Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes,
Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info
|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
|
Peripheral Anatomy Clinical-Anatomic Disorders Pharmacology Physiology Central Baroreceptor pathways |
Autonomic Nervous System: Anatomy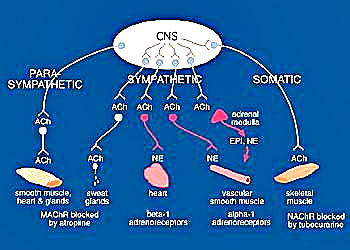 From: University of Queensland |
Baroreceptor Pathways: Central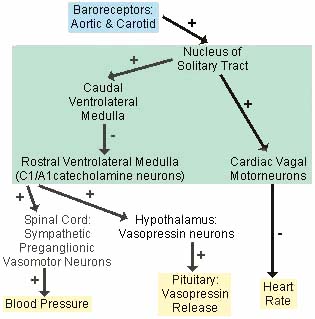
|
Principles
|
|
General Principles
| ||
| Organ | Sympathetic Stimulation | Parasympathetic Stimulation |
|---|---|---|
| Heart | ↑ Rate (β1 & β2) | ↓ Rate |
| ↑ Contractile force (β1 & β2) | ↓ Contractile force | |
| ↑ Conduction velocity | ↓ Conduction velocity | |
| Artery | Constriction (α1) | Dilation |
| Dilation (β2) | ||
| Vein | Constriction (α1) | |
| Dilation (β2) | ||
| Lung | Bronchial muscle: |
Bronchial muscle contraction |
| Bronchial gland secretion | ||
| Gastrointestinal tract | ↓ Motility (β2) | ↑ Motility |
| Sphincter: Contraction (α) | Sphincter: Relaxation | |
| Liver | Glycogenolysis (β2 & α) | Glycogen synthesis |
| Gluconeogenesis (β2 & α) | ||
| Lipolysis (β2 & α) | ||
| Kidney | Renin secretion (β2) | |
| Bladder | Detrusor: Relaxation (β2) | Detrusor: Contraction |
| Sphincter: Contraction (α) | Sphincter: Relaxation | |
| Uterus | Contraction: Pregnant uterus (α) | |
| Relaxation: Pregnant & |
||
| Eye | Pupil: Dilate (α) | Pupil: Constrict |
| Lacrimal gland secretions | ||
| Salivary glands Submandibular Parotid |
Viscous secretions (α) | Watery secretions |
 T Willis Autonomic & Other nerves: In Cerebri Anatome |