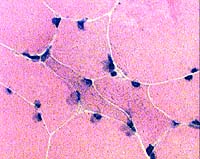
H & E stain
Image: Small angular muscle fibers
Answers
Subacute partial denervation
Type 2 muscle fiber atrophy
Myosin-loss (Critical illness) myopathy
Inclusion body myopathies
What stains are useful in this differential diagnosis?
Answers
ATPase
Denervation: Small fibers of both types
Type 2 atrophy: Smallest fibers are type 2
Myosin loss: ATPase pH 9.4 shows muscle fibers with staining intensity less than type 1
H&E: Small angular fibers have large nuclei
Non-specific esterase & NADH stain of small fibers: Denervation dark; Type 2 atrophy pale
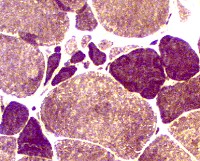
ATPase pH 9.4 stain
Image: Region of grouped atrophy with muscle fibers of mixed types
Answer: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Multiple small regions of grouped atrophy
Fibers in area of grouped atrophy commonly have varied types.
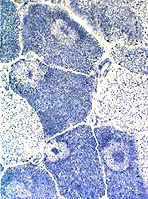
NADH-TR stain
What muscle most frequently shows this change?
Could these be cores?
Image: Rounded clear regions with dark rim & internal regions of staining
Answers: Targets
Most sensitive stains: NADH; COX; SDH; Caveolin-3
Occur with: Subacute denervation, possibly with some reinnervation; Tenotomy
Especially common in the gastrocnemius muscle
Often have darker rims and central staining regions, but cores do not
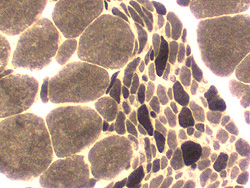
ATPase pH 9.4 stain
Image
Large grouped atrophy
Large muscle fibers: Predominantly type 1
Small fibers: Mixed type
Answers: Spinal muscular atrophy
Small fibers in SMA may be mostly type 2 or of mixed type
Other causes of chronic partial denervationgwith reinnervation may also produce this pattern
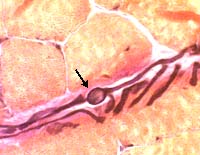
VvG stain
What stains best visualize it?
Answer: Polyglucosan body
Polyglucosan bodies in terminal axons in muscle are non-specific.
They are most easily seen on VvG stain.
The swellings are positively staind by PAS.
Diseases that cause polyglucosan bodies and other axonal swellings
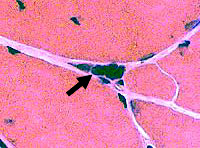
H & E stain
Answer: Pyknotic nuclear clump
How did it develop?
Answer: A muscle fiber that is so severely atrophied that only its pyknotic (dark shrunken) nuclei remain.
What disorders can produce it?
Answers
Chronic denervation of a muscle fiber without reinnervation
Neuropathies, chronic
Myasthenia gravis: Under-treated
Myotonic dystrophy
General: Pyknotic nuclear clumps suggest a neuropathy but are not specific for denervation.