SPINAL MUSCULAR ATROPHY (5q)
|
SMA Mechanisms of pathology General features SMA Types Related to Severity SMA, Congenital (Type 0) SMA, Type 1 SMA, Type 2 SMA, Type 3 Age 2 years Age 6 years Age 27 years Also see Spinal Muscular Atrophy, 5q XBSMA pathology |
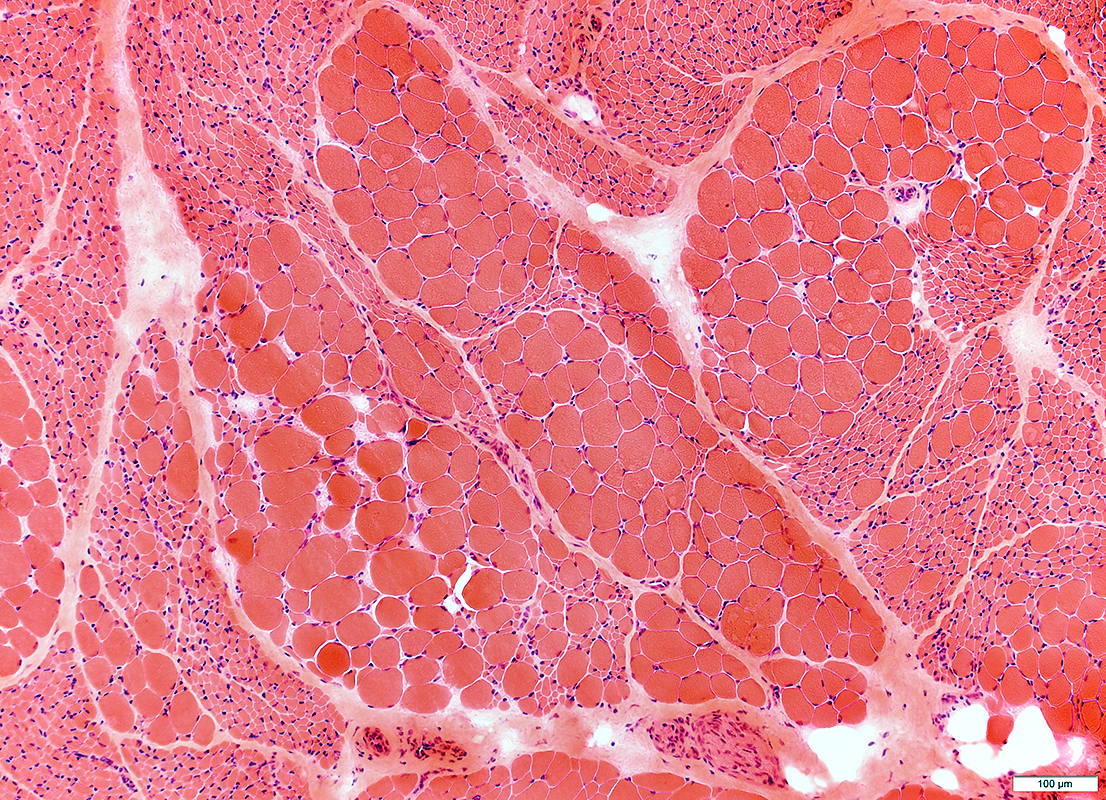 H&E stain |
SMA: Mechanisms Underlying Pathology
- Initial innervation
- By reduced nubers of motor axons
- Functional axons
- Innervate, & maintain size of, larger muscle fibers
- Abnormal patterns of activity produce
- Hypertrophy: Larger muscle fibers have
- Very increased size for age
- Type 1 fiber predominance
- Atrophy
- Some muscle fibers may be innervated by non-functioning axons
- Esterase stain: NMJs are preserved with Strongly staining on some small & large muscle fibers
- Younger patients: Many 2C fibers
- ATPase pH 4.6: No 2A fibers; Many degrees of staining of 2B fibers
- Abnormal fiber types
- Type I fibers by ATPase: May be pale on COX or dark on PAS
- Darker fibers on COX: May also be dark on PAS
- Hypertrophy: Larger muscle fibers have
- Disease progression
- Axon loss: Not proven
- Axons may become progressively dysfunctional or lost
SMA 5q: General Features
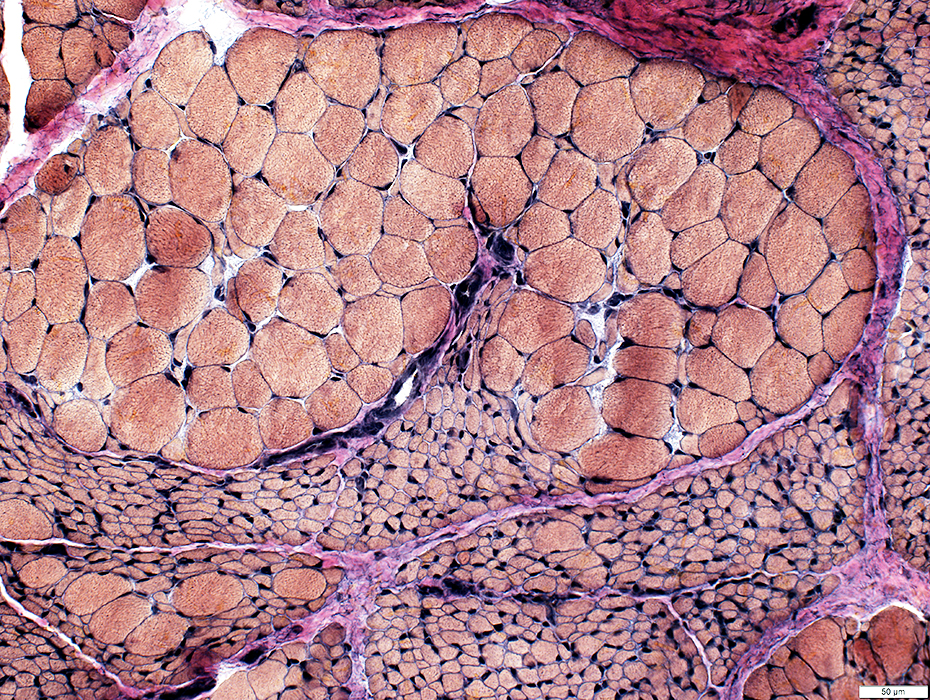 VvG stain |
Small fibers: Large groups
Large fibers: Clustered; Hypertrophied, especially for age
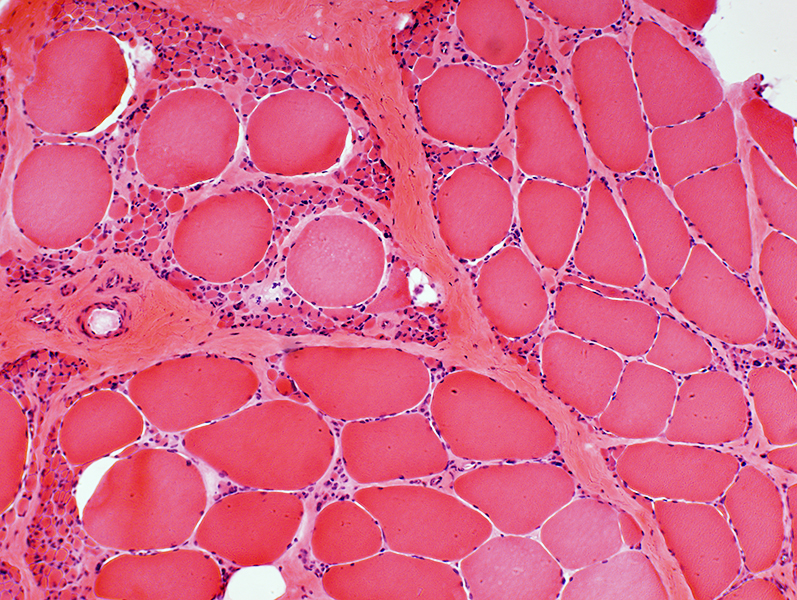 H&E stain Grouped atrophy Small muscle fibers: Often rounded Pyknotic nuclear clumps: None Large muscle fibers: Hypertrophy |
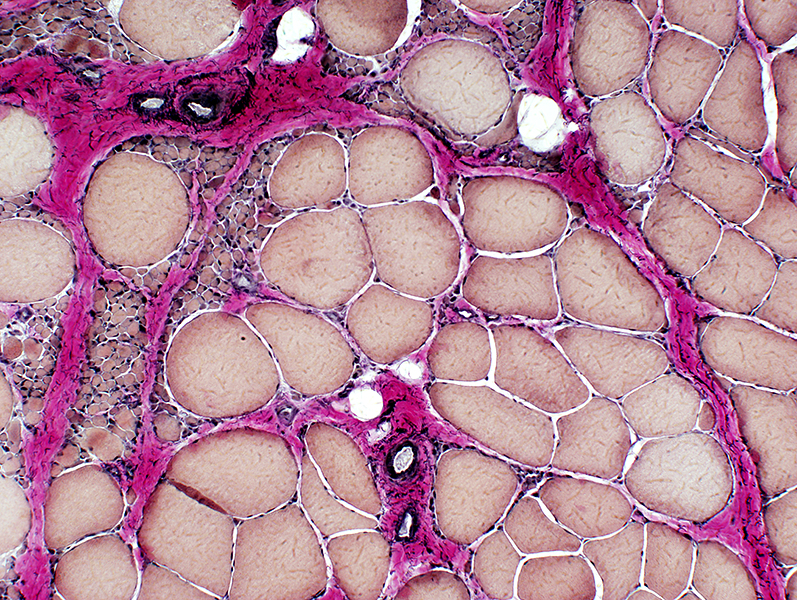 VvG stain |
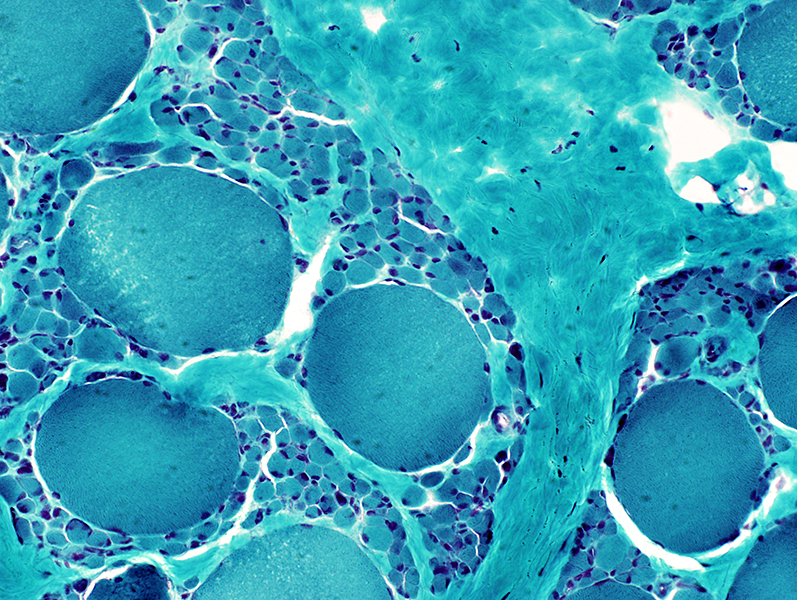 Gomori trichrome stain |
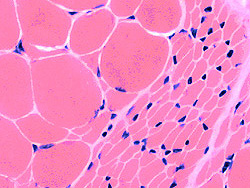 H&E stain Larger muscle fibers Hypertrophied Commonly type I Clustered Smaller muscle fibers Round Commonly type II, May also be I or IIC Clustered 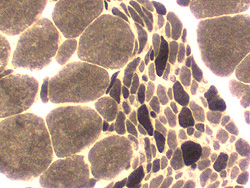 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
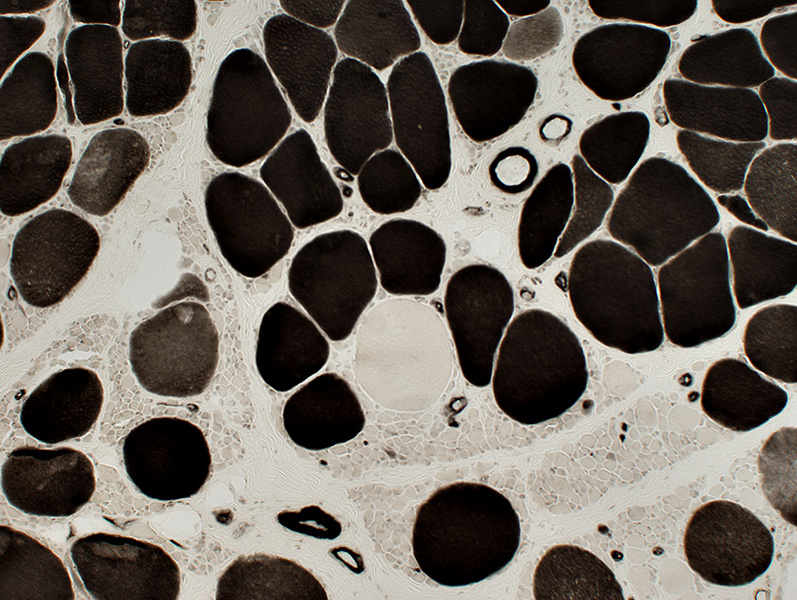 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
SMA, Congenital (Type 0)
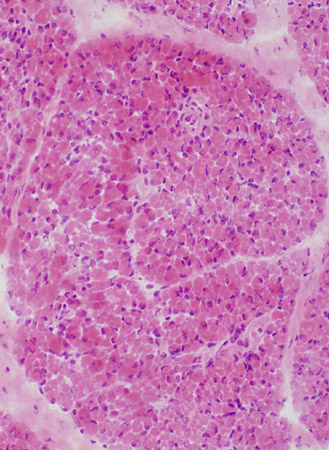 H & E |
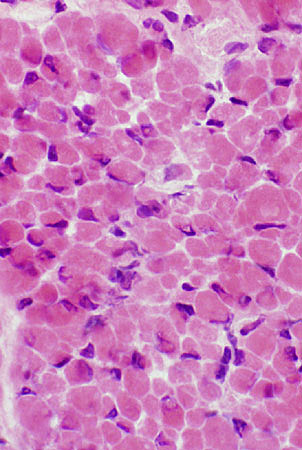 H & E |
|
Only small muscle fibers are present. Small fibers have moderate variation in size. | |
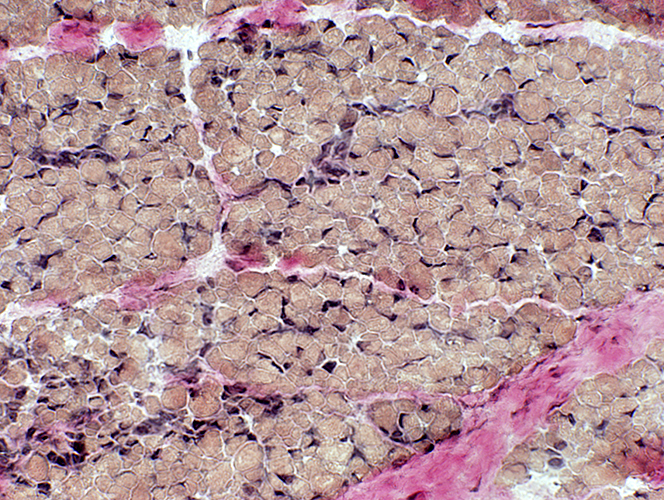 VvG |
SMA0: Fiber type properties
Many small fibers are Type 2C. (Intermediate stained at ATPase pH 4.3)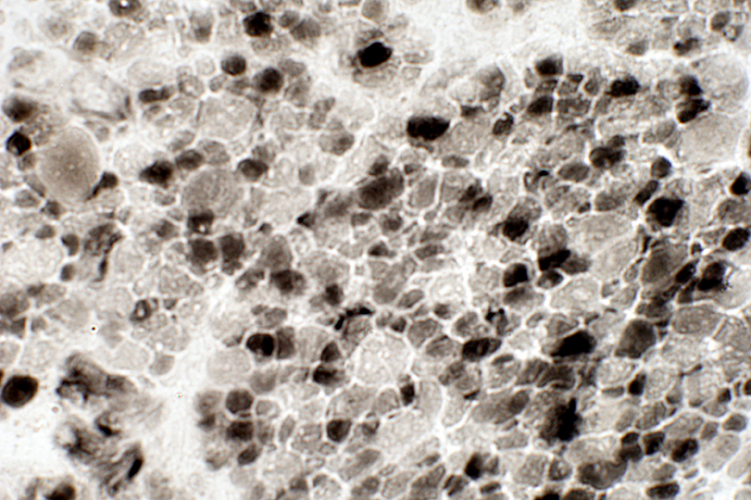 ATPase pH 4.3 |
Most muscle fibers are dark (Like type 2C) on ATPase pH 9.4
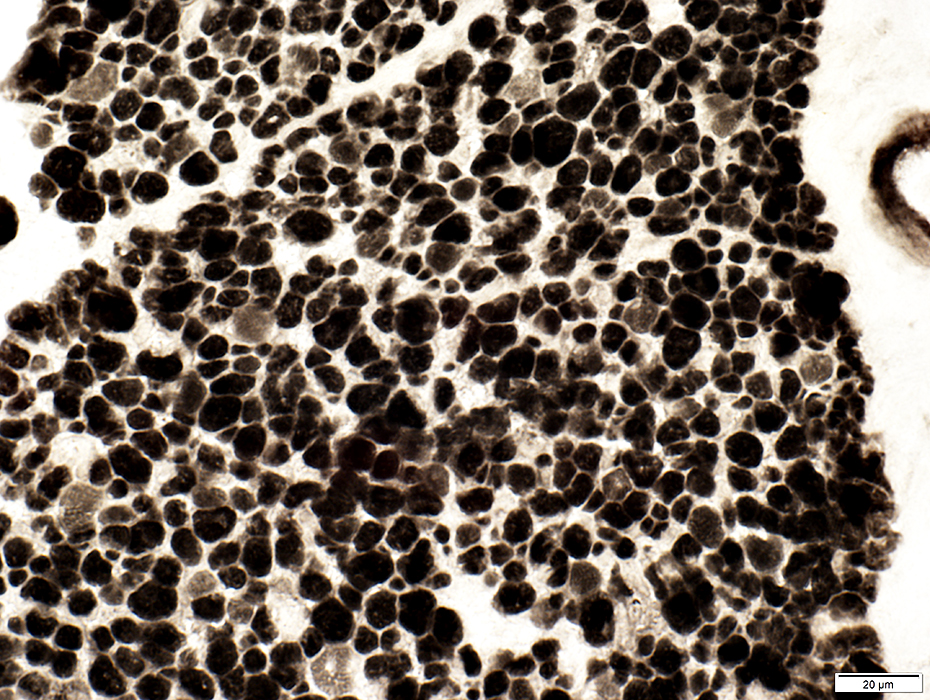 ATPase pH 9.4 |
Most muscle fibers are intermediate stained (Like type 2C) on ATPase pH 4.3
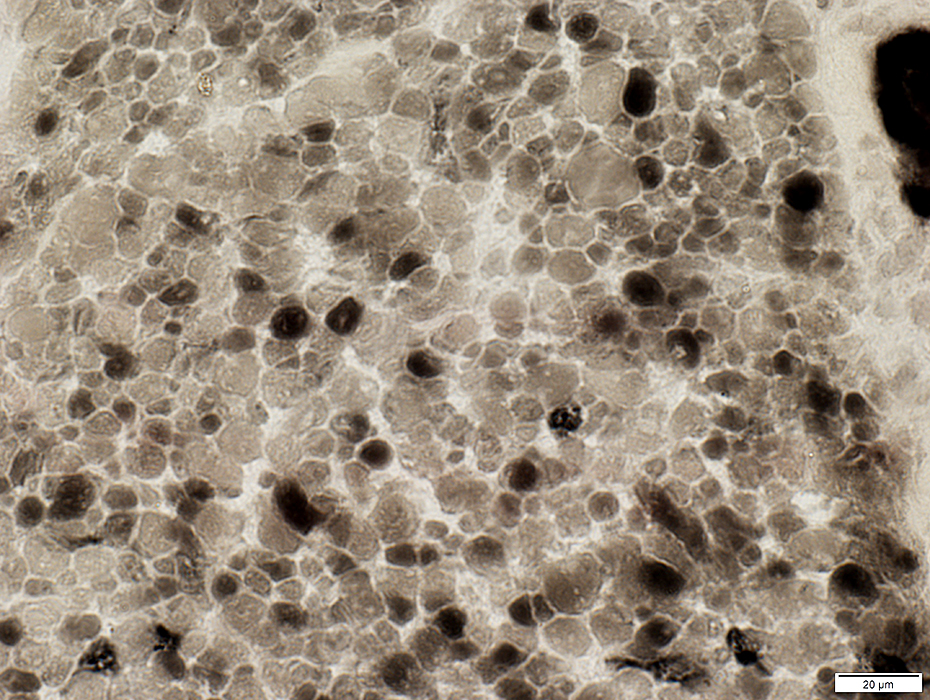 ATPase pH 4.3 |
Muscle fibers are variably intermediate stained (Like type 2B) on ATPase pH 4.6
There are no 2A muscle fibers
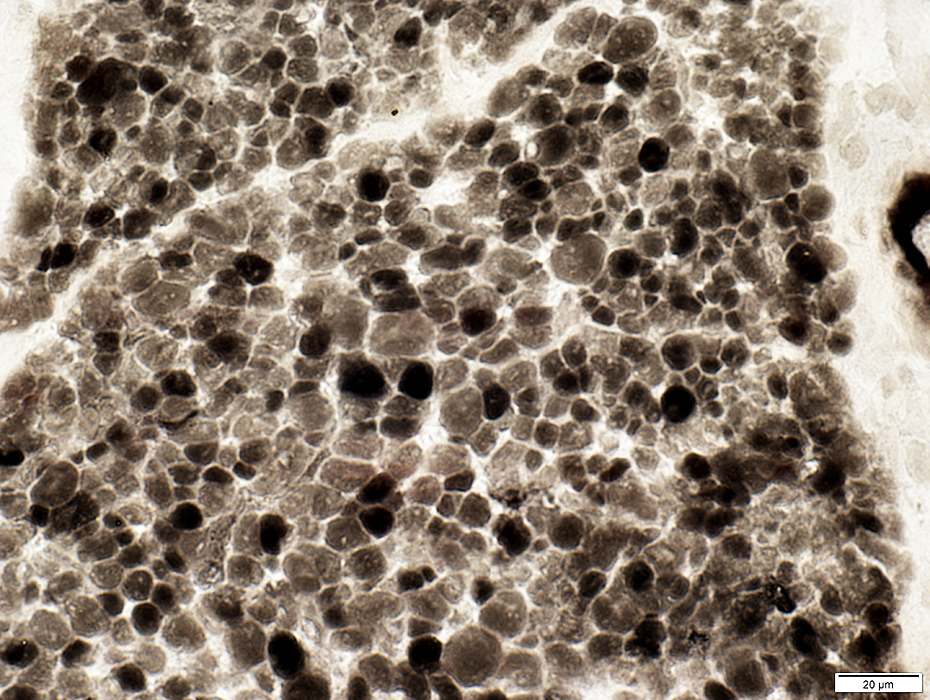 ATPase pH 4.6 |
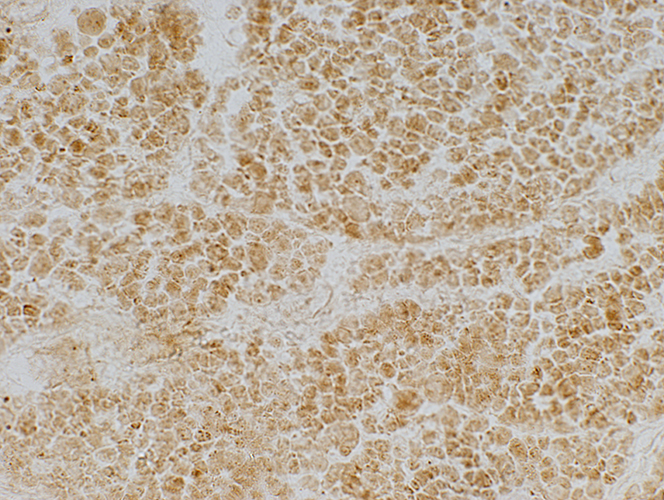 COX Mitochondrial stains are pale  SDH |
SMA, Type 1
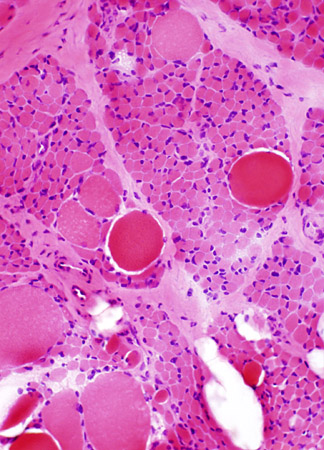 H & E |
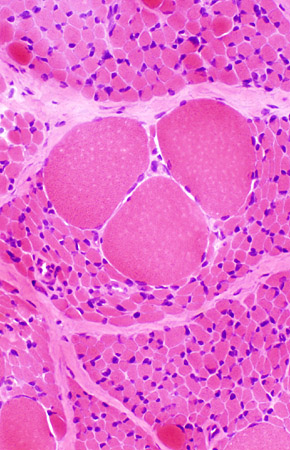 H & E |
|
Many muscle fibers are small. A few hypertrophied fibers are present | |
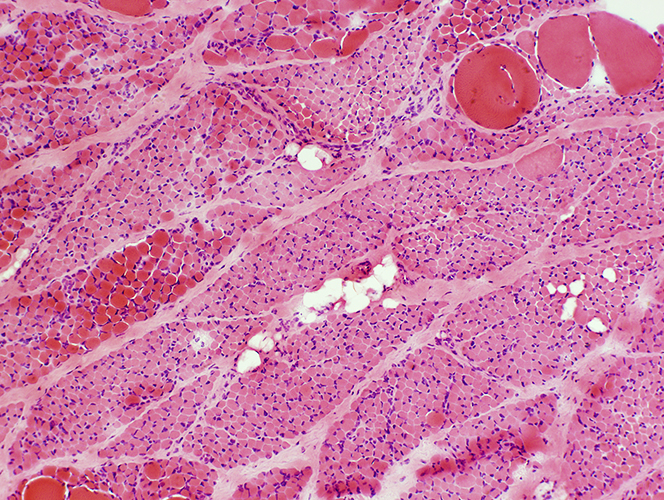
| |
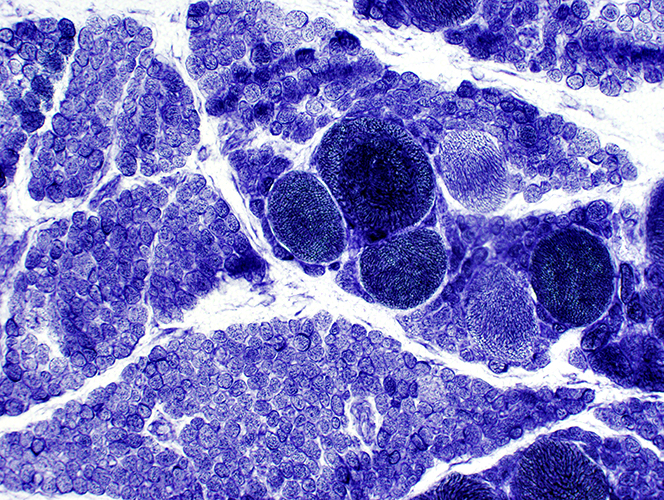
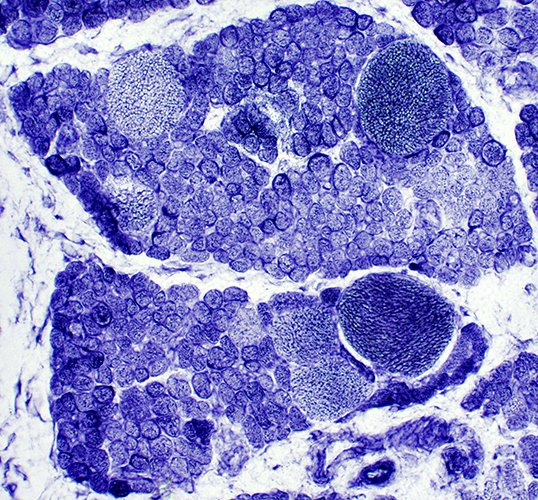 NADH |
Some large & small muscle fibers have reduced or absent glycogen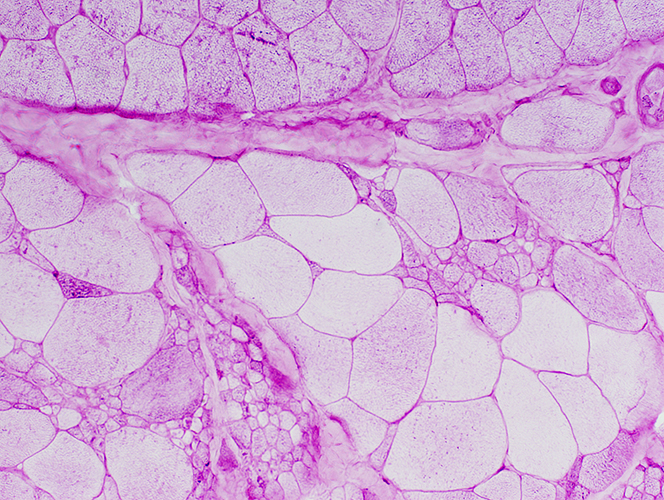 PAS |
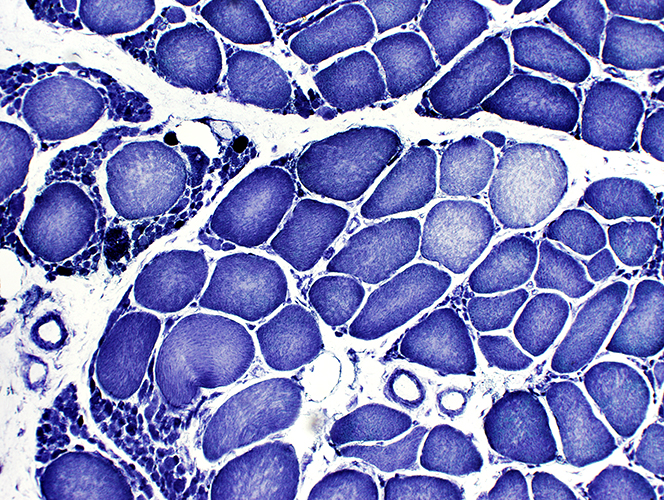
SMA Type 2
Age: 9 months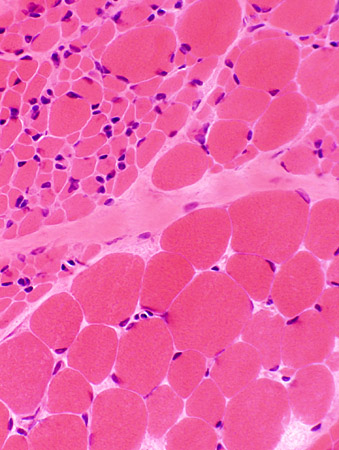 H&E stain Large groups of atrophic muscle fibers |
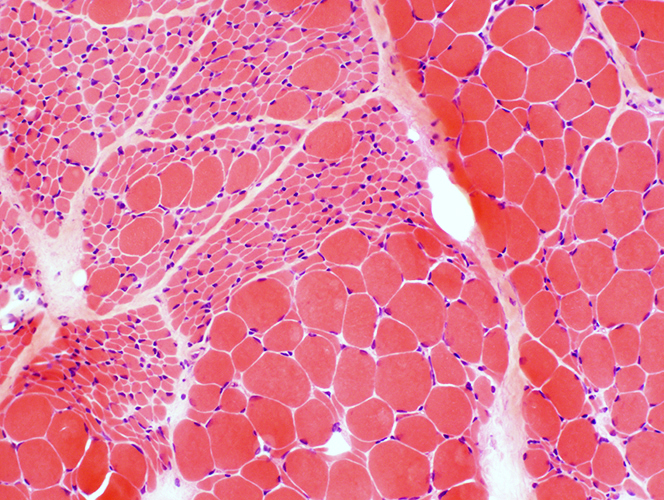 H&E stain |
Patterns of fiber size changes: Varied among fascicles
Hypertrophic muscle fibers with scattered small angular fibers (Top; Left)
Intermediate, variably sized fibers (Bottom; Left)
Very small fibers: No pyknotic nuclear clumps (Middle)
Large & Small fibers with grouped atrophy (Right)
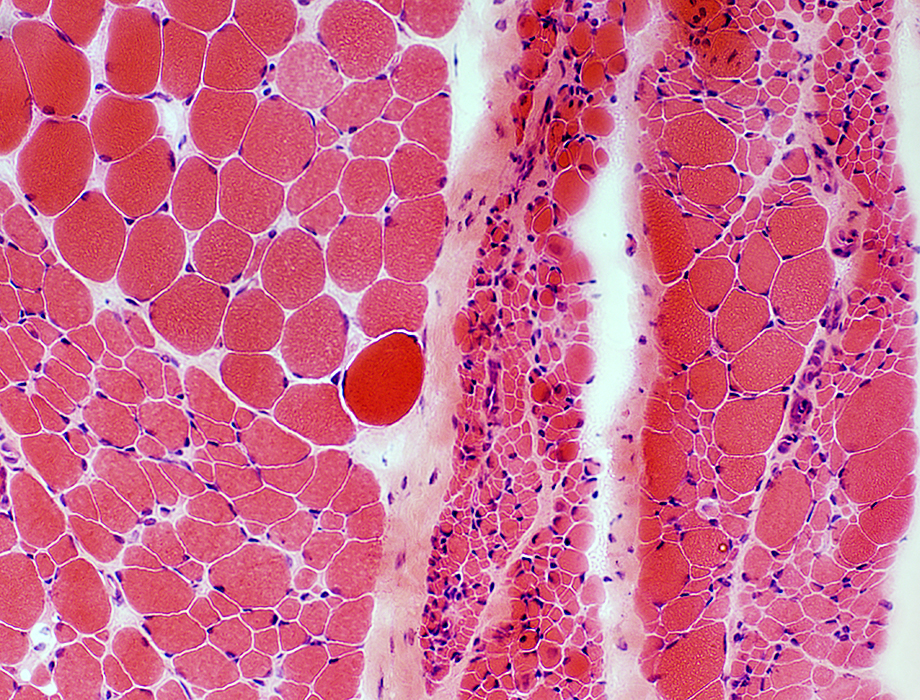 H&E stain |
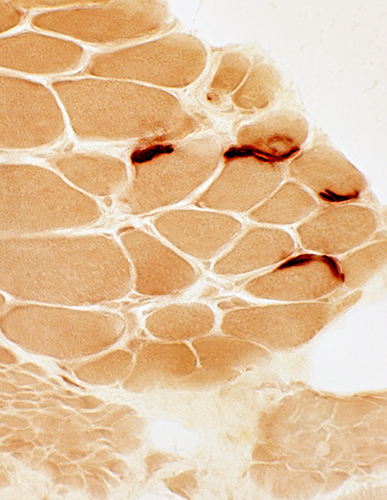 Esterase |
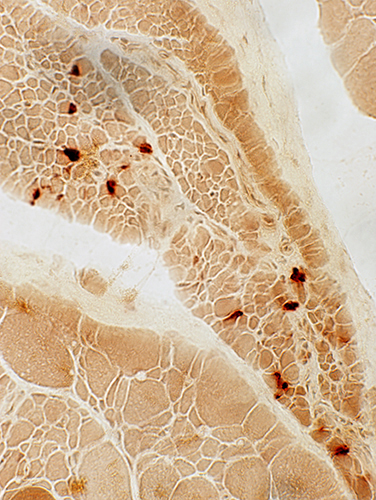 Esterase |
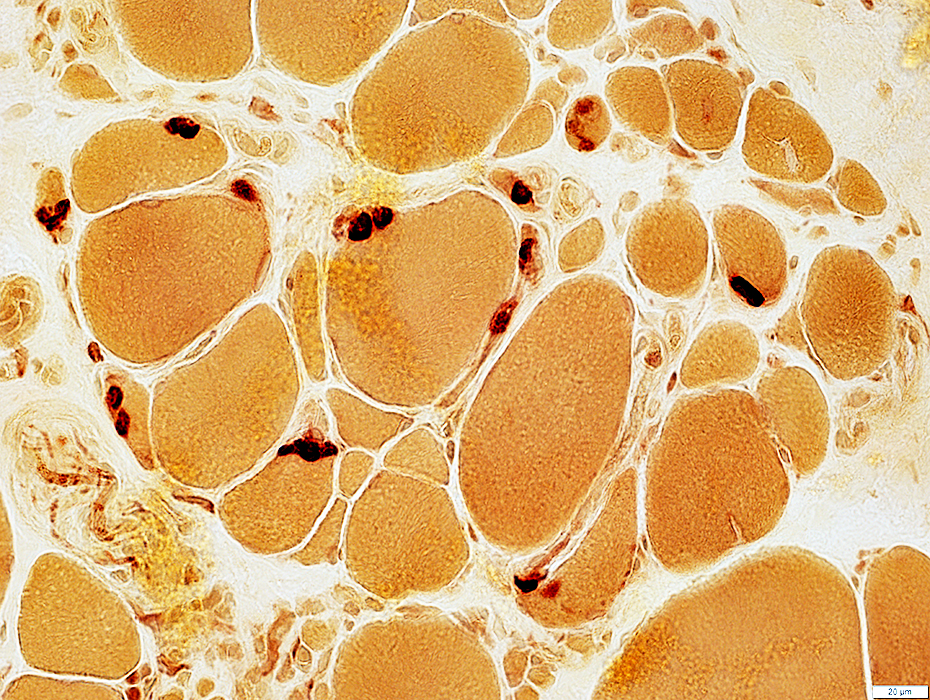 Esterase stain |
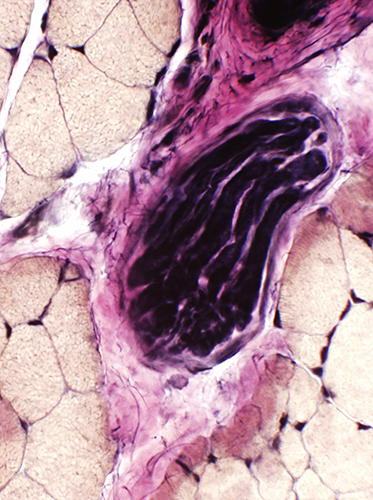 VvG Intramuscular nerves: Unremarkable |
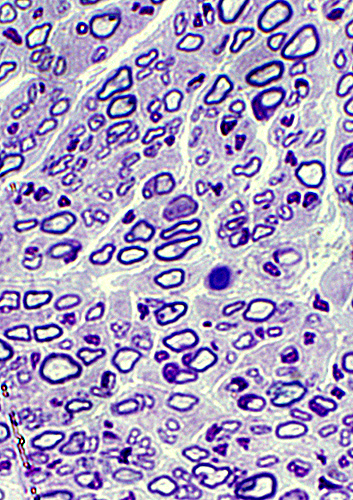 Toluidine blue Sensory nerve Normal numbers of large & small myelinated axons Thinly myelinated larger axons: Consistent with young age. |
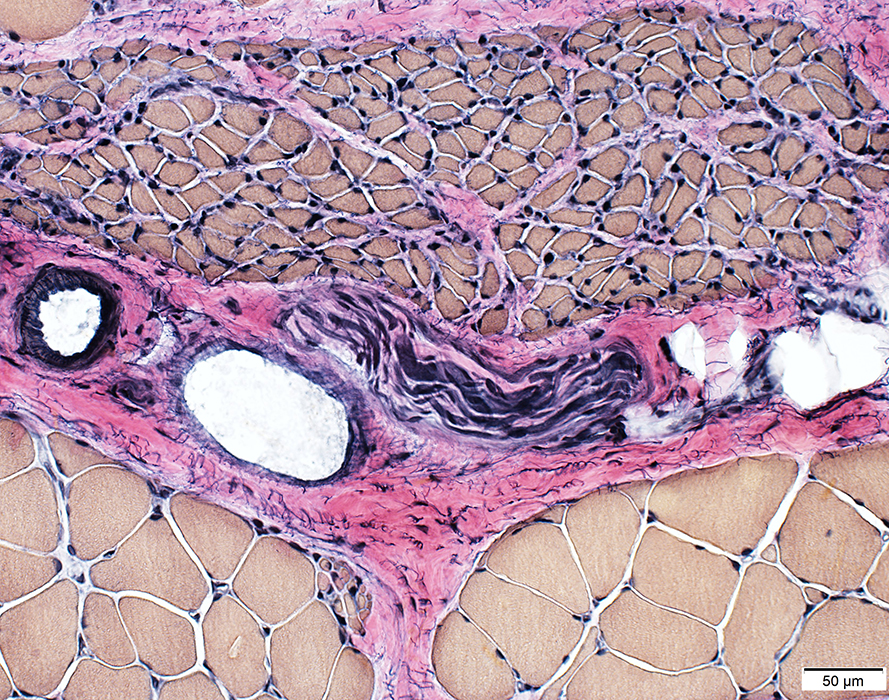 VvG |
 NADH |
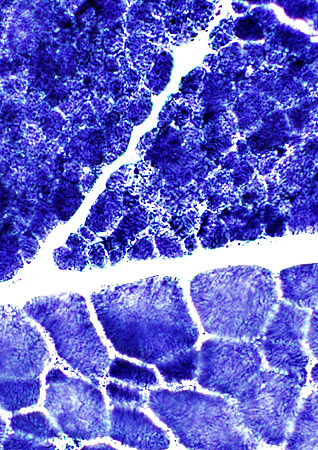 NADH |
Stain darkly on NADH
Large muscle fibers
Coarse internal architecture
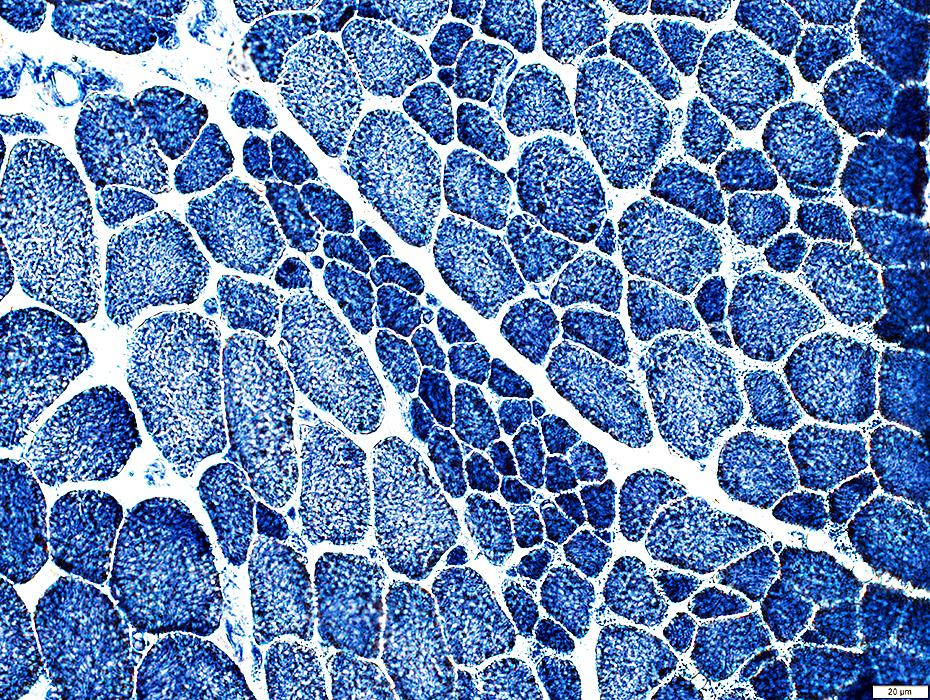 NADH |
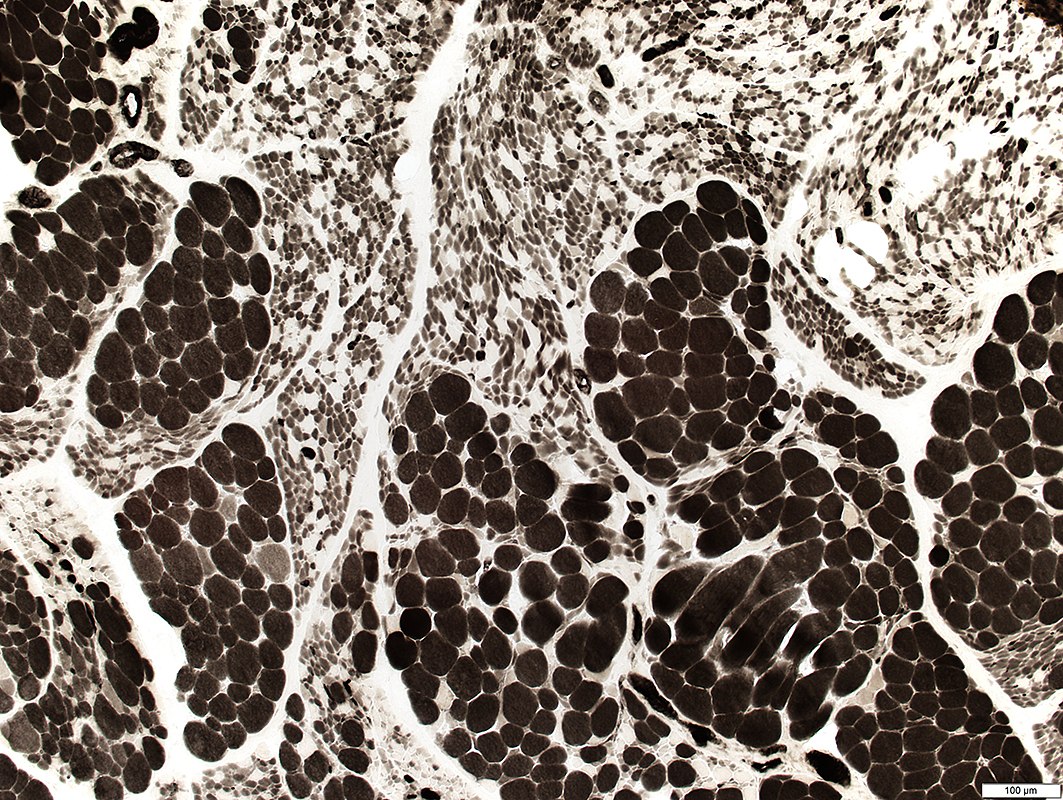
SMA 2: Fiber type properties
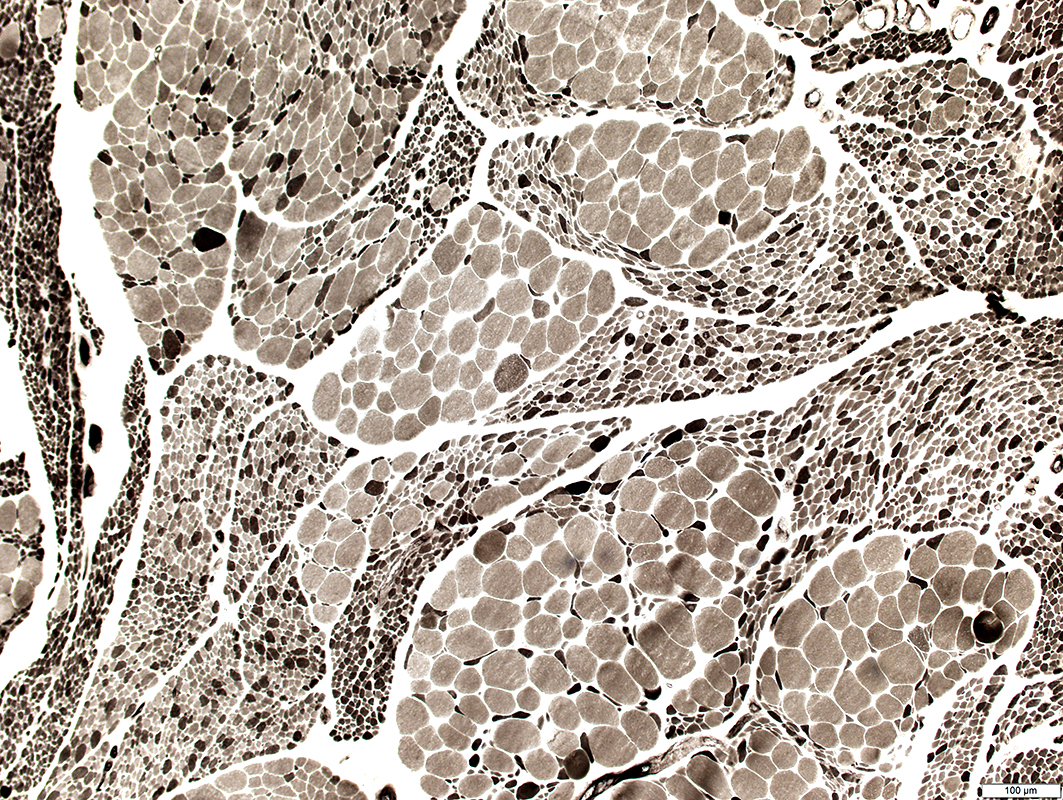 ATPase pH 9.4 |
Large muscle fibers: Hypertrophied; Clustered; Type I or Abnormal intermediate staining
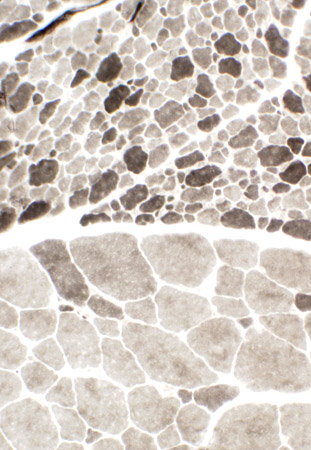
 ATPase pH 4.3 |
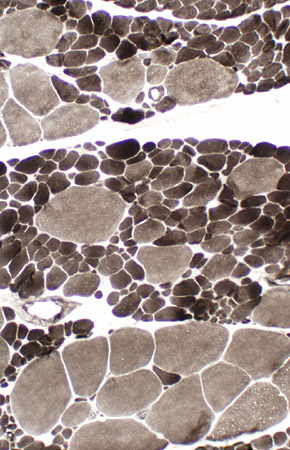
 ATPase, pH 9.4 |
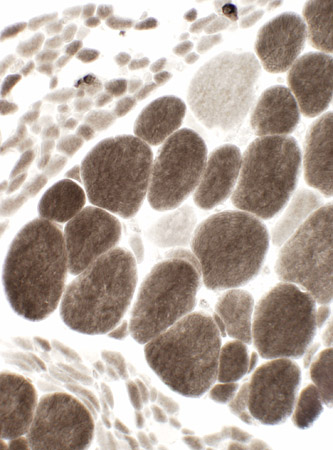
 ATPase, pH 9.4 |
 ATPase, pH 4.3 |
|
Small muscle fibers: May be varied types (Left) or mostly type II (Middle) Large muscle fibers: Clustered; Type I or Abnormal intermediate staining |
Many small fibers are type 2C | |
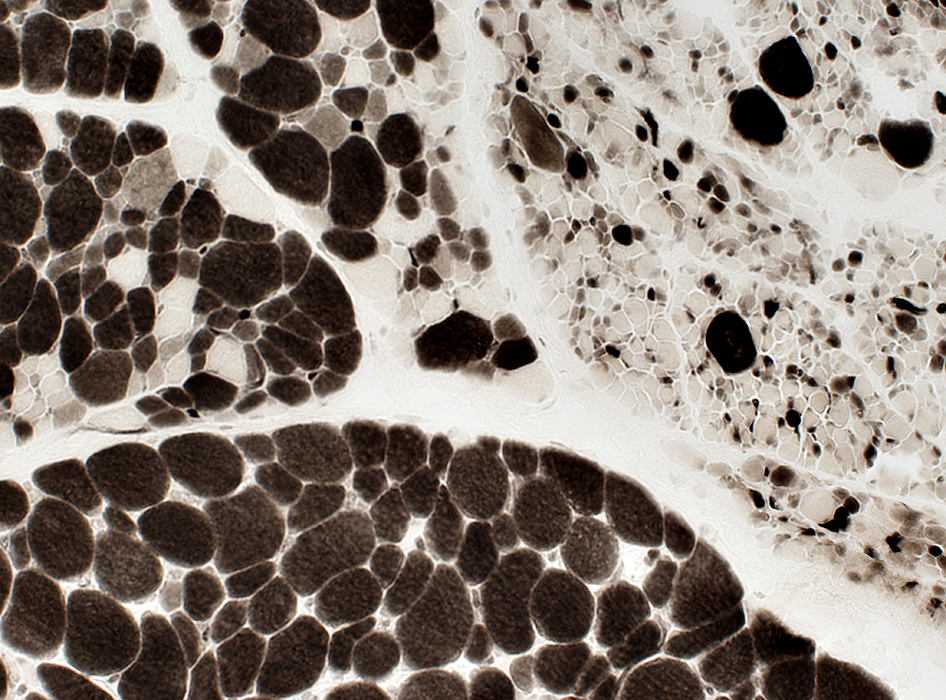 ATPase, pH 4.3 |
Incomplete Fiber Type Switching (Abnormal fiber types): ATPase doesn't entirely correspond to COX & PAS
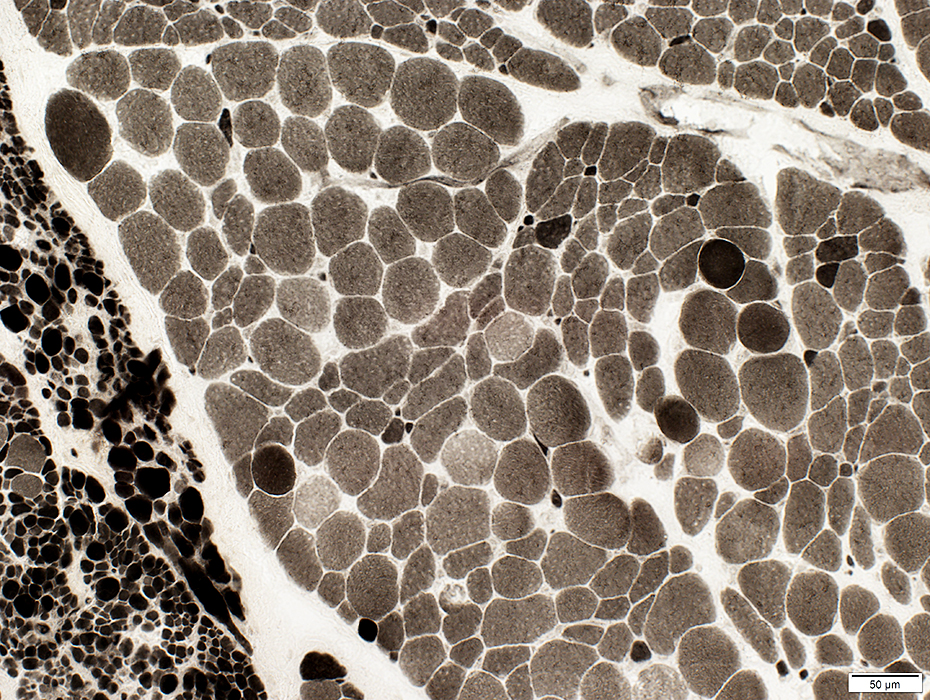 ATPase, pH 9.4 |
Small muscle fibers: Mostly type II (Dark staining)
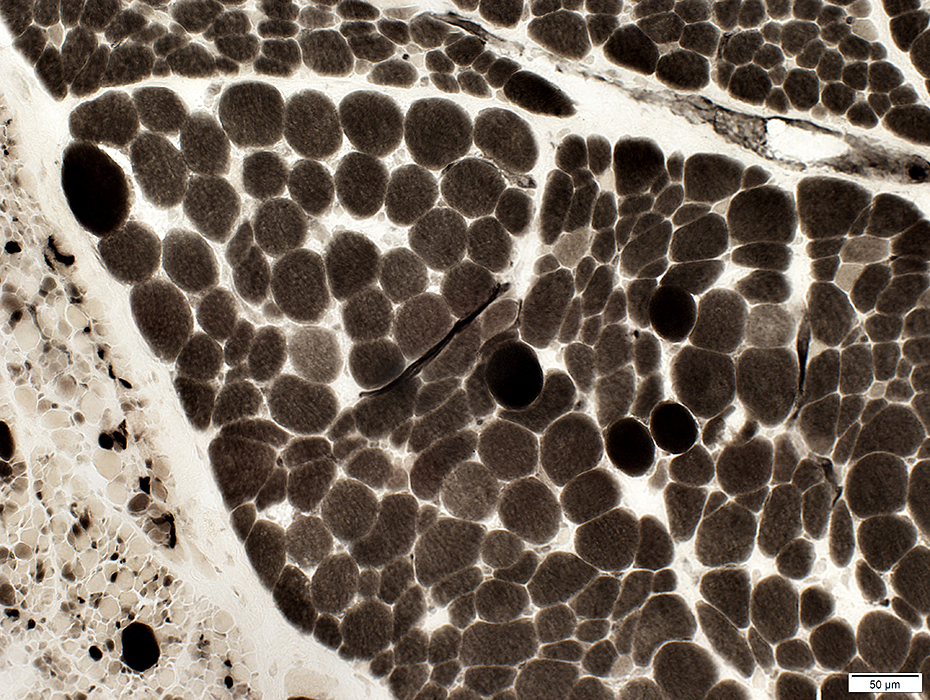 ATPase, pH 4.3 |
Small muscle fibers (Bottom left): Many type IIC (Varied degrees of intermediate staining)
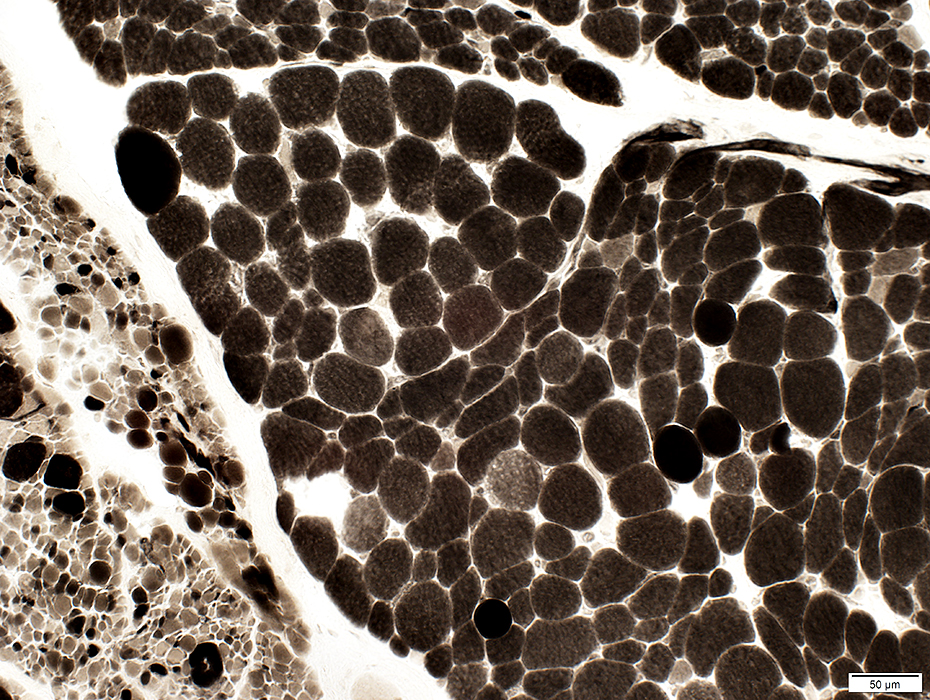 ATPase, pH 4.6 |
Small muscle fibers (Bottom left): Many type IIB (Varied degrees of intermediate staining); Few, or no IIA (Pale staining)
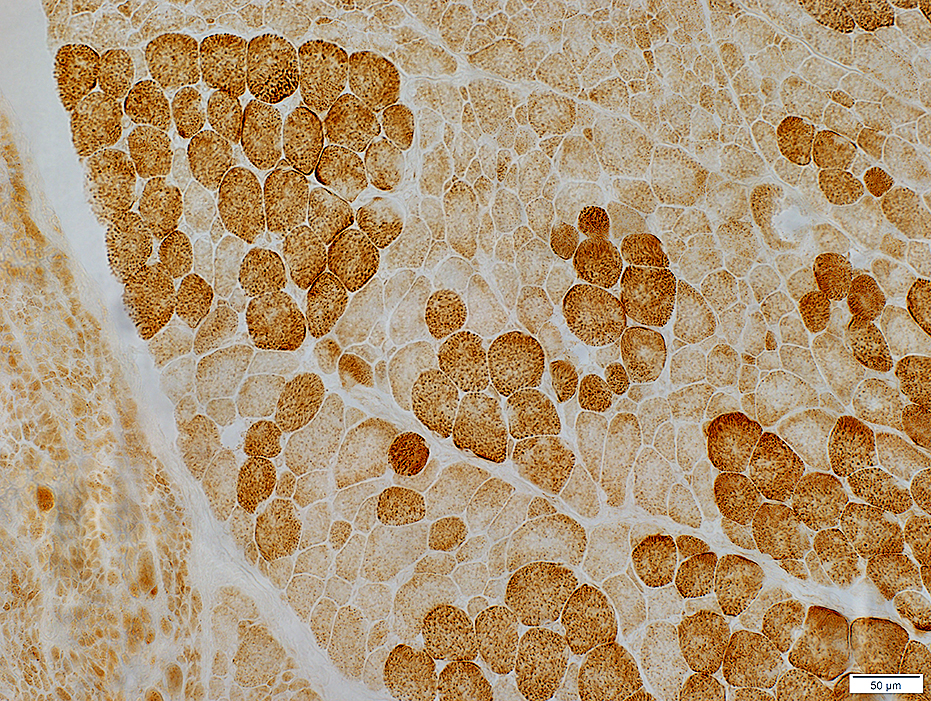 Cytochrome oxidase |
Large muscle fibers
Clusters of type I (Dark staining) & Type II (Pale staining)
Some pale stained fiber clusters (Type II pattern) are Type I patterns on ATPase
Small muscle fibers: Intermediate & Pale staining
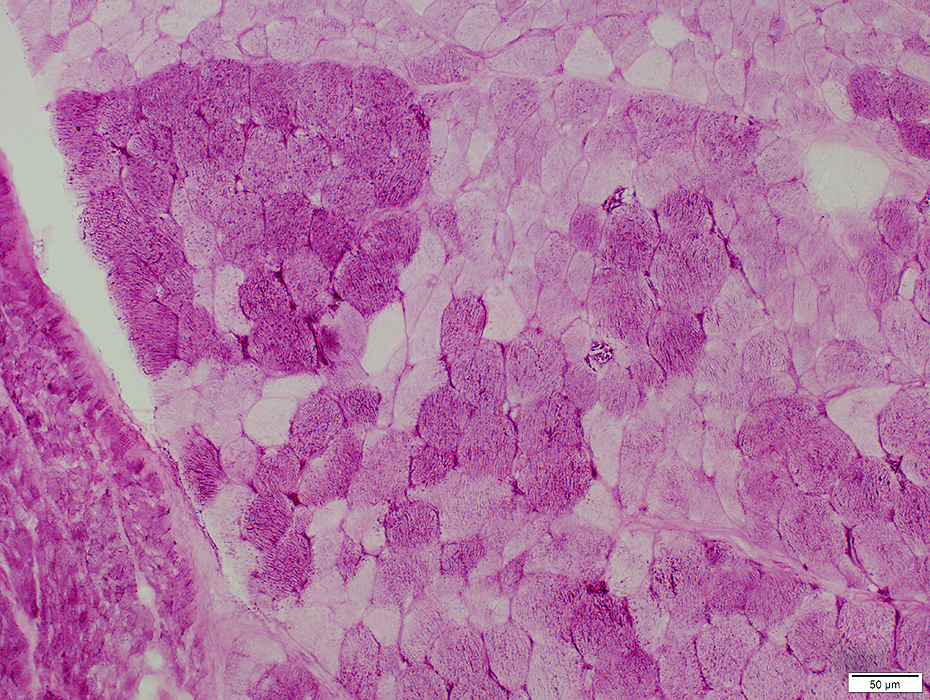 PAS |
Clusters of abnormal type II pattern (Dark staining) in type I fibers on ATPase & COX
Some clusters have Type I pattern (Pale staining)
Fiber types are opposite of COX pattern
Small muscle fibers: Type 2 pattern (Darker staining)
SMA Type 3, Age 2 years
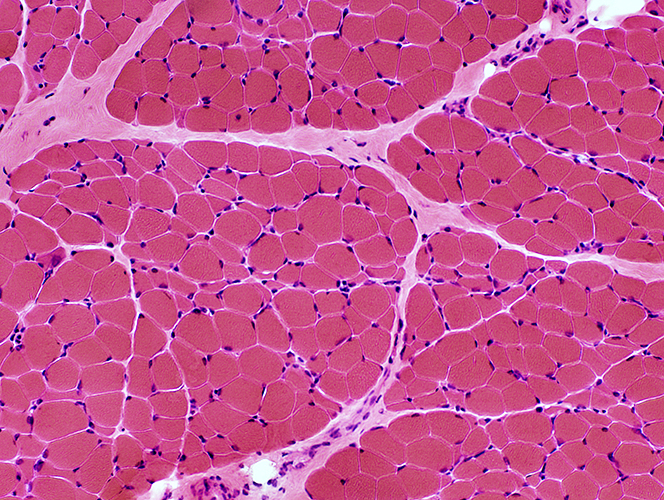 H & E |
|
|
Grouped atrophy. Larger muscle fibers are not promiently hypertrophied. | |
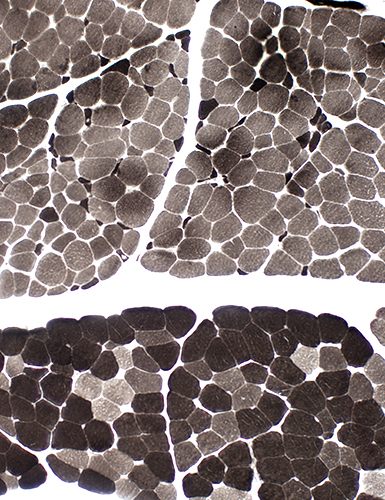 ATPase pH 9.4 |
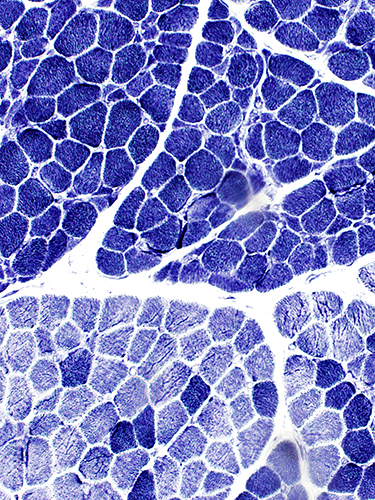 NADH |
|
Variable involvement of fascicles. Top: Scattered small fibers. Large fibers are type 1. Bottom: Few small fibers. Type 2 predominance. Abnormal intermediate-staining fibers. |
Variable involvement of fascicles. Top: Scattered small fibers. Most fibers are dark-stained. Bottom: Few small fibers. Most fibers are pale-stained. |
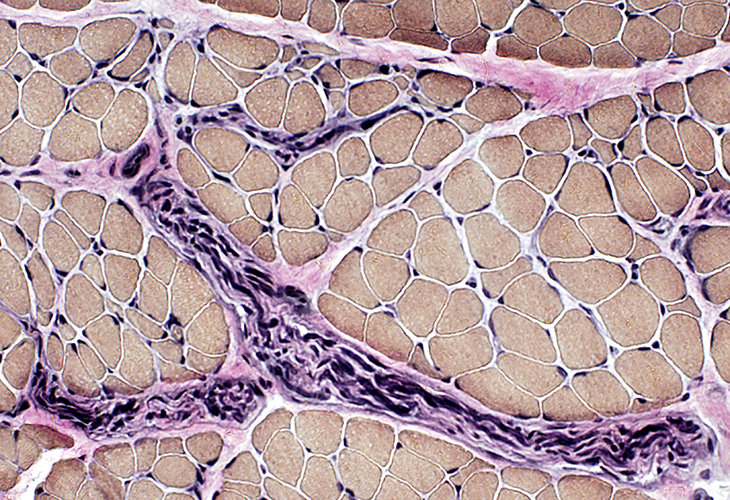 VvG |
|
|
Grouped atrophy. Larger muscle fibers: Not promiently hypertrophied. Intramuscular nerves: Mildly reduced axon numbers. | |
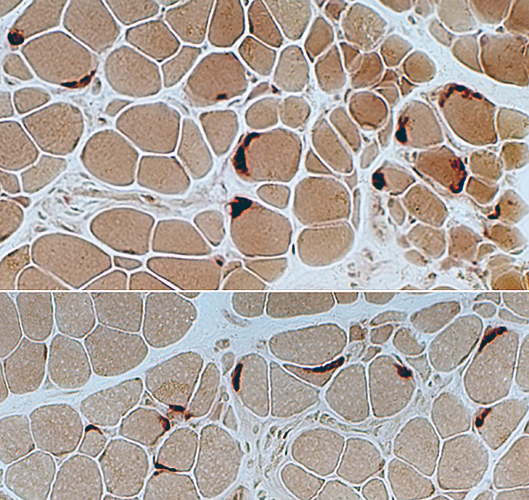 Esterase |
|
Neuromuscular junctions. Present on large and small muscle fibers. Shape: Large; Increased extent around muscle fibers; Not multi-segmented. |
SMA Type 3, Age 6 years
Same patient as above
 H & E stain |
Large muscle fibers: Hypertrophied
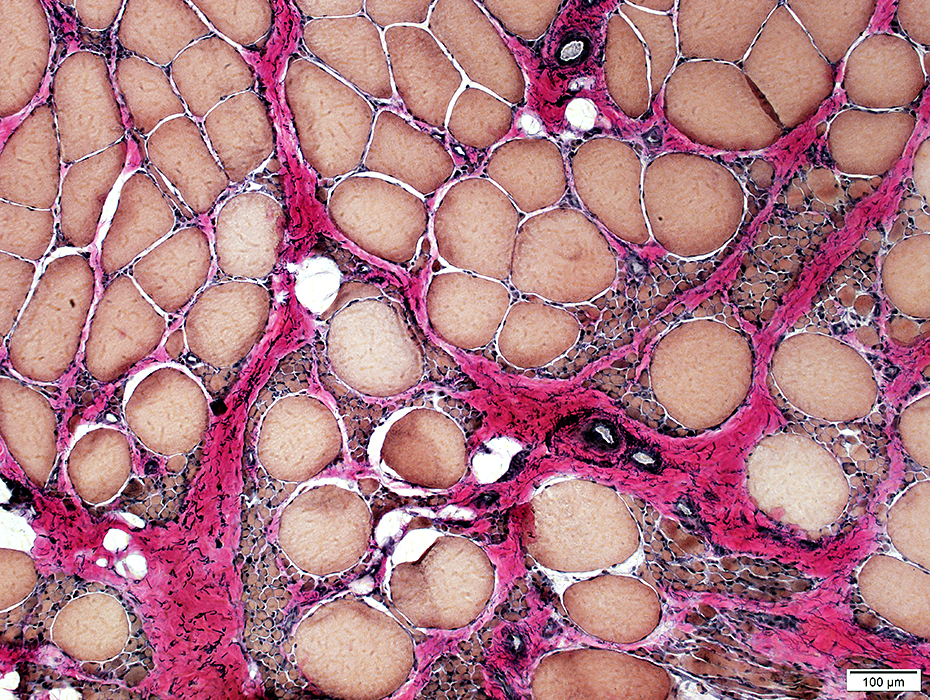 VvG stain |
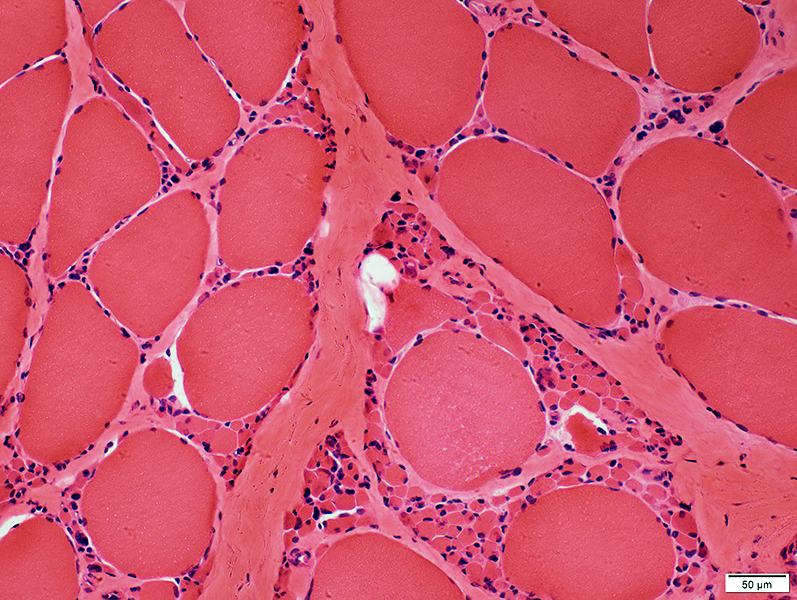 H & E stain |
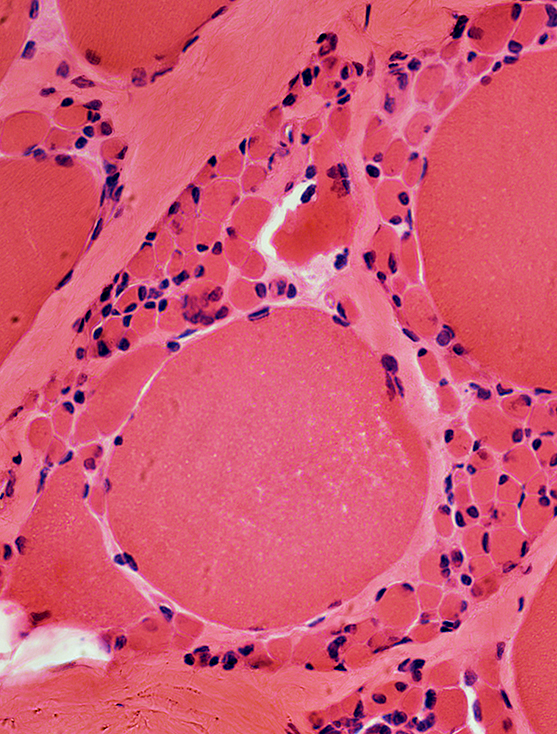 H & E stain |
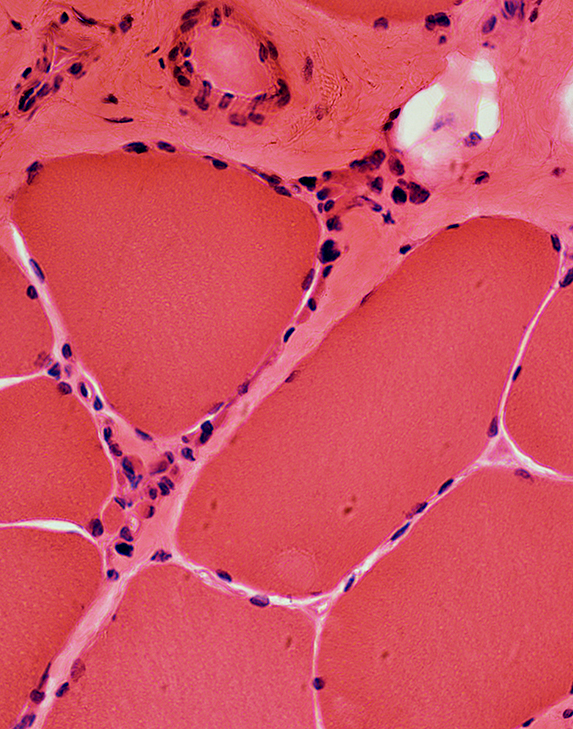 H & E stain |
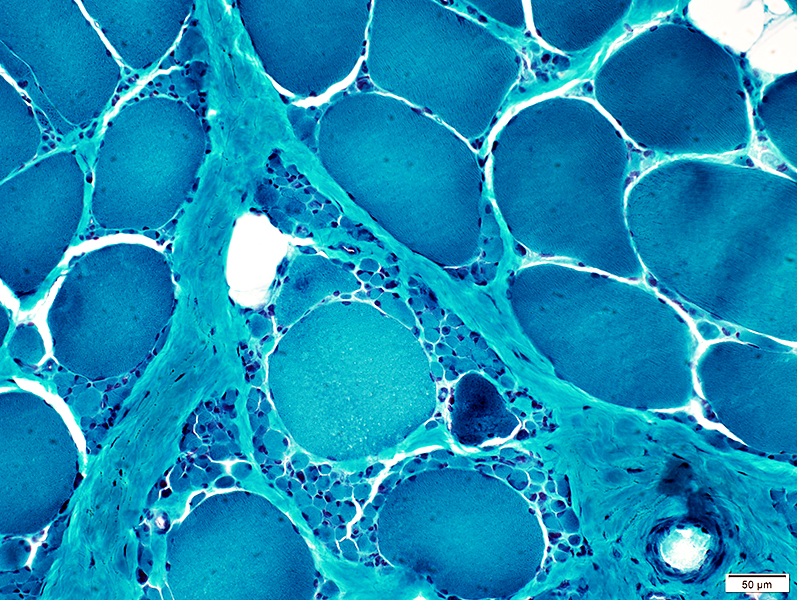 Gomori trichrome stain |
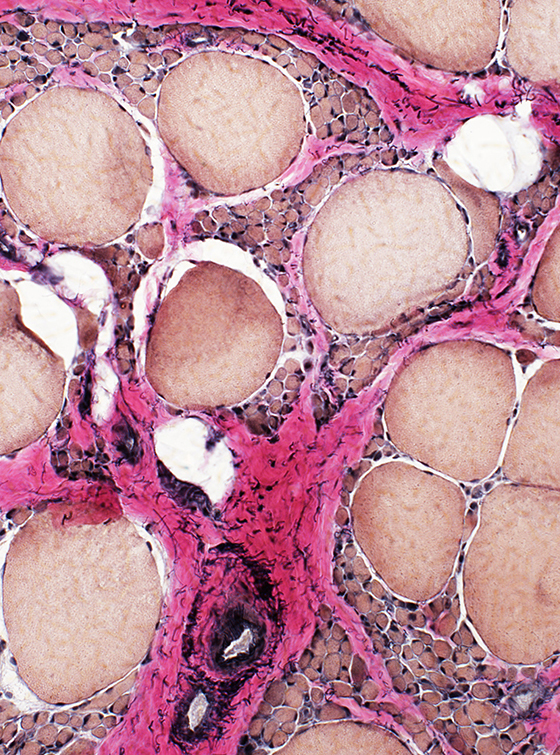 VvG stain |
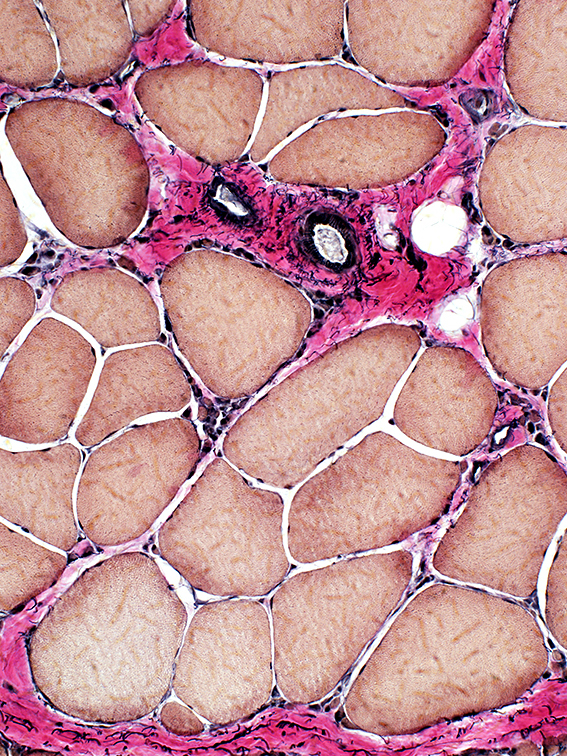 VvG stain |
Small muscle fibers: Dark-stained
Large fibers: Irregular internal architecture
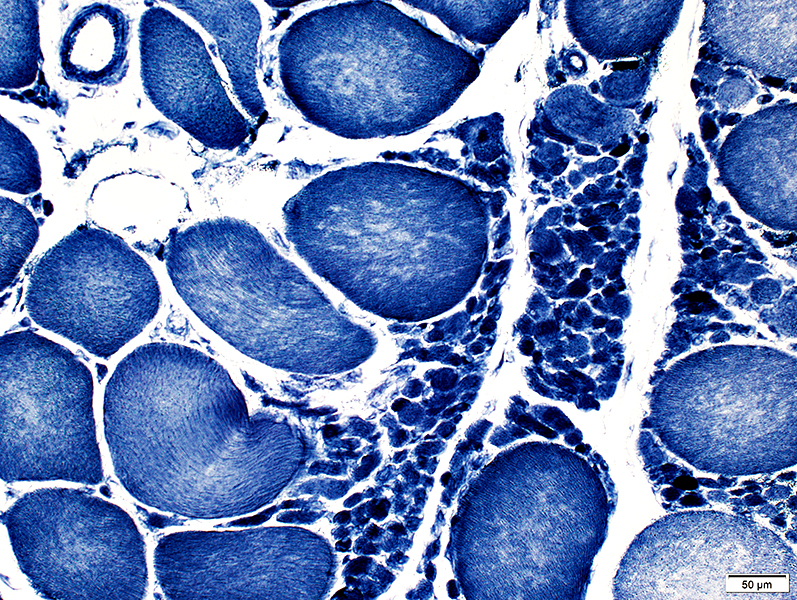 NADH stain |
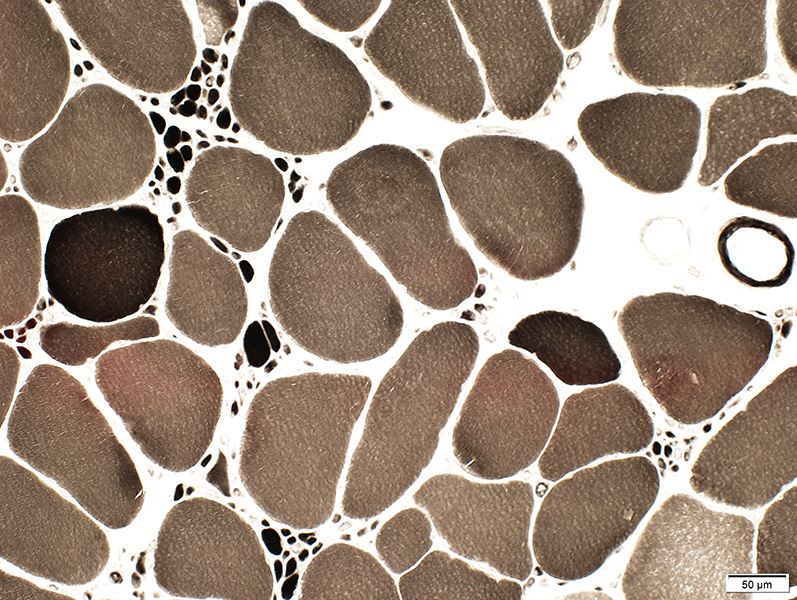 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
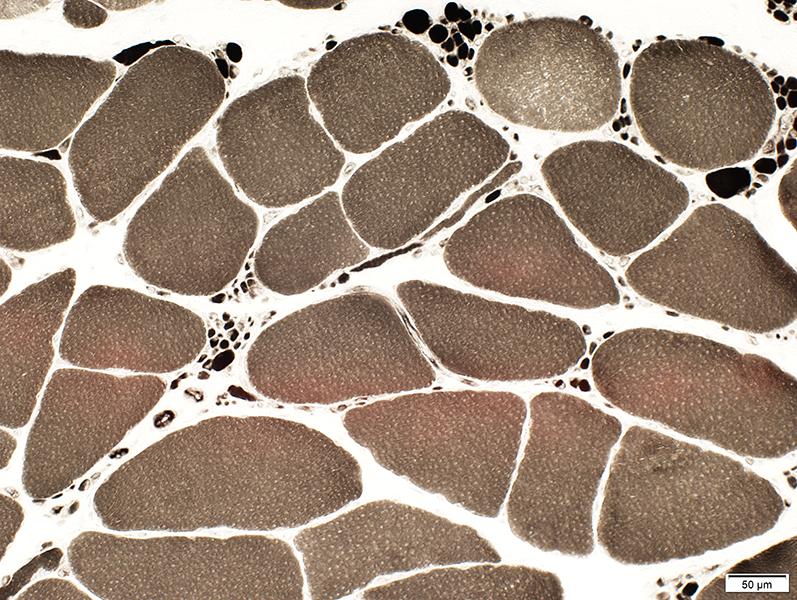 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
Small muscle fibers: Type II predominance
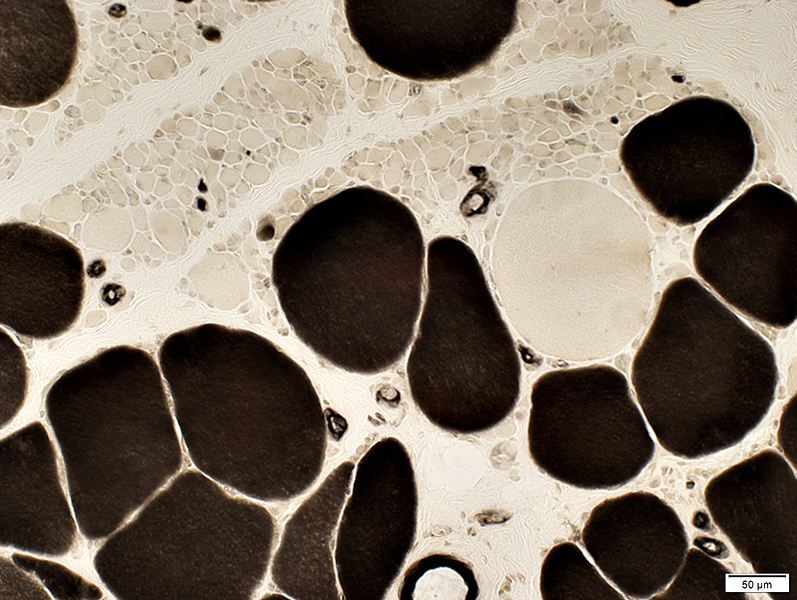 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
SMA Type 3, Age 27 years
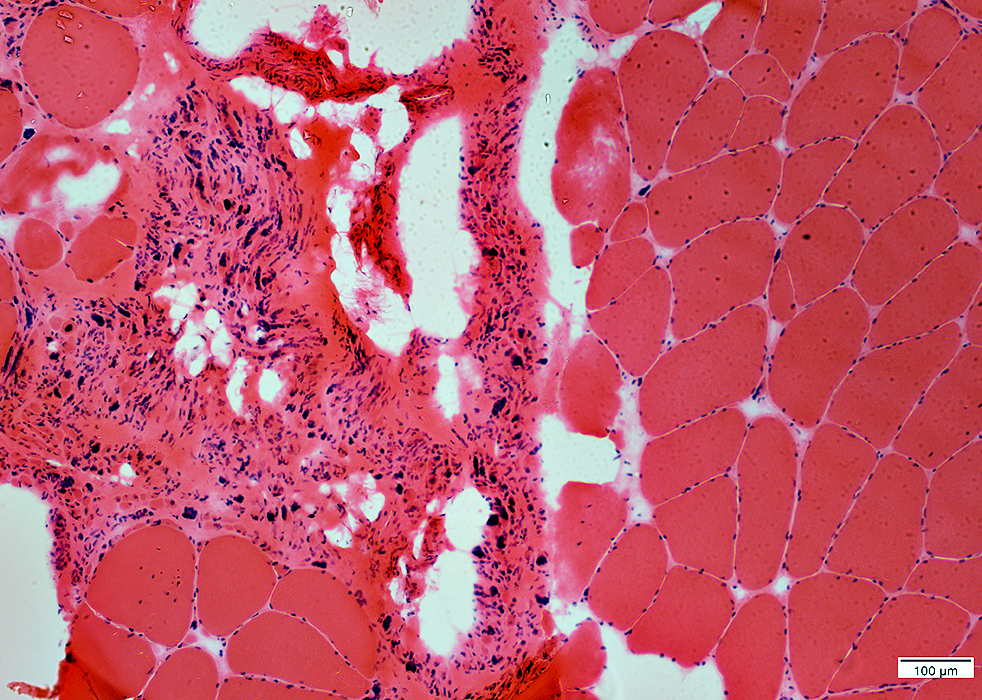 H&E stain |
Very small muscle fibers & pyknotic nuclear clumps
Increased connective tissue & fat
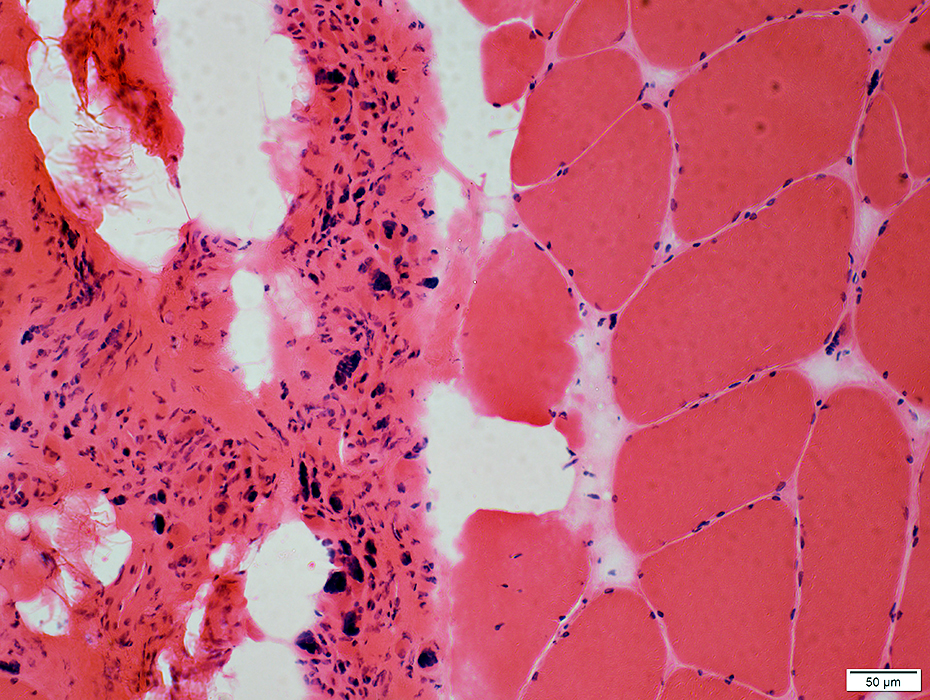 H&E stain |
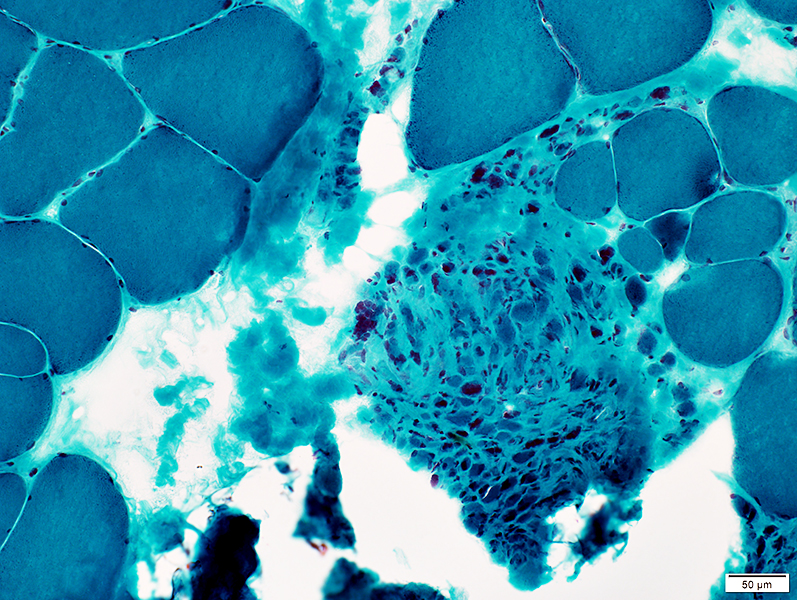 Gomori trichrome stain |
Very small muscled fibers
Increased connective tissue & fibrils between muscle fibers
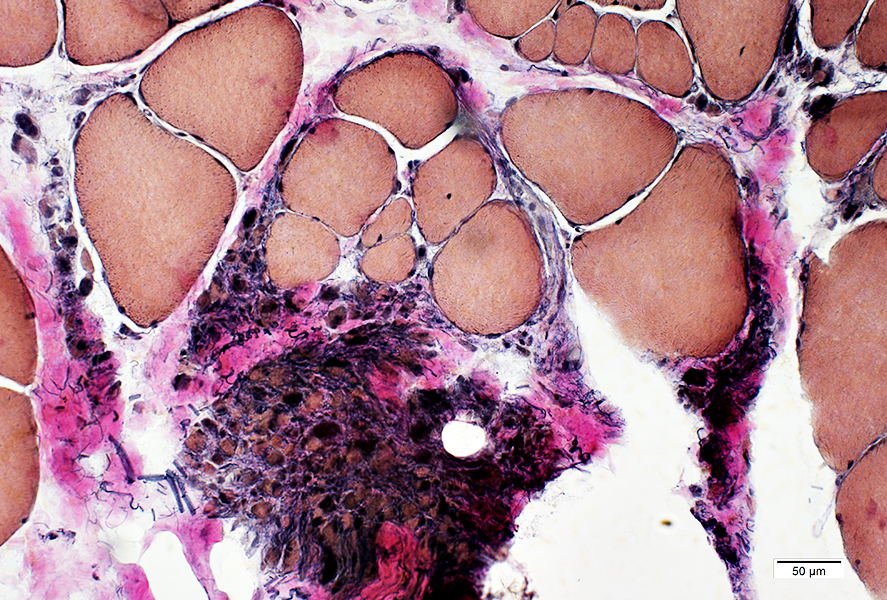 VvG stain |
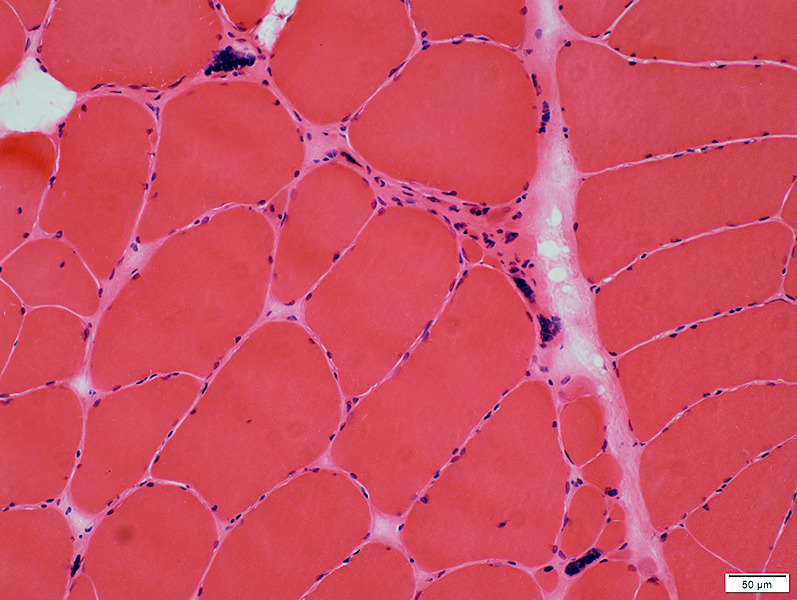 H&E stain |
Hypertrophic muscle fibers
Small regions of grouped muscle fiber atrophy
Pyknotic nuclear clumps
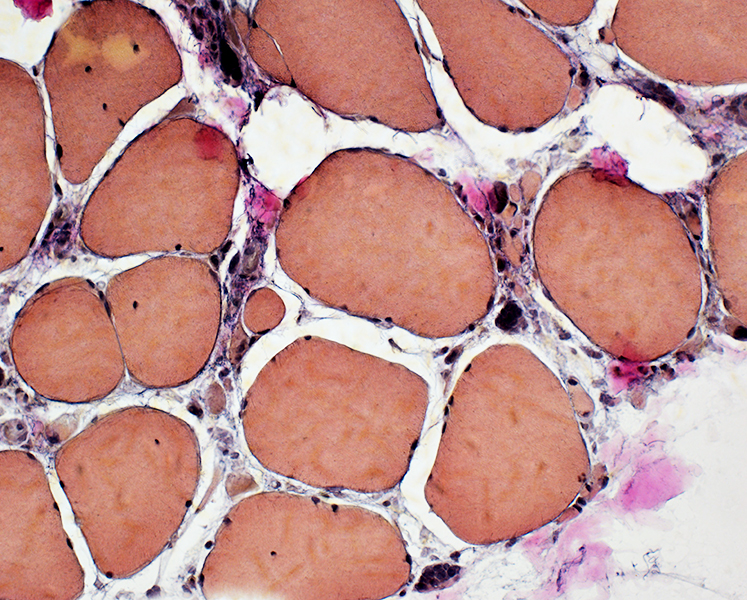 VvG stain |
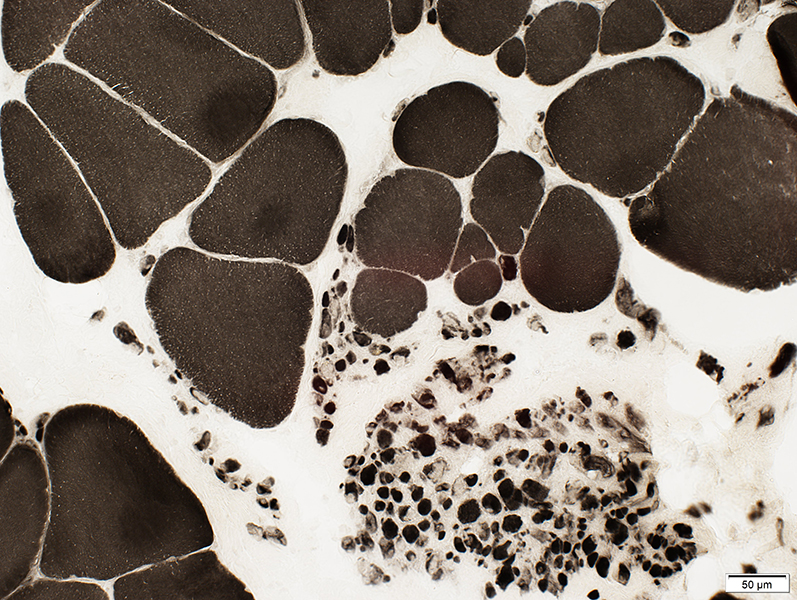 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Large fibers: Type I predominance
Small muscle fibers: Many 2C
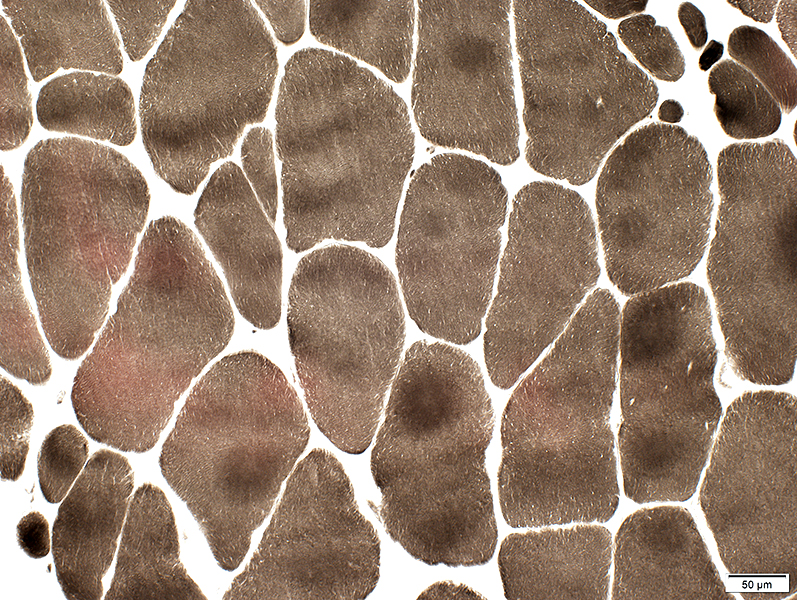 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
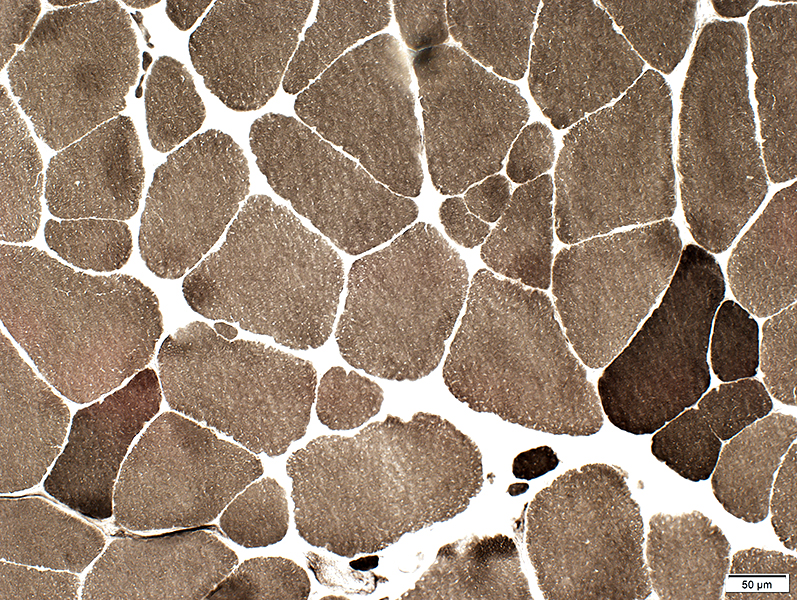 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
Small muscle fibers, individually & in region of grouped atrophy stain for esterase
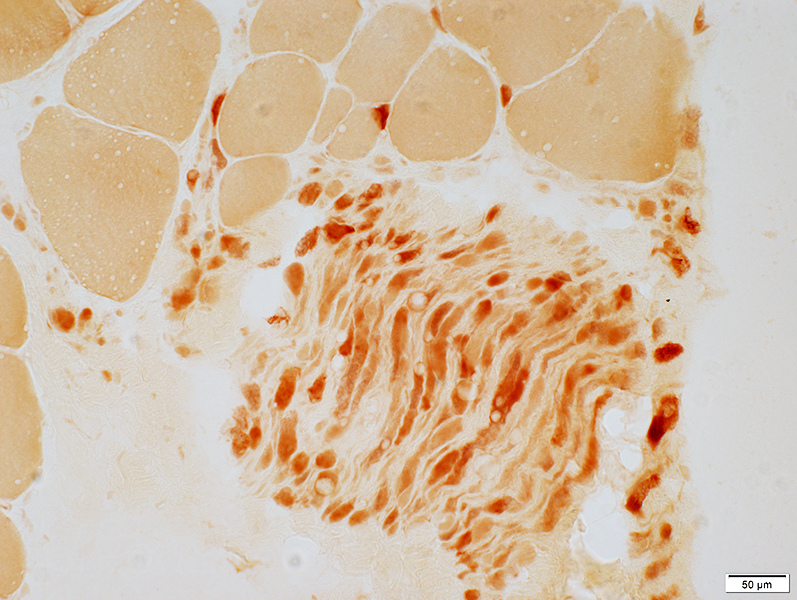 Esterase stain |
Also see
Active Denervation
Fiber type grouping
Return to Neuromuscular syndromes
Return to Neuromuscular home page
Return to Hereditary motor syndromes
8/28/2019