Axons, Myelin & Schwann Cells: Molecular Features 1
Peripheral Nerve: Molecular Pathology of Schwann cells & Myelin
| Axon associations with 3 most abundant Myelin components: Myelin Basic Protein (MBP); P0 (MPZ); Periaxin (PRX) Non-myelinating Schwann cell marker: Nerve cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) Myelin: Two types Large myelinated axons: Myelin contains both P0 & MBP Smaller myelinated axons: Myelin contains P0 but little MBP Schwann cells Types: Several Development: Changes |
Axon properties compared with Schwann cell/Myelin molecular features |
||
| Feature | Axon Properties | Schwann Cell/Myelin features |
| Control Nerves | ||
| Normal Adult | Large-size; Myelinated | P0 + MBP |
| Intermediate-size; Myelinated | P0 | |
| Small size; Unmyelinated | NCAM, Clustered distribution | |
| Perinatal | Myelinated | MBP + P0 + NCAM |
| Unmyelinated | MBP + NCAM | |
| Axon Disorders | ||
| Axon loss, Chronic | No Axon | P0 + NCAM, or NCAM alone Büngner bands |
| Small remaining Axons | MBP (Pale) | |
| Axon Degeneration, Acute | Myelinated Neurofilament stain: Lost |
MBP + P0 + NCAM Phagocytic cells (Acid Phosphatase+) |
| Regeneration | Axon Size: Intermediate Myelin sheath: Thin |
MBP + P0 ± NCAM |
| Myelin Disorders | ||
| Demyelination, Ongoing | Large axon, Demyelinated | No or ↓ P0 ± MBP co-stain |
| Demyelination, Active | Myelin: Acid phosphatase + | |
| Axon loss, Small | NCAM: Normal or ↓#s | |
| IgM vs MAG | Large size | MBP + P0 + NCAM |
| Neurofascin-186, Acute | Axon atrophy Small axon loss |
NCAM: Reduced Schwann cells |
| Demyelination, Chronic | Remaining Larger axons |
P0 + NCAM (Onion bulb cells) |
| Other patterns | Schwann cells: Reduced #s Myelin structure: Abnormal | |
Schwann cells (SC)/Myelin Plasticity
|
|
MBP: Immature SC around Demyelinated axons & Remaining Small axons after Axon loss ↓ MBP + NCAM: Perinatal nerve SC → NCAM: Non-myelinating SC, Adult ↓ ↓ P0 + MBP + NCAM: Regenerated, or Damaged, Axon SC NCAM + P0: Denervated SC ↓ P0 + MBP: Myelin on Large axons ↓ P0: Myelin on Intermediate-sized axons |
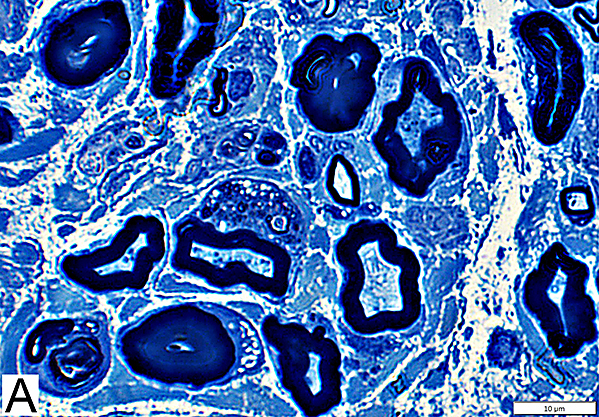
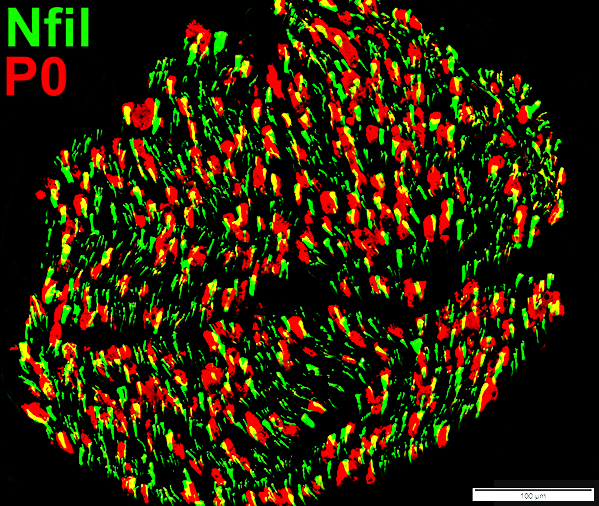
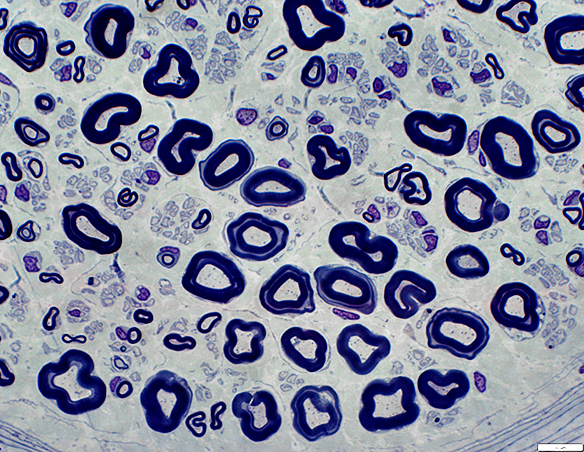
Axon Types: Normal Adult Nerve
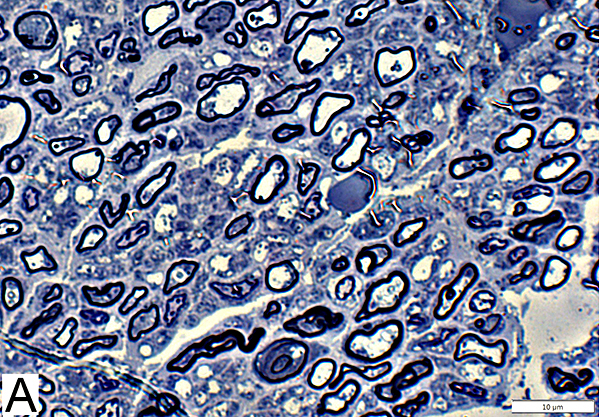
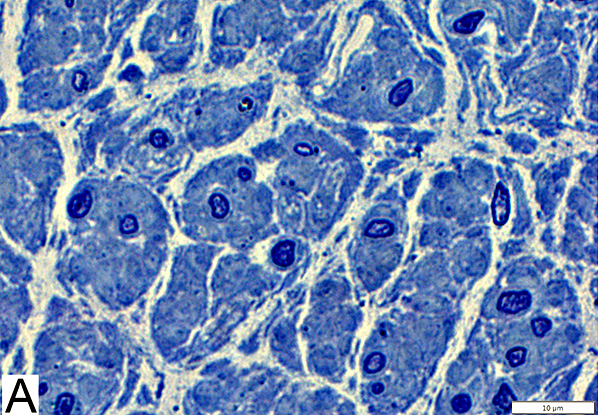
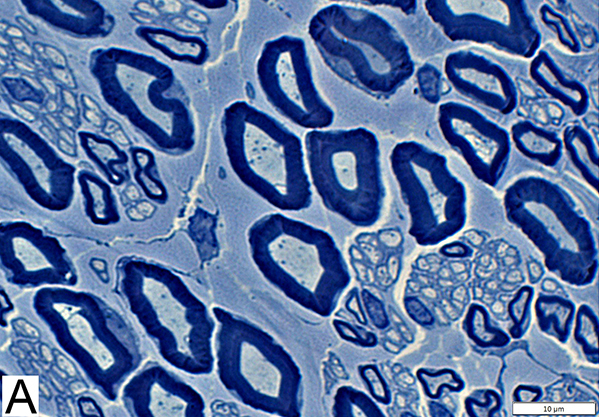 Toluidine blue stain Normal Adult Nerve: 3 Axon Populations Myelinated axons Large size; Thick myelin Intermediate-size; Thinner myelin Unmyelinated axons: Small size; Grouped |
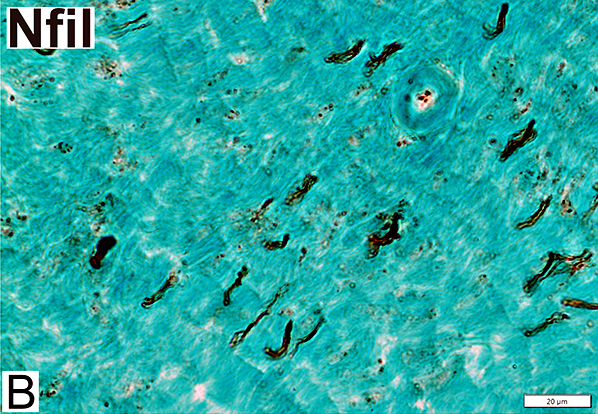
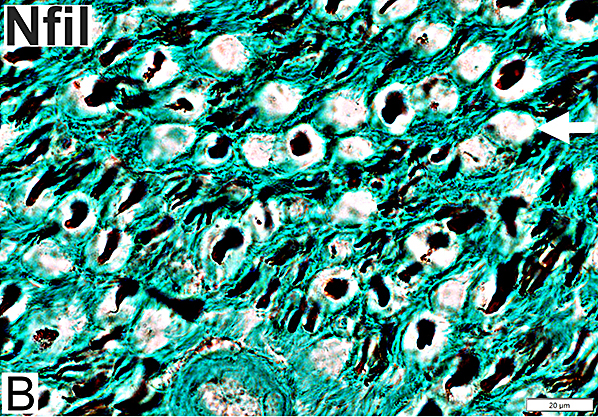
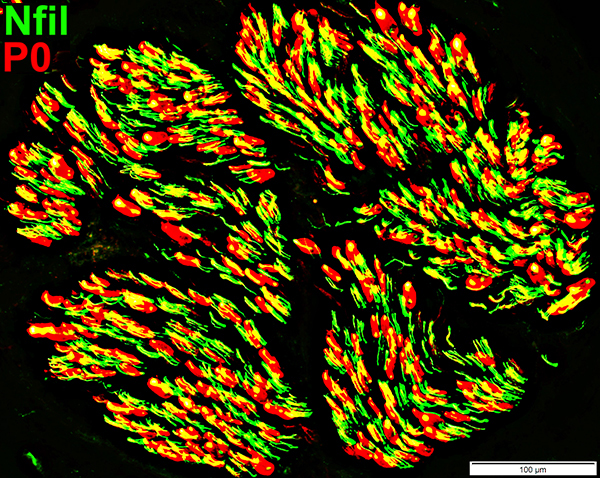
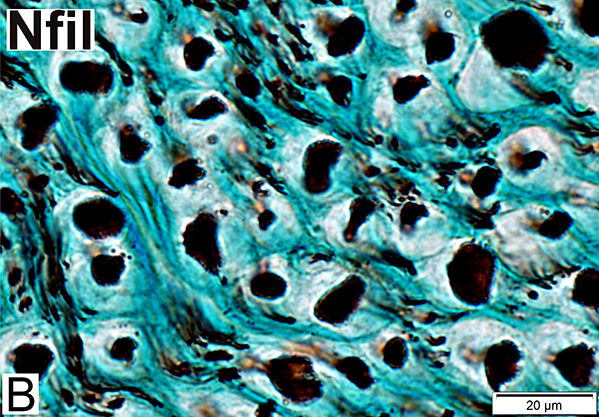 Nfil = Neurofilaments Normal Adult Nerve: 3 Axon Populations Sizes Large Intermediate Small: Grouped; Not cut in cross section |
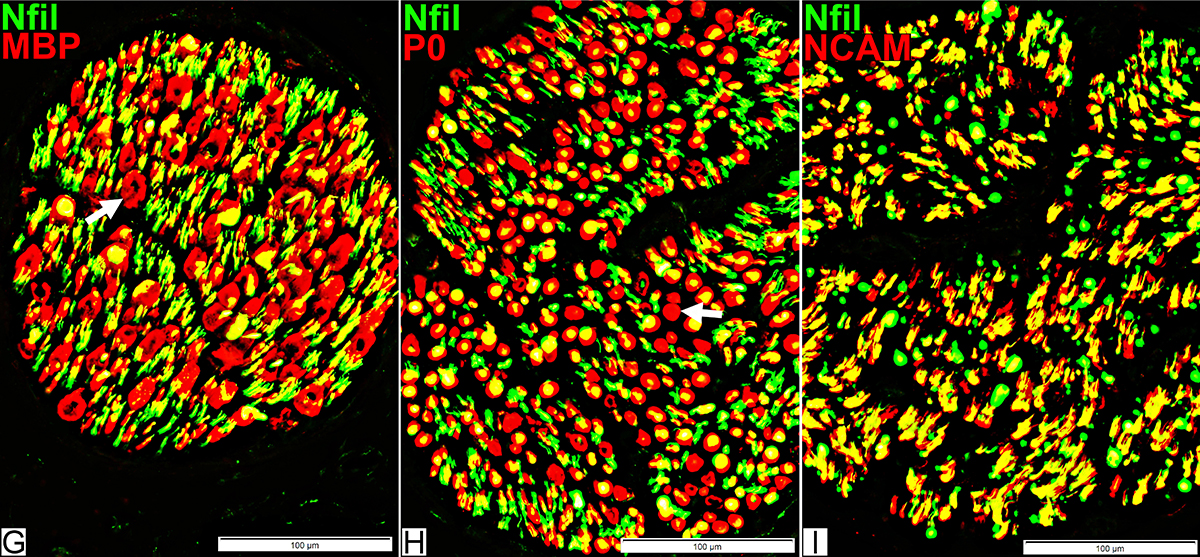
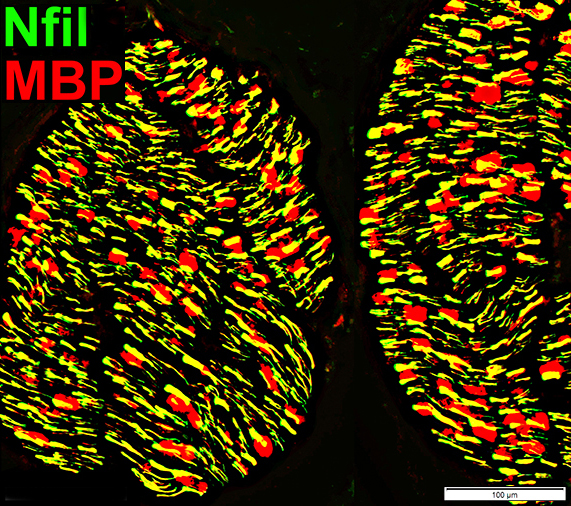
Axons & Schwann cells/Myelin: Normal
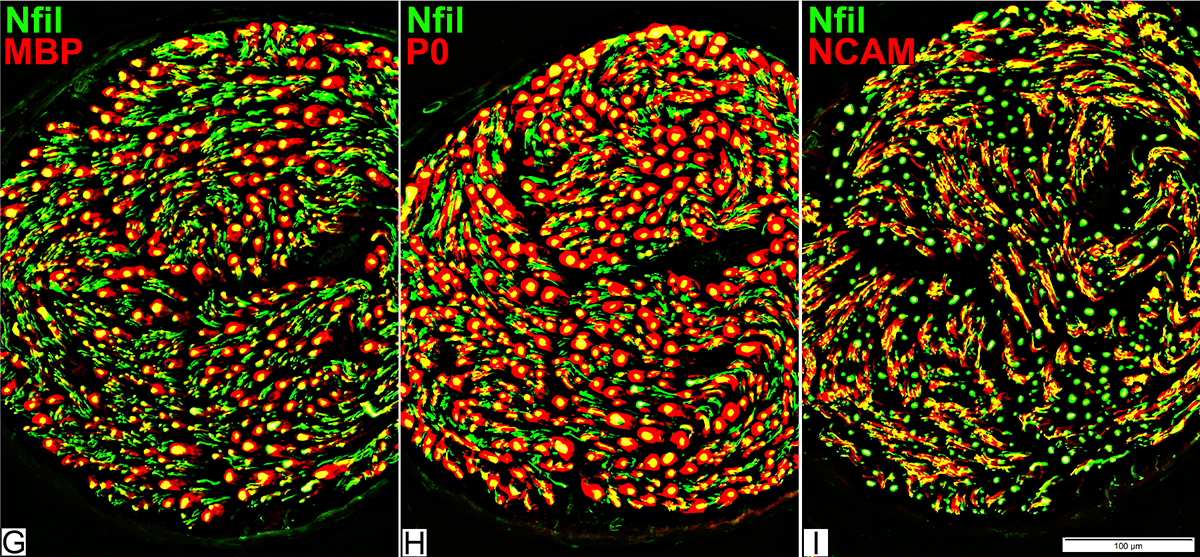 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule |
Myelinated axons
Large size
Myelin has both Myelin Basic Protein (MBP) & P0 protein (P0)
Intermediate-size
Myelin has mainly P0 with little MBP
Small, Unmyelinated
Schwann cells have NCAM but no P0 or MBP
Note: MBP is never present alone in normal adult Myelin or Schwann cells: See below
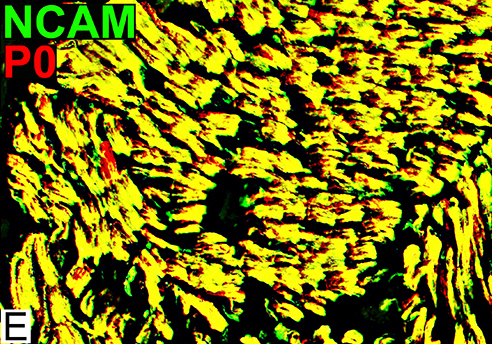
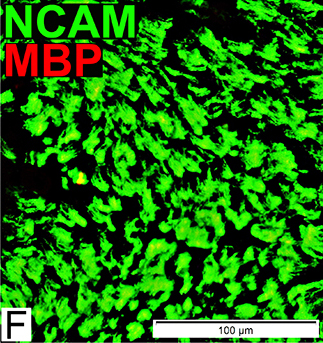
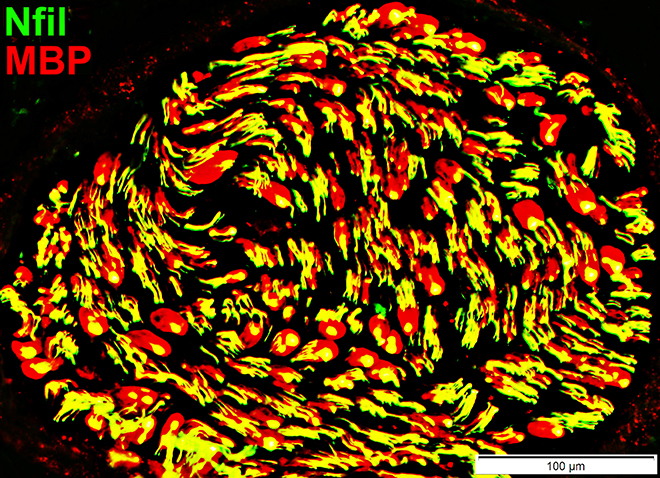
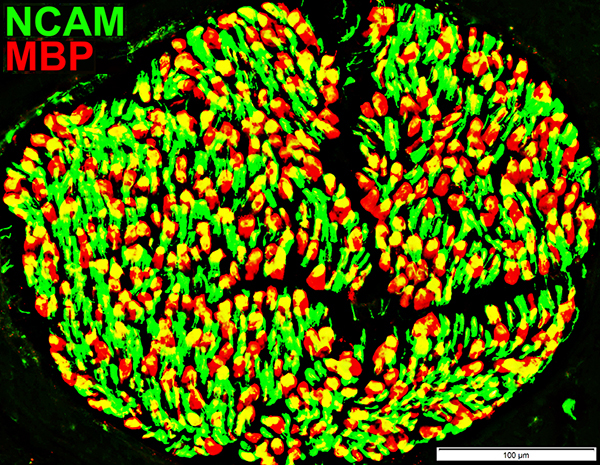
Schwann cells & Myelin: Normal
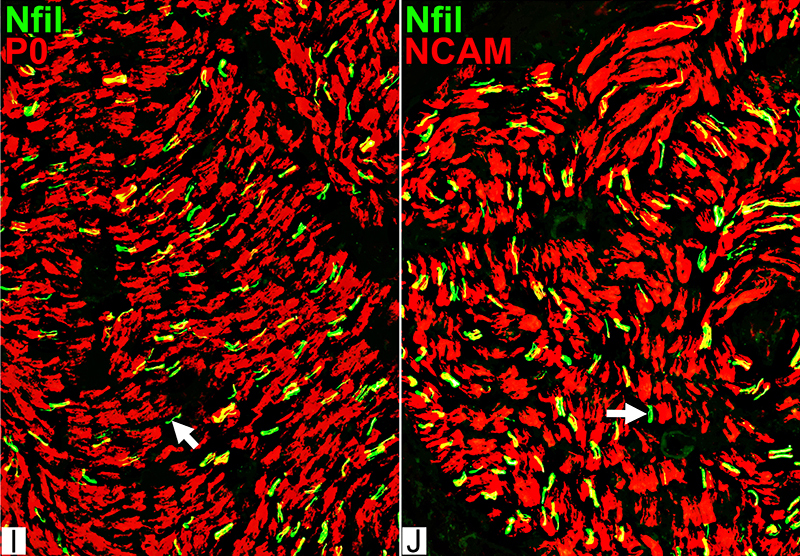
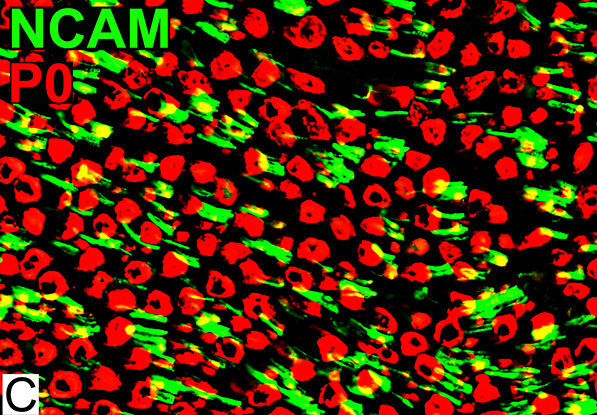 P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Normal Adult Nerve: Myelin/Schwann cell Populations Non-myelinating Schwann cells Stain for NCAM (Green), but not P0 or MBP Surround: Several, clustered small axons Myelin Most, or all, sheaths stain for P0 (Red) Few cells stain for both NCAM & P0 (No Yellow) |
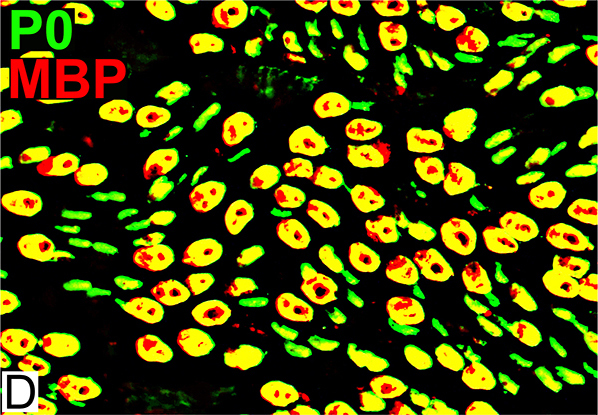 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein Normal Adult Nerve: 2 Myelin Populations Large (Thick) Myelin sheaths: Myelin has abundant MBP & P0 (Yellow) Small (Thinner) Myelin sheaths: Myelin has mainly P0 (Green), but little MBP No sheaths have only MBP (Red) |
Myelin & Periaxin: Normal Nerve
3 Most abundant myelin proteins in peripheral nerveMBP
P0
Periaxin
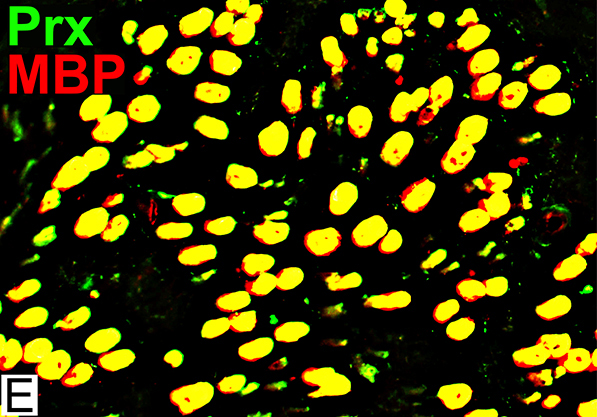 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; Prx = Periaxin Normal Adult Nerve: Myelin Populations Periaxin (Green) colocalizes (Yellow) mostly with MBP around large axons |
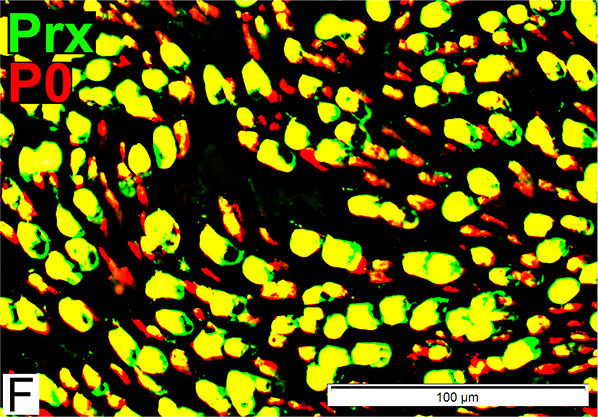 P0 = P0 protein; Prx = Periaxin Normal Adult Nerve: Myelin Populations P0 (Red) has some, patchy associated Periaxin |
Infant Sural Nerve: Normal
Axon Sizes: Smaller than adultsImmature Schwann cells: Contain MBP
Myelin: 1 population, Contains P0 & MBP
Axon types: Normal Infant
 Toluidine blue stain Infant Nerve: Axon Populations Large Myelinated: Smaller than adult large axons; Thin myelin sheath Intermediate-sized: Thinly Myelinated or Unmyelinated |
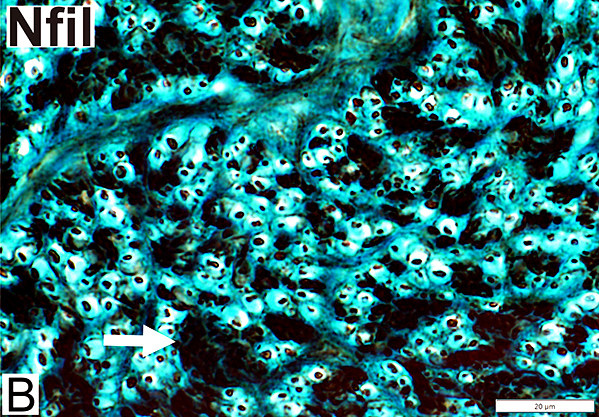 Nfil = Neurofilaments Infant Nerve: Axon Populations Large (Myelinated): Smaller than adult large axons Small Unmyelinated (Arrow): Present in clusters |
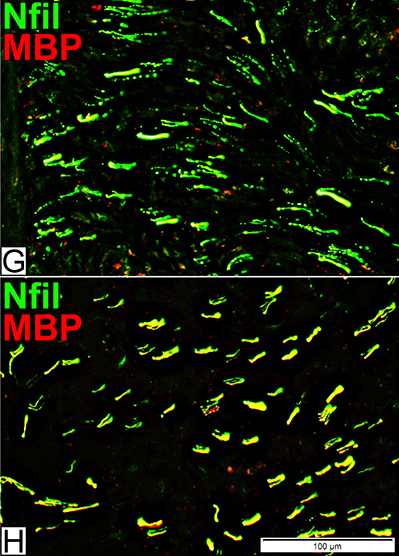
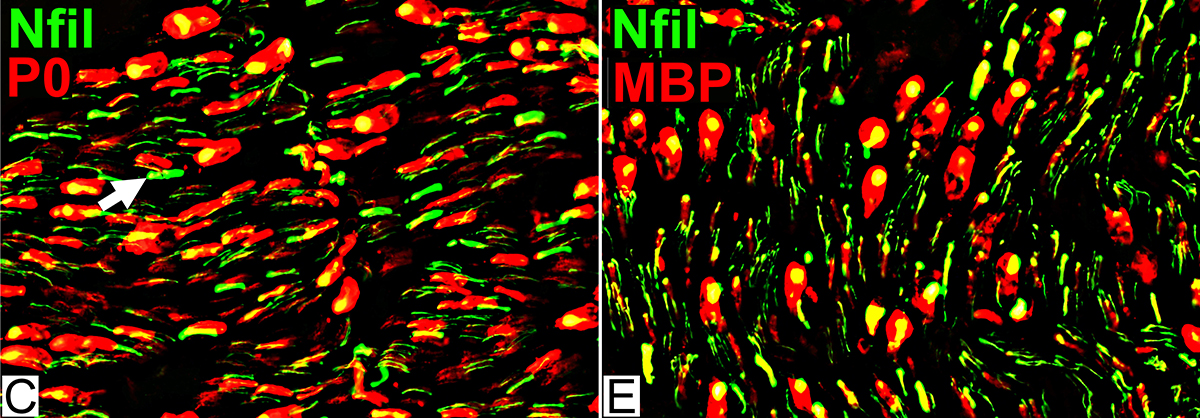
Axons & Schwann cells/Myelin: Normal Infant
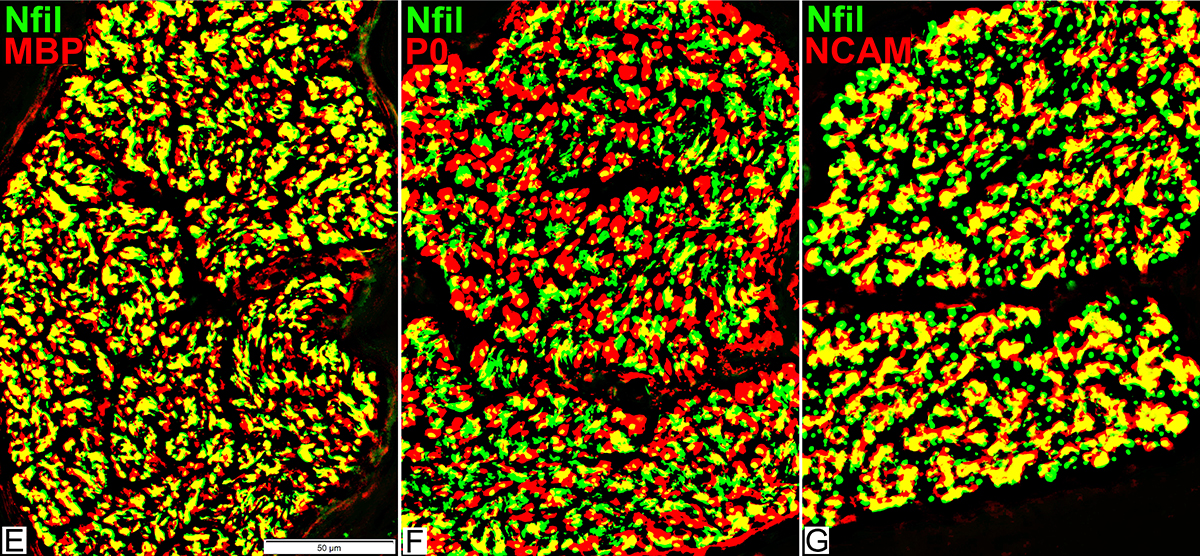 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule |
| Largest Axons (F & G) Smaller than in adults MBP (Left; E) (Red or Yellow): Present In most Schwann cells Alone, without P0, in some cells |
P0 Present in sheaths around most myelinated axons (Center; F) Patchy presence in Schwann cells around unmyelinated axons NCAM (Right; G) Present with most unmyelinated, but not myelinated axons |
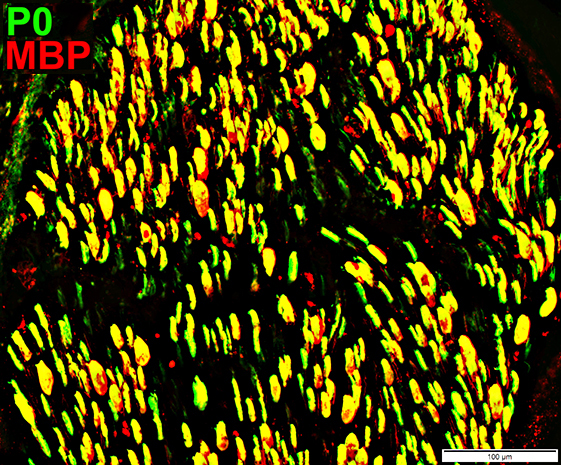
Schwann cells & Myelin: Normal Infant
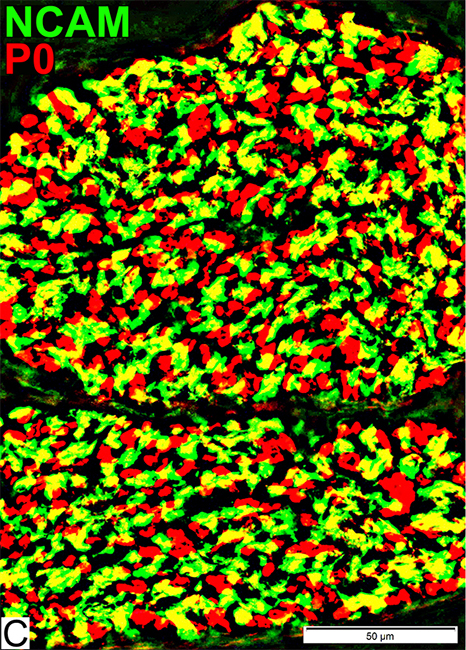 P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Schwann cells Stain for NCAM (Green; Yellow) Also contain patchy regions of P0 (Yellow), different from adults Myelin Stains for P0 (Red) |
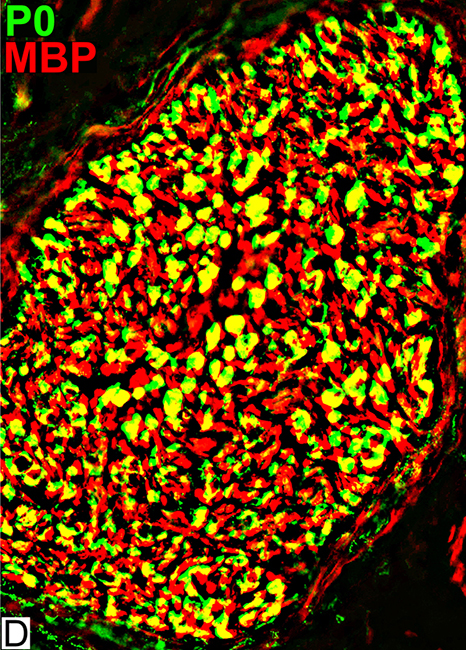 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein Schwann cells MBP (Red; Yellow) Present in all Schwann cells & Myelin Present in Schwann cells without P0 (Red) Myelin Contents: MBP & P0 |
Adult Sural Nerve: Axon loss, Severe, Chronic
Remaining Small axonsStructure
Continuous or Beaded
Single unmyelinated axon in a Schwann cell
Associated Schwann cells
Immature
Contain MBP
May have no NCAM or p0
Denervated Schwann cells (Büngner bands)
May contain both NCAM & p0
Axon loss: Morphology
 Toluidine blue stain Severe axon loss Few, or No axons, are visible |
 Nfil = Neurofilaments Neurofilament stain A few, scattered clusters of small axons are visualized |
Axon loss: Schwann cells around Remaining Singleton Axons
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein Remaining Small axons Structure: Continuous or Beaded (Above) Associated Schwann cells Stain for MBP (Yellow) on axons without myelin sheath Myelin None visible around remaining singleton axons |
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Remaining Small Axons Size: Small May have no staining for p0 or NCAM (Arrows) Schwann cells Abundant: Remain after axon loss Most have no associated axons Stain for: NCAM & P0 |
MBP on small axons with no myelin
Some remaining axons may appear beaded with Neurofilament/MBP stain
Normal small axons have no MBP staining
MBP(r)sm.jpg) Neurofilament = Green; MBP = Red; Co-stain = Yellow |
Singleton Unmyelinated Axons
Small Single AxonsSurrounded by Schwann cell processes (Arrow)
May contain small blebs (Sprouts; Right)
Stain for MBP, even without myelin
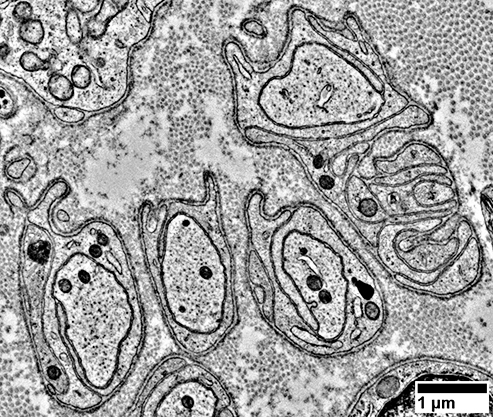 From: R Schmidt |
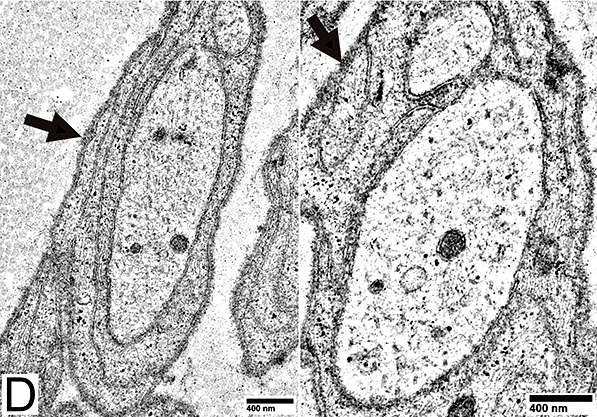 From: R Schmidt |
Denervated Schwann Cells (Büngner Band Cells)
 P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Schwann cells: Denervated No associated Axons Costain NCAM + P0 (Yellow) Also see: Onion bulb cells |
 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Schwann cells: Denervated No associated Axons Contain NCAM (Green) but not MBP |
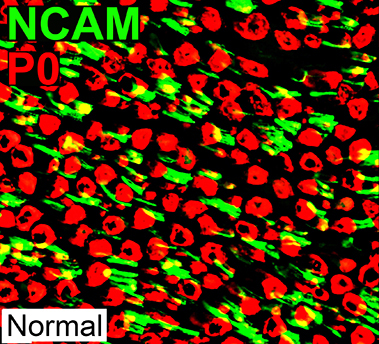 P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Schwann cells: Normal NCAM (Green) No co-staining with P0 (Red) P0 (Red) Stains myelin, not Schwann cells |
Büngner bands: Clusters of Schwann cell processes with no axons
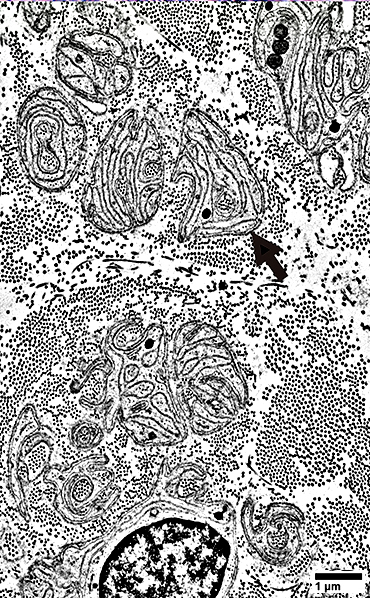 From: R Schmidt |
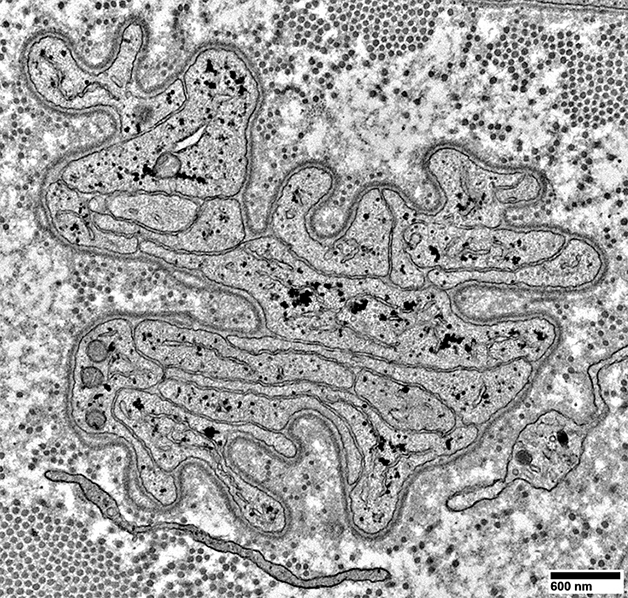
|
Interdigitated Schwann cell processes
Axon Regeneration
Regenerated Myelinated AxonsSize: Intermediate
Myelin Thickness: Thin; Similar thickness in each axon cluster
Myelin molecular components
MBP + P0 ± NCAM
Smaller myelinated axons have MBP in myelin
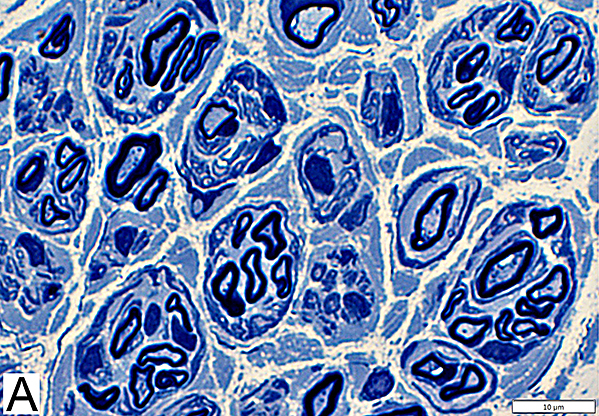 Toluidine blue stain Regenerated Axons Many clusters of intermediate-sized thinly myelinated axons Axons in individual clusters have similar myelin thickness |
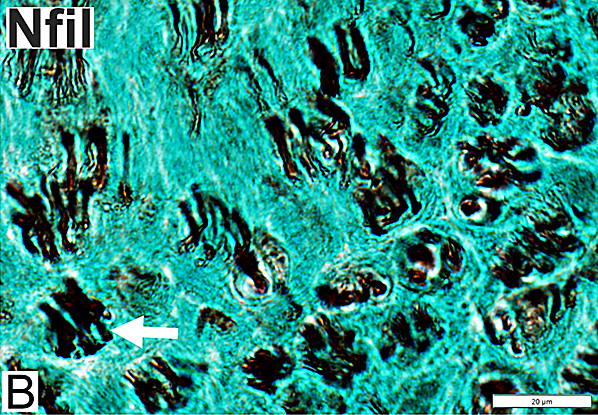 Nfil = Neurofilaments Regenerated Axons (Neurofilament stain) Clusters of regenerated larger axons are present (Arrow) |
Axons & Schwann cells/Myelin: Axon Regeneration
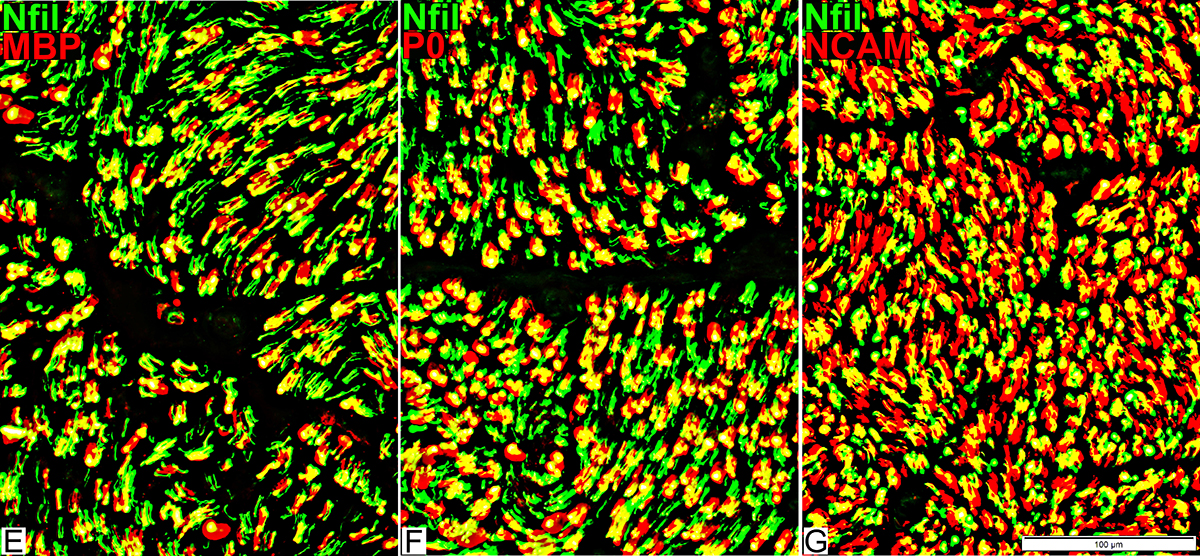 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule |
P0: Stains myelin around many axons (Center; F)
NCAM (Right; G)
Stains around some, but not all, larger axons
Some NCAM profiles have no associated axon: Suggests incomplete axon regeneration with remaining denervated Schwann cells
Axon Regeneration: Myelin Features
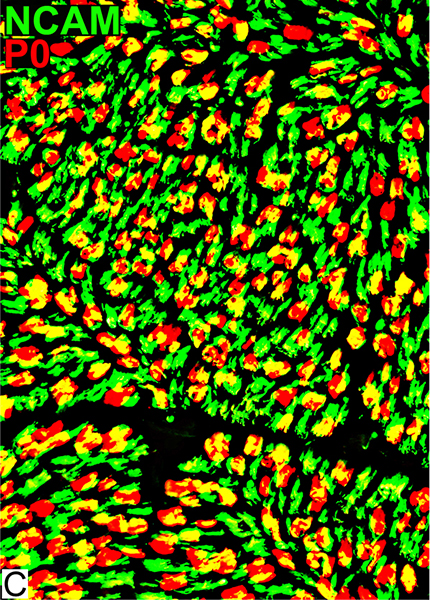 P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule NCAM Patchy co-stain (Yellow) with P0 (Red) in myelin sheaths Stains many non-myelinating Schwann cells (Green) |
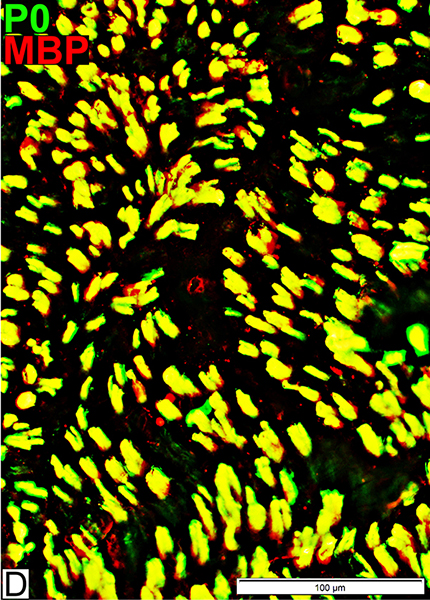 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein Myelin Most myelin sheaths, even small, costain for both P0 & MBP |
Adult Sural Nerve: Wallerian Degeneration
Wallerian Degeneration: Active
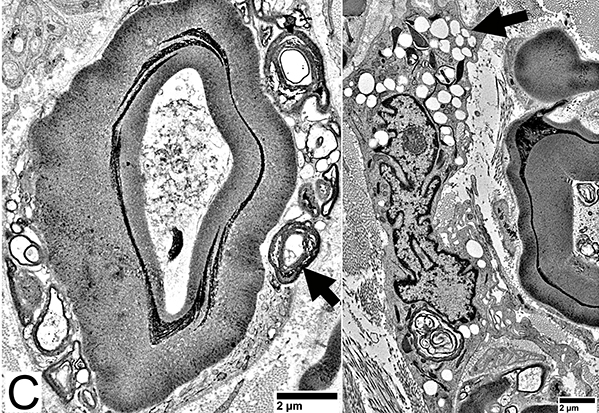
 Toluidine blue stain Phagocytic Cells Types: Phagocytic Schwann cells; Macrophages Contents: Myelin debris; Lipid droplets Myelin sheaths: Collapsed |
 Nfil = Neurofilaments Degenerated axons: No neurofilament stain (Arrow) Neurofilament fragments, or Empty regions with no axon |
Axon Degeneration: Acute
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule |
No axon staining within MBP stained myelin (Left; G) (Arrow)
No axon staining within P0 stained myelin (Center; H) (Arrow)
Minor loss of small axons: Scattered empty NCAM (Red) sheaths (Right; I)
Wallerian Degeneration: Active, Phagocytic cells
 Phagocytic Cells Types Phagocytic Schwann cells (Left) Macrophages (Center) Contents: Myelin debris (Left; Arrow); Lipid droplets (Center; Arrow) |
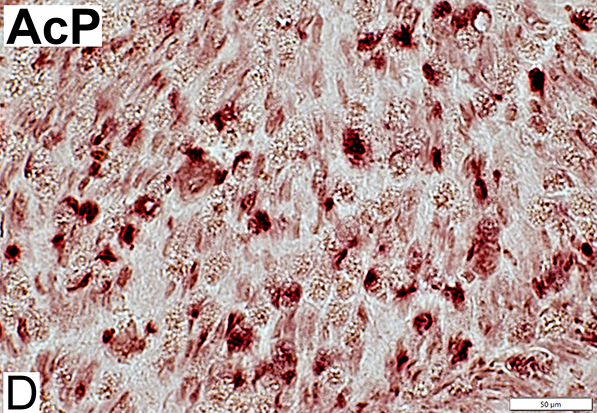 AcP = Acid Phosphatase Phagocyte Stain (Acid phosphatase): Endoneurial cells, scattered (Red) Compare to: Demyelination |
Adult Sural Nerve: Demyelination
Demyelination: Macrophage-Mediated
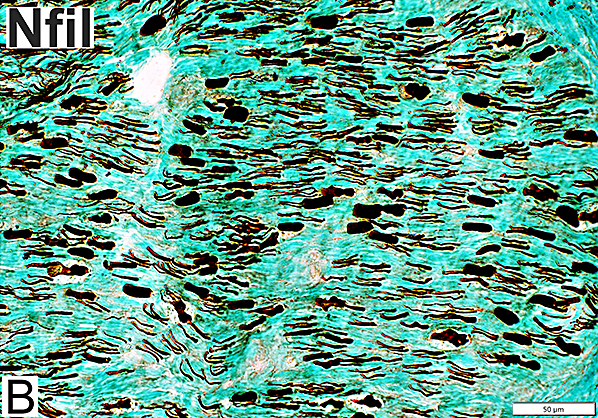 Nfil = Neurofilaments Demyelinated Large Axons Large axons: No surrounding myelin space |
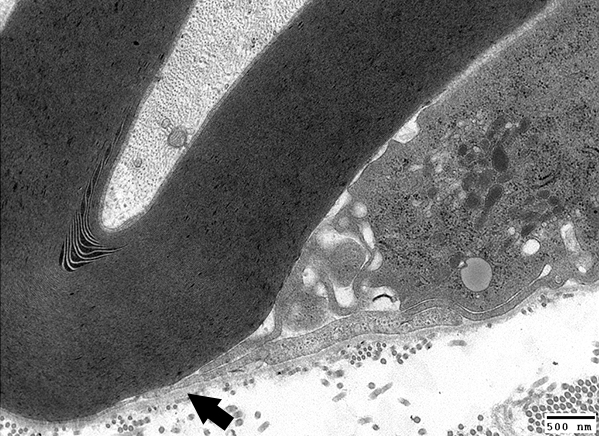 From: R Schmidt Macrophage-mediated Demyelination Macrophage process (Arrow) extends underneath Schwann cell basal lamina |
Demyelinated Axons
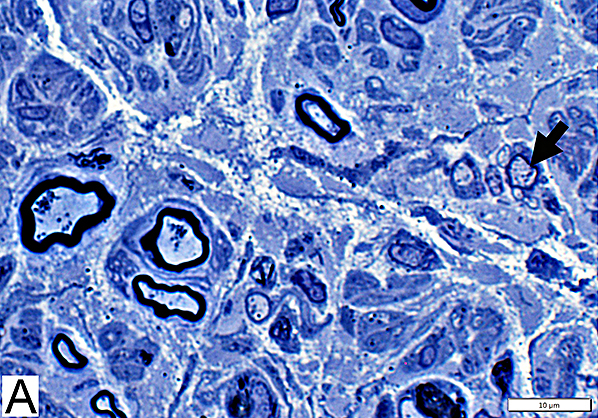 Toluidine blue stain Large Demyelinated Axons (Arrow) Other axons often have thin myelin sheath for size |
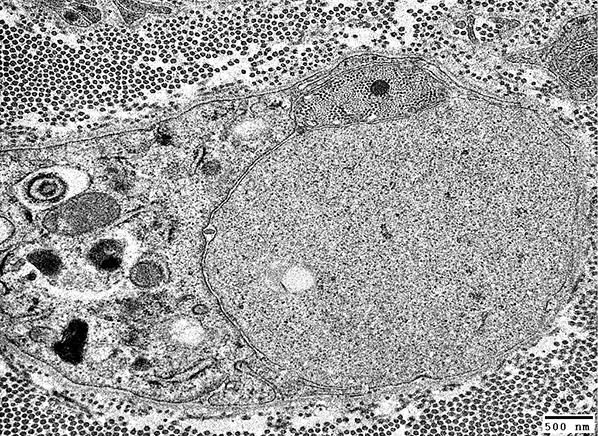 From: R Schmidt Demyelinated Axon: Surrounded by Schwann cell processes |
Demyelinated Large Axons: No surrounding Myelin sheath
Schwann cells surrounding Demyelinated axons: MBP+; P0 & NCAM-
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; P0 = P0 protein Demyelinated Large Axons (P0 stain) No surrounding myelin (Arrow; Below) |
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein Demyelinated Large Axons Co-stain (Yellow) for MBP: Immature non-myelinating Schwann cells |
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein |
Myelin Disorders: MAG Neuropathy
 Toluidine blue stain Myelin sheaths: Irregular structure |
 From: R Schmidt Myelin Wide-spacing Cleft, contatining a few layers, within compact myelin |
MAG Neuropathy
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; P0 = P0 protein No demyelinated axons |
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein Small axons: Many have associated MBP co-staining (Immature Schwann cells) |
 NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein NCAM (Yellow): Abnormally expressed within MBP-containing (Red) myelin sheaths |
 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein MBP & P0 expressed in Large & Smaller myelin sheaths Smaller myelinated axons normally have myelin that stains only for P0 |
Chronic Demyelinating Neuropathy: Onion Bulbs
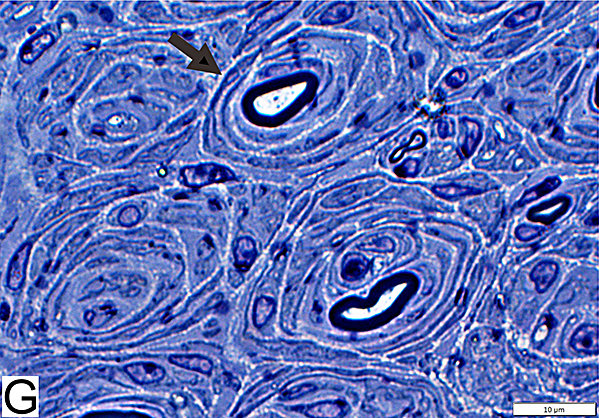 Toluidine blue stain Onion bulbs Structure: Concentric layers of Schwann cells & Collagen (Arrow) Center: Some have myelinated axon |
 Neurofilament stain Onion bulbs (OB): Relation to axons Some have large central axon Others have no central axon Small, unmyelinated axons May be present within onion bulb layers or around OB periphery |
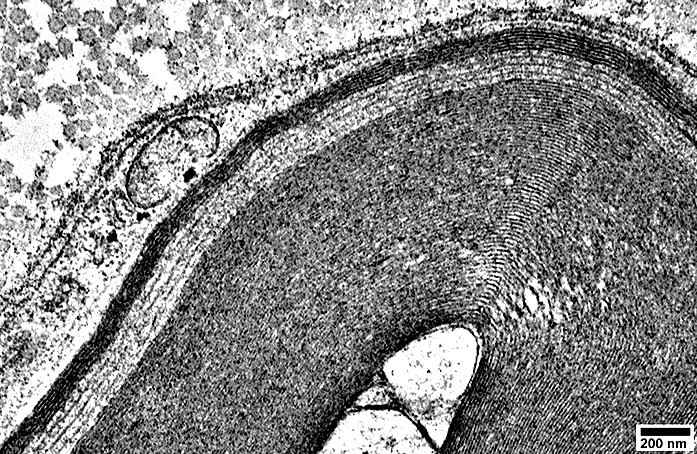
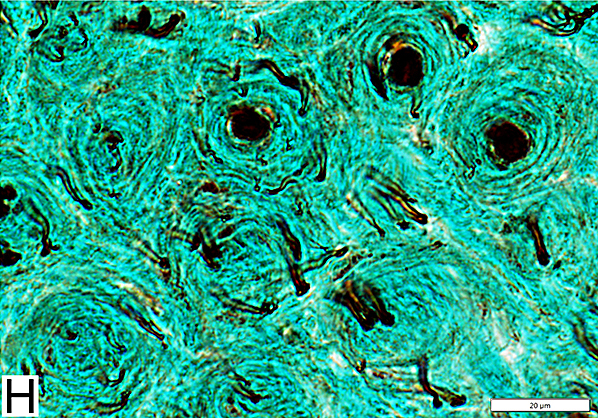
Onion Bulbs: Ultrastructure
Onion Bulb with Thinly Myelinated Central Axon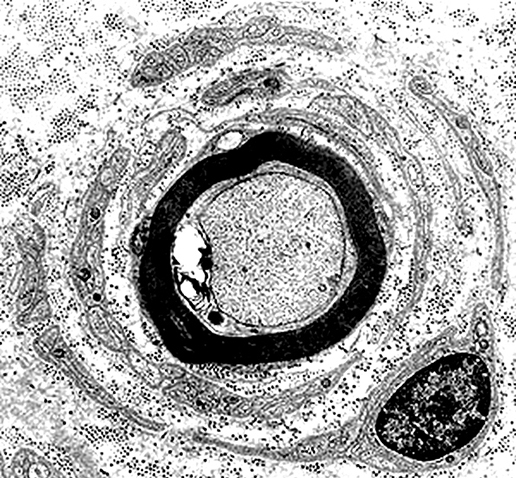 From: R Schmidt Onion Bulb structure Alternating layers of Schwann Cell processes & Collagen |
"Obsolete" Onion bulb: No remaining Central axon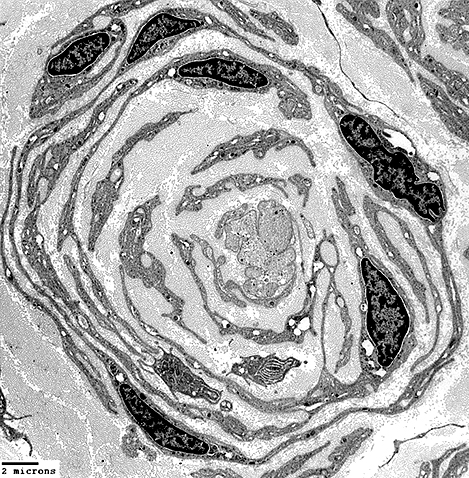 From: R Schmidt Onion Bulb structure Alternating layers of Schwann Cell processes & Collagen |
Onion Bulb Schwann cells: Molecular features
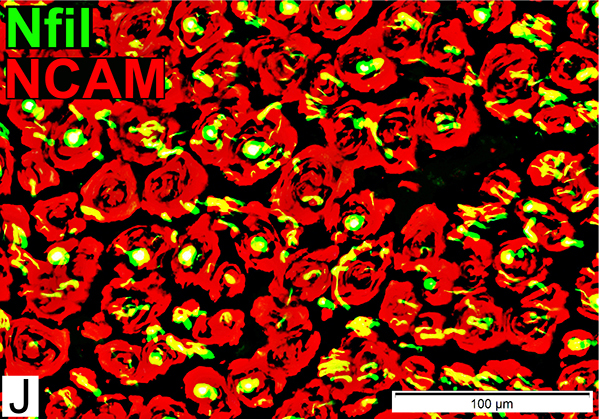 Nfil = Neurofilaments; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Onion Bulb cells NCAM Abundant in onion bulb Schwann cell processes Some onion bulbs contain central axons (Yellow) |
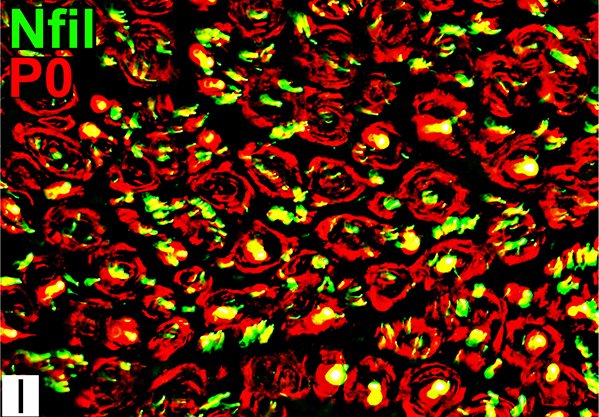 Nfil = Neurofilaments; P0 = P0 protein Onion Bulb cells P0 Present in most onion bulb Schwann cell processes Some onion bulbs contain central axons (Yellow) |
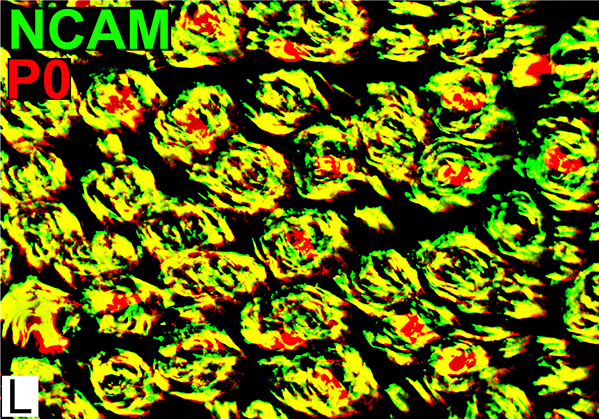 NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule; P0 = P0 protein Onion bulb Cells Contain both NCAM & P0 (Yellow) P0 (Red) also stains myelin around central axon in some onion bulbs |
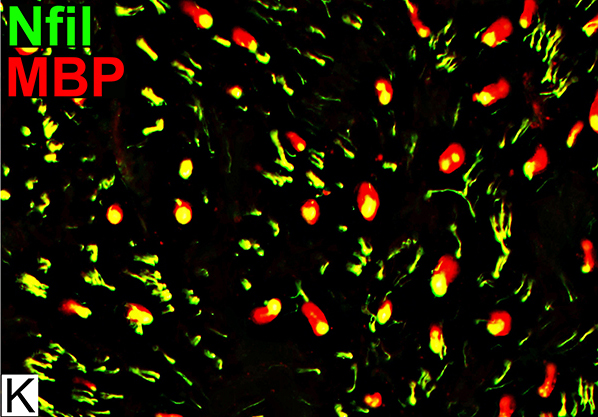 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein Onion bulb Cells MBP (Red) Present in myelin around a few large axons Not in onion bulb cells Costains unmyelinated small axons (Immature SC) |
Neurofascin-186 antibodies: Axon Atrophy & Small Axon Loss
Axon Atrophy
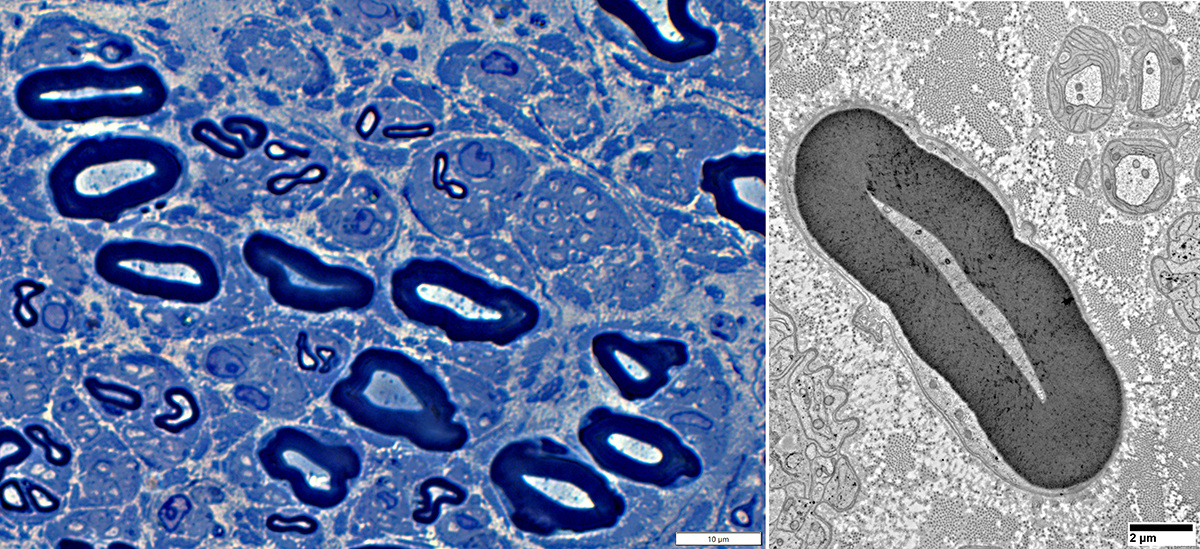 Larger myelinated axons: Axon atrophy Morphology: Small & Slit-like shape Myelin sheath: Thick for axon size See: Normal |
Axon atrophy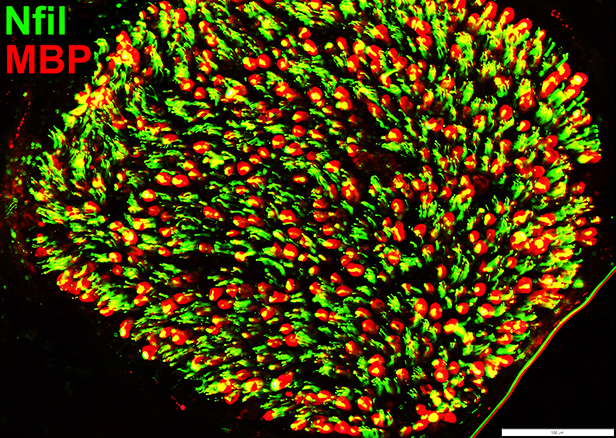 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein Axons within MBP myelin sheaths Many are smaller than Normal |
Myelin: Irregular Structure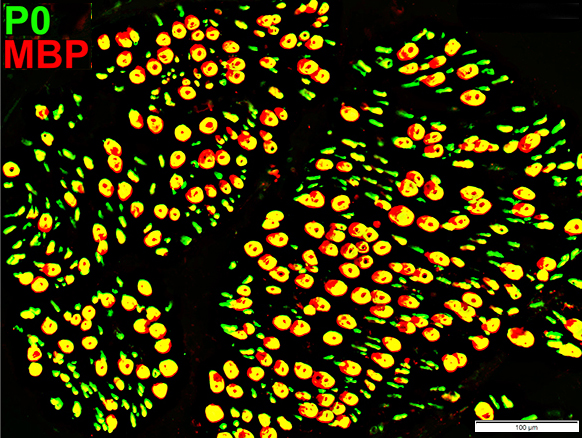 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein Larger myelin sheaths Irregular co-stain for P0 & MBP |
Neurofascin-186 antibody: Reduced numbers of Non-myelinating Schwann cells & Small axons
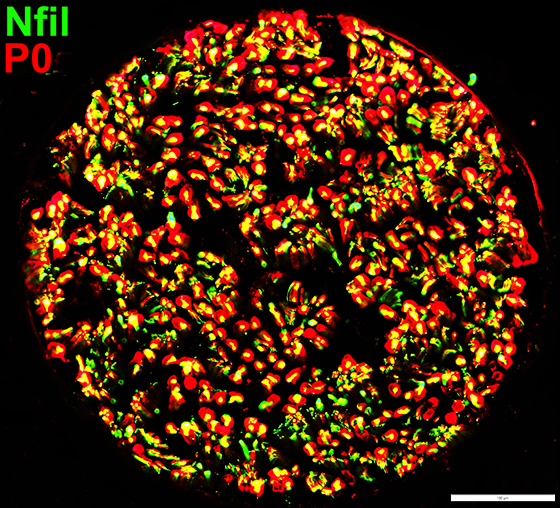 Nfil = Neurofilaments; P0 = P0 protein Small Axons (Green): Reduced numbers |
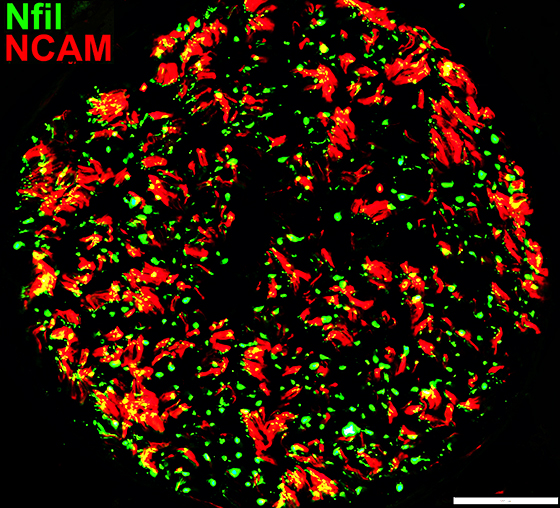 Nfil = Neurofilaments; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Non-myelinating Schwann cells (Red): Reduced numbers Small Axons: Reduced numbers (Many empty non-myelinating Schwann cells (Red)) Myelinated axons (Green): Generally small size |
Myelin Disorders: Other Pathology Patterns
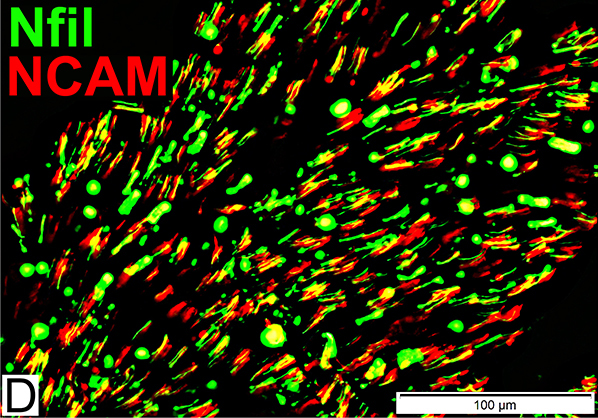 Nfil = Neurofilaments; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Schwann Cells (Red): Reduced numbers |
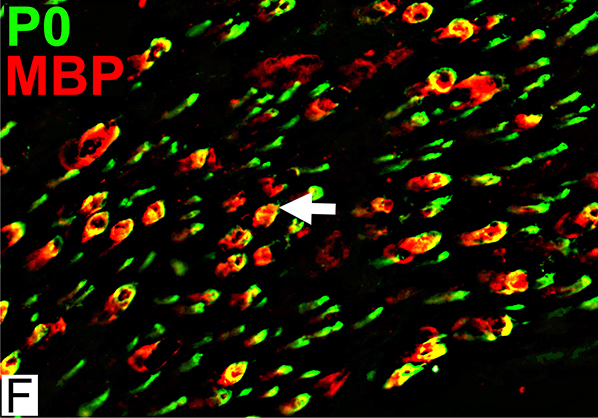 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein Abnormal Myelin Composition P0 lost from myelin on large axons; MBP (Red) remains (Arrow) |
Active Demyelination: Histiocytic Schwann cells & Myelin
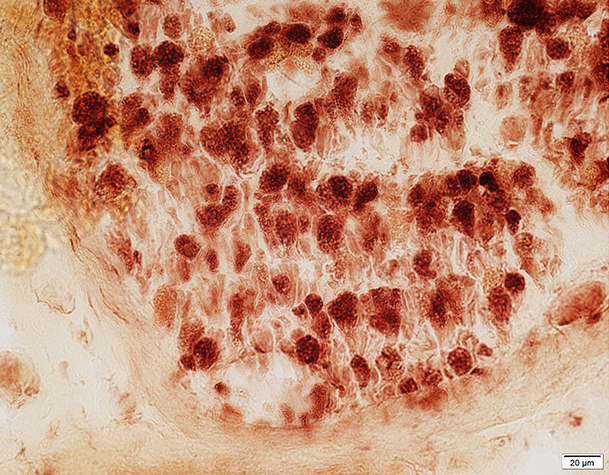 Acid phosphatase stain Most Myelin sheaths: Acid phosphatase+ Compare to: Wallerian degeneration |
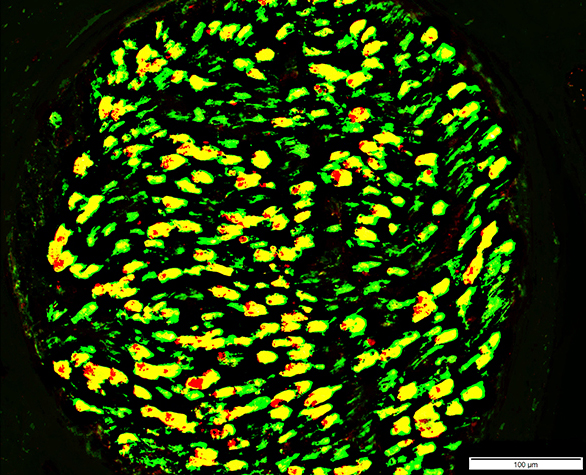 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein Myelin Structure: Irregular P0 & P0+MBP Sheaths |
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Pathology Index
References
1. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2023;49:e12898
3/25/2024