Acute Immune Neuropathies
|
AIDP AMN AMSAN Demyelination Active Macrophage-mediated |
Acute Immune Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (AIDP)
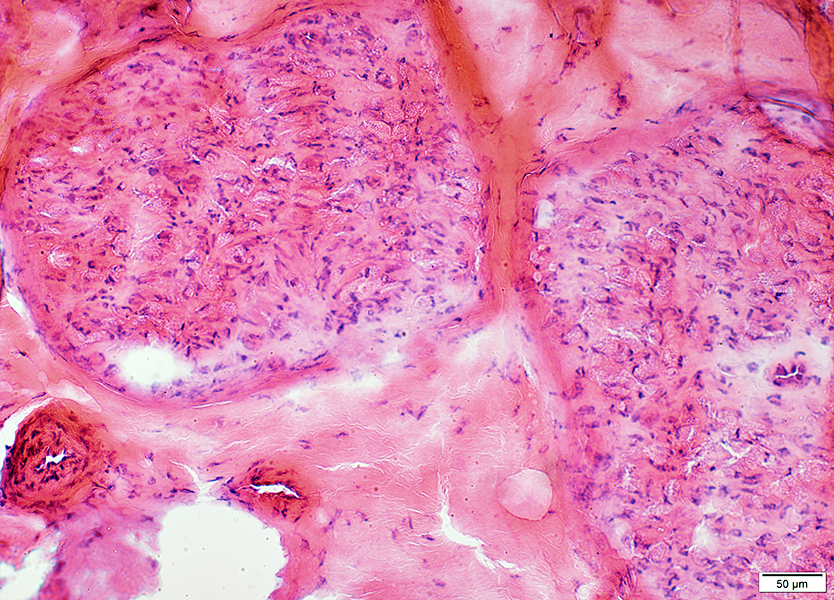 H&E stain |
Perineurium, Epineurium & Vessels: Normal
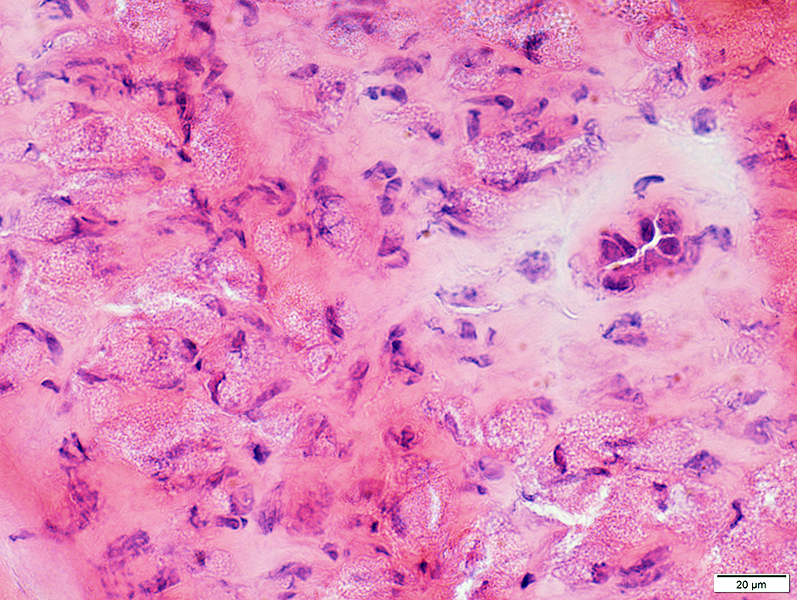 H&E stain |
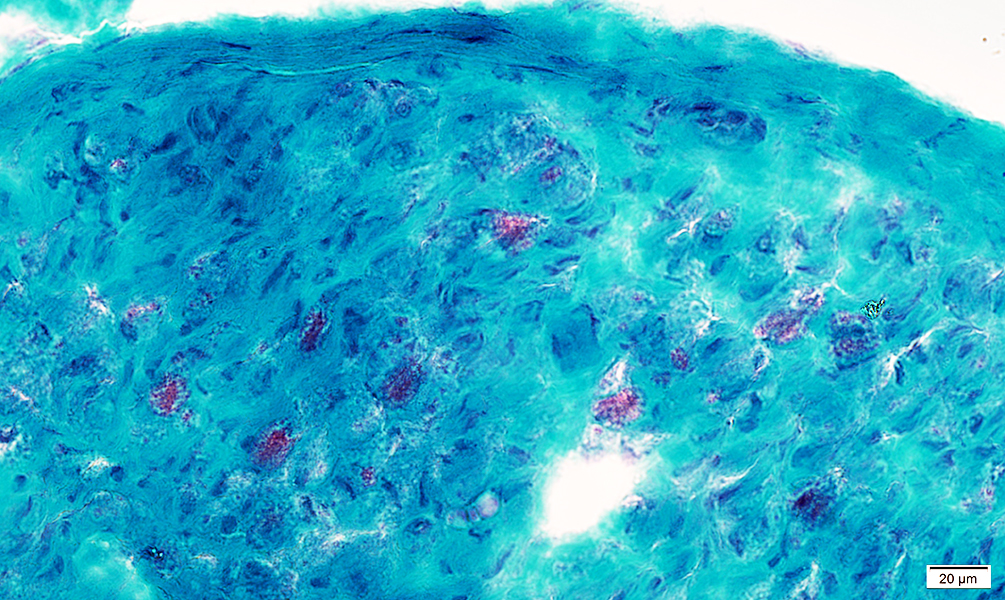 Gomori trichrome stain |
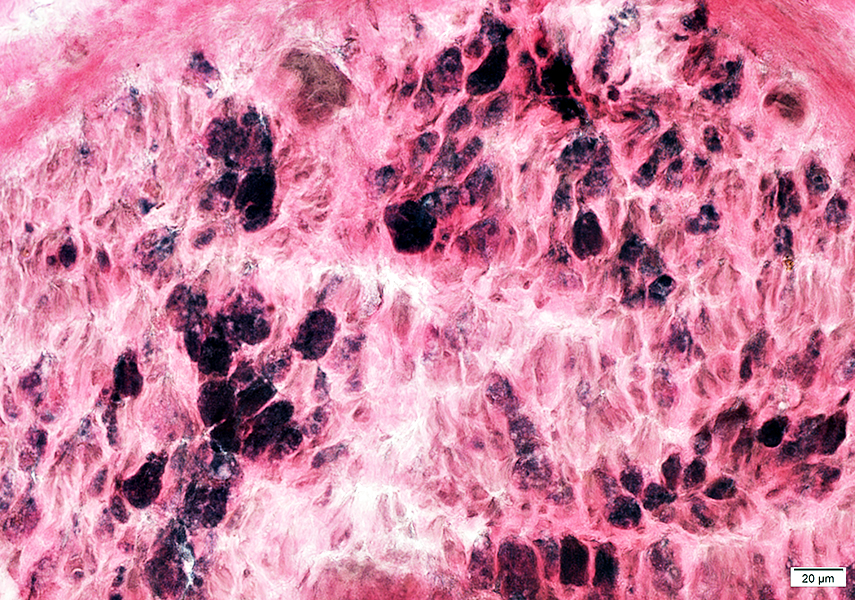 VvG stain |
|
Large & Small Axons Relatively preserved compared to myelin loss Focal loss in some endoneurial areas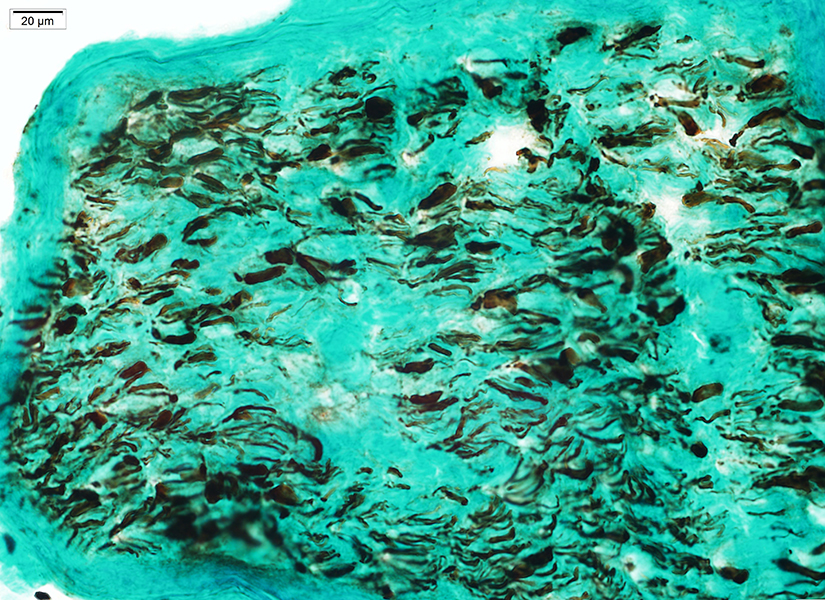  Neurofilament stain |
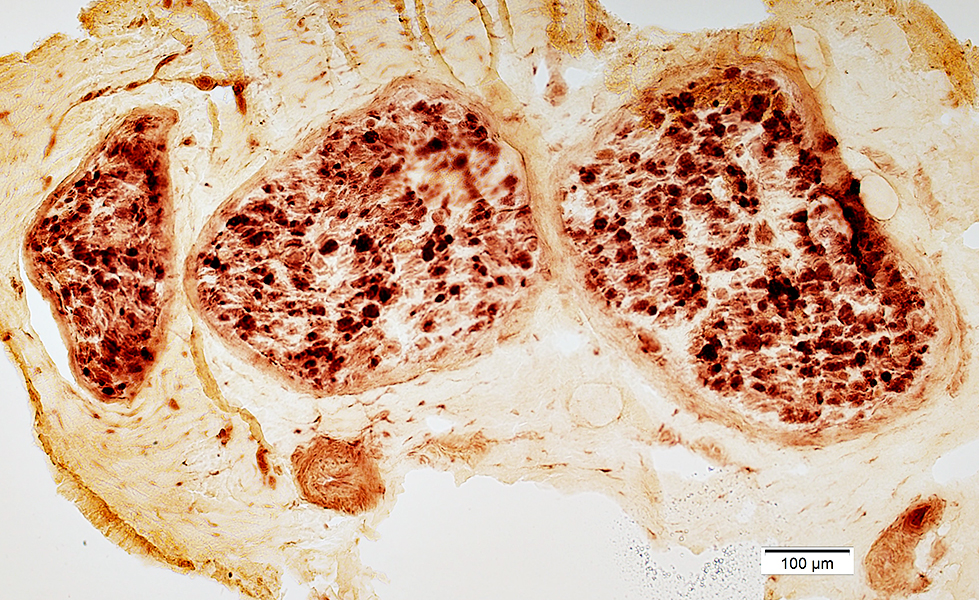 Acid phosphatase stain |
Stain for lysosomal & Macrophage markers
Ultrastructure
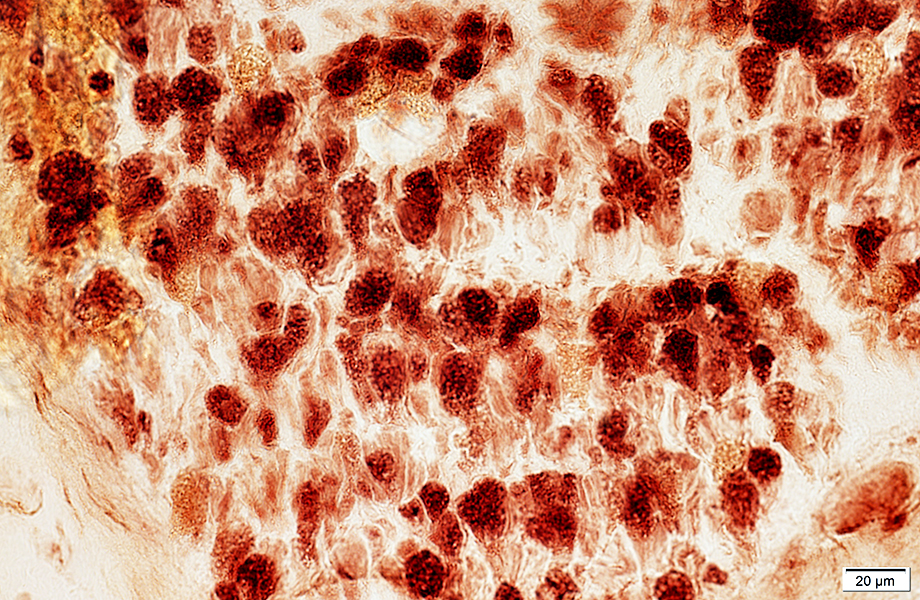 Acid phosphatase stain |
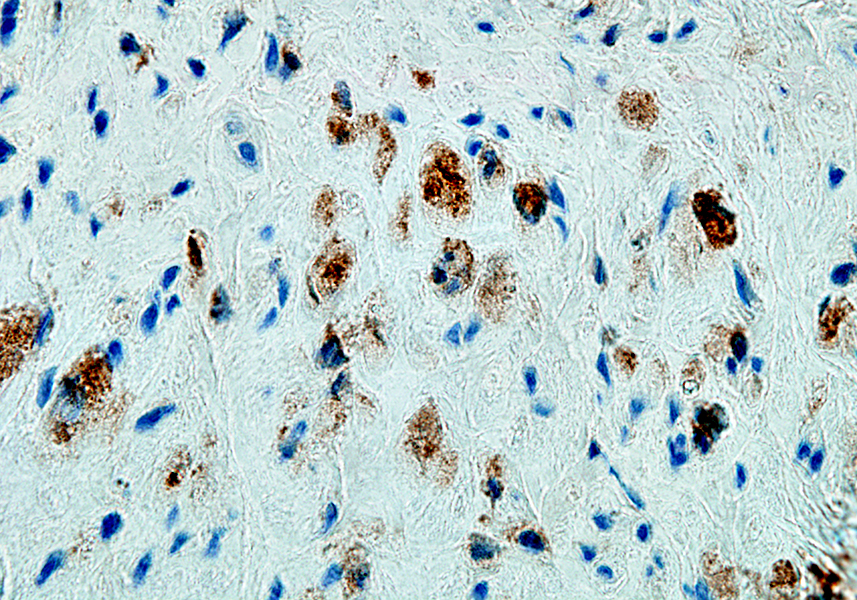 CD163 stain |
Stages of Macrophage (Histiocyte)-mediated Myelin Stripping (Active Demyelination) 1,2
- Histiocytes
- Attracted to myelinated axon
- Initially associated with: Outside of Schwann cell basal lamina
- May be preferentially located at
- Internode
- Common in AIDP or CIDP Subacute
- Node of Ranvier
- Not common inNeurofascin-155 or Contactin-1 antibody disorders
- Axon (AMAN)
- Internode
- Penetration through Schwann cell basal lamina
- Locate between basal lamina & myelin
- Histiocytes extend processes
- Grow between layers of myelin (Between adjacent major dense lines)
- Phagocytosis & degradation of myelin
- Generates myelin debris & lipid droplets within histiocytes
- Migration of histiocytes out of Schwann cell basal lamina
- Into endoneurium & toward vessels
- Attracted to myelinated axon
- Demyelinated Axons
- No associated myelin
- Surrounded by Schwann cell basal lamina
- May be associated with
- May become chronic
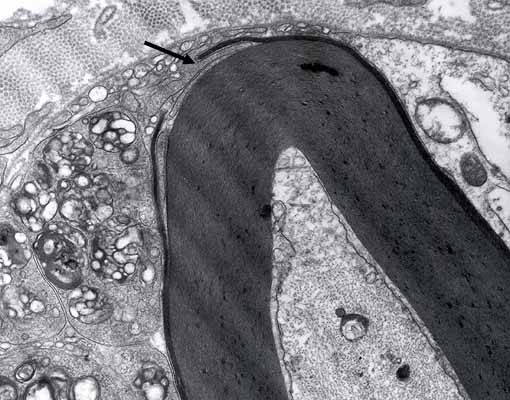
Macrophage
Adherent to Schwann cell basal lamina
Outside myelin sheath
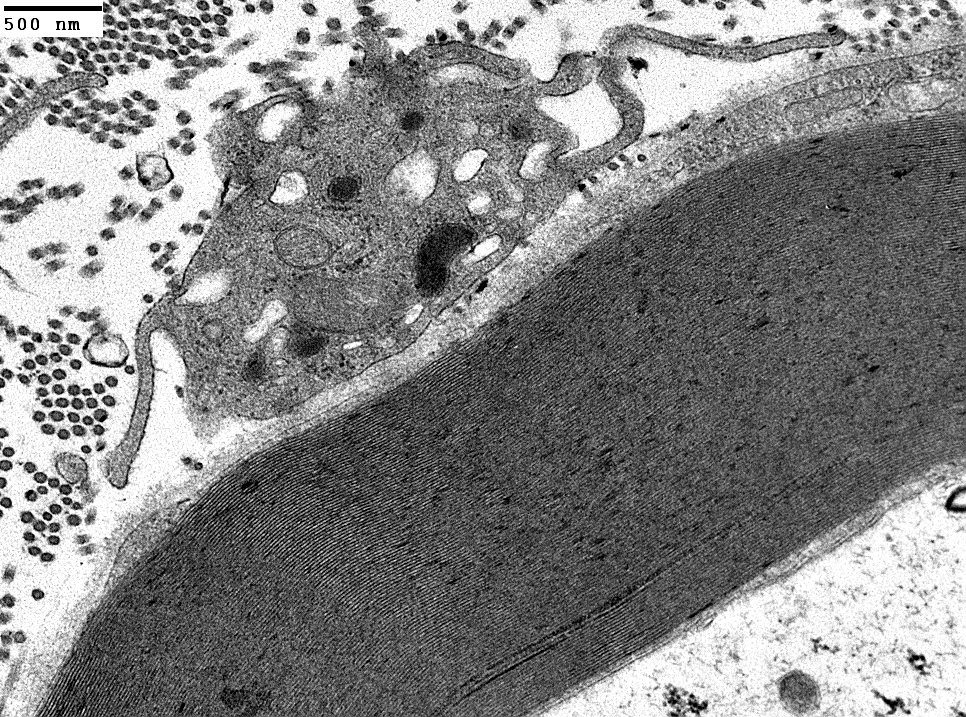
|
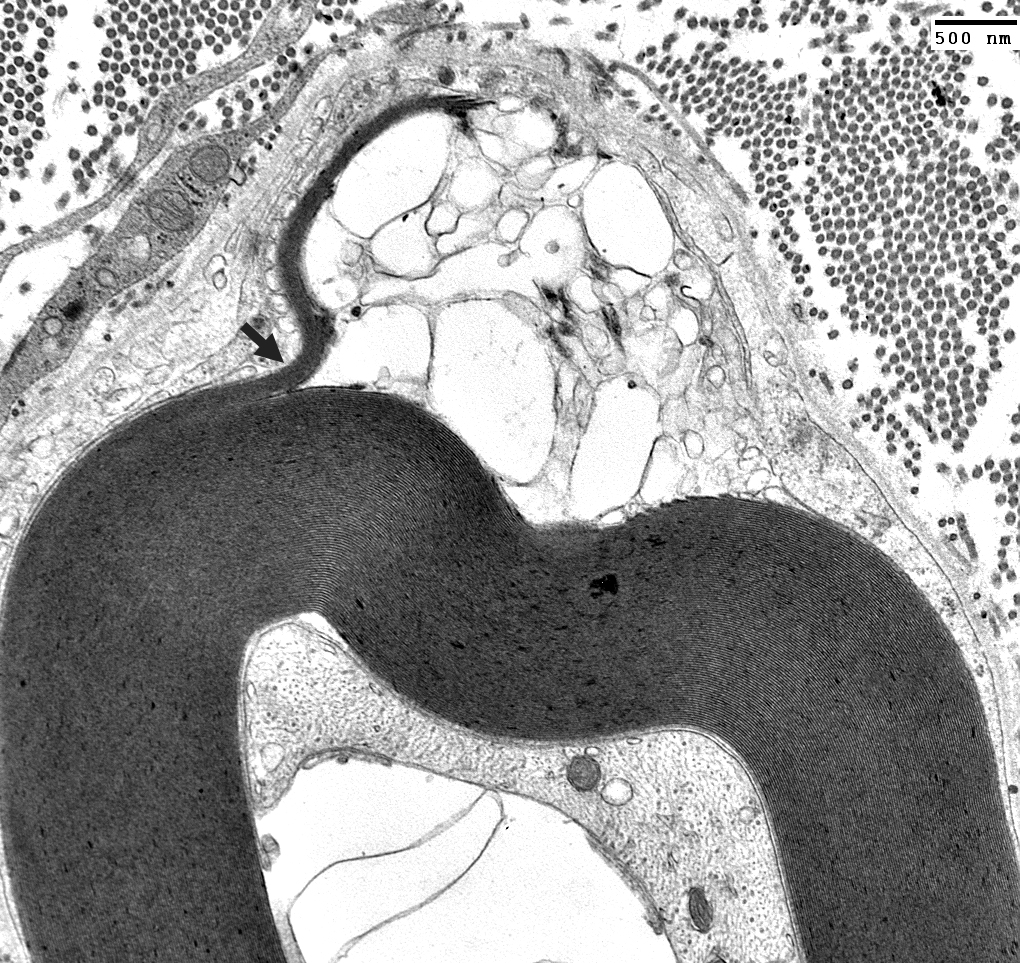
|
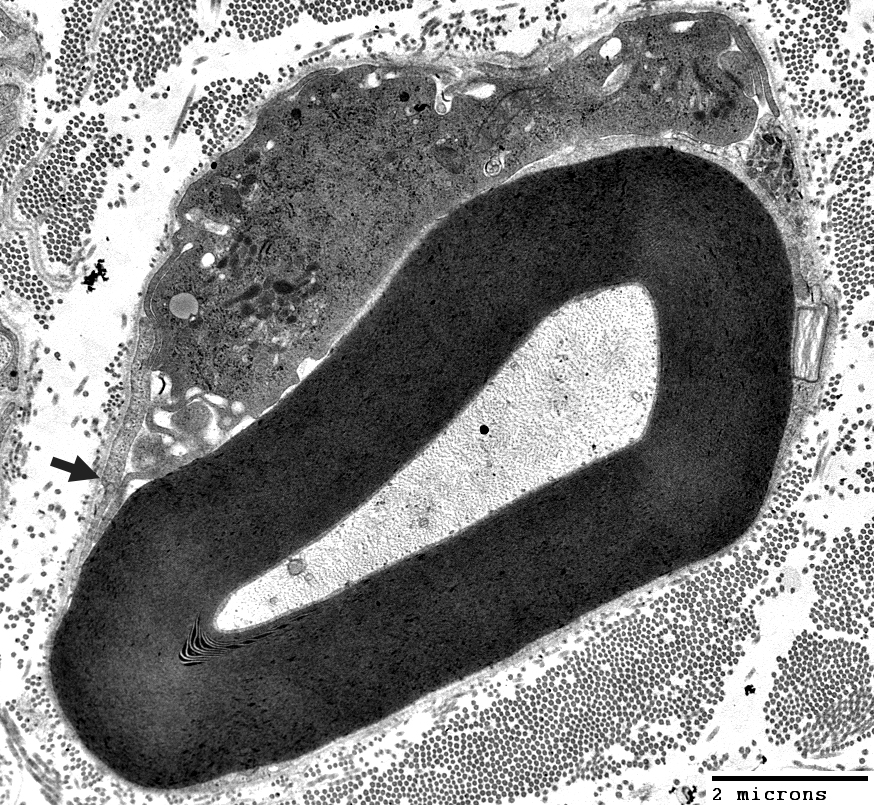
Macrophage is inside Schwann cell basal lamina
Macrophage process extends under outer myelin layer (Arrows)
Also see; Active demyelination
|
|
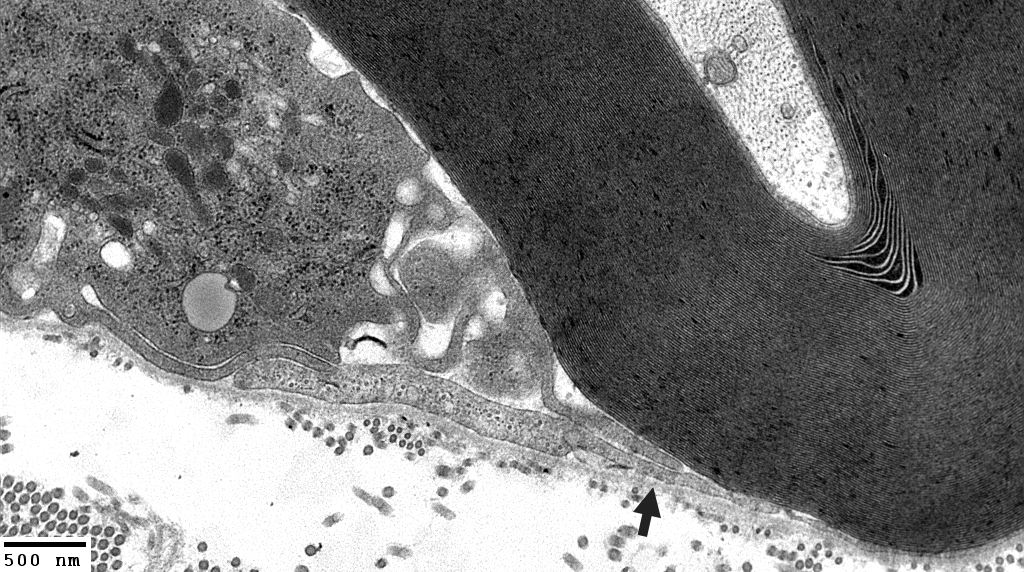
Histiocyte processes: Extend between layers of myelin (Arrows)
 Electron micrograph: From Robert Schmidt MD |
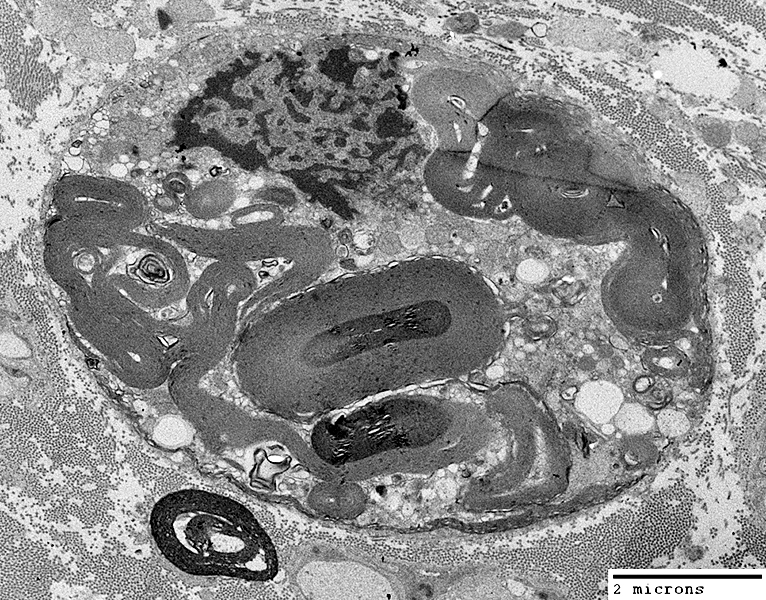
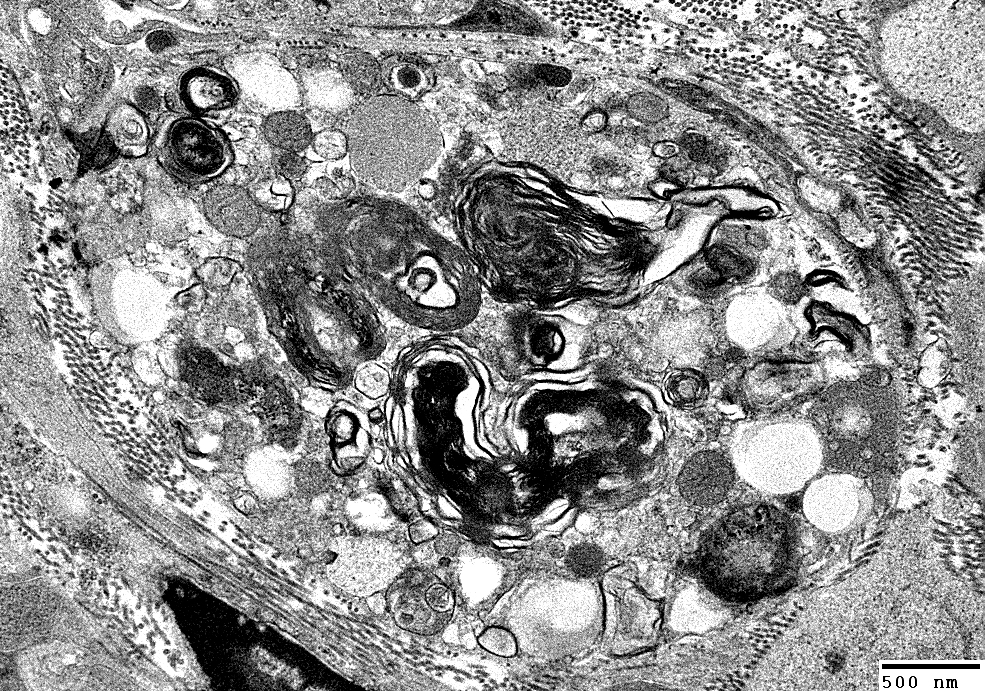
Demyelination: Autophagic Schwann cells & Histiocytes containing Myelin & Lipid debris
|
|
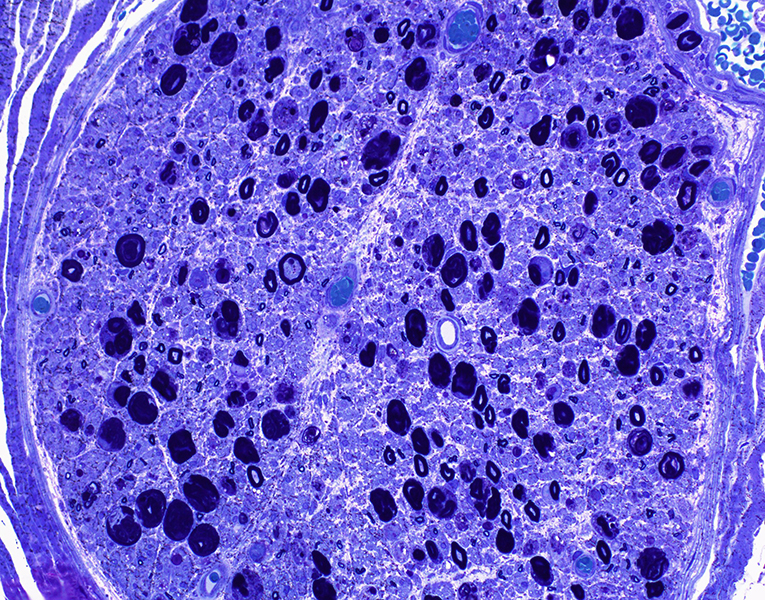
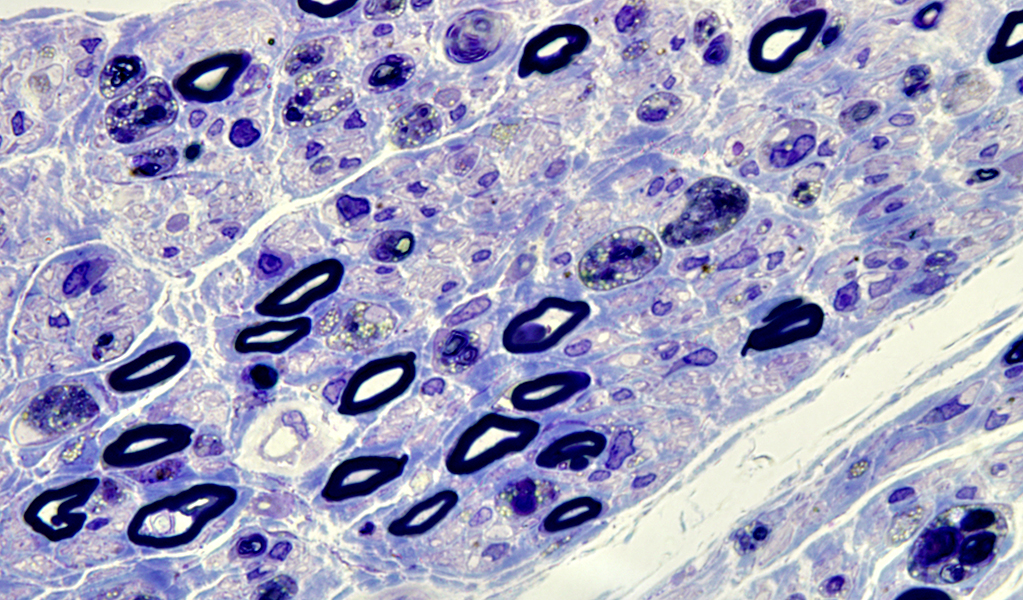 Toluidine blue stain |
Multiple round regions in autophagic Schwann cells
Autophagic Schwann cell: Basal lamina surrounds cell
|
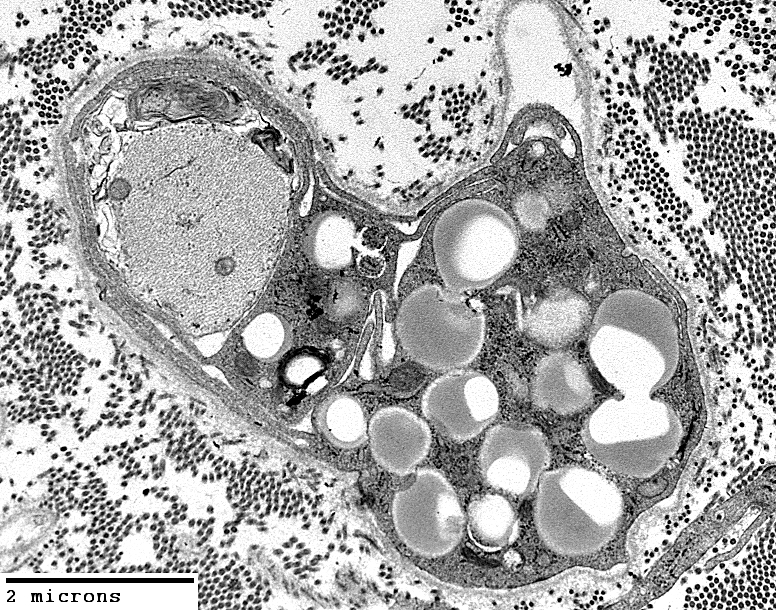
Demyelinated Axons: Surrounded by cell processes
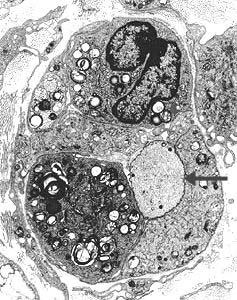
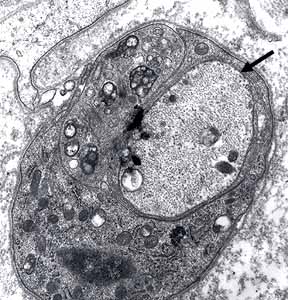 Electron micrographs: From Robert Schmidt MD |
Axons, without myelin, surrounded by phagocytic cells (Histiocytes)
Axon cytoplasm is dark, containing closely spaced neurofilaments.
Phagocytic cells contain myelin debris, lipid droplets & inclusions.

|
Patially surrounded by Schwann cell basal lamina (Above, Arrow)
May be near cells containing myelin debris
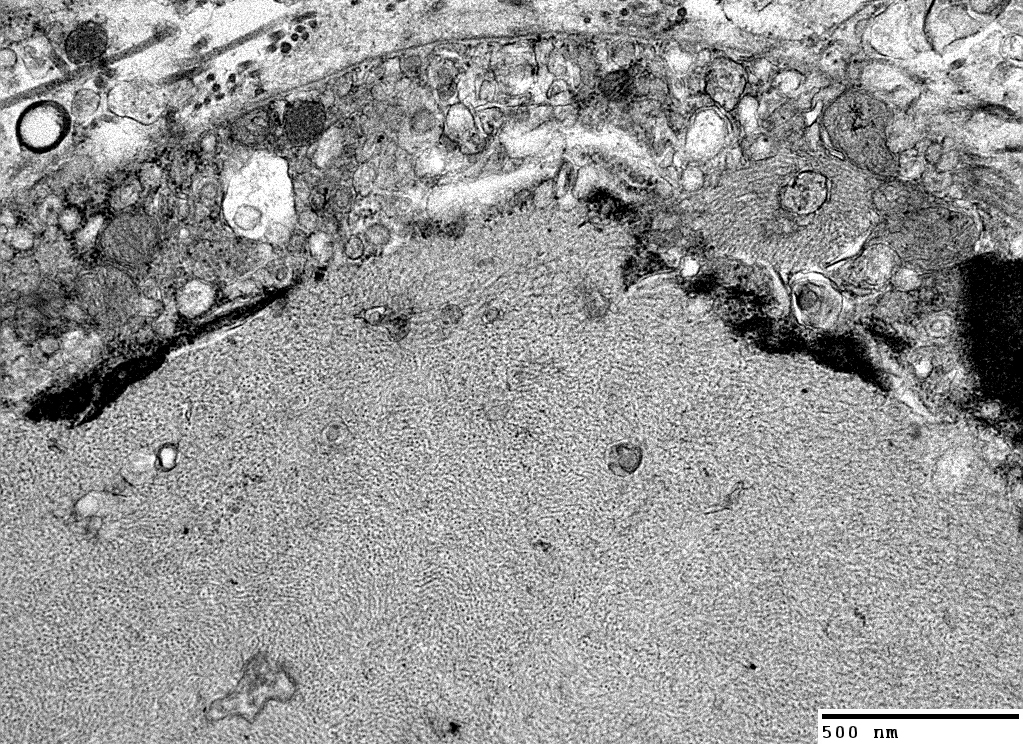

|
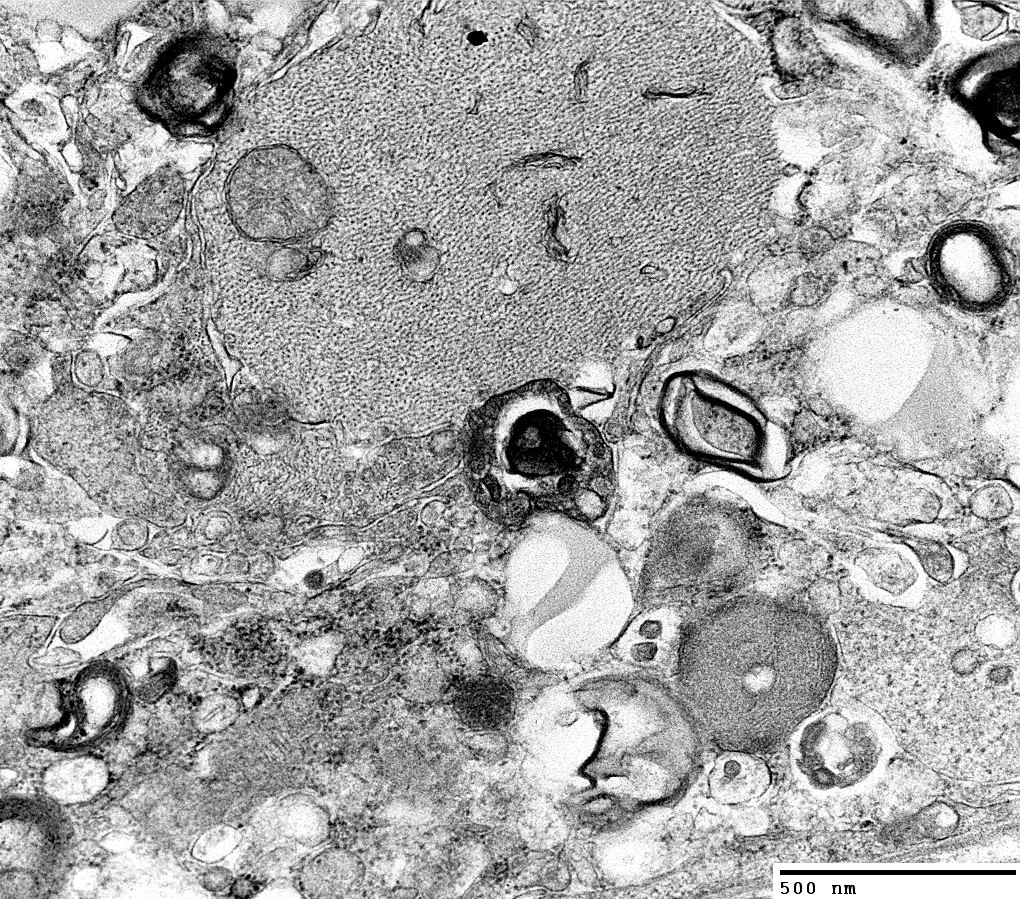
|
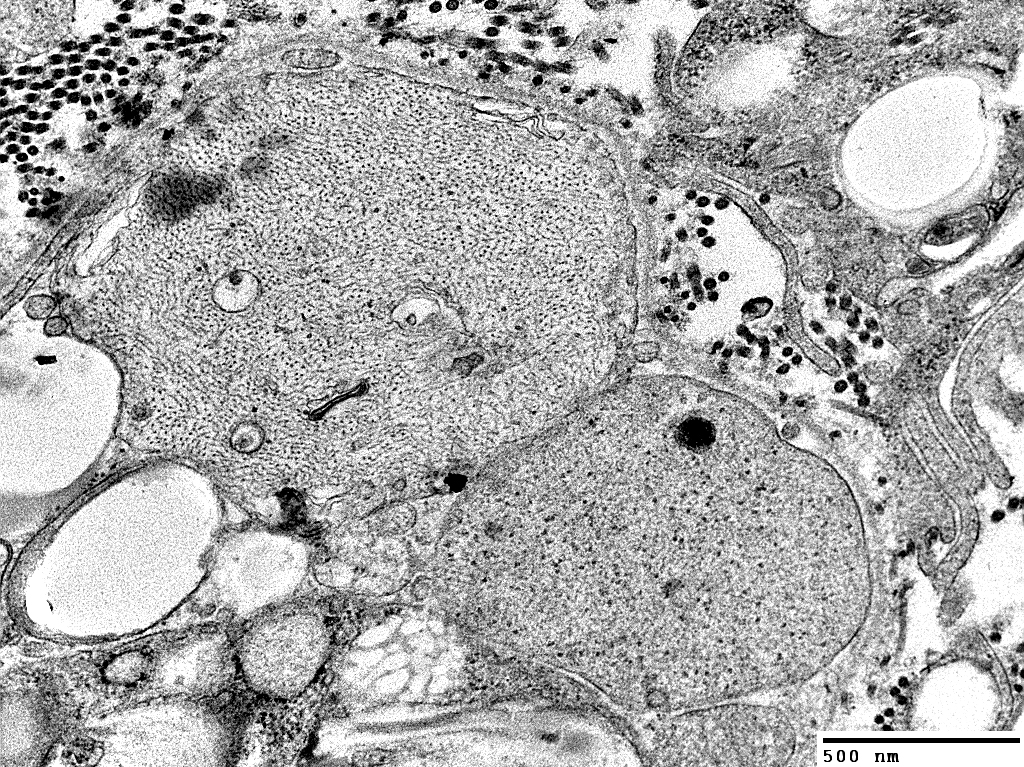
|
Surrounded, in part, by Schwann cell basal lamina and some Schwann cell processes
A macrophage (Top; Right) is located outside the basal lamina
Subperineurial edema
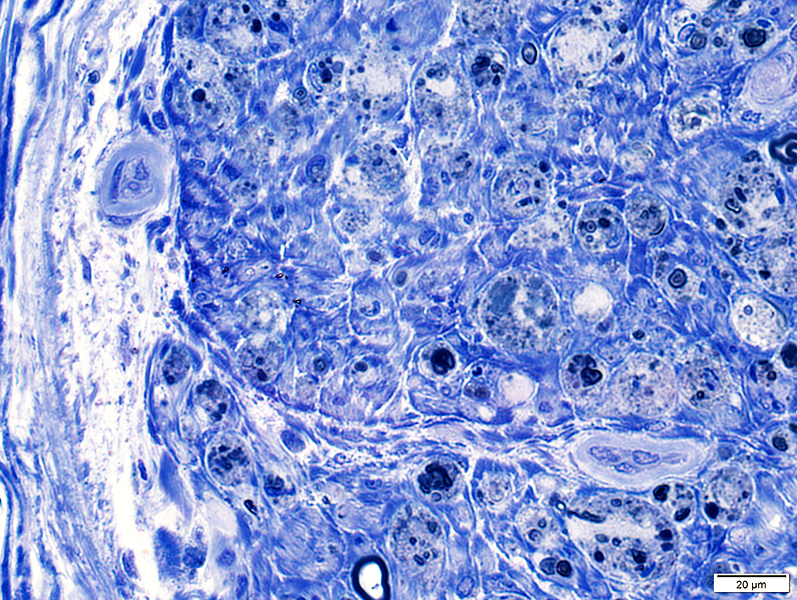 Toluidine blue stain |
Endoneurial vessels & Endothelial cells: Large
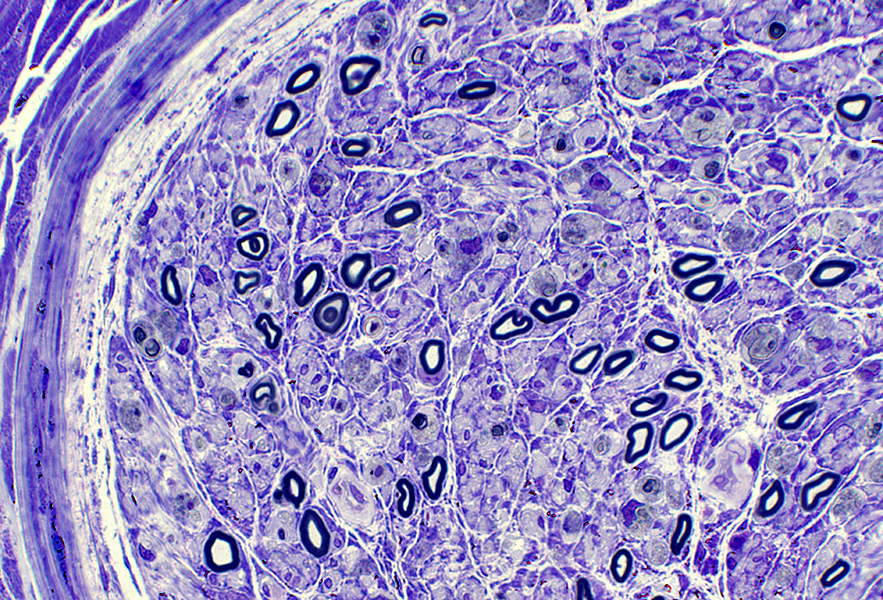 Toluidine blue stain |
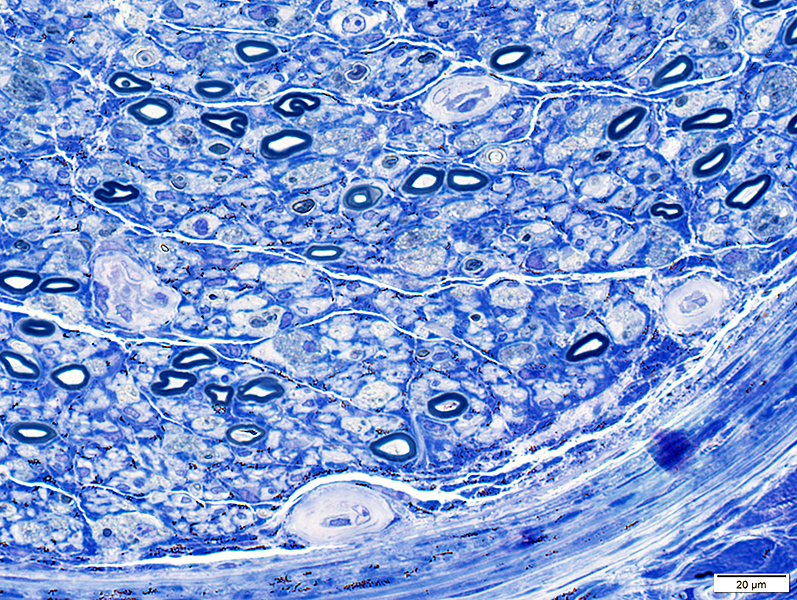 Toluidine blue stain |
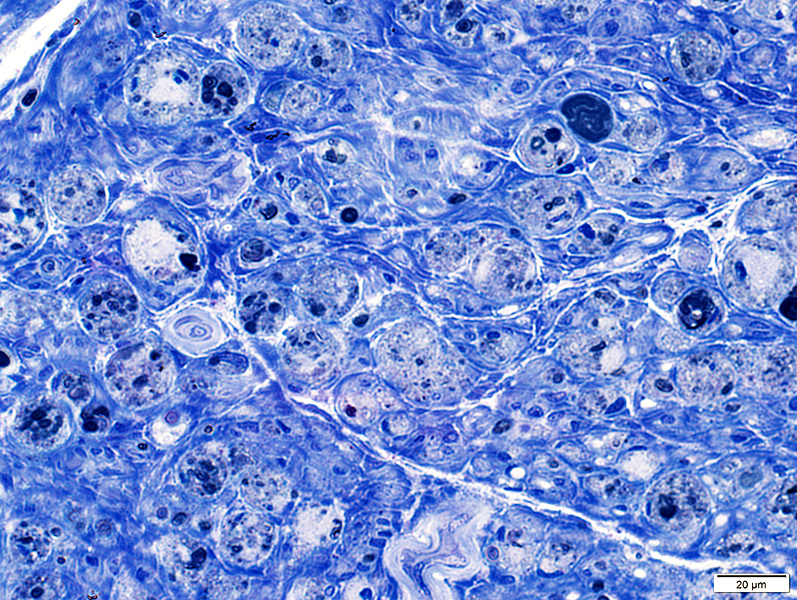 Toluidine blue stain |
Acute Motor > Sensory Axonal Neuropathy with serum IgG binding to GalNAc-GD1a ganglioside
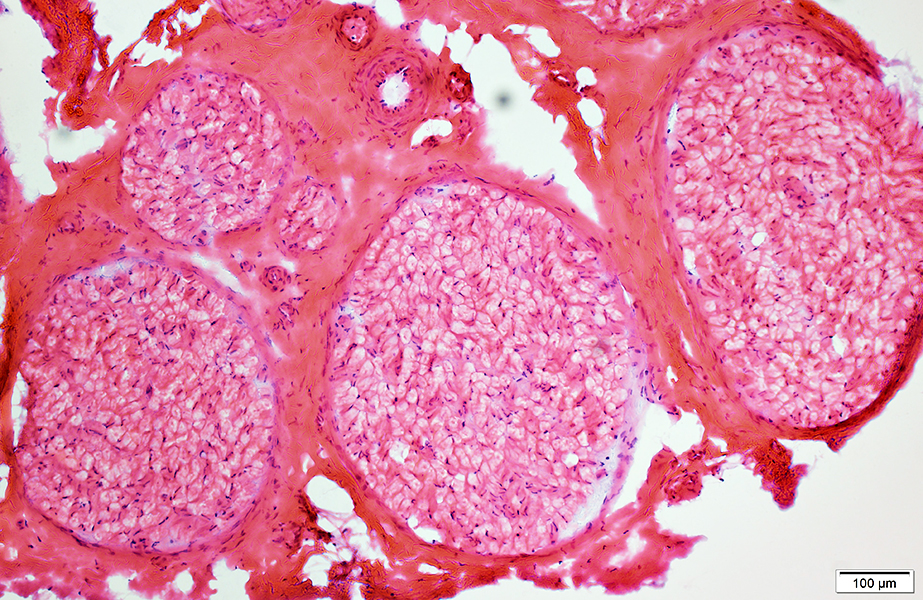
|
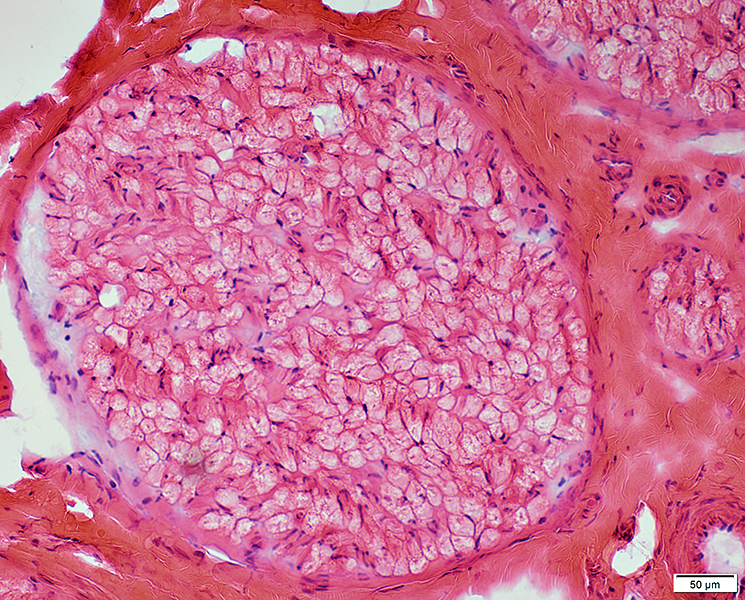
|
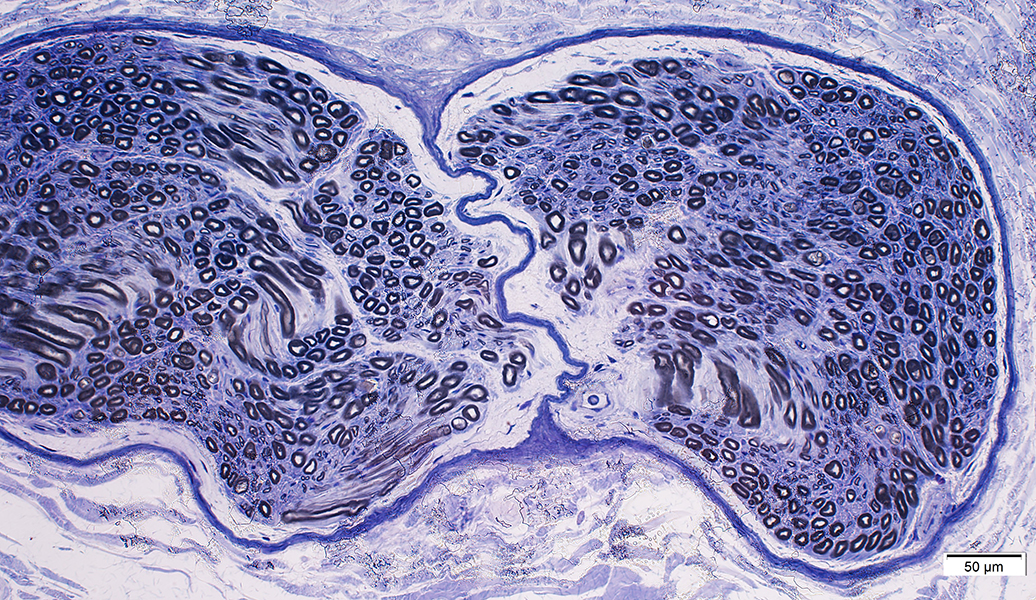 Toluidine blue stain |
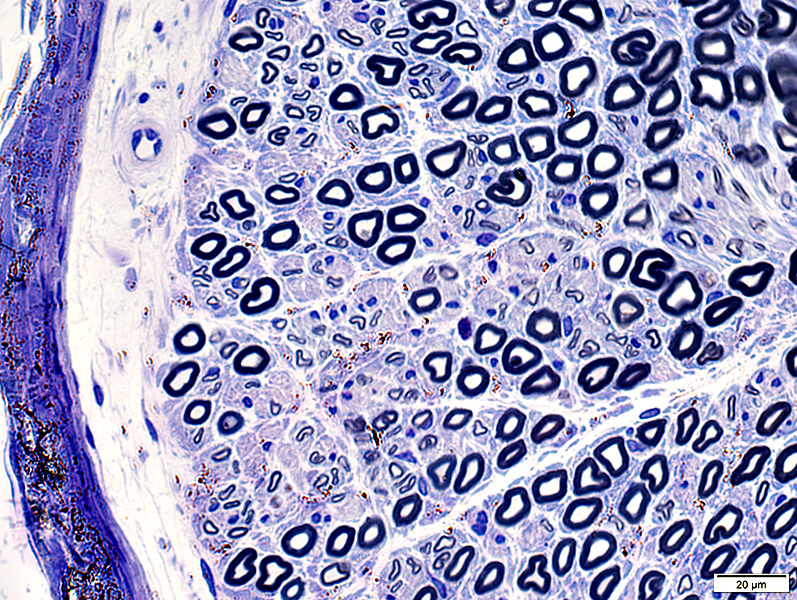 Toluidine blue stain |
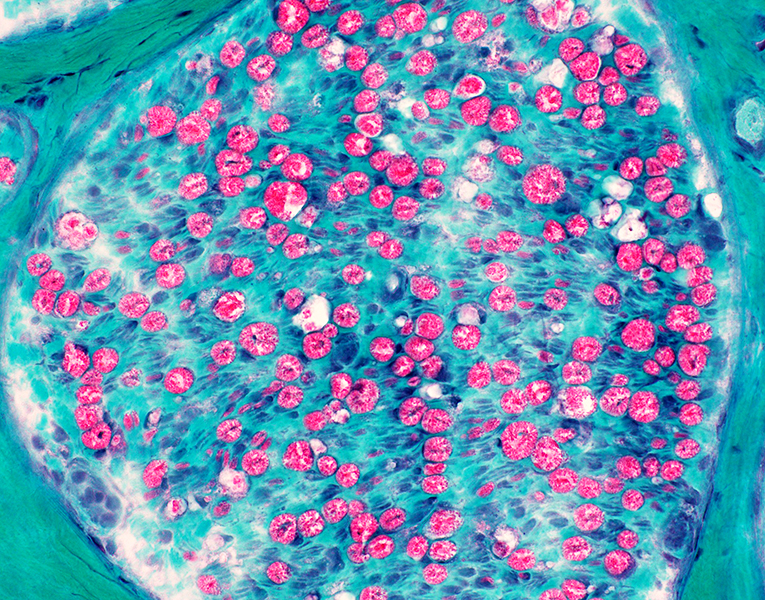
 Gomori trichrome stain |
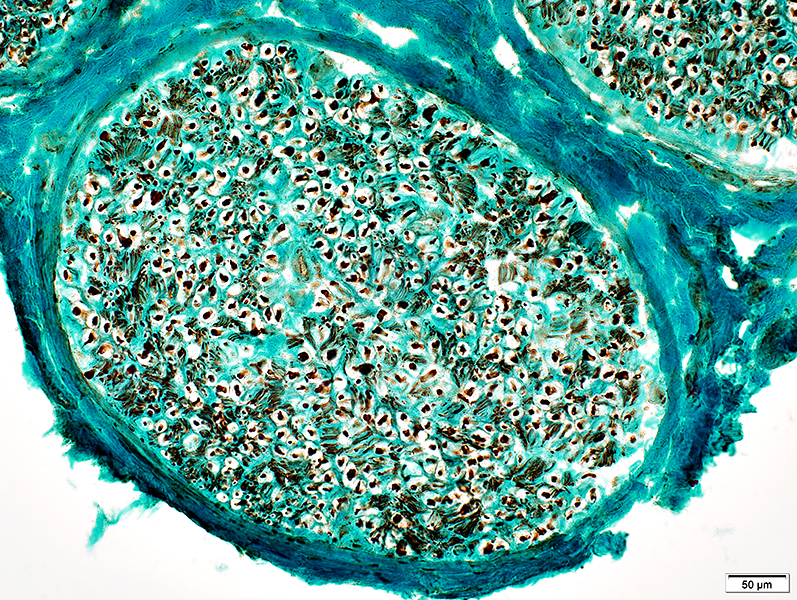
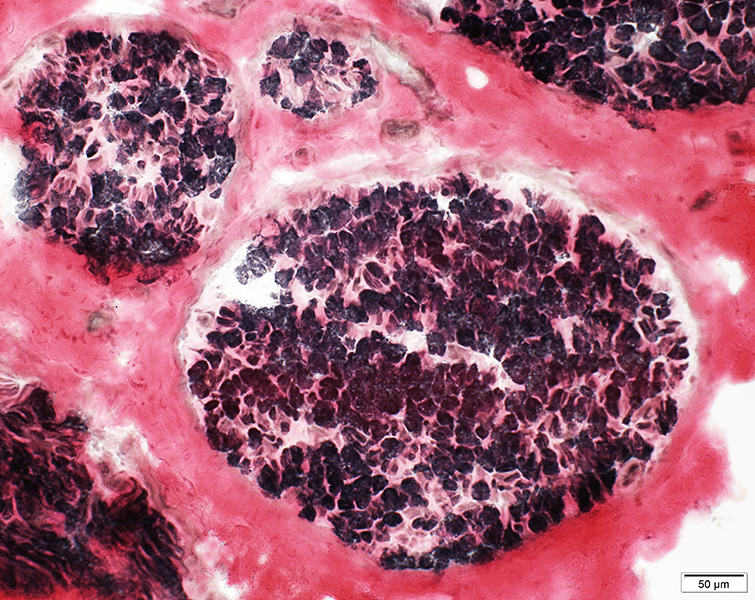 VvG stain |
Few phagocytic cells
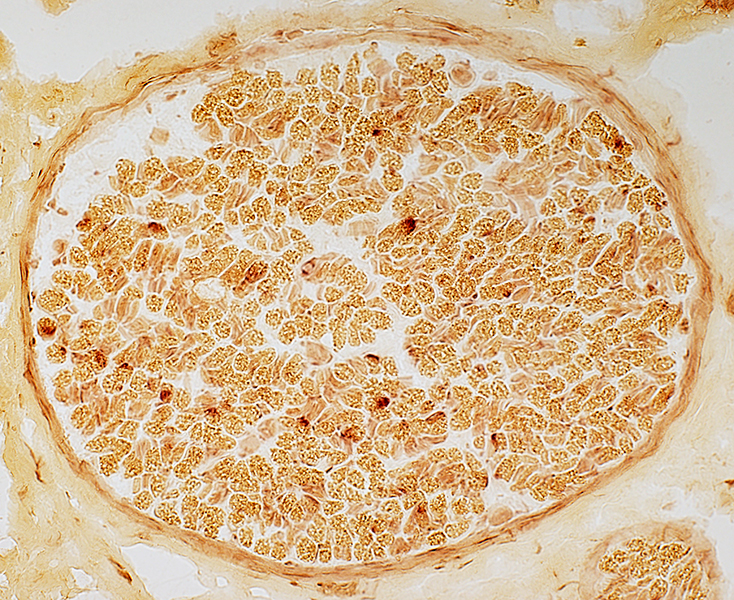 Acid phosphatase stain |
Large & Small axons: Preserved numbers
 Neurofilament stain |
C5b-9 stain: Reduced on perineurium
Patient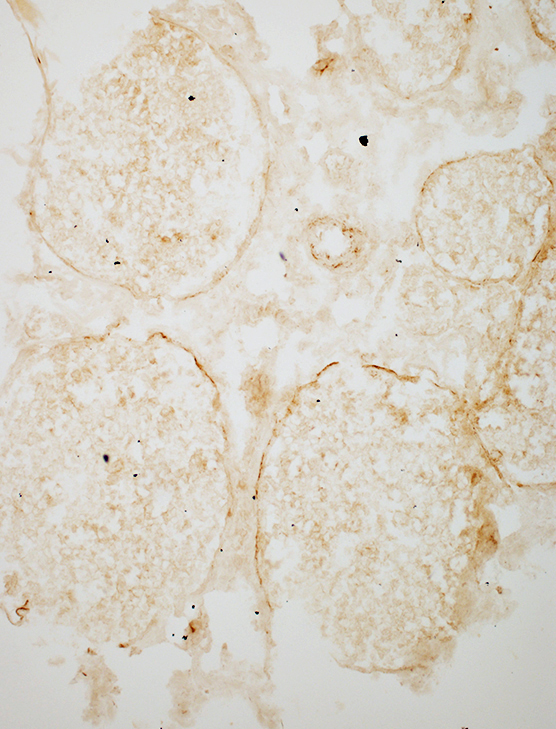
|
Control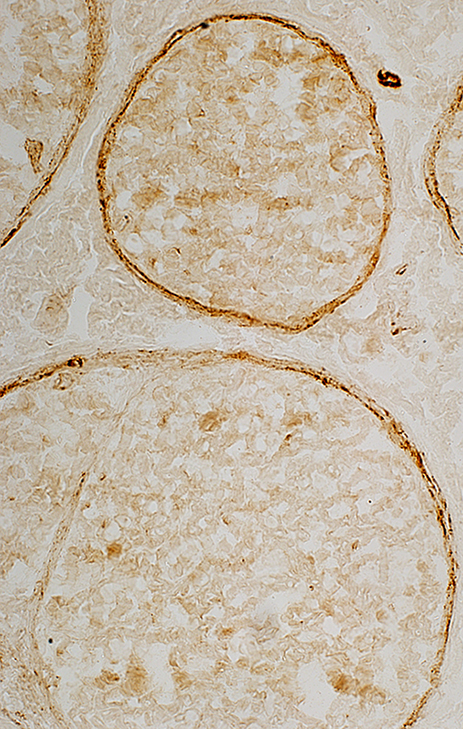
|
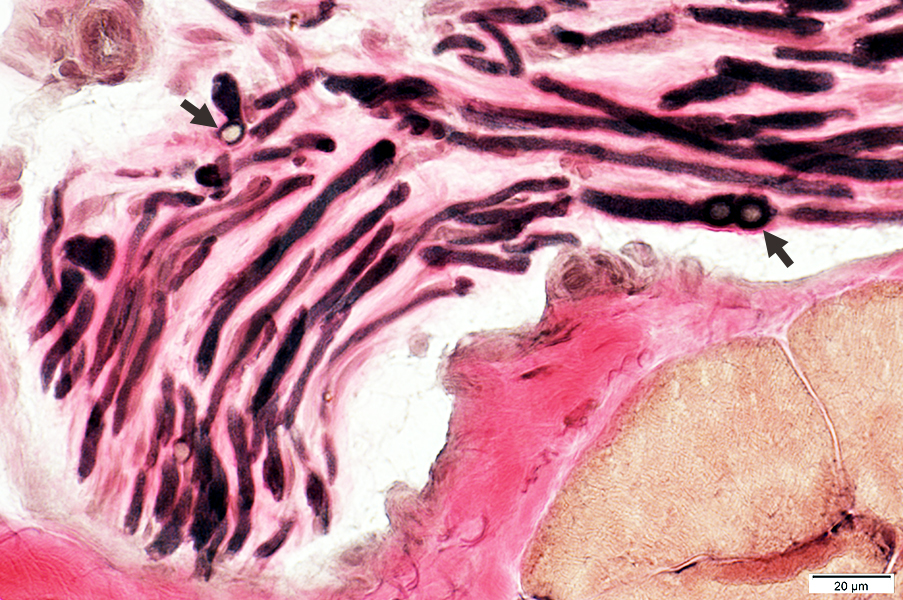 VvG stain |
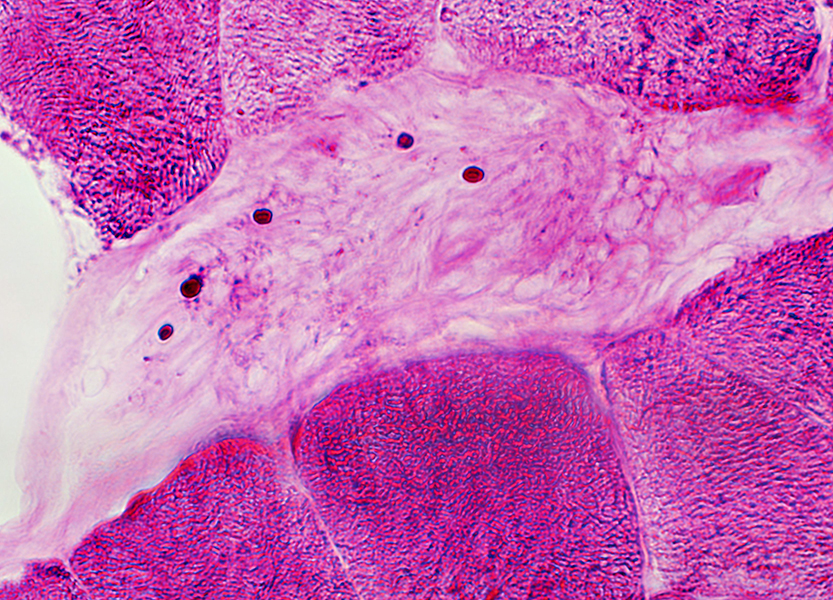 PAS stain |
Acute Motor-Sensory Axonal Neuropathy (AMSAN)
From: Chunyu Cai, Dallas
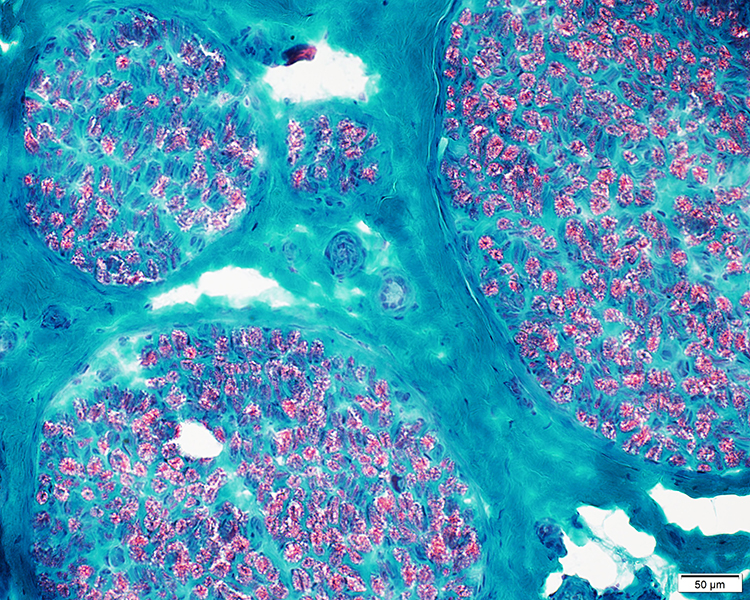
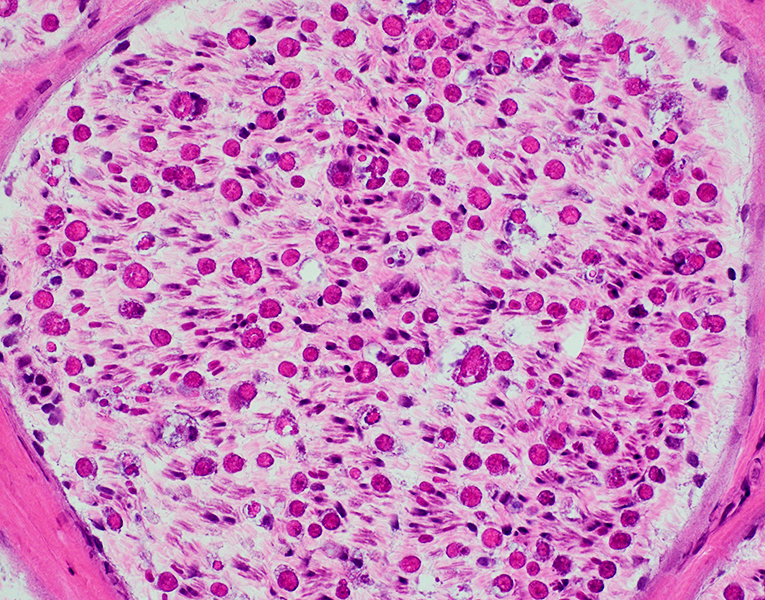
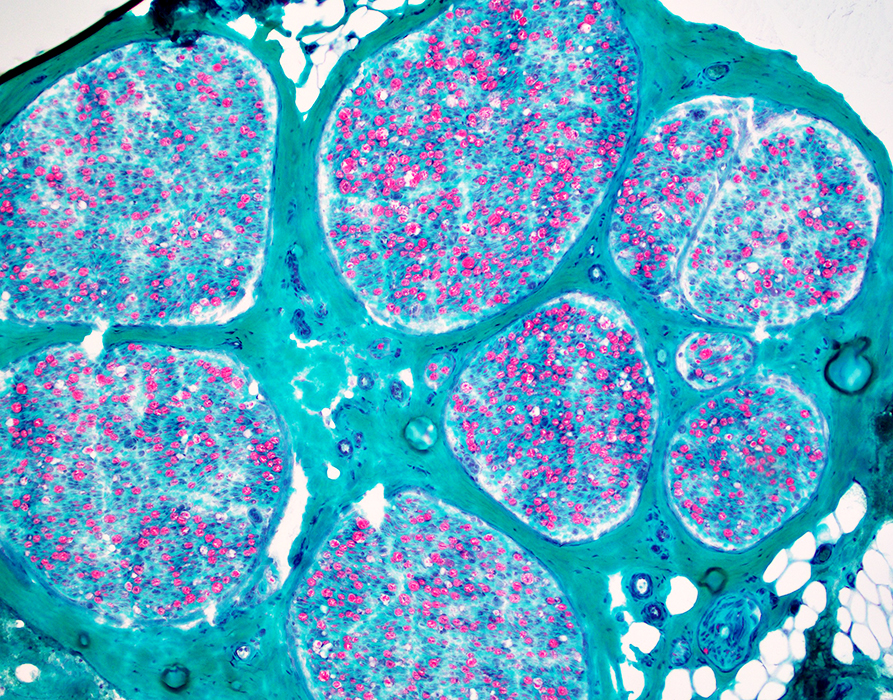 Gomori trichrome stain |
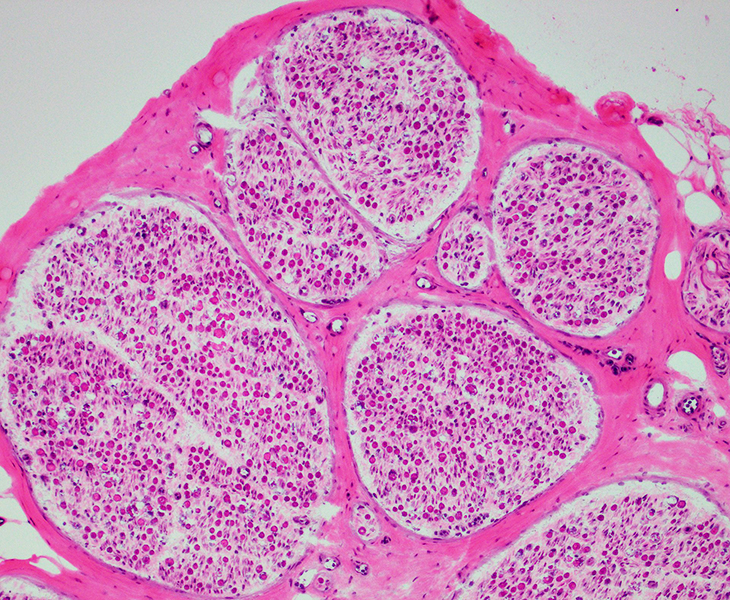 H& E stain |
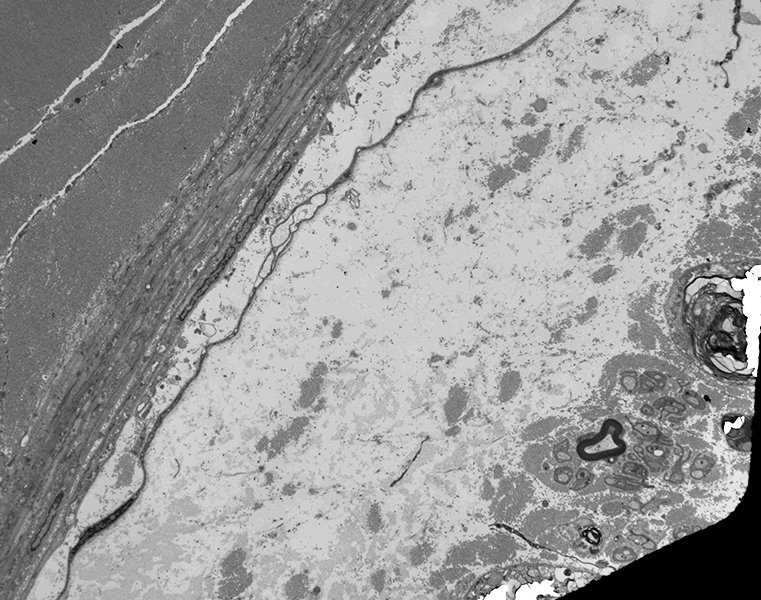
|
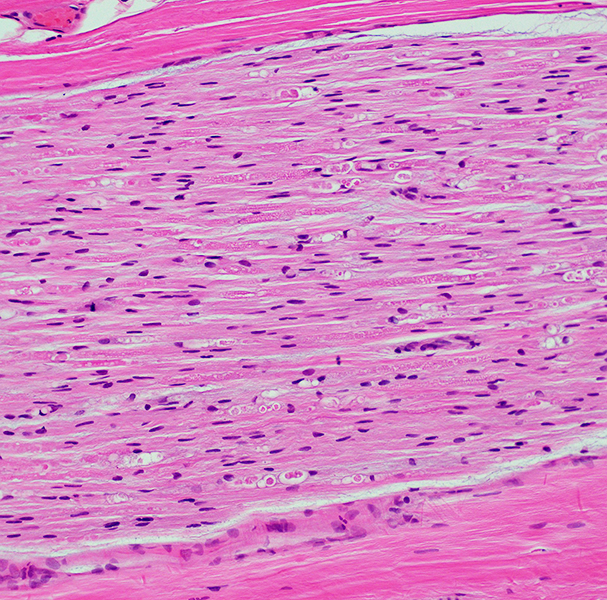 H& E stain |
 Trichrome stain |
Wallerian Degeneration: Phagocytic cells associated with myelin debris
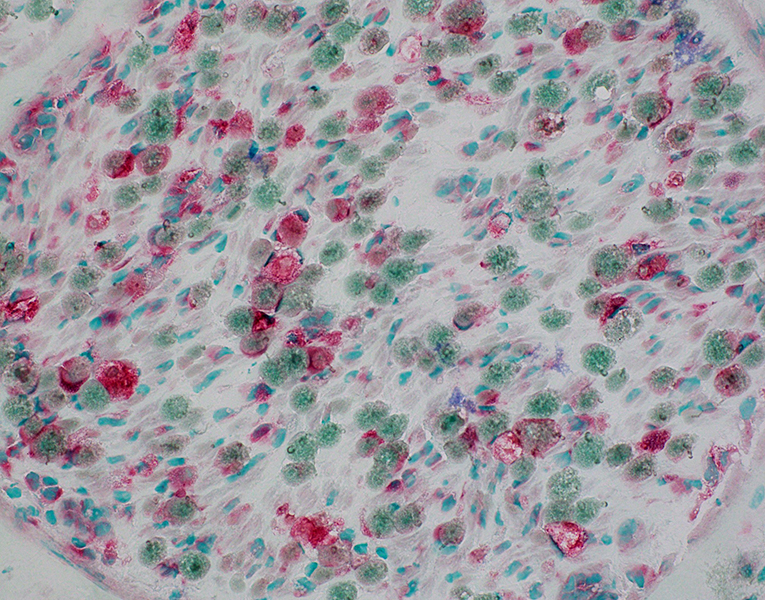
|
Myelin ovoids
|
|
|
Myelinated axons: Reduced numbers
|
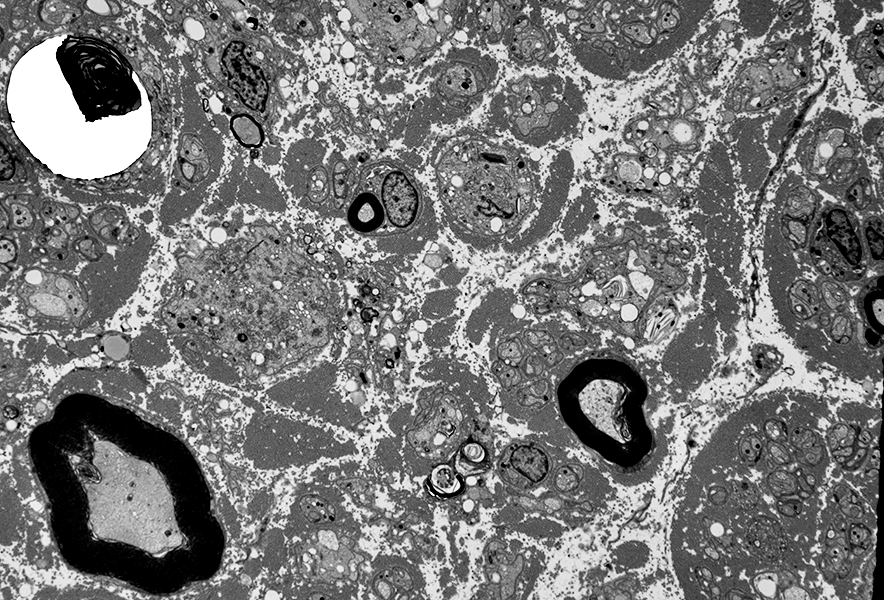
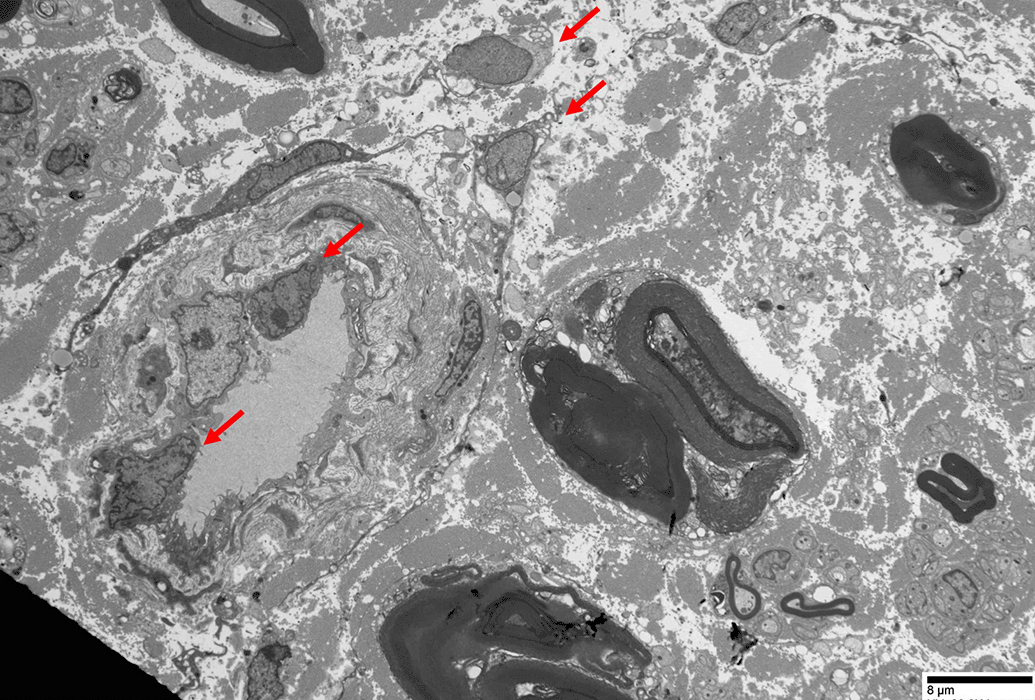
Macrophages (Arrow)
Marginated in vessel
Extravasated in endoneurium
|
Return to Neuromuscular Home
9/26/2022