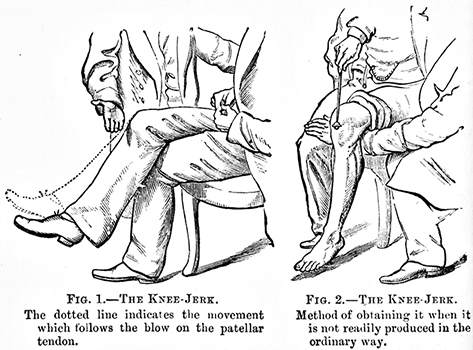
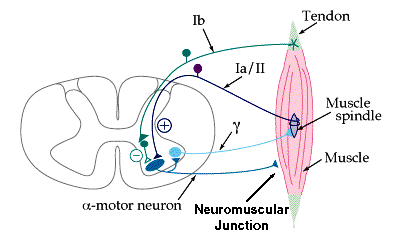
Tendon Tap: Physiology
- Initial phase
- Phasic stretch stimulates axon terminals in muscle spindles
- Afferent conduction of impulses
- Axon type
- Fastest conducting (Ia) afferents
- Terminals respond to phasic changes in muscle length
- NOTE: Group II afferents in spindles respond to static muscle length
- Impulses: Synchronized central conduction
- Motor neuron excitation
- Monosynaptic
- Location: Proximal dendrites & cell body
- Other central pathways involved in tendon reflex
- Stimulation of spinal interneurons by afferents
- At same & neighboring segmental levels as motor neuron
- Excitation & Inhibition of segmental neurons
- Via reticulospinal, vestibulospinal & corticospinal pathways
H-reflex
2
- Definition: Electrical equivalent of the tendon jerk
- 2-neuron, monosynaptic pathway
- Elicited by: Electrical stimulation of afferent Ia axons
- Stimulus: Low amplitude (submaximal) & Long duration (1 ms)
- Stimulate the IA afferent axons but not efferent motor axons
- Ia axons have lower electrical threshold than motor axons
- No role of muscle spindle or fusimotor drive in stimulation of H reflex
- Efferent limb of H-reflex
- Anatomical: α-motor neurons, Smallest motor neurons 1st
- Electrophysiology
- Consistent latency & configuration
- Normal latency ~30 ms
- Initial deflection: Downward (Positive)
- Measure: H-reflex with shortest latency
- Normal latency increases with greater height
- Pathology
- Unilateral lesion: Diference of ≥ 1.5 ms between sides
- Upper motor neuron lesion
- High H-reflex amplitude to M-wave amplitude (H/M) ratio
- Modulated by
- Central excitation & inhibition
- Jendrasik maneuver: May potentiate H-reflex
- Operant conditioning: Via corticospinal tract
- Down-regulation: May be related to
- ↑ numbers of GABAergic terminals on motoneurons
- Immobilization
- Increases H-reflex amplitude via reduced presynaptic inhibition
- Antagonistic muscles: Contraction reduces H-reflex
- Golgi tendon organ afferents (Ib): Inhibit H-reflex
- Whole body vibration: Reduces H-reflex
- High amplitude stimulus
- Stimulates motor neurons as well as Ia afferents
- Inhibits H reflex: via Collision
- Antidromic motor volley vs Orthodromic afferent volley
- Spinal cord injury
- Increased H-reflex
- Onset 7 to 21 days after injury
- Assessment
- Decreased low frequency-dependent depression of H-reflex
- Discovered by: Hoffman in 1918
- Upper extremity: Flexor carpi radialis H reflex
- Most easily obtainable H-reflex in upper extremity
- Elicited by: Median nerve stimulation in antecubital fossa
- Record over: Flexor carpi radialis muscle
- Abnormal in
- Radiculopathies: C6 & C7
- Proximal median nerve lesions
- Brachial plexus lesions
- Lower extremity: Posterior tibial H-reflex
- Elicited by: Tibial nerve stimulation in popliteal fossa
- Record over: Soleus muscle
- Also see: F-wave
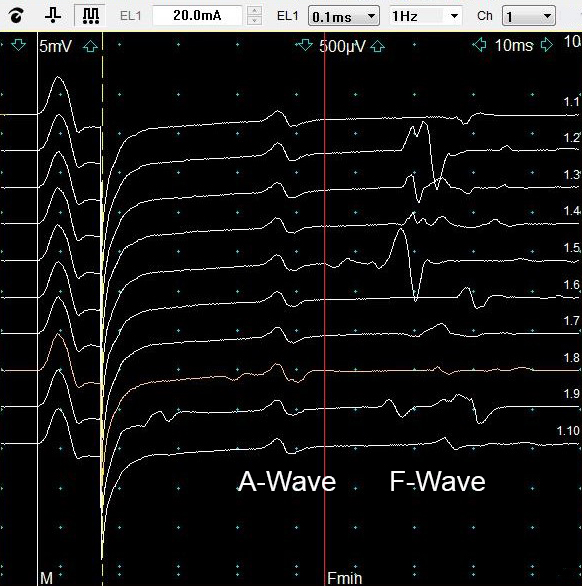
Axon reflex (A-wave)
- Features
- Late potential
- Timing: Occurs between M-response & F-response
- Same latency & configuration with each stimulation
- Mechanisms after Antidromic potential (AP)
- AP Travels back orthodromically down collateral branch
- AP Ephaptically stimulates neighboring axon
- Clinical associations
|
From: Bhavesh Trikamji
|