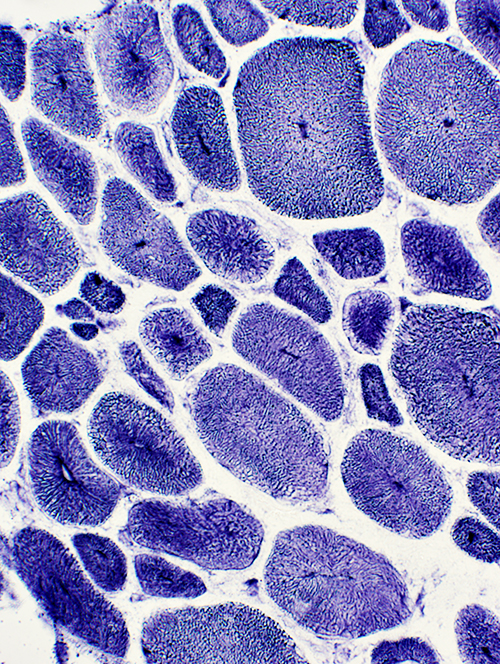 NADH stain |
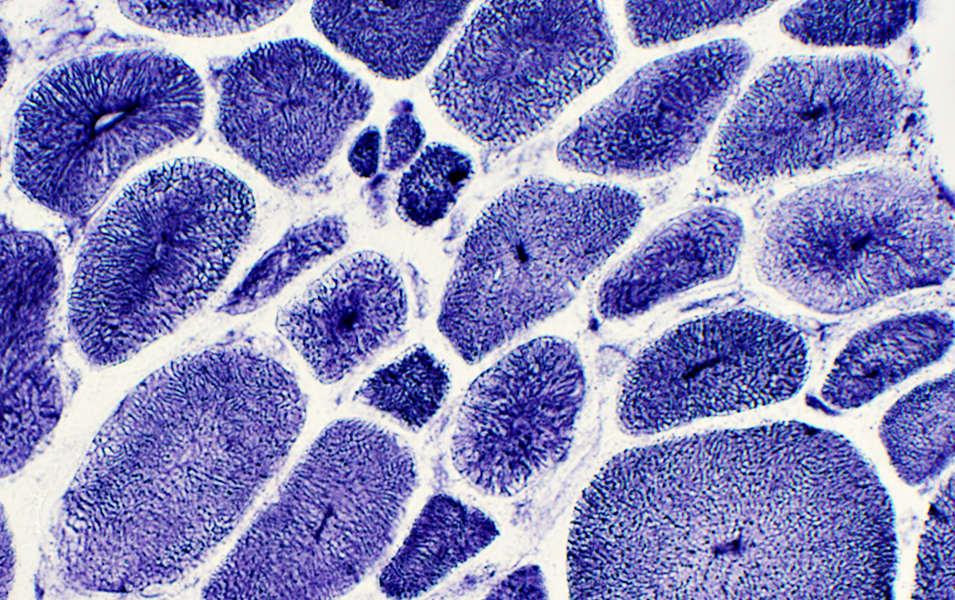 NADH stain |
|
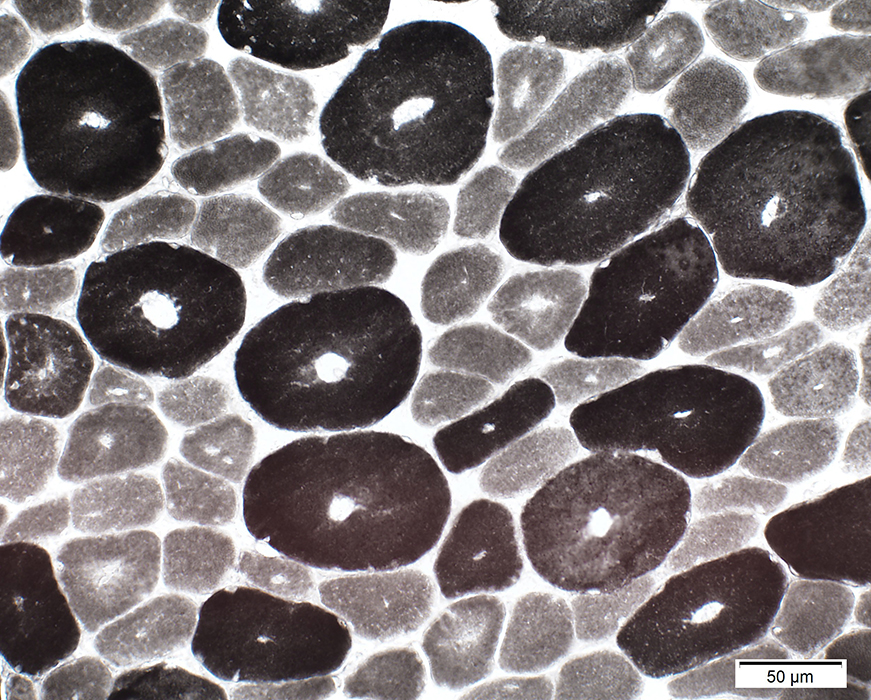 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
Type 1 fibers: Small, Predominant
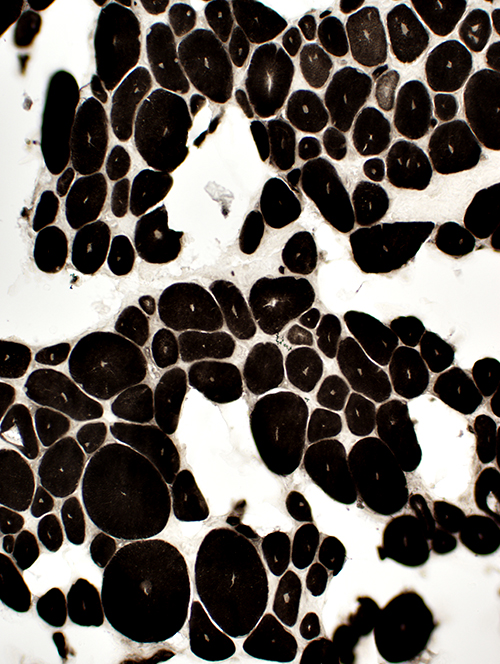 ATPase pH 4.3 stain Fiber types: All type I |
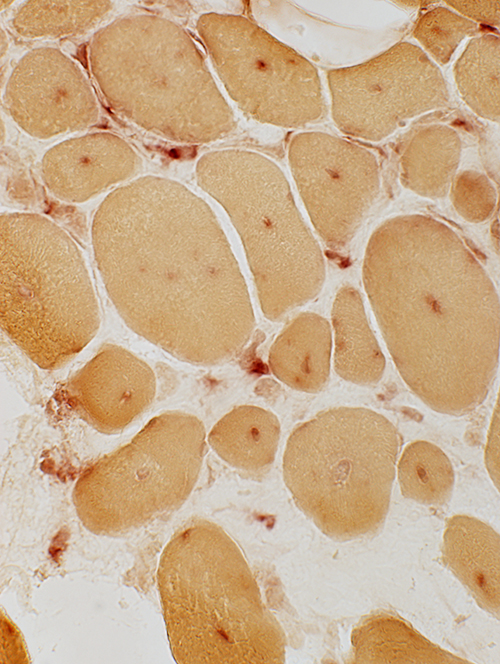 Acid phosphatase stain |
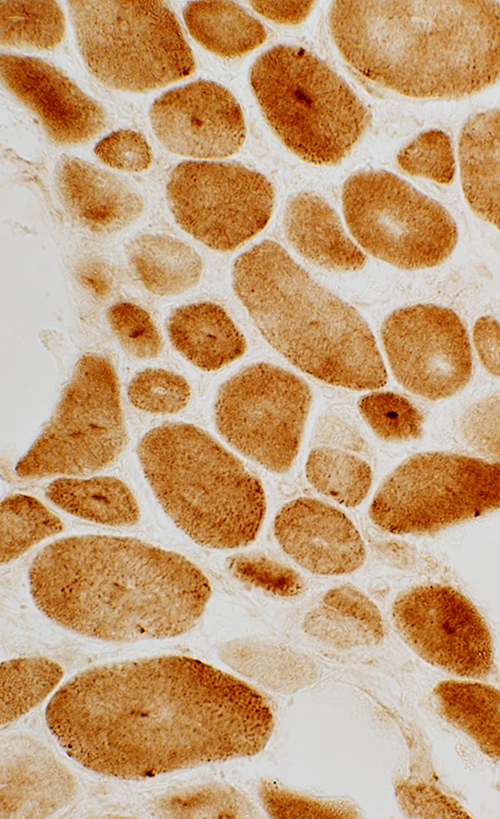 Cytochrome oxidase stain |
Central abnormalities in internal architecture Lysosomal (Acid phosphatase positive; Above) Mitochondrial (COX positive; Left) Endoplasmic reticulum (Caveolin-3 positive; Below) 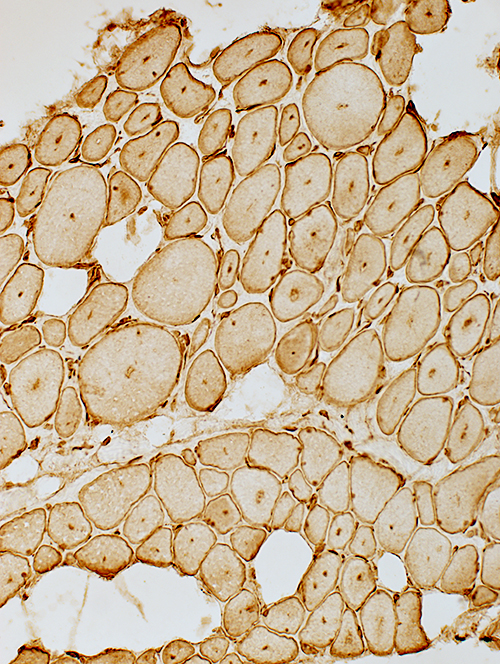 Caveolin-3 stain |
|
Cytoplasmic abnormalities: Dystrophin & Desmin staining 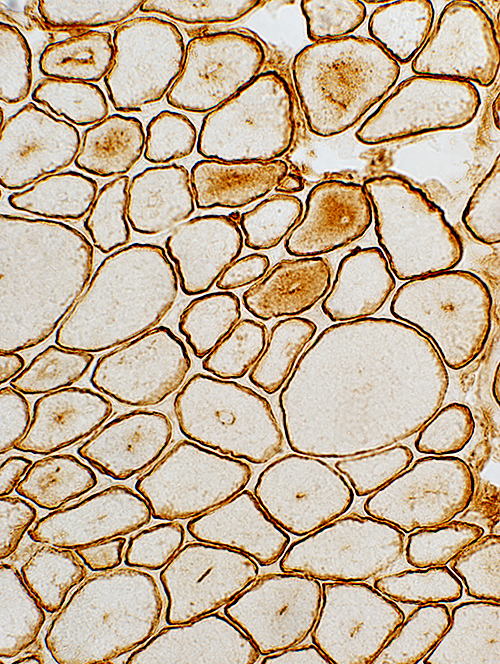 Dystrophin stain |
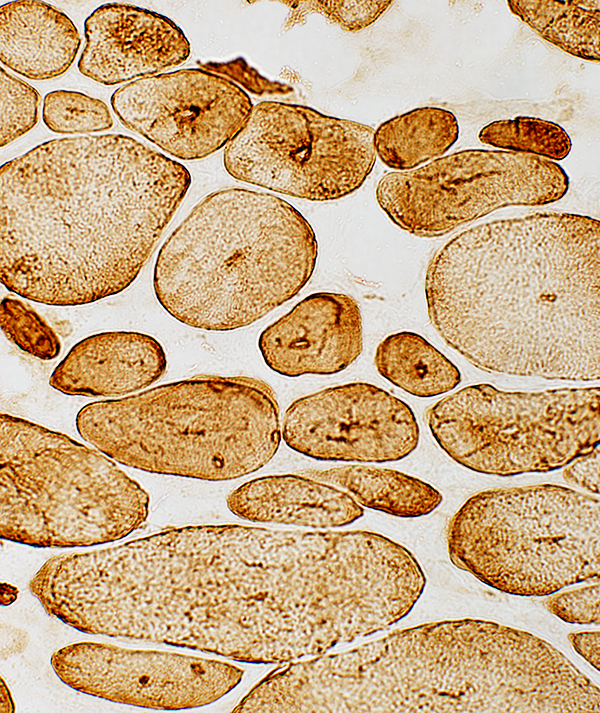 Desmin stain |
|
Nuclei: Large central nuclei with irregular emerin 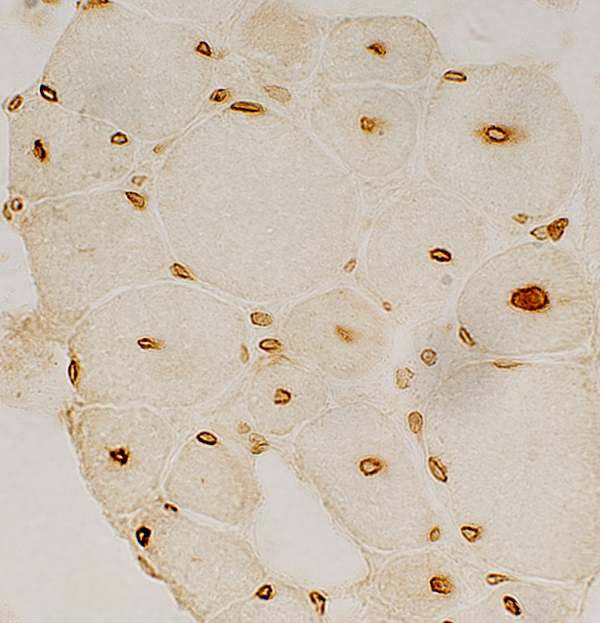 Emerin stain | |
Centronuclear Myopathy, DNM2 mutations: Individual muscle fibers
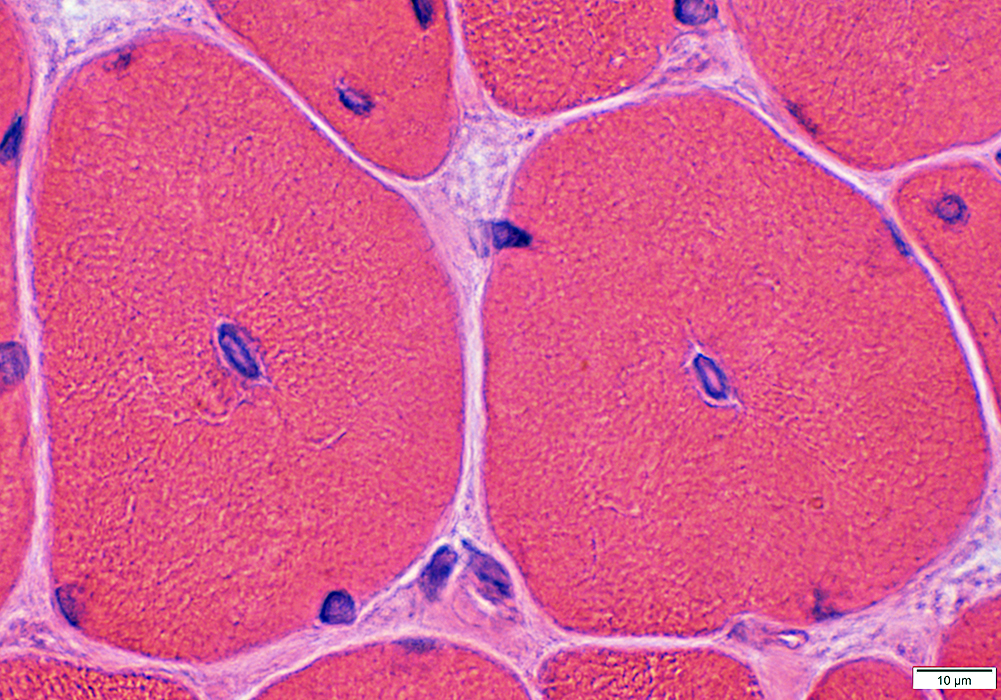 H&E stain stain |
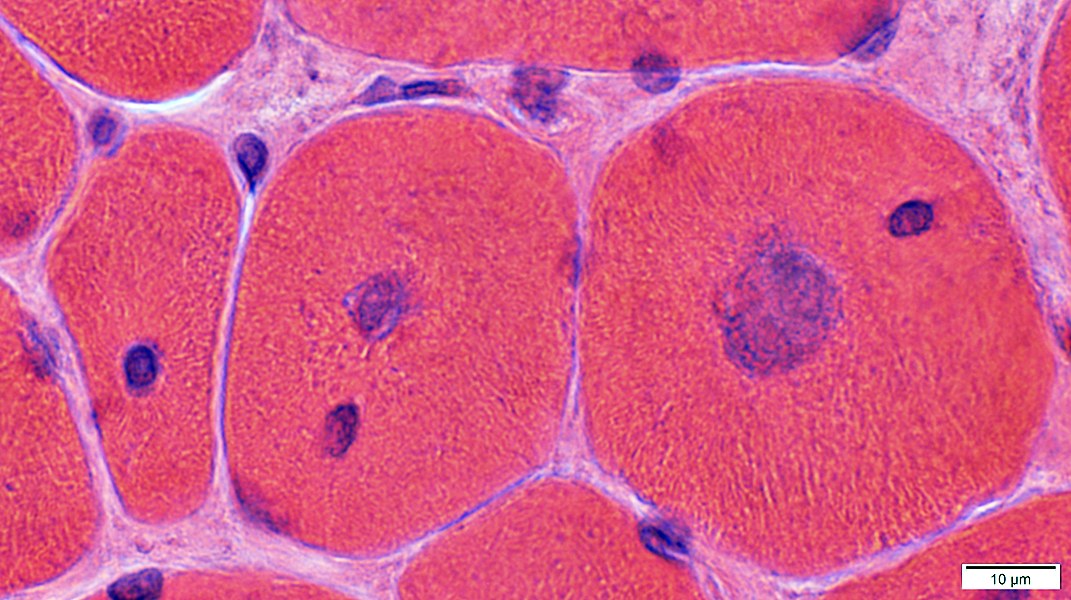 H&E stain |
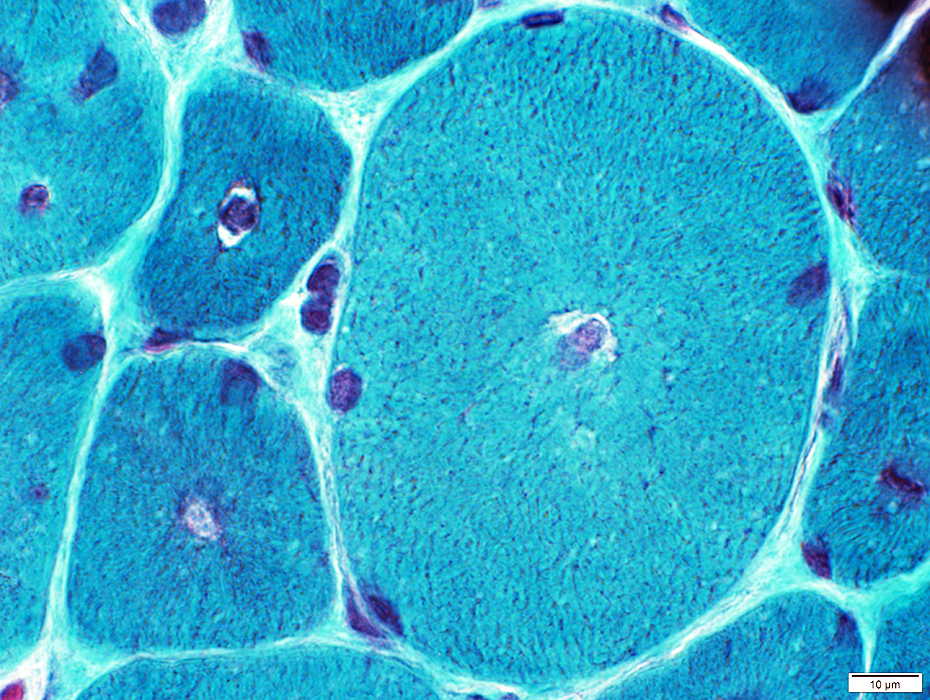 Gomori trichrome stain |
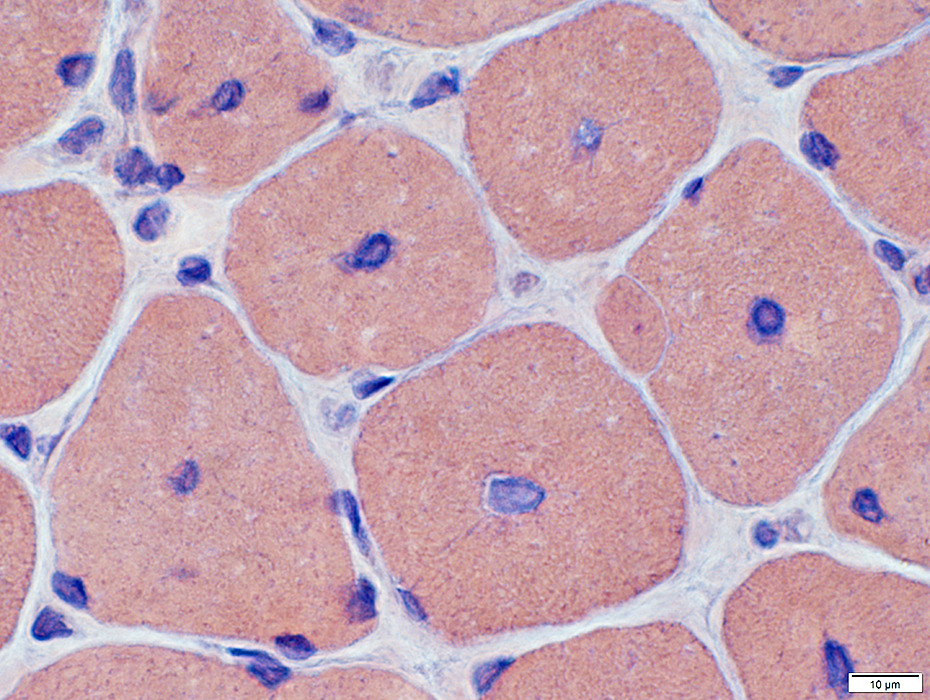 Congo red stain |
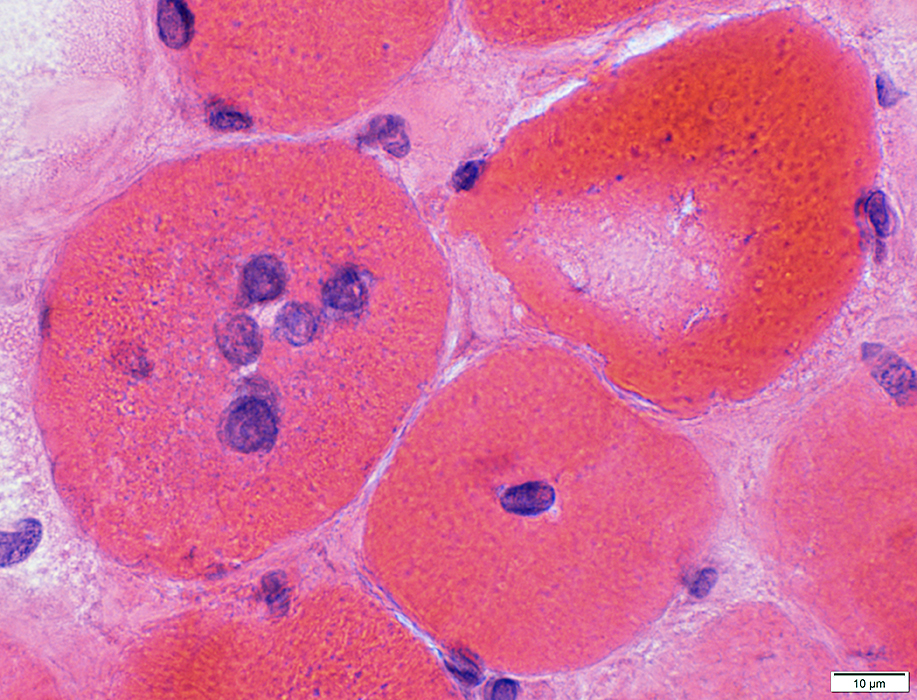 H&E stain |
Multiple central nuclei
Central pallor
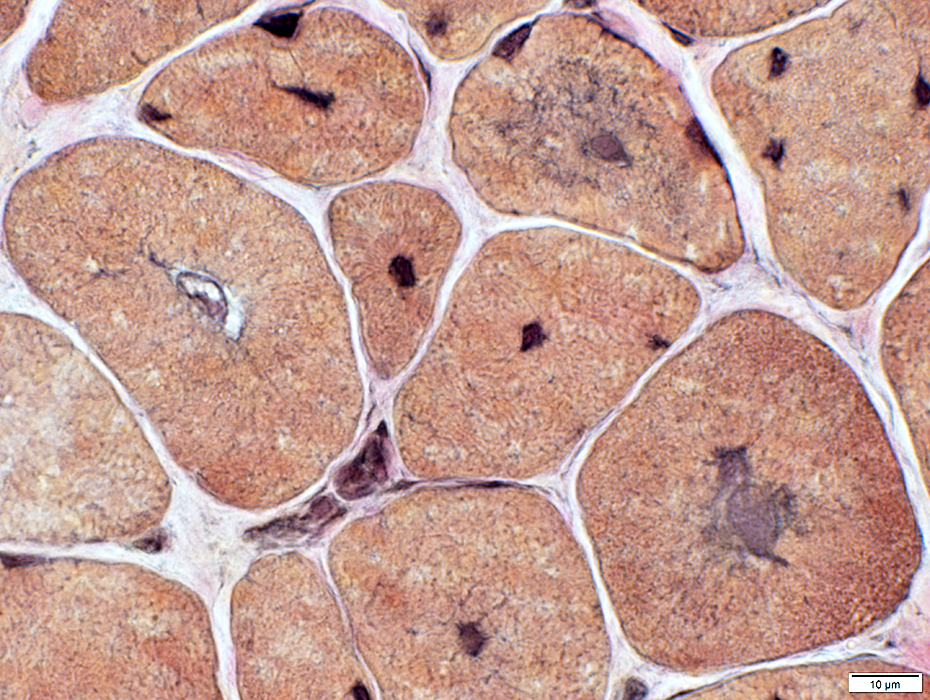 VvG stain |
Abnormal internal regions
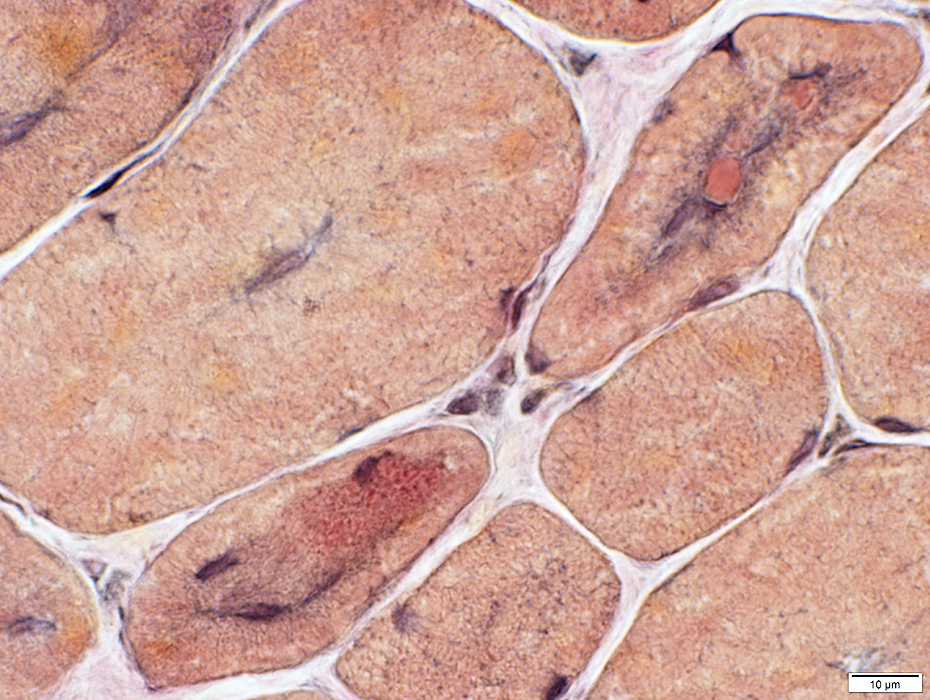 VvG stain |
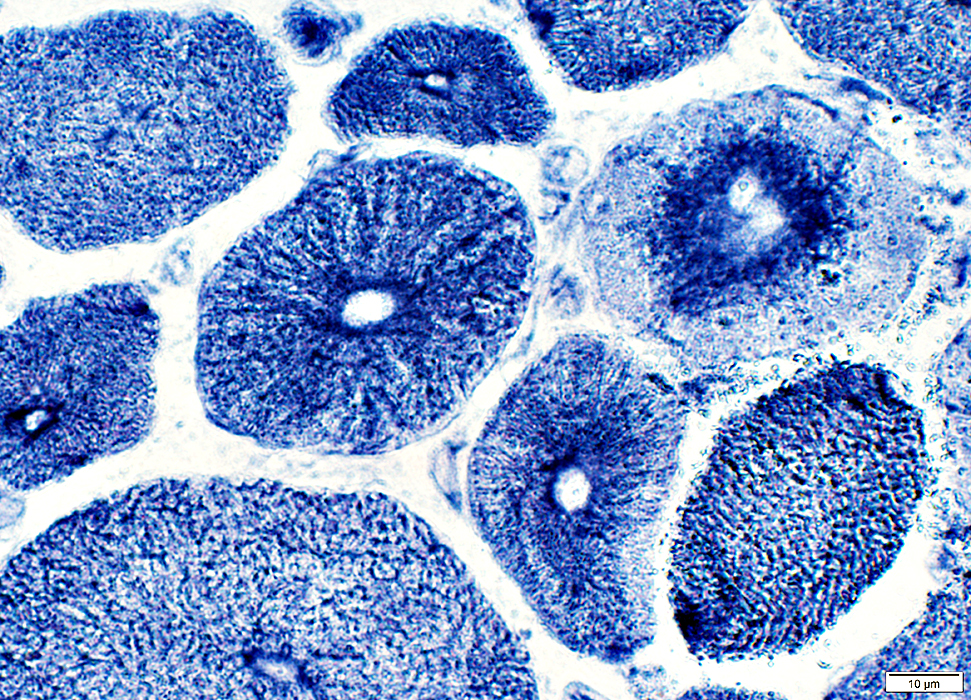 NADH stain |
Radial strands
Central clustering
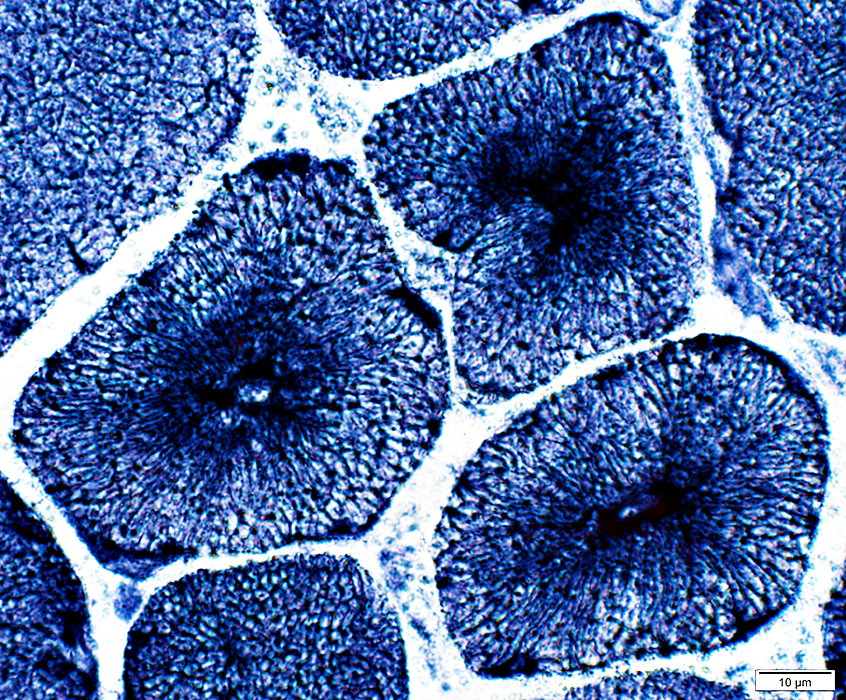 NADH stain |
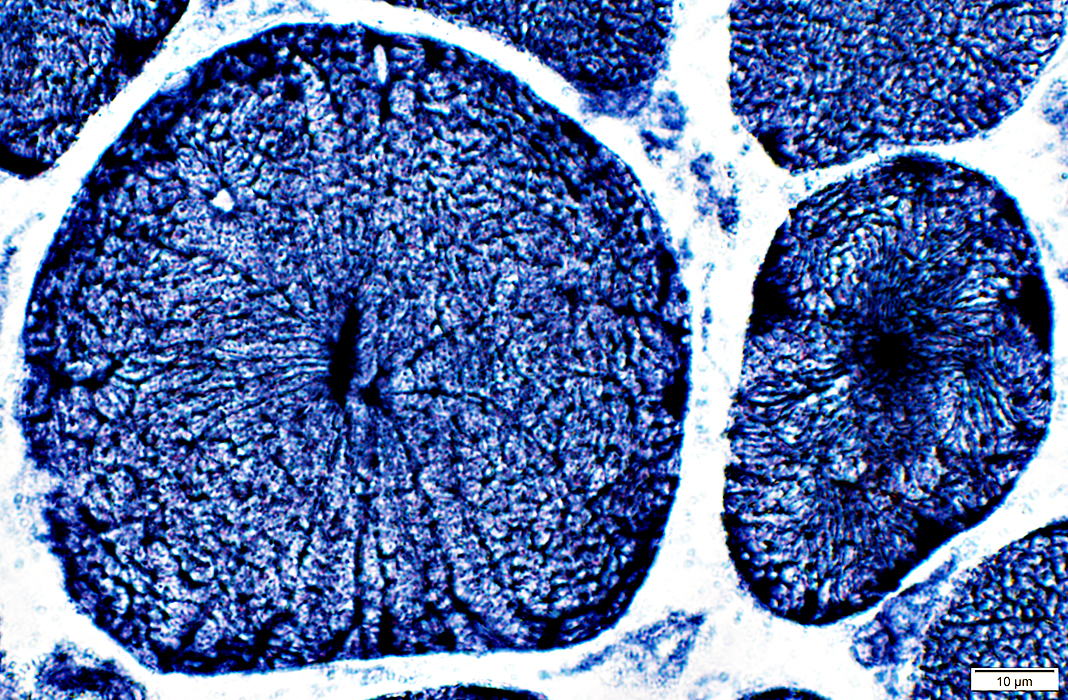 NADH stain |
Radial strands
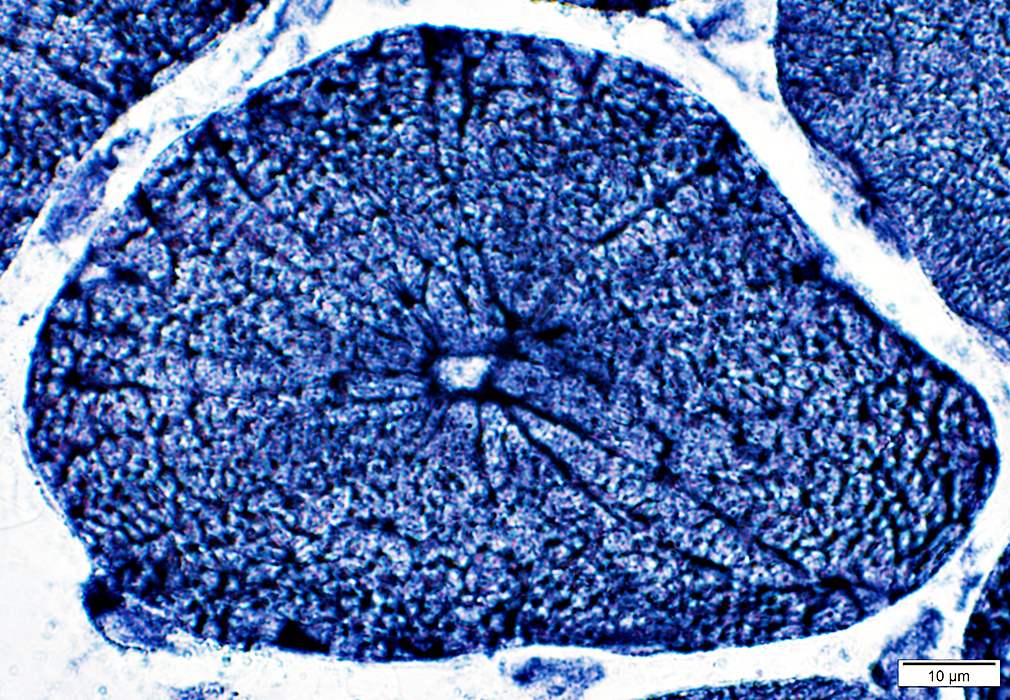 NADH stain |
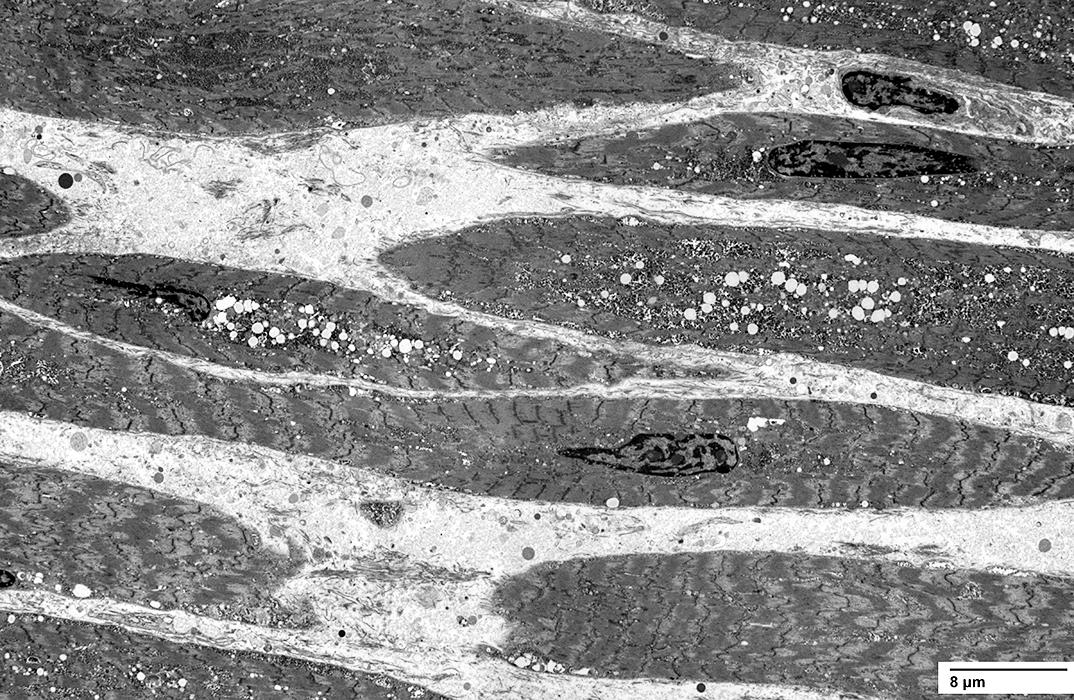 Ultrastructure From C Cai |
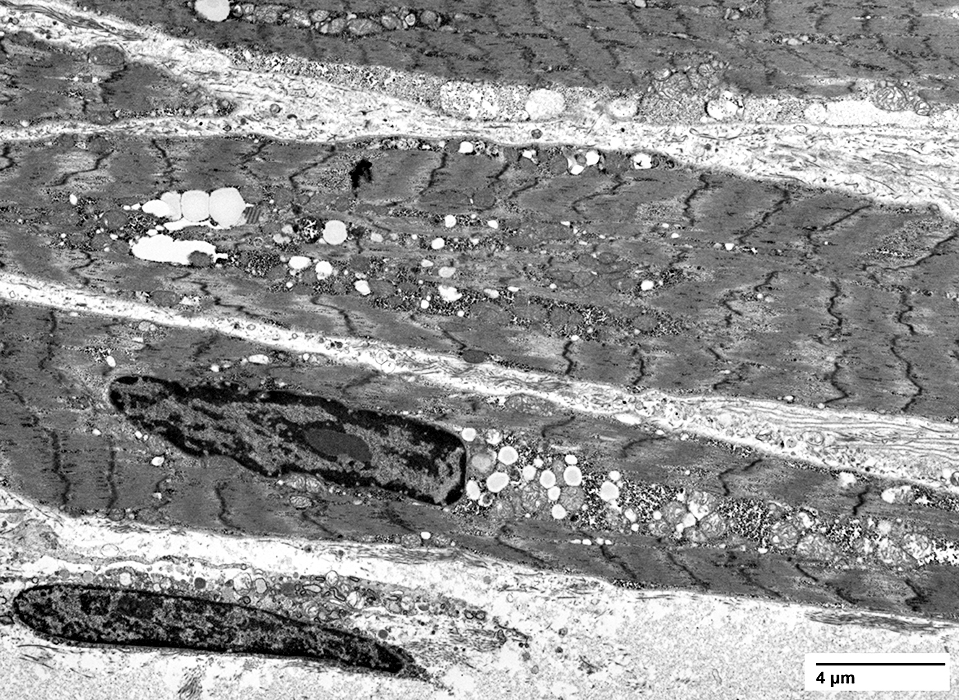 Ultrastructure From C Cai |
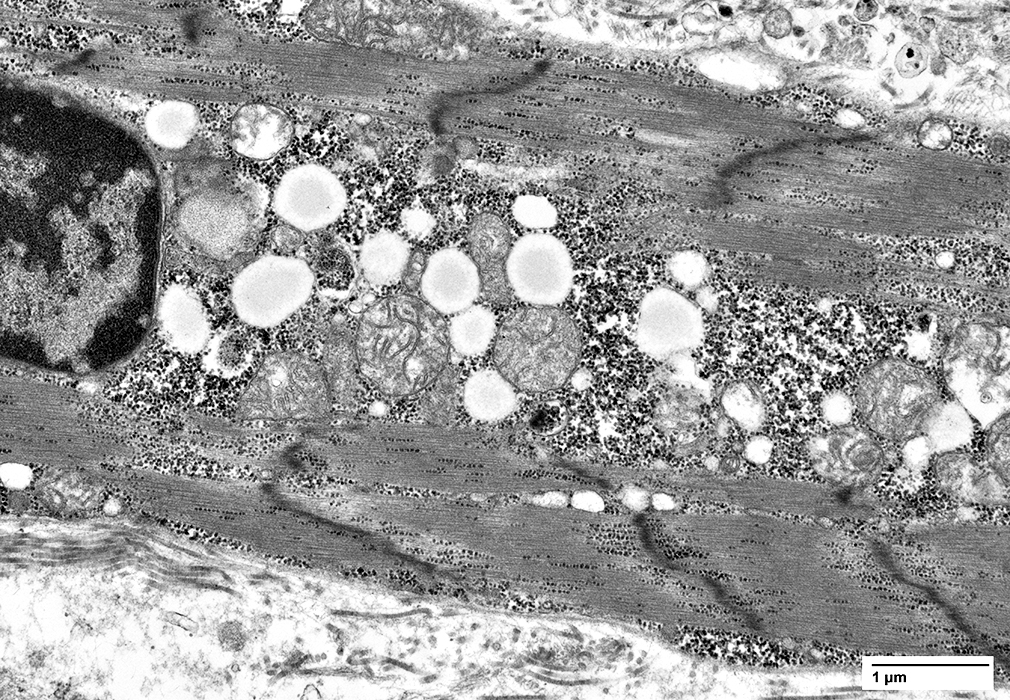 Ultrastructure From C Cai |
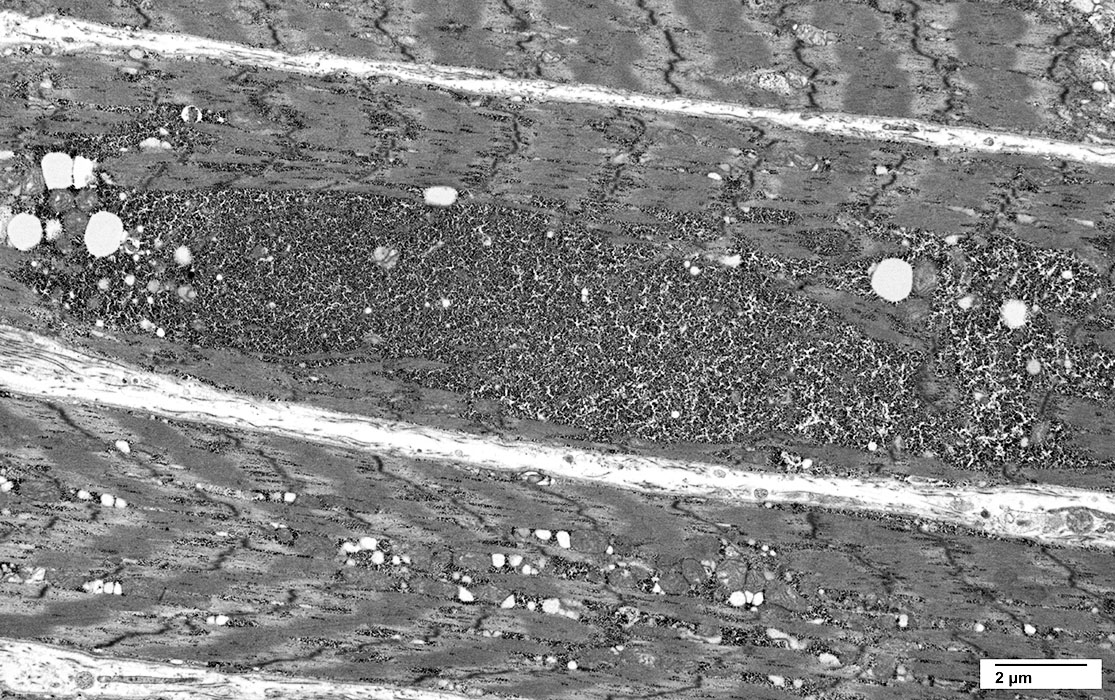 Ultrastructure From C Cai |
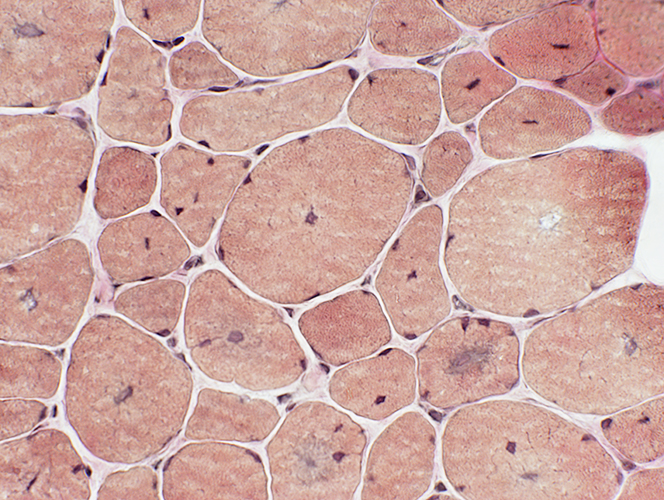
Centronuclear myopathy: Infant male (1 year), MTM1 stop mutation (Arg24X) 1
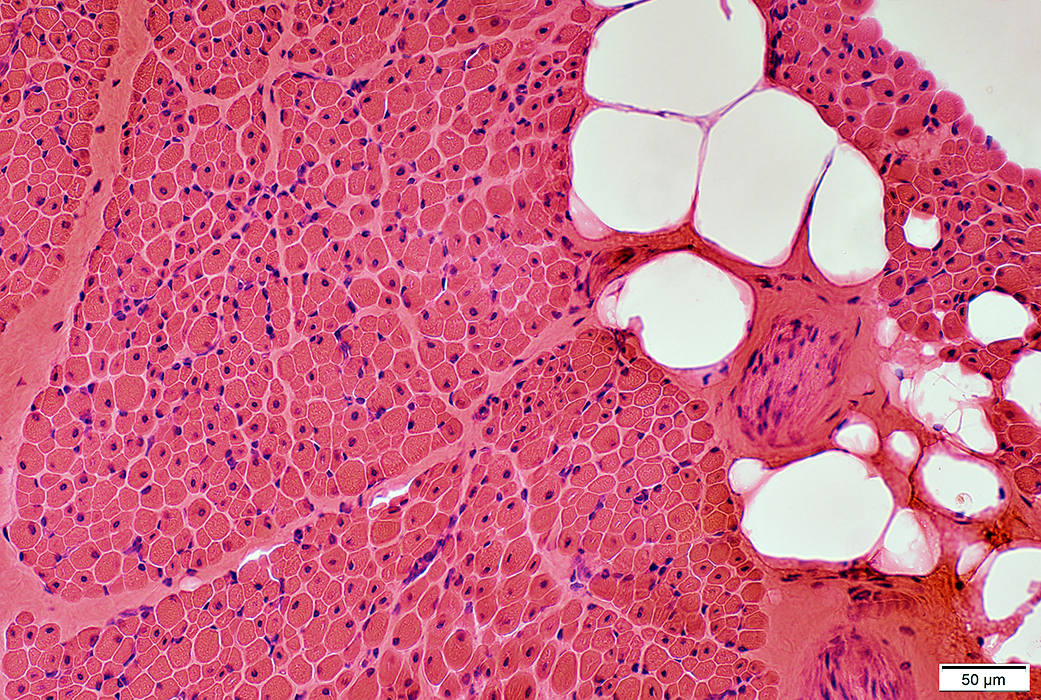 H&E stain |
Muscle fiber size: Moderately varied
Perimysium: Replaced by fat in some regions
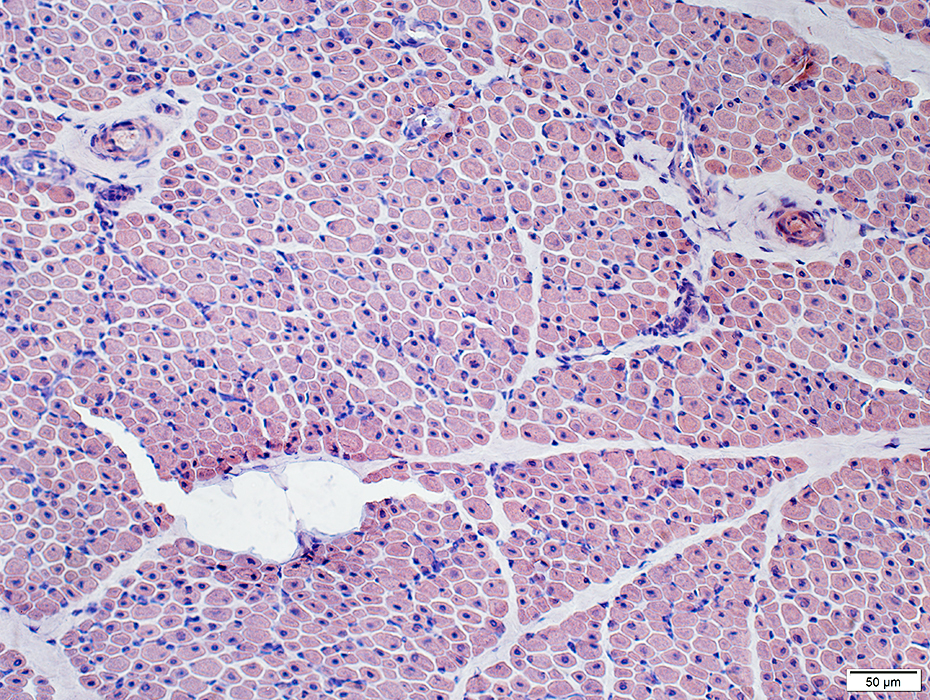 Congo red stain |
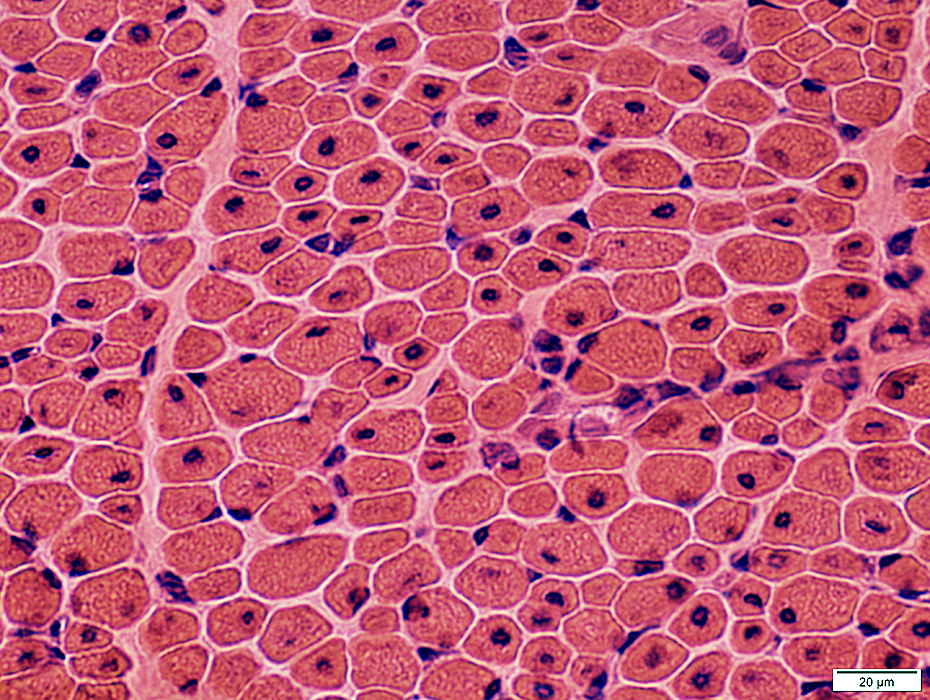 H&E stain |
Muscle fiber size: Moderately varied
Endomysial connective tissue: Normal to slightly increased
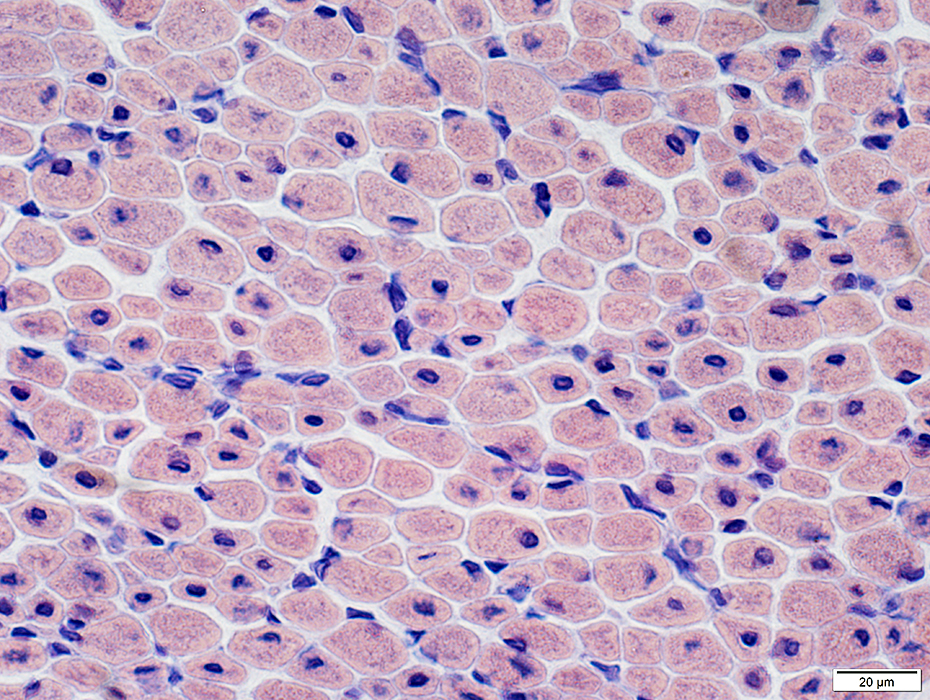 Congo red stain |
Abnormal Muscle Fibers
Many fibers have central nuclei
A few smaller muscle fibers have basophilic cytoplasm & clustered, irrregular-shaped nuclei
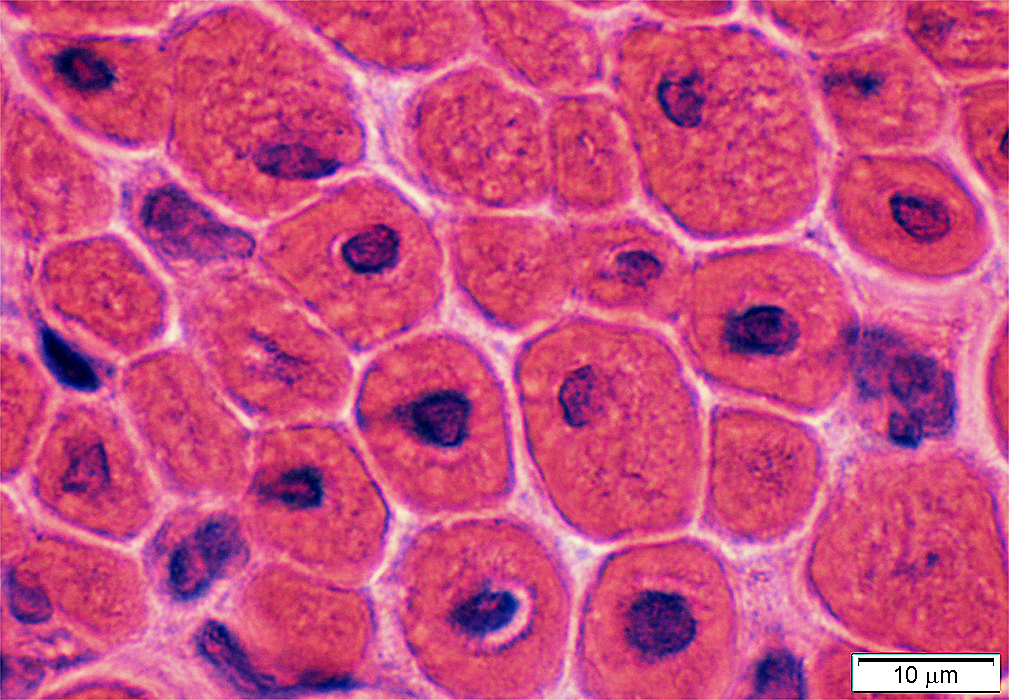 H&E stain |
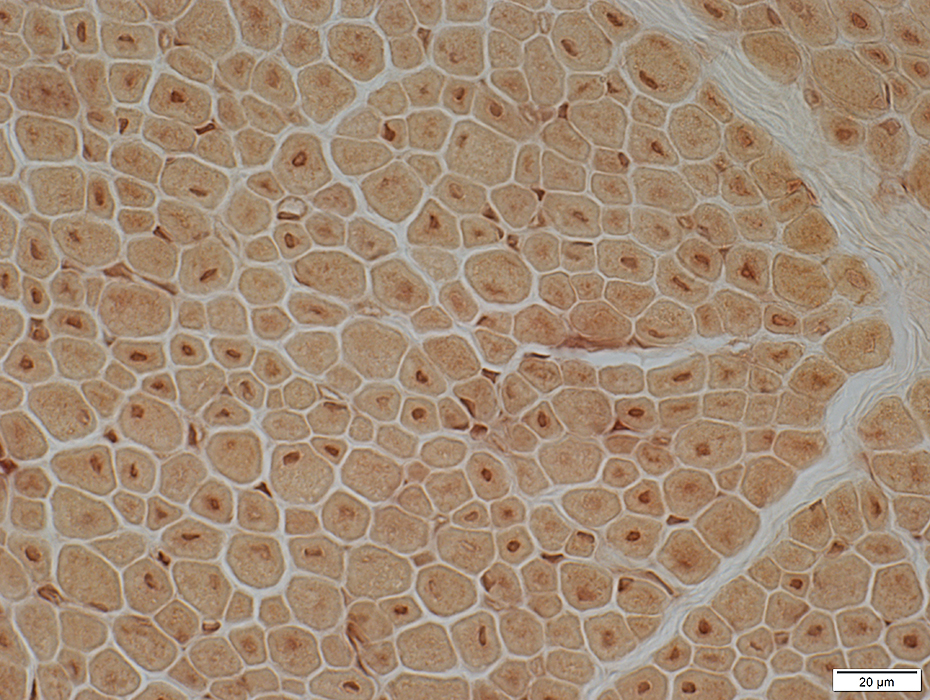 Acid phosphatase stain |
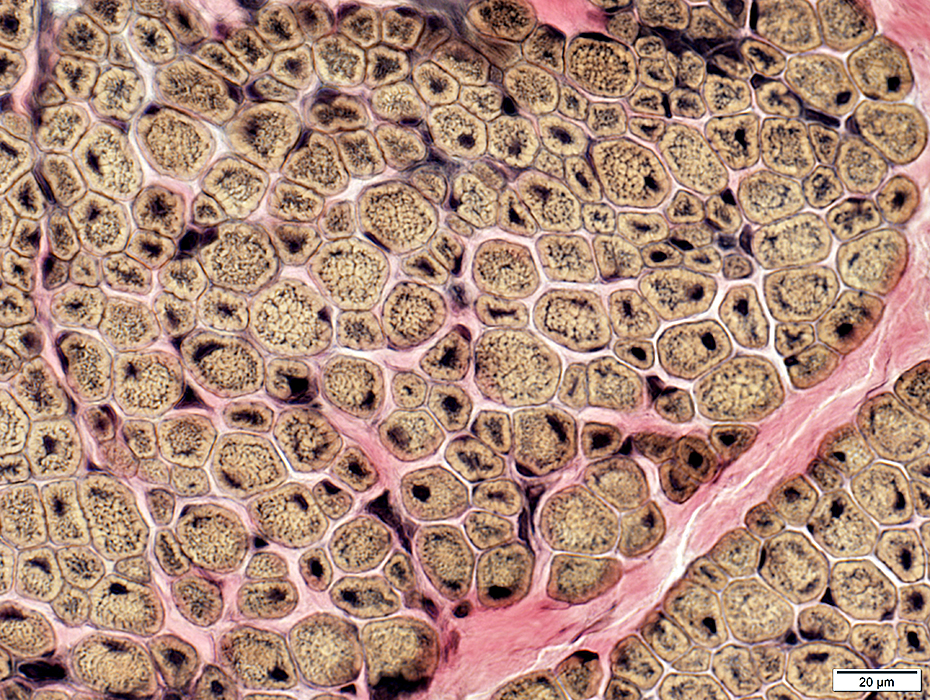 VvG stain |
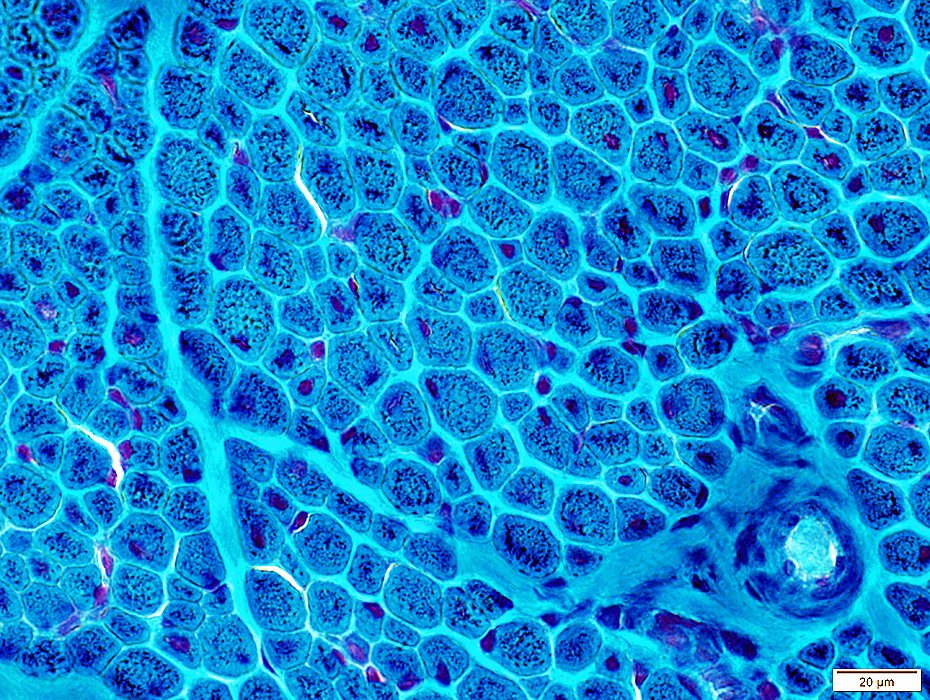 Gomori trichrome stain |
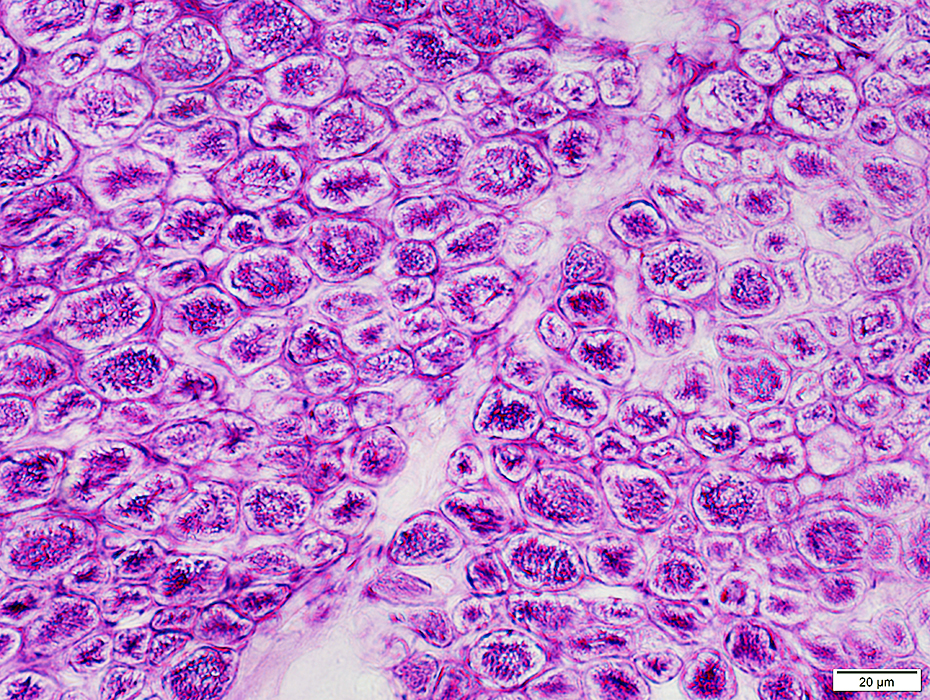 PAS stain |
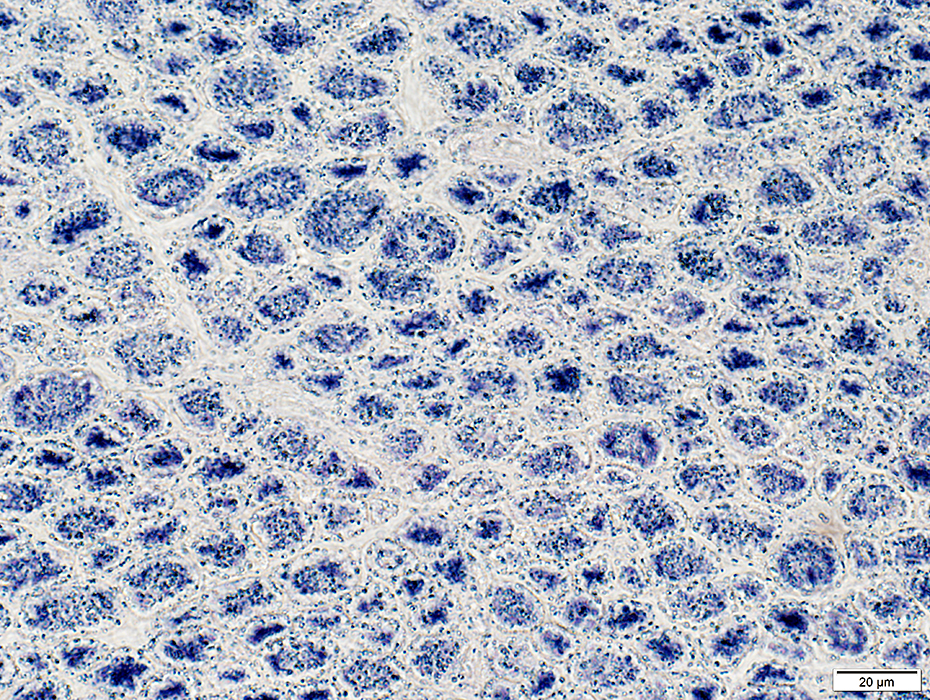 SDH stain |
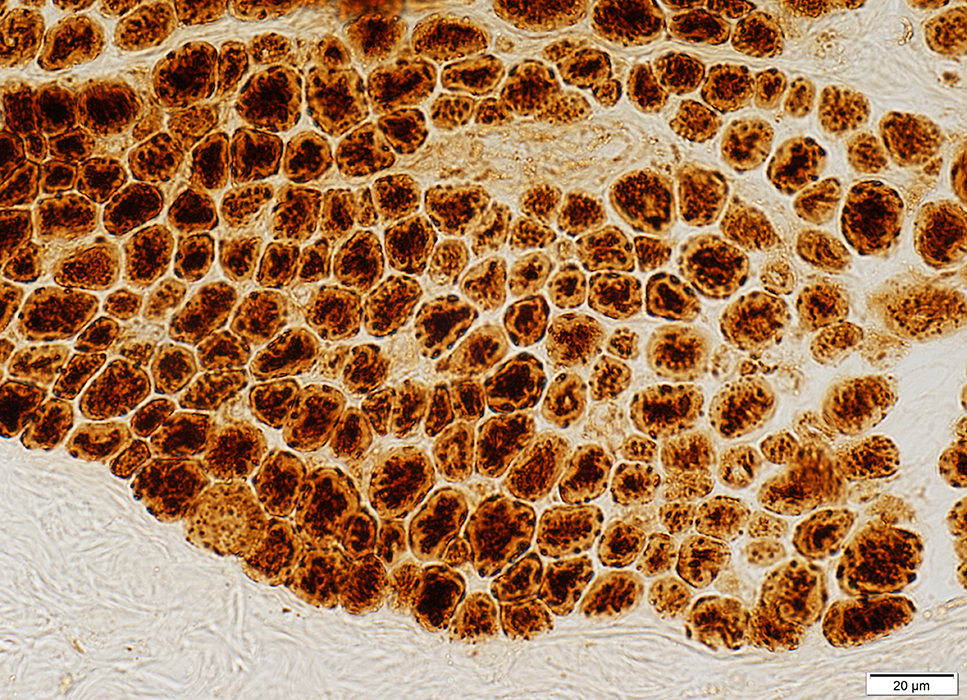 COX stain |
Peripheral halos: SR concentrated in center of muscle fibers
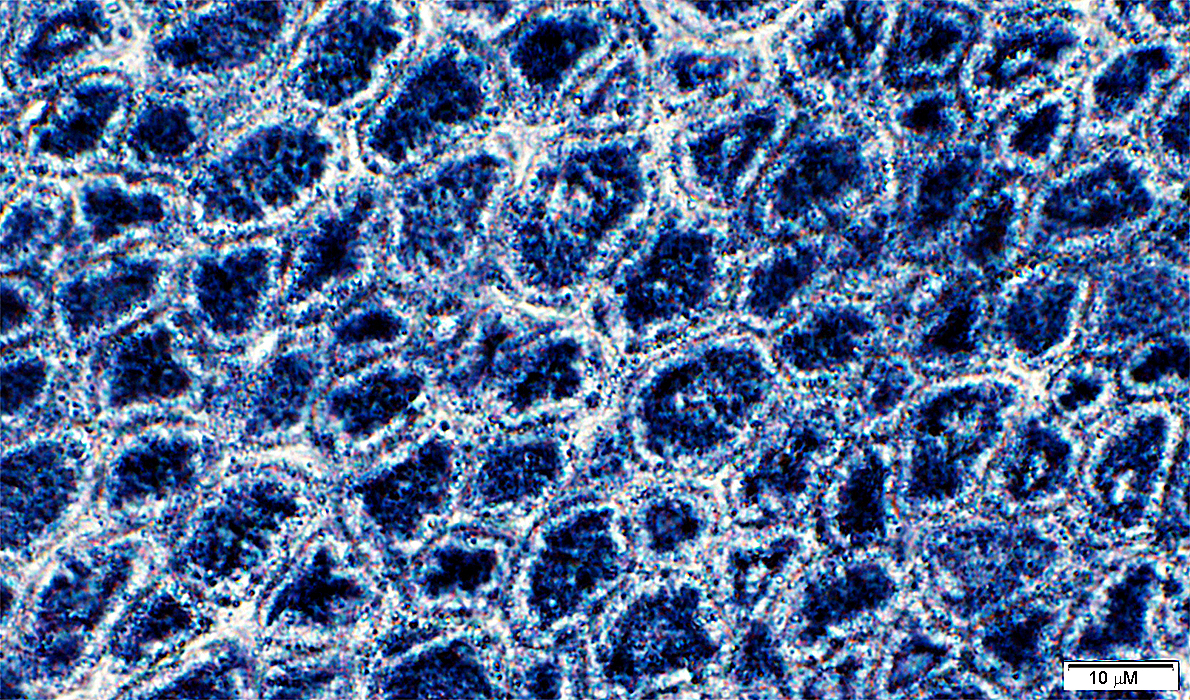 NADH stain |
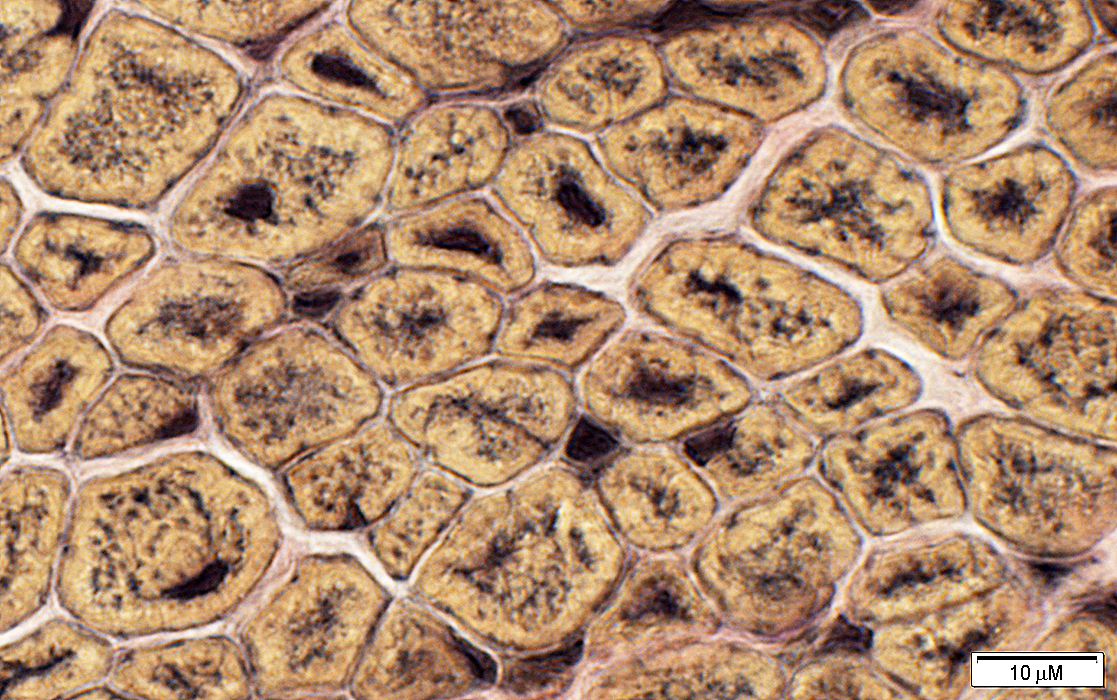 VvG stain |
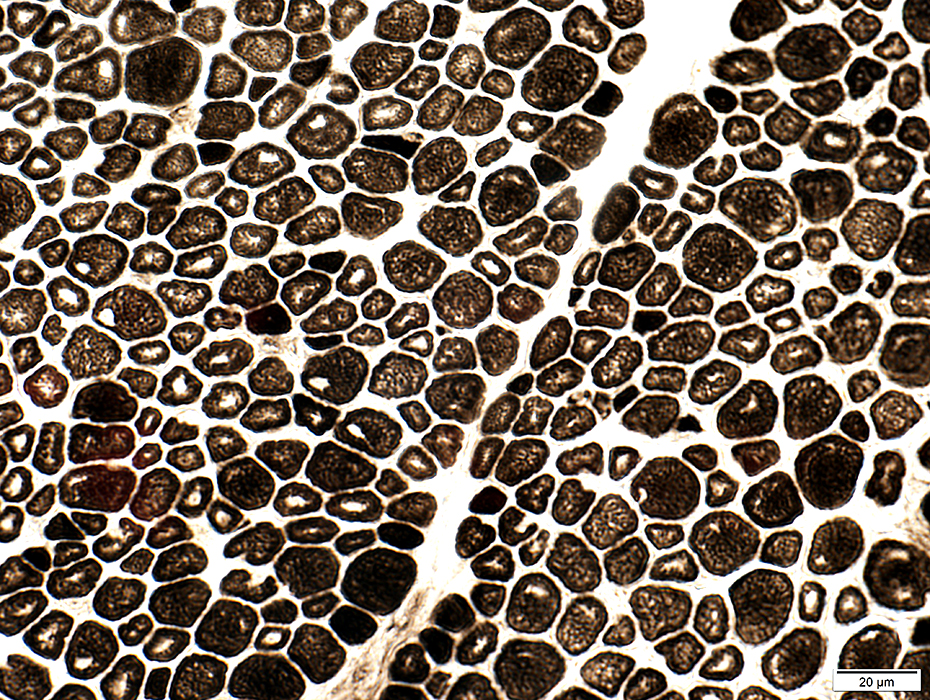 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
Type 1 predominance
Central clear regions
No halos
Some small muscle fibers are type 2C (Below)
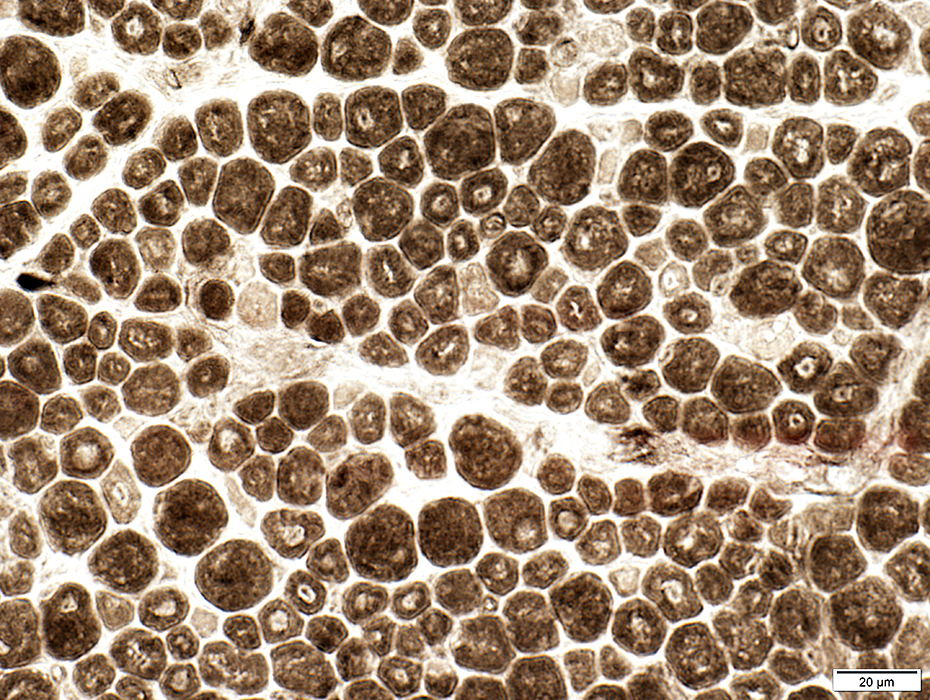 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Neuromuscular junctions: Dark stained; Large
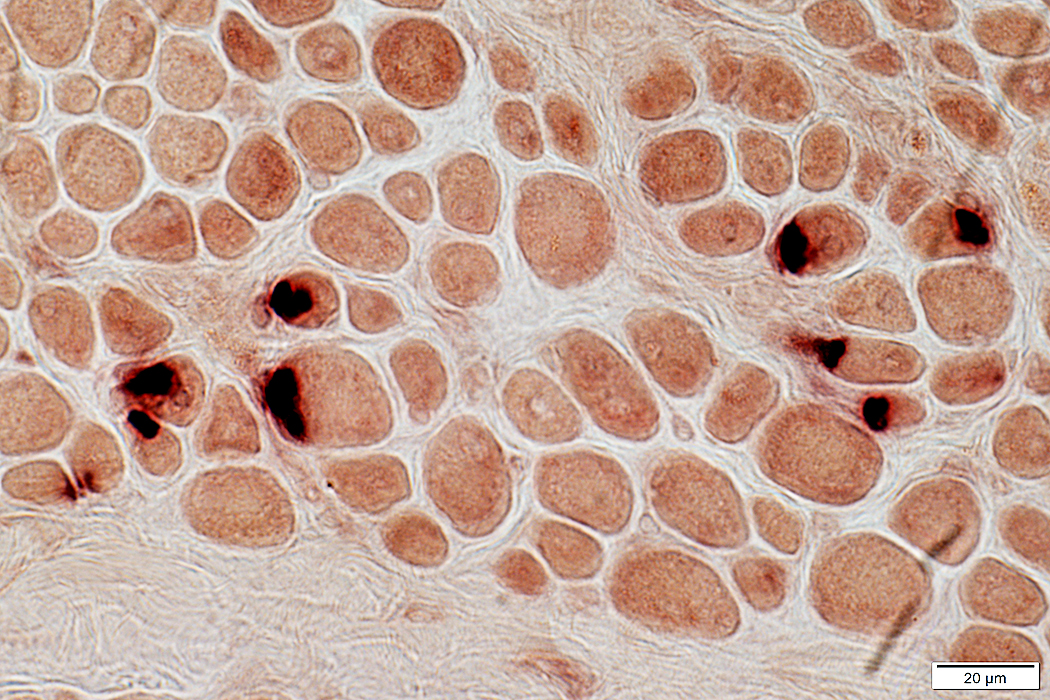 Esterase stain |
CNM: Spindles
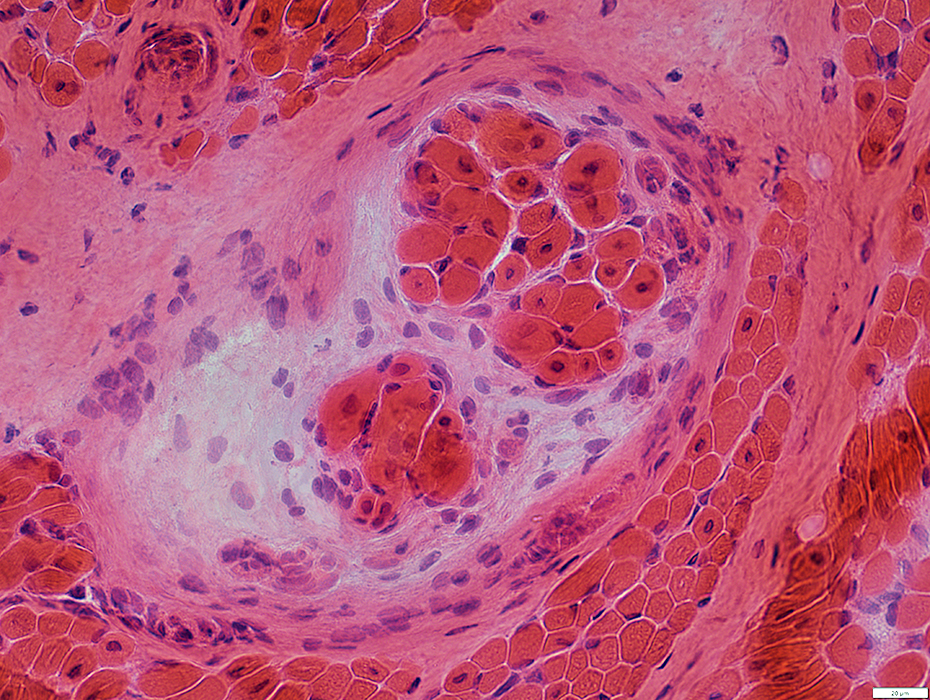 H&E stain |
Central nuclei
Present in extrafusil muscle fibers, due to Centronuclear Myopathy
Normally present in intrafusil fibers
Spindle with thick capsule
Central nuclei
Present in extrafusil muscle fibers, due to Centronuclear Myopathy
Normally present in intrafusil fibers
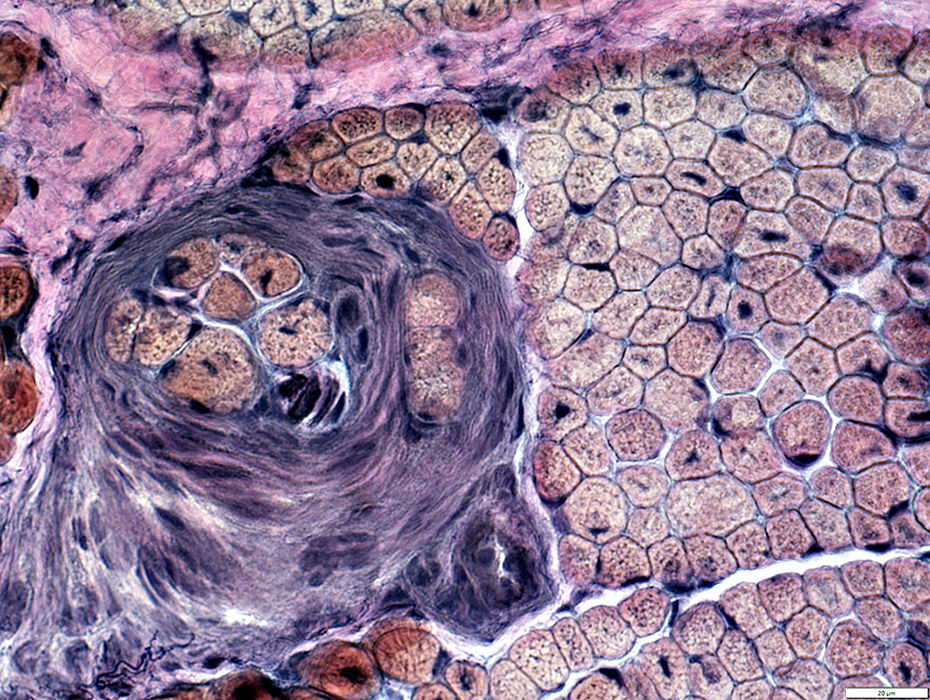 VvG stain |
Perimysial Vein & Artery
Normal structure
 VvG stain |
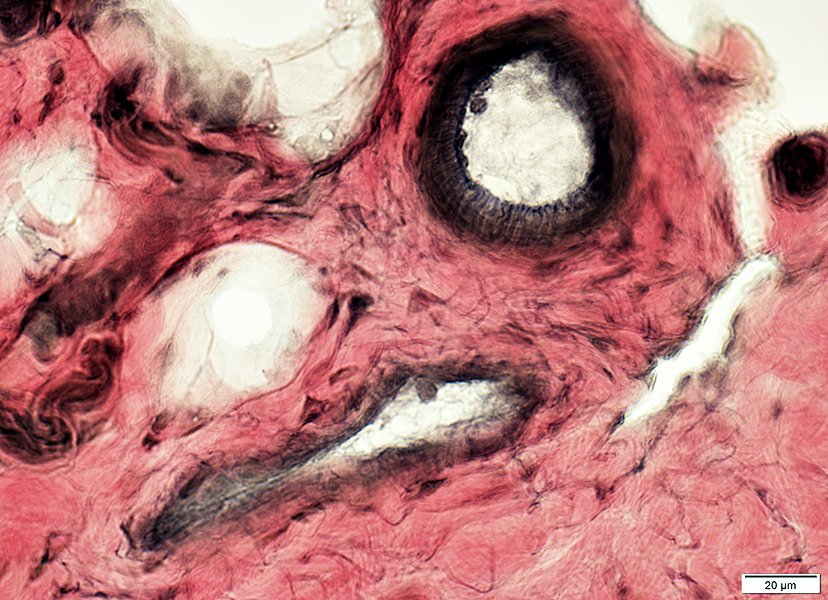
Centronuclear myopathy (CNMX): Adult male (43 years), MTM1 missense mutation (V447M)
 H&E stain |
Internal nuclei: 3 populations of muscle fibers
Single: Often central
Multiple: Often somewhat linear arrangement
None
Fiber size vatiation
Moderate
Scattered intermediate-sized round or polygonal fibers
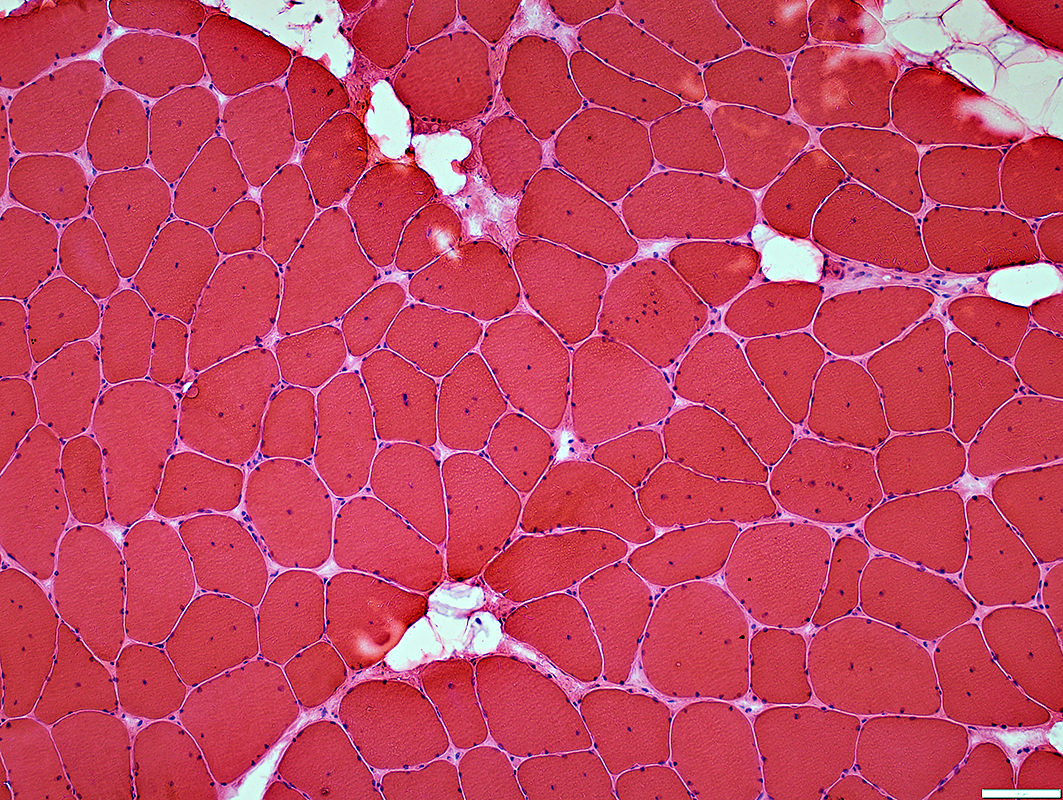
 VvG stain |
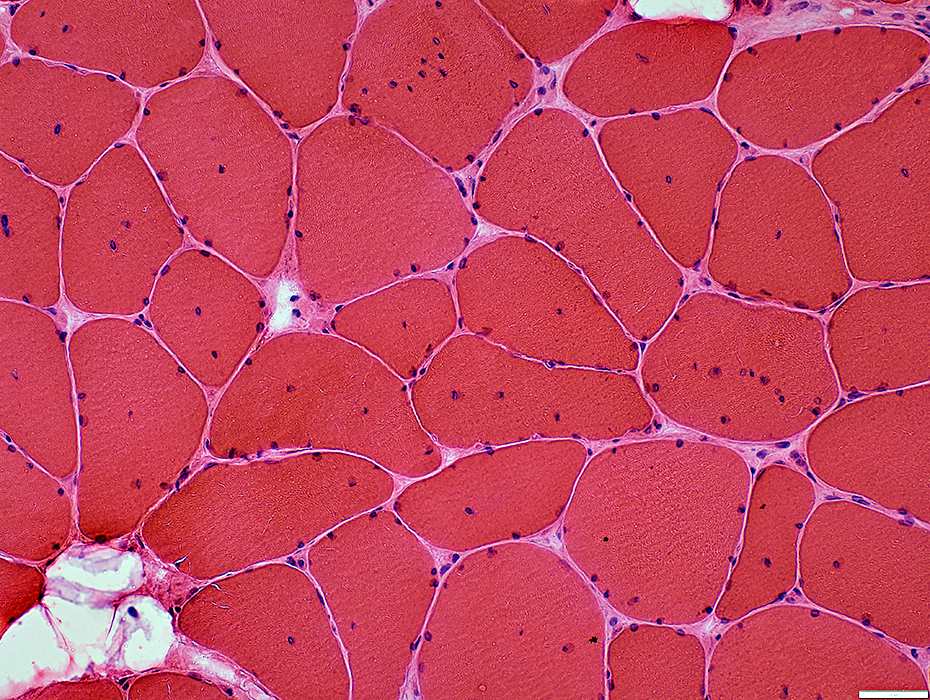 H&E stain |
Internal nuclei: 3 populations of muscle fibers
Single: Often central
Multiple: Often somewhat linear arrangement
None
Endomysial connective tissue: Normal
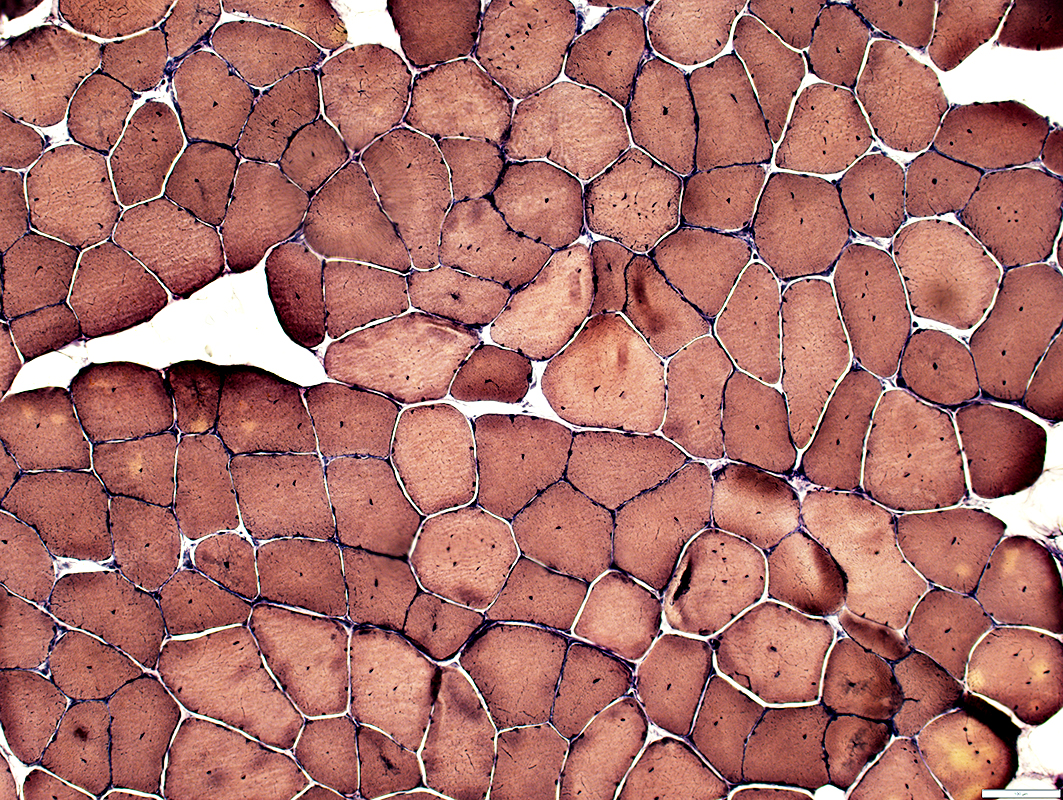
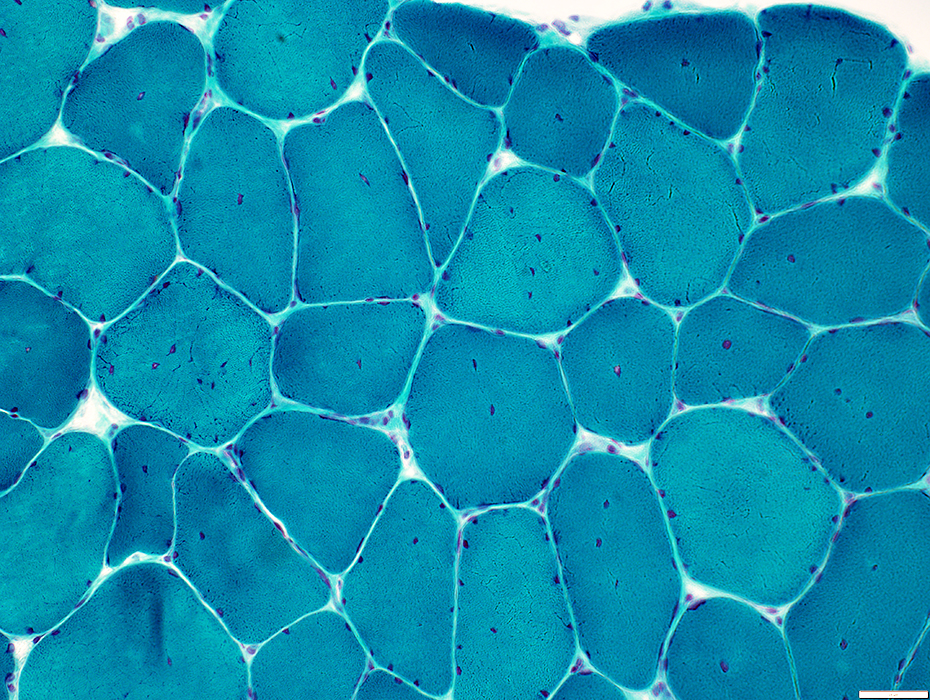 Gomori trichrome stain |
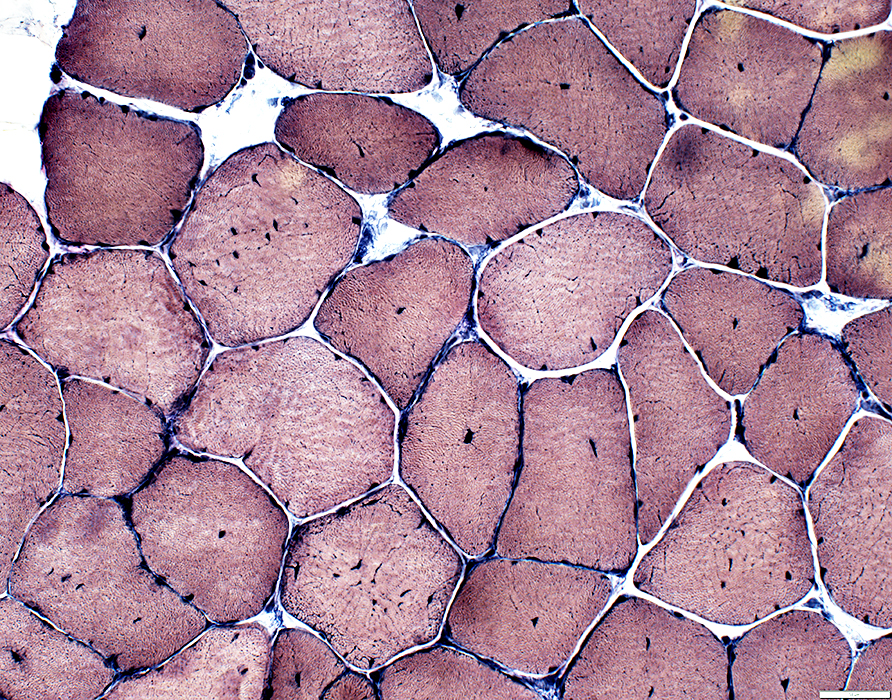 VvG stain |
Internal nuclei: 3 populations of muscle fibers
Single: Often central
Multiple: Often somewhat linear arrangement
None: Some fibers with abnormal central regions but no nuclei (Below)
Muscle fiber internal architecture
Some fibers have
Central dark staining
Sarcoplasmic reticulum with radial strands or irregular shapes
Irregular cytoplasm staining around central nuclei
Fiber size vatiation
Moderate
Scattered intermediate-sized round or polygonal fibers
Endomysial connective tissue: Normal
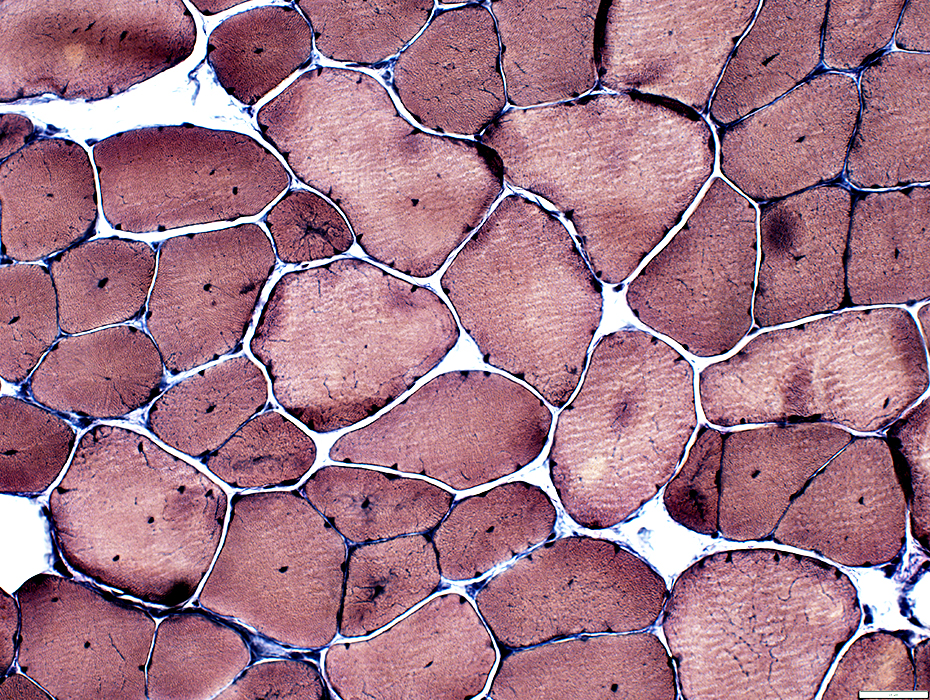 VvG stain |
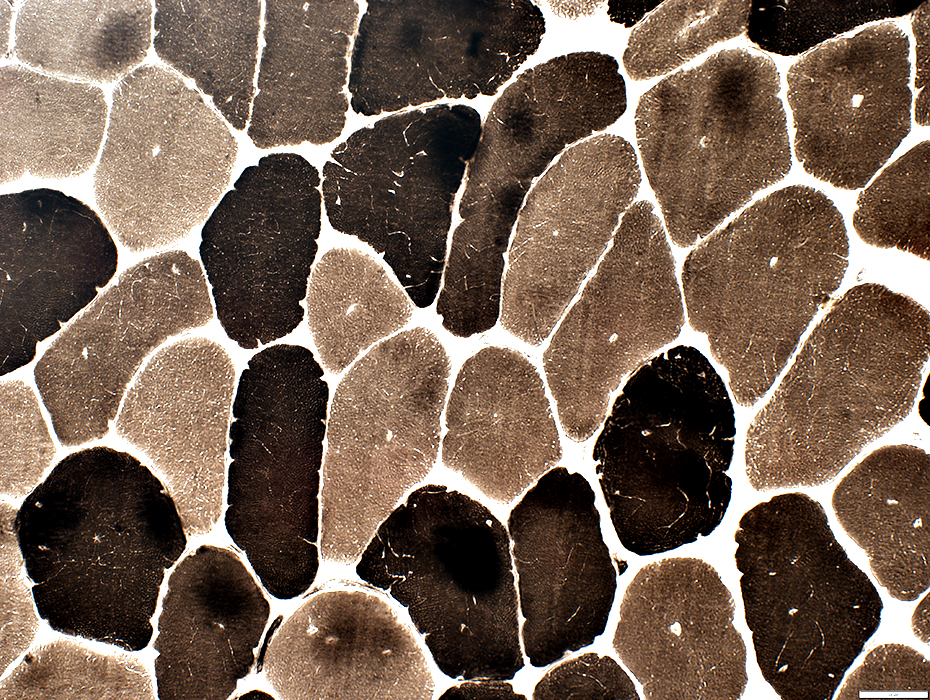 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
Internal nuclei: 3 populations of muscle fibers
Single: Often central; Mostly in Type 1 fibers
Multiple: Often somewhat linear arrangement; Mostly in Type 2 fibers
None: Some fibers with abnormal central regions but no nuclei, Mostly in Type 1 fibers (Below)
Muscle fiber internal architecture
Type 2 fibers have more irregular internalarchitecture (Above)
Fiber types
Type 1 fibers
Predominance: In some areas (Below)
Smallness: In some areas; Intermediate sized; More smallness in fibers with central nuclei
Type 2 fibers
More likely to have: Multiple or No internal nuclei
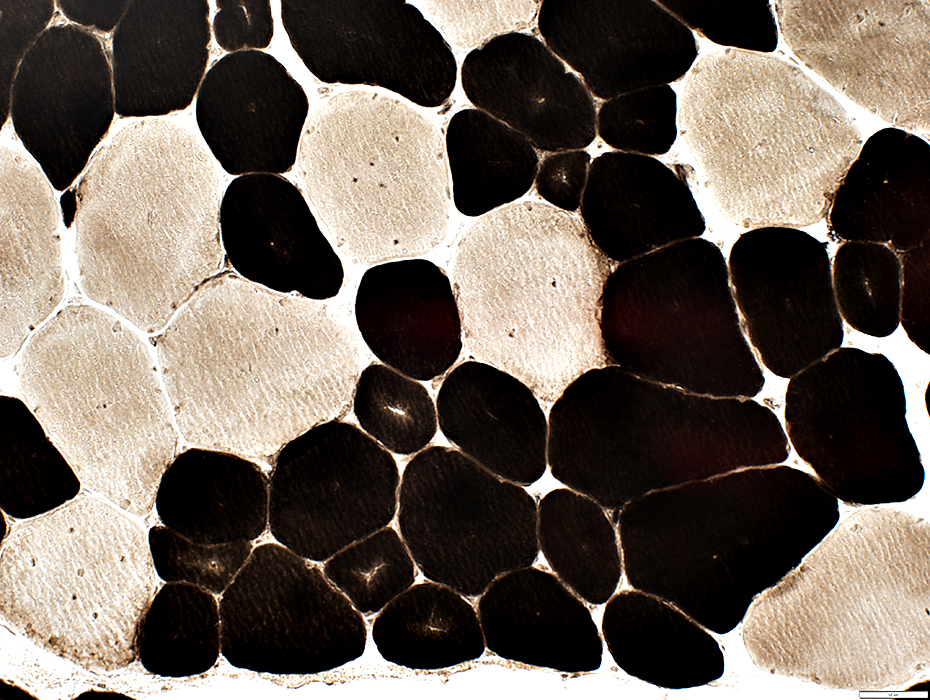 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
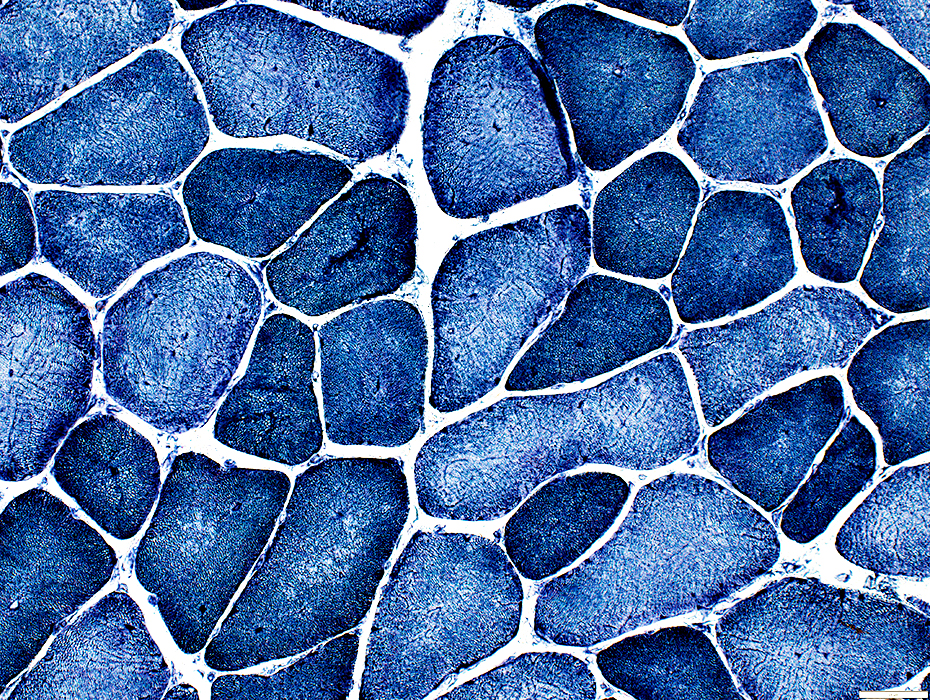 NADH stain |
Type 1 fibers (Dark)
Predominance: In some areas
Smallness
More likely to have
Aggregates, some clustered around internal nuclei
Radial strands
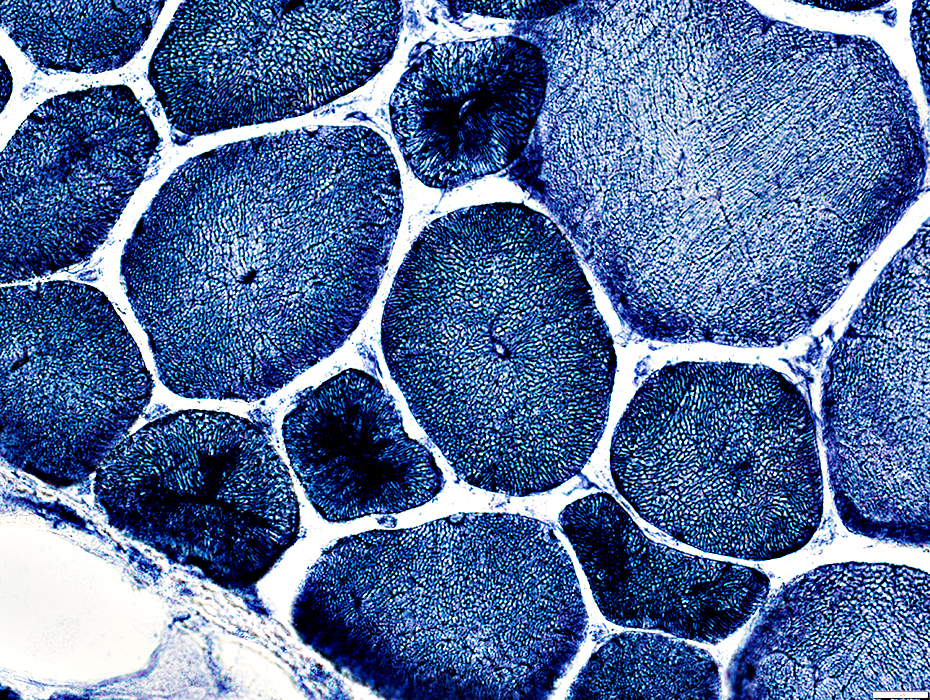 NADH stain |
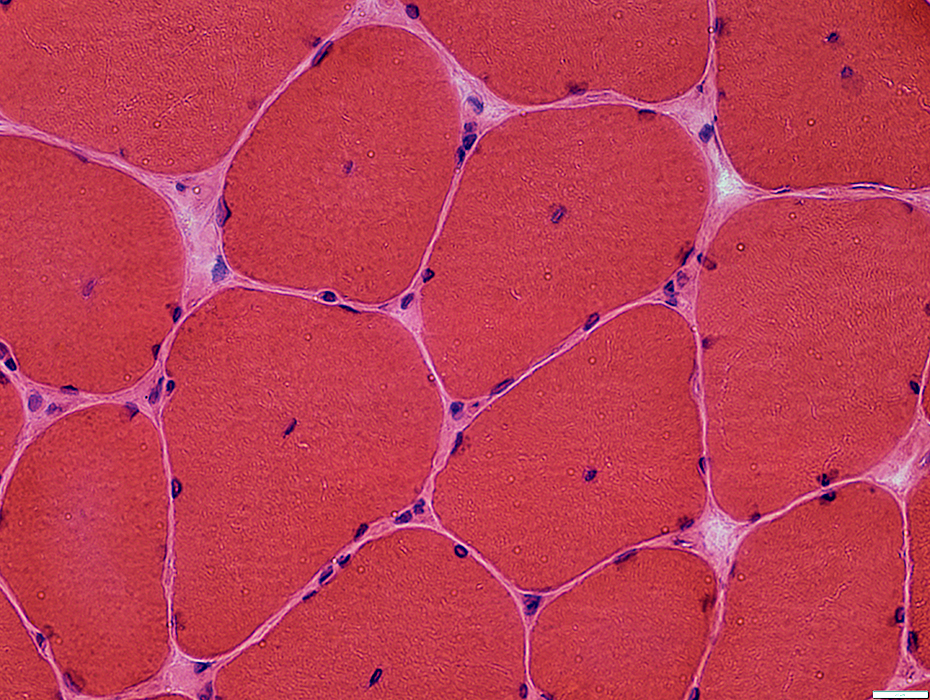 H&E stain |
Internal nuclei
Many fibers have single central nuclei
Gomori trichrome stain (Below)
Myonuclei often have clear centers
One fiber has a central red-stained region (Arrow)
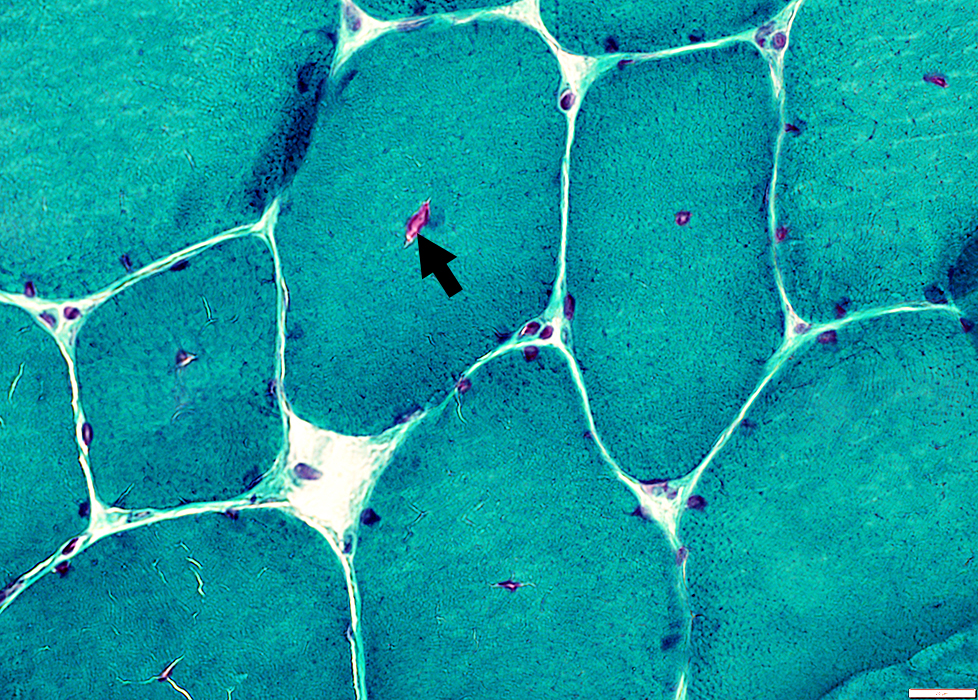 Gomori trichrome stain |
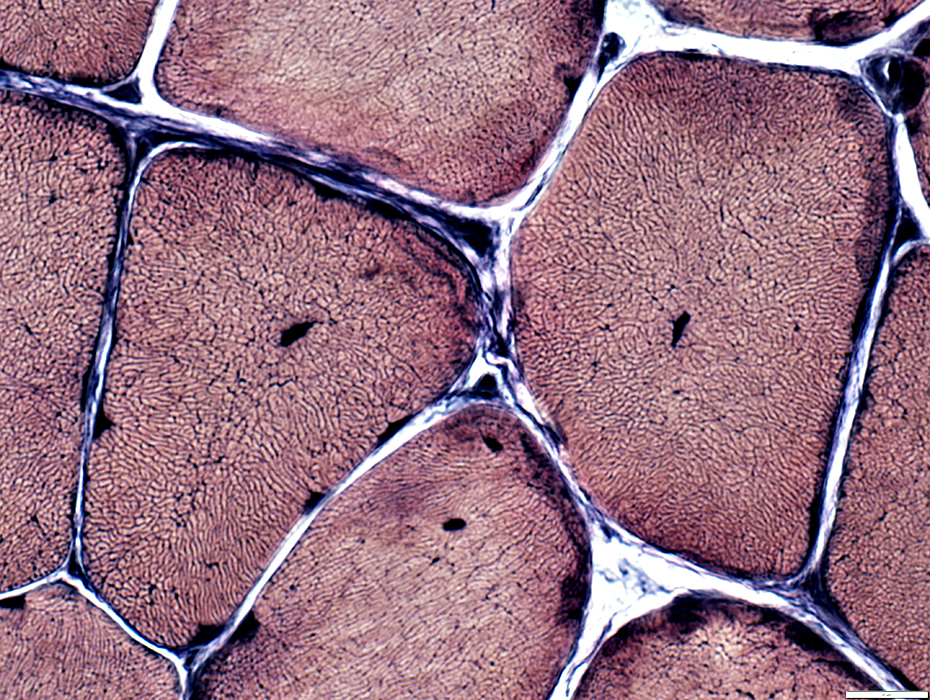 VvG stain |
Internal nuclei
Many fibers have single central nuclei
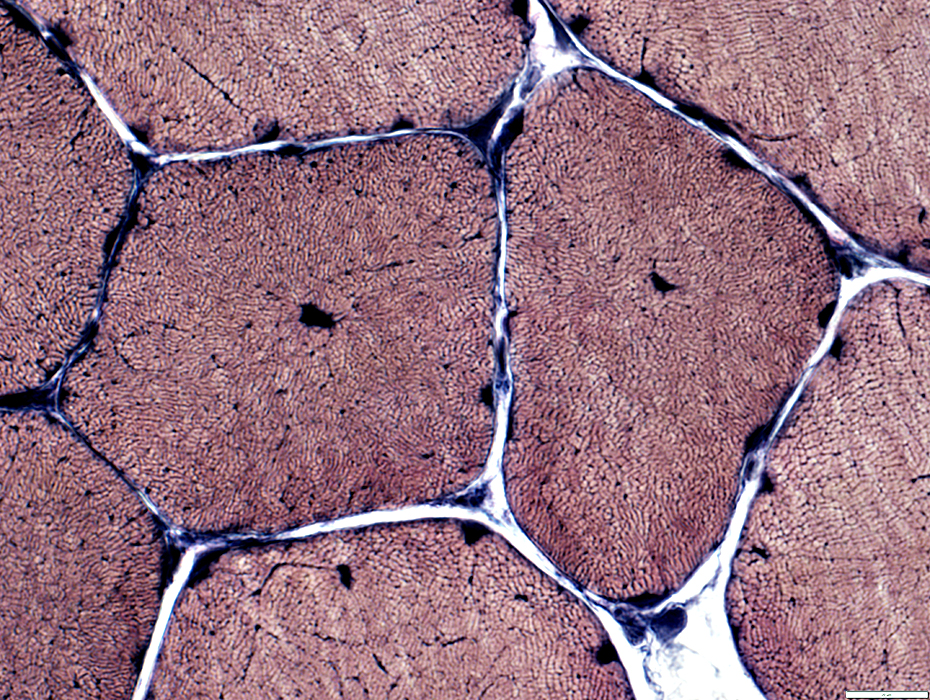 VvG stain |
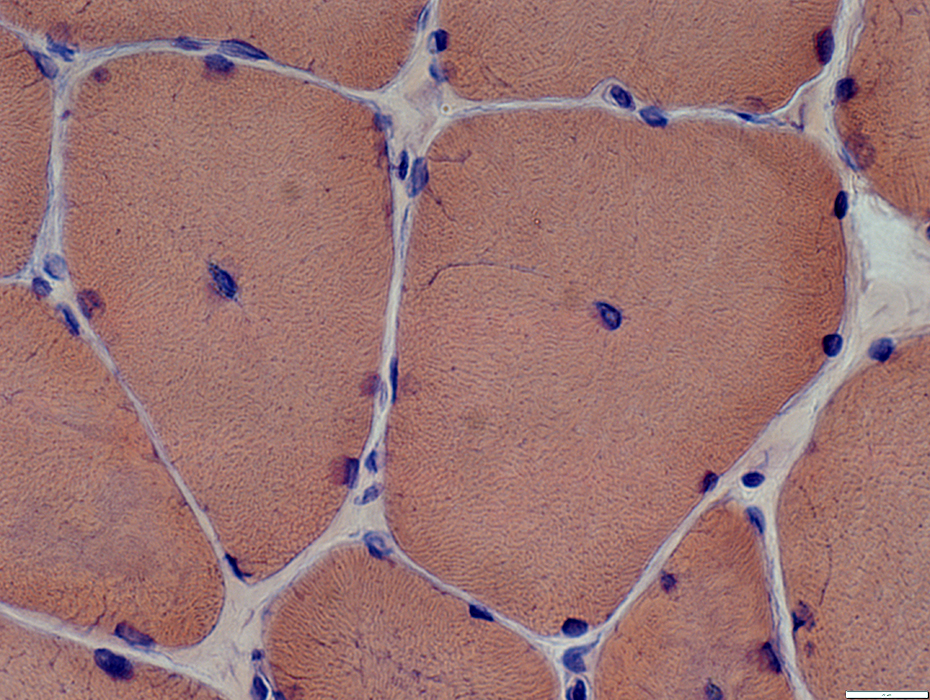 Congo red stain |
Internal nuclei
Many fibers have single central nuclei
Some fibers have abnormal (blurred) internal architecture around internal nuclei (Below)
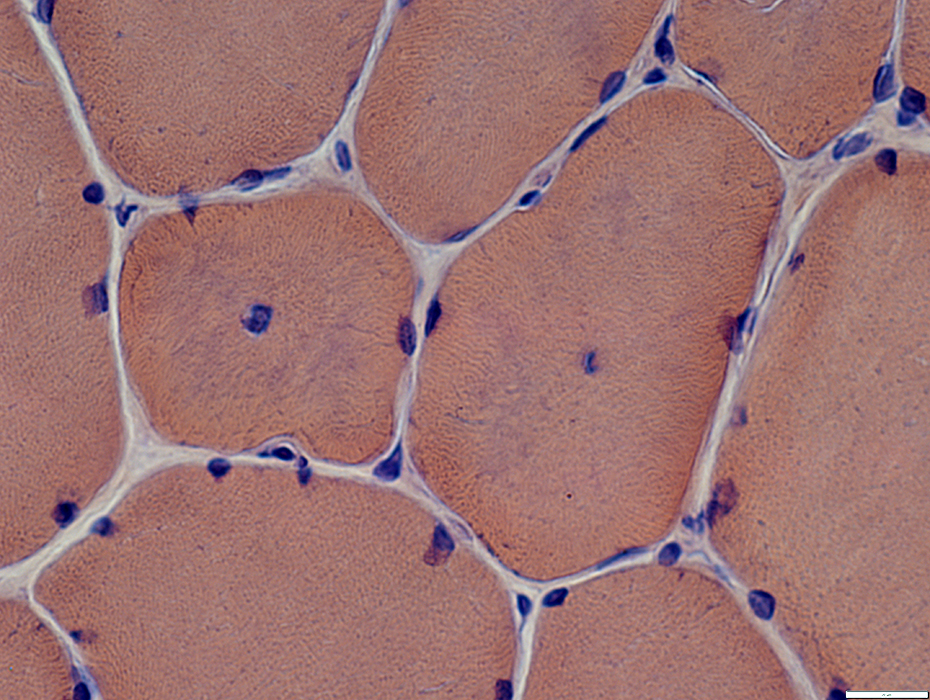 Congo red stain |
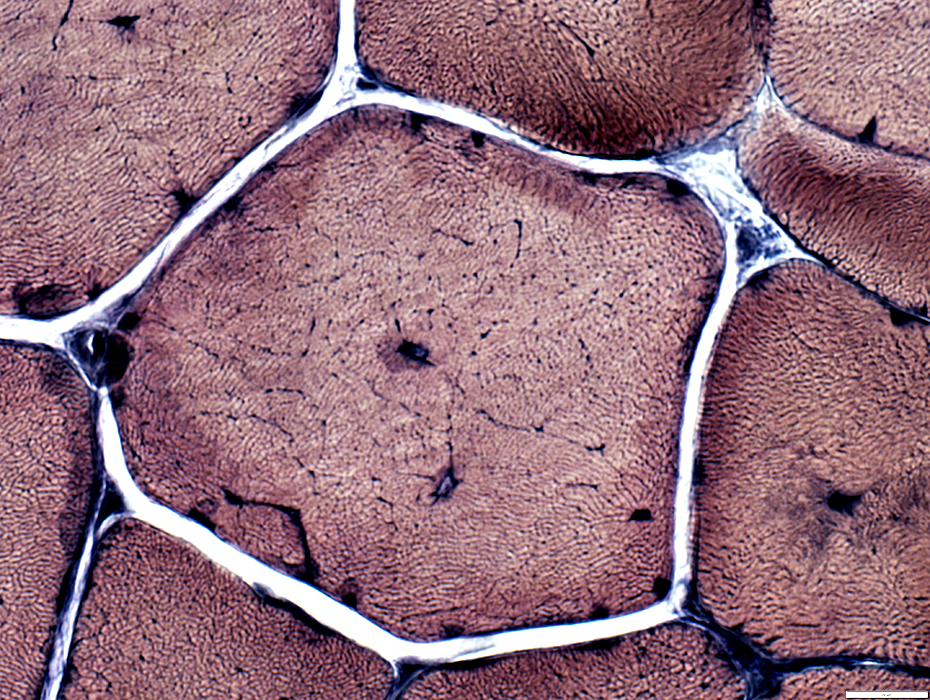 VvG stain |
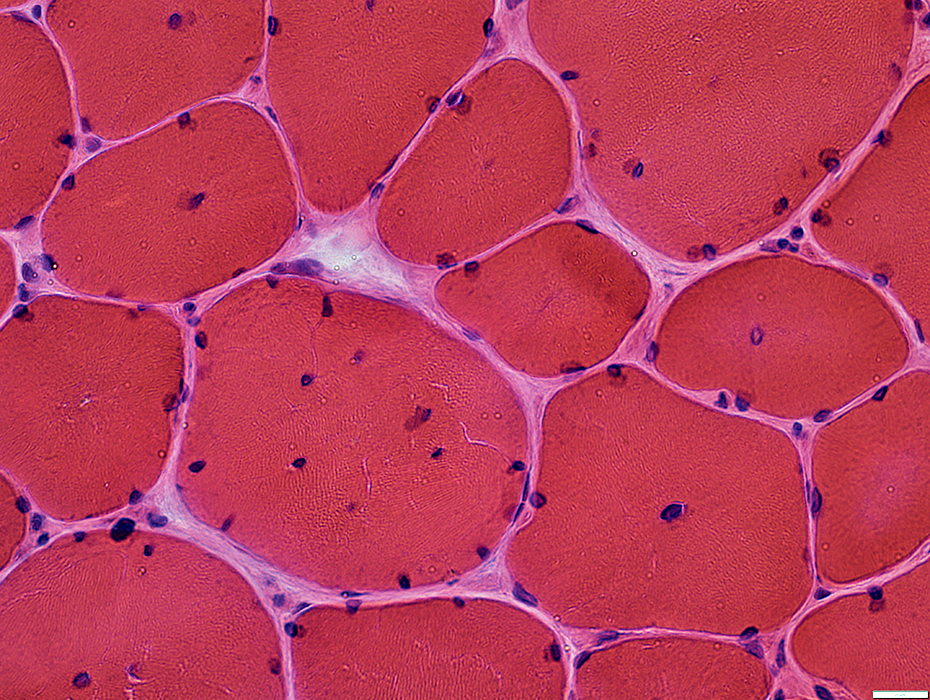 H&E stain |
Internal nuclei
A minority of fibers have several internal nuclei
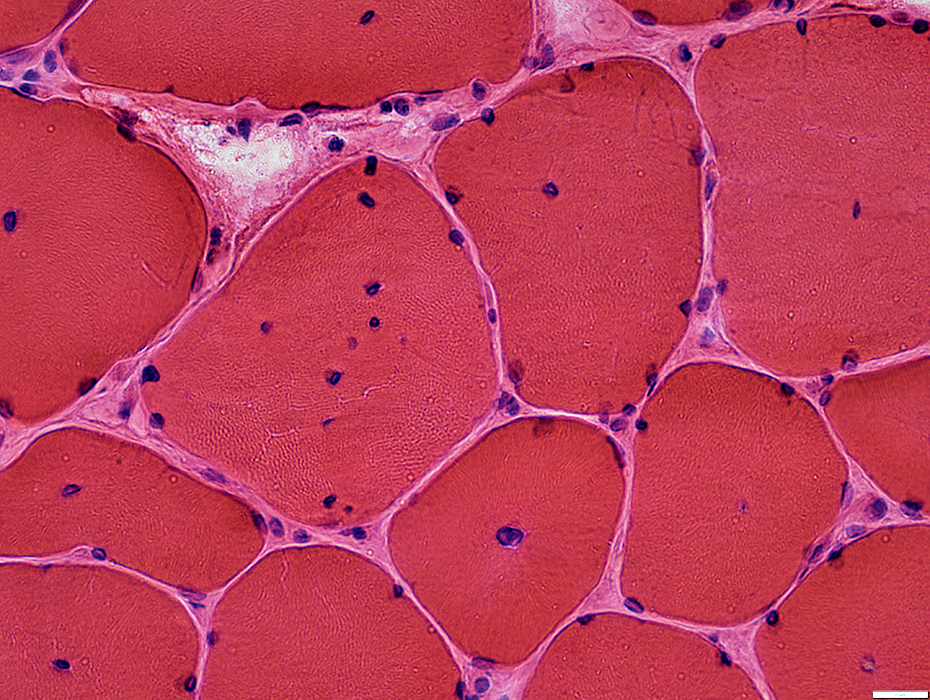 H&E stain |
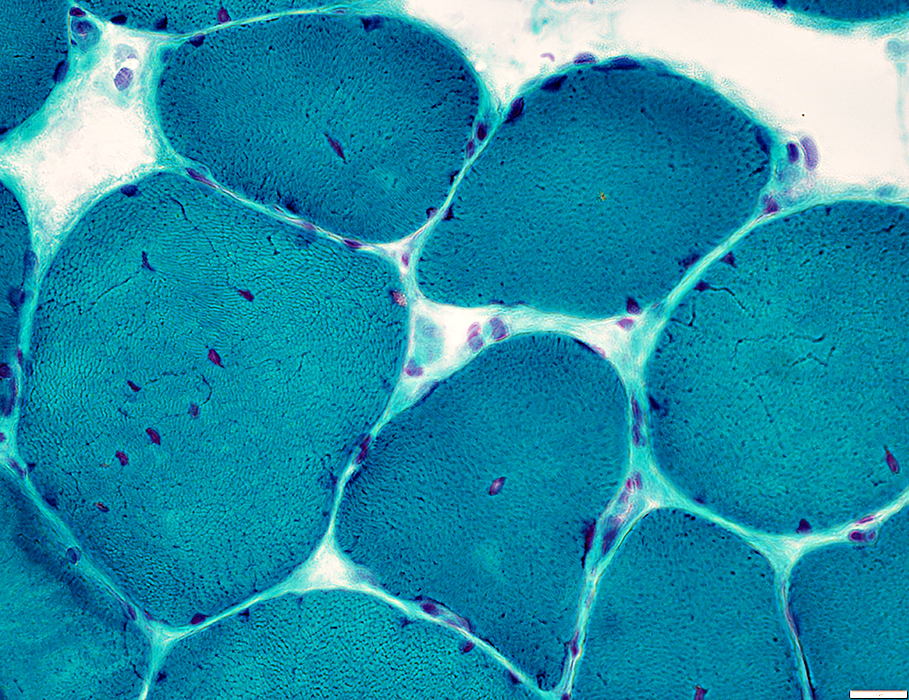 Gomori trichrome stain |
Internal nuclei
A minority of fibers have several internal nuclei
These fibers tend to have more irregular internal architecture
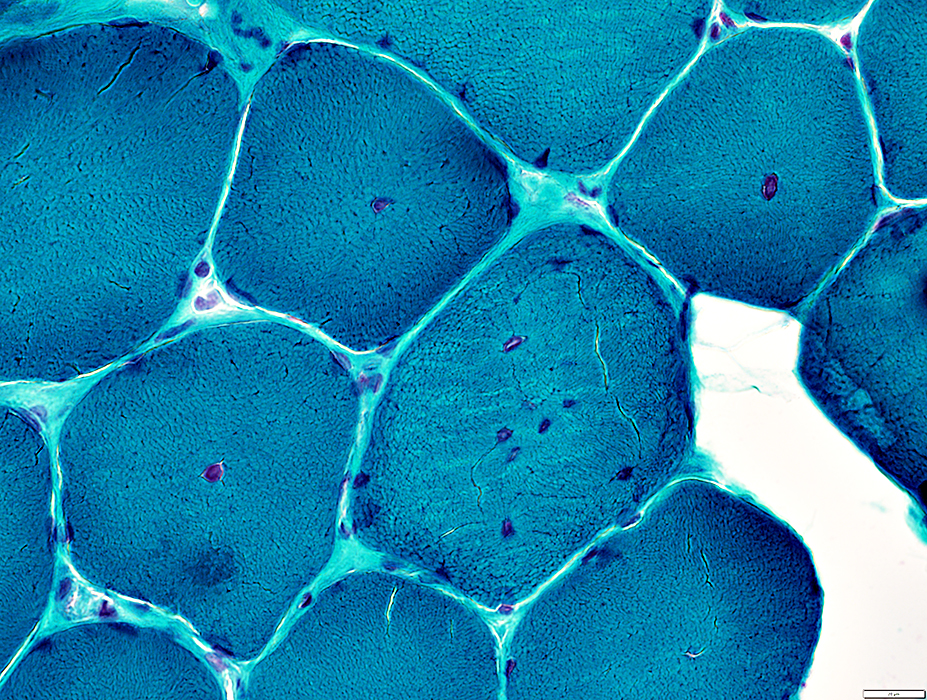 Gomori trichrome stain |
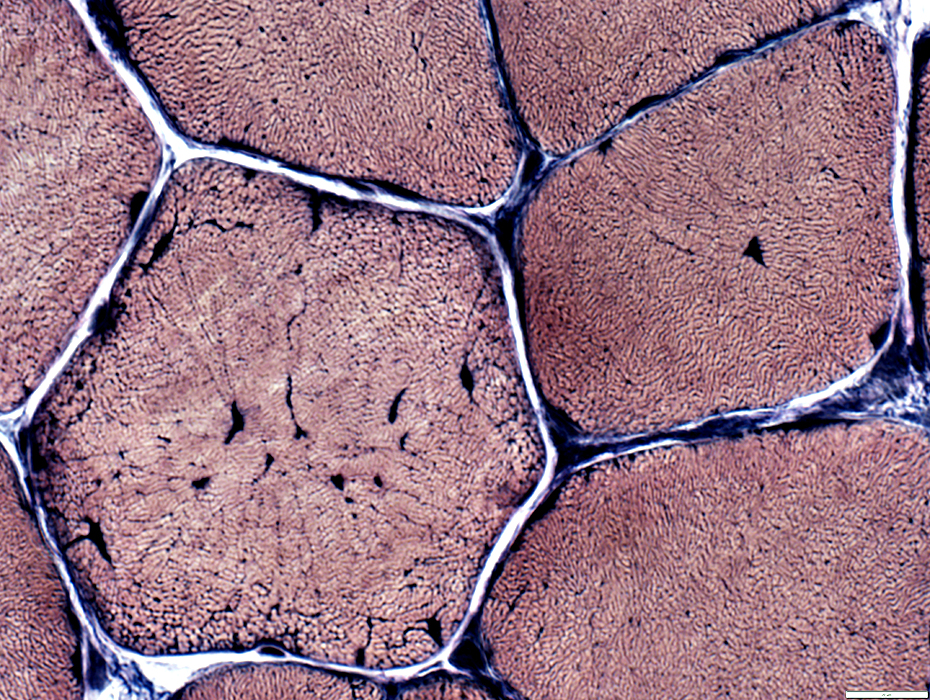 VvG stain |
Internal nuclei
A minority of fibers have several internal nuclei
These fibers tend to have more irregular internal architecture
v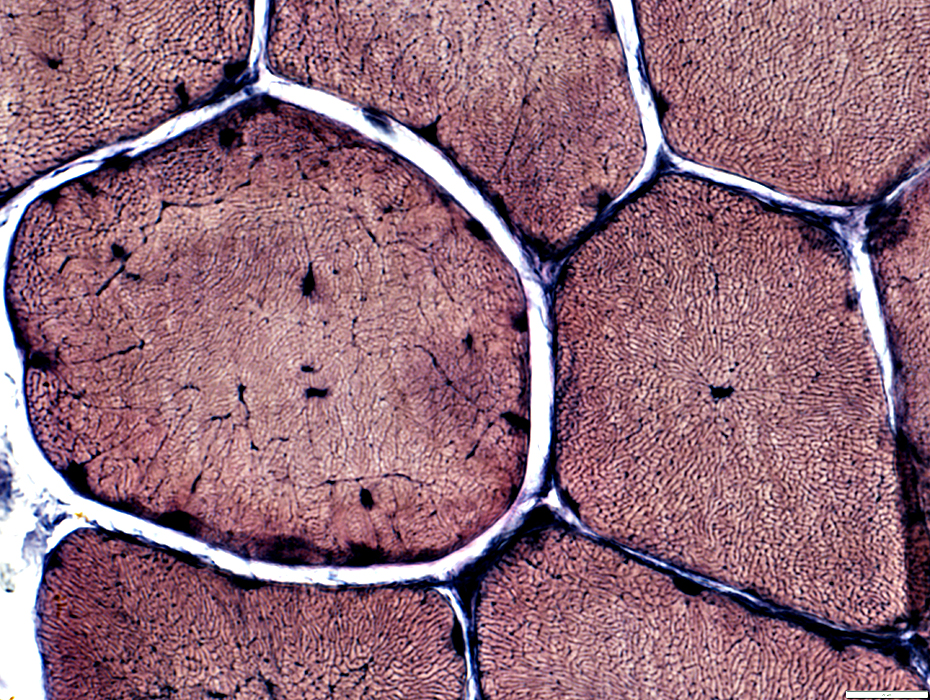 VvG stain |
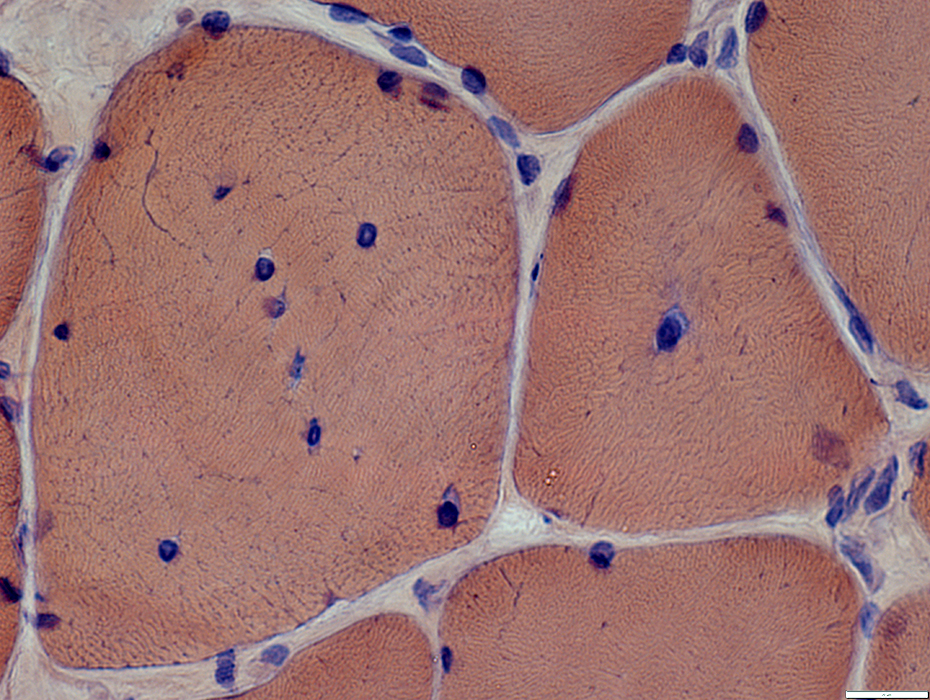 Congo red stain |
 VvG stain |
Muscle fibers: Internal architecture
Some fibers have irregular internal architcture extending from their center
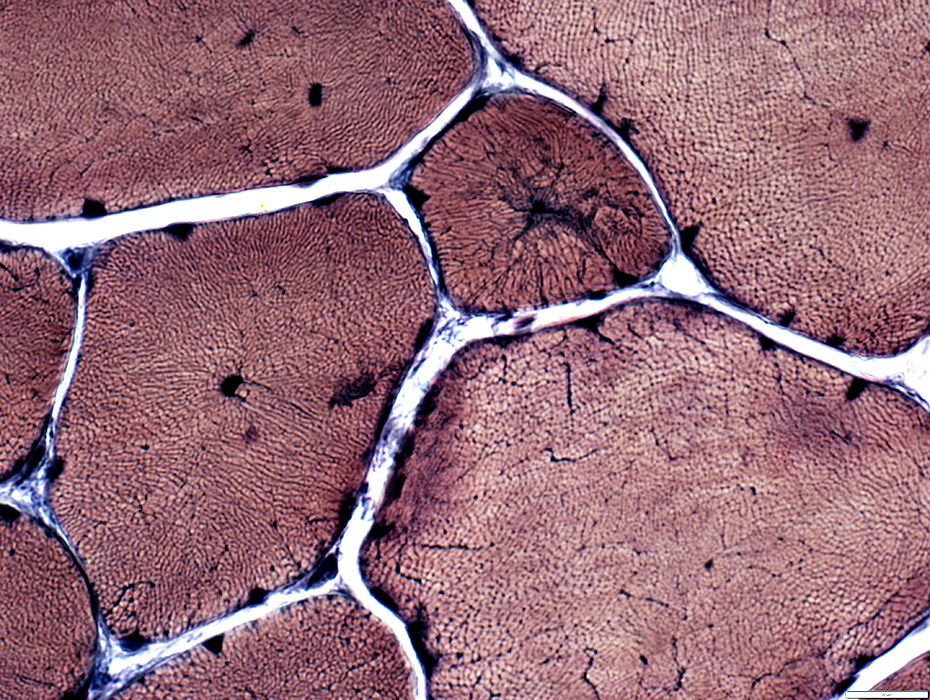
 VvG stain |
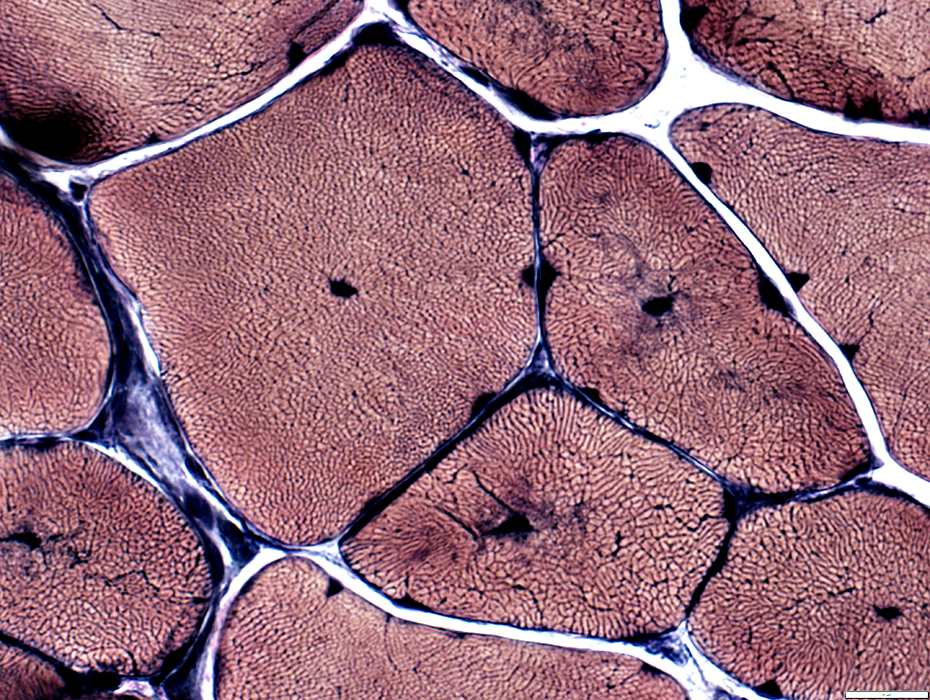
 VvG stain |
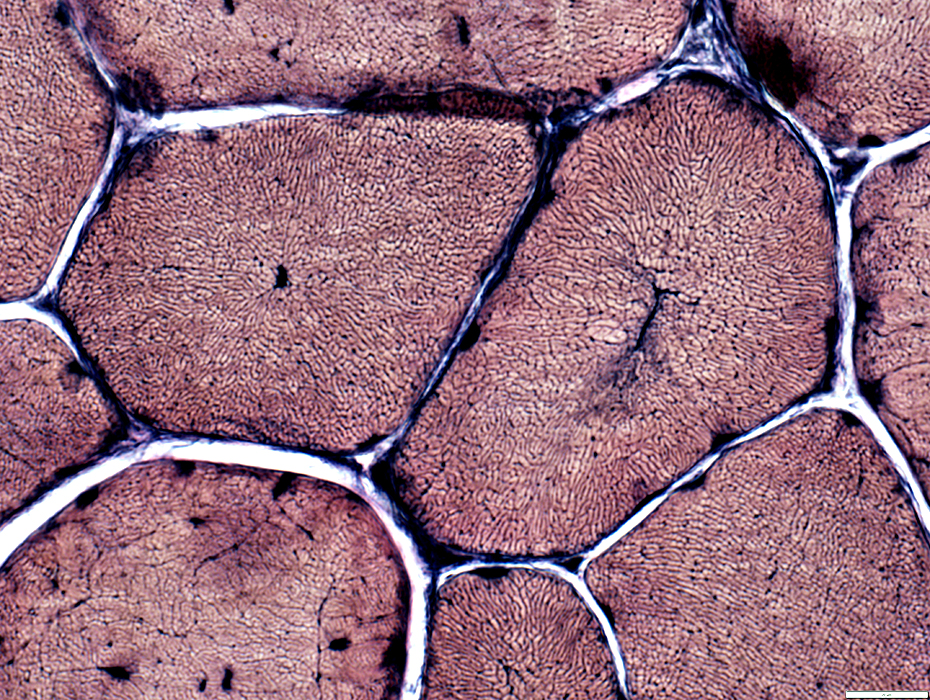
Muscle fibers: Internal architecture
Some fibers have central structural abnormality without central nuclei
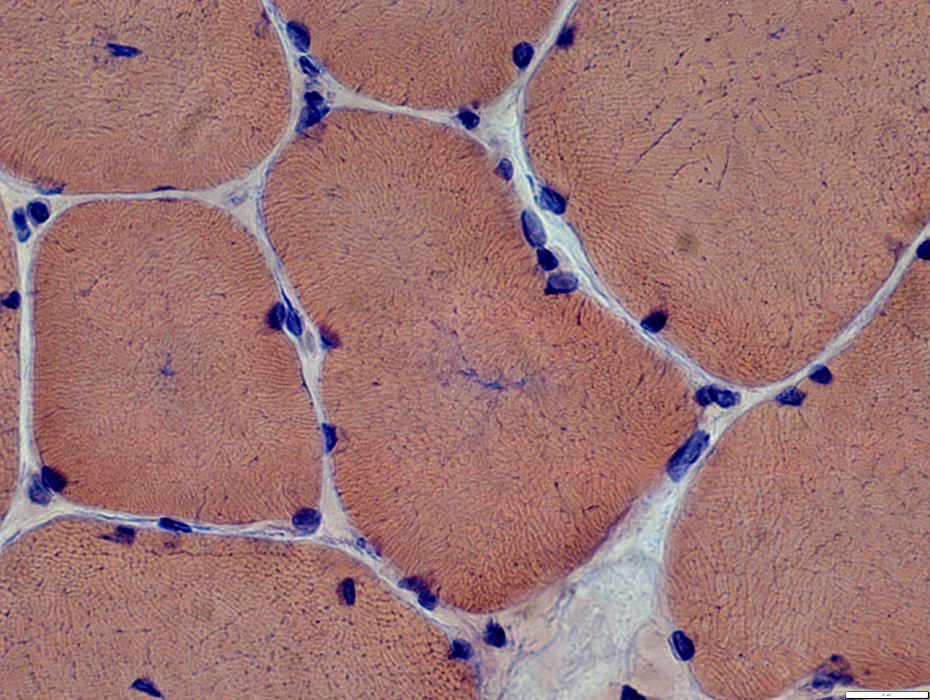 Congo red stain |
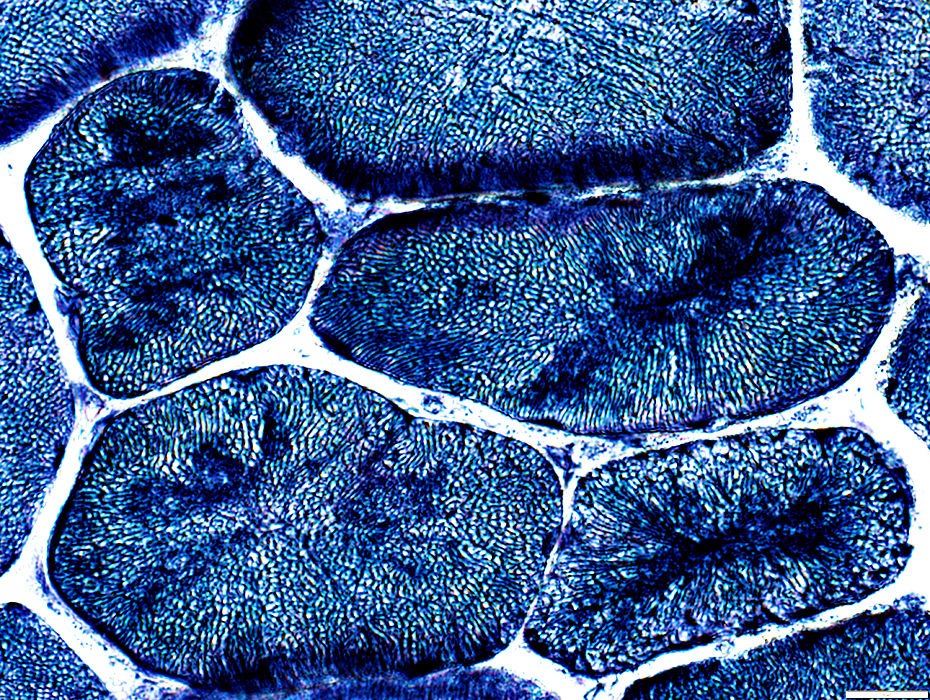 NADH stain |
Muscle fibers: Internal architecture changes include
Irregular sarcoplasmic aggregates
Sarcoplasmic staing around internal nuclei
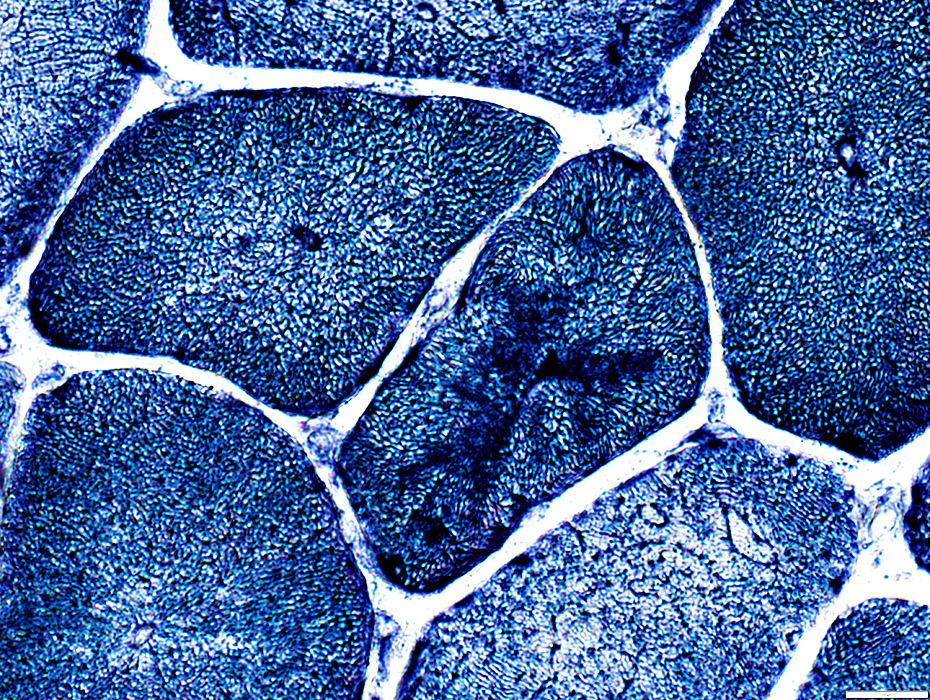 NADH stain |
Muscle fibers: Internal architecture changes include
Dark central structures with radial strands
Irregular sarcoplasmic aggregates
Sarcoplasmic staing around internal nuclei
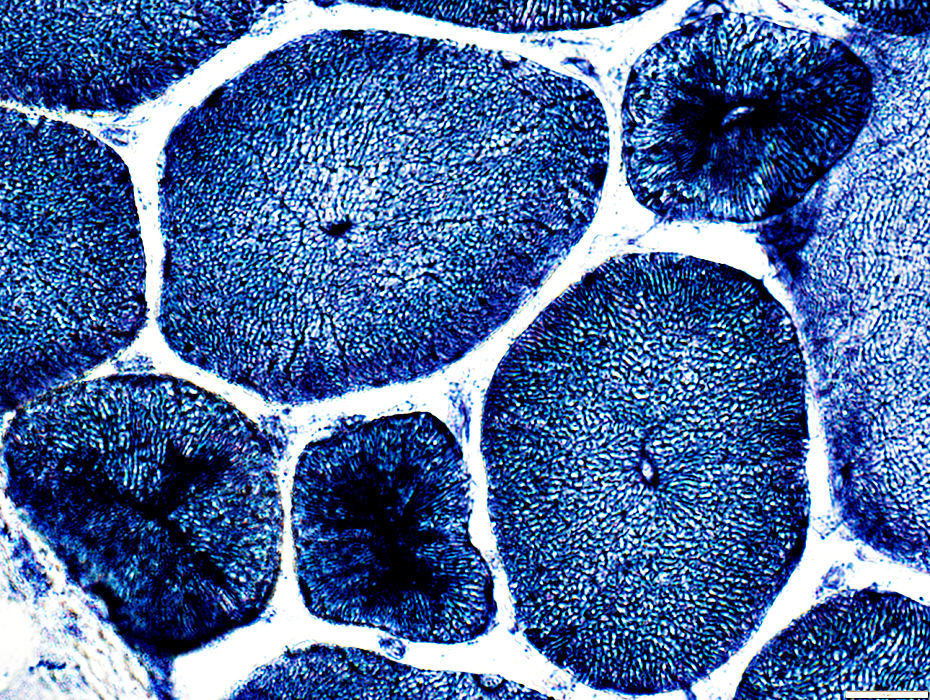 NADH stain |
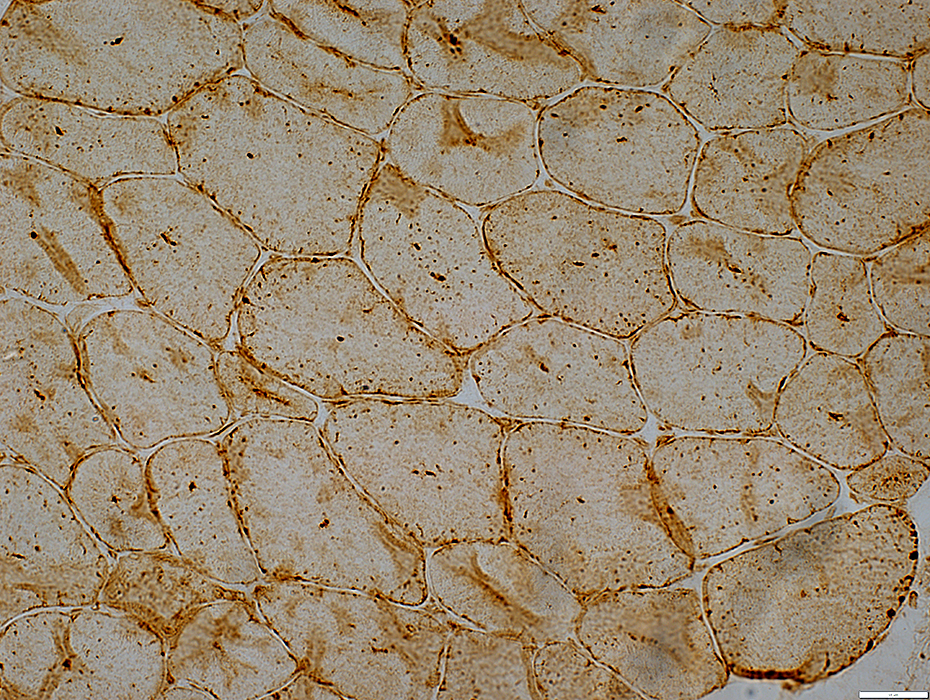 LAMP2 stain |
Central Lysosomal Dots: Stain for LAMP2
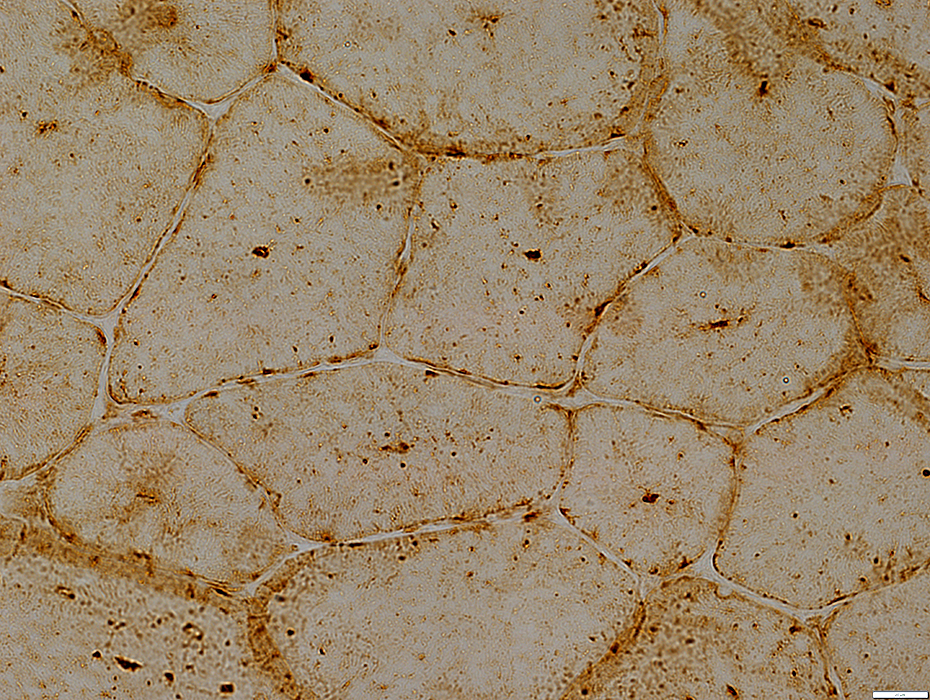 LAMP2 stain |
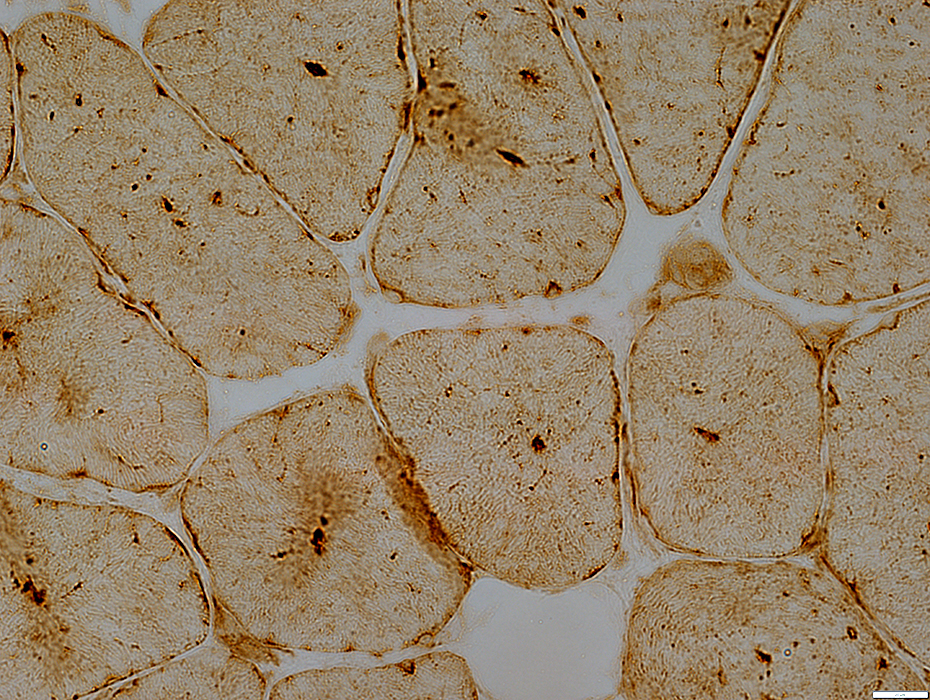 LAMP2 stain |
LAMP2 stain: Normal muscle
No central lysosomal dots
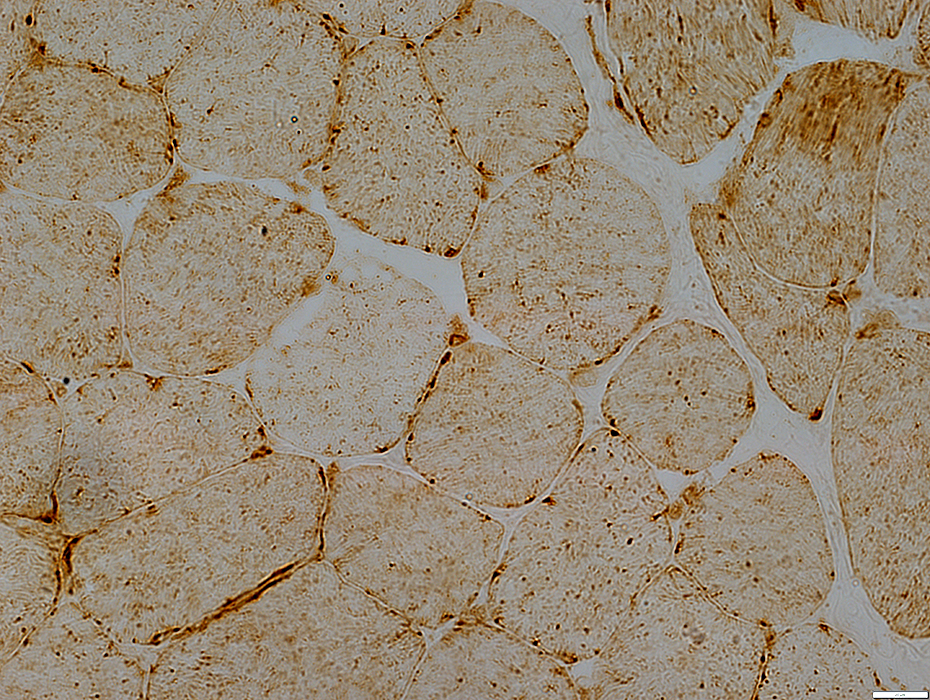 LAMP2 stain |
Centronuclear Myopathy: Adult
Titin
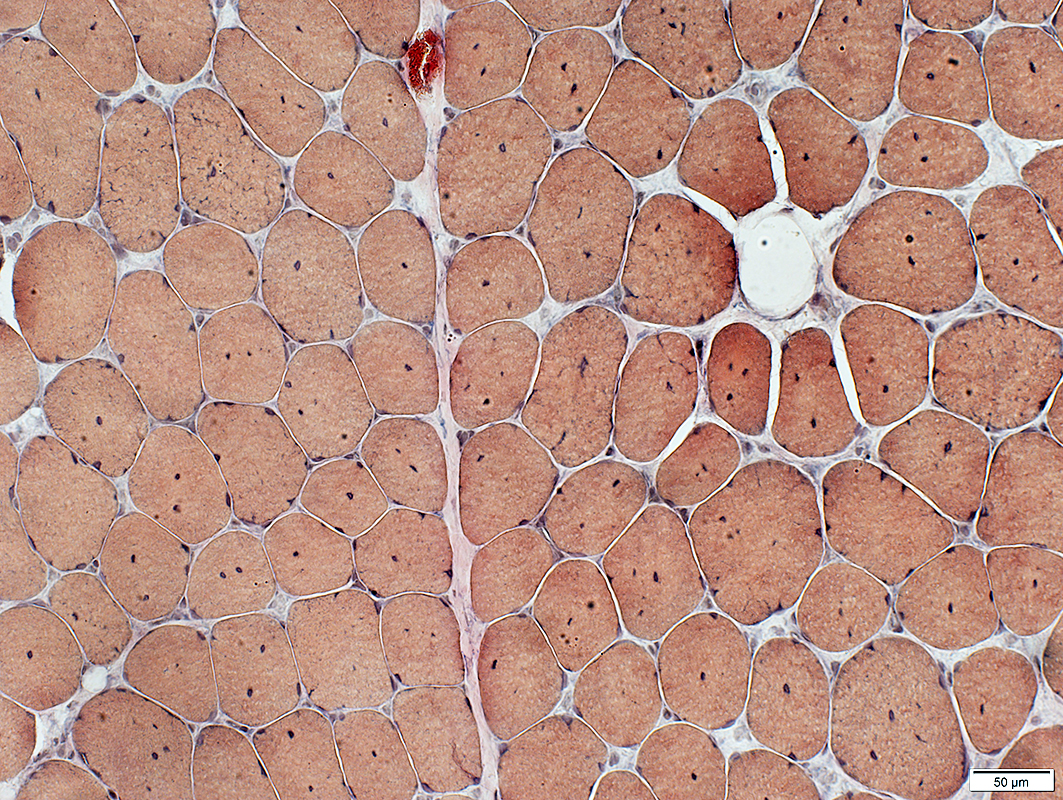 VvG stain |
Internal nuclei: One or Several
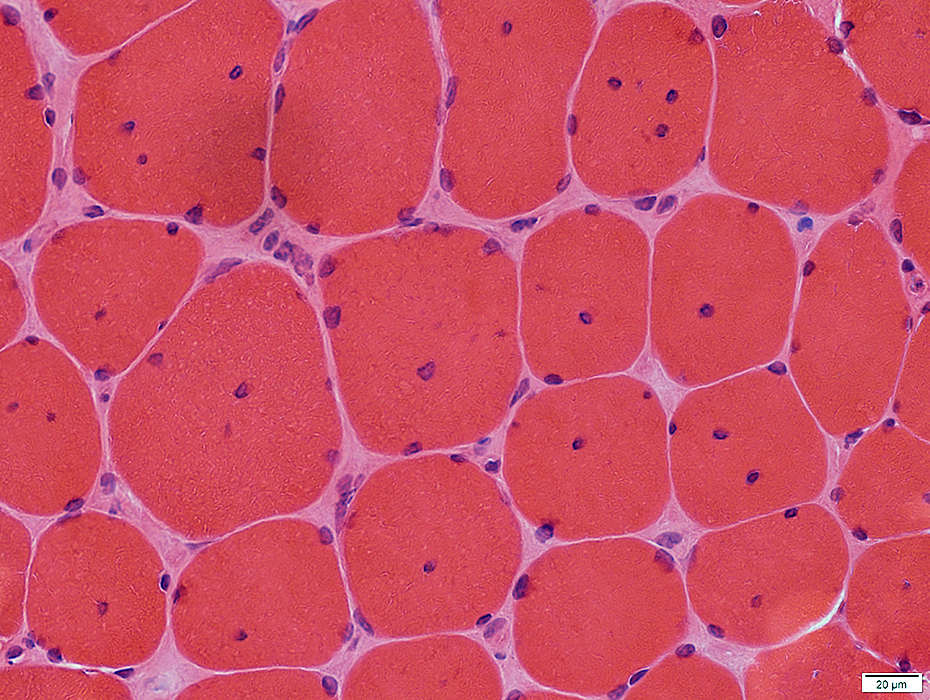 H&E stain |
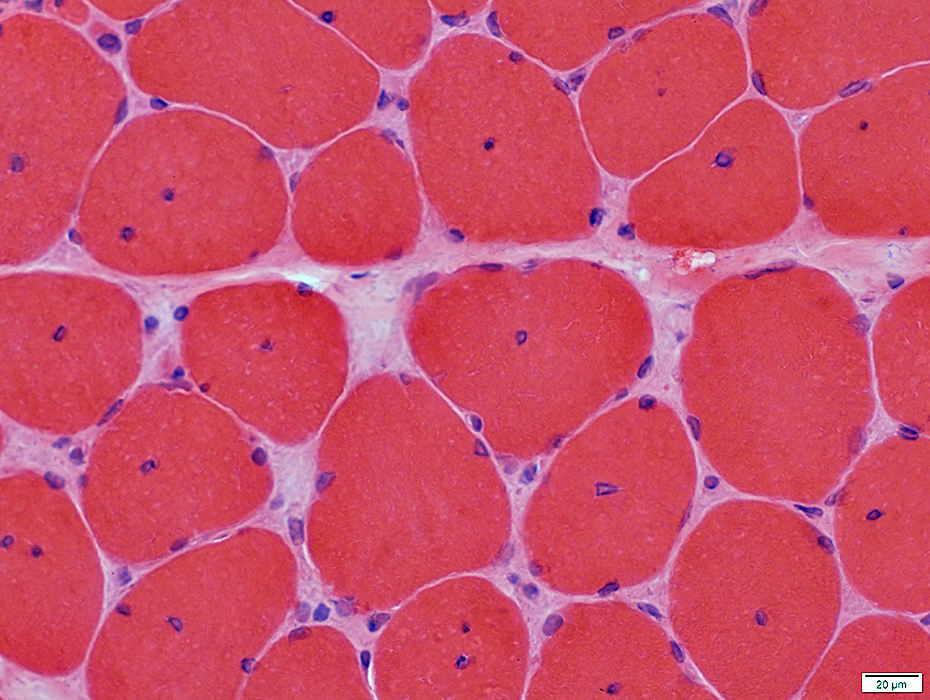 H&E stain |
Internal nuclei: One or Several
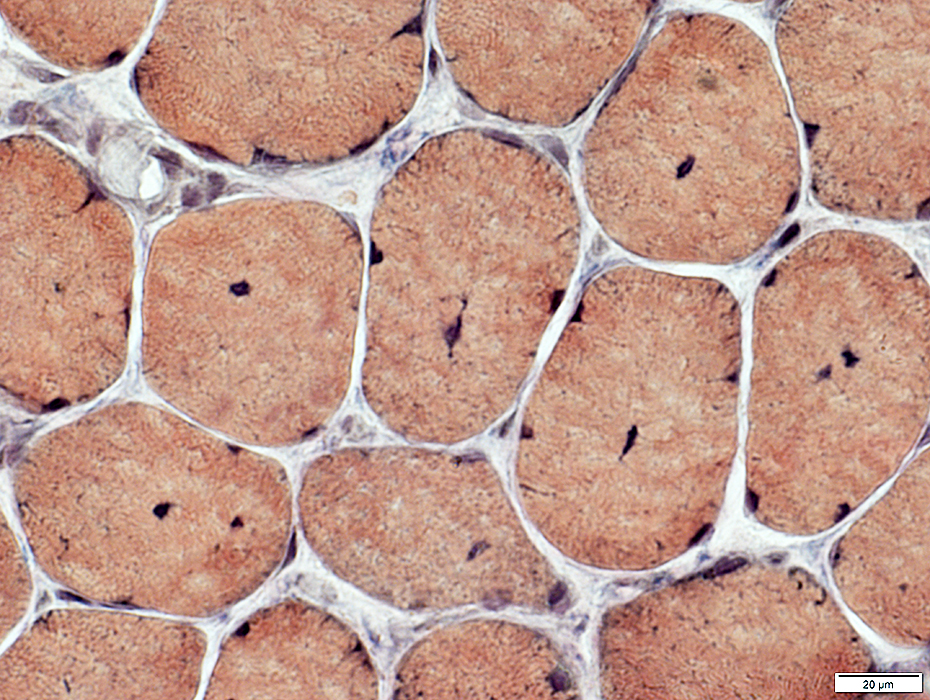 VvG stain |
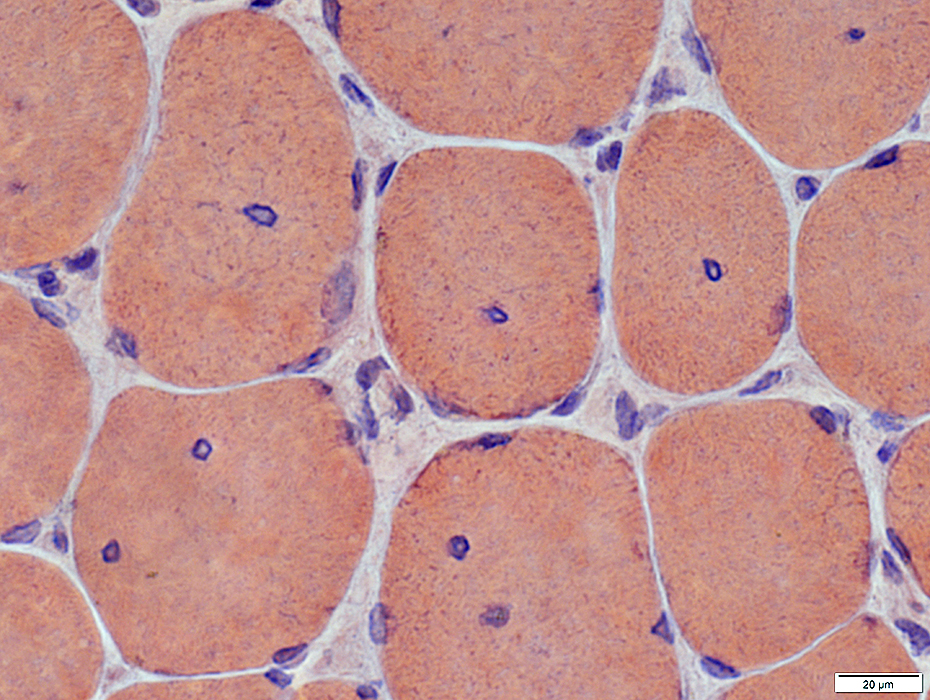 Congo red stain |
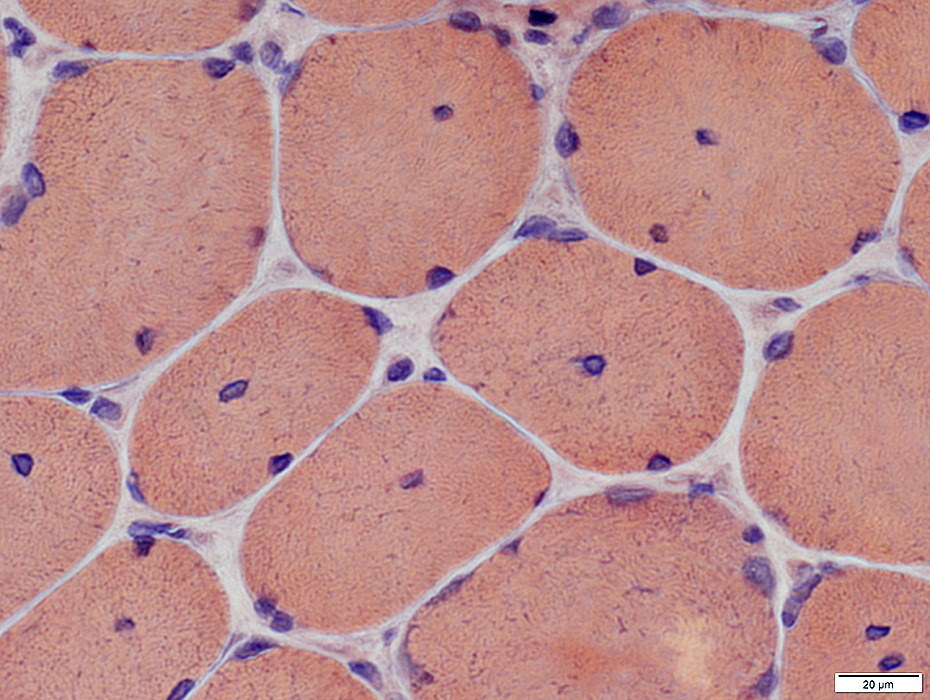 Congo red stain |
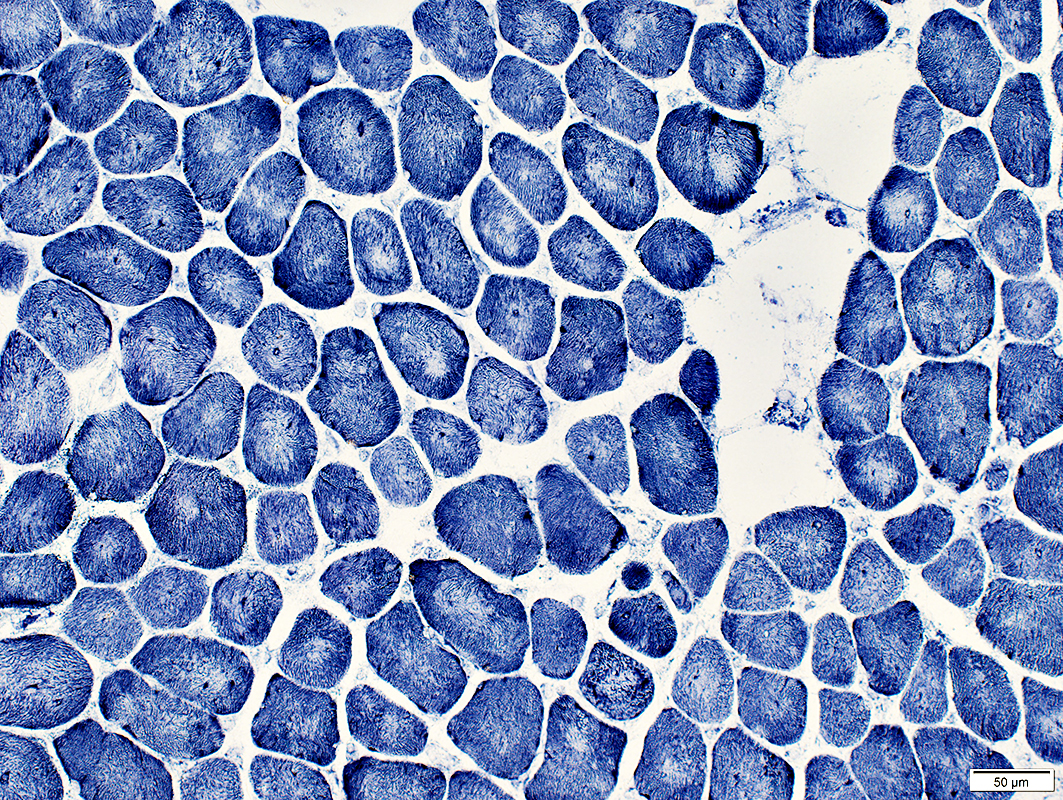 NADH stain |
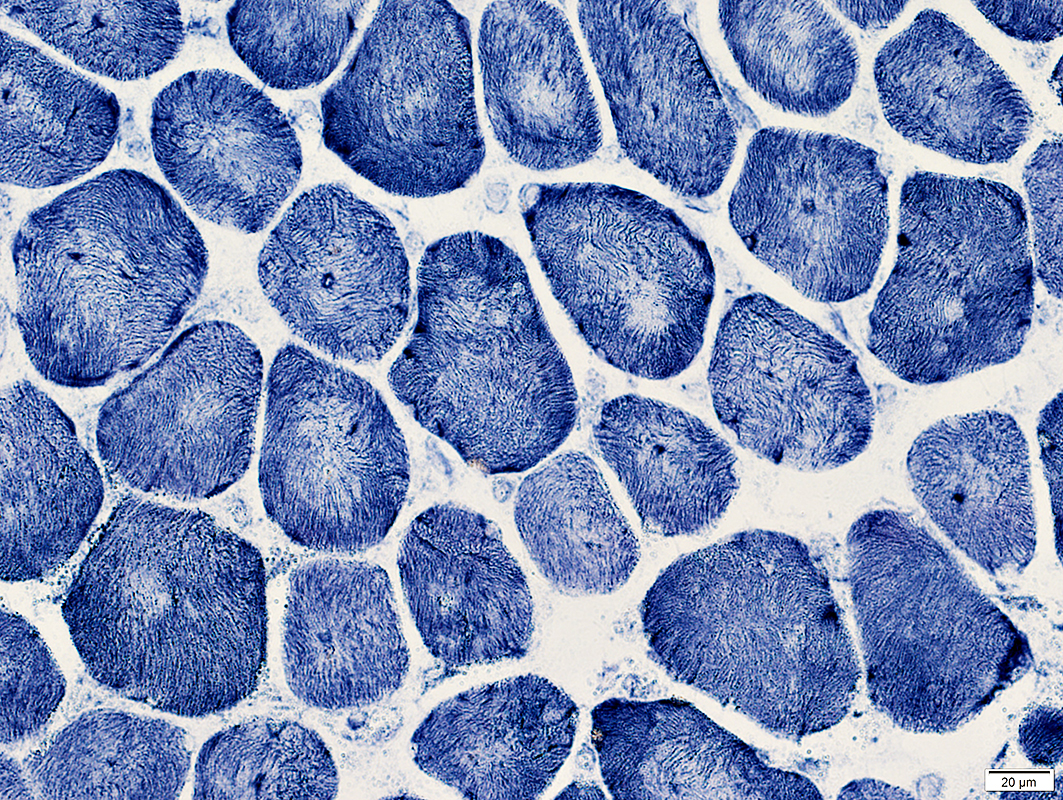 NADH stain |
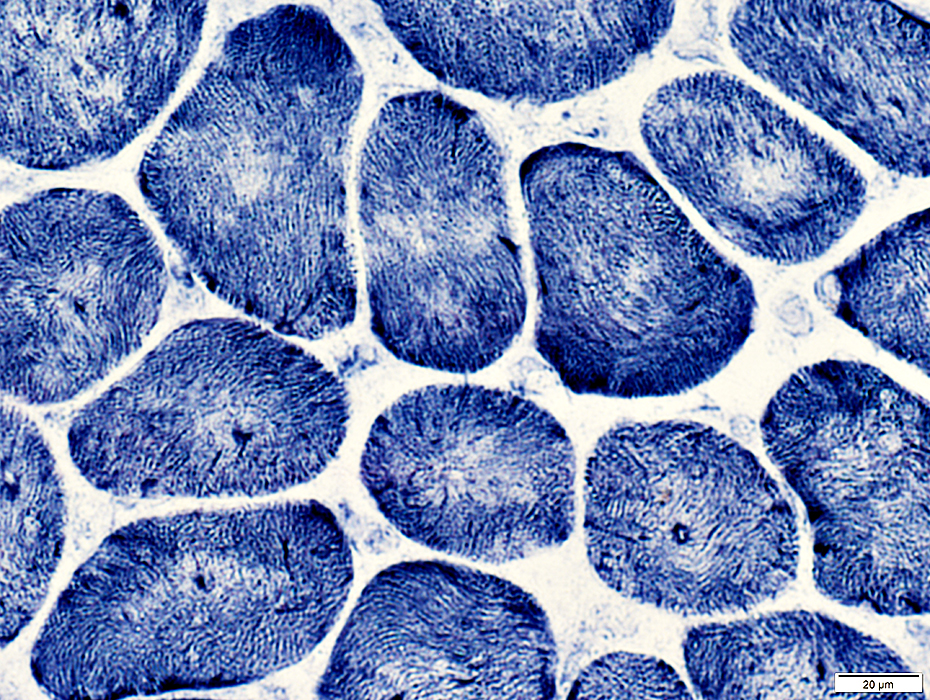 NADH stain |
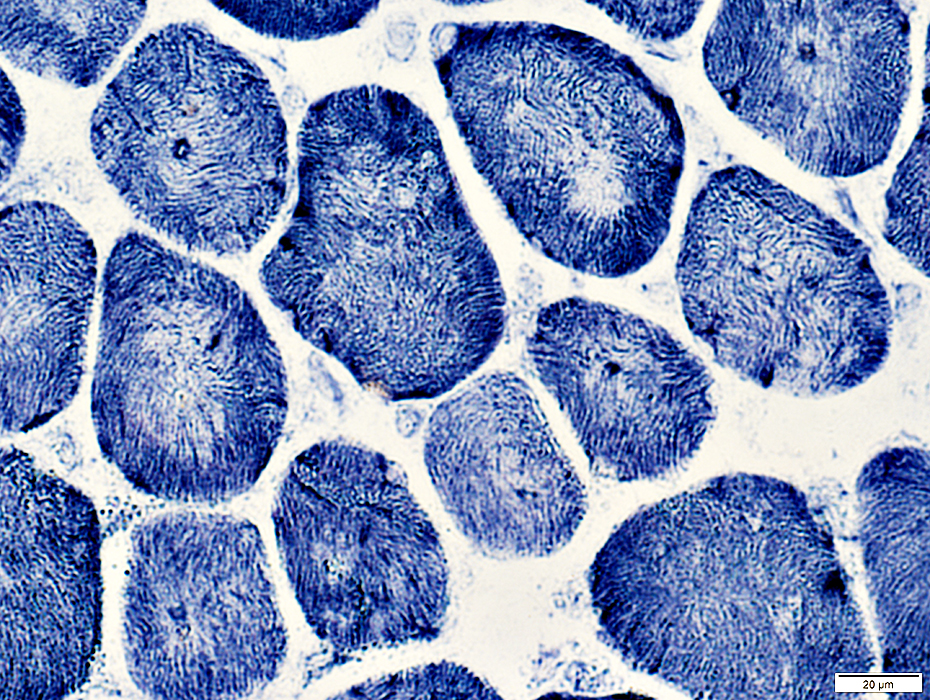 NADH stain |
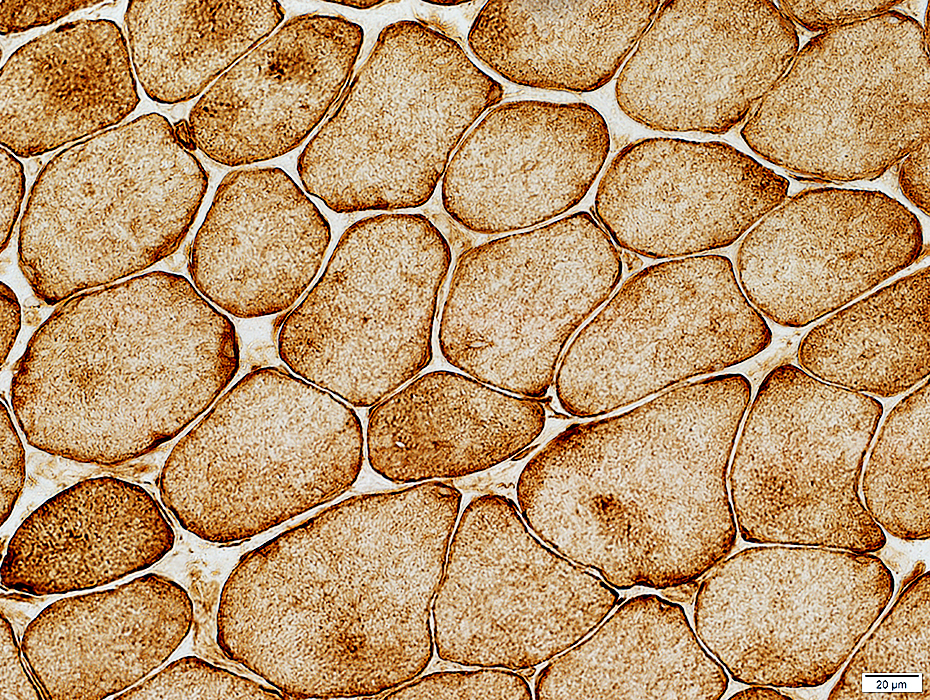 Desmin stain |
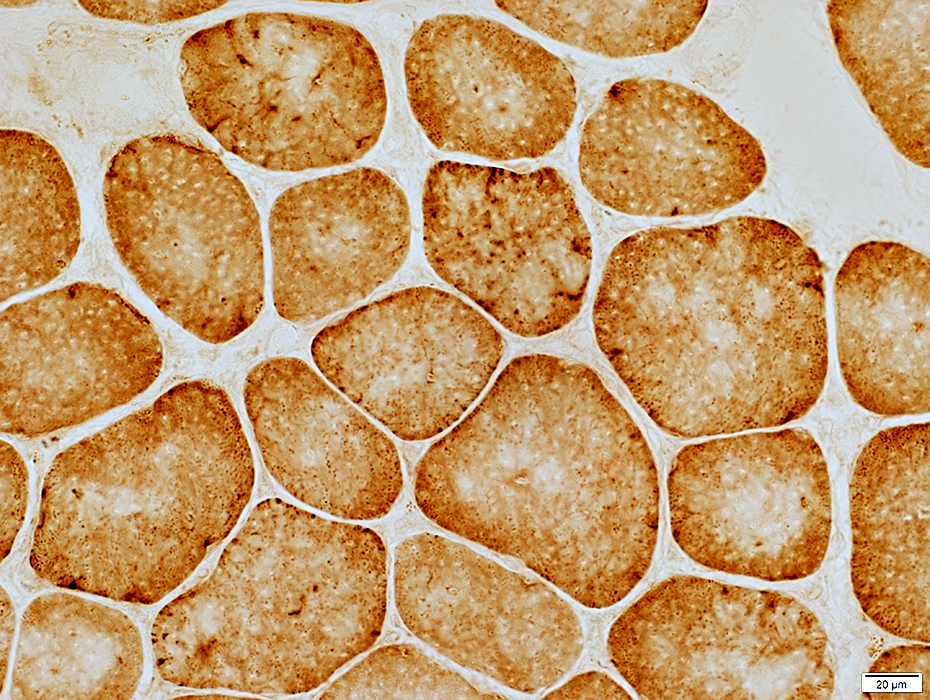 COX stain |
Internal nuclei; Surrounded by acid phosphatase stain
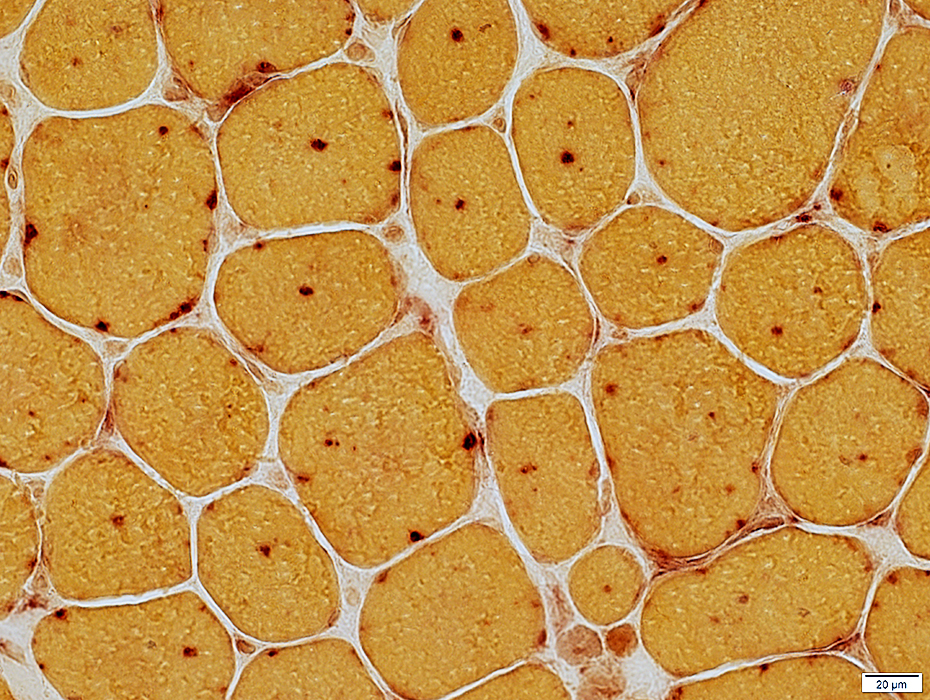 Acid phosphatase stain |
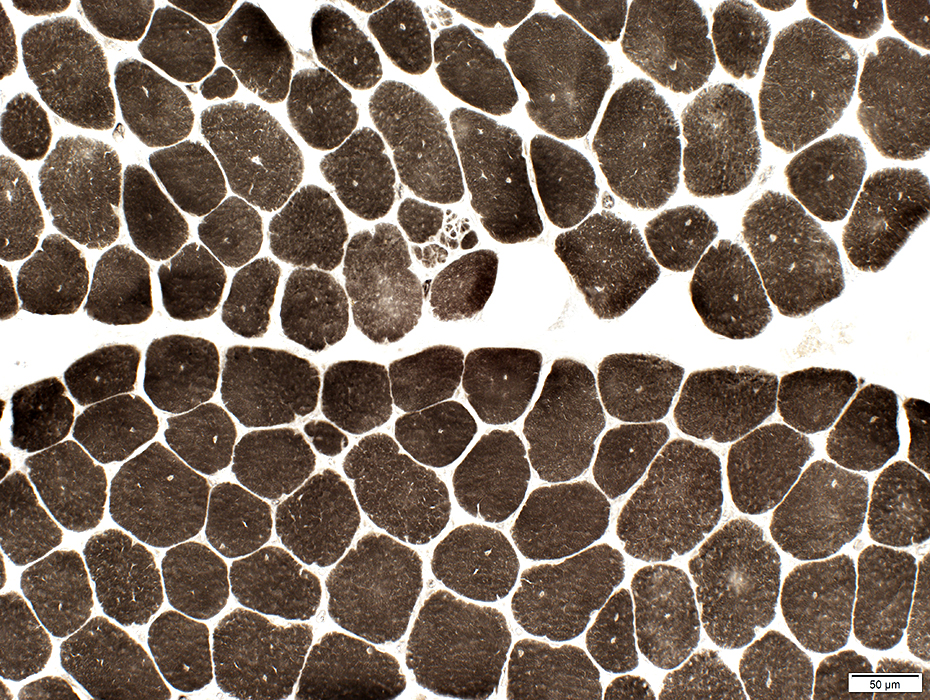 ATPase ph 9.4 stain |
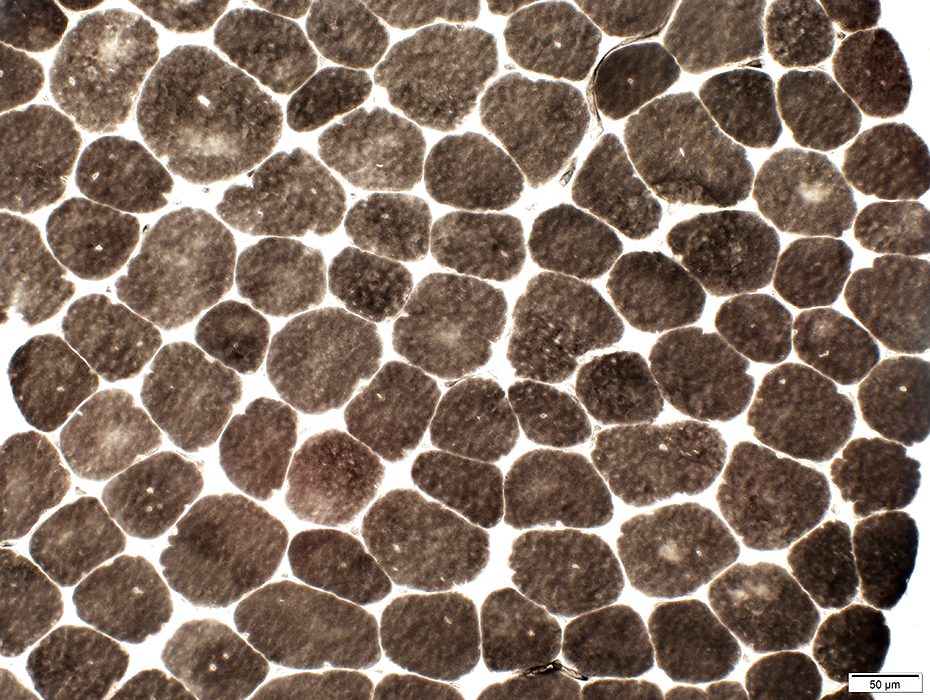 ATPase ph 4.3 stain |
Also see: Congenital fiber type size disproportion
Return to Centronuclear myopathy
References
1. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2016 Jan 28
12/18/2024