HIV: Vasculitis
|
Nerve Artery damage Epineurial vessels, Small Muscle involvement Veinitis Also see: IM-VAMP pathology |
HIV: Arteritis
Arteritis during HIV
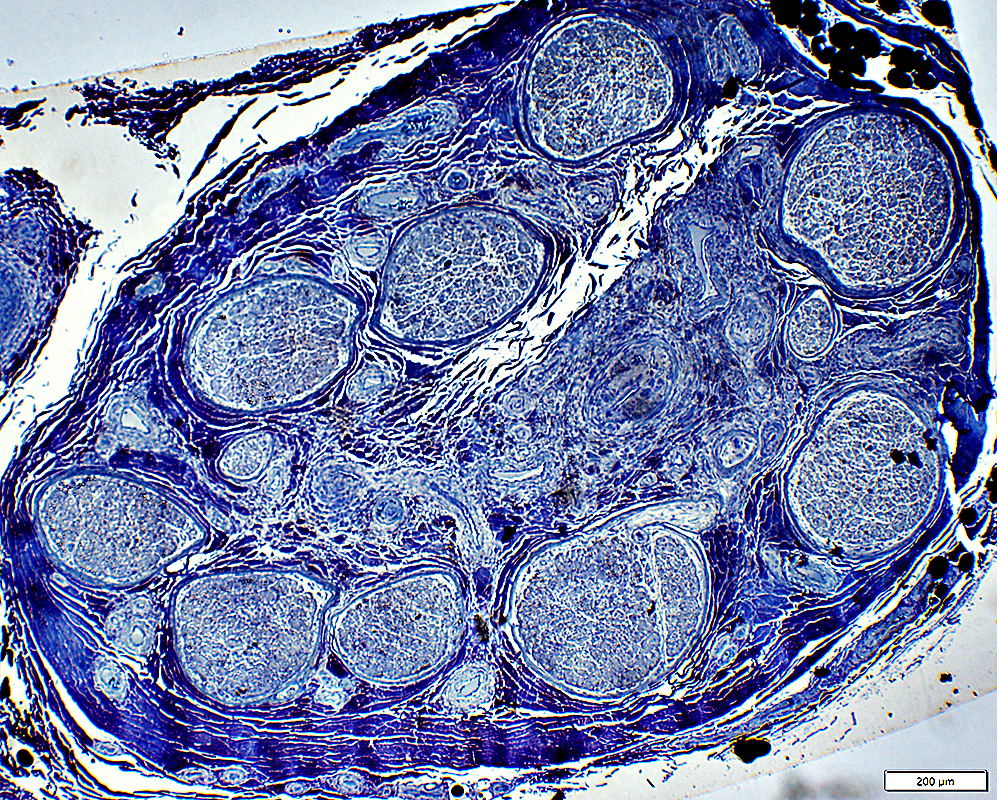 Toluidine blue stain |
|
Epineurium Artery Damaged structure Fibril layer: Irregular or Interrupted Connective tissue inside fibril layer Neovascularization Histiocytes in wall No lumen Epineurial connective tissue Neovascularization Structure: Fragmented, Pale stained Hemosiderin |
Endoneurium Axon loss Myelinated axons: Severe (Above) Unmyelinated axons: May be relatively preserved Wallerian degeneration: Early or Later stage Subperineurial Edema Microvessels: Prominent endothelium, especially during Wallerian degeneration Pale staining: Patchy |
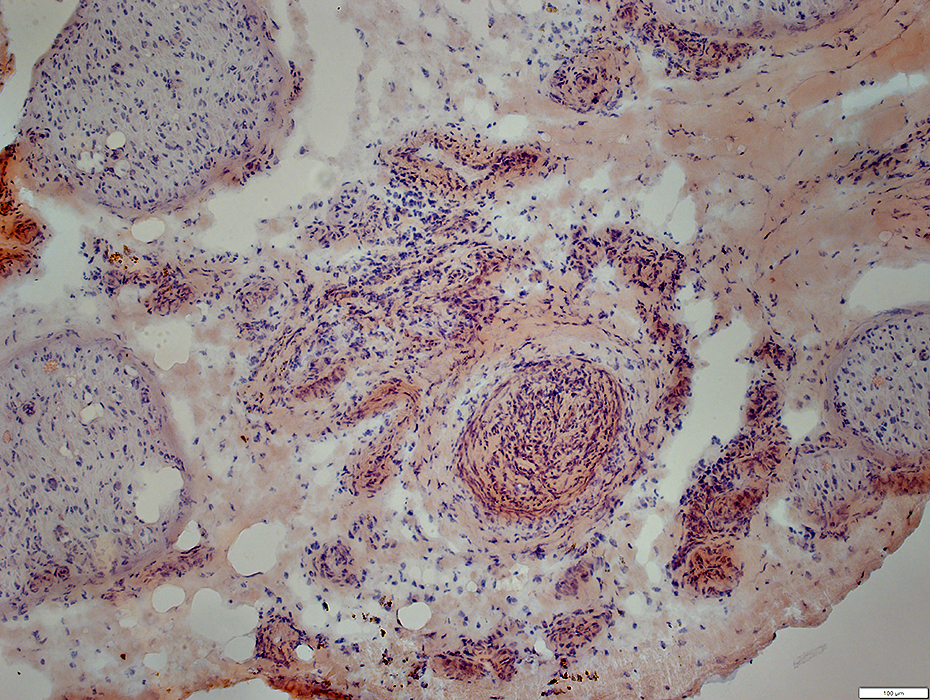 Congo red |
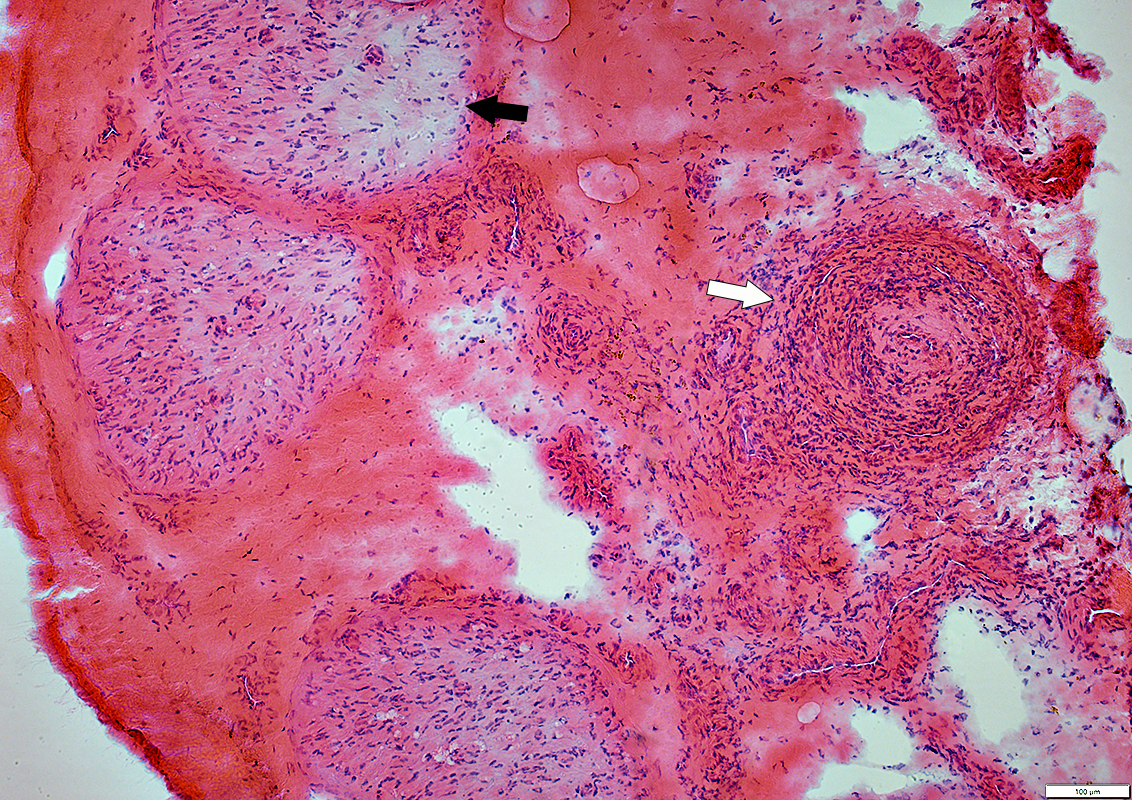 H&E stain |
Artery (Above, White arrow): Occluded; Wall damaged; Histiocytic cells (Below; White Arrow)
Endoneurium: Pale regions (Above, Black arrow); Moderately prominent microvessels; Histiocytes, scattered (Below; Black Arrow)
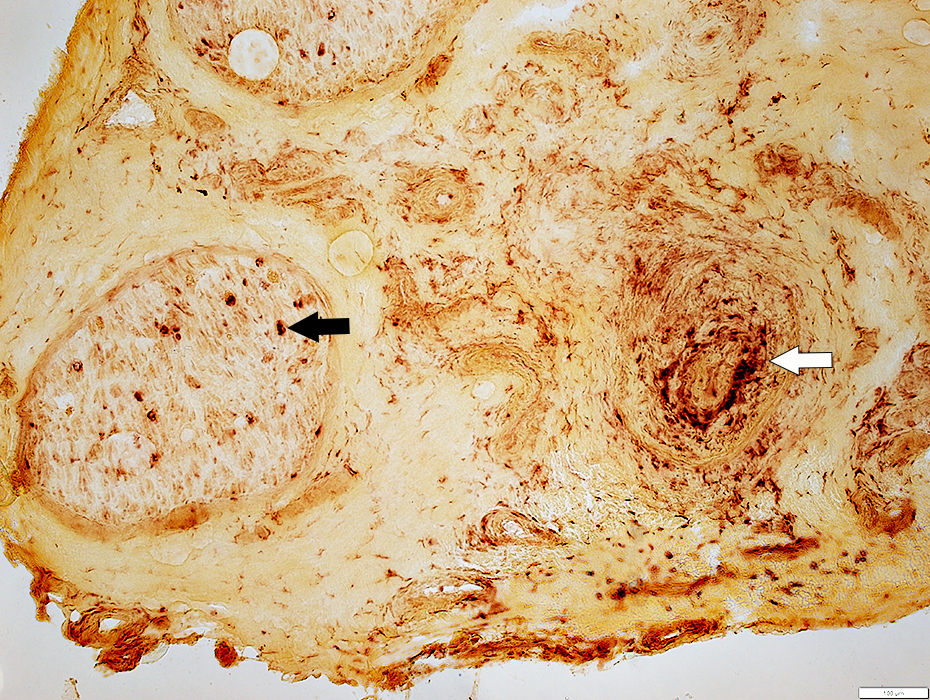 Acid phosphatase |
Epineurial Artery
Increased cells in most of wall
Neovascularization
Lumen: Occluded
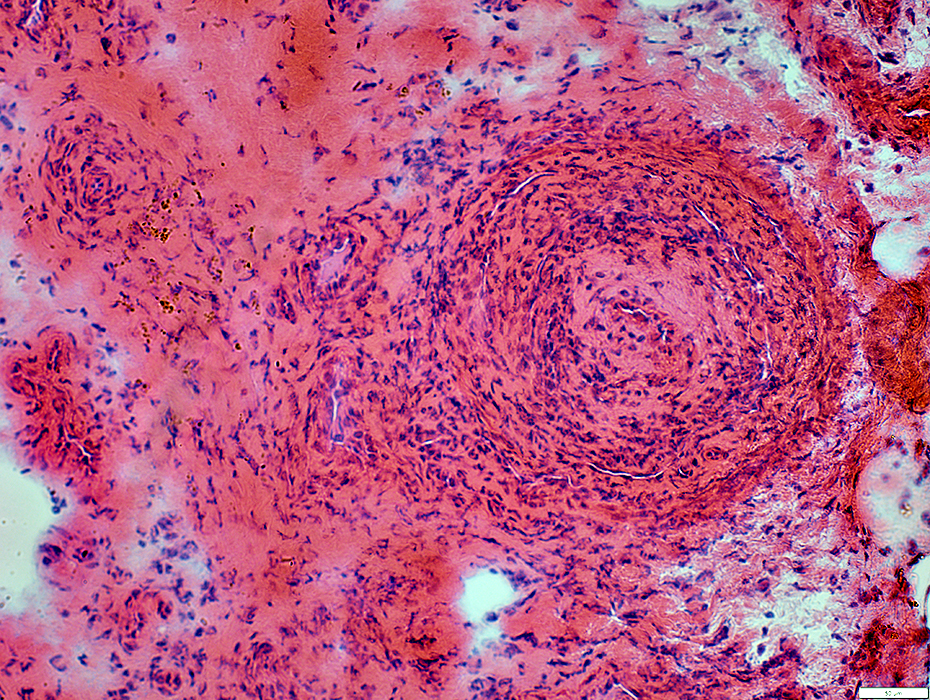 H&E stain |
Hemosiderin
Deposits in epineurium (Arrow)
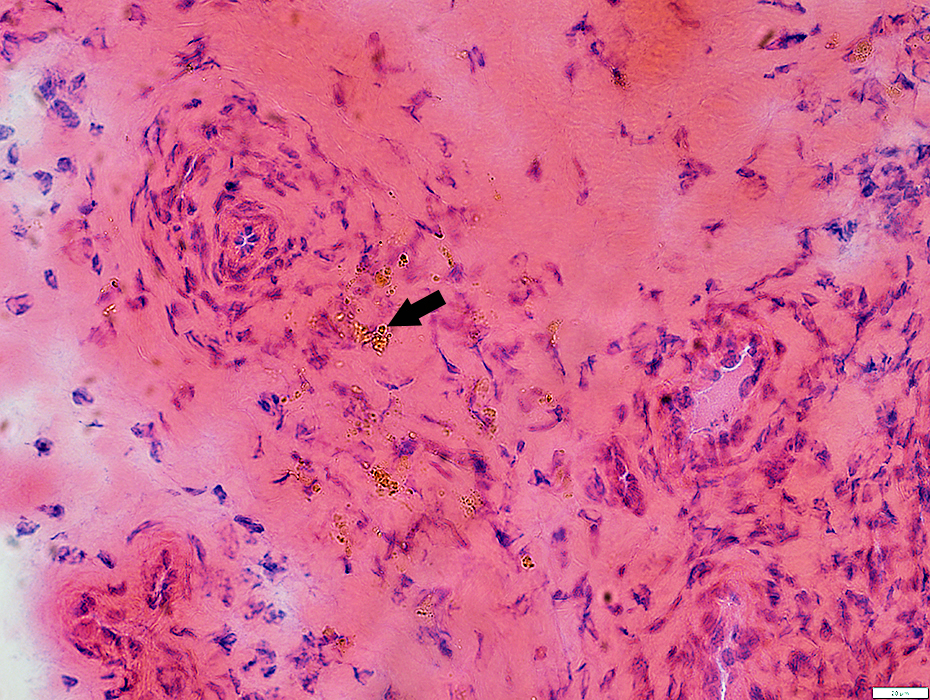 H&E stain |
Neovascularization: Within lumen of Occluded artery
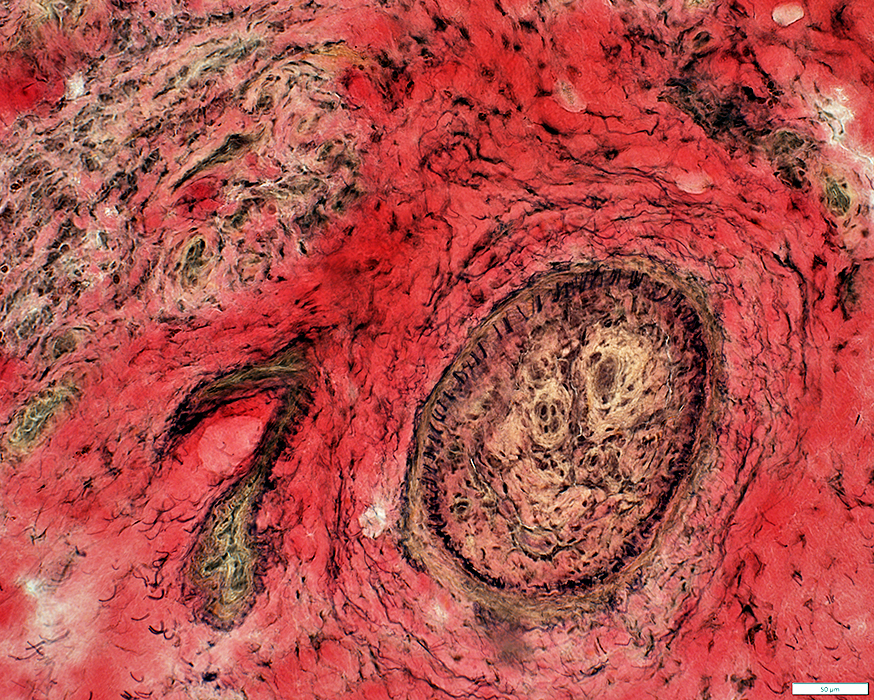 VvG stain |
Fibril layer: Irregular (Arrow)
Neovascularization
Lumen: Occluded
Connective tissue around artery: Damaged in some areas (Below)
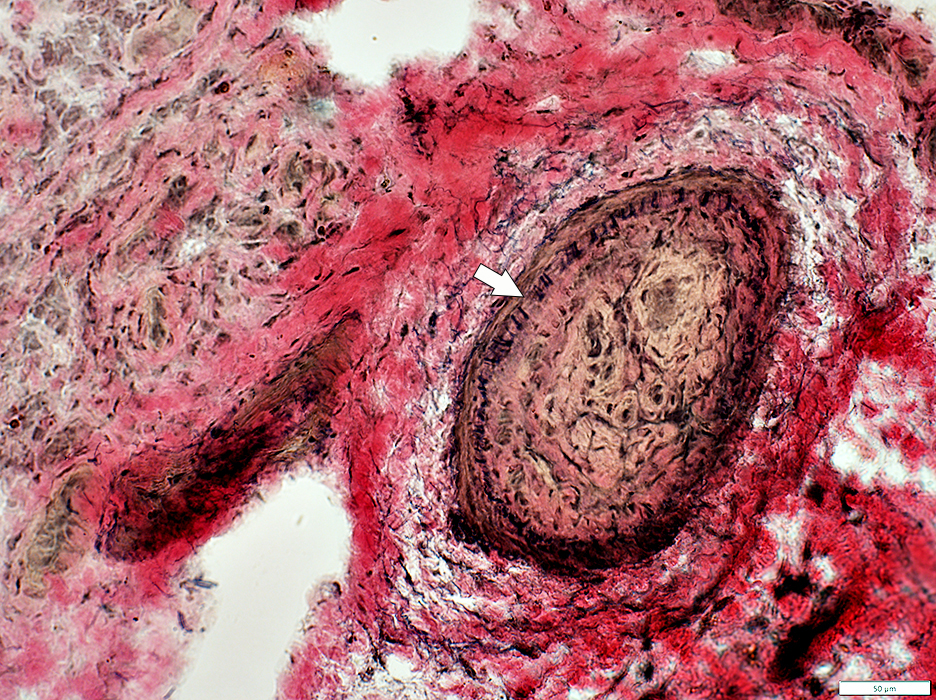 VvG stain |
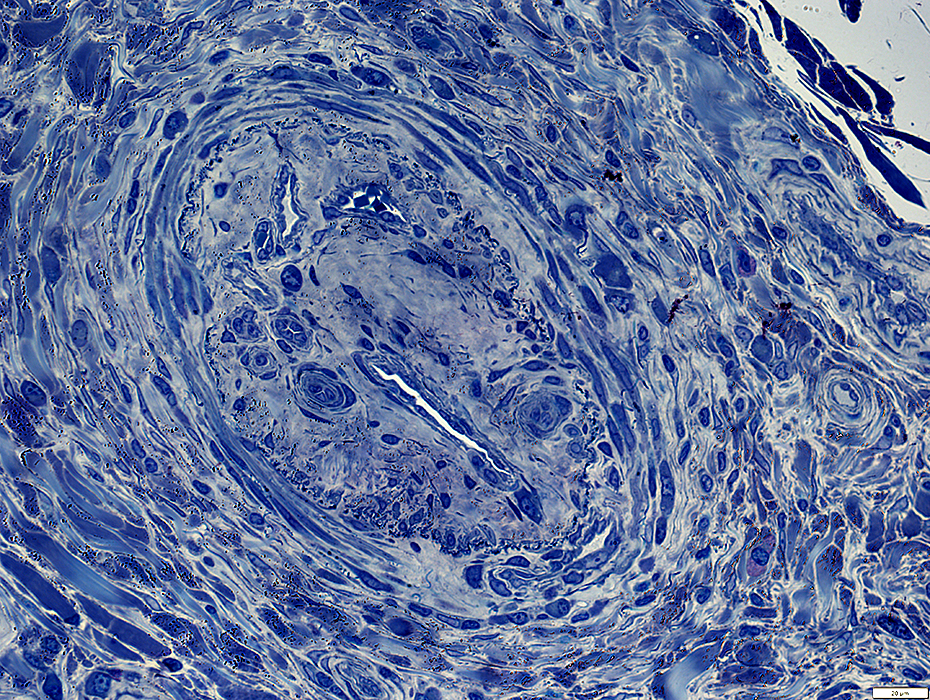 Toluidine blue stain |
Neovascularization
Connective tissue around artery: Damaged in some areas; Irregular structure
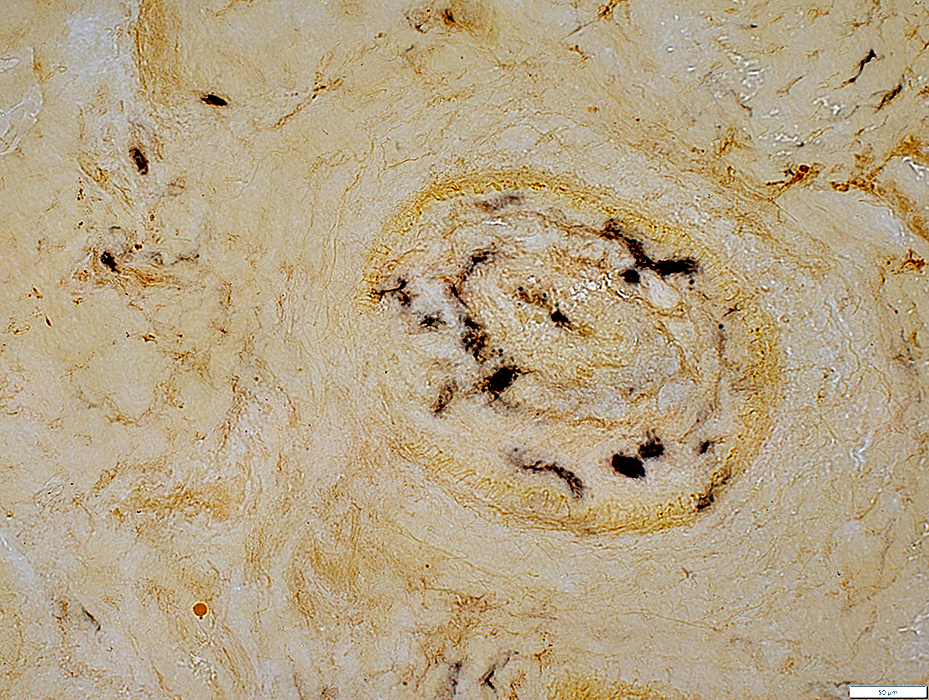 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Neovascularization: New vessels within larger vessel stained with alkaline phosphatase
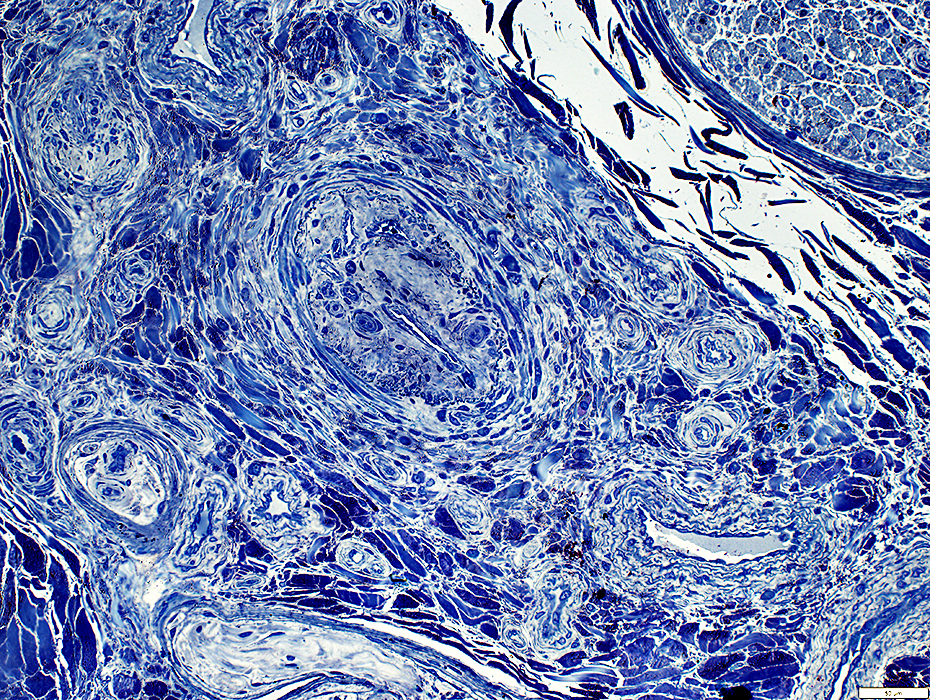 Toluidine blue stain |
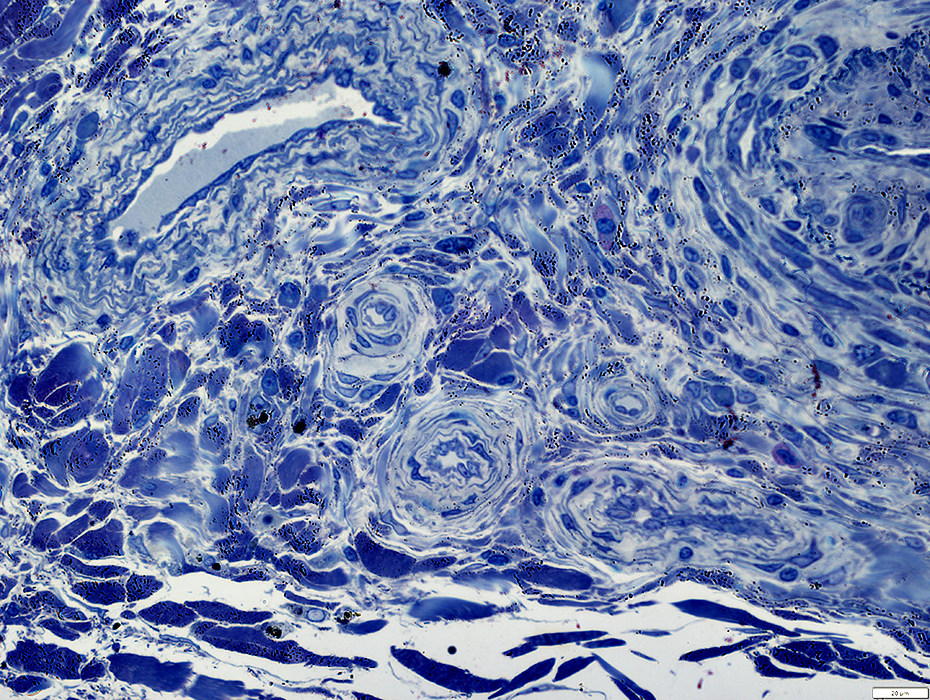 Toluidine blue stain |
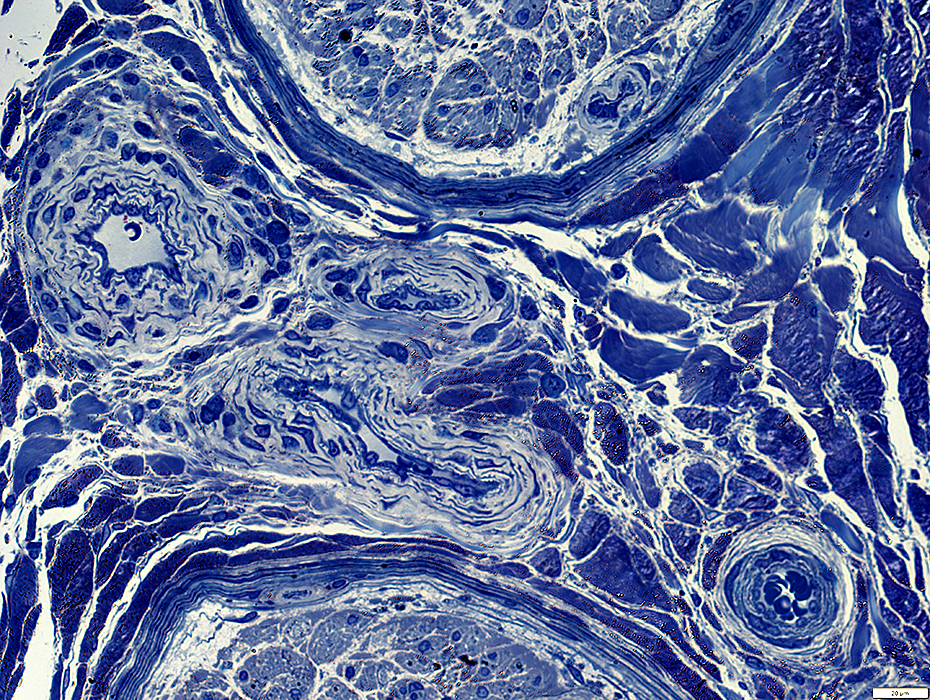 Toluidine blue stain |
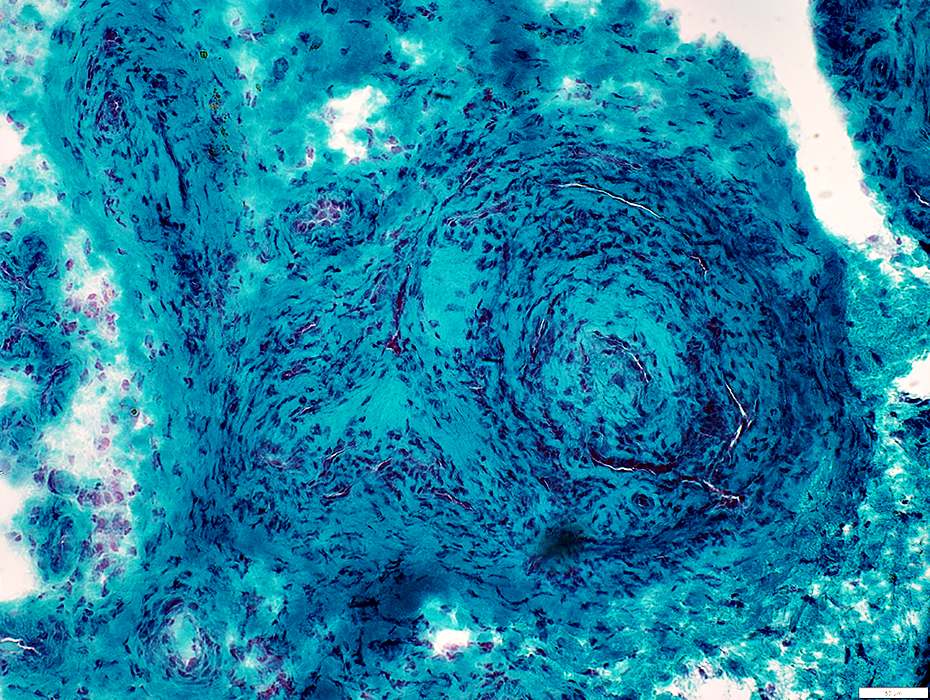 Gomori trichrome |
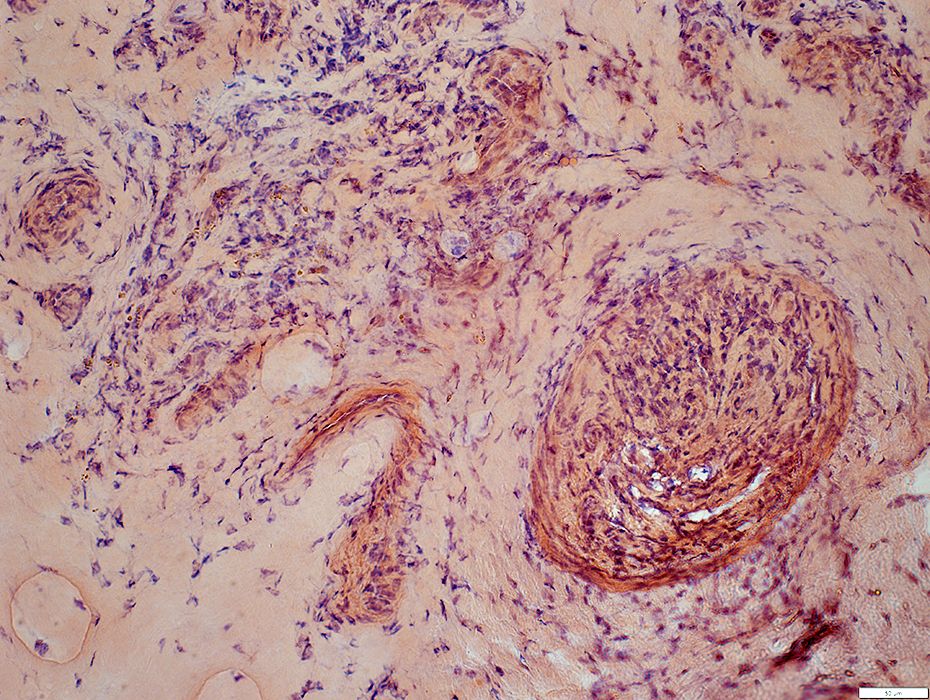 Congo red |
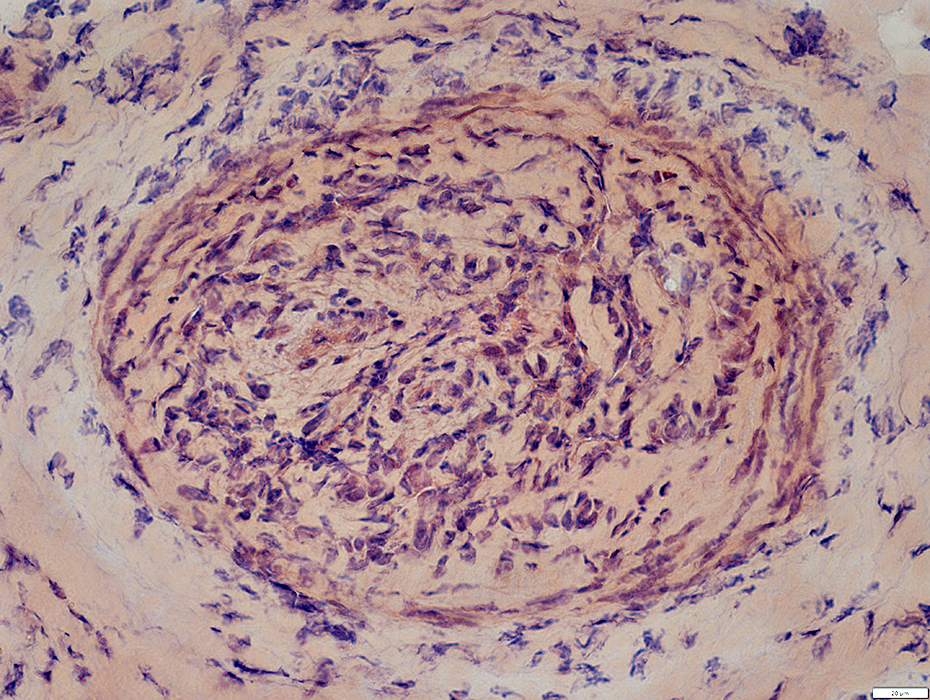 Congo red |
No lumen
Histiocytes within vessel wall: In patchy regions & Scattered
Lymphocytes: Not prominent
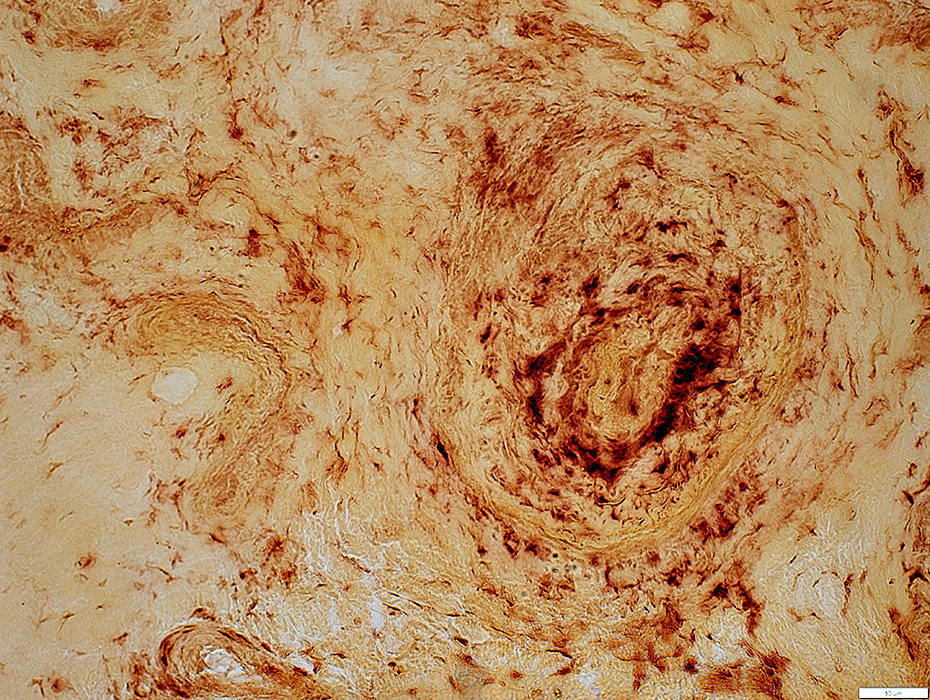 Acid phosphatase |
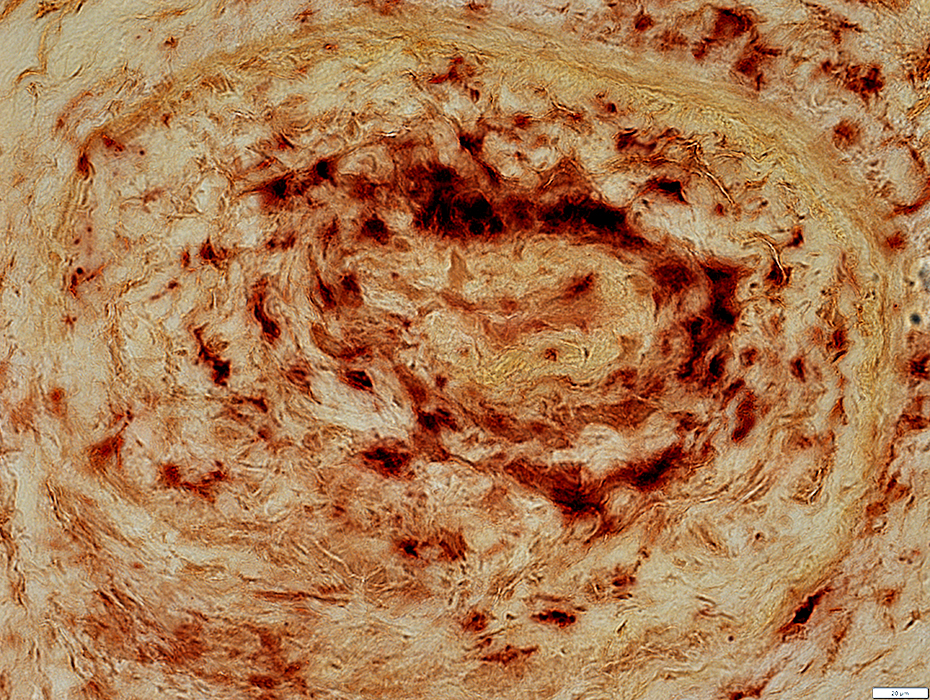 Acid phosphatase |
Artery: Abnormal
Many cells all through wall
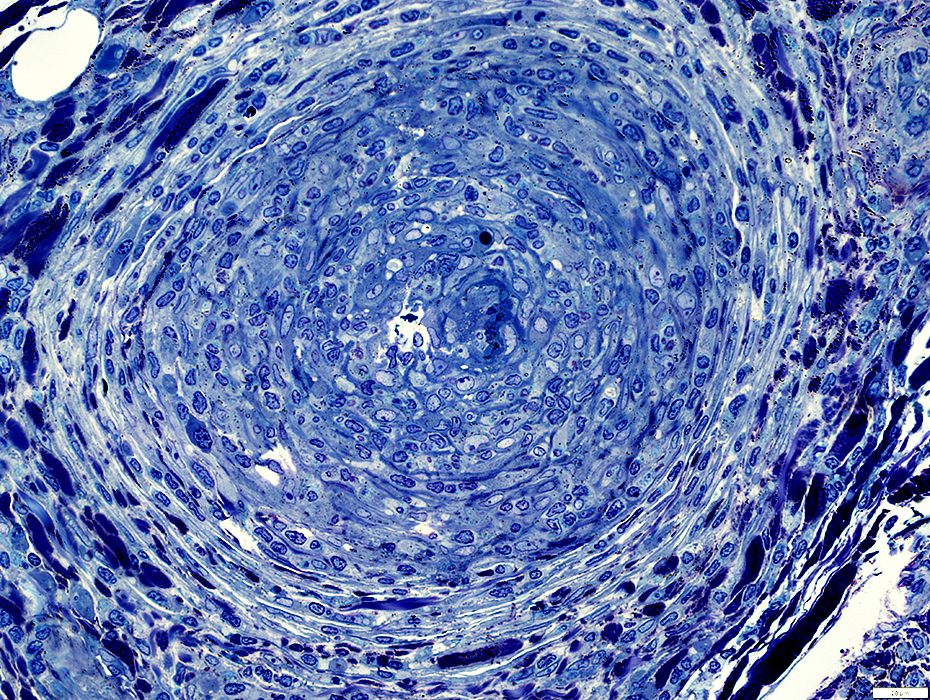 Toluidine blue stain |
Wallerian Degeneration: Myelinated Axon loss, Later stages
Myelinated axons: Severe loss
Remaining myelin fragments: Reduced staining (Arrows)
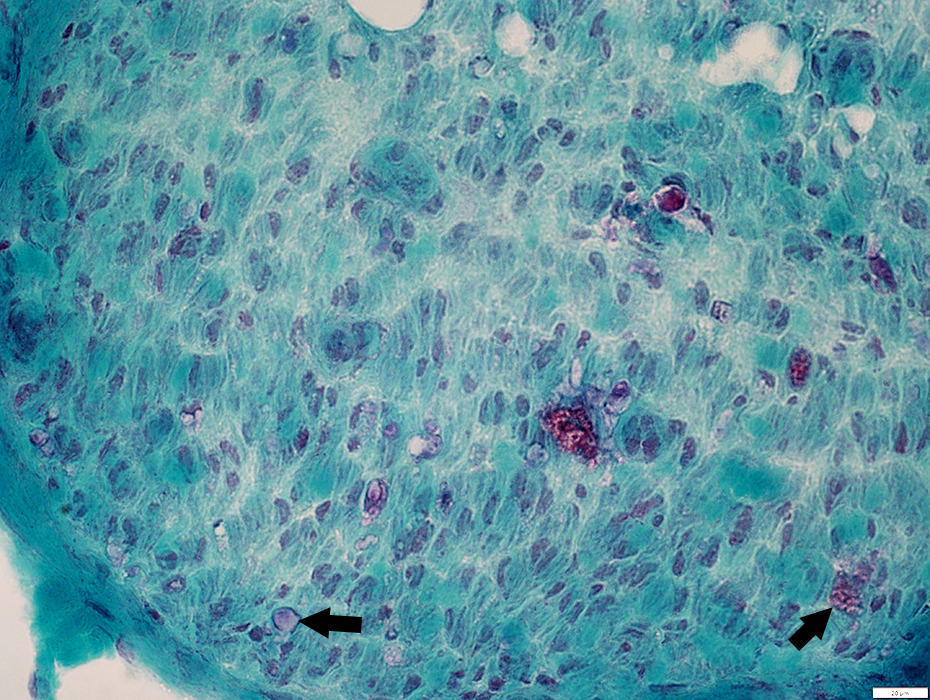 Gomori trichrome stain |
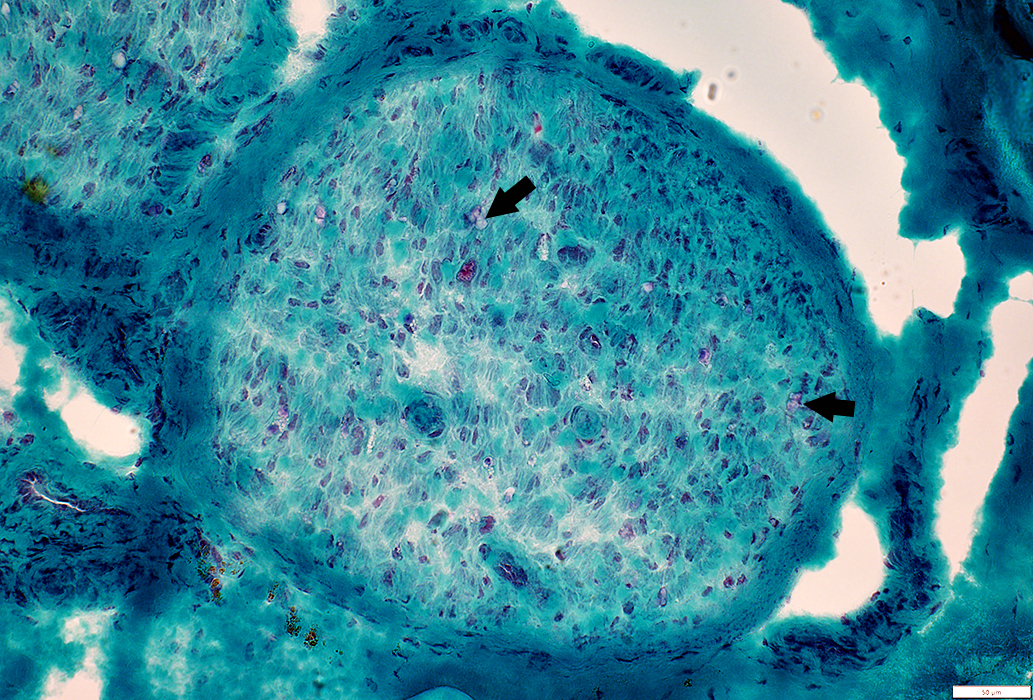 Gomori trichrome stain |
Myelinated axons: Severe loss
Myelin remnants: Minimal staining on Gomori trichrome & VvG (Arrows)
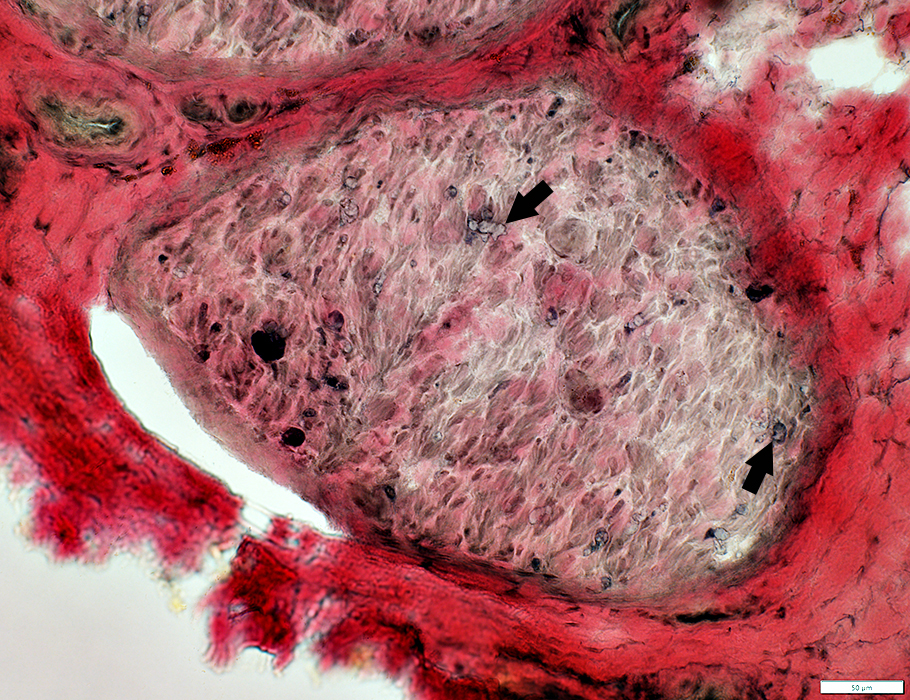 VvG stain |
Axon loss
Myelinated axons: Severe loss
Perineurium
Normal
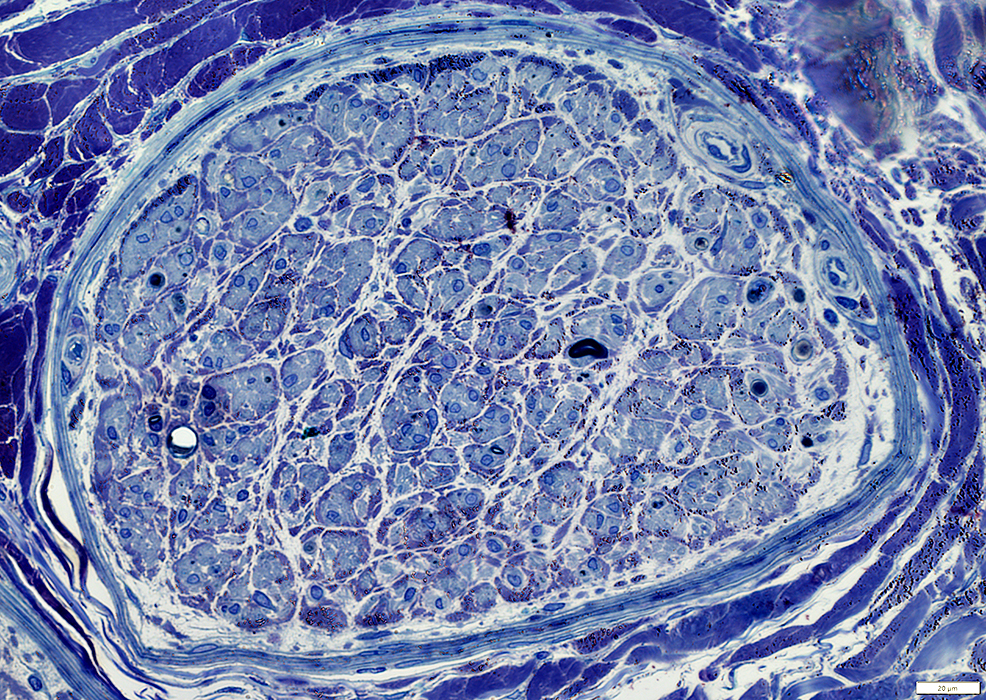 Toluidine blue stain |
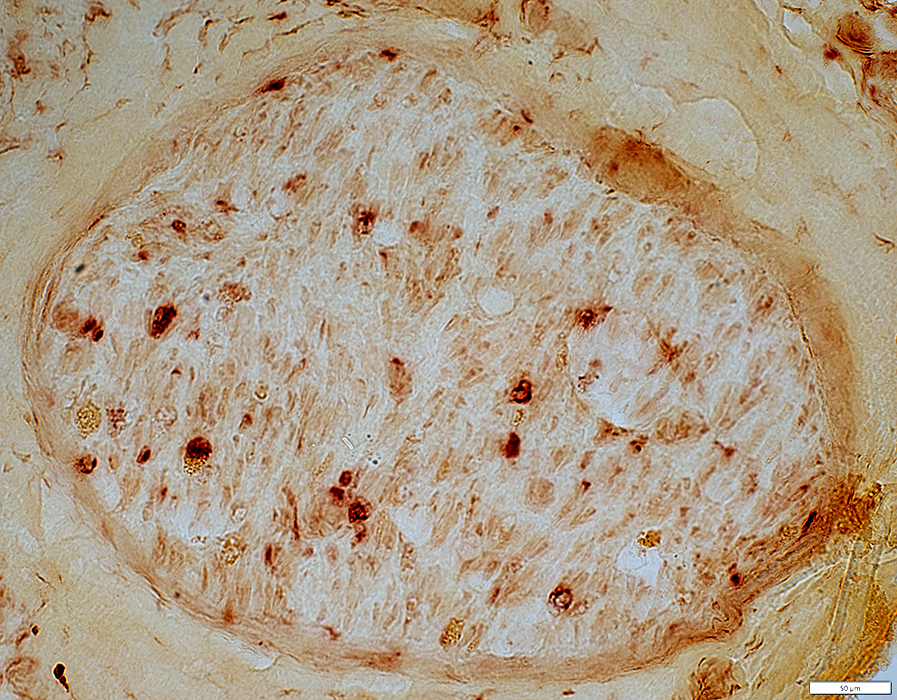 Acid phosphatase stain |
Histiocytic cells scattered in endomysium (Above)
Probable histiocytic cells around an endoneurial microvessel (Below; Arrow)
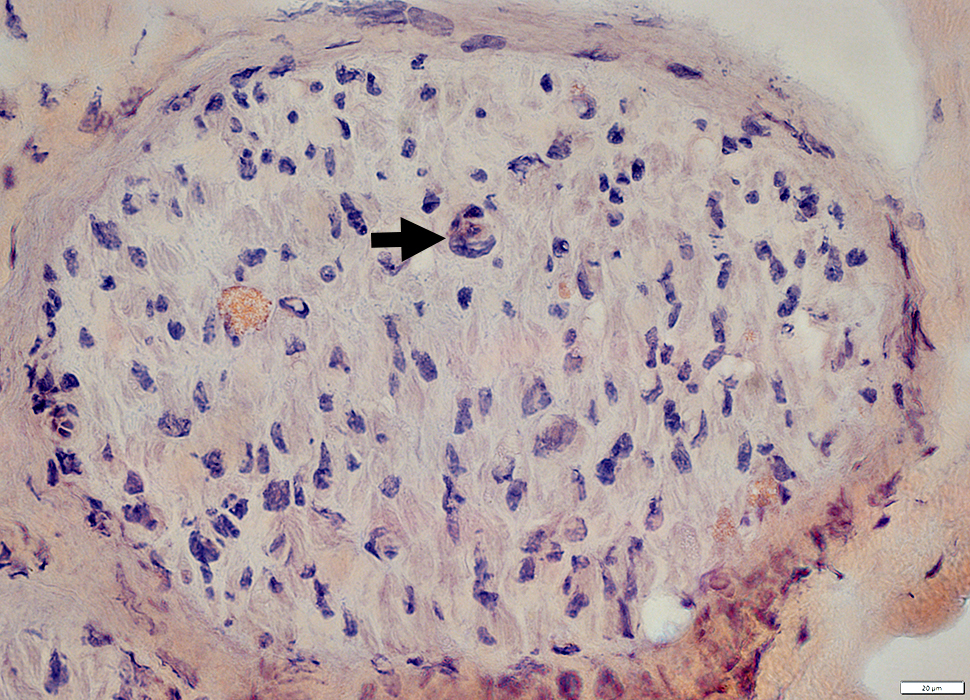 Congo red stain |
Complement C5b-9 stain
Wallerian degeneration: Present in endomysium
Endomysial microvessels: Mild staining
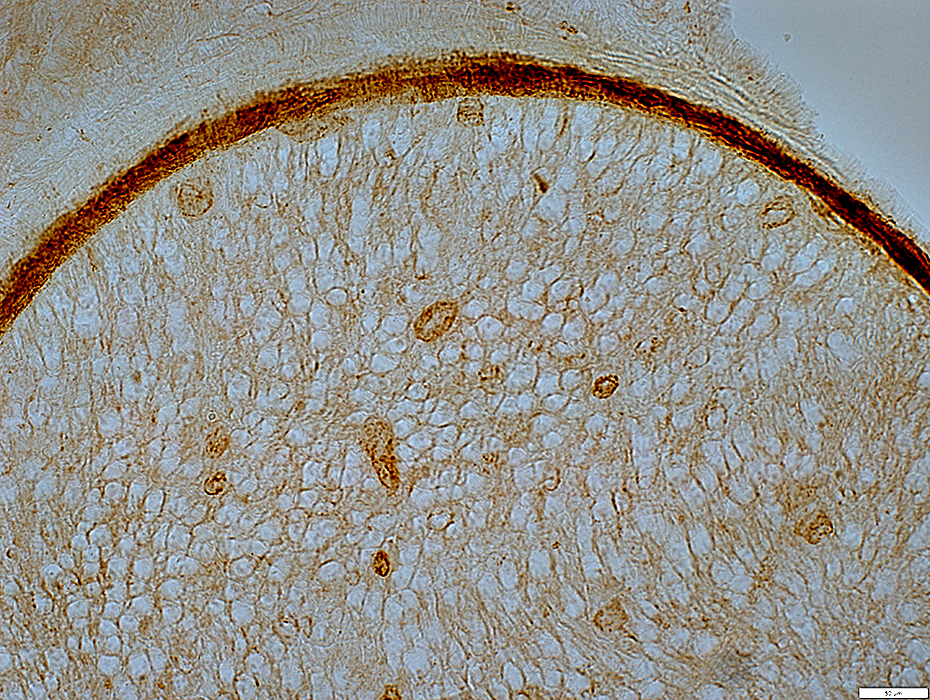
C5b-9 stain |
HIV: Inflammatory Vasculopathy, Small Epineurial Vessels (Venitis in muscle)
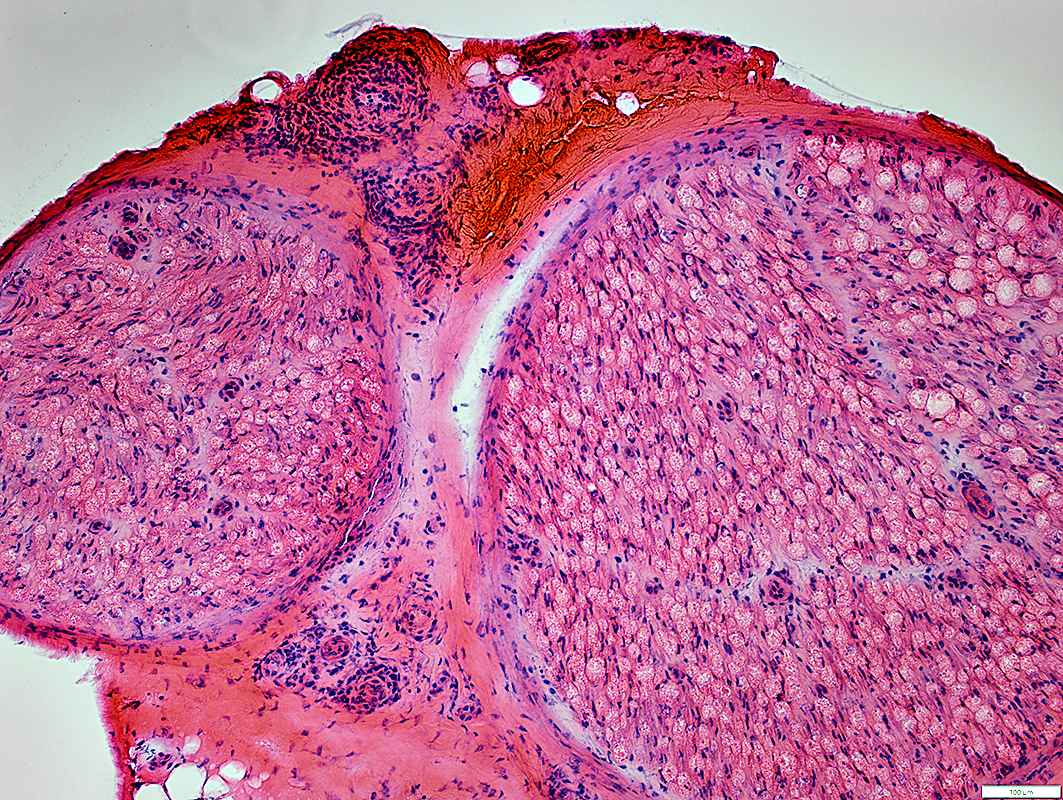 H&E stain |
Lymphocytes: Present around & within walls of small epineurial vessels
Epineurial connective tissue: Neovascularization
Endoneurium
Myelinated axons: Wallerian Degeneration
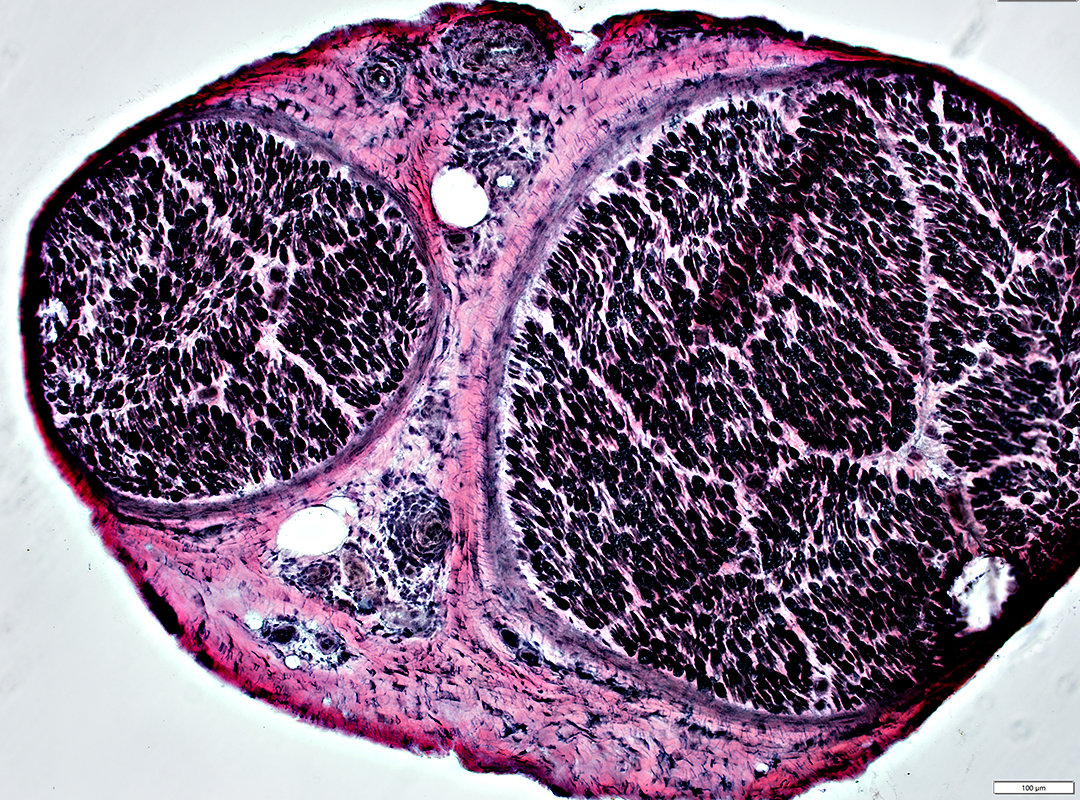 VvG stain |
Epineurial connective tissue: MHC I
Increased staining
Epineurial Perivascular cells: MHC I
Increased staining
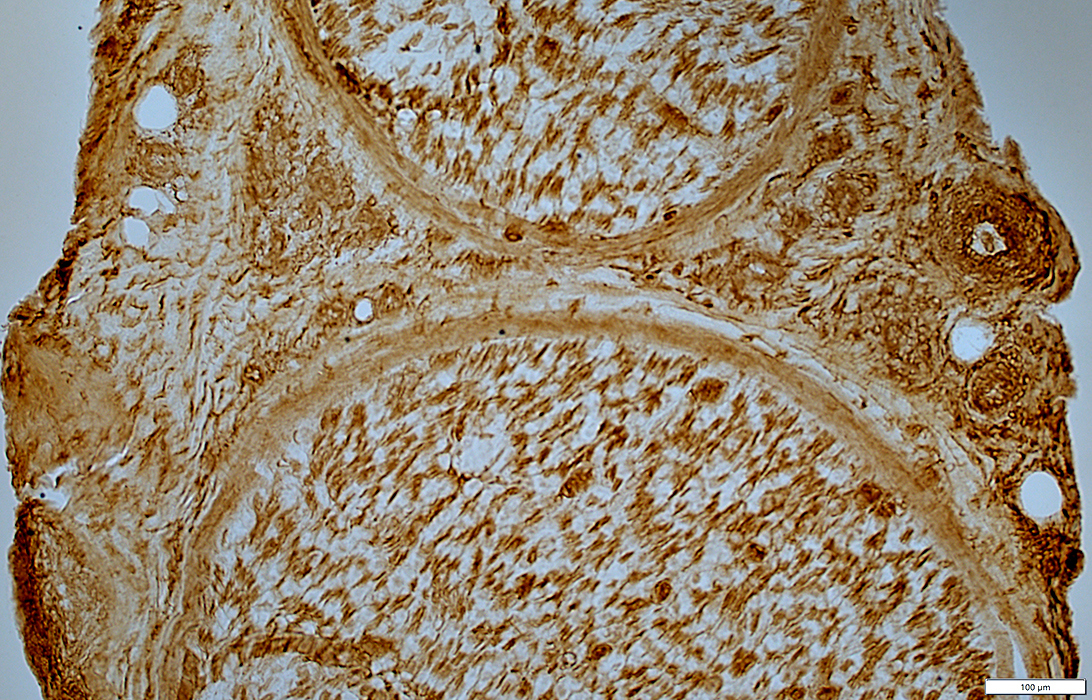 MHC I stain |
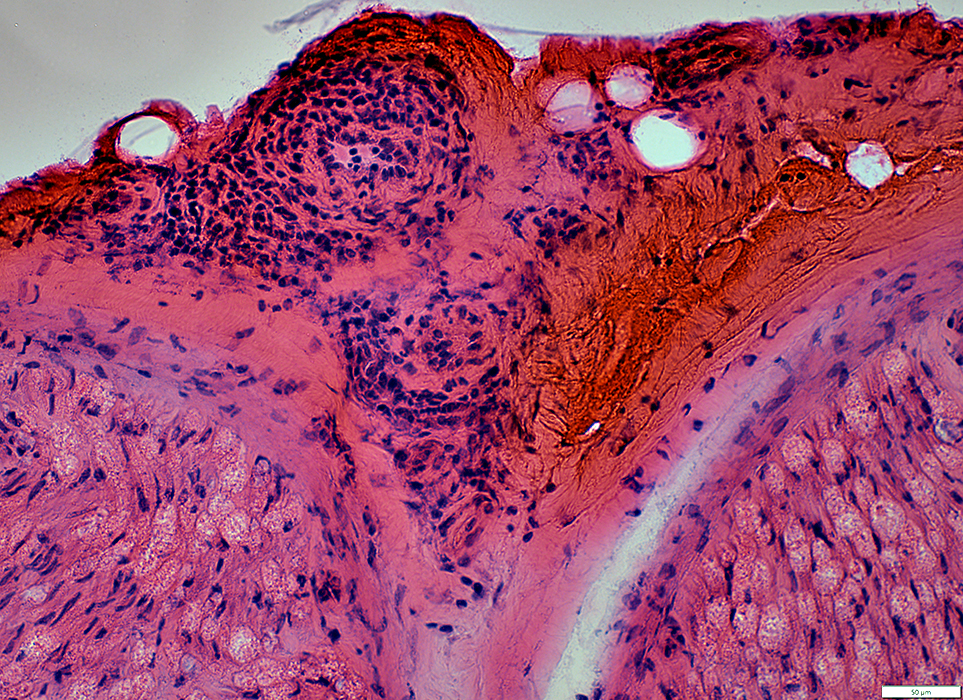 H&E stain |
Inflammation: Surrounds small epineurial vessels
MHC I
Stains
Cells around epineurial small vessels
Epineurial connective tissue
Wallerian Degeneration of Myelinated Axons: Common
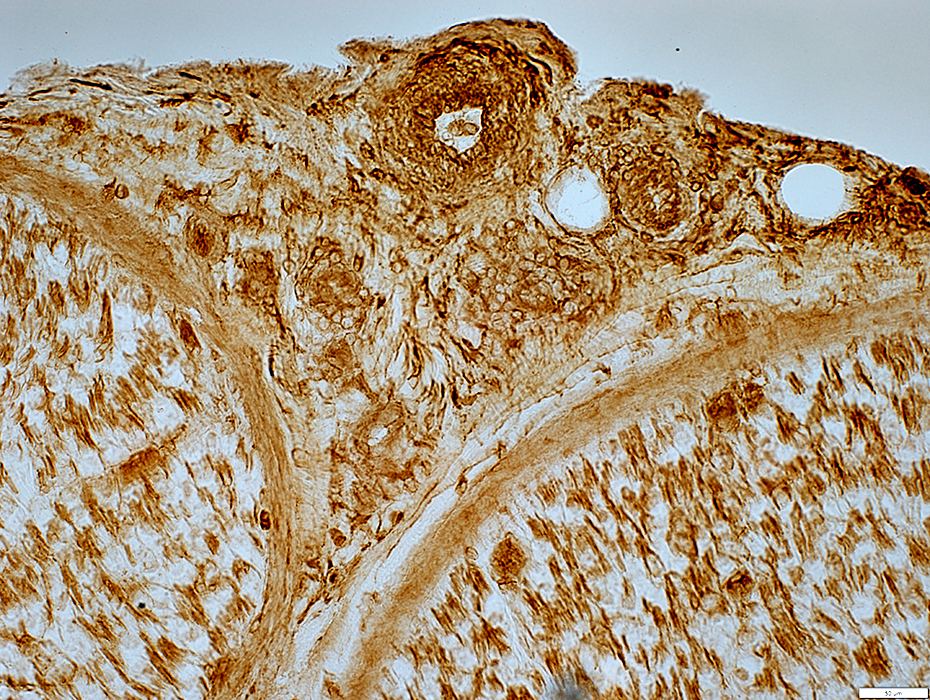 MHC I stain |
Small Vessel Inflammatory Vasculopathy: Epineurial Neovascularization
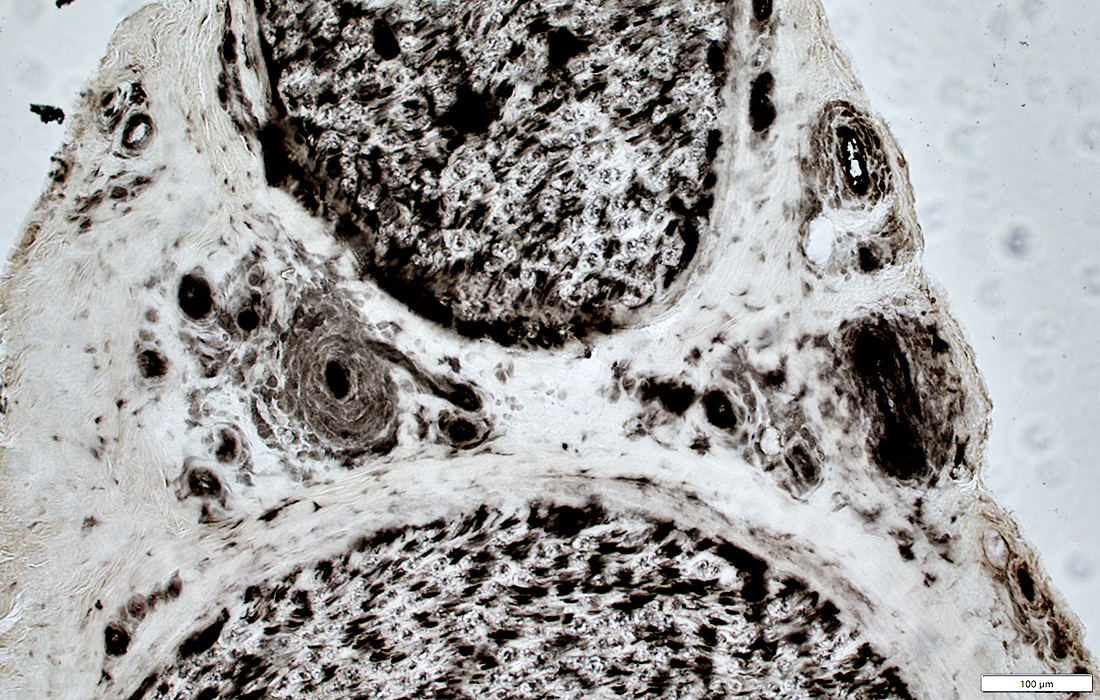 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
New vessels
Small; Multiple
Stained by: ATPase; Alkaline phosphatase
Associated connective tissue: Pale; Fragmented; Cellular, including histiocytes
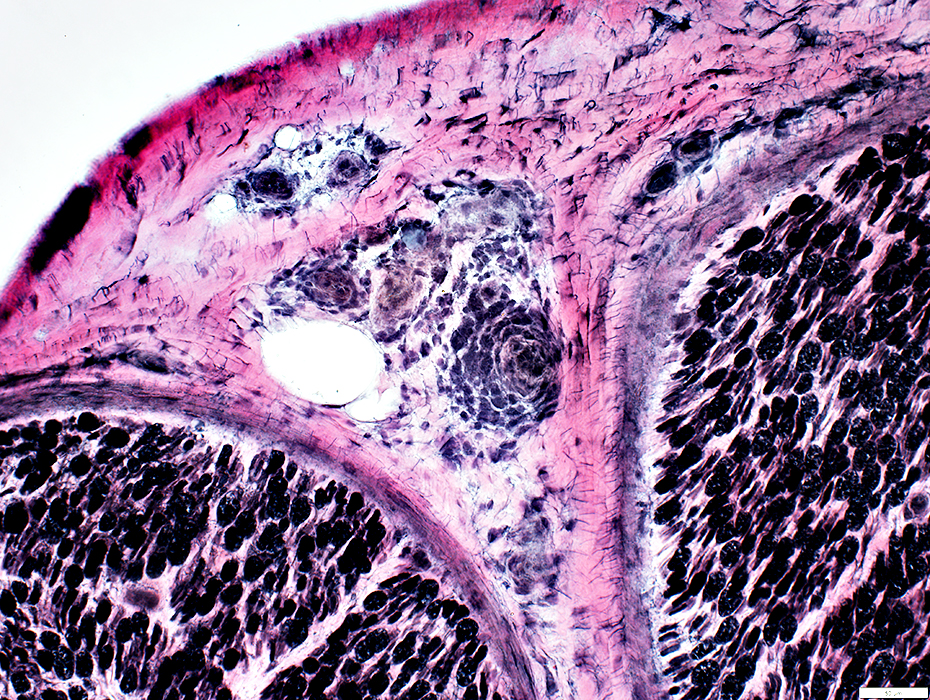 VvG stain |
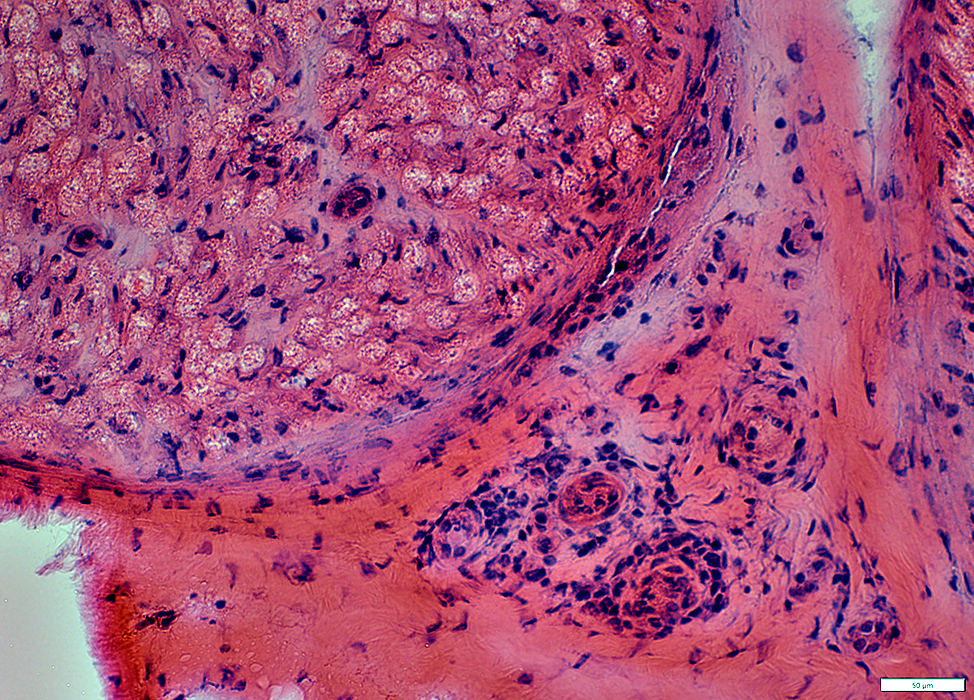 H&E stain |
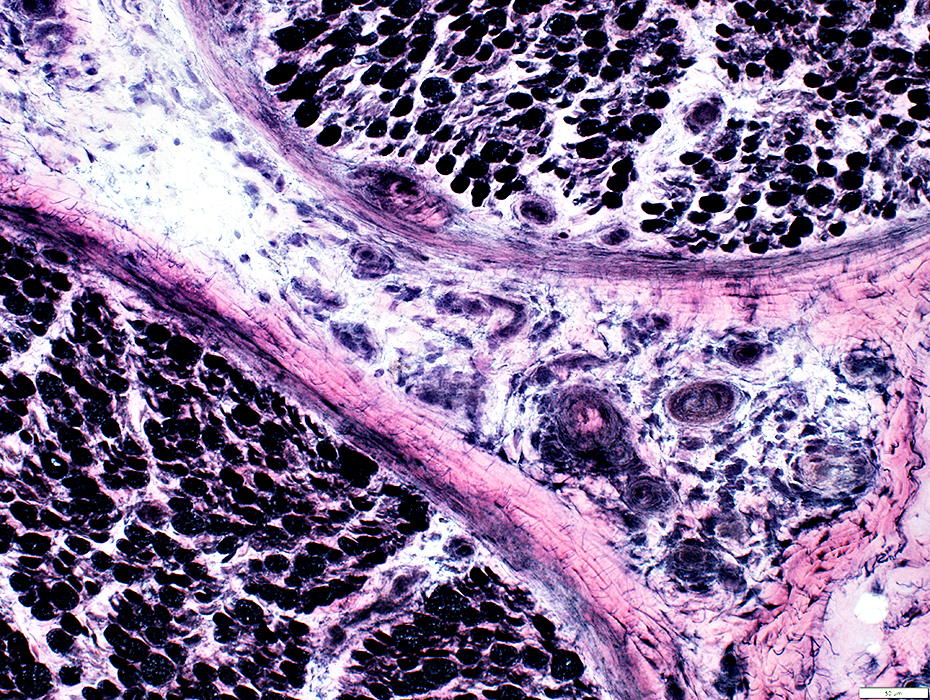 VvG stain |
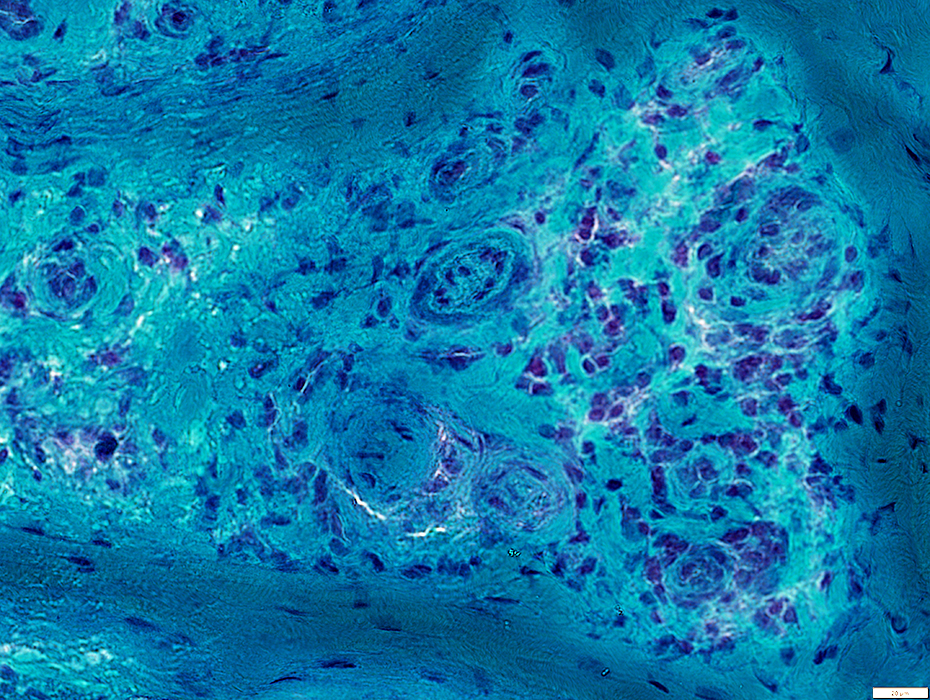 Gomori trichrome stain |
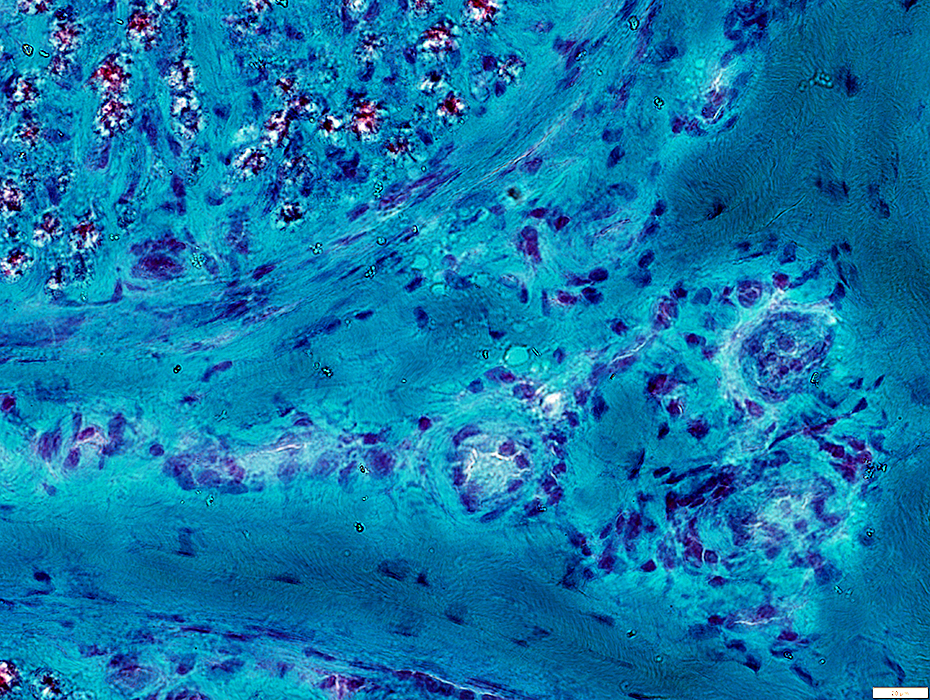 Gomori trichrome stain |
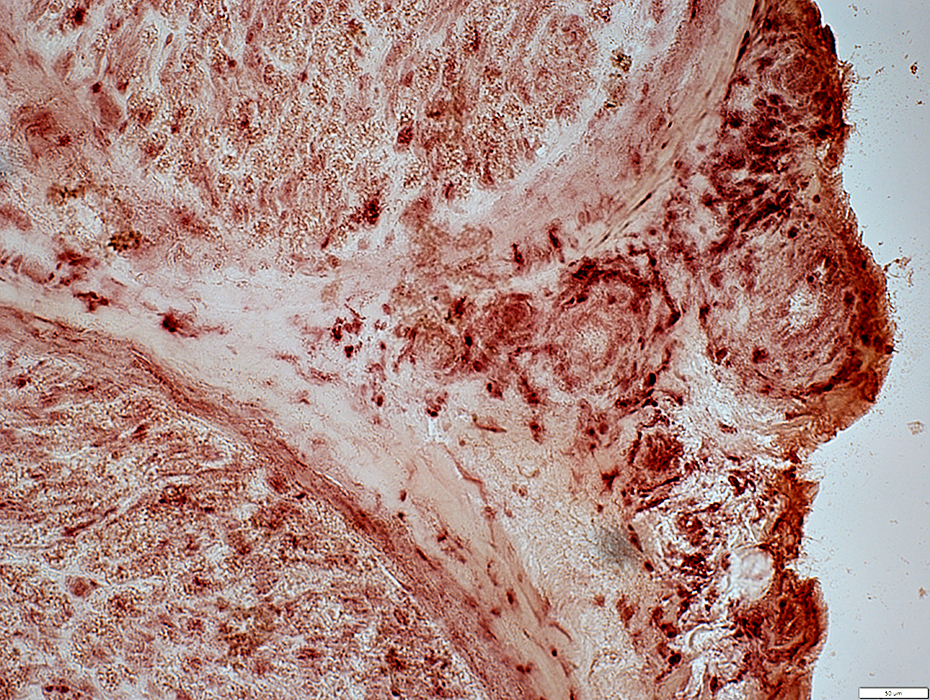 Acid phosphatase stain |
Often present in epineurial connective tissue & around vessels in regions of neovascularization
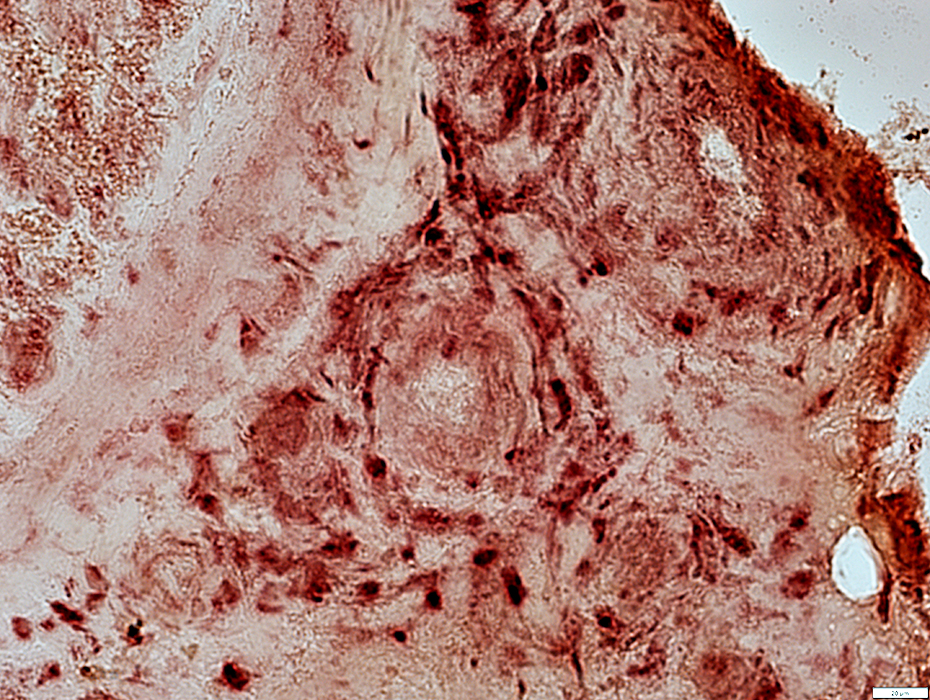 Acid phosphatase stain |
Endothelium in new Epineurial vessels stains with Alkaline phosphatase
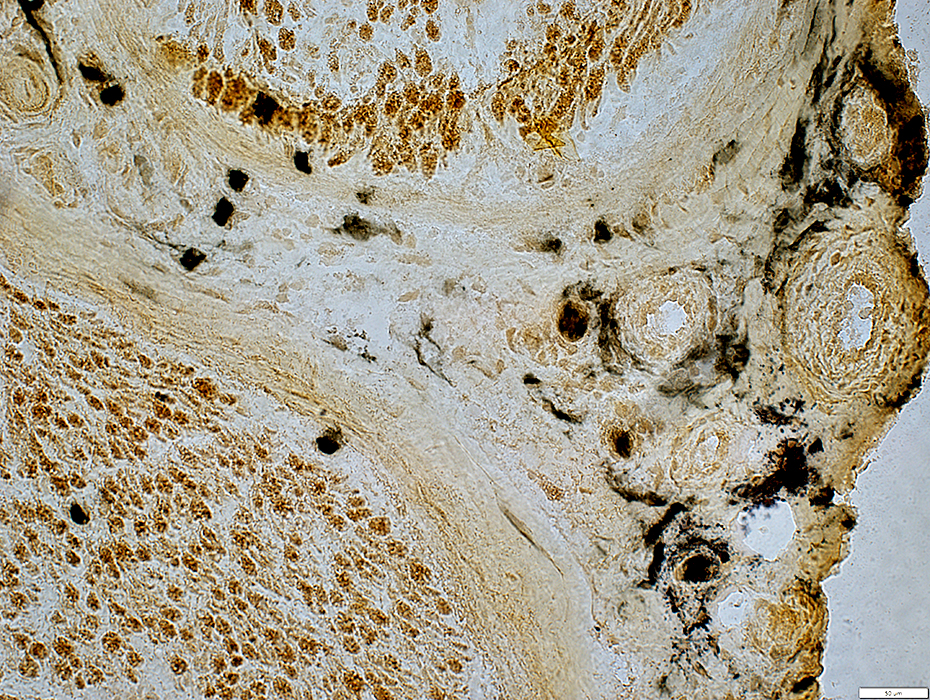 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
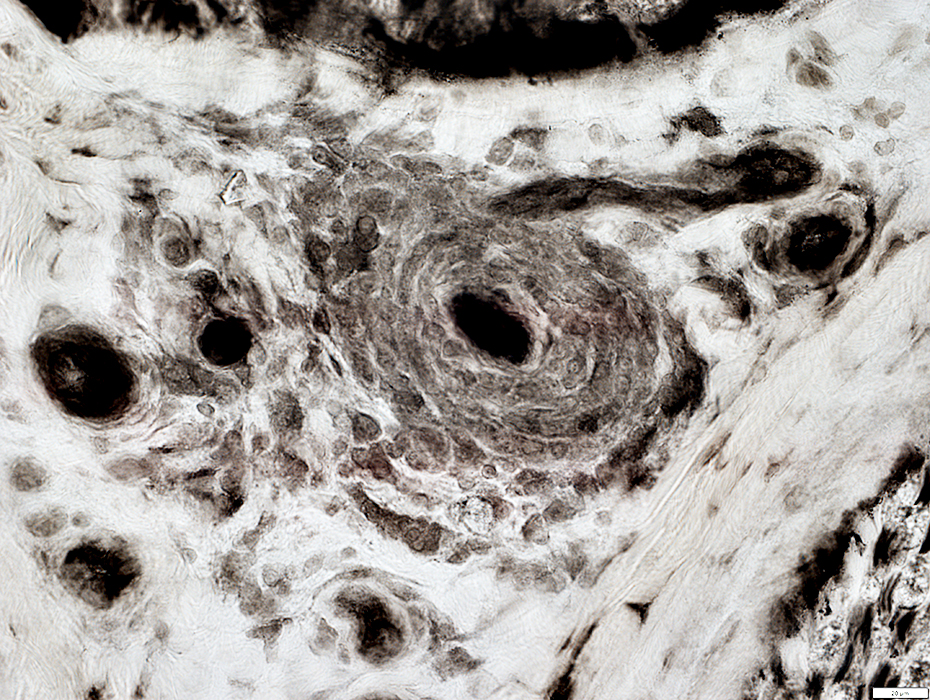 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
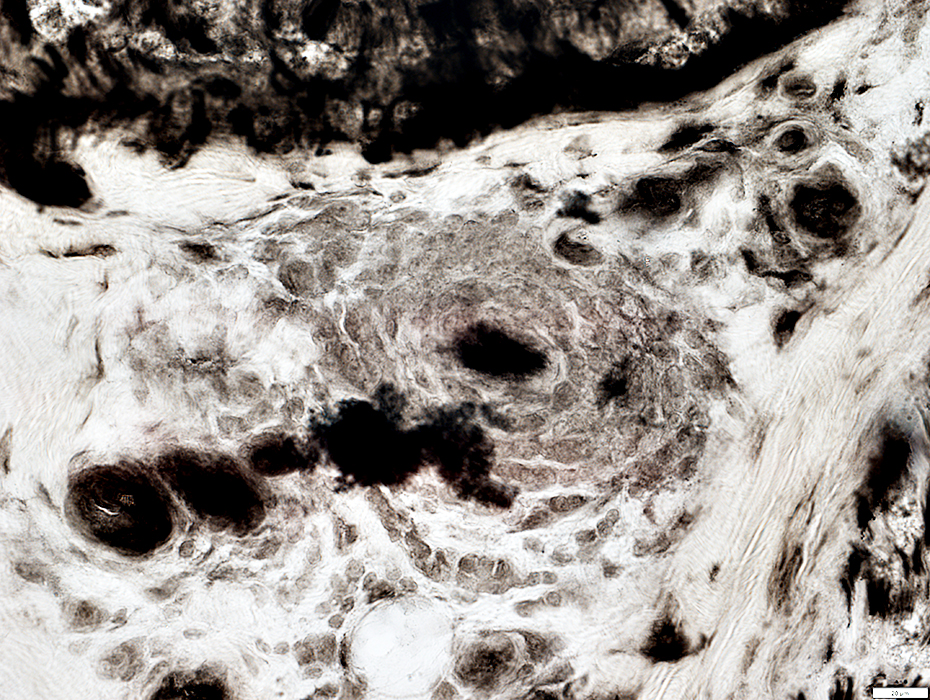 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
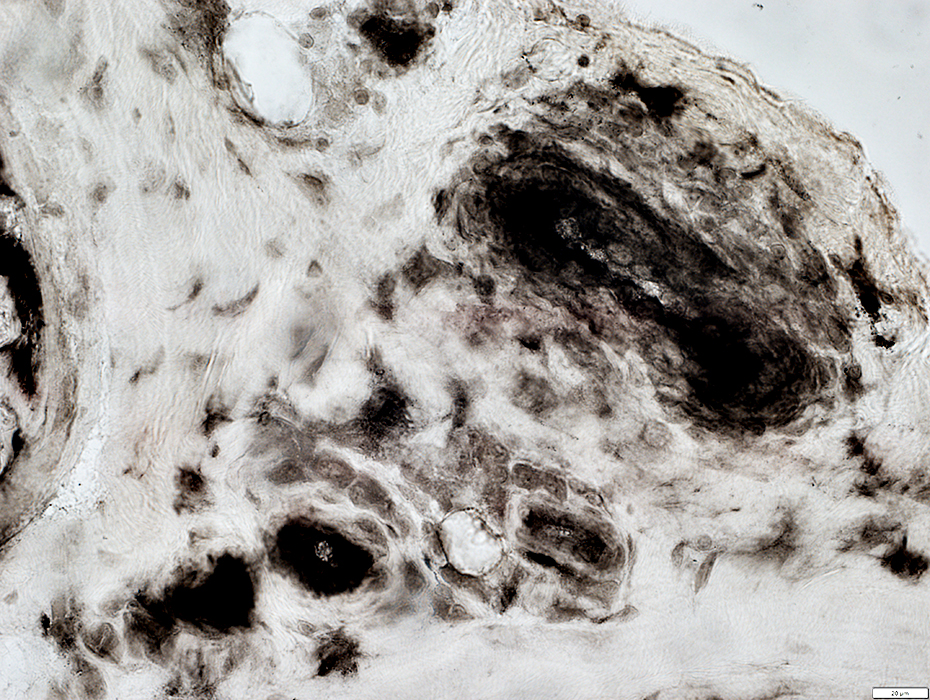 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
MHC I positive cells & epineurium
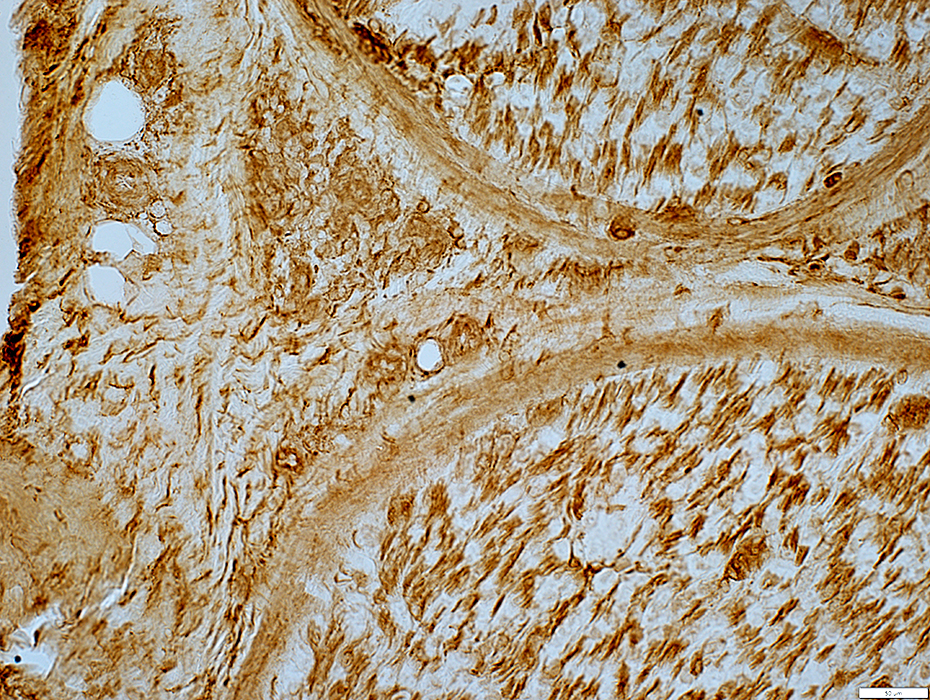 MHC I stain |
Wallerian Degeneration: Early, Active & Acute
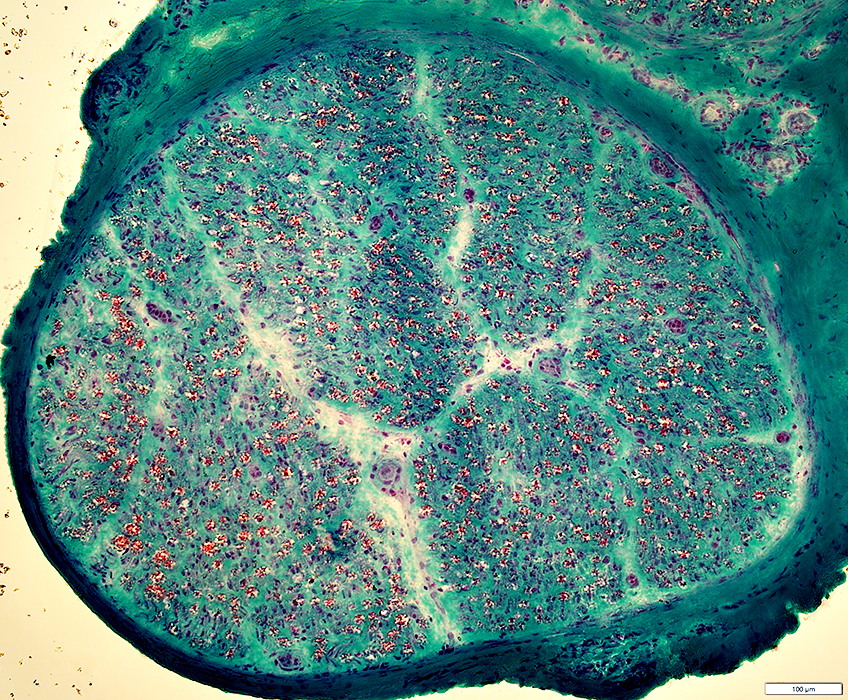 Gomori trichrome stain |
Myelin: Irregular structure or Pale stain
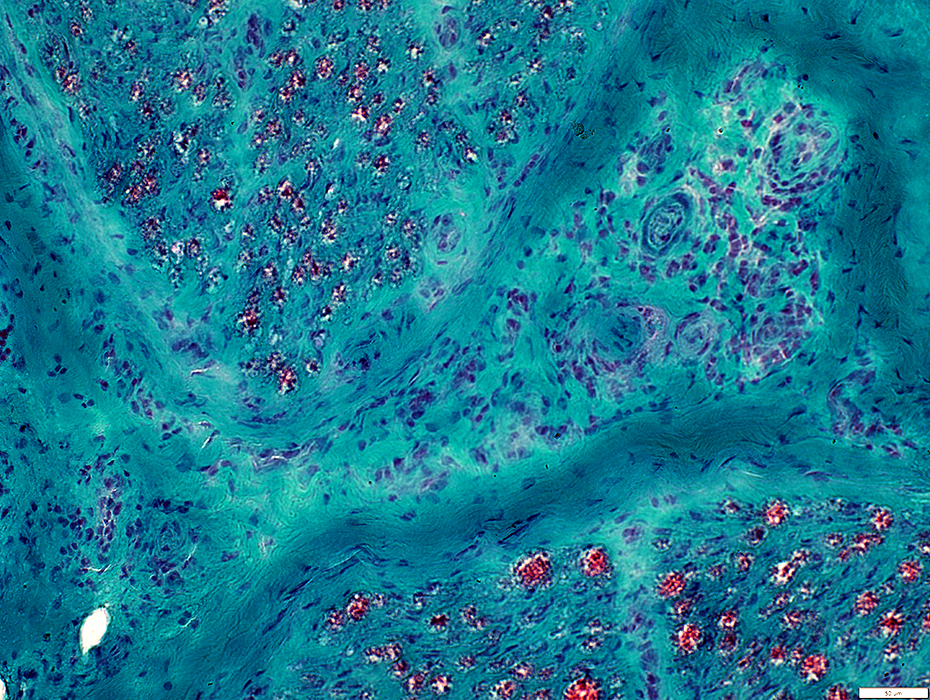 Gomori trichrome stain |
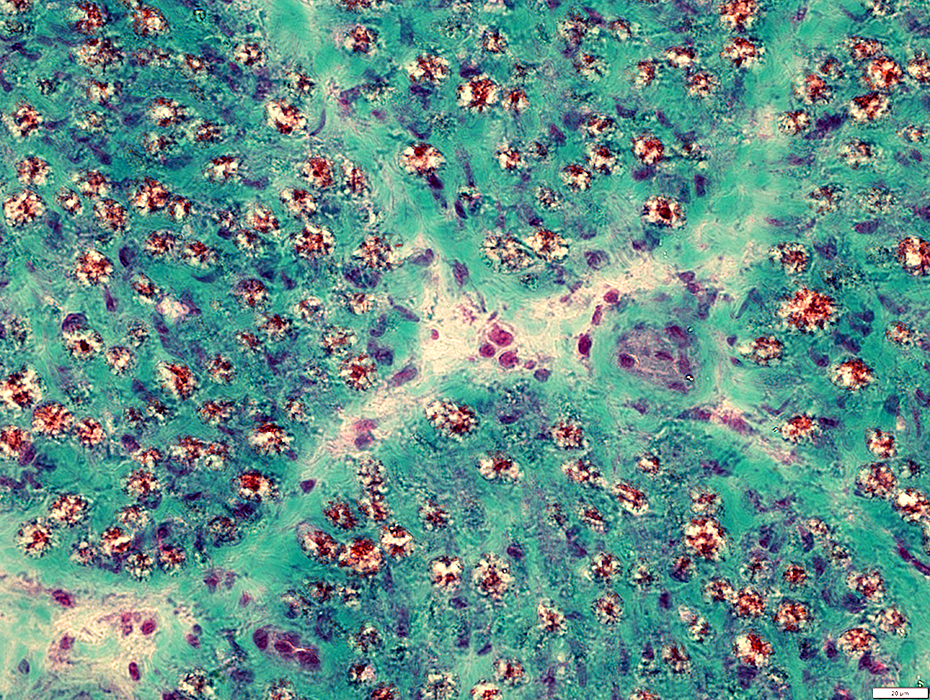 Gomori trichrome stain |
Myelin: Irregular structure
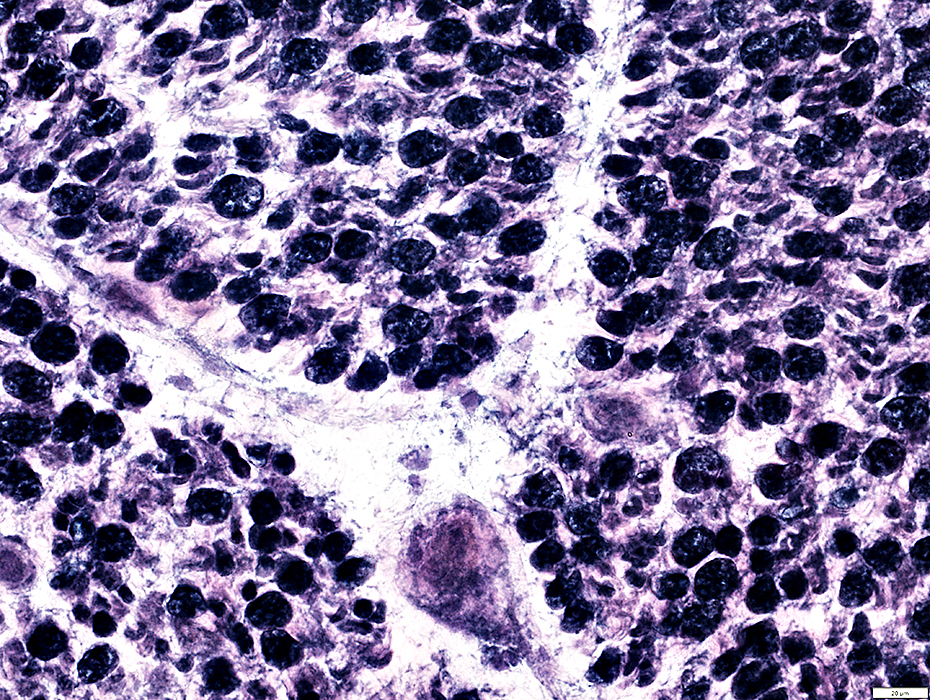 VvG stain |
Wallerian Degeneration (Early)
Histiocytes: Scattered in endoneurium
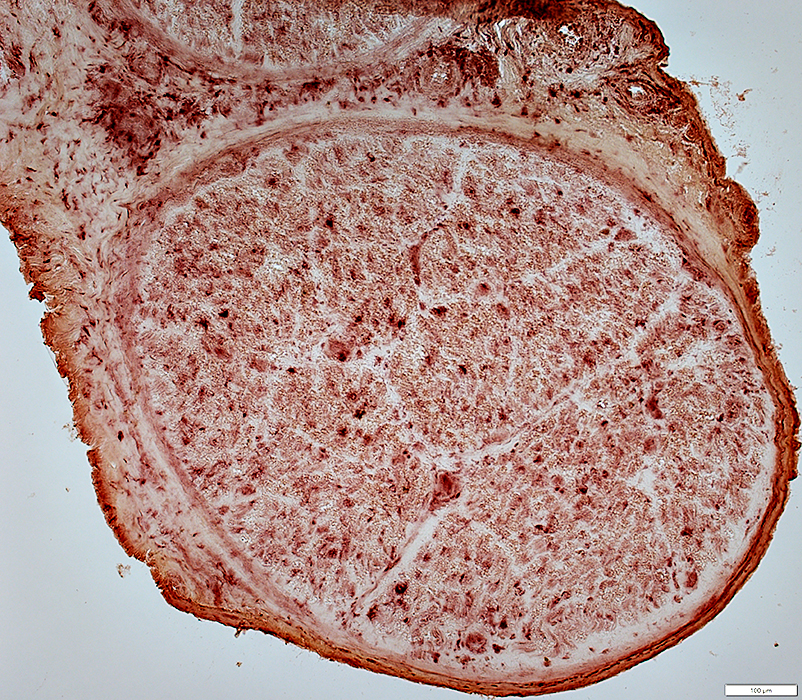 Acid phosphatase stain |
Wallerian Degeneration (Early)
NCAM: Mild staining of myelin
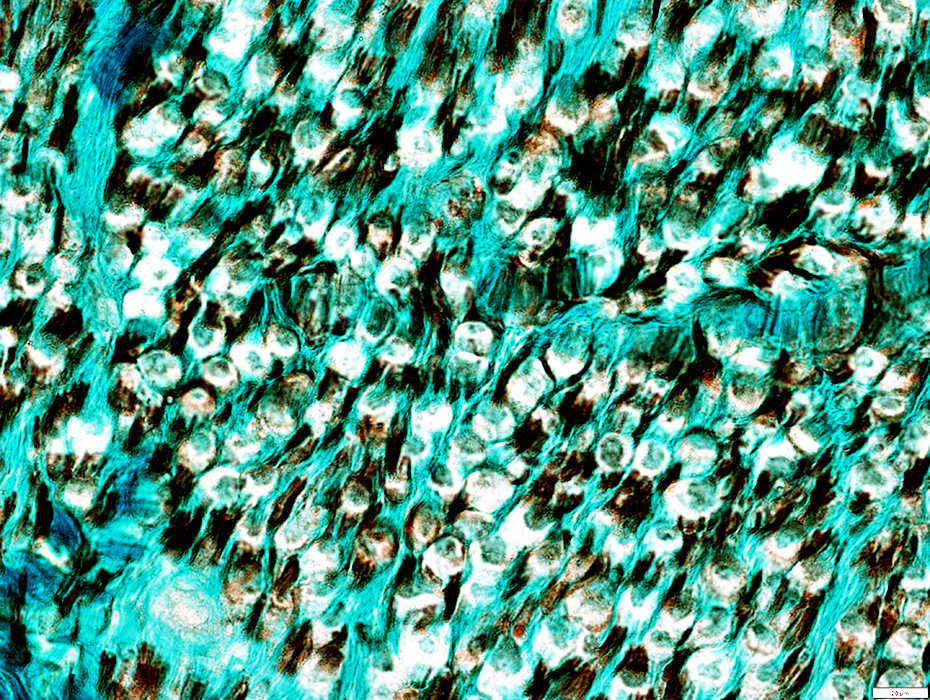 NCAM stain |
Wallerian Degeneration (Early)
Neurofilament staining of myelinated axons: Lost or fragmented
Neurofilament staining of unmyelinaterd axons: Relatively preserved
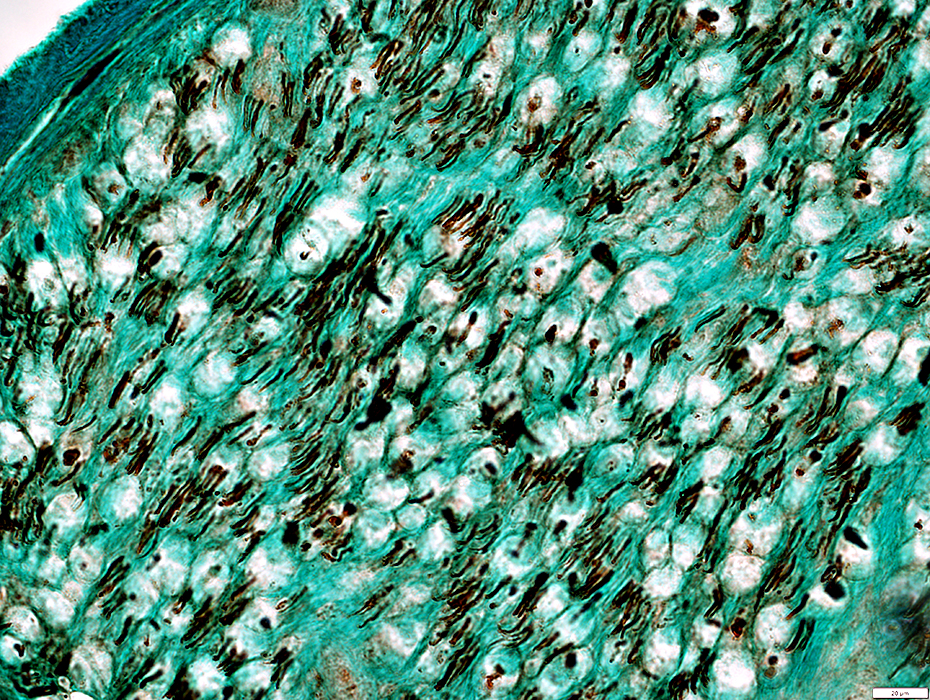 Neurofilament stain |
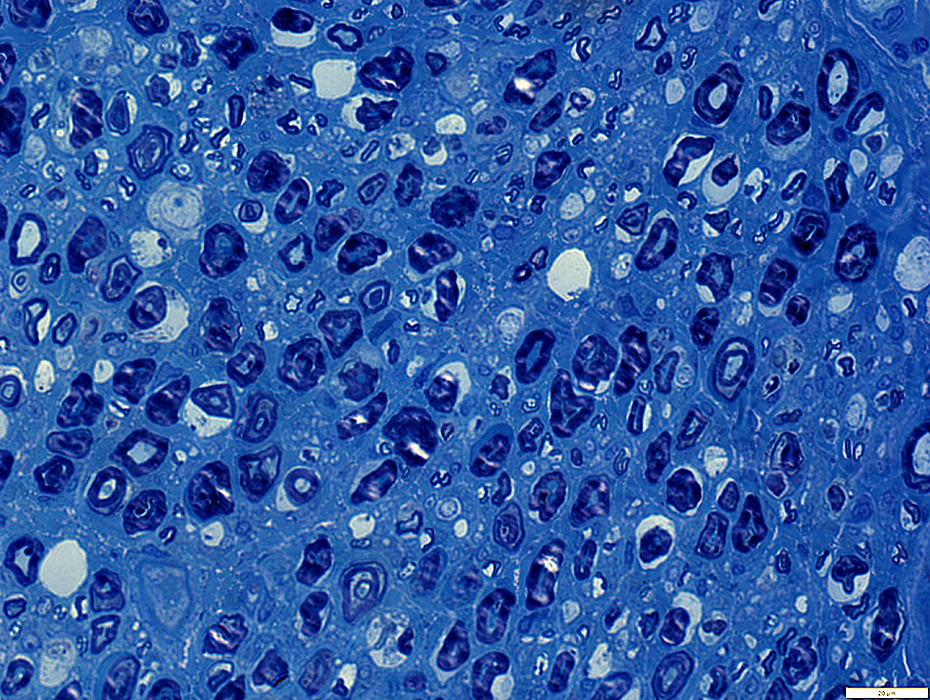 Toluidine blue stain |
Myelin structure: Irregular
Large myelin fragments: Present in cytoplasm of large "Degradative" Schwann cells
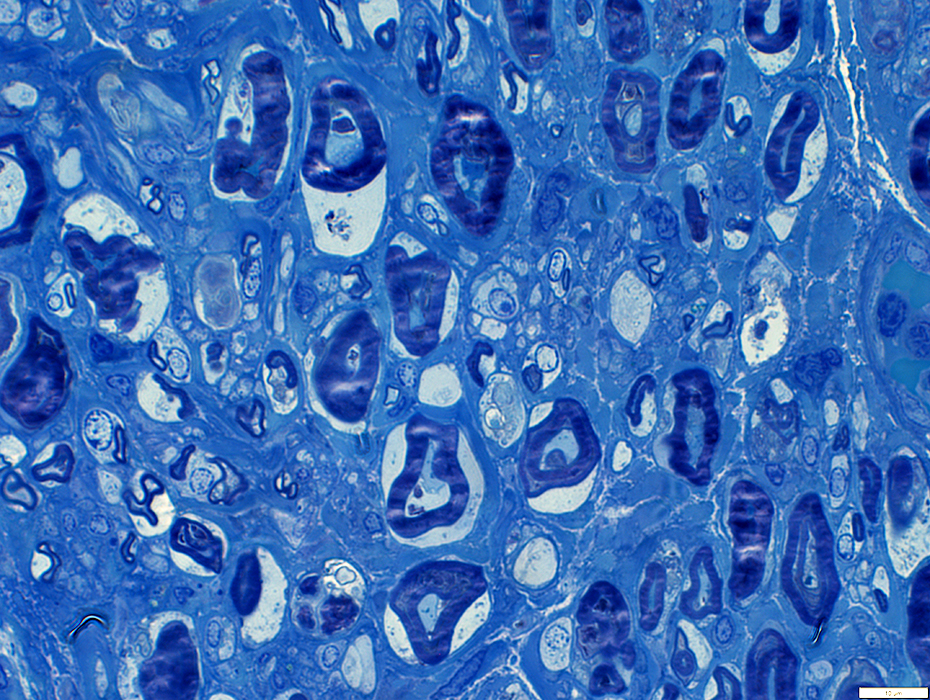 Toluidine blue stain |
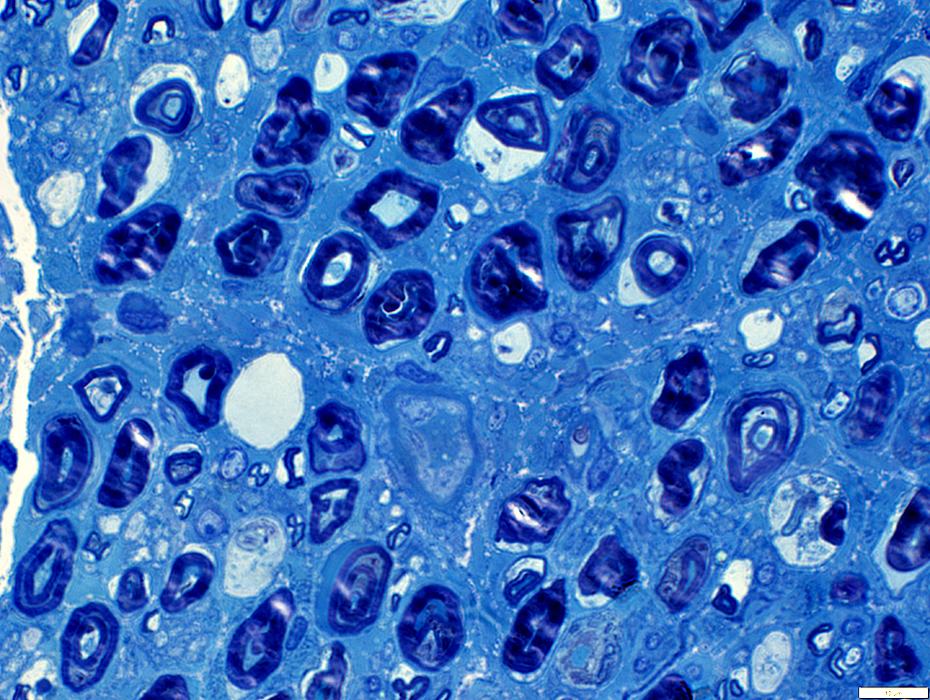 Toluidine blue stain |
Myelin structure: Irregular
Large myelin fragments: Present in cytoplasm of large "Phagocytic" Schwammm cells
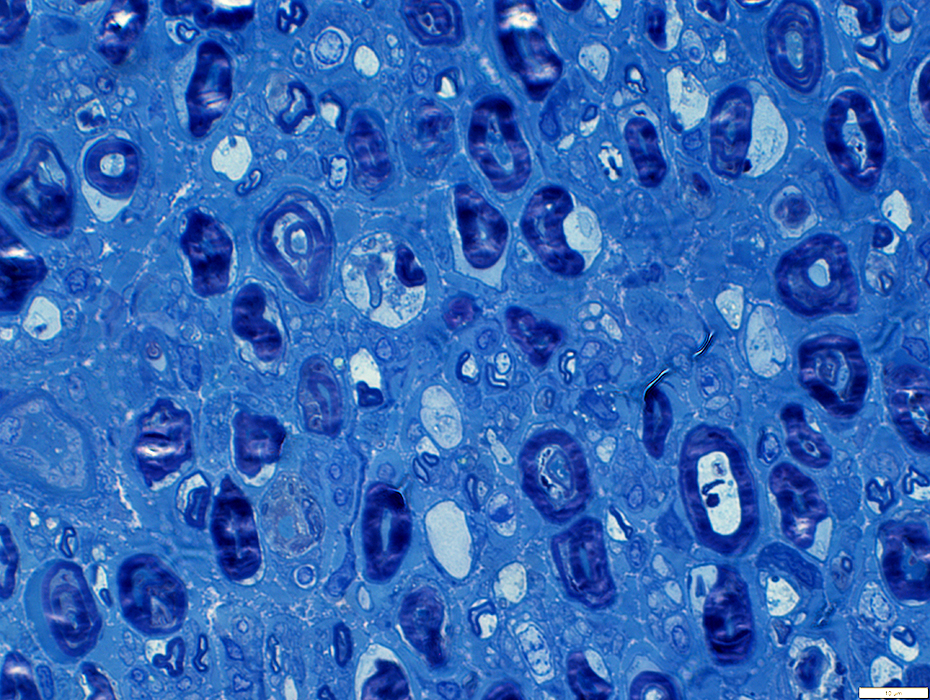 Toluidine blue stain |
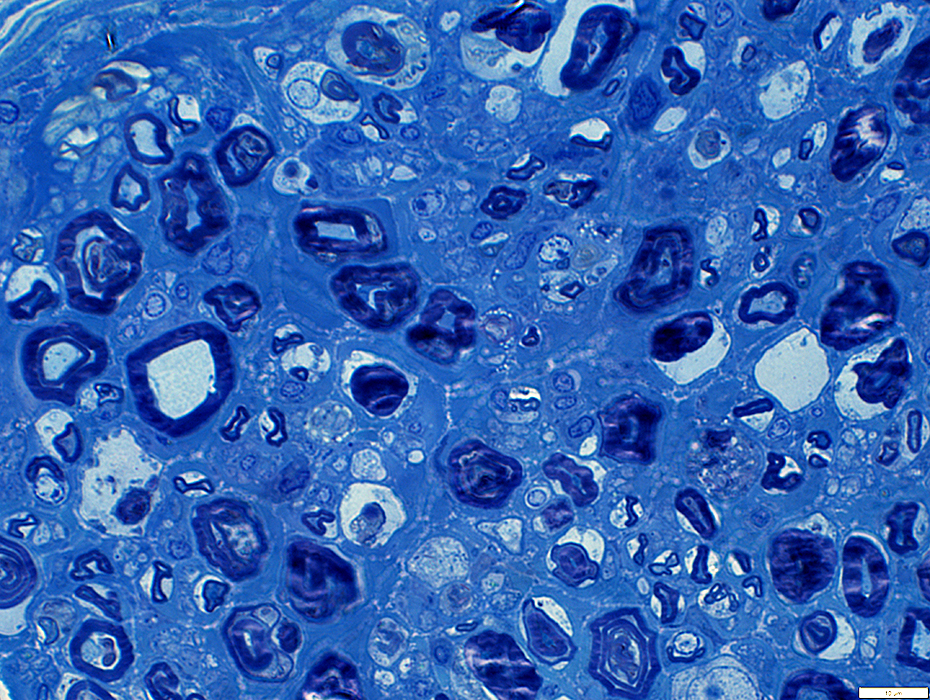 Toluidine blue stain |
Myelin structure: Irregular
Large myelin fragments: Present in cytoplasm of large "Phagocytic" Schwammm cells
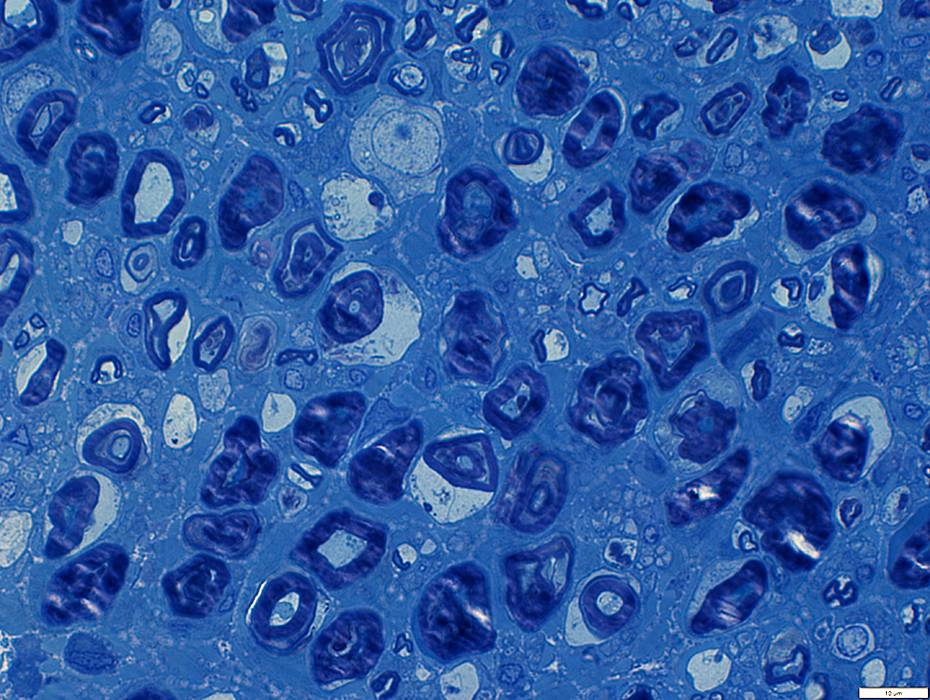 Toluidine blue stain |
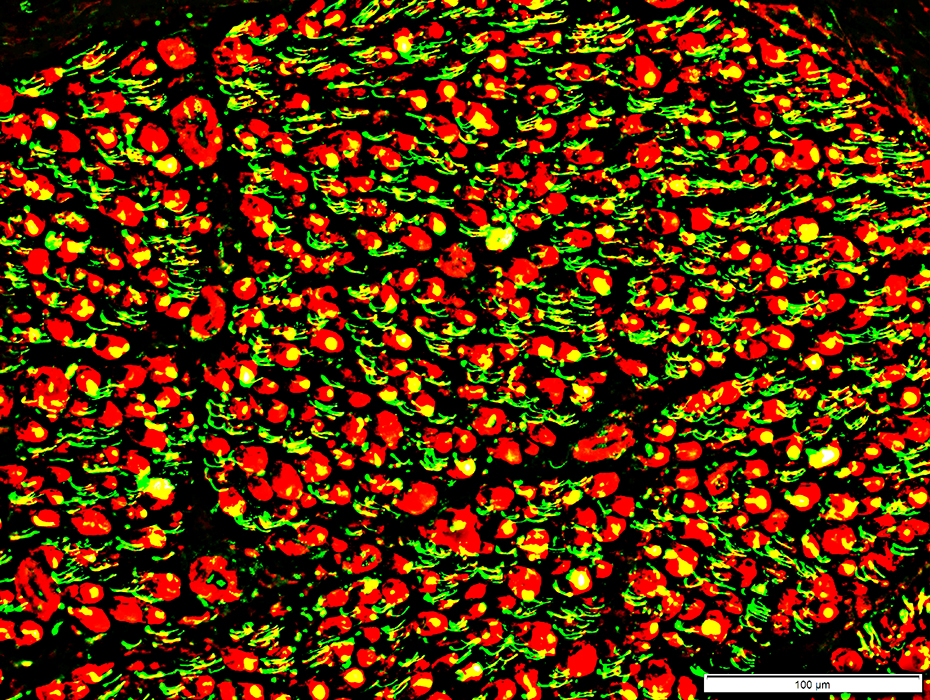 Neurofilament (Green) + MBP (Red) |
Neurofilament staining of myelinated axons
Lost or fragmented
MBP & P0 stained myelin have no associated axons
Neurofilament staining of unmyelinaterd axons: Relatively preserved
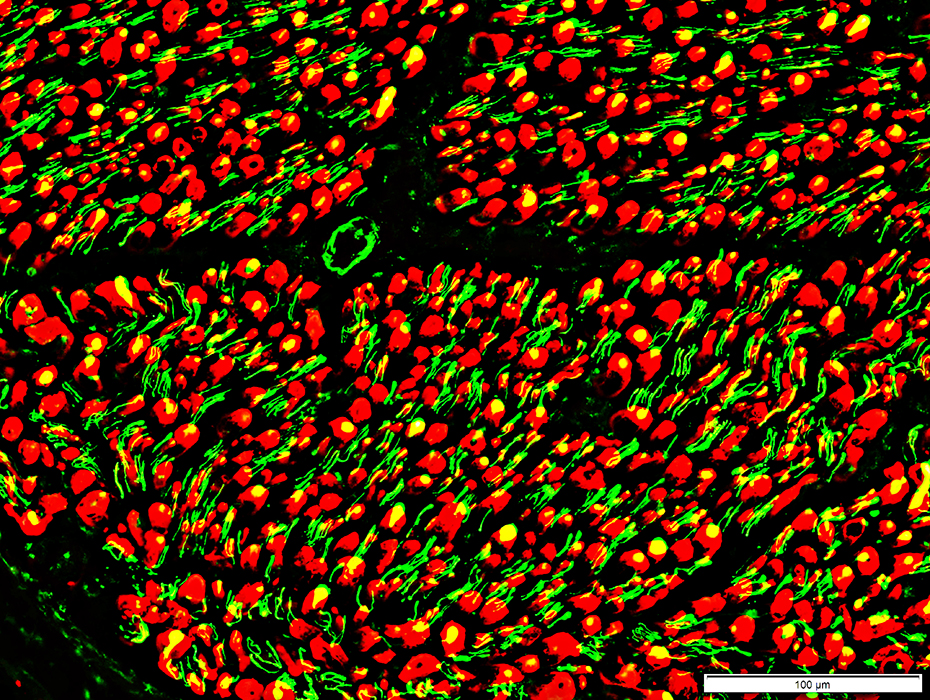 Neurofilament (Green) + P0 (Red) |
 Neurofilament (Green) + NCAM (Red) |
Neurofilament staining of myelinated axons
Lost or fragmented
Neurofilament staining of unmyelinaterd axons
Some Loss: Empty (red) non-myeliating Schwann cells
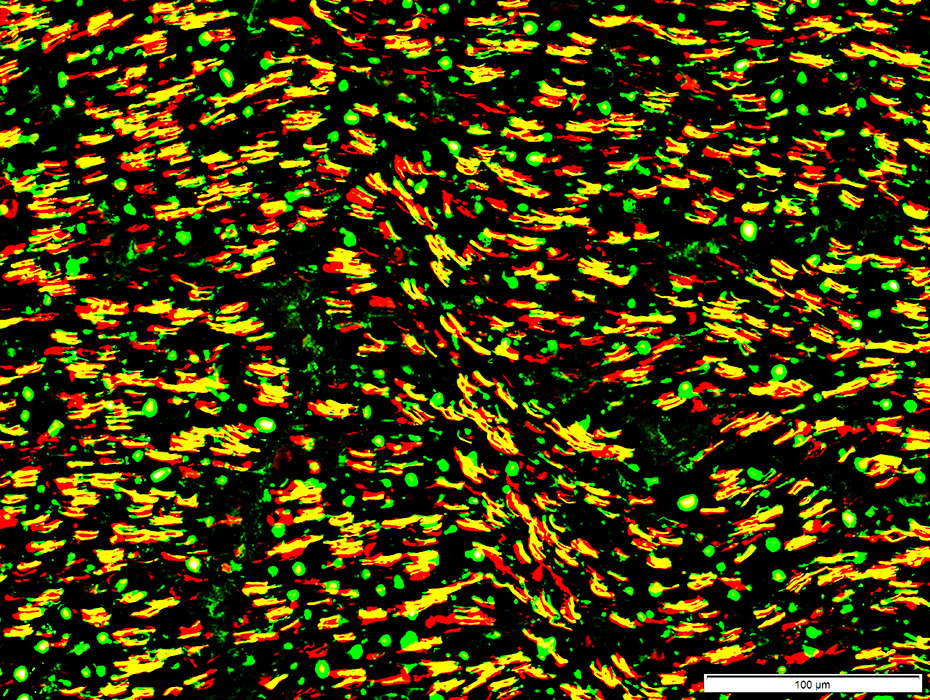
Myelin in Peripheral Nerve: 2 types
Small myelin sheaths (Green): Contain only P0
Large myelin sheaths (Yellow): Contain both P0 & MBP
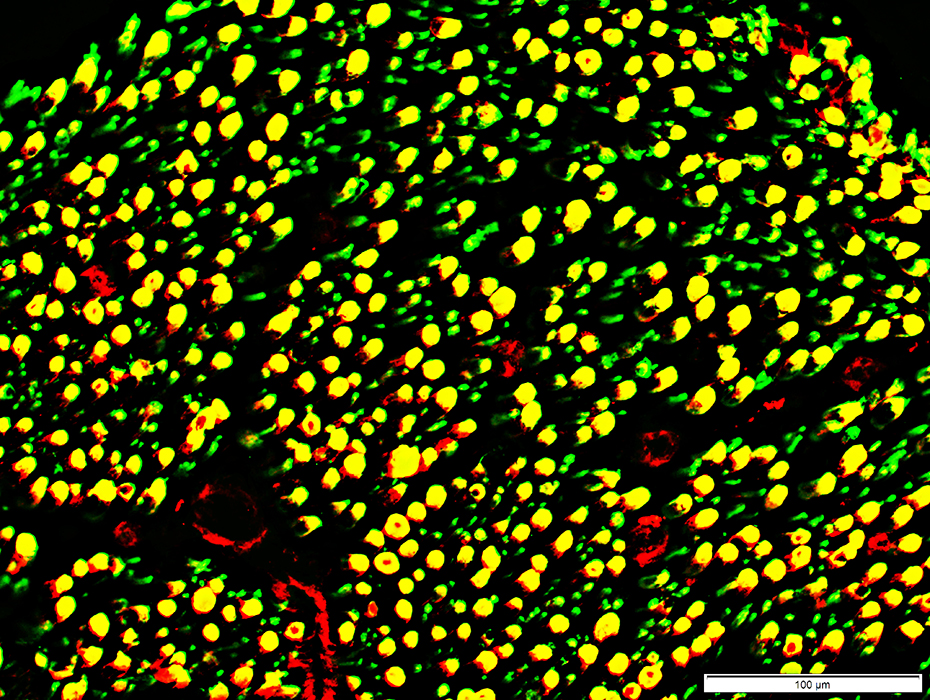 P0 (Green) + MBP (Red) |
Wallerian Degeneration
Endothelial cells in Endoneurial microvessels: Often large
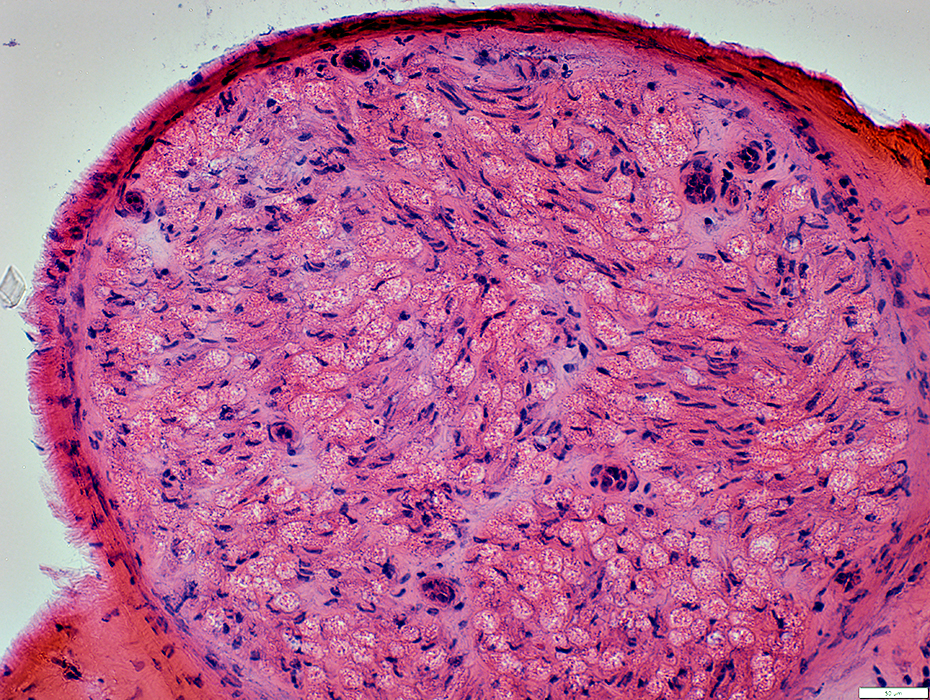 H&E stain |
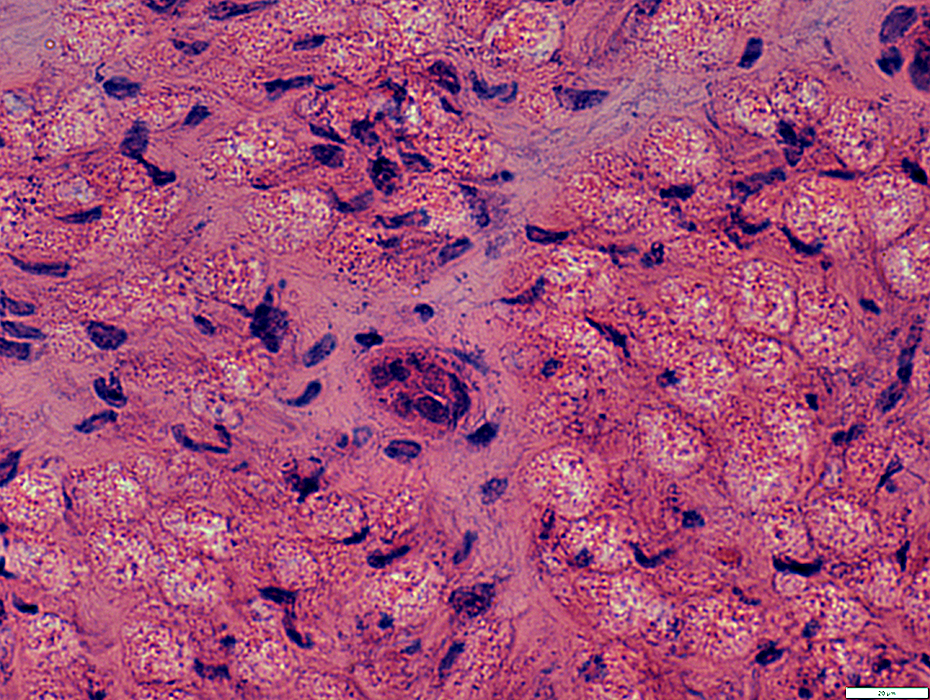 H&E stain |
Endothelial cells in Endoneurial microvessels: Often large
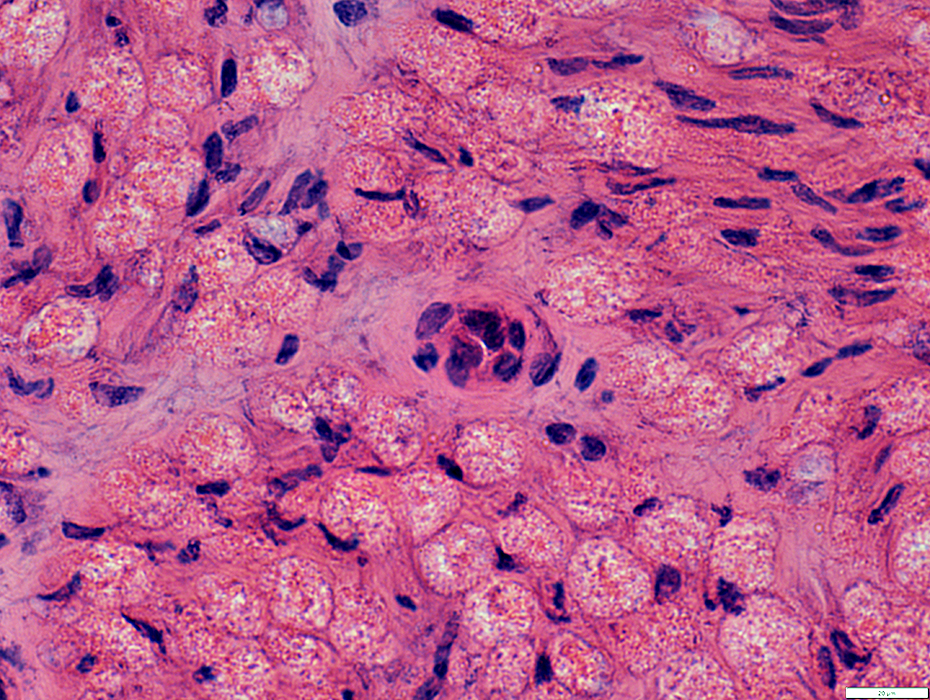 H&E stain |
HIV: Inflammatory Veinopathy
Same patient as: Small Vessel Inflammatory Neuropathy
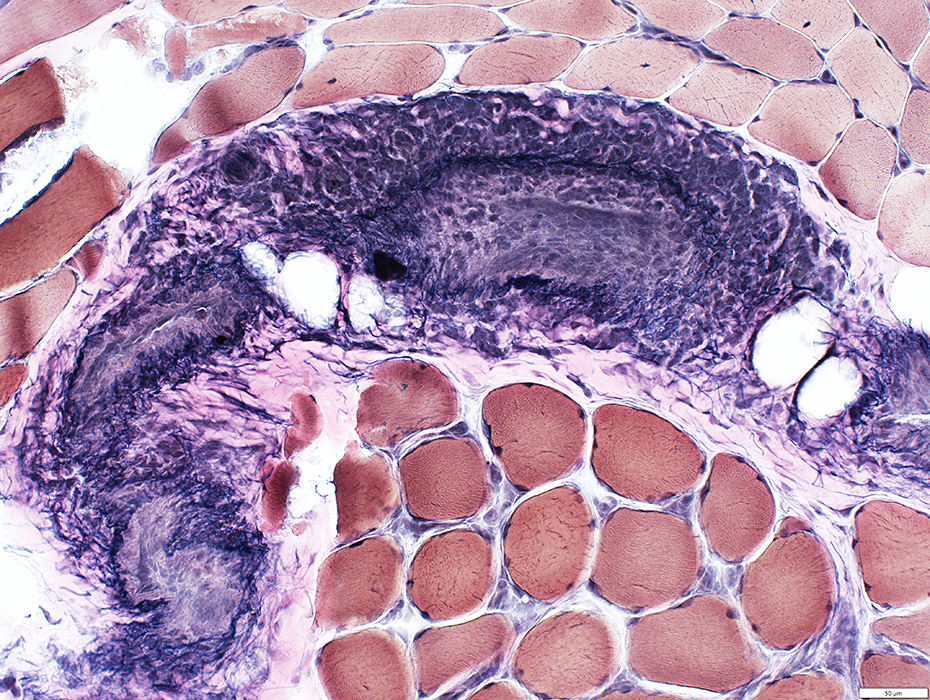 VvG stain |
Outer fibril layer: Damaged & Incomplete
Inner layers: Pale & Cellular
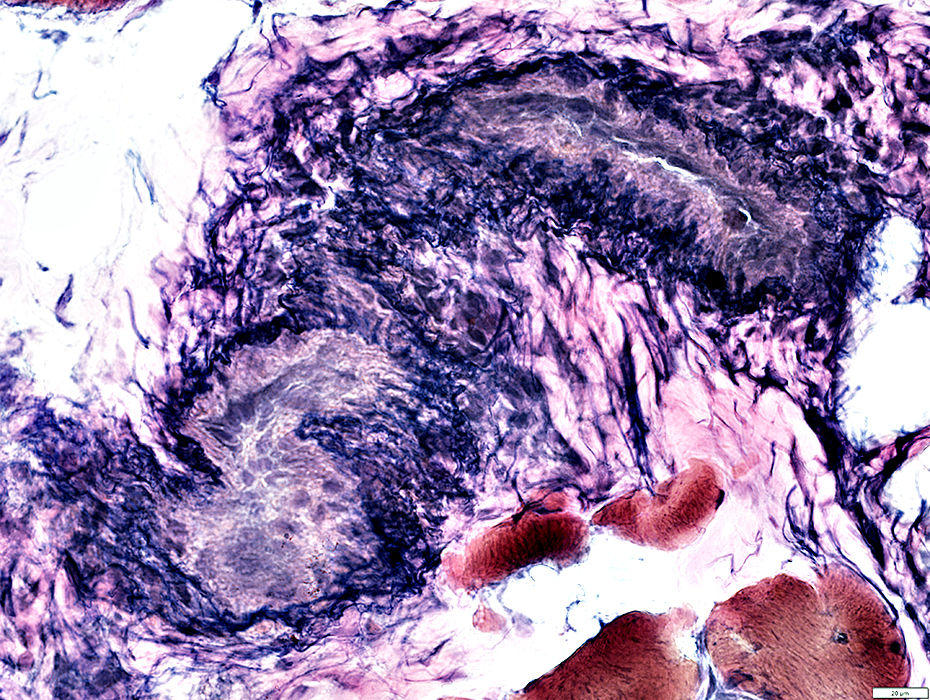 VvG stain |
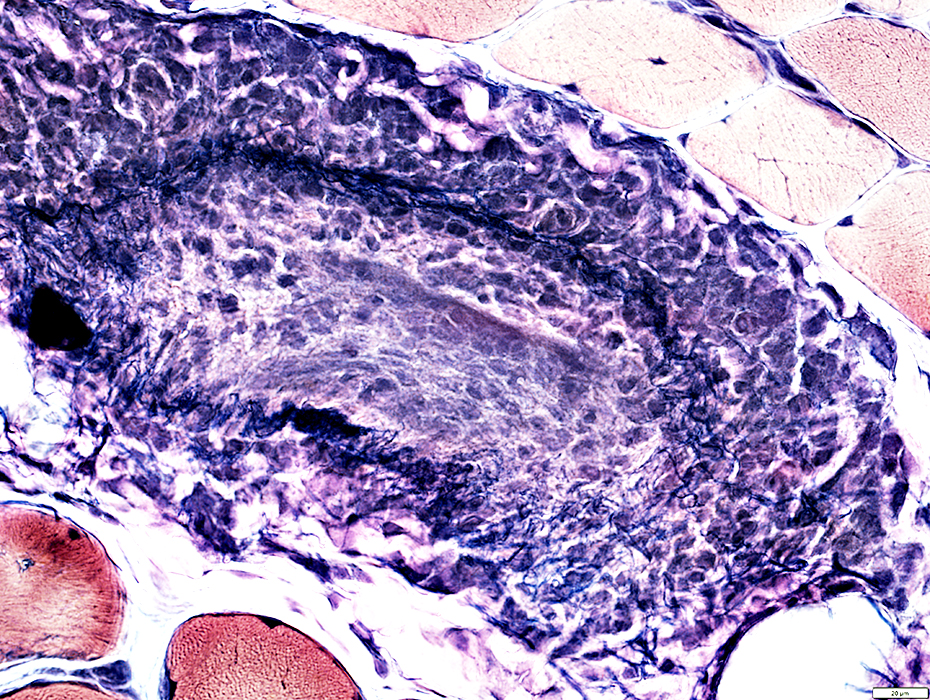 VvG stain |
Outer fibril layer: Damaged & Incomplete
Inflammatory cells: Present around outside of vein
Inner layers: Pale & Cellular
Perimysial Artery: Normal
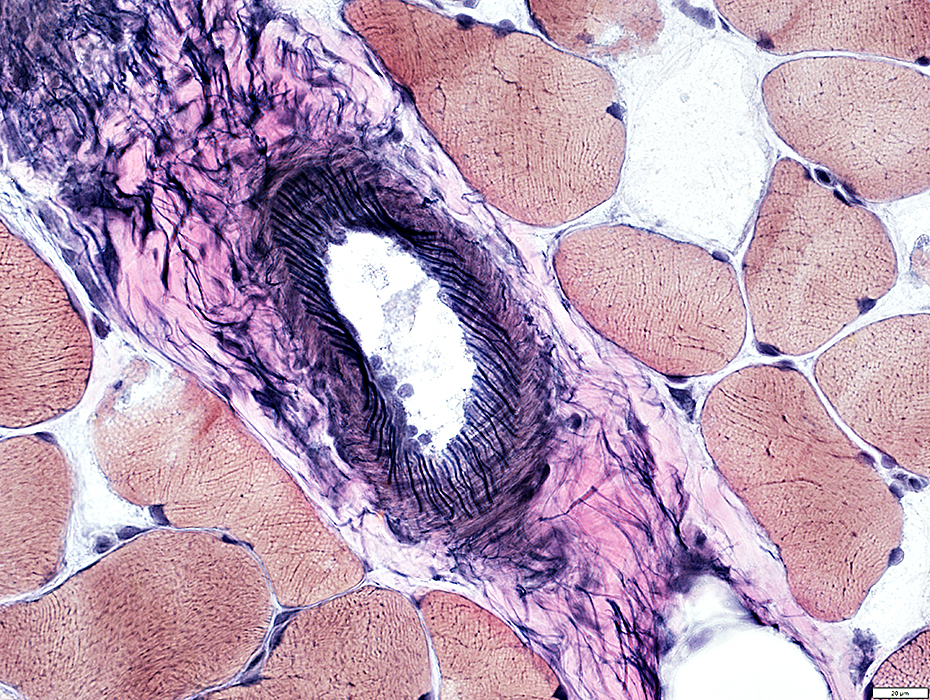 VvG stain |
Perimysial Veins
Histiocytic Inflammatory cells: Present around periphery of vein
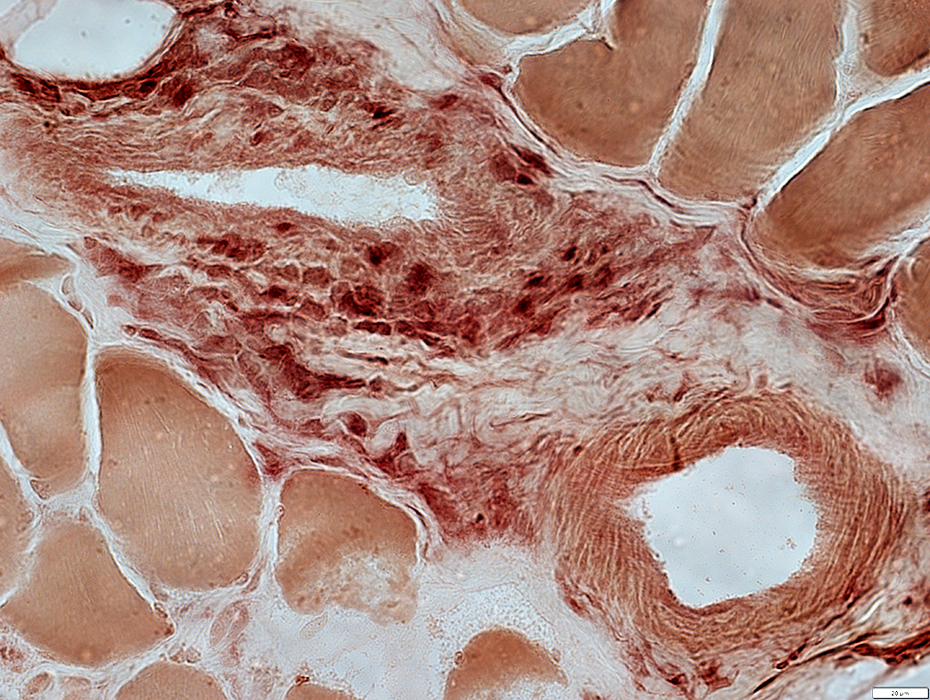 Acid phosphatase stain |
Perimysial Veins
Inflammatory cells: Present around periphery of vein & In perimysium
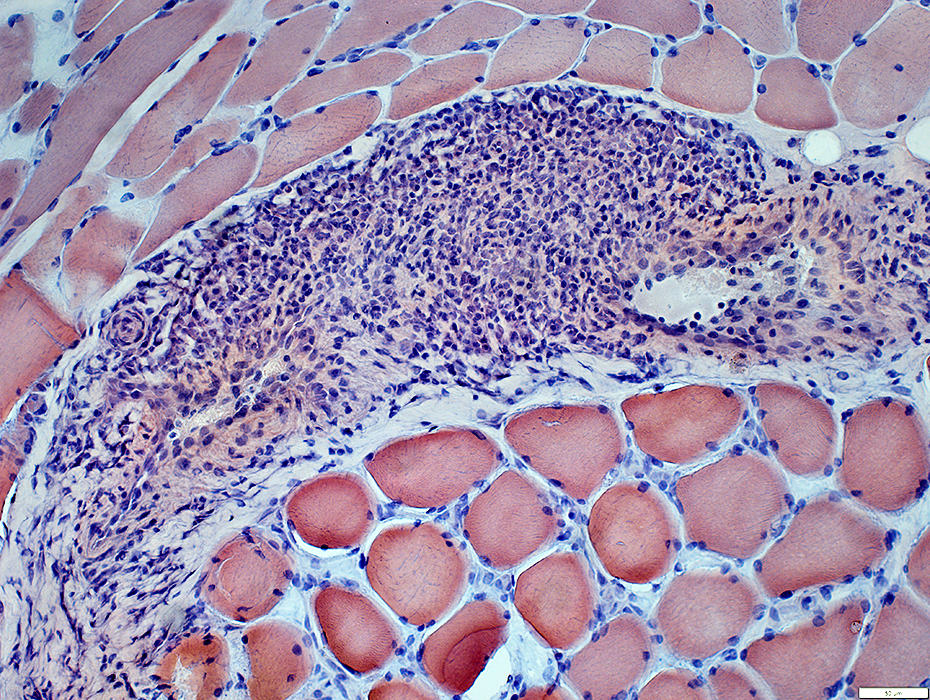 Congo red stain |
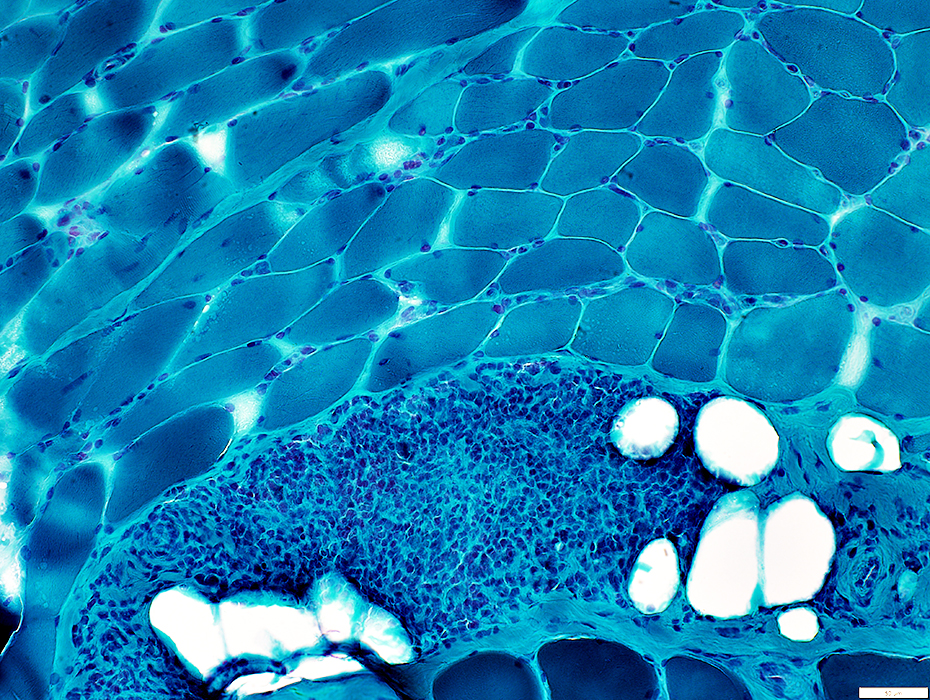 Gomori trichrome stain |
Contain scattered esterase-positive histiocytes (Below)
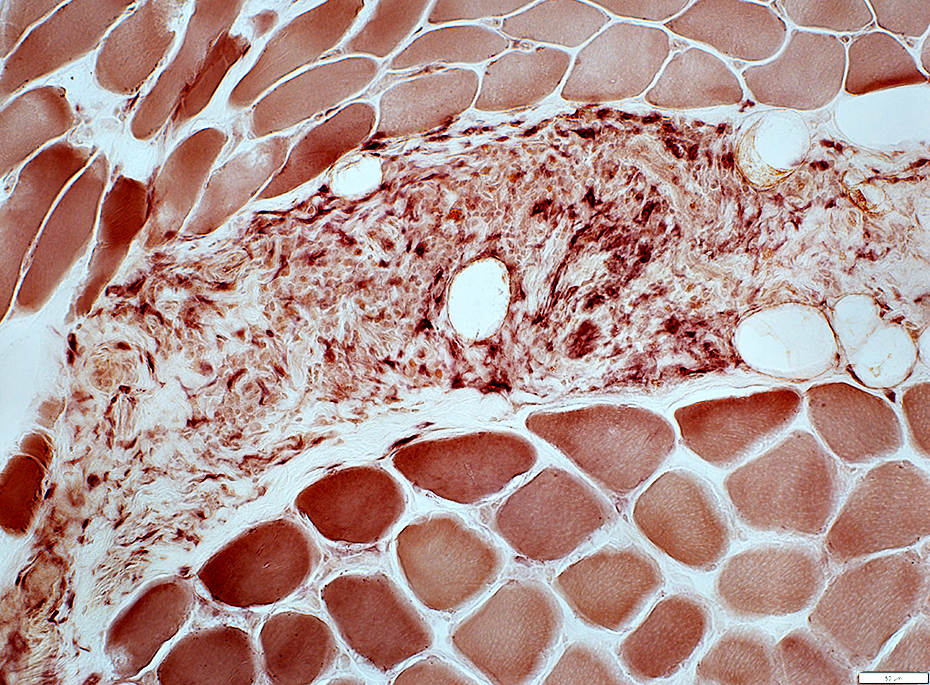 Esterase stain |
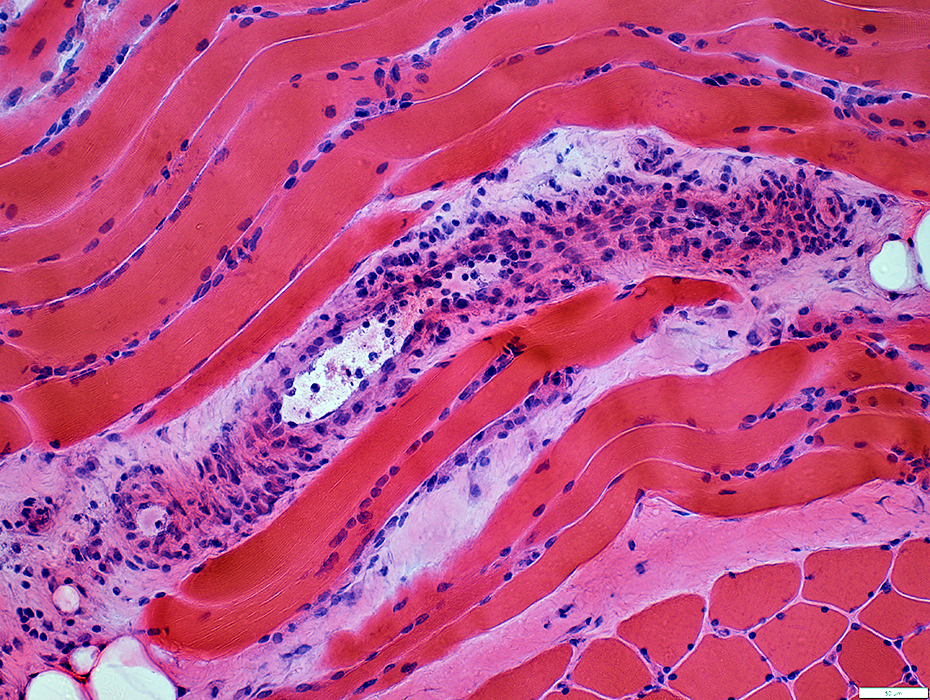 H&E stain |
HIV-Vasculitis: Muscle fiber involvement
Morphology: Mostly normla
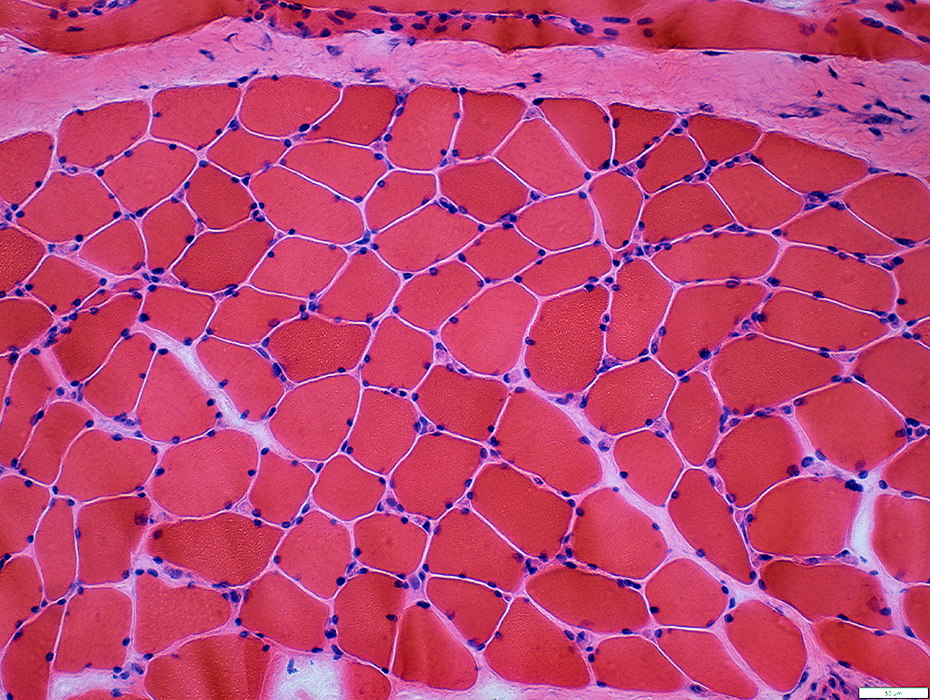 H&E stain |
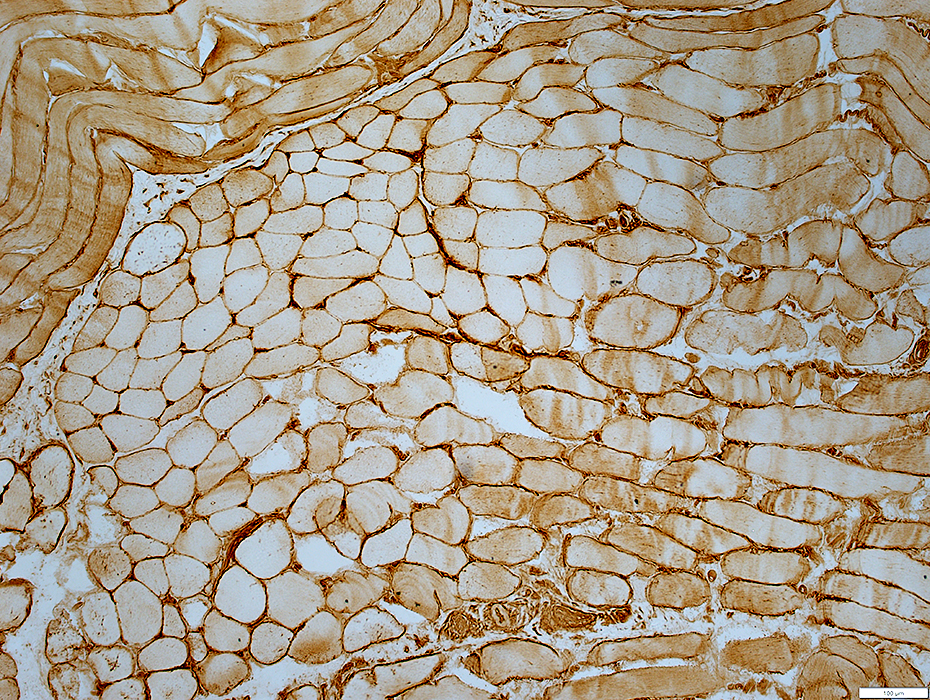 MHC I stain |
MHC I: Upregulated on muscle fiber surfaces
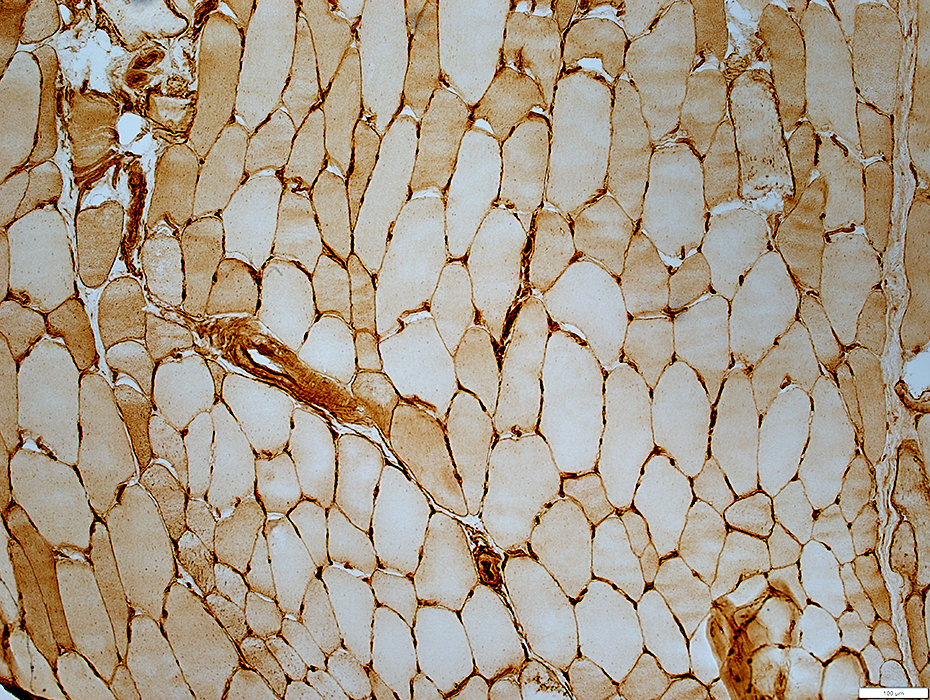 MHC I stain |
HIV-Vasculitis: Capillaries
Sizes: Midly large
Numbers: Normal or Mildly increased
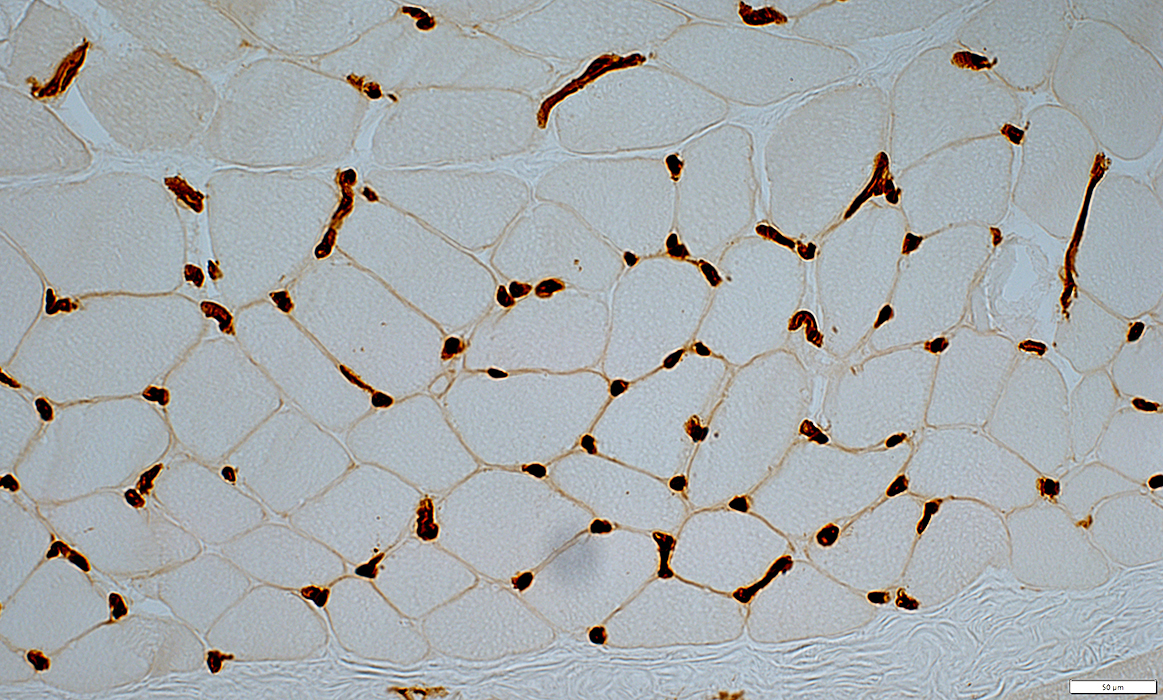 UEA I stain |
Return to: Neuromuscular Home Page
6/1/2023